Analytical Performance of Electromembranes as a Tool for Nanoconcentrations of Silver in Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Equipment
2.3. EME Procedure
2.4. Optimization
2.5. Effect of Saline Matrix
2.6. Application to Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization
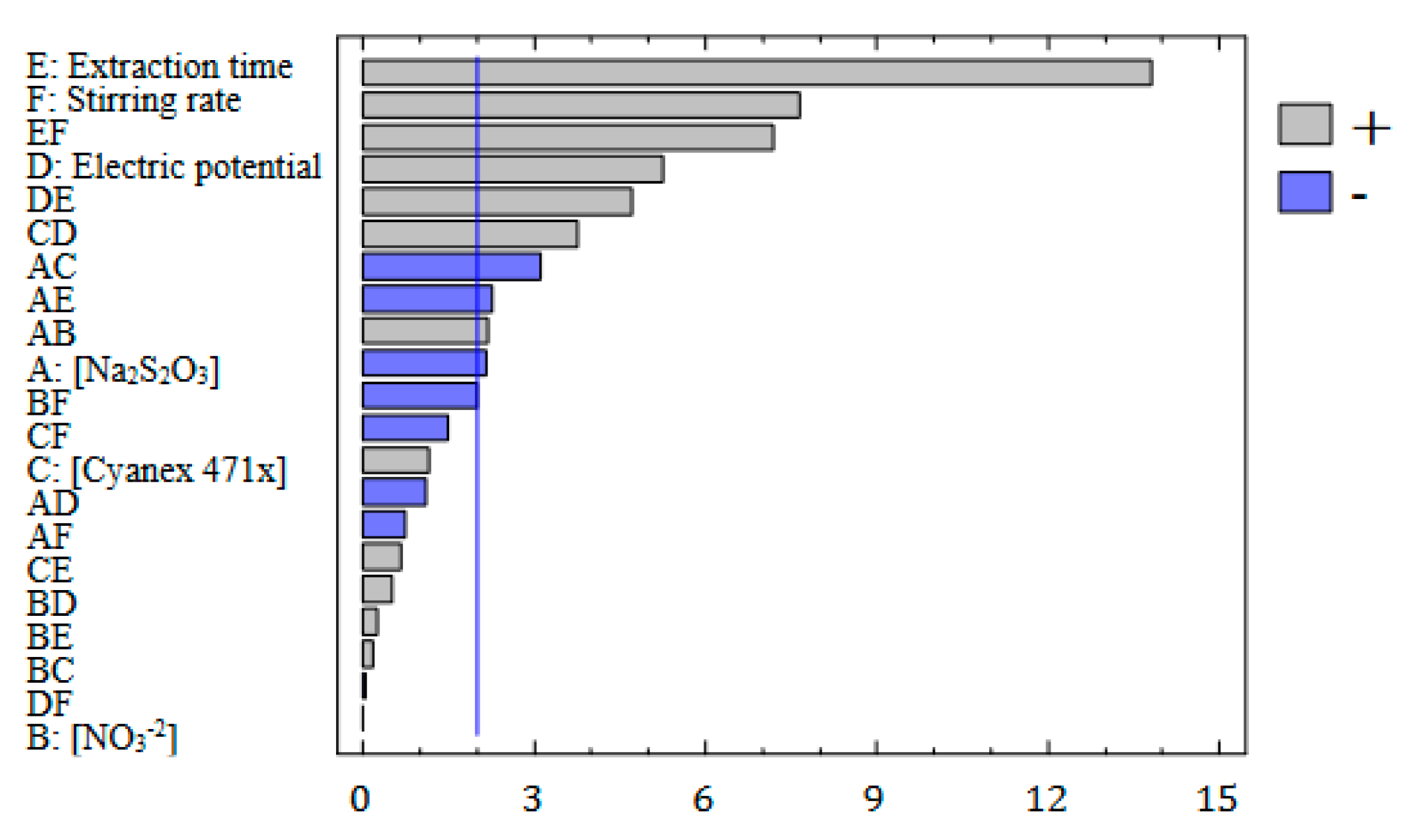
3.1.1. Screening of Factors
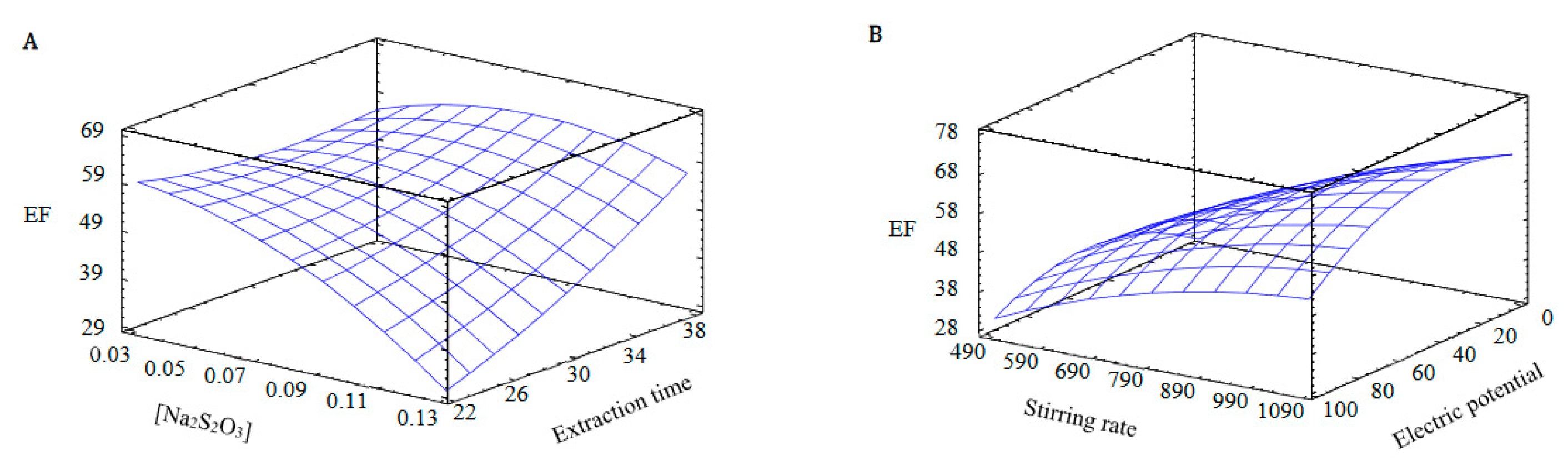
3.1.2. Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
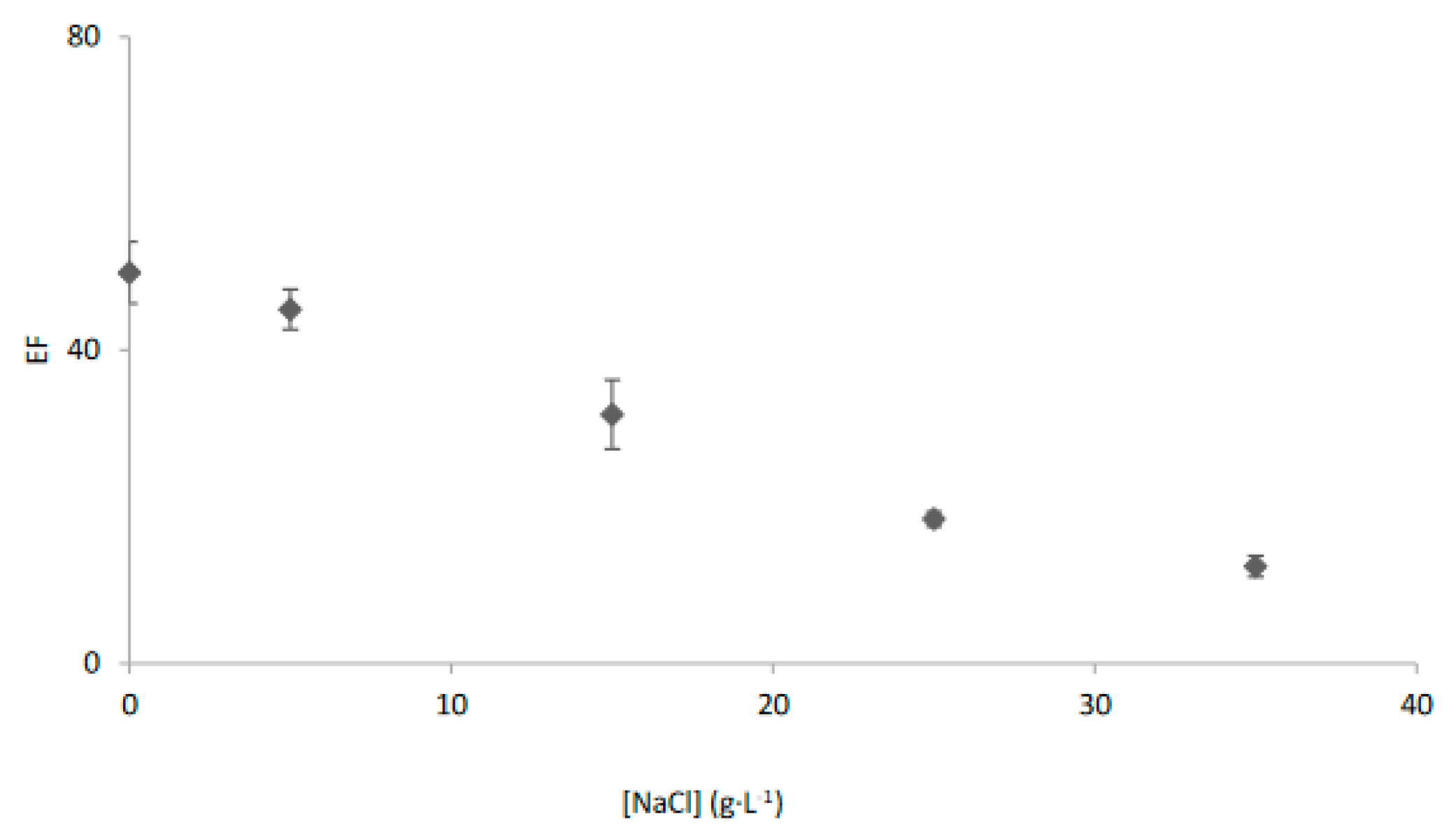
3.2. Effect of Saline Matrix
3.3. Applicability of EME System
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eie, L.V.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Hansen, F.A. Electromembrane extraction of polar substances-Status and perspectives. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 207, 114407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Huang, C.; Gjelstad, A. Electromembrane extraction–Recent trends and where to go. J. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 7, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Yamini, Y.; Seidi, S.; Ebrahimpour, B. Electromembrane surrounded solid phase microextraction: A novel approach for efficient extraction from complicated matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1280, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjelstad, A.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S. Recent developments in electromembrane extraction. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4549–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Mendiguchía, C.; Moreno, C. Key factors in electromembrane microextraction systems for metals analysis in natural waters. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Arain, M.B.; Yamini, Y.; Shah, N.; Kazi, T.G.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Tajik, M. Hollow fiber-based liquid microextraction followed by analytical instrumental techniques for quantitative analysis of heavy metals ions and pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narenderan, S.T.; Meyyanathan, S.N.; Karri, V.V.S.R. Experimental design in pesticide extraction methods: A review. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, L.; Tamiji, Z.; Khoshayand, M.R. Applications and opportunities of experimental design for the dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method—A review. Talanta 2018, 190, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaripour, S.; Nojavan, S.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Mohammadi, A. Electromembrane extraction of phenytoin from biological fluids: A survey on the effects of molecularly imprinted polymer and carbon nanotubes on extraction efficiency. Microchem. J. 2020, 156, 104800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmar, H.; Fakhari, A.R.; Tabani, H.; Shahsavani, A. Optimization of electromembrane extraction combined with differential pulse voltammetry using modified screen-printed electrode for the determination of sufentanil. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 96, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarani, S.S.H.; Pourahadi, A.; Ghasemzadeh, P. Quantification of controlled release leuprolide and triptorelin in rabbit plasma using electromembrane extraction coupled with HPLC-UV. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Yamini, Y.; Seidi, S.; Esrafili, A. Pulsed electromembrane extraction: A new concept of electrically enhanced extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1262, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asl, Y.A.; Yamini, Y.; Rezazadeh, M.; Seidi, S. Electromembrane extraction using a cylindrical electrode: A new view for the augmentation of extraction efficiency. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Yamini, Y.; Seidi, S.; Esrafili, A. One-way and two-way pulsed electromembrane extraction for trace analysis of amino acids in foods and biological samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 773, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer, C.; Tan, S.H.; Lee, H.K. Extraction of lead ions by electromembrane isolation. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1213, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strieglerová, L.; Kubáň, P.; Boček, P. Rapid and simple pretreatment of human body fluids using electromembrane extraction across supported liquid membrane for capillary electrophoretic determination of lithium. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarani, S.S.H.; Moazami, H.R.; Keshtkar, A.R.; Banitaba, M.H.; Nojavan, S. A selective electromembrane extraction of uranium(VI) prior to its fluorometric determination in water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 783, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.; Nojavan, S.; Davarani, S.H.H.; Morteza-Najarian, A. Speciation of chromium in environmental samples by dual electromembrane extraction system followed by high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 789, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajeh, M.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Barkhordar, A.; Bohlooli, M. Application of hollow cylindrical wheat stem for electromembrane extraction of thorium in water samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Sprectrosc. 2015, 137, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashi, A.; Yaftian, M.R.; Zamani, A. Electromembrane extraction-preconcentration followed by microvolume UV–Vis spectrophotometric determination of mercury in water and fish samples. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyabi, M.A.; Aghaei, A. Electromembrane extraction and spectrophotometric determination of As(V) in water samples. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanthasakda, N.; Nitiyanontakit, S.; Varanusupakul, P. Electro-enhanced hollow fiber membrane liquid phase microextraction of Cr(VI) oxoanions in drinking water samples. Talanta 2016, 148, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atikarnsakul, U.; Varanusupakul, P.; Alahmad, W. Isolation of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution by electromembrane extraction. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarani, S.S.H.; Sheikhi, N.; Nojavan, S.; Ansari, R.; Mansori, S. Electromembrane extraction of heavy metal cations from aqueous media based on flat membrane: Method transfer from hollow fiber to flat membrane. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2680–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyabi, M.A.; Aghaei, A. A simple and selective approach for determination of trace Hg(II) using electromembrane extraction followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2017, 128, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubáň, P.; Strieglerová, L.; Gebauer, P.; Boček, P. Electromembrane extraction of heavy metal cations followed by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Mendiguchía, C.; Moreno, C.; Kubáň, P. Electromembrane extraction and capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection: Multi-extraction capabilities to analyses trace metals from saline samples. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, J.A.; Jönsson, J.Å.; García-Vargas, M.; Moreno, C. Simple hollow fiber liquid membrane based pre-concentration of silver for atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1462–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, J.A.; Herce-Sesa, B.; Moreno, C. Three-phase solvent bar micro-extraction as an approach to silver ultra-traces speciation in estuarine water samples. Talanta 2015, 132, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herce-Sesa, B.; López-López, J.A.; Moreno, C. Selective ionic liquid solvent bar micro-extraction for estimation of ultra-trace silver fractions in marine waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, J.A.; Herce-Sesa, B.; Moreno, C. Solvent bar micro-extraction with graphite atomic absorption spectrometry for the determination of silver in ocean water. Talanta 2016, 159, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-López, J.A.; García-Vargas, M.; Moreno, C. A new contamination-free method for the determination of traces of anthropogenic silver in freshwaters. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2012, 92, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergel, C.; Montoya, R.; Mendiguchía, C.; García-Vargas, M.; Moreno, C. HF-LPME as a green alternative for the preconcentration of nickel in natural waters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruland, K.W.; Franks, R.P.; Knauer, G.A.; Martin, J.H. Sampling and analytical methods for the determination of copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel at the nanogram per liter level in sea water. Anal. Chim. Acta 1979, 105, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batley, G.E.; Gardner, D. Sampling and storage of natural waters for trace metal analysis. Water Res. 1977, 11, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Álvarez, R.J.; Bellido-Milla, D.; Pinto, J.J.; Moreno, C. Determination of silver in seawater by the direct analysis of solvent bars by high resolution continuum source solid sampling graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1925–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, R.; Shen, X.; Huang, C. Functional materials and chemicals in electromembrane extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 150, 116574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, L.; Bayatloo, M.R.; Chalavi, S.; Nojavan, S.; Rahmani, T.; Azimi, S.B. Selective extraction and determination of Cr(VI) in food samples based on tandem electromembrane extraction followed by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, J.A.; García-Vargas, M.; Moreno, C. A new analytical method for selective pre-concentration of free silver in estuarine waters using liquid membranes. Talanta 2013, 108, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Step | Temperature (°C) | Ramp (°C/s) | Hold (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | 80 | 6 | 20 |
| Dry | 90 | 3 | 20 |
| Dry | 110 | 5 | 10 |
| Pyrolysis | 350 | 50 | 20 |
| Pyrolysis | 1000 | 300 | 10 |
| Atomization | 1900 | 1500 | 3 |
| Clean-out | 2450 | 500 | 4 |
| Factors | Levels |
|---|---|
| [Na2S2O3] | 0.05–1 N |
| [KNO3] | 0.05–1 M |
| [Cyanex 471x] | 0.05–1 M |
| Electric potential | 0–30 V |
| Extraction time | 5–20 min |
| Stirring rate | 300–1000 rpm |
| Factors | Levels |
|---|---|
| [Na2S2O3] | 0.05–0.1 N |
| Electric potential | 25–75 V |
| Extraction time | 25–35 min |
| Stirring rate | 600–900 rpm |
| Sample | 1 [Ag]ref. ng·L−1 | [Ag]EME ng·L−1 | %Recovery | %Error | t | t-Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.99 ± 2.71 1 | 6.02 ± 0.81 | 86.08 | −13.87 | 0.60 | Accepted a |
| 2 | 17.58 ± 1.40 1 | 18.83 ± 1.89 | 107.15 | −7.11 | 0.87 | Accepted b |
| 3 | 28.61 ± 6.52 1 | 22.68 ± 6.23 | 79.27 | 20.73 | 1.14 | Accepted a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, M.; Mendiguchía, C.; Moreno, C. Analytical Performance of Electromembranes as a Tool for Nanoconcentrations of Silver in Waters. Membranes 2023, 13, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010011
Silva M, Mendiguchía C, Moreno C. Analytical Performance of Electromembranes as a Tool for Nanoconcentrations of Silver in Waters. Membranes. 2023; 13(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Macarena, Carolina Mendiguchía, and Carlos Moreno. 2023. "Analytical Performance of Electromembranes as a Tool for Nanoconcentrations of Silver in Waters" Membranes 13, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010011
APA StyleSilva, M., Mendiguchía, C., & Moreno, C. (2023). Analytical Performance of Electromembranes as a Tool for Nanoconcentrations of Silver in Waters. Membranes, 13(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010011









