Abstract
Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)-based copolymers are at the forefront of advanced membrane materials for selective CO2 separation. In this work, free-standing composite membranes were prepared by blending imidazolium-based ionic liquids (ILs) having different structural characteristics with a PEO-based copolymer previously developed by our group, targeting CO2 permeability improvement and effective CO2/gas separation. The effect of IL loading (30 and 40 wt%), alkyl chain length of the imidazolium cation (ethyl- and hexyl- chain) and the nature of the anion (TFSI-, C(CN)3-) on physicochemical and gas transport properties were studied. Among all composite membranes, PEO-based copolymer with 40 wt% IL3-[HMIM][TFSI] containing the longer alkyl chain of the cation and TFSI- as the anion exhibited the highest CO2 permeability of 46.1 Barrer and ideal CO2/H2 and CO2/CH4 selectivities of 5.6 and 39.0, respectively, at 30 °C. In addition, almost all composite membranes surpassed the upper bound limit for CO2/H2 separation. The above membrane showed the highest water vapor permeability value of 50,000 Barrer under both wet and dry conditions and a corresponding H2O/CO2 ideal selectivity value of 1080; values that are comparable with those reported for other highly water-selective PEO-based polymers. These results suggest the potential application of this membrane in hydrogen purification and dehydration of CO2 gas streams.
1. Introduction
The increase of carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in the atmosphere due to anthropogenic activities such as burning of fossil fuels (i.e., coal, oil and natural gas), deforestation and wildfires is the main cause of global warming and climate change [1]. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is an approach for reducing CO2 emissions by removing CO2 from large industrial and power plants, followed by its compression, transport and permanent storage [2]. Removal of CO2 from hydrogen streams produced by the steam reforming process and water gas shift reaction can also be viewed in a similar context. CO2 separation using polymeric membranes is a promising technology and has many advantages over other methods, namely absorption, pressure swing adsorption and cryogenic distillation [3]. The advantages include low energy consumption, simple installation and scale-up and eco-friendly characteristics [4,5].
Copolymer and polymeric ionic liquid (PIL)-based membranes containing poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) units, such as Pebax® (poly(amide-b-ethylene oxide)), PolyactiveTM (PEO75PBT25), PEGMA-9502 and PIL750-MeSO4, have shown improved CO2 permeation properties with increasing PEO weight content owing to the higher contribution of polar ethylene oxide (EO) units in the system, which interact favorably with CO2 [6,7,8,9]. Considering the high CO2 affinity of PEO groups due to the quadrupole-dipole intermolecular forces between the ether oxygen of PEO (C-O-C) and CO2 molecules, PEO-based membranes exhibit enhanced CO2 permeability and selectivity towards other gases [10,11]. However, it is well known that pure PEO suffers from poor film-forming properties and also has the tendency to crystallize, thereby leading to free volume reduction and deterioration of its CO2 separation performance. For this reason, our group has recently developed aromatic polyether copolymers bearing flexible, amorphous PEO pendants with excellent mechanical properties [8]. The copolymer membrane with the highest PEO content (Py-PEO750-49) exhibited the highest CO2 permeability (11.2 Barrer) with a corresponding maximum ideal CO2/H2 selectivity of 9.6, surpassing the upper bound. In order to further improve CO2 permeability, the latter was converted to its PIL analogue containing CO2-philic counter anions (C(CN)3-, TFSI-) [9]. However, the prepared PILs showed lower CO2 permeability values compared to that of the precursor due to their denser polymer chain packing, which hinders gas diffusion and thus results in a gas permeability decrease.
One different approach to enhancing CO2 transport through polymers is the incorporation of ionic liquids (ILs) into the polymer matrix [12,13,14,15,16]. In addition, such composite membranes show improved thermal and mechanical stability compared to supported ionic liquid membranes (SILMs) [16,17,18]. Ionic liquids act both as physical crosslinkers and plasticizers, thereby contributing to the reduction of polymer crystallinity of PEO-based membranes [19,20]. As a result, gas permeability increases, while ideal selectivity decreases following the “trade off” behavior [21,22].
PEO-based copolymer/IL membranes have been investigated as CO2-selective membranes, and the effect of PEO-based copolymer and IL nature, as well as IL loading, on gas permeation properties has also been studied. In specific, Bernardo et al. [20] prepared composite membranes by entrapping different amounts of [BMIM][CF3SO3] into two different, Pebax®1657 and Pebax®2533, matrices. In the less permeable Pebax®1657, the addition of IL resulted in a gas permeability increase and a slight ideal selectivity decrease for most gas pairs. However, for Pebax®2533, the gas permeation properties were not particularly affected by the presence of IL, suggesting that the polymer matrix plays a major role in gas permeation.
Regarding the effect of IL nature on gas separation performance, imidazolium-based ILs containing different alkyl chain length and glycine ([Gly]-) as a counter anion were incorporated into a Pebax®1657 matrix for the preparation of composite membranes [23]. A significant CO2 permeability and CO2/gas ideal selectivity enhancement was observed by increasing the alkyl chain length. The Pebax®1657/[C6MIM][Gly] membrane showed the best performance, exhibiting a CO2 permeability of 1490 Barrer and a corresponding CO2/N2 ideal selectivity of 95. On the other hand, it is well documented that anions dominate the interaction and affinity with CO2. For this reason, ILs with fluorinated anions such as [TFSI]− [16,17,19,24,25,26,27,28,29], [TFO]- [20,25], [BF4]− [18,30] and [FAP]− [25] are usually chosen due to their high CO2 affinity. For example, PolyActiveTM was blended with [BMIM][TFSI], and single and mixed gas transport properties of the prepared composite membranes were studied as a function of IL loading [31]. Upon addition of the IL, the crystallinity of the polyether phase was reduced and, as a result, gas diffusion and permeability were increased. The CO2/gas separation factors were close to ideal selectivity and remained unaffected at pressures up to 6 bar.
Aromatic polyethers that bear main chain, 2,6-substituted pyridine segments and short side chain PEO groups were already reported for CO2 separation by our group [8]. Despite their low CO2 permeability, these copolymers exhibit many advantageous characteristics, as they combine the excellent film-forming ability and thermomechanical stability with the high PEO content and amorphicity. Similar copolymer structures containing short side PEO segments have been synthesized and investigated as polymer electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries [32]. Therefore, in an attempt to improve both CO2 permeability and selectivity of the neat copolymer, it was blended with ionic liquids with different structural characteristics to afford composite membranes. Imidazolium-based ionic liquids containing CO2-philic anions were chosen to be incorporated into the polymer matrix, owing to their high CO2 solubility, as already reported [16,18]. In addition, it should be stressed that the presence of polar pyridine moieties along with sulfone groups in the polyether backbone enables the formation of hydrogen bonds with water, thereby promoting water vapor permeability towards water-selective membranes.
In this study, three different imidazolium-based ionic liquids containing alkyl chains with varying length and counter anions bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([TFSI]−) or tricyanomethanide ([C(CN3)]-) were incorporated into an aromatic polyether bearing side PEO units (2,6Py-PEO350) to yield free-standing, soft composite membranes. The effect of IL nature and loading on morphological, thermal and gas transport properties of the prepared 2,6Py-PEO350/IL composite membranes were studied. The water vapor transport properties were also evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Dimethylacetamide (DMAc, 99%) was supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (Burlington, MA, USA). Lithium bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonamide (LiTFSI, 99%), 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([EMIM][Cl], 98%), 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tricyanomethanide ([EMIM][C(CN)3], 98%) and 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonamide ([HMIM] [TFSI], 99%) were purchased from IoLiTec (Heilbronn, Germany). All chemicals were used without further purification. Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), hydrogen (H2) and helium (He) with a 99.999% level of minimum purity (for CH4, 99.99%) were provided by Air Liquide Hellas (Athens, Greece).
2.2. IL Preparation
For the preparation of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonamide ([EMIM][TFSI]), 1 g (6.82 mmol) of [EMIM][Cl] was dissolved in 6 mL of acetonitrile, and a solution of LiTFSI (2.34 g, 8.184 mmol) in 6 mL of acetonitrile was also prepared. Then, the LiTFSI solution was added dropwise to the IL solution at room temperature and left under stirring for 2 days to achieve maximum yield of anion exchange. The mixture was filtered and washed with acetonitrile and methanol for the removal of the excess LiTFSI salt. Finally, the obtained IL was recrystallized in dichloromethane for further purification.
2.3. Synthesis of Precursor Copolymer (2,6Py-PEO350)
The synthesis of 2,6Py-PEO350 copolymer was carried out according to our previous work [8]. In particular, a polycondensation reaction was used to produce aromatic polyethers containing main chain 2,6-substituted pyridine segments and short side chain PEO groups (MW = 350, ethylene oxide repeating units) with a composition of 60/40 (Scheme 1) corresponding to a 39 wt% PEO content. This copolymer exhibits excellent film-forming ability, owing to its high molecular weights (Mn = 36,400, Mw = 57,000, PDI = 2.2).
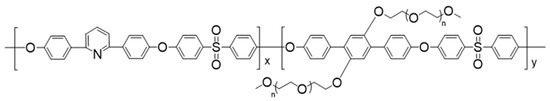
Scheme 1.
The precursor copolymer 2,6Py-PEO350 with composition x = 60 and y = 40.
2.4. Membrane Preparation
All composite and precursor membranes were prepared using the solution-casting method. First, the polymer solution was prepared by dissolving 200 mg of 2,6Py-PEO350 polymer in DMAc (5 wt% concentration) at room temperature. Different amounts of three different ionic liquids (IL1-[EMIM][TFSI], IL2-[EMIM][C(CN)3] and IL3-[HMIM][TFSI]) were added to the polymer solution under stirring to form a homogeneous mixture. Then, it was poured onto a flat glass plate and the solvent was slowly evaporated at 80 °C for 24 h. All prepared membranes were dried under vacuum at 80 °C until a constant weight was achieved. Polymer-IL composite membranes are hereafter referred to as 2,6Py-PEO350-xILz, where x denotes the wt% concentration of IL used, and z defines the kind of IL used, as shown in Scheme 2.
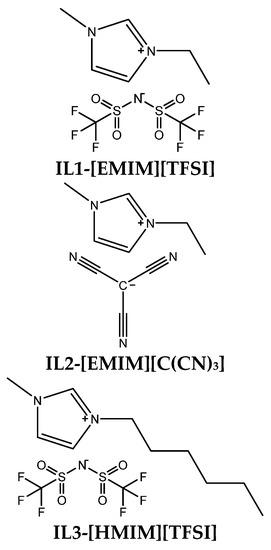
Scheme 2.
Chemical structures of the ionic liquids used to prepare polymer-IL composite membranes.
2.5. Membrane Characterization
ATR spectra of all membranes were collected from 4000 to 400 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1 using a platinum ATR Bruker spectrometer. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed on a Labys TG (Setaram Instrumentation, Caluire-et-Cuire, France) under N2 flow from 25 to 800 °C with a heating rate of 10 °C min−1. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was conducted on a Perkin Elmer DSC Q100 instrument (Waltham, MA, USA) under N2 flow, in the temperature range from −100 °C to 200 °C and with a heating rate of 10 °C min−1. Two heating cycles were performed, and the glass transition temperature was derived from the second cycle. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was conducted using a LEO Supra 35VP microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). The cross-sections of the membranes were prepared after fracturing in liquid N2.
2.6. Single Gas and Gas/Water Vapor Permeation Properties
Single gas permeation properties of precursor 2,6Py-PEO350 and composite membranes were studied at 30 °C using the Wicke–Kallenbach method. The experimental procedure and the description of the permeation cell were previously reported [33]. The addition of 3% H2O in each single gas at the retentate side was only studied for the 2,6Py-PEO350-40IL3 composite membrane, which showed the best single gas permeation properties. While He flow rate of 20 cm3 min−1 was employed in the permeate side for measurements under dry conditions, He flow rate of 100 cm3 min−1 was used for wet conditions. The gas permeability (P) was calculated according to the equation:
where A is the effective membrane area, pr and pp are the retentate and permeate side partial pressures of the measured gas, respectively, F is the volume fraction of the measured gas present in helium flow, l is the membrane thickness and φv,tot is the volumetric flow rate of helium at the permeate side.
Selectivity (αA/B) was calculated as the ratio of the permeabilities PA and PB of the gases A and B, respectively, using the following equation:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Polymer-IL Composite Membranes
Mechanically robust, amorphous, soft PEO-based membranes with high PEO contents based on aromatic polyether copolymers bearing main chain 2,6-substituted pyridine segments and short side chain PEO groups (2,6Py-PEO350) have recently been prepared and investigated as CO2 and water-selective membranes by our group [8]. The high content of CO2-philic PEO groups induces severe plasticization of the rigid polymer backbone, as reflected by the shifting of Tg values to lower temperatures (close to room temperature), thereby resulting in increased chain mobility and flexibility, which in turn leads to increased gas/vapor diffusion. In addition, it has been proven that the incorporation of ionic liquids into the polymer matrix can further improve CO2 permeability based on their ionic character. For this reason, 2,6Py-PEO350 copolymer containing 39 wt% PEO was blended with ionic liquids (30 and 40 wt% contents) to prepare composite membranes aiming at CO2 permeability and separation performance enhancement. In this case, imidazolium-based ILs including IL1-[EMIM][TFSI], IL2-[EMIM][C(CN)3] and IL3-[HMIM][TFSI] were chosen, owing to their high CO2 solubility [16,18]. All the fabricated composite membranes were flexible, self-standing and soft, as illustrated in Figure 1. It should be noticed that the fabrication of free-standing films with IL loading higher than 40 wt% was not possible because of the instability of the resulting membranes.
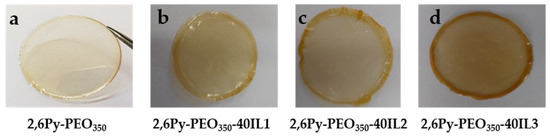
Figure 1.
Pictures of the prepared neat polymer (a) and polymer-IL composite membranes with (b) 40 wt% of IL1, (c) 40 wt% of IL2 and (d) 40 wt% of IL3.
As illustrated in Figure 2, the precursor copolymer 2,6Py-PEO350 membrane along with the polymer-IL composite membranes were studied by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Regarding the precursor spectrum, the peak signal at 2868 cm−1 is assigned to methylene group vibrations of the PEO units [8,34]. In addition, the doublet peak at 1487 and 1471 cm−1 and the peak signal at 1583 cm−1 correspond to the C=C/C=N vibrations of the pyridine ring [8,35]. Considering that all ILs used in this work for the preparation of polymer-IL composite membranes contain a common imidazolium cation, the characteristic peak at 1574 cm−1 assigned to the imidazolium ring in plane symmetric/asymmetric stretch and –CH2(N)/-CH3(N)CN could not be observed in all composite membrane spectra due to overlapping with the peak at 1583 cm−1. However, after the addition of ILs containing a TFSI- anion, a new peak at 1350 cm−1 appears that can be attributed to the asymmetric stretching of the SO2 group [9]. The symmetric bending vibrations of the same group are located at 616 cm−1 and 604 cm−1. The peak located at 1053 cm−1 is assigned to the asymmetric stretching band of the S–N–S group, and its bending vibrations can be identified as very weak peaks at 650 cm−1 and 612 cm−1. The bands at 789 cm−1 and 509 cm−1 are also attributed to asymmetric bending of the CF3 group and the C-S bond of the TFSI- anion, respectively. After addition of IL containing a C(CN)3- anion, a new strong peak arose at 2158 cm−1, attributed to the stretching vibration of the -CN group [9,36]. No shifts were observed in the ATR-IR spectra of 2,6Py-PEO350-IL membranes compared to those of neat 2,6Py-PEO350 copolymers.
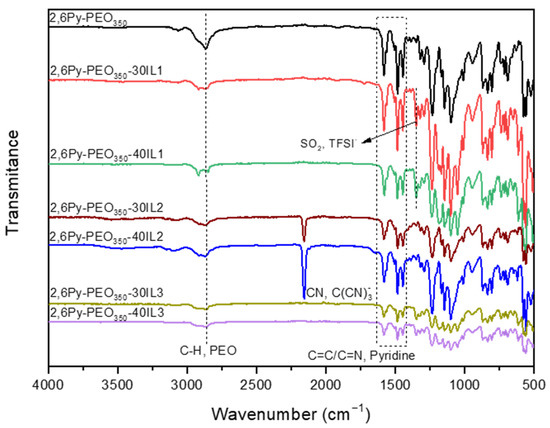
Figure 2.
ATR-FTIR spectra of the precursor polymer and the polymer-IL composite membranes.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to investigate the thermal stability of polymer-IL composite membranes. The TGA curves of precursor polymer and composite membranes containing 30 wt% IL are given in Figure 3. The precursor shows two main degradation steps, where the first step is observed at around 330 °C, assigned to the loss of PEO side groups [8] and the second one is at 430 °C, corresponding to the polymer backbone degradation. Regarding composite membranes containing IL1-[EMIM][TFSI] and IL3-[HMIM][TFSI], an initial weight loss up to 210 °C (1.5 and 3.5 wt%, respectively) was observed, attributed to DMAc residual solvent. For the latter, a second small weight loss at around 320 °C was evident, attributed to the evaporation of the corresponding IL3 [37]. All composite membranes show two main weight loss steps. The first starts at around 305–330 °C, associated with the degradation of side PEO groups, and the second one, at about 400–430 °C, is due to polymer backbone and ionic liquid degradation simultaneously. Indeed, for example, the reported degradation temperature of IL1 is 393 °C, which is in good agreement with our results [38]. Comparison of the TGA curves of the composite membranes containing imidazolium ILs with different alkyl chain length reveals that thermal degradation of the composite membrane with an imidazolium cation with a shorter alkyl chain length (IL1) starts at a higher temperature (Td ~ 330 °C) than the degradation of the corresponding with the longer alkyl chain (Td ~ 320 °C). This result may be explained by the stronger electrostatic interactions between the precursor copolymer and ionic liquid containing imidazolium cations with a shorter alkyl chain length, thus delaying the composite decomposition. In addition, the effect of anion nature on thermal stability was also investigated. Among composite membranes containing 30 wt% IL, the one with the TFSI- anion shows higher thermal stability than the corresponding with the C(CN)3- anion (the decomposition for the former starts at 330 °C, and for the latter at 305 °C). This is in agreement with the degradation temperatures determined for neat ILs [38]. The thermal stability of all prepared membranes incorporated with ionic liquid was found to be sufficient at temperatures up to ~300 °C, suggesting the suitability of these membranes for gas separation applications.
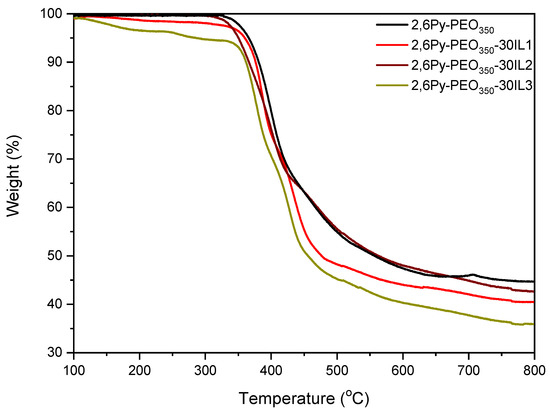
Figure 3.
Comparative TGA curves of precursor-PEO350 and polymer composite membranes with 30 wt% IL.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to determine the glass transition temperatures of the polymer-IL composite membranes, as depicted in Figure 4. Generally, all composite membranes display lower glass transition temperatures (Tgs) compared to the neat copolymer, with a more pronounced reduction for higher IL contents. For instance, the composite membrane containing 30 wt% IL1-[EMIM][TFSI] has a Tg value of 15.4 °C, while an increase in IL1 content (40 wt%) is followed by a further Tg decrease to −7.3 °C. This is due to the plasticization effect, resulting in flexible and soft membrane structures [18] with increased free volume and, consequently, lower Tg, as already reported [35,38]. Regarding the effect of the anion’s chemical structure on Tg, the comparison of composite membranes containing the same IL content (40 wt%) but ILs with different counter anions (TFSI- and C(CN)3-), reveals that the Tg of composite membranes containing IL2-[EMIM][C(CN)3] is higher (4 °C) than the corresponding of composite membranes with IL1. This can probably be attributed to the lower molar volume of the C(CN)3- anion (123.33 Å3) [39] compared to the TFSI- anion (208.3 Å3) [40]. As a consequence, the chain mobility is restricted since the C(CN)3- anion can be accommodated in the available free interchain space, thus leading to the free volume reduction and, thereby, to Tg increase. The lowest Tg value of −18.3 °C was observed for the composite membrane comprising an imidazolium cation with hexyl groups (IL3) having 40 wt% IL content, while the corresponding one with shorter chain length (ethyl groups) has a Tg value of −7.3 °C. The increase of the alkyl chain length of the cation results in free volume and chain mobility increase, thus leading to Tg decrease. For all composite membranes, the presence of a single Tg indicates the successful incorporation of the three different ILs into the polymer matrix. It should be noted that all composite membranes are in the rubbery state at 30 °C, the temperature used for water vapor and gas permeation experiments in this study.
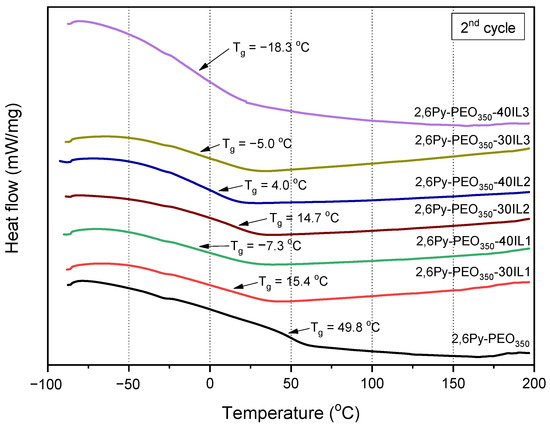
Figure 4.
DSC curves for the precursor polymer and the polymer-IL composite membranes.
The membrane morphology plays a vital role in gas separation and purification performance. The cross-sectional SEM micrographs of polymer-IL composite membranes containing 40 wt% of each IL are illustrated in Figure 5. It was revealed that all membranes are dense, smooth and not phase-separated. This suggests that ILs were uniformly distributed into the polymer matrix, leading to non-porous, homogeneous structures. Similar observations were reported for the Pebax®1657/(Emim]BF4]) polymer IL pair by Rabiee et al. [18]. The thickness of the membranes ranges from 47 to 165 μm.
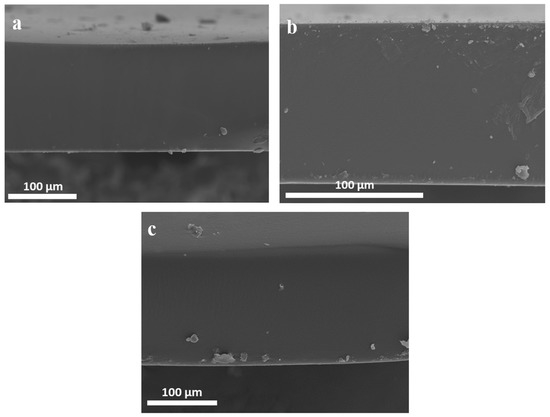
Figure 5.
SEM micrographs of composite membranes containing 40 wt%. (a) [EMIM][TFSI], (b) [EMIM][C(CN)3] and (c) [HMIM][TFSI].
3.2. Gas Separation Properties of Polymer-IL Composite Membranes
The gas separation properties of the 2,6Py-PEO350 precursor copolymer and the composite membranes were determined using the Wicke–Kallenbach method at 30 °C. The gas permeability data (CO2, CH4, H2) are shown in Table 1. It was observed that the precursor copolymer exhibits much lower gas permeability than composite membranes containing the imidazolium-based ILs with TFSI- (IL1 and IL3). Generally, IL molecules plasticize the polymer matrix, leading to improved chain mobility and increased free volume, and consequently to enhanced gas diffusivity and permeability [18,41,42,43,44]. However, solubility also plays a significant role in permeability according to the solubility-diffusion mechanism for dense membranes [45]. For instance, ILs with TFSI- and C(CN)3- as counter anions are reported to show high CO2 solubility due to chemical interactions of CO2 molecules with the anions [46,47,48]. In addition, the higher fractional free volume of ILs compared to polymers facilitates the CO2 diffusion across composite membranes [38]. In contrast to this, CH4 and H2 have no significant interactions with ILs [38], thus very small additional solubility contribution is expected for CH4 and H2 in composite membranes, and, therefore, diffusion mainly contributes to CH4 and H2 permeability increases. As a result, the permeability increment is more significant for CO2 instead of H2 and CH4 due to the high diffusivity and solubility of CO2 in a polymer and IL matrix, respectively. For this reason, CO2/CH4 and CO2/H2 ideal selectivities are also increased with the addition of ILs. In contrast, the incorporation of the imidazolium-based IL with C(CN)3- (IL2) into the polymer matrix caused a clear reduction of CH4 and H2 permeability, while CO2 permeability was almost not affected. The reduction is more pronounced for H2 than CH4. This phenomenon could be possibly attributed to two reasons. The lower molar volume of the C(CN)3- counter anion enables IL accommodation in the initial available free interchain spacing, thus restricting chain mobility and resulting in smaller interchain spacing for gas transport. Another reason could be the strong interactions of the IL cation with the C(CN)3- anion and/or PEO groups of the precursor with IL ionic moieties that can lead to a tighter and more compact structure. As the restriction induced by the strong interactions has a more considerable effect on permeability than plasticization, the CH4 and H2 permeabilities were decreased.

Table 1.
Single gas permeability and CO2 selectivity over other gases of the precursor polymer and the polymer-IL composite membranes (1 Barrer = 10−10 cm3(STP) cm cm−2 s−1 cm Hg−1).
The effect of IL content on gas separation properties was studied. The permeability of all gases is significantly increased by increasing the IL loading in the host polymer matrix for all composite membranes. Besides plasticization effect and free volume increase discussed above, the higher intrinsic permeability of ILs may also contribute significantly to the increase of gas permeabilities [46]. For instance, 2,6Py-PEO350 containing 40 wt% [EMIM][TFSI] (IL1) exhibited almost 40% higher gas permeabilities than the corresponding membrane with IL loading 30 wt%. In specific, CO2 permeability is increased from 17.3 Barrer to 24.7 Barrer by increasing the IL1 content from 30 to 40 wt%, while ideal selectivity of CO2/CH4 remains constant. The same trend is also reported for systems including Pebax®1657/[BMIM][CF3SO3] and PolyActiveTM/[EMIM][BF4] composite membranes [18,19]. The positive effect of IL content on CO2 permeability and CO2/CH4 selectivity was observed for glassy polyether sulfone/[EMIM][TFSI] membranes as well, where CO2 permeability increased from 196.11 Barrer to 255.30 Barrer with increasing IL content from 30 to 40 wt% [38].
Another factor that may influence the gas separation properties is the alkyl chain length in the imidazolium cation. As shown in Table 1, by comparing the CO2 and CH4 permeability values of 2,6Py-PEO350-40IL3 containing the hexyl chain substituent in the cation with the corresponding membrane having the ethyl chain substituent (IL1), it is evident that the former has 1.9- and 2.5-times higher values, respectively, than the latter. The longer alkyl chains probably enable the better distribution of the IL into the polymer matrix, thus inducing a stronger plasticization and free volume increase, which facilitates gas diffusion and, consequently, gas permeability increase. The same trend was also reported by X. Li et al. [23]. In particular, Pebax®1657 composite membranes containing imidazolium ILs having different alkyl chain lengths (ethyl and hexyl groups in the cation) were prepared, and a significant CO2 permeability increment was observed with increasing alkyl chain length.
Concerning the effect of the IL anion on gas transport, it was observed that composite membranes containing the C(CN)3- anion (IL2) exhibit significantly lower permeability for all gases than the corresponding membranes with the TFSI- anion (with 30 or 40 wt% IL content). This is attributed to the denser polymer chain packing due to strong interactions of IL cation and anion and/or PEO groups with IL ionic moieties, thus contributing to gas diffusion decrease and, thereby, to gas permeability decrease [9]. However, in supported IL membranes containing TFSI- and C(CN)3- anions, the CO2 permeability appears not to be affected by the type of anion under the same measurement conditions [49]. On the other hand, it would be expected that, due to the high number of cyano groups contained in IL2, CO2 permeability and solubility should be high [48]. However, this seems not to be the case neither for the prepared composite membranes of this work as evidenced by the gas permeability data, nor for other PEO-based PILs [9].
Pure gas permeabilities of the precursor and the polymer-IL composite membranes follow the order CO2 (3.30 Å) > H2 (2.87 Å) > CH4 (3.80 Å) [50], where CO2 has higher permeability than H2, although the latter has smaller kinetic diameter. Consequently, the precursor and all composite membranes exhibit CO2/H2 “reverse selectivity”, in which CO2 is preferentially transported across the membrane over H2. This is mostly characteristic for rubbery polymers or those that can strongly interact with CO2 molecules such as PEO-based membranes [8]. In specific, these polymers exhibit high CO2 solubility due to significant interactions of quadrupole CO2 molecules with polar PEO groups, thus resulting in higher CO2 permeability. In glassy polymers, the opposite trend is observed, as the diffusion-controlled gas transport dominates leading to the preferential transport of H2 over CO2. The composite membrane with 40 wt% [HMIM][TFSI] (IL3) achieved the highest CO2 gas permeability value of 46.1 Barrer with corresponding ideal selectivity values of 39 and 5.6 for CO2/CH4 and CO2/H2 pairs, respectively.
Comparison of gas permeability and selectivity of the precursor and the prepared composite membranes for the CO2/CH4 gas pair with a PEO-based polymer and other polymer/IL membranes reported in the literature is shown in Figure 6A. It can be noticed that their separation performance is comparable or even higher than the other membranes investigated. In addition, all prepared composite membranes show improved CO2/CH4 separation performance (selectivity varying in the range of 39–64) compared to the precursor membrane (33), owing to the presence of ILs, which exhibit high CO2 solubility and permeability. These data lie close but below the 2008 Robeson upper bound line. The composite membrane containing 30 wt% IL3 exhibits the highest CO2/CH4 selectivity (64) among all composite membranes. The significant increase of CO2/CH4 selectivity (almost 2 times higher than the precursor membrane) can be ascribed to the relative permeability increment of CO2, which is more pronounced compared to that of CH4. While for methane the permeability increase is mostly owed to diffusivity increase, the contribution of both solubility and diffusivity on permeability enhancement for CO2 is evident. A similar CO2/CH4 selectivity value of 72 for Pebax®MH 1657 blended with 20 wt% of [C4MIM][Gly] was reported [23]. Although with increasing IL content there is no clear trend for CO2/CH4 selectivity, in the case of composite membranes containing IL2, both CO2 permeability and CO2/CH4 selectivity increased, suggesting that this system does not follow the typical “trade off” behavior between permeability and selectivity. On the contrary, the increase of IL content in composite membranes containing IL3 results in the deterioration of CO2/CH4 separation performance. In addition, the anion’s effect on CO2/CH4 selectivity was studied and revealed that by switching from TFSI-- (IL3) to C(CN)3--containing composite membranes, the selectivity is reduced from 64 to 39, respectively. This is mainly related to the reduction of CO2 permeability, which is more significant compared to that of CH4. A possible explanation is that composite membranes containing the C(CN)3- counter anion exhibit a tighter polymer chain packing due to strong interchain electrostatic interactions between the IL cation and anion and/or between PEO groups and IL ionic moieties, which hinders gas diffusion and thus leads to permeability decrease.
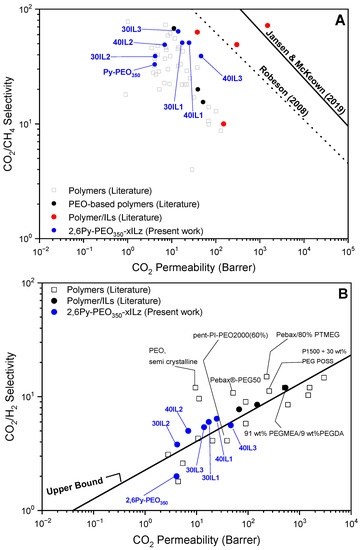
Figure 6.
Permeability–selectivity upper bound plots of 2,6Py-PEO350 and composite membranes (blue circles) for (A) CO2/CH4 and (B) CO2/H2 selectivity. The 2008 and 2019 upper bounds for CO2/CH4 (35 °C) were adapted from refs. [22,51]. The upper bound for CO2/H2 (25 °C) was adapted from refs. [52,53]. The rest of the data points were taken from refs. [7,52,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64].
As evidenced in Figure 6B, almost all polymer-IL composite membrane surpassed the upper bound limit for CO2/H2 separation, while precursor polymer 2,6Py-PEO350 lies below this limit. All composite membranes (with 30 wt% IL) showed simultaneously higher CO2 permeability and CO2/H2 selectivity than the neat copolymer. The CO2/H2 ideal selectivity enhancement can be mainly attributed to the increased CO2 diffusivity and CO2 solubility of the ILs. By increasing IL content from 30 to 40 wt%, the CO2/H2 selectivity was further increased. The positive effect of increasing IL content on CO2/H2 selectivity was also reported for Pebax®1657/[Emim][BF4] [18]. The 2,6Py-PEO350 with 40 wt% [EMIM][TFSI] (IL1) has the best CO2/H2 selectivity value of 6.4 and a CO2 permeability value of 24.7 Barrer. The separation performance of the composite membranes of this work is comparable with other PEO-based copolymer membranes and polymer/IL composite membranes reported in the literature, despite their lower CO2 permeability, as depicted in Figure 6B. For instance, Bernardo et al. studied the separation performance of Pebax®1657 blended with 20–80 wt% [BMIM][CF3SO3] and reported that the composite membrane containing 40 wt% IL content exhibited an ideal CO2/H2 selectivity value of 8.5 and a CO2 permeability value of 150 Barrer [12].
In conclusion, a prospective strategy for enhancing the CO2 separation properties of polymer-IL composite membranes comprises the successful tailoring of IL types (cation, anion) having high CO2 solubility combined with a high CO2 affinity polymer matrix.
3.3. Water Vapor Separation Properties of Polymer-IL Composite Membranes
The water vapor permeation properties of the precursor polymer and the 2,6Py-PEO350-40IL3 composite membrane with the highest gas permeabilities (CO2, CH4, H2), were also studied (Figure 7, Table 2). In specific, the precursor polymer had a water vapor permeability of 8900 Barrer, as the presence of polar pyridine units in the polyether backbone and side hydrophilic PEO groups enables the formation of hydrogen bonds with water, thus promoting water vapor permeability. The addition of 40 wt% [HMIM][TFSI] (IL3) into the polymer matrix had a positive effect on water vapor permeability. In specific, a substantial increase of water vapor permeability by 5.6 times to 50,000 Barrer was observed. The strong plasticization induced by the incorporation of IL3 causes a significant increase of free volume, thus facilitating water vapor diffusion and, consequently, water vapor permeability enhancement. It should be stressed that water vapor permeability is mainly governed by the hydrophilicity and hydrogen bond basicity of the counter anion in PILs, as recently reported by our group [9]. In the case of the 2,6Py-PEO350-40IL3 composite membrane, despite the hydrophobic character of [HMIM][TFSI] (IL3) and its weak proton acceptor ability (due to the electron-withdrawing effect of fluorine atoms in TFSI-), the hydrogen bond between water molecules and the TFSI- anion do form. However, the water vapor permeability improvement is mainly attributed to the high diffusivity and to a lesser extent to solubility. The H2O/CO2 selectivity of the composite membrane was significantly declined by 50% to 1080 compared to the corresponding one of precursor membrane. To the best of our knowledge, water vapor permeability data of polymer-IL composite membranes are limited, and, consequently, a comparison can be made only with hydrophilic polymers containing PEO groups. As illustrated in Figure 7, the water vapor permeation behavior of the present composite membrane is on par with other PEO-based polymers such as Pebax®1074, PolyactiveTM and PEO-PBT. These results underline the potential of this composite membrane for dehydration applications.
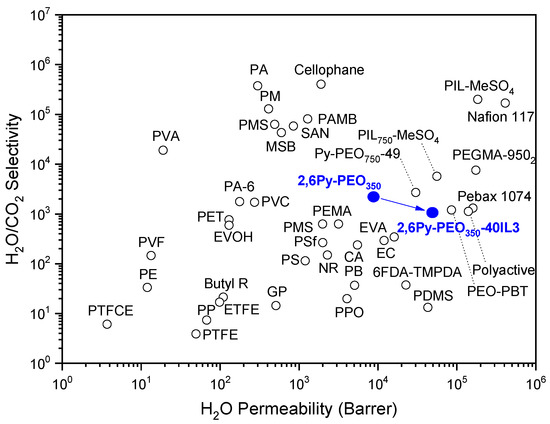
Figure 7.
Comparison of H2O permeability with H2O/CO2 selectivity of 2,6Py-PEO350 and 2,6Py-PEO350-40IL3 membranes (blue circles) with other polymers reported in the literature (25–35 °C) [33].

Table 2.
Water vapor permeation properties of the precursor polymer and composite membrane containing 40 wt% [HMIM][TFSI] IL under dry and wet conditions (1 Barrer = 10−10 cm3(STP) cm cm−2 s−1 cm Hg−1).
Gas permeation properties of the 2,6Py-PEO350-40IL3 membrane were also studied under wet conditions. A total of 3% H2O was added in the feed flow of each gas at the retentate side to investigate how the presence of water can affect gas permeability and selectivity. The gas permeation properties of 2,6Py-PEO350-40IL3 under dry and wet conditions are given in Table 2. It is evident that CO2 and CH4 permeability remained unchanged (considering the given errors), while H2 permeability was slightly increased (11.0 Barrer). As a result, gas selectivities/separation factors (SF) were not noticeably affected, and H2O/gas separation factors remained unaltered. On the other hand, Dai et al. [65] used the IL [TETA][tfa] for the preparation of Pebax®/TSIL blends and reported that the presence of water vapor (high relative humidity) in feed gas enables membrane swelling, which favors gas diffusion. In specific, CO2 permeability of a composite membrane containing 30 wt% IL changed from around 250 to 567 GPU, denoting the positive role of water vapor on gas transport through membranes. As [TETA][tfa] is a very hydrophilic IL, the membrane is strongly plasticized by water molecules, thus leading to gas diffusion increase. In contrast, in the case of the prepared membrane containing the [HMIM][TFSI], swelling is not favored due to the IL’s hydrophobic character. For this reason, the presence of water vapor does not affect the separation properties.
4. Conclusions
Free-standing PEO-based copolymer-IL composite membranes were successfully prepared via the solution casting method by incorporating up to 40 wt% of three different ILs into the 2,6Py-PEO350 polymer matrix. The prepared composite membranes are amorphous and rubbery with low Tg values, as revealed by DSC. In addition, they are homogeneous, indicative of the good dispersion of the ILs into the polymer matrix and have high thermal stability up to ~300 °C, as evidenced by SEM and TGA analysis, respectively. The addition of ILs containing different alkyl chain length in imidazolium and anions (TFSI-, C(CN3)-) into the polymer matrix (30 wt%) caused a significant increase of both CO2 and CO2/H2 selectivity compared to the neat PEO-based copolymer. The composite membrane with 40 wt% [HMIM][TFSI] (IL3) achieved the highest CO2 gas permeability value of 46.1 Barrer with corresponding ideal selectivity values of 39 and 5.6 for CO2/CH4 and CO2/H2 pairs, respectively. Almost all polymer-IL composite membranes surpassed the upper bound limit for CO2/H2 separation, while the precursor polymer 2,6Py-PEO350 lies below this limit. The CO2/H2 ideal selectivity enhancement can be mainly attributed to the increased CO2 diffusivity and CO2 solubility of the ILs. Regarding the alkyl chain length in the imidazolium cation, the comparison of the CO2 and CH4 permeability values of 2,6Py-PEO350-40IL3 containing the hexyl chain substituent in the cation with the corresponding membrane having the ethyl chain substituent (IL1) revealed that longer alkyl chains lead to free volume increase, which facilitates gas diffusion and, consequently, gas permeability increase. The positive effect of increasing IL loading on gas permeabilities was also revealed. Concerning the IL anion’s nature effect on gas transport, it was observed that composite membranes containing the C(CN)3- anion (IL2) exhibit significantly lower permeability for all gases than the corresponding membranes with the TFSI- anion (with 30 or 40 wt% IL content), which is attributed to the denser polymer chain packing that hinders gas diffusion and therefore results in reduced permeability. The composite membrane with 40 wt% [HMIM][TFSI] (IL3) also exhibits the highest water vapor permeability value of 50,000 Barrer and a corresponding H2O/CO2 ideal selectivity value of 1080, which are comparable to those reported for other highly water-selective PEO-based polymers. Therefore, it could be a potential candidate for hydrogen purification and dehydration of CO2 gas streams.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.D.; methodology, V.D.; investigation, E.S. and D.V.; resources, V.D. and T.I.; writing—original draft preparation, D.V.; writing—review and editing, V.D. and T.I.; supervision, V.D. and T.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the project “Bioconversion of lignite power plant emissions to fuels and fine chemicals (ΒΙOΜΕΚ)” (MIS Τ1ΕΔΚ-00279), which is implemented under the “EPAnEK 2014-2020 Operational Programme”, funded by the Operational Programme “Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation” (NSRF 2014-2020) and co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Regional Development Fund).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jacobson, M.Z. Review of Solutions to Global Warming, Air Pollution, and Energy Security. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 148–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot-Handford, M.E.; Abanades, J.C.; Anthony, E.J.; Blunt, M.J.; Brandani, S.; Mac Dowell, N.; Fernandez, J.R.; Ferrari, M.-C.; Gross, R.; Hallett, J.P.; et al. Carbon capture and storage update. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 130–189. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro, D.M.; Smit, B.; Long, J.R. Carbon Dioxide Capture: Prospects for New Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6058–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal, K.; Freeman, B.D. Gas separation using polymer membranes: An overview. Polym. Technol. 1994, 5, 673–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, S.J.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Wessling, M. Gas-permeation properties of poly(ethylene oxide) poly(butylene terephthalate) block copolymers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4590–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.H.; Kumar, M.; Vovusha, H.; Shevate, R.; Villalobos, L.F.; Schwingenschlögl, U.; Peinemann, K.-V. Scalable Synthesis of Amphiphilic Copolymers for CO2- and Water-Selective Membranes: Effect of Copolymer Composition and Chain Length. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 6213–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidi, A.; Vroulias, D.; Kallitsis, J.; Ioannides, T.; Deimede, V. Synthesis and characterization of poly(ethylene oxide) based copolymer membranes for efficient gas/vapor separation: Effect of PEO content and chain length. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 632, 119353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidi, A.; Anastasopoulos, C.; Vroulias, D.; Kallitsis, J.; Ioannides, T.; Deimede, V. Synthesis and properties of Polymeric ionic liquids (PILs) bearing hydrophilic PEO groups: Evaluation of gas and water vapor separation performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Shao, L.; Chua, M.L.; Lau, C.H.; Wang, H.; Quan, S. Recent progress in the design of advanced PEO-containing membranes for CO2 removal. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1089–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Jiang, X.; He, S.; Yang, X.; Long, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, L. Rational design of poly (ethylene oxide) based membranes for sustainable CO2 capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 24233–24252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, W.; Mansouri, J.; Li, H.; Chen, V. Improving CO2 separation performance of thin film composite hollow fiber with Pebax®1657/ionic liquid gel membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Bai, L.; Han, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Functionalized ionic liquid membranes for CO2 separation. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12671–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, M.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.H. Hybrid membranes based on ionic-liquid-functionalized poly(vinyl benzene chloride) beads for CO2 capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaeva, D.; Azcune, I.; Tanczyk, M.; Warmuzinski, K.; Jaschik, M.; Sandru, M.; Dahl, P.I.; Genua, A.; Loïs, S.; Sheridan, E.; et al. The performance of affordable and stable cellulose-based poly-ionic membranes in CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.C.; Friess, K.; Clarizia, G.; Schauer, J.; Izák, P. High Ionic Liquid Content Polymeric Gel Membranes: Preparation and Performance. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, K.; Jansen, J.C.; Bazzarelli, F.; Izák, P.; Jarmarová, V.; Kačírková, M.; Schauer, J.; Clarizia, G.; Bernardo, P. High ionic liquid content polymeric gel membranes: Correlation of membrane structure with gas and vapour transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Ghadimi, A.; Mohammadi, T. Gas transport properties of reverse-selective poly(ether-b-amide6)/[Emim][BF4] gel membranes for CO2/light gases separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepić, M.; Fuoco, A.; Monteleone, M.; Esposito, E.; Friess, K.; Petrusová, Z.; Izák, P.; Jansen, J.C. Tailoring the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of PolyActiveTM Poly(Ether-Ester) Multiblock Copolymers Via Blending with CO2-Phylic Ionic Liquid. Polymers 2020, 12, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Jansen, J.C.; Bazzarelli, F.; Tasselli, F.; Fuoco, A.; Friess, K.; Izák, P.; Jarmarová, V.; Kačírková, M.; Clarizia, G. Gas transport properties of Pebax®/room temperature ionic liquid gel membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, eaab0530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ding, S.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Z. Optimizing microstructure of polymer composite membranes by tailoring different ionic liquids to accelerate CO2 transport. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2020, 101, 103136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchytil, P.; Schauer, J.; Petrychkovych, R.; Setnickova, K.; Suen, S.Y. Ionic liquid membranes for carbon dioxide–methane separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdni-Goryaev, E.M.; Alentév, A.Y.; Belov, N.A.; Ponkratov, D.O.; Shaplov, A.S.; Lozinskaya, E.I.; Vygodskii, Y.S. Gas separation characteristics of new membrane materials based on poly(ethylene glycol)-crosslinked polymers and ionic liquids. Pet. Chem. 2012, 52, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Li, P.; Chung, T.-S. PVDF/ionic liquid polymer blends with superior separation performance for removing CO2 from hydrogen and flue gas. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 11796–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.C.; Clarizia, G.; Bernardo, P.; Bazzarelli, F.; Friess, K.; Randová, A.; Schauer, J.; Kubicka, D.; Kacirková, M.; Izák, P. Gas transport properties and pervaporation performance of fluoropolymer gel membranes based on pure and mixed ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 109, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohshim, D.F.; Mukhtar, H.; Man, Z. The effect of incorporating ionic liquid into polyethersulfone-SAPO34 based mixed matrix membrane on CO2 gas separation performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Gan, Q.; Nancarrow, P. Composite ionic liquid and polymer membranes for gas separation at elevated temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.U.; Park, D.; Ko, Y.; Baek, I. Polymer-ionic liquid gels for enhanced gas transport. Chem. Commun. 2009, 7227–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepić, M.; Setničkova, K.; Lanč, M.; Žák, M.; Izák, P.; Dendisová, M.; Fuoco, A.; Jansen, J.C.; Friess, K. Permeation and sorption properties of CO2-selective blend membranes based on polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide ([EMIM][DCA]) ionic liquid for effective CO2/H2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 97, 117623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vöge, A.; Deimede, V.; Paloukis, F.; Neophytides, S.G.; Kallitsis, J.K. Synthesis and properties of aromatic polyethers containing poly(ethylene oxide) side chains as polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 148, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deimede, V.; Vroulias, D.; Kallitsis, J.K.; Ioannides, T. Pyridinium based PIL membranes with exceptional high water vapor permeability and selectivity. Sep. Pur. Technol. 2020, 251, 117412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deimede, V.; Voege, A.; Lainioti, G.; Elmasides, C.; Kallitsis, J.K. Large-Scale Separators Based on Blends of Aromatic Polyethers with PEO for Li-Ion batteries: Improving Thermal shrinkage and wettability behavior. Energy Technol. 2014, 2, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouliaras, T.; Vollas, A.; Ioannides, T.; Deimede, V.; Kallitsis, J. Synthesis of imidazolium based PILs and investigation of their blend membranes for gas separation. Membranes 2019, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, A.S.L.; Malcaitè, E.; Lozinskaya, E.I.; Shaplov, A.S.; Tomé, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Poly(ionic liquid)–Ionic Liquid Membranes with Fluorosulfonyl-Derived Anions: Characterization and Biohydrogen Separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 7087–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xue, Z.; Mu, T. Quantitative Research on the Vaporization and Decomposition by Thermogravimetric Analysis-Mass Spectroscopy. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 7418–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, H.A.; Mohshim, D.F.; Mukhtar, H.; Murugesan, T.; Man, Z.; Bustam, M.A. Synthesis, characterization, and CO2 separation performance of polyether sulfone/[EMIM][Tf2N] ionic liquid-polymeric membranes (ILPMs). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 54, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardas, R.L.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Extension of the Ye and Shreeve group contribution method for density estimation of ionic liquids in a wide range of temperatures and pressures. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2008, 263, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelyubina, Y.V.; Shaplov, A.S.; Lozinskaya, E.I.; Buzin, M.I.; Vygodskii, Y.S. A New Volume-Based Approach for Predicting Thermophysical Behavior of Ionic Liquids and Ionic Liquid Crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10076–10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yave, W.; Car, A.; Peinemann, K.-V. Nanostructured membrane material designed for carbon dioxide separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 350, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Ren, J.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Hua, K.; Li, X.; Deng, M. Poly(amide-12-b-ethylene oxide)/glycerol triacetate blend membranes for CO2 separation. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2013, 19, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Ren, J.; Hua, K.; Li, H.; Ren, X.; Deng, M. Poly(amide-12-b-ethylene oxide)/polyethylene glycol blend membranes for carbon dioxide separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 116, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, A.; Amirilargani, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Kasiri, N.; Sadatnia, B. Preparation of alloyed poly(ether block amide)/poly(ethylene glycol diacrylate) membranes for separation of CO2/H2 (syngas application). J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 458, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.; Low, B.T. Gas separation membrane materials: A perspective. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6999–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muldoon, J.; Aki, S.N.V.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Dixon, J.K.; Brennecke, J.F. Improving Carbon Dioxide Solubility in Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 9001–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almantariotis, D.; Gefflaut, T.; Pádua, A.A.H.; Coxam, J.Y.; Costa Gomes, M.F.J. Effect of Fluorination and Size of the Alkyl Side-Chain on the Solubility of Carbon Dioxide in 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2010, 114, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Florindo, C.; Freire, C.S.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Playing with ionic liquid mixtures to design engineered CO2 separation membranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 17172–17182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahurin, S.M.; Yeary, J.S.; Baker, S.N.; Jiang, D.-e.; Dai, S.; Baker, G.A. Ring-opened heterocycles: Promising ionic liquids for gas separation and capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, S.; Yampolskii, Y.; Freeman, B.D.; Pinnau, I. Transport of gases and vapors in glassy and rubbery polymers. In Materials Science of Membranes for Gas and Vapor Separation, 1st ed.; Yampolskii, Y., Pinnau, I., Freeman, B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Comesaña-Gándara, B.; Chen, J.; Grazia Bezzu, C.; Carta, M.; Rose, I.; Ferrari, M.-C.; Esposito, E.; Fuoco, A.; Jansen, J.C.; McKeown, N.B. Redefining the Robeson upper bounds for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separations using a series of ultrapermeable benzotriptycene-based polymers of intrinsic microporosity. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; van Wagner, E.; Freeman, B.D.; Toy, L.G.; Gupta, R.P. Plasticization enhanced hydrogen purification using polymeric membranes. Science 2006, 311, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, B.W.; Robeson, L.M.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R. Influence of temperature on the upper bound: Theoretical considerations and comparison with experimental results. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Freeman, B.D. Gas solubility, diffusivity and permeability in poly(ethylene oxide). J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 239, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Stevens, K.A.; Park, J.S.; Moon, J.D.; Liu, Q.; Freeman, B.D.; Guo, R. Highly CO2-selective gas separation membranes based on segmented copolymers of poly(ethylene oxide) reinforced with pentiptycene-containing polyimide hard segments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2306–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, H.; Ghadimi, A.; Abbasi, S. CO2 separation performance of poly (ether-b-amide6)/PTMEG blended membranes: Permeation and sorption properties. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 98, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, S.; Shao, L. Pushing CO2-philic Membranes performance to the limit by designing semi-interpenetrating networks (SIPN) for sustainable CO2 separations. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, I.; Kim, D.; Al Munsur, A.Z.; Roh, J.M.; Park, H.B.; Kim, T.-H. PEG/PPG-PDMS-based Crosslinked Copolymer Membranes Prepared by ROMP and in situ Membrane Casting for CO2 Separation: An approach to endow rubbery materials with properties of rigid polymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27286–27299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Clark, K.; Lin, H. Maximizing ether oxygen content in polymers for membrane CO2 removal from natural gas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10933–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; He, S.; Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Shao, L. Penetrating chains mimicking plant root branching to build mechanically robust, ultra-stable CO2-philic membranes for superior carbon capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16704–16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Liu, S.; Chung, T.-S. Effect of end groups and grafting on the CO2 separation performance of poly(ethylene glycol) based membranes. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 7727–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Car, A.; Stropnik, C.; Yave, W.; Peinemann, K.-V. PEG modified poly(amide-b-ethylene oxide) membranes for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 307, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Filiz, V.; Shishatskiy, S.; Abetz, C.; Georgopanos, P.; Khan, M.M.; Neumann, S.; Abetz, V. Influence of poly(ethylene glycol) segment length on CO2 permeation and stability of poly active membranes and their nanocomposites with PEG POSS. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12289–12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammakakam, I.; Bara, J.E.; Jacson, E.M.; Lertxundi, J.; Mecerreyes, D.; Tomé, L.C. Tailored CO2-philic anionic poly(ionic liquid) composite membranes: Synthesis, characterization, and gas separation properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5954–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Bai, L.; Hval, K.N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Deng, L. Pebax®/TSIL blend thin film composite membranes for CO2 separation. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).