Preparation of Lateral Flow PVDF Membrane via Combined Vapor- and Non-Solvent-Induced Phase Separation (V-NIPS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Material
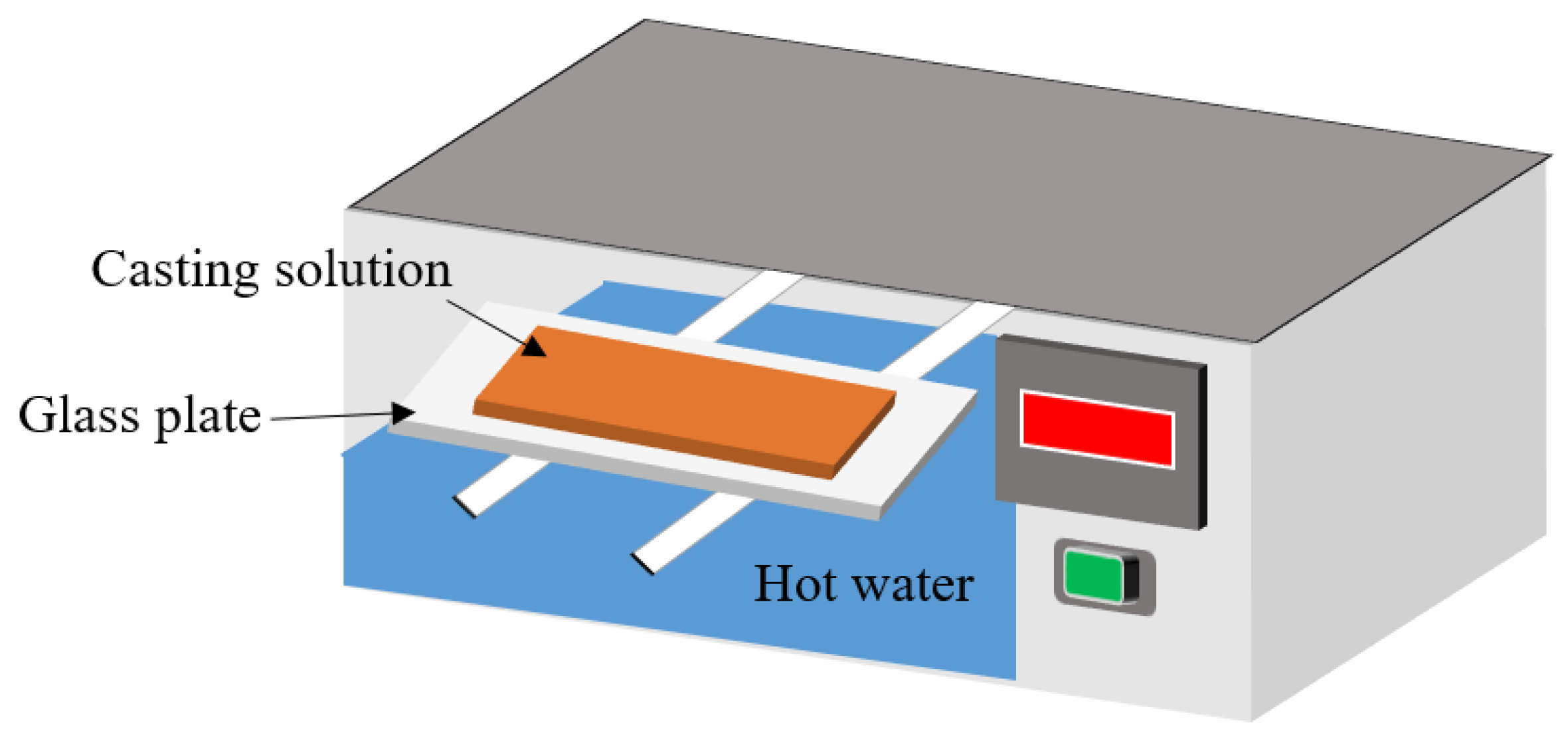
2.2. PVDF Membrane Preparation
2.3. PVDF Membrane Characterization
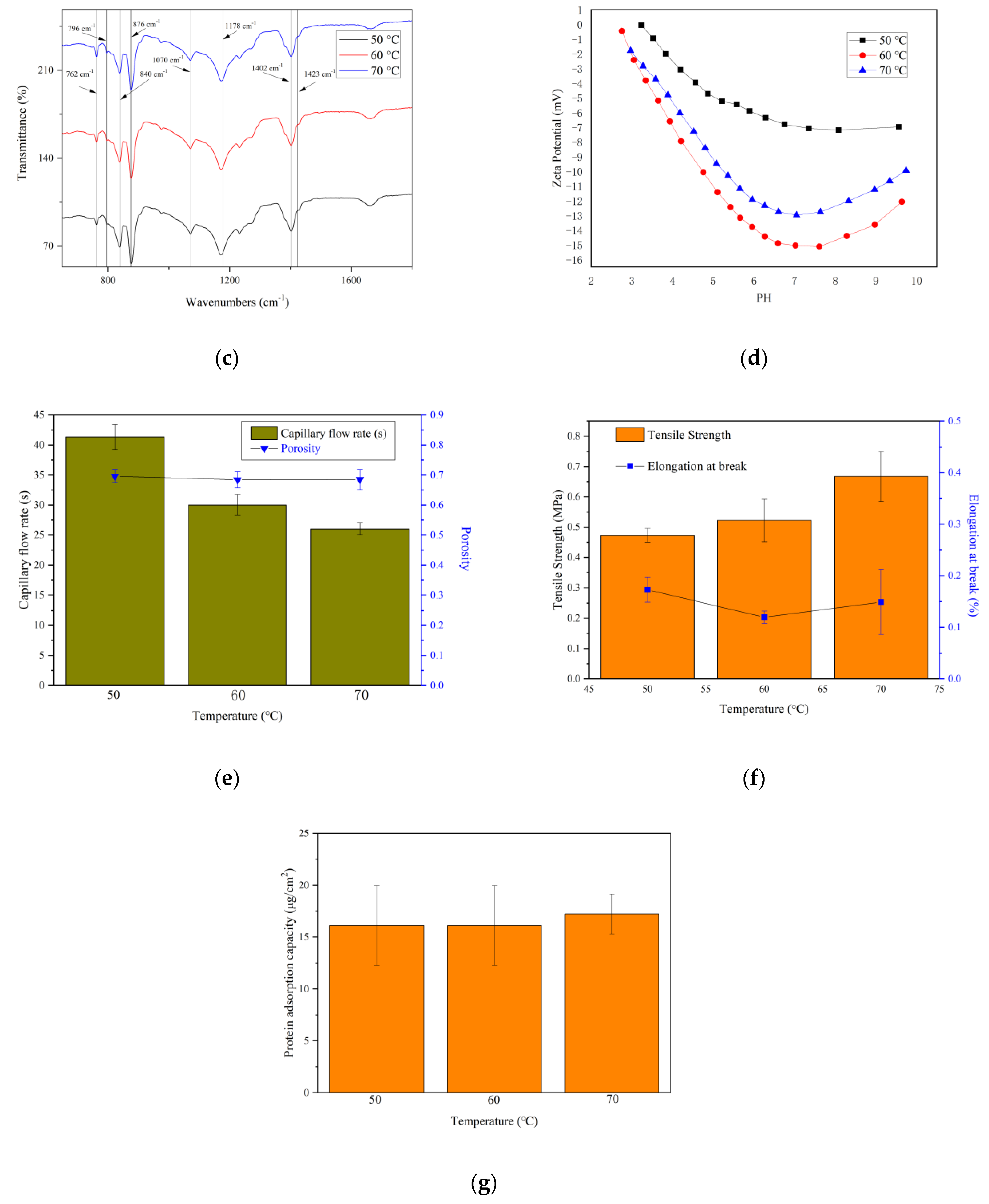
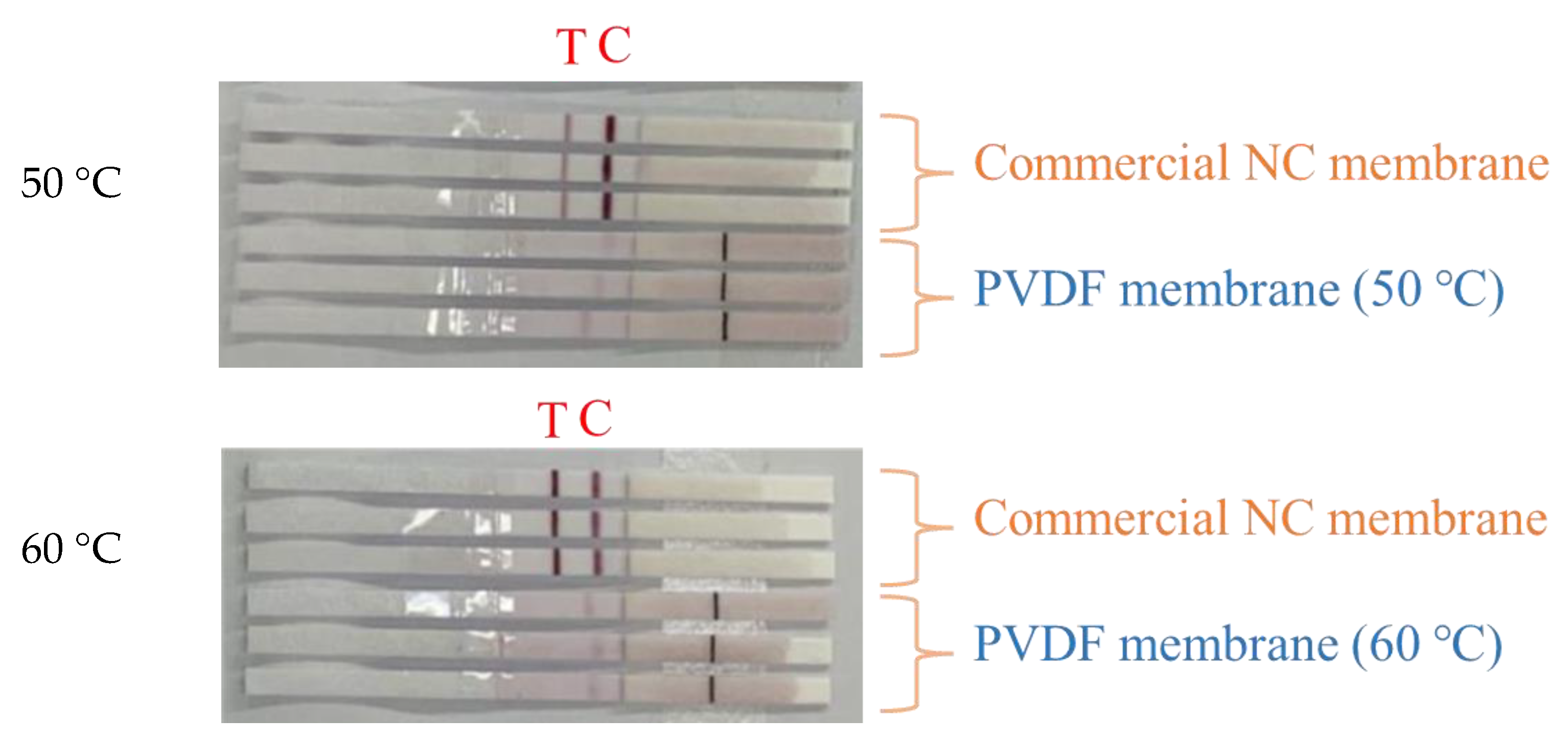
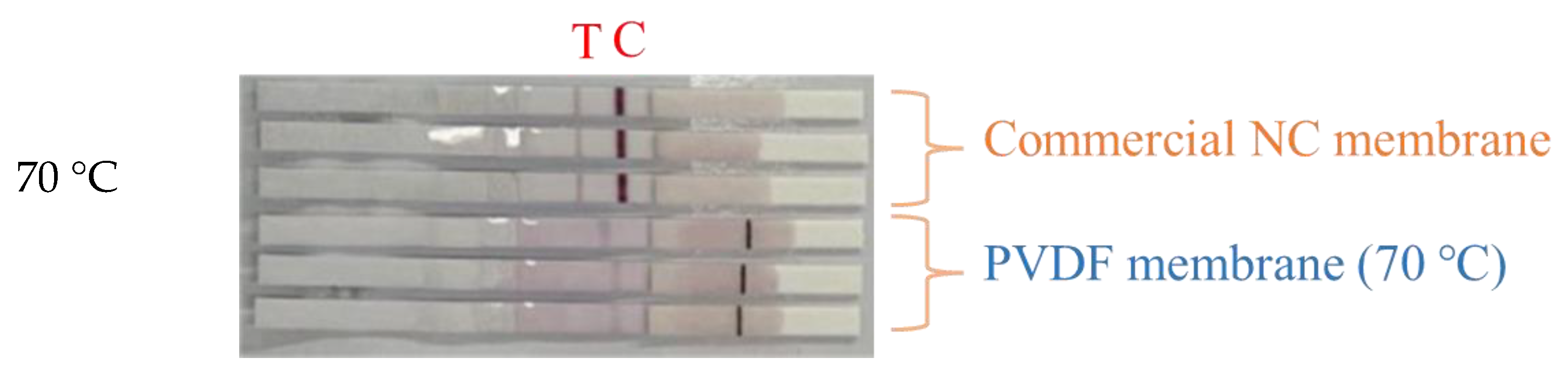
3. Results and Discussion
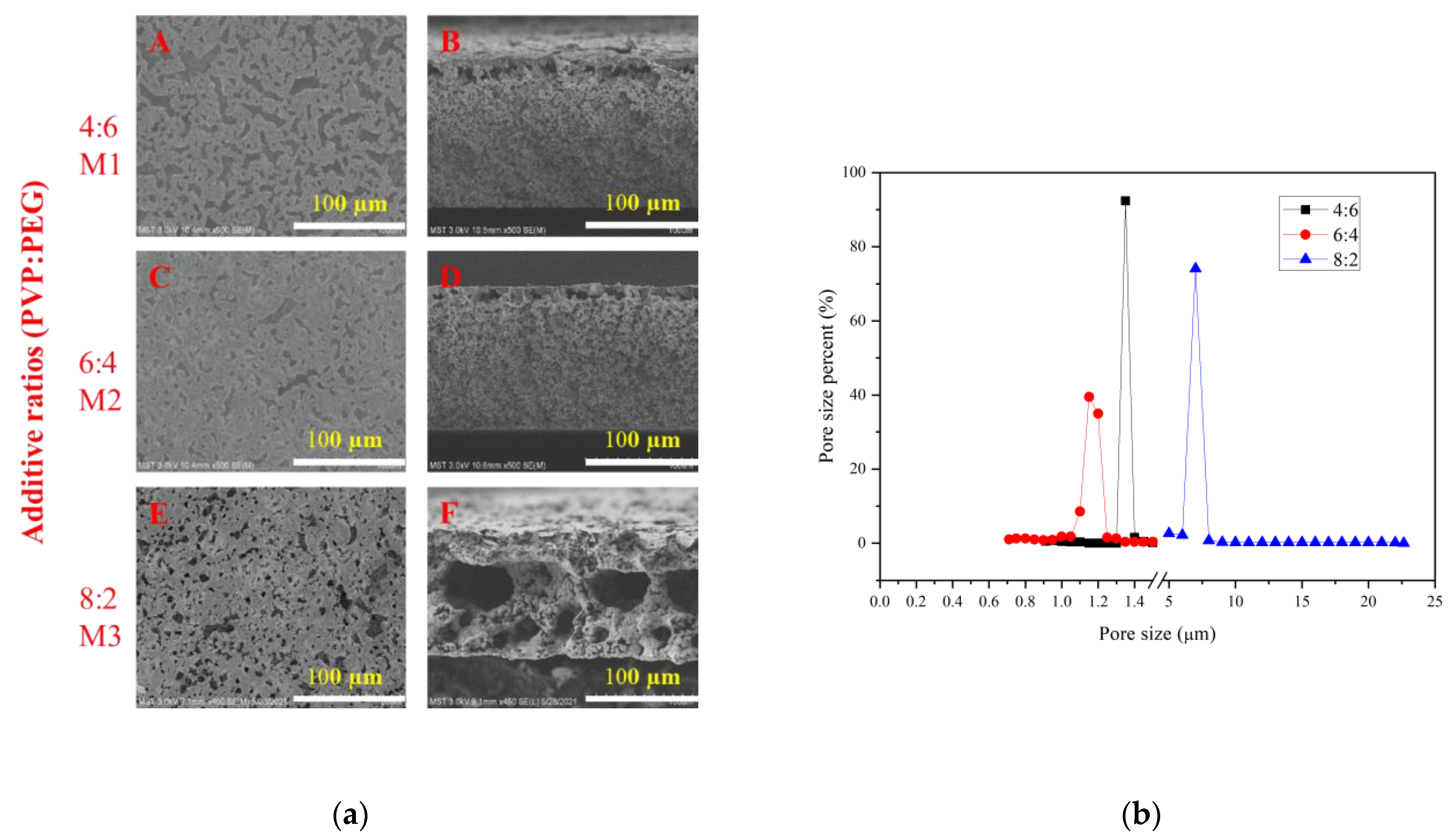
3.1. Additive Ratios
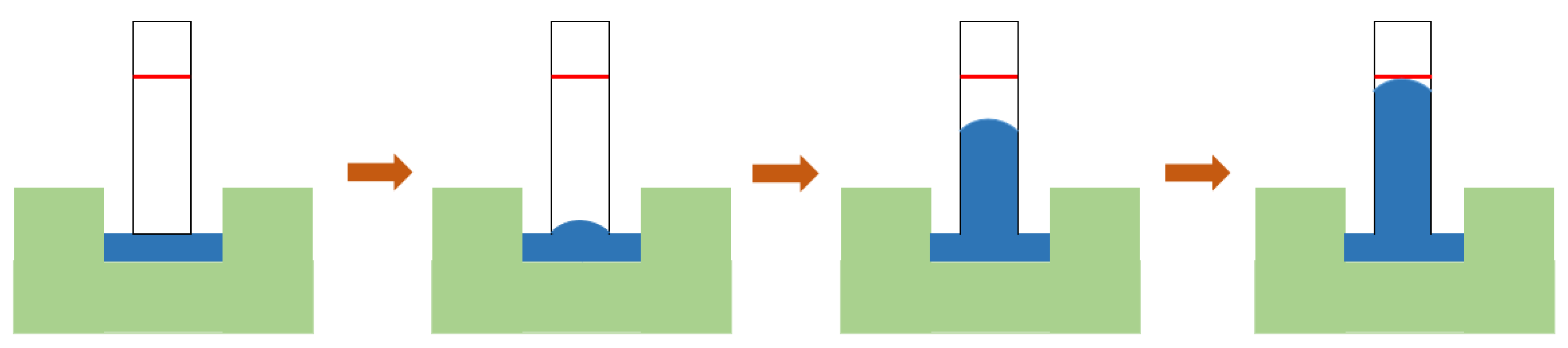
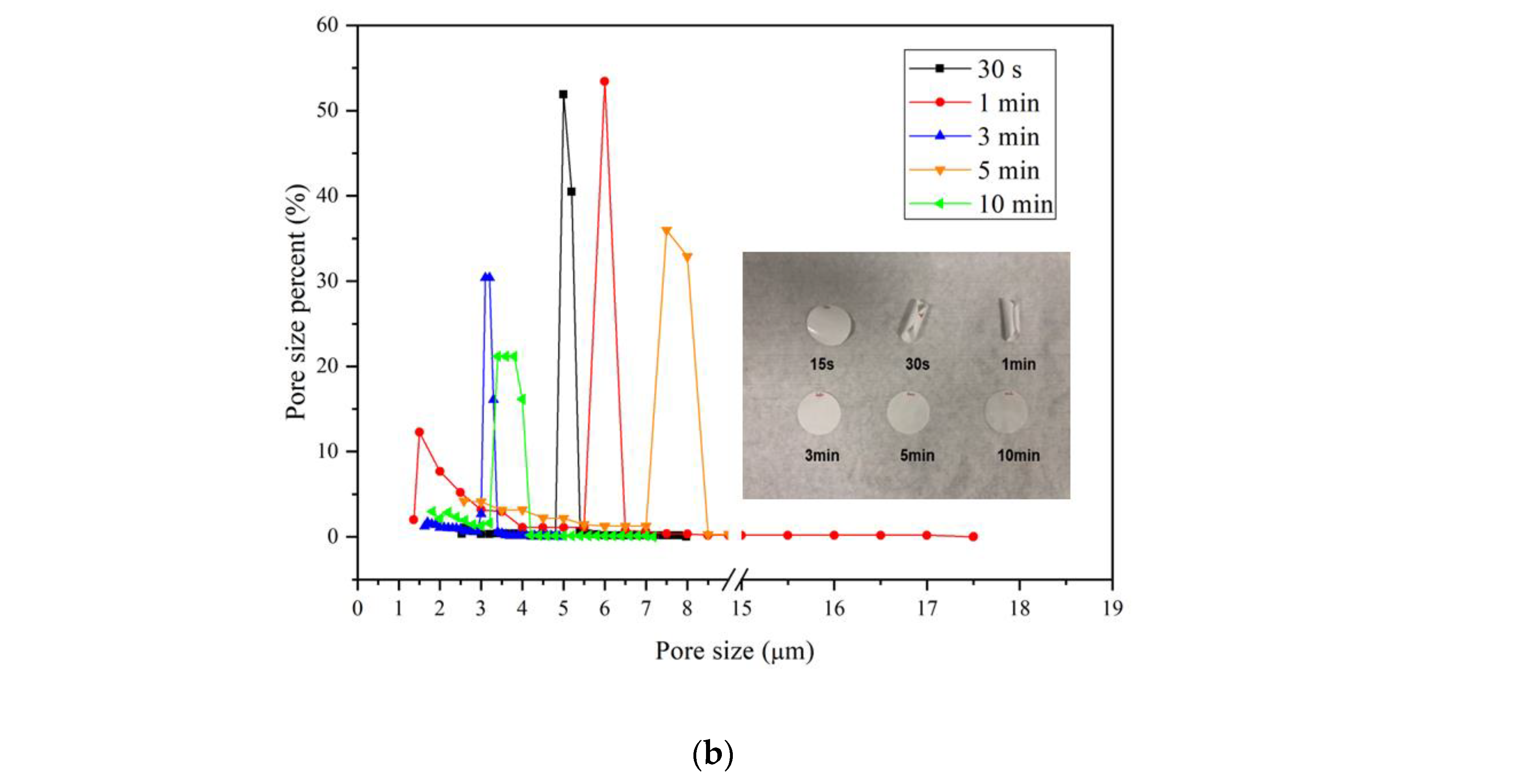
3.2. Exposure Time
3.3. Vapor Temperature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral flow assays: Principles, designs and labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, C.H.T.; Azari, P.; Choi, J.R.; Muhamad, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B. Electrospun Polycaprolactone Nanofibers as a Reaction Membrane for Lateral Flow Assay. Polymers 2018, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, S.C.; Shaimi, R.; Thandaithabany, Y.; Lim, J.K.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ismail, A. Electrophoretic interactions between nitrocellulose membranes and proteins: Biointerface analysis and protein adhesion properties. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 110, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, G.-d.; Cao, Y.-m. Application and modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameduri, B. From Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) to the Applications of VDF-Containing Polymers and Copolymers: Recent Developments and Future Trends. ChemInform 2010, 41, 6632–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Ideris, N.; Ooi, B.S.; Low, S.C.; Ismail, A. Morphology and polymorph study of a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane for protein binding: Effect of the dissolving temperature. Desalination 2011, 278, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, K.; Teo, W. Preparation and characterization of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 163, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Tseng, H.-H.; Wang, D.K. Uncovering the effects of PEG porogen molecular weight and concentration on ultrafiltration membrane properties and protein purification performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, A.; Cameraroda, G.; Capannelli, G.; Munari, S. The formation of microporous polyvinylidene difluoride membranes by phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.P.; Dwan, A.H.; Gryte, C.C. Isothermal phase behavior of Nylon-6, -66, and -610 polyamides in formic acid–water systems. J. Polym. Sci. B—Polym. Phys. 2010, 32, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H. Preparation of poly (vinyl butyral) hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane via wet-spinning method using PVP as additive. Desalination 2011, 278, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.A.; Medeiros, V.d.N.; Silva, B.I.A.; Araújo, E.M.; Lira, H.d.L. Study of the influence of viscosity on the morphology of polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes/additives. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20180913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.-H.; Cheng, L.-P.; You, W.-M.; Chen, L.-Y. Prediction of EVAL membrane morphologies using the phase diagram of water–DMSO–EVAL at different temperatures. Polymers 1999, 40, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.I.M.; Sait, N.R.; Bilad, M.R.; Shamsuddin, N.; Jaafar, J.; Nordin, N.A.H.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Mohshim, D.F. Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane via Vapour Induced Phase Separation for Oil/Water Emulsion Filtration. Polymers 2021, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. The Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Ge, B.; Xing, L.; Chen, H. Cellulose nitrate membrane formation via phase separation induced by penetration of nonsolvent from vapor phase. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 295, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Deng, M.; Chen, Y.; He, G.; Wu, M.; Wang, J. Preparation and performance of cellulose acetate/polyethyleneimine blend microfiltration membranes and their applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 235, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Rodrigue, D. A Review on Porous Polymeric Membrane Preparation. Part I: Production Techniques with Polysulfone and Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride). Polymers 2019, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xing, W. Preparation of PVDF membrane via synergistically vapor and non-solvent-induced phase separation. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehban, A.; Saeedavi, F.H.; Kargari, A. A study on the mechanism of pore formation through VIPS-NIPS technique for membrane fabrication. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 108, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Zhuang, Y.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Crystalline polymorphism in poly(vinylidenefluoride) membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 51, 94–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaccio, T.; Bottino, A.; Capannelli, G.; Piaggio, P. Characterization of PVDF membranes by vibrational spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 210, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, H.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y. Effect of surface hydrophilic modification on the wettability, surface charge property and separation performance of PTFE membrane. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 8, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, P.; Su, Y.S.; Chinpa, W.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Deratani, A.; Wang, D.M.; Huguet, P.; Kuo, C.Y.; Lai, J.Y.; Dupuy, C. A top surface liquid layer during membrane formation using vapor-induced phase separation (VIPS)—Evidence and mechanism of formation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, R.; Luo, F.; Faraj, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.-Y. Preparation of high strength poly(vinylidene fluoride) porous membranes with cellular structure via vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Membrane Code | Additive Ratio (PVP:PEG) | Exposure Time (min) | Vapor Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 4:6 | 5 | 60 |
| M2 | 6:4 | 5 | 60 |
| M3 | 8:2 | 5 | 60 |
| M4 | 8:2 | 0.25 | 60 |
| M5 | 8:2 | 0.5 | 60 |
| M6 | 8:2 | 1 | 60 |
| M7 | 8:2 | 3 | 60 |
| M8 | 8:2 | 5 | 60 |
| M9 | 8:2 | 10 | 60 |
| M10 | 8:2 | 5 | 50 |
| M11 | 8:2 | 5 | 60 |
| M12 | 8:2 | 5 | 70 |
| Additive Ratio (PVP:PEG) | Viscosity (cp) |
|---|---|
| 4:6 | 7230 ± 42 |
| 6:4 | 12,660 ± 85 |
| 8:2 | 21,930 ± 127 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, D.; He, T.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, L.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Z. Preparation of Lateral Flow PVDF Membrane via Combined Vapor- and Non-Solvent-Induced Phase Separation (V-NIPS). Membranes 2023, 13, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010091
Wang X, Chen D, He T, Zhou Y, Tian L, Wang Z, Cui Z. Preparation of Lateral Flow PVDF Membrane via Combined Vapor- and Non-Solvent-Induced Phase Separation (V-NIPS). Membranes. 2023; 13(1):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010091
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoyun, Dejian Chen, Ting He, Yue Zhou, Li Tian, Zhaohui Wang, and Zhaoliang Cui. 2023. "Preparation of Lateral Flow PVDF Membrane via Combined Vapor- and Non-Solvent-Induced Phase Separation (V-NIPS)" Membranes 13, no. 1: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010091
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, D., He, T., Zhou, Y., Tian, L., Wang, Z., & Cui, Z. (2023). Preparation of Lateral Flow PVDF Membrane via Combined Vapor- and Non-Solvent-Induced Phase Separation (V-NIPS). Membranes, 13(1), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010091







