Anti-Pectin Fouling Performance of Dopamine and (3-Aminopropy) Triethoxysilane-Coated PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.4. Filtration Experiments
2.5. XDLVO
3. Results and Discussion
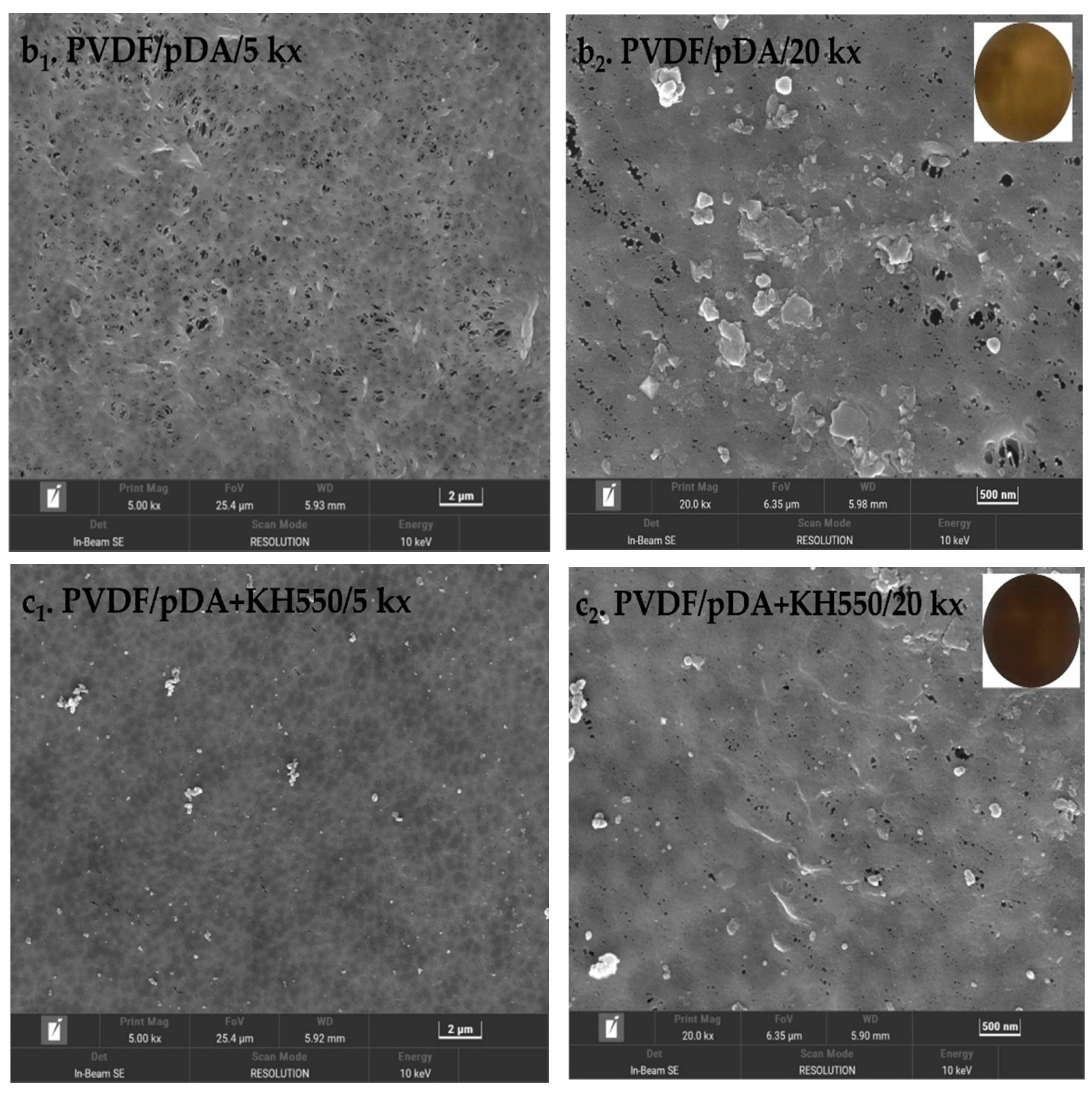
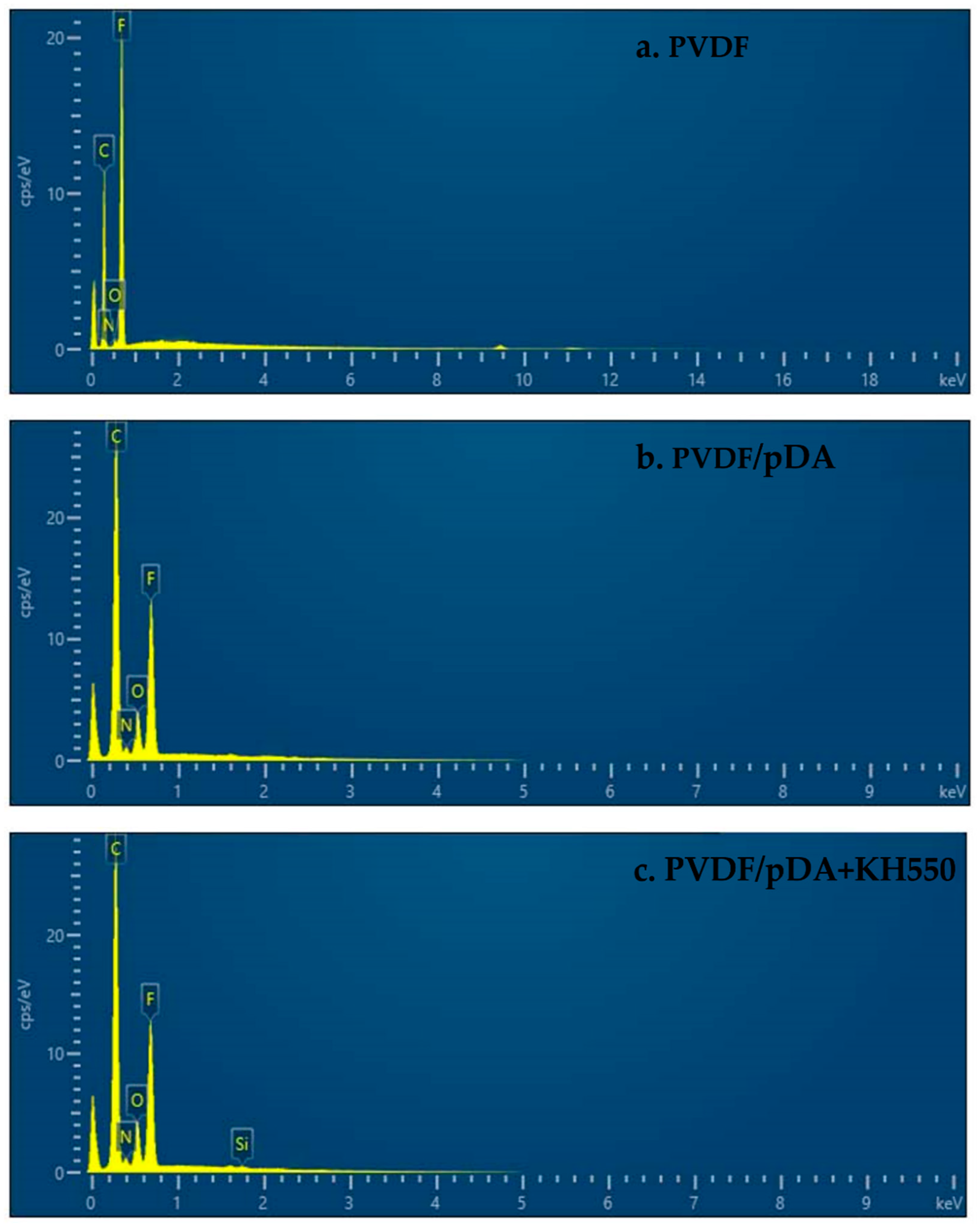
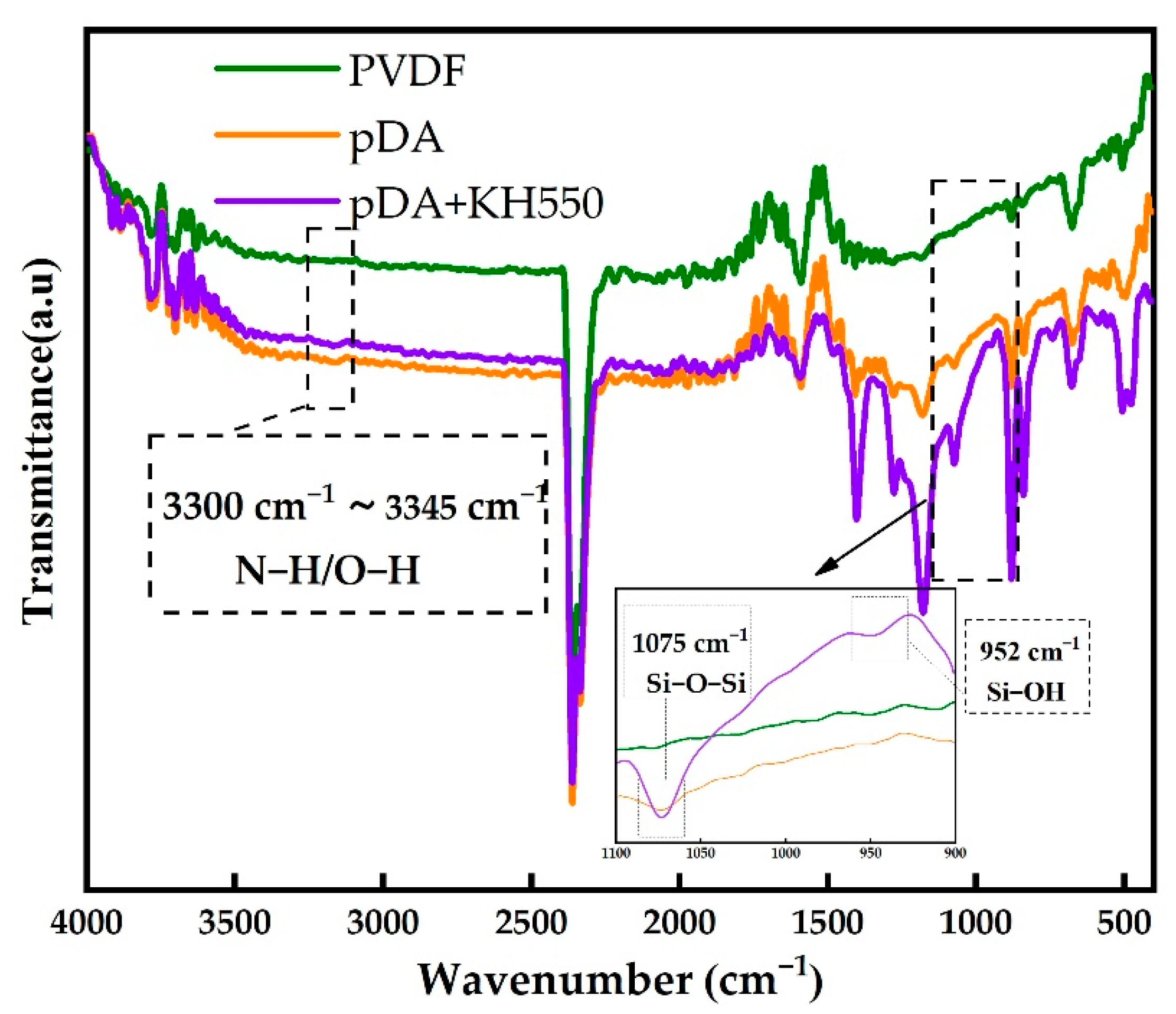
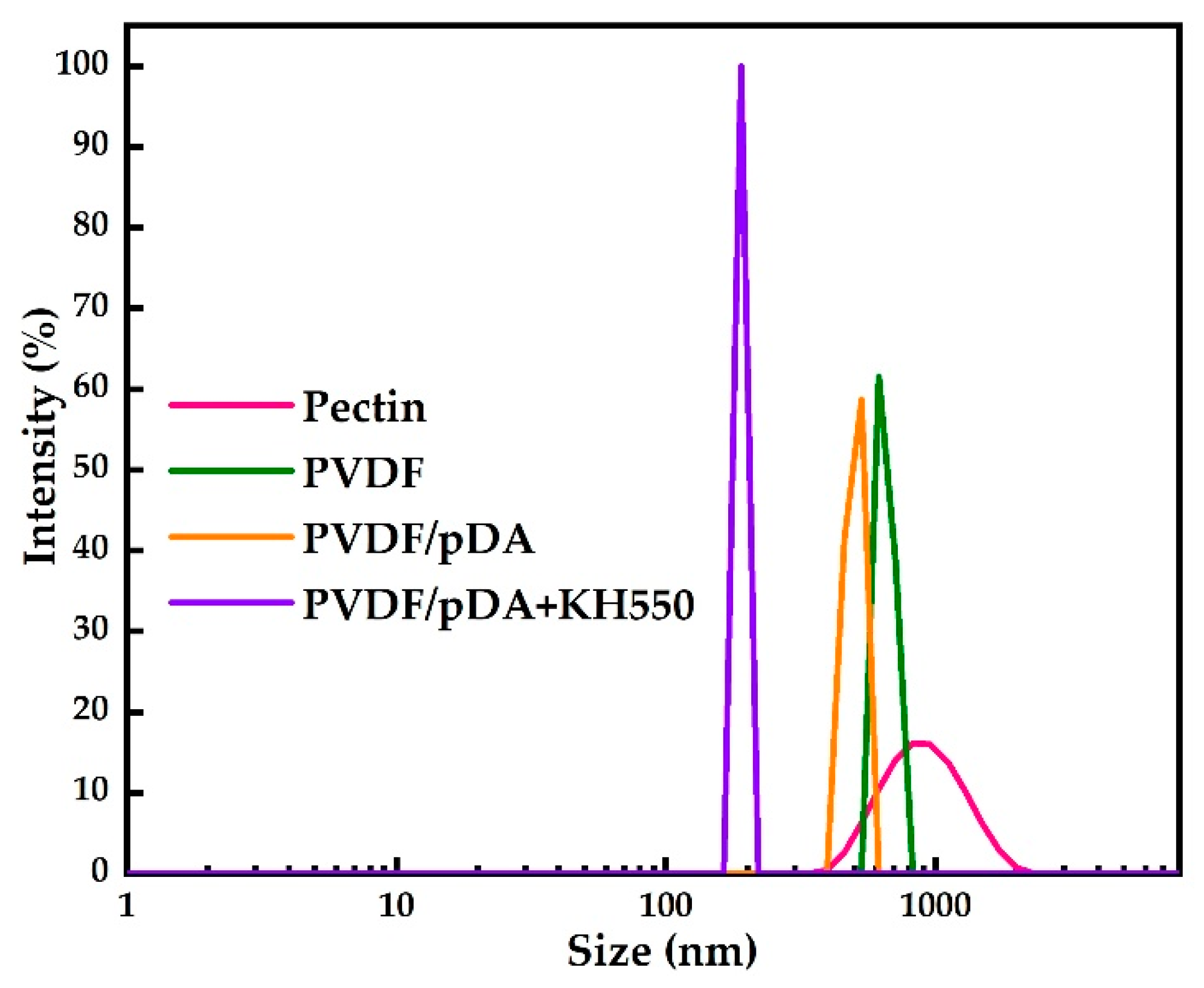
3.1. Contact Angle, SEM, and ATR-FTIR Analyses
3.2. Analysis of Anti-Fouling and Separation Performance
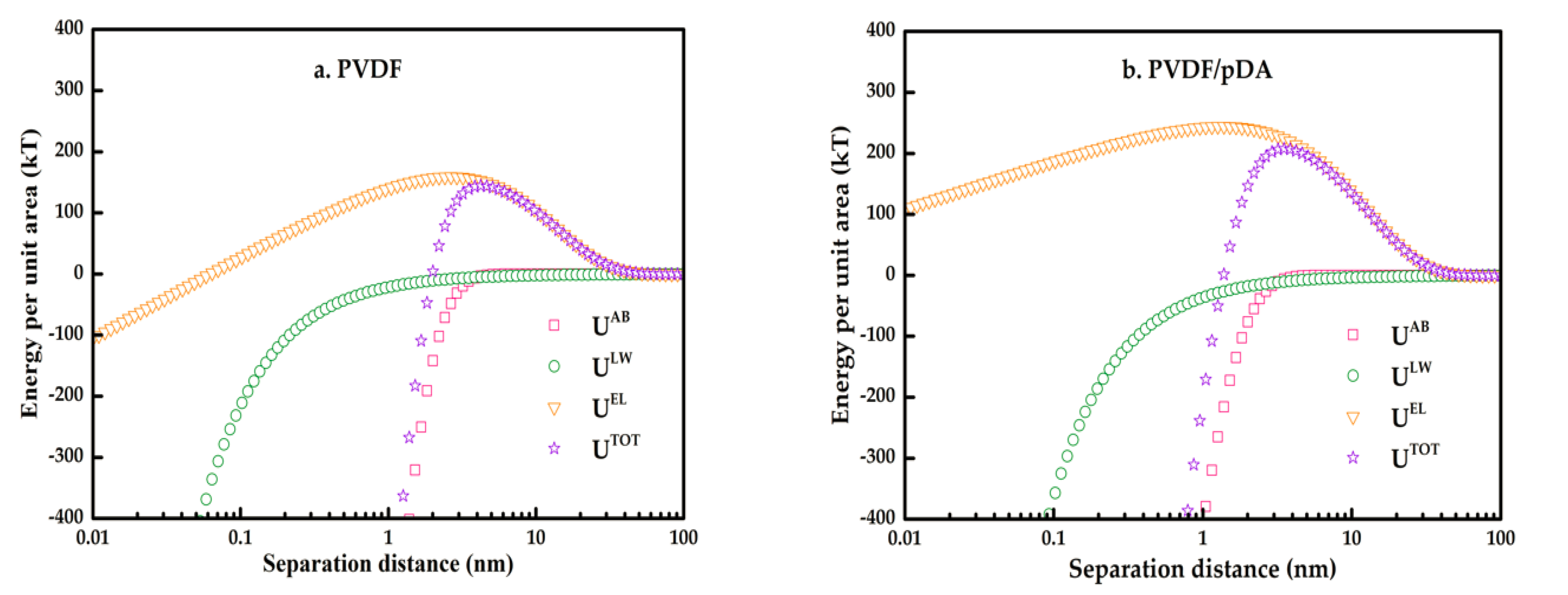
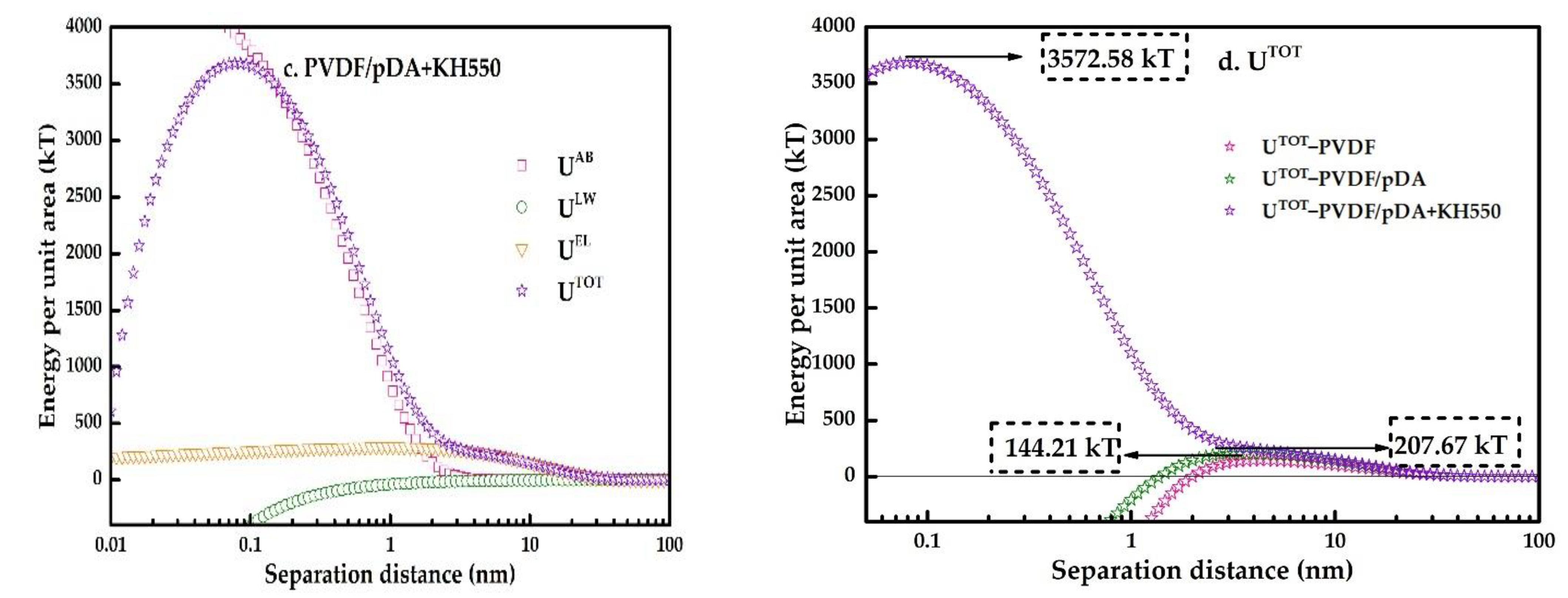
3.3. XDLVO Theory
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saxena, A.; Tripathi, B.P.; Kumar, M.; Shahi, V.K. Membrane-based techniques for the separation and purification of proteins: An overview. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohnen, D. Pectin structure and biosynthesis. Curr. Opin Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhu, H.; Guo, L.; Li, B.; Mao, X. Fouling mechanisms of ultrafiltration membranes fouled with traditional Chinese medicine pectin based on Hermia model. Chin. Tradit. Herb Drug 2019, 50, 4051–4059. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Liu, H.; Qian, D.; Tnag, Z. Analysis of ultrafiltration membrane fouling behavior of common polymers in traditional Chinese medicine using XDLVO theory. Chin. Tradit. Herb Drug 2022, 53, 2642–2649. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Hong, H.; Zhang, Y. A review on anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Applications, membrane fouling and future perspectives. Desalination 2013, 314, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Jakaj, G.; Lin, H. Polymeric Membranes Incorporated With ZnO Nanoparticles for Membrane Fouling Mitigation: A Brief Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 224–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Membrane fouling in osmotically driven membrane processes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Liu, P.; Shon, H.K. Fatty acid fouling of forward osmosis membrane: Effects of pH, calcium, membrane orientation, initial permeate flux and foulant composition. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 46, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Shon, H.K.; Li, Q. Fouling of forward osmosis membrane by protein (BSA): Effects of pH, calcium, ionic strength, initial permeate flux, membrane orientation and foulant composition. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 13415–13424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, C. Antifouling and antibacterial improvement of surface-functionalized poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane prepared via dihydroxyphenylalanine-initiated atom transfer radical graft polymerizations. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394–395, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.R.; Peldszus, S.; Huck, P.M.; Feng, X. Modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) ultrafiltration membranes with poly(vinyl alcohol) for fouling control in drinking water treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4559–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.T.; Martin-Martinez, F.J.; Jung, G.S.; Buehler, M.J. Polydopamine and eumelanin molecular structures investigated with ab initio calculations. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Jiang, Z.X.; Liu, Y.Y. A facile strategy to enhance PVDF ultrafiltration membrane performance via self-polymerized polydopamine followed by hydrolysis of ammonium fluotitanate. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 461, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghami, S.; Mohammadi, T.; Sadrzadeh, M. Preparation, characterization and fouling analysis of in-air hydrophilic/underwater oleophobic bio-inspired polydopamine coated PES membranes for oily wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Ma, L.; Wu, G. Mussel-Inspired Co-Deposition of Polydopamine/Silica Nanoparticles onto Carbon Fiber for Improved Interfacial Strength and Hydrothermal Aging Resistance of Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sa, R.; Yan, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Tian, M. Surface modification of aramid fibers by bio-inspired poly(dopamine) and epoxy functionalized silane grafting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21730–21738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; He, Y.; Shi, H.; Xiao, G.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, J. One-pot route to synthesize HNTs@PVDF membrane for rapid and effective separation of emulsion-oil and dyes from waste water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proner, M.C.; Ramalho Marques, I.; Ambrosi, A.; Rezzadori, K.; da Costa, C.; Zin, G.; Tres, M.V.; Luccio, M.D. Impact of MWCO and Dopamine/Polyethyleneimine Concentrations on Surface Properties and Filtration Performance of Modified Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X.; Chen, C. The preparation of a modified PVDF hollow fiber membrane by coating with multiwalled carbon nanotubes for high antifouling performance. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, Z.; Jinfu, C.; Chunmei, G.; Fanxin, K. Fabrication and modification of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane and anti-oil fouling property evaluation. Ch. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 12, 705–711. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Yin, X.; Ma, J.; Jiang, Z. Bioinspired fabrication of composite pervaporation membranes with high permeation flux and structural stability. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 344, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Mai, W.; Min, C.; Zhou, B.; Shan, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Qian, X. Improved hydrophilicity, permeability, antifouling and mechanical performance of PVDF composite ultrafiltration membranes tailored by oxidized low-dimensional carbon nanomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Yu, Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Kweon, J.; Chung, H. Improvement in fouling resistance of silver-graphene oxide coated polyvinylidene fluoride membrane prepared by pressurized filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H. Light sheet fluorescence microscopy applied for in situ membrane fouling characterization: The microscopic events of hydrophilic membrane in resisting DEX fouling. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, N. Mechanism analysis of membrane fouling behavior by humic acid using atomic force microscopy: Effect of solution pH and hydrophilicity of PVDF ultrafiltration membrane interface. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 487, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.G.; Santos, H.G.; Bila, D.M.; da Fonseca, F.V. Assessment of fouling mechanisms on reverse osmosis (RO) membrane during permeation of 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) solutions. Environ. Technol. 2021, 191, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xing, Y.; Cao, T.; Dong, J.; Liang, S. Evaluation of the fouling potential of sludge in a membrane bioreactor integrated with microbial fuel cell. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, B.; Lv, W.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, W.; Lv, W. Investigation of membrane fouling mechanism of intracellular organic matter during ultrafiltration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Hong, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, J. Quantification of interfacial energies associated with membrane fouling in a membrane bioreactor by using BP and GRNN artificial neural networks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Muylaert, K.; Szymczyk, A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Harvesting microalgal biomass using negatively charged polysulfone patterned membranes: Influence of pattern shapes and mechanism of fouling mitigation. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, B.J.; Hsiao, J.C.; Park, J.; Zydney, A.L.; Fissell, W.H.; Roy, S. Silicon nanoporous membranes as a rigorous platform for validation of biomolecular transport models. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 536, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Lou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, G.; Liao, B.Q.; Shen, L.; Lin, H. Effects of surface morphology on alginate adhesion: Molecular insights into membrane fouling based on XDLVO and DFT analysis. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, S.; Childress, A.; Brant, J. Propagation-of-uncertainty from contact angle and streaming potential measurements to XDLVO model assessments of membrane-colloid interactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 428, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, L. Superoleophobic micro-nanostructure surface formation of PVDF membranes by tannin and a condensed silane coupling agent. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32021–32026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Mei, X.; Wu, Z. Assessment of SMP fouling by foulant–membrane interaction energy analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Ding, Y.; Lu, Y. Identification of the change in fouling potential of soluble microbial products (SMP) in membrane bioreactor coupled with worm reactor. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Weng, X.; Yu, H.; Lin, H. Thermodynamic analysis of membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor and its implications. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Modified Membrane | Sample | Pure Water Flux (L·m−2·h−1) | Contact Angle (°) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF-PVDF/pDA | HF-PVDF | 5670 (30 kPa) | 87.50 | [21] |
| HF-PVDF/pDA | 637 (30 kPa) | 43.60 | ||
| CFs/PDA + TEOS | CFs | / | 71.50 | [17] |
| CFs/PDA + TEOS | / | 41.89 | ||
| PES/pDA + PEI | PES | 45 (100 kPa) | 70.00 | [20] |
| PES/pDA + PEI | 55 (100 kPa) | 50.00 | ||
| PVDF/pDA + TiO2 | PVDF | 135 (100 kPa) | 80.10 | [15] |
| PVDF/pDA + TiO2 | 225 (100 kPa) | 47.05 | ||
| PSF/TiO2 + pDA + KH550 | PSF | 548 (100 kPa) | 66.50 | [22] |
| PSF/TiO2 + pDA + KH550 | 275 (100 kPa) | 35.30 |
| Element | Weight (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | PVDF/pDA | PVDF/pDA + KH550 | |
| C | 60.59 | 62.13 | 62.33 |
| N | / | 3.05 | 3.30 |
| O | 1.03 | 7.08 | 7.49 |
| F | 38.37 | 27.24 | 26.37 |
| Si | / | / | 0.51 |
| Sample | Porosity (%) | Mean Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| PVDF | 53.11 | 40.18 |
| PVDF/pDA | 47.02 | 38.69 |
| PVDF/pDA + KH550 | 43.69 | 27.25 |
| Sample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | 82.82 ± 0.99 | 78.22 ± 1.61 | 50.42 ± 1.73 | −22.51 ± 0.14 |
| PVDF/pDA | 74.57 ± 2.68 | 59.38 ± 1.23 | 31.30 ± 5.10 | −28.51 ± 5.66 |
| PVDF/pDA + KH550 | 43.34 ± 5.05 | 36.80 ± 2.47 | 23.51 ± 1.95 | −31.45 ± 1.93 |
| Pectin | 58.74 ± 4.20 | 59.10 ± 2.40 | 41.51 ± 2.07 | −48.93 ± 2.05 |
| Sample | /(mJ·m−2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | 0.0220 | 8.2154 | 34.0387 | 0.1689 | 33.0717 |
| PVDF/pDA | 0.4425 | 5.2811 | 44.0964 | 3.0573 | 47.1537 |
| PVDF/pDA + KH550 | 1.1556 | 23.8494 | 46.6695 | 10.4994 | 57.1689 |
| Pectin | 0.1091 | 23.5819 | 38.8412 | 3.2082 | 42.0495 |
| Sample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | −3.6230 | −21.7788 | −0.0007 | −25.4225 |
| PVDF/pDA | −6.1637 | −11.7145 | −0.0009 | −17.8791 |
| PVDF/pDA + KH550 | −6.7608 | 24.2249 | −0.0002 | 17.4639 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, D.; Liu, H.; Tang, Z.; Wang, M.; Song, Z.; Zhu, H.; Qian, D.; Shi, X.; Li, G.; Li, B. Anti-Pectin Fouling Performance of Dopamine and (3-Aminopropy) Triethoxysilane-Coated PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane. Membranes 2022, 12, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080740
Lu D, Liu H, Tang Z, Wang M, Song Z, Zhu H, Qian D, Shi X, Li G, Li B. Anti-Pectin Fouling Performance of Dopamine and (3-Aminopropy) Triethoxysilane-Coated PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane. Membranes. 2022; 12(8):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080740
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Dengrong, Hongbo Liu, Zhishu Tang, Mei Wang, Zhongxing Song, Huaxu Zhu, Dawei Qian, Xinbo Shi, Guolong Li, and Bo Li. 2022. "Anti-Pectin Fouling Performance of Dopamine and (3-Aminopropy) Triethoxysilane-Coated PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane" Membranes 12, no. 8: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080740
APA StyleLu, D., Liu, H., Tang, Z., Wang, M., Song, Z., Zhu, H., Qian, D., Shi, X., Li, G., & Li, B. (2022). Anti-Pectin Fouling Performance of Dopamine and (3-Aminopropy) Triethoxysilane-Coated PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane. Membranes, 12(8), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080740






