Polysulfone Membranes Doped with Human Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitors: Assessment of Bioactivity and Biocompatibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of the HNEIs
2.2.2. Determination of HNEIs IC50
2.2.3. Hemocompatibility of HNEIs
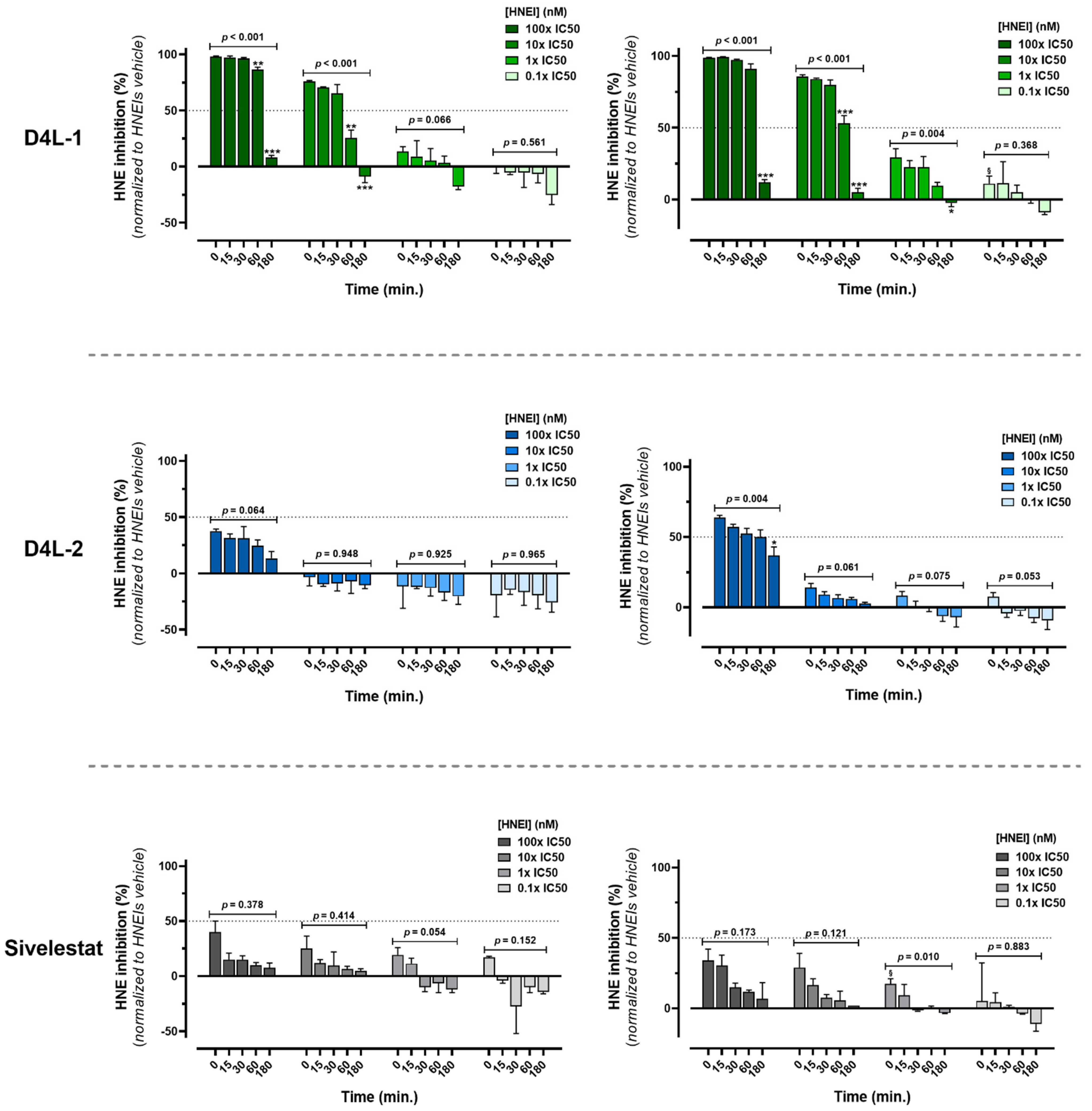
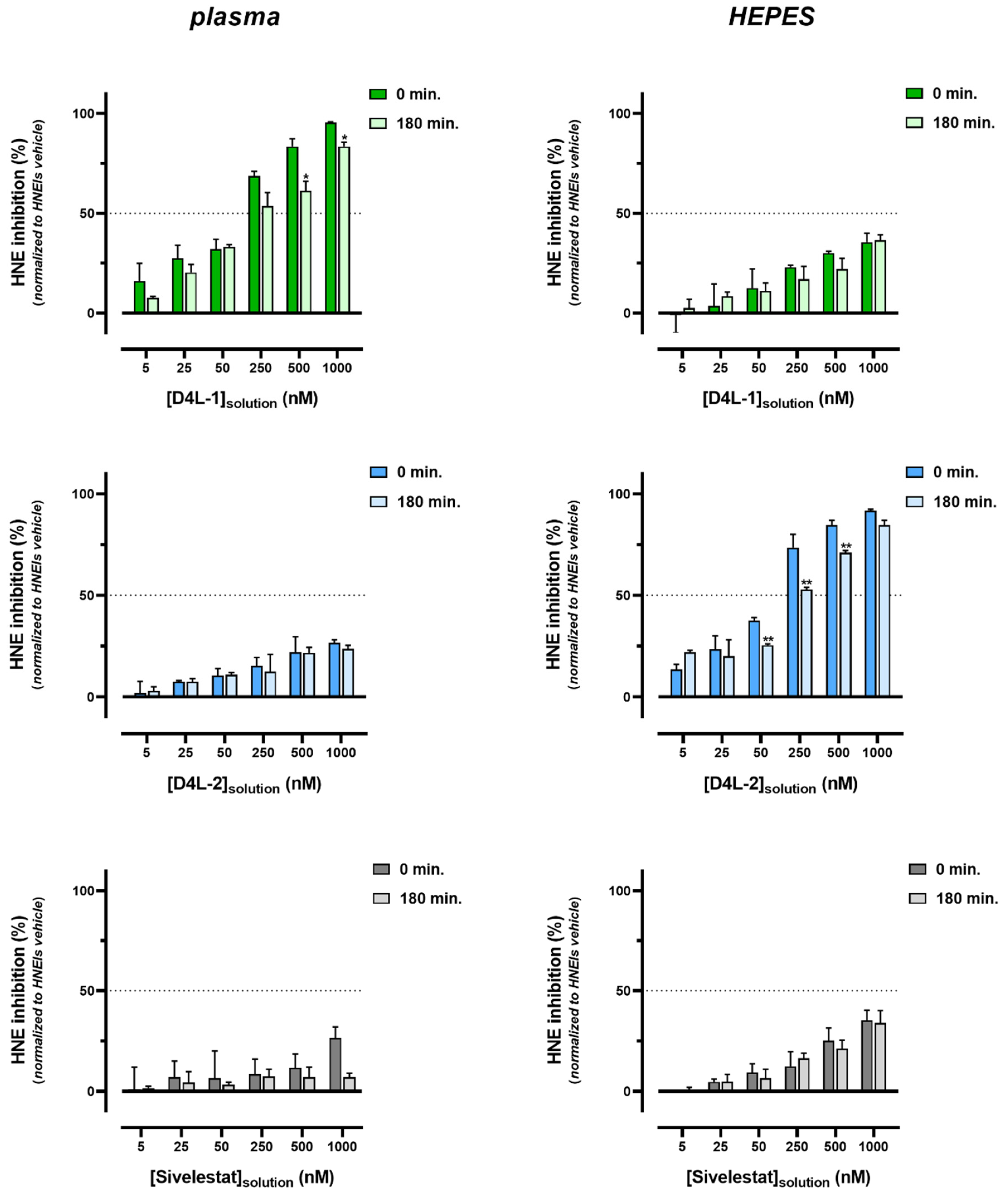
2.2.4. Bioactivity Kinetic Assay of HNEIs on Human Plasma
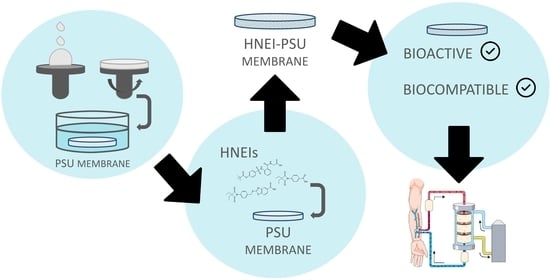
2.2.5. Preparation of HNEI-PSU Membranes
2.2.6. Characterization of HNEI-PSU Membranes
Bioactivity (In Vitro)
Adsorption Extension
UHPLC-MS/MS Conditions
2.2.7. Biocompatibility of HNEI-PSU Membranes
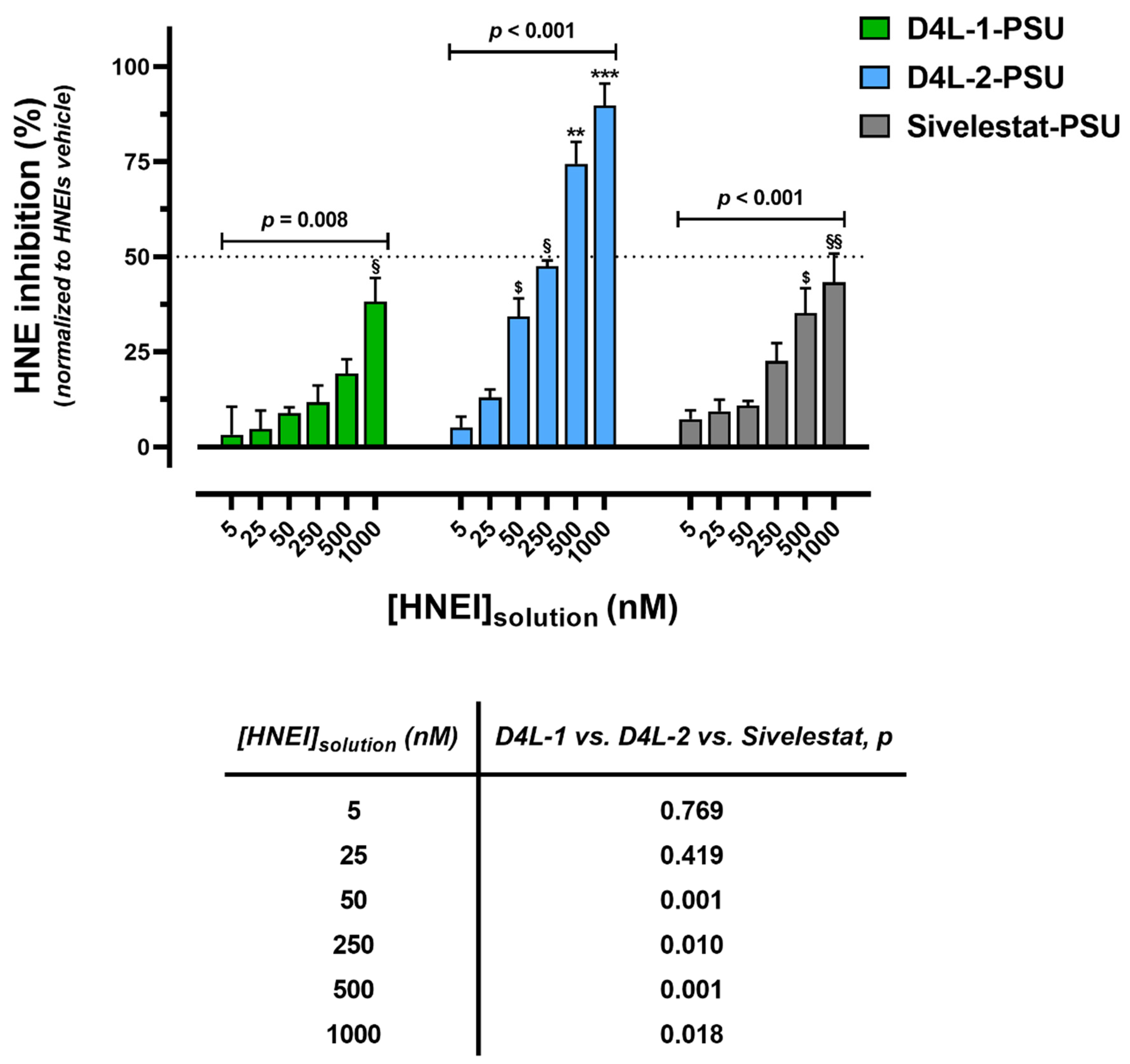
2.2.8. Bioactivity Effectiveness of HNEI-PSU Membranes on Human Plasma
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HNEIs
3.1.1. HNEIs’ Characterization
3.1.2. Ex Vivo Biological Effectiveness of HNEIs in Solution
3.2. HNEI-PSU Membranes
3.2.1. HNEI-PSU Membranes’ Characterization
3.2.2. Bioactivity Effectiveness of HNEI-PSU Membranes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Update Work Group. KDIGO 2017 Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int. Suppl. 2017, 7, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2012, 379, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Bohm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiological Insights and Therapeutic Options. Circulation 2021, 143, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akchurin, O.M.; Kaskel, F. Update on inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2015, 39, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuwese, C.L.; Stenvinkel, P.; Dekker, F.W.; Carrero, J.J. Monitoring of inflammation in patients on dialysis: Forewarned is forearmed. Nat. Rev. Nephrol 2011, 7, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib-Massalha, E.; Michelis, R.; Trabelcy, B.; Gerchman, Y.; Kristal, B.; Ariel, A.; Sela, S. Free circulating active elastase contributes to chronic inflammation in patients on hemodialysis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 314, F203–F209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, B.; Horwitz, M.S.; Jenne, D.E.; Gauthier, F. Neutrophil elastase, proteinase 3, and cathepsin G as therapeutic targets in human diseases. Pharm. Rev. 2010, 62, 726–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronze-da-Rocha, E.; Santos-Silva, A. Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitors and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1343–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Mazor, M.; Mazor, R.; Kristal, B.; Sela, S. Elastase and cathepsin G from primed leukocytes cleave vascular endothelial cadherin in hemodialysis patients. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 459640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Costa, E.; Goncalves, M.; Miranda, V.; do Sameiro Faria, M.; Quintanilha, A.; Belo, L.; Lima, M.; Santos-Silva, A. Neutrophil and monocyte activation in chronic kidney disease patients under hemodialysis and its relationship with resistance to recombinant human erythropoietin and to the hemodialysis procedure. Hemodial. Int. 2010, 14, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanska, B.; Augustyniak, D.; Makulska, I.; Niemczuk, M.; Jankowski, A.; Zwolinska, D. Elastase, alpha1-proteinase inhibitor, and interleukin-8 in children and young adults with end-stage kidney disease undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Arch. Immunol. Exp. 2014, 62, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetti, L.; Quinn, M.T.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Giovannoni, M.P. A patenting perspective on human neutrophil elastase (HNE) inhibitors (2014-2018) and their therapeutic applications. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Nussbaum, F.; Li, V.M. Neutrophil elastase inhibitors for the treatment of (cardio)pulmonary diseases: Into clinical testing with pre-adaptive pharmacophores. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4370–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groutas, W.C.; Dou, D.; Alliston, K.R. Neutrophil elastase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2011, 21, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, S.D.; Costa, E.; Guedes, R.C.; Moreira, R. Targeting COPD: Advances on low-molecular-weight inhibitors of human neutrophil elastase. Med. Res. Rev. 2013, 33, E73–E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, T.; Matsuyama, M.; Funao, K.; Tanaka, T.; Tsuchida, K.; Takemoto, Y.; Kawahito, Y.; Sano, H.; Nakatani, T.; Yoshimura, R. Benefical effect of neutrophil elastase inhibitor on renal warm ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. Transpl. Proc. 2006, 38, 2201–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumasaka, R.; Nakamura, N.; Fujita, T.; Murakami, R.; Shimada, M.; Osawa, H.; Yamabe, H.; Okumura, K. Beneficial effect of neutrophil elastase inhibitor on anti-Thy1.1 nephritis in rats. Nephrology 2008, 13, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jia, J.; Ji, K.; Gong, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zang, B. The neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, attenuates sepsis-related kidney injury in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, M.; Hayama, T.; Funao, K.; Naganuma, T.; Kawahito, Y.; Sano, H.; Chargui, J.; Touraine, J.L.; Nakatani, T.; Yoshimura, R. The effect of neutrophil elastase inhibitor on acute tubular necrosis after renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008, 1, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grano, V.; Tasco, G.; Casadio, R.; Diano, N.; Portaccio, M.; Rossi, S.; Bencivenga, U.; Compiani, M.; De Maio, A.; Mita, D.G. Reduction of active elastase concentration by means of immobilized inhibitors: A novel therapeutic approach. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchande, J.; Oliveira, R.; Carrasco, M.; Gouveia, L.; Guedes, R.C.; Iley, J.; Moreira, R. 4-Oxo-beta-lactams (azetidine-2,4-diones) are potent and selective inhibitors of human leukocyte elastase. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruivo, E.F.; Goncalves, L.M.; Carvalho, L.A.; Guedes, R.C.; Hofbauer, S.; Brito, J.A.; Archer, M.; Moreira, R.; Lucas, S.D. Clickable 4-Oxo-beta-lactam-Based Selective Probing for Human Neutrophil Elastase Related Proteomes. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchande, J.; Simoes, S.I.; Gaspar, M.M.; Eleuterio, C.V.; Oliveira, R.; Cruz, M.E.; Moreira, R.; Iley, J. Synthesis, stability, biochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of a new potent and selective 4-oxo-beta-lactam inhibitor of human leukocyte elastase. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2011, 26, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlova, M.; Amorim, C.G.; Araujo, A.; Santos-Silva, A.; Solich, P.; Montenegro, M. The biocompatibility and bioactivity of hemodialysis membranes: Their impact in end-stage renal disease. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 22, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.A.; Ou, S.M.; Lin, C.C. Influence of Dialysis Membranes on Clinical Outcomes: From History to Innovation. Membranes 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Abdelrasoul, A.; Shoker, A. A critical review of recent advances in hemodialysis membranes hemocompatibility and guidelines for future development. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 248, 122911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olczyk, P.; Malyszczak, A.; Kusztal, M. Dialysis membranes: A 2018 update. Polim. Med. 2018, 48, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M. Development of vitamin E-modified polysulfone membrane dialyzers. J. Artif. Organs 2006, 9, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlová, M.; Amorim, C.G.; da Nova Araújo, A.; Santos-Silva, A.; Solich, P.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. In vitro assessment of polyethylene glycol and polyvinylpyrrolidone as hydrophilic additives on bioseparation by polysulfone membranes. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 1292–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlova, M.; Rocha, S.; Gomes Amorim, C.; de Nova Araujo, A.; Santos-Silva, A.; Solich, P.; Branco da Silva Montenegro, M.C. Doping Polysulfone Membrane with Alpha-Tocopherol and Alpha-Lipoic Acid for Suppressing Oxidative Stress Induced by Hemodialysis Treatment. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, e2000046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.; Marto, J.; Goncalves, L.M.; Simoes, S.; Felix, R.; Ascenso, A.; Lopes, F.; Ribeiro, H.M. Novel and Modified Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitor Loaded in Topical Formulations for Psoriasis Management. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee for Standardization in Haematology. ICSH reference method for staining of blood and bone marrow films by azure B and eosin Y (Romanowsky stain). Br. J. Haematol. 1984, 57, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, A.; Toro-Vazquez, J.F. The Freundlich isotherm in studying adsorption in oil processing. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Odagaki, Y.; Fujita, S.; Matsuoka, S.; Hamanaka, N.; Nakai, H.; Toda, M. Clarification of mechanism of human sputum elastase inhibition by a new inhibitor, ONO-5046, using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Bioorg. Med. Chem Lett. 2002, 12, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, K.; Suzuki, M.; Sugitani, M.; Imaki, K.; Toda, M.; Miyamoto, T. ONO-5046, a novel inhibitor of human neutrophil elastase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 177, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| D4L-1 | D4L-2 | Sivelestat | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular structure | 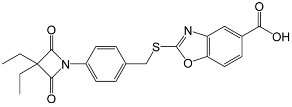 | 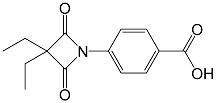 |  |
| Molecular formula | C22H20N2O5S | C14H15NO4 | C20H22N2O7S |
| Molecular weight (g mol−1) | 424.47 | 261.28 | 434.46 |
| tPSA (Å2) | 96.27 | 74.68 | 138.87 |
| CLogP | 4.738 | 2.445 | 2.771 |
| LogS | −5.157 | −2.909 | −4.846 |
| pKa | 3.704 | 3.714 | 3.783 |
| Adsorption Yield (%) | D4L-1 | D4L-2 | Sivelestat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [HNEI solution] nM | 5 | 99.2 | 98.2 | 89.6 |
| 25 | 99.0 | 95.3 | 90.3 | |
| 50 | 99.1 | 96.3 | 92.9 | |
| 250 | 99.2 | 96.4 | 92.5 | |
| 500 | 99.6 | 92.0 | 93.5 | |
| 1000 | 99.4 | 86.5 | 89.8 | |
| Adsorption Capacity (KF) mg g−1 | 98.5 | 0.824 | 3.56 | |
| Intensity of Adsorption (n) | 0.89 | 1.36 | 0.96 | |
| % of HNE Inhibition Variation after 3 h Incubation In: | HNEIs in Solution | HNEIs Immobilized in PSU | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D4L-1 | D4L-2 | Sivelestat | D4L-1 | D4L-2 | Sivelestat | |
| Diluted plasma (50%; PBS, pH 7.4) | −86.6 ± 1.6 | −26.8 ± 2.9 | −27.0 ± 4.1 | −12.0 ± 1.8 | −2.0 ± 0.7 | −19.5 ± 2.5 |
| HEPES 0.1M buffer | 0.3 ± 0.3 | −2.0 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 2.2 | 0.0 ± 0.7 | −7.5 ± 2.5 | −1.3 ± 7.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocha, S.; Félix, R.; Valente, M.J.; Bento-Silva, A.; Rebelo, R.; Amorim, C.G.; Araújo, A.d.N.; Moreira, R.; Santos-Silva, A.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. Polysulfone Membranes Doped with Human Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitors: Assessment of Bioactivity and Biocompatibility. Membranes 2023, 13, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010089
Rocha S, Félix R, Valente MJ, Bento-Silva A, Rebelo R, Amorim CG, Araújo AdN, Moreira R, Santos-Silva A, Montenegro MCBSM. Polysulfone Membranes Doped with Human Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitors: Assessment of Bioactivity and Biocompatibility. Membranes. 2023; 13(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010089
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocha, Susana, Rita Félix, Maria João Valente, Andreia Bento-Silva, Rute Rebelo, Célia Gomes Amorim, Alberto da Nova Araújo, Rui Moreira, Alice Santos-Silva, and Maria Conceição B. S. M. Montenegro. 2023. "Polysulfone Membranes Doped with Human Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitors: Assessment of Bioactivity and Biocompatibility" Membranes 13, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010089
APA StyleRocha, S., Félix, R., Valente, M. J., Bento-Silva, A., Rebelo, R., Amorim, C. G., Araújo, A. d. N., Moreira, R., Santos-Silva, A., & Montenegro, M. C. B. S. M. (2023). Polysulfone Membranes Doped with Human Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitors: Assessment of Bioactivity and Biocompatibility. Membranes, 13(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010089