Applications of Ionic Liquids in Carboxylic Acids Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Green Aspects in Relation with Ionic Liquids
3. Biosynthetic Products Separation Processes Using Ionic Liquids
Solvation Properties of Ionic Liquids
4. Carboxylic Acid Extraction Using Ionic Liquids
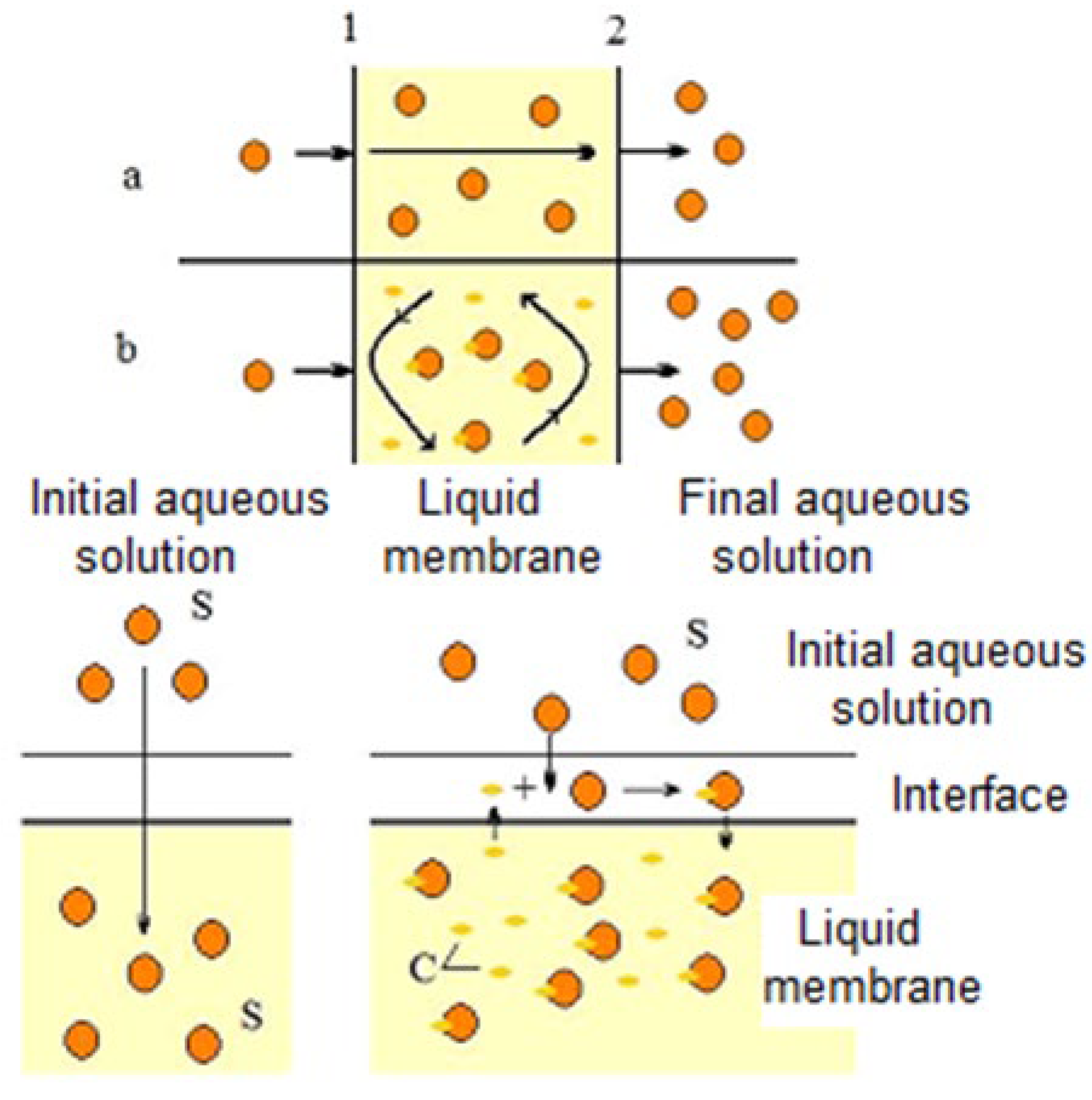
5. Carboxylic Acid Separation by Pertraction Using Ionic Liquids
- Physical (a) or reactive (b) extraction of the solute at the separation interface (1) between the initial aqueous phase and the liquid membrane. In the first case, the transfer is based only on the phenomena of solubilization and diffusion of the solute through the membrane, while in the second case (facilitated extraction), the solute is solubilized in the liquid membrane by reaction with an ionic liquid (carrier).
- Diffusion of the solute or complex formed as a result of the interfacial reaction between the solute and the carrier from the interface (1) to the interface (2), through the liquid membrane
- Re-extraction of the solute at the separation interface (2) between the organic phase and the final aqueous phase, with the regeneration of the solvent and the carrier.
- The destruction of inverse micelles at the interface of the initial aqueous phase and the liquid membrane
- The formation of a hydrated complex between undissociated lactic acid, LAH and ionic liquid according to the following equation:
- The transport of this complex through the liquid membrane
- The decomposition of the complex at the interface between the membrane and the final aqueous phase according to this equation:
- The formation of inverse micelles at the re-extraction interface between free molecules of ionic liquid, IL and water molecules
- Their transport through the liquid membrane
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.; Cai, P.; Sun, C.; Pan, Y. Application of ionic liquids in separation and analysis of carbohydrates: State of the art and future trends. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, D.; Colombi, S.; Nitti, A.; Simari, C.; Nicotera, I.; Ferrara, C.; Mustarelli, P.; Pasini, D.; Quartarone, E. Autonomous Self-Healing Strategy for Stable Sodium-Ion Battery: A Case Study of Black Phosphorus Anodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 13170–13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, M.; Brown, C.l.; Pasini, D.; Stoddart, J.F.; Wyatt, P.G. Enantioselective Recognition of Amino Acids by Axially-Chiral π-Electron-Deficient Receptors. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 7234–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, G.A.; Baker, S.N.; Pandey, S.; Bright, F.V. An analytical view of ionic liquids. Analyst 2005, 130, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajó, J.J.; Macário, I.P.E.; De Gaetano, Y.; Dupont, L.; Salgado, J.; Pereira, J.L.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Mohamadou, A.; Ventura, S.P.M. Glycine-betaine-derived ionic liquids: Synthesis, characterization and ecotoxicological evaluation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109580–109602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavhane, R.J.; Madkar, K.R.; Kurhe, D.N.; Dagade, D.H. Room Temperature Ionic Liquids from Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleobases. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 5823–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandra, R.; Reddy, S.R. A remarkable chiral recognition of racemic Mosher’s acid salt by naturally derived chiral ionic liquids using 19F NMR spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 39758–39761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhecker, S.; Esposito, D. Amino acid based ionic liquids: A green and sustainable perspective. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2016, 2, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodo, E. Modelling biocompatible ionic liquids based on organic acids and amino acids: Challenges for computational models and future perspectives. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 4002–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.K.; Materny, A.; Kiefer, J.; Singh, D.K. Quantification of the interactions in halide-anion-based imidazolium ionic liquids. J. Ion. Liq. 2022, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Koo, Y.-M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Introduction: Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6633–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullo, A.H. The time is now for ionic liquids. C&En 2020, 98, 24. Available online: https://cen.acs.org/materials/ionic-liquids/time-ionic-liquids/98/i5 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Greer, A.J.; Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus, S.S.; Filho, R.M. Are ionic liquids eco-friendly? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112039–112061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eno, E.A.; Louis, H.; Unimuke, T.O.; Gber, T.E.; Mbonu, I.J.; Ndubisi, C.J.; Adalikwu, S.A. Reactivity, stability, and thermodynamics of para-methylpyridinium-based ionic liquids: Insight from DFT, NCI, and QTAIM. J. Ion. Liq. 2022, 2, 100094–100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, J.; Husson, P.; Padua, A.A.H.; Majer, V. Density and viscosity of several pure and water saturated ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.J.; MacFarlane, D.R. Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids: An Overview. Aust. J. Chem. 2009, 62, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Panigrahi, A.; Murakami, Y.; Kondo, K. Effect of Ammonium- and Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids on the Separation of Lactic Acid by Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes (SILMs). Membranes 2011, 1, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Hua, D.; Hong, Y.; Ibrahim, A.-R.; Yao, A.; Pan, J.; Zhan, G. Functions of Ionic Liquids in Preparing Membranes for Liquid Separations: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmiah, S.; Srinivasadesikan, V.; Tseng, M.-C.; Chu, Y.-H. On the Chemical Stabilities of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2009, 14, 3780–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Row, K.H. Recent Applications of Ionic Liquids in Separation Technology. Molecules 2010, 15, 2405–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y. Effect of Ionic Composition on Physicochemical Properties of Mono-Ether Functional Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2019, 24, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Mikkola, J.-P. Use of Ionic Liquids in Protein and DNA Chemistry. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 598662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.; Zanatta, M.; Ferreira, A.S.; Corvo, M.C.; Cabrita, E.J. Revisiting Ionic Liquid Structure-Property Relationship: A Critical Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Li, B.; Sarman, S.; Mocci, F.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Yuan, J.; Laaksonen, A.; Fayer, M.D. Microstructural and dynamical heterogeneities in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 5798–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, P.; Kundu, S.; Patel, S.; Ramezani, M.; Parthasarathy, R.; Shah, K. A Comparison of Ionic Liquids and Organic Solvents on the Separation of Cellulose-Rich Material from River Red Gum. BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Savoy, A.W. Ionic liquids synthesis and applications: An overview. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperato, G.; Konig, B.; Chiappe, C. Ionic green solvents from renewable resources. Eur. J. Chem. 2007, 7, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsbosch, J.; de Vos, D.E.; Binnemans, K.; Ameloot, R. Biobased ionic liquids: Solvents for a green processing industry? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2917–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Synthesis of chiral ionic liquids from natural amino acids. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavier, H.; Boulanger, L.; Audic, N.; Toupet, L.; Mauduit, M.; Guillemin, J.C. Design and synthesis of imidazolinium salts derived from (L)-valine. Investigation of their potential in chiral molecular recognition. Chem. Commun. 2004, 10, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, D.; Metz, S.J.; Kroon, M.C. Tetraalkylammonium oleate and linoleate based ionic liquids: Promising extractants for metal salts. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhecker, S.; Antonietti, M.; Esposito, D. Hydrothermal decarboxylation of amino acid derived imidazolium zwitterions: A sustainable approach towards ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3705–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wang, P.; Hao, X.; Zang, S. Dual amino-functionalized ionic liquids as effic ient catalysts for carbonate synthesis from carbon dioxide and epoxide under solvent and cocatalyst-free conditions. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 21, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jing, G.; Zhou, X.; Lv, B.; Zhou, Z. A novel biphasic solvent of amino-functionalized ionic liquid for CO2 capture: High efficiency and regenerability. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintra, T.E.; Gantman, M.G.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Wasserscheid, P.; Schulz, P.S. Synthesis and characterization of chiral ionic liquids based on quinine, L-proline and L-valine for enantiomeric recognition. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 283, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.T.; Okello, M.; Dickenson, G. Solvents from biorenewable sources: Ionic liquids based on fructose. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2513–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, L.; Chiappe, C.; Lay, L.; Pieraccini, D.; Polito, L.; Russo, G. Glucose-derived ionic liquids: Exploring low-cost sources for novel chiral solvents. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Pei, C.; Olsen, C.E.; Schaffer, S.J.C.; Parmar, V.S.; Malhotra, S.V. Novel carbohydrate-based chiral ammonium ionic liquids derived from isomannide. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2008, 19, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, P.G.J.; Bhongade, B.A.; Singh, G. Synthesis of chiral carbohydrate ionic liquids. Synlett 2008, 19, 2973–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Jain, N. Synthesis of glucose-tagged triazolium ionic liquids and their application as solvent and ligand for copper (I) catalyzed amination. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 4738–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, A.M.; Parthasarathi, R.; Shi, J.; Pattathil, S.; Whyte, D.; Bergeron, M.; George, A.; Tran, K.; Stavila, V.; Venkatachalam, S.; et al. Efficient biomass pretreatment using ionic liquids derived from lignin and hemicellulose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3587–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeczek-Szafran, A.; Erfurt, K.; Blacha-Grzechnik, A.; Krzywiecki, M.; Boncel, S.; Chrobok, A. Carbohydrate ionic liquids and salts as all-in-one precursors for N-doped carbon. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19880–19888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiß, M.; Brietzke, A.; Eickner, T.; Stein, F.; Villinger, A.; Vogel, C.; Kragl, U.; Jopp, S. Synthesis of novel carbohydrate based pyridinium ionic liquids and cytotoxicity of ionic liquids for mammalian cells. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 14299–14304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sernaglia, M.; Blanco, D.; Hernández Battez, A.; Viesca, J.L.; González, R.; Bartolomé, M. Two fatty acid anion-based ionic liquids—Part I: Physicochemical properties and tribological behavior as neat lubricants. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 305, 112827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, N.; Ismail, M.H.; Ramlee, M.Z.; Jalil, M.A.; Yong, F.-S.J.; Wang, Y.; Sidek, N.; Misran, M.; Suhana, N.; Manan, A.; et al. An efficient and chemical oxidants-free protocol of synthesizing carboxylic acids from aldehydes catalyzed by the betaine-fatty acids ionic liquid derived from vegetable oil. Catal. Today 2022, in press, corrected proof. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Jia, H.; Song, L.; Qin, X.; Fan, F.; Li, Z.; Huang, P. Investigation of anionic group effects on the shale inhibition performance of fatty acid-based ionic liquids and their inhibition mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 636, 128135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, R.; Mir, A.W.; Shaheen, A. Synthesis, aggregation behavior and drug-binding interactions of fatty acid-imidazolium-based surface-active ionic liquids. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2022, 243, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, L.; Jia, H.; Yan, H. Systematic investigation on the abnormal surface and interfacial activity of fatty acid ionic liquids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 634, 127902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, M.S.; Shmukler, L.E.; Kudryakova, N.O.; Kolker, A.M.; Safonova, L.P. Synthesis and properties of triethanolamine-based salts with mineral and organic acids as protic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janković, B.; Manić, N.; Buchner, R.; Płowaś-Korus, I.; Pereiro, A.B.; Amado-González, E. Dielectric properties and kinetic analysis of nonisothermal decomposition of ionic liquids derived from organic acid. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 672, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Pan, J.; Huang, S.; Sun, P.; Gao, W. Target polishing of KDP crystals by organic acid-ionic liquid-in-oil microemulsions. JCIS Open 2022, 6, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedade, P.J.; Kochańska, E.; Lukasik, R.M. Biodegradable ionic liquids in service of biomass upgrade. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 35, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.W.; Pham, T.P.T.; Zhao, Y.; Stolte, S.; Yun, Y.S. Review of the toxic effects of ionic liquids. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarpalezos, D.; Tzani, A.; Avraam, E.; Politidis, C.; Kyritsis, A.; Detsi, A. Synthesis, structure-properties relationship and biodegradability assessment of novel protic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Verma, A.; Mondal, M.; Prasad, N.E.; Srivastava, J.; Singh, S.; Verma, J.P.; Saha, S. Drastic influence of amide functionality and alkyl chain length dependent physical, thermal and structural properties of new pyridinium-amide cation based biodegradable room temperature ionic liquids. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1250, 131679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulego, P.; Faes, J.; González, R.; Viesca, J.L.; Blanco, D.; Battez, A.H. Relationships between the physical properties and biodegradability and bacteria toxicity of fatty acid-based ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 292, 111451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, I.F.; Diaz, E.; Palomar, J.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Mohedano, A.F. Cation and anion effect on the biodegradability and toxicity of imidazolium- and choline-based ionic liquids. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Steudte, S.; Cho, C.-W.; Thöming, J.; Stolte, S. Biodegradability of 27 pyrrolidinium, morpholinium, piperidinium, imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquid cations under aerobic conditions. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2174–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.; Abdullah, S.; Pradhan, R.C. Review on the extraction of bioactive compounds and characterization of fruit industry by-products. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Pale, M.; Meli, L.; Doherty, T.V.; Linhardt, R.J.; Dordick, J.S. Room Temperature Ionic Liquids as Emerging Solvents for the Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B. Analysis of solvation in ionic liquids using a new linear solvation energy relationship. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, D.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Solvation properties of protic ionic liquids and molecular solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Yao, J.; Li, H. The Polarity of Ionic Liquids: Relationship between Relative Permittivity and Spectroscopic Parameters of Probe. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 7352–7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirpour, N.; Mohammadpourfard, M.; Heris, S.Z. Ionic liquids: Promising compounds for sustainable chemical processes and applications. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 160, 264–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosallanejad, M.R.; Khosravi-Nikou, M.R.; Shariati, A. Separation of ethanol from n-decane-ethanol mixtures using imidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 131, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Meng, D.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y. Molecular mechanism and extraction performance evaluation of ionic liquids for extraction process of n-heptane/n-propanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 35, 119342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, H.S.; Khoshsima, A.; Pazuki, G. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as green extractant for the efficient extraction of 1-butanol or 2-butanol from azeotropic n-heptane + butanol mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 313, 113524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yao, D.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Cui, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Molecular kinetic extraction mechanism analysis of 1-butanol from n-heptane-1-butanol by choline-based DESs as extractants. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 322, 114665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xin, H.; Lv, M.; Zhang, Z. COSMO-RS prediction, liquid-liquid equilibrium experiment and quantum chemistry calculation for the separation of n-butanol and n-heptane system using ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2021, 111, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marták, J.; Athankar, K.; Liptaj, T.; Polakovič, M.; Schlosser, S. Extraction equilibria of propionic Acid in systems with phosphonium phosphinate ionic liquid, dodecane, and water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Negi, D.; Swarna, M.; Munshi, N.B. Reactive extraction of butyric acid from water using trioctyl amine in 1-decanol and green natural oils. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 2733–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marták, J.; Liptaj, T.; Polakovič, M.; Schlosser, S. New phosphonium ionic liquid with neodecanoate anion as butyric acid extractant. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 3965–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalikoglu, M. Separation of butyric acid from aqueous media using menthol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent and modeling by response surface methodology. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharani, D.; Ananthasubramanian, M. Process intensification in separation and recovery of biogenic volatile fatty acid obtained through acidogenic fermentation of organics-rich substrates. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2021, 169, 108592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Huang, X.; Ding, X.; Lin, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, X. Extraction of proteins with ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system based on guanidine ionic liquid. Talanta 2013, 116, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fang, F.; Sun, M.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, Y.; Sui, Z.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Ionic liquid-assisted protein extraction method for plant phosphoproteome analysis. Talanta 2020, 213, 120848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, A.; Rao, J.R.; Fathima, N. Insights into protein-ionic liquid interaction: A comprehensive overview on theoretical and experimental approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moattar, M.T.Z.; Shekaari, H.; Jafaro, P. Structural effects of choline amino acid ionic liquids on the extraction of bovine serum albumin by green and biocompatible aqueous biphasic systems composed of polypropylene Glycol400 and choline amino acid ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phakoukaki, Y.V.; O’Shaughnessy, P.; Angeli, P. Intensified liquid-liquid extraction of biomolecules using ionic liquids in small channels. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanov, I.; Shanmugam, S.; Kikas, T. Extraction and isolation of lignin from ash tree (Fraxinus excelsior) with protic ionic liquids (PILs). Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Kumar, H.; Singla, M. Diverse applications of ionic liquids: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidén, G. Carboxylic Acid Production. Fermentation 2017, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, R.A.; McCubbin, T.; Navone, L.; Stowers, C.; Nielsen, L.K.; Marcellin, E. Microbial Propionic Acid Production. Fermentation 2017, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas, M.; Greses, S.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; González-Fernández, C. Carboxylic acids production via anaerobic fermentation: Microbial communities’ responses to stepwise and direct hydraulic retention time decrease. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, E.M.; Cywar, R.M.; Manker, L.P.; Saboe, P.O.; Nimlos, C.T.; Salvachúa, D.; Wang, X.; Black, B.A.; Reed, M.L.; Michener, W.E.; et al. Post-fermentation recovery of biobased carboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15273–15283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Garzón, C.S.; Straathof, A.J.J. Recovery of carboxylic acids produced by fermentation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 873–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marták, J.; Schlosser, S. Influence of anion and cation. Structure of ionic liquids on carboxylic acids extraction. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Alves de Freitas, A.; Burba, C.M. Cation-anion and cation-cation interactions in mixtures of hydroxy-functionalized and aprotic ionic liquids. J. Ion. Liq. 2022, 2, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprakel, L.M.J.; Schuur, B. Solvent developments for liquid-liquid extraction of carboxylic acids in perspective. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 935–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, N.; Schmidt, C.H.; Thielemann, G.; Heid, E.; Schröder, C.; Spange, S. The physical significance of the Kamlet–Taft π* parameter of ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlosser, Š.; Marták, J.; Blahušiak, M. Specific phenomena in carboxylic acids extraction by selected types of hydrophobic ionic liquids. Chem. Papers 2018, 72, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, Q.R.; Schneider, W.F.; Maginn, E.J. Anion dependent dynamics and water solubility explained by hydrogen bonding interactions in mixtures of water and aprotic heterocyclic anion ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 12679–12686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marták, J.; Schlosser, S. Extraction of lactic acid by phosphonium ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonova, K.; Svinyarov, I.; Bogdanov, M.G. Biocompatible ionic liquids in liquid–liquid extraction of lactic acid: A comparative study. Int. J. Chem. Nuclear Mater. Metall. Eng. 2015, 9, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Ferreira, R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Extraction of l-lactic, l-malic, and succinic acids using phosphonium-based ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 85, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çevik, A.; Aşçı, Y.S.; Lalikoglu, M. Investigation of the effects of ionic liquid as diluent in separation of lactic acid from aqueous media by reactive extraction. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marták, J.; Schlosser, S. New Mechanism and model of butyric acid extraction by phosphonium ionic liquid. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 2979–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blahušiak, M.; Schlosser, S.; Marták, J. Extraction of butyric acid with a solvent containing ammonium ionic liquid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 119, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, A.I.; Yokouchi, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Kondo, K. Extraction of succinic acid by aqueous two-phase system using alcohols/salts and ionic liquids/salts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 155, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurob, E.; Rivas, D.; Olea, F.; Plaza, A.; Merlet, G.; Araya-López, C.; Romero, J.; Quijada-Maldonado, E.; Cabezas, R. Succinic acid recovery from a glycerol-based solution using phosphonium ionic liquids supported by COSMO-RS. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2022, 559, 113471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aşçı, Y.S. Examination of the efficiency of ionic liquids in glycolic acid separation from aqueous solution by using reactive extraction method. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. A Chem. 2017, 4, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylan, N. Separation of valeric acid from aqueous solutions by reactive extraction using 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 172, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Ma, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y. Separation of thioglycolic acid from its aqueous solution by ionic liquids: Ionic liquids selection by the COSMO-SAC model and liquid-liquid phase equilibrium. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 118, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, L.; González, B.; Díaz, I.; Domínguez, Á.; González, E.J. Role of the cation on the liquid extraction of levulinic acid from water using NTf2-based ionic liquids: Experimental data and computational analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 302, 112561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, A. Experimental design of reactive extraction of levulinic acid using green solvents. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2019, 23, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brabander, P.; Uitterhaegen, E.; Verhoeven, E.; Vander Cruyssen, C.; De Winter, K.; Soetaert, W. In situ product recovery of bio-based industrial platform chemicals: A guideline to solvent selection. Fermentation 2021, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Cai, D.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L. Extraction behavior of nicotinic acid and nicotinamide in ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 146, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonova, K. State-of-the-art recovery of fermentative organic acids by ionic liquids: An overview. Hung. J. Ind. Chem. 2017, 45, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shah, S.N.; Ibrahim, M.; Mutalib, A.; Mohd Pilus, R.B.; Lethesh, K.C. Extraction of naphthenic acid from highly acidic oil using hydroxide-based ionic liquids. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Zhang, R.; Wu, L.; Tang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, C.; Meng, X. High-efficiency separation and extraction of naphthenic acid from high acid oils using imidazolium carbonate ionic liquids. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 41, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imdad, S.; Dohare, R.K. A critical review on heavy metals removal using ionic liquid membranes from the industrial wastewater. Chem. Eng. Process-Process Intensif. 2022, 173, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zante, G.; Boltoeva, M.; Masmoudi, A.; Barillon, R.; Trébouet, D. Supported ionic liquid and polymer inclusion membranes for metal separation. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2022, 51, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaulkiflee, N.D.; Ahmad, A.L.; Che Lah, N.F. Removal of emerging contaminants by emulsion liquid membrane: Perspective and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12997–13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avinash Thakur, P.; Jawa, G.K. Comparative study on effect of ionic liquids on static stability of green emulsion liquid membrane. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2022, 644, 128776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Ohtani, T.; Kondo, K. Comparison of solvent extraction and supported liquid membrane permeation using an ionic liquid for concentrating penicillin G. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 289, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martak, J.; Schlosser, S.; Vlckova, S. Pertraction of lactic acid through supported liquid membranes containing phosphonium ionic liquid. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.W.; Reddy, A.V.B.V.; Bustam, M.A.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Development and optimization of ionic liquid-based emulsion liquid membrane process for efficient recovery of lactic acid from aqueous streams. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 176, 108216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Thakur, A.; Panesar, P.S. Lactic acid extraction using environmentally benign green emulsion ionic liquid membrane. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylan, N.; Çehreli, S. Ionic liquids as bulk liquid membranes on levulinic acid removal: A design study. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Porfiri, P.; González-Miquel, M.; Gorgojo, P. Green supported liquid membranes: The permeability activity-based linear operation (PABLO) method. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446 Pt 3, 137253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylan, N.; Çehreli, S. Removal of acetic acid from aqueous solutions using bulk ionic liquid membranes: A transport and experimental design study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Companies Producing Ionic Liquids | Companies Using Ionic Liquids |
|---|---|
| Solvay | BASF (also a supplier of imidazolium-based ionic liquids) |
| Scionix | Eastman Chemical Company |
| Proionic | Sinopec |
| Iolitec | PetroChina |
| Solvionic | QUILL (Queen’s University Ionic Liquid Laboratories) |
| Ionic Liquid | Density, g/mL, 25 °C | Viscosity, cP, 25 °C | Melting Point, °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium decanoate, CYPHOS® IL 103 | 0.89 | 319 | 24 |
| Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinate, CYPHOS® IL 104 | 0.895 | 805.8 (1198) | Not determined |
| Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium dicyanamide, CYPHOS® IL 105 | 0.898 | 28.2–1646.8 | Not determined |
| 1-Butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium-hexafluorophosphate, [BMIM] [PF6] | 1.367 | 274 (381) | 6.5 |
| 1-Hexyl-3-methyl-imidazolium-hexafluorophosphate [HMIM] [PF6] | 1.38 | 585 | −73.5 |
| 1-Methyl-3-octyl-imidazolium-hexafluorophosphate [OMIM] [PF6] | 1.24 | 682 (608) | −88 |
| Carboxylic Acid | Ionic Liquid | Distribution Coefficient | Loading | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactic acid | Cyphos IL-104, trihexyl-(tetradecyl)phosphonium bis 2,4,4-trimethylpentylphosphinate | 40 | 2.4 | [94] |
| [P4444]Cl, tetrabutylphosphonium chloride, [P444,14]Cl, tributyltetradecylphosphonium chloride, [P666,14]Cl, trihexyltetradecylphosphonium chloride | 6.08 2.71 3.28 | 2 | [95] | |
| [P66614] [Cl], Tetradecyltrihexyl phosphonium chloride [P66614] [Dec], Tetradecyltrihexyl phosphonium decanoate [P66614] [Phos], Tetradecyltrihexyl phosphonium bis (2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinate | 1.6 20.9 (two step extraction) 5 | - | [96] | |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | 255 | 0.91 | [97] | |
| Butyric acid | Cyphos IL-104, trihexyl-(tetradecyl) phosphonium bis 2,4,4-trimethylpentylphosphinate | 100 (45 °C) | 3 | [98] |
| trialkylmethylammonium bis-(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinate | 5.47 | 7.12 | [99] | |
| Succinic acid | 40 wt% [C6C1Im]Br—10 wt% (NH4)2SO4 | 1.06 | 85.5 | [100] |
| [P6,6,6,14] [PHOS] trihexyltetradecylphosphonium phosphinate | 3.04 (78.4% extraction efficiency) | [101] | ||
| Glycolic Acid | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | 410 | 0.895 | [102] |
| Valeric acid | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | 7.31 | 0.26 | [103] |
| Thioglycolic acid | [OMIM]OTf, 1-octyl-3- methyl-imidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate | 24.09 | - | [104] |
| Levulinic acid | 1-ethylpyridinium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide, [Epy] [NTf2] | 3.5 | - | [105] |
| BMIMPF6 | 1.05 | - | [106] | |
| Propionic acid | [HMIM] [PF6] [HMIM] [Tf2N] | Extraction efficiency 87.56% 88.16% | [71] | |
| Protocatechuic acid | BMIM[TF2N] BMIM[PF6] MPPyr[Tf2N] MOA[Tf2N] CYPHOS IL-101 CYPHOS IL-104 | 0.16 0 0.11 0.12 47.1 54.2 | - | [107] |
| Adipic acid | BMIM[TF2N] BMIM[PF6] MPPyr[Tf2N] MOA[Tf2N] CYPHOS IL-101 CYPHOS IL-104 | 0.06 0.05 0.0 0 14.7 2.25 | - | [107] |
| Para-aminobenzoic acid | BMIM[TF2N] BMIM[PF6] MPPyr[Tf2N] MOA[Tf2N] CYPHOS IL-101 CYPHOS IL-104 | 0.94 4.39 0.61 0 22.7 3.7 | - | [107] |
| Nicotinic acid | [C6mim]ClO4 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium perchlorate | 22 | - | [108] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blaga, A.C.; Tucaliuc, A.; Kloetzer, L. Applications of Ionic Liquids in Carboxylic Acids Separation. Membranes 2022, 12, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080771
Blaga AC, Tucaliuc A, Kloetzer L. Applications of Ionic Liquids in Carboxylic Acids Separation. Membranes. 2022; 12(8):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080771
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlaga, Alexandra Cristina, Alexandra Tucaliuc, and Lenuta Kloetzer. 2022. "Applications of Ionic Liquids in Carboxylic Acids Separation" Membranes 12, no. 8: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080771
APA StyleBlaga, A. C., Tucaliuc, A., & Kloetzer, L. (2022). Applications of Ionic Liquids in Carboxylic Acids Separation. Membranes, 12(8), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080771