Multilamellar Liposomes as a Model for Biological Membranes: Saturation Recovery EPR Spin-Labeling Studies
Abstract
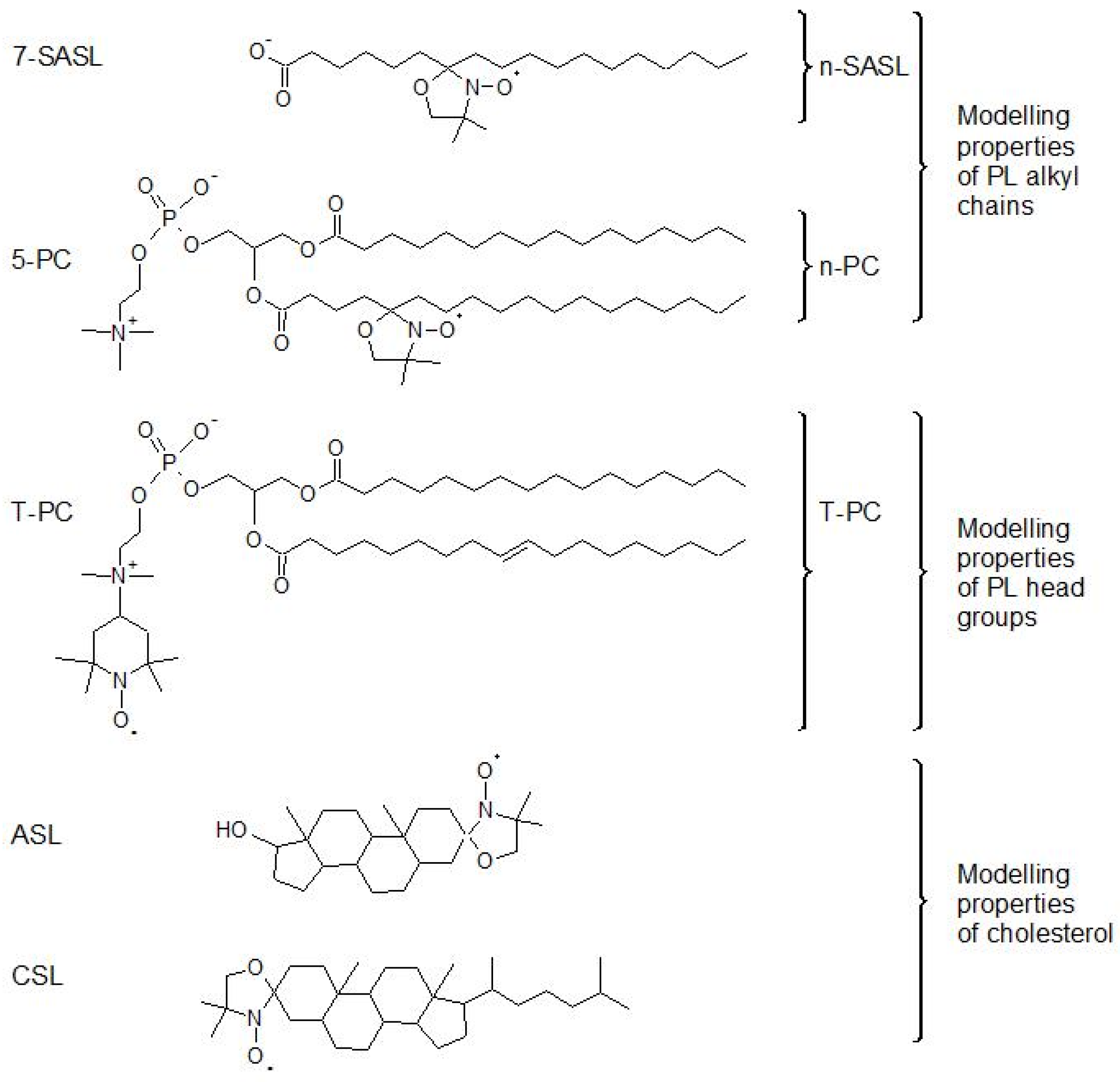
1. Short Overview of Previous Applications of EPR Spin Labeling in Studies of the Properties of Multilamellar Liposomes
2. Background for the Application of SR EPR for Membrane Studies
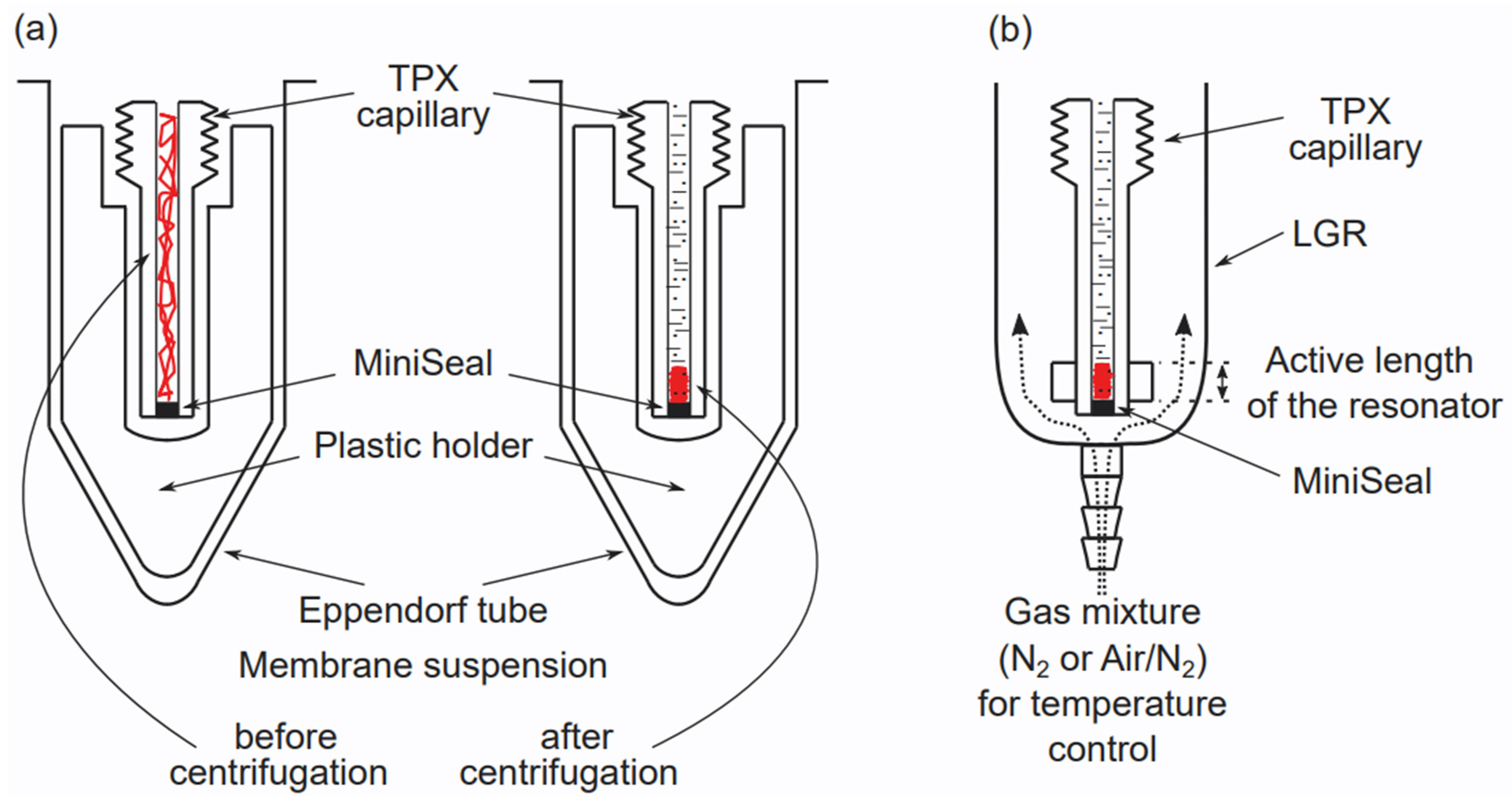
3. Preparation of Multilamellar Liposomes and Handling Samples for EPR Measurements
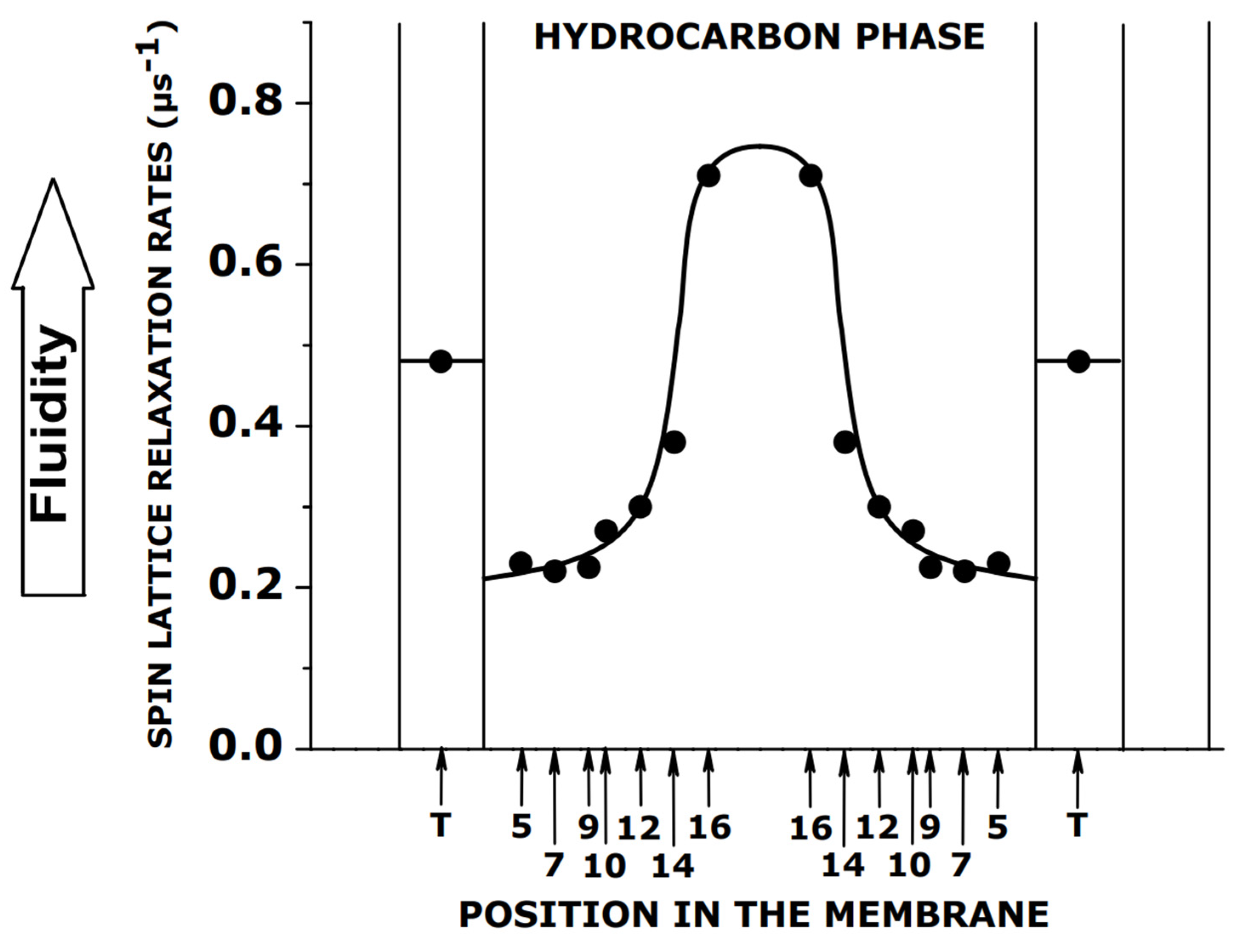
4. Spin–Lattice Relaxation Rate as a Convenient Parameter of Membrane Fluidity
5. Oxygen Transport Parameter as a Convenient Monitor of Membrane Fluidity
6. Discrimination by the OTP Method and Its Applications in Model Multilamellar Liposomes
7. Summary and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hubbell, W.L.; McConnell, H.M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaux, P.; McConnell, H.M. Lateral diffusion in spin-labeled phosphatidylcholine multilayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 4475–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waggoner, A.S.; Kingzett, T.J.; Rottschaefer, S.; Griffith, O.H.; Keith, A.D. A spin-labeled lipid for probing biological membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1969, 3, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, R.D.; McConnell, H.M. Inside-outside transitions of phospholipids in vesicle membranes. Biochemistry 1971, 10, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, W.L.; McConnell, H.M. Motion of steroid spin labels in membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1969, 63, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keana, J.F.; Keana, S.B.; Beetham, D. A new versatile ketone spin label. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 3055–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.K.; Henderson, A.T. A new stable free radical: Di-t-Butyl nitroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozantsev, E.G.; Neiman, M.B. Organic radical reactions involving no free valence. Tetrahedron 1964, 20, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, H.; Seelig, J. EPR spectra of spin labels in lipid bilayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 59, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, B.J. Practical considerations for the calculation of order parameter for fatty acid or phospholipid spin labels in membranes, Appendix IV. In Spin Labeling. Theory and Applications; Berliner, L.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 567–571. [Google Scholar]
- Berliner, L.J. Spin labeling in enzymology: Spin-labeled enzymes and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 49, 418–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, H.M.; McFarland, B.G. The Flexibility Gradient in Biological Membranes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1972, 195, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, P.; Libertini, L.J.; Hebert, V.C.; Griffith, O.H. Lipid spin labels in lecithin multilayers. A study of motion along fatty acid chains. J. Mol. Biol. 1971, 59, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, R.D.; McConnell, H.M. Lateral diffusion of phospholipids in a vesicle membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2564–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, M.G.; McConnell, H.M. Transmembrane potentials and phospholipid flip-flop in excitable membrane vesicles. Biochemistry 1973, 12, 2951–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackmann, E.; Trauble, H. Studies of the crystalline-liquid crystalline phase transition of lipid model membranes. II. Analysis of electron spin resonance spectra of steroid labels incorporated into lipid membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 4492–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackmann, E.; Trauble, H. Studies of the crystalline-liquid crystalline phase transition of lipid model membranes. I. Use of spin labels and optical probes as indicators of the phase transition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 4482–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauble, H.; Sackmann, E. Studies of the crystalline-liquid crystalline phase transition of lipid model membranes. 3. Structure of a steroid-lecithin system below and above the lipid-phase transition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 4499–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbell, W.L.; McConnell, H.M. Orientation and motion of amphiphilic spin labels in membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1969, 64, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libertini, L.J.; Waggoner, A.S.; Jost, P.C.; Griffith, O.H. Orientation of lipid spin labels in lecithin multilayers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1969, 64, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, O.H.; Dehlinger, P.J.; Van, S.P. Shape of the hydrophobic barrier of phospholipid bilayers (evidence for water penetration in biological membranes). J. Membr. Biol. 1974, 15, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Wisniewska, A.; Yin, J.J.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Hydrophobic barriers of lipid bilayer membranes formed by reduction of water penetration by alkyl chain unsaturation and cholesterol. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 7670–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, H.M.; McFarland, B.G. Physics and chemistry of spin labels. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1970, 3, 91–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Keith, A.D.; Sharnoff, M.; Cohn, G.E. A summary and evaluation of spin labels used as probes for biological membrane structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 300, 379–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, S.; Polnaszek, C.F.; Smith, I.C. Spin labels in membranes. Problems in practice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 515, 395–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, B.J.; McNamee, C.M. Spin-label measurements in membranes. With appendix: A use of computers in EPR spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1974, 32, 161–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jost, P.; Waggoner, A.S.; Griffith, O.H. Spin labeling and membrane structure. In Structure and Function of Biological Membranes; Rothfield, L., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 83–144. [Google Scholar]
- Melhorn, R.J.; Keith, A.D. Spin-labeling biological membranes. In Membrane Molecular Biology; Fox, C.F., Keith, A.D., Eds.; Sinauer: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1972; pp. 192–225. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, D. Electron Spin resonance: Spin labels. In Membrane Spectroscopy; Grell, E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1981; pp. 51–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, K.; Yin, J.J.; Subczynski, W.K.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Pulse EPR detection of lipid exchange between protein-rich raft and bulk domains in the membrane: Methodology development and its application to studies of influenza viral membrane. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Popp, C.A.; Hyde, J.S. Electron-electron double resonance and saturation-recovery studies of nitroxide electron and nuclear spin-lattice relaxation times and Heisenberg exchange rates: Lateral diffusion in dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2559–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.J.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; Hyde, J.S. Lateral diffusion of lipids in membranes by pulse saturation recovery electron spin resonance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, A.; Subczynski, W.K.; Hyde, J.S. Oxygen transport parameter in membranes as deduced by saturation recovery measurements of spin-lattice relaxation times of spin labels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Oxygen permeability of phosphatidylcholine--cholesterol membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4474–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Effect of alkyl chain unsaturation and cholesterol intercalation on oxygen transport in membranes: A pulse ESR spin labeling study. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 8578–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.J.; Hyde, J.S. Spin-label saturation-recovery electron spin resonance measurements of oxygen transport in membranes. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1987, 153, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisjen, M.; Hyde, J.S. A pulsed EPR spectrometer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1974, 45, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, P.W.; Hyde, J.S. Pulsed EPR spectrometer, II. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1975, 46, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Camenisch, T.G.; Hyde, J.S.; Subczynski, W.K. Saturation recovery EPR spin-labeling method for quantification of lipids in biological membrane domains. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2017, 48, 1355–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Felix, C.C.; Klug, C.S.; Hyde, J.S. Concentration by centrifugation for gas exchange EPR oximetry measurements with loop-gap resonators. J. Magn. Reson. 2005, 176, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennis, R.B. Biomembranes. Molecular Structure and Function; Cantor, C.R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; Paris, France; Tokyo, Japan, 1989; pp. 40–55. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Buboltz, J.T.; Feigenson, G.W. Maximum solubility of cholesterol in phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1417, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buboltz, J.T.; Feigenson, G.W. A novel strategy for the preparation of liposomes: Rapid solvent exchange. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1417, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buboltz, J.T. A more efficient device for preparing model-membrane liposomes by the rapid solvent exchange method. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Formation of cholesterol bilayer domains precedes formation of cholesterol crystals in cholesterol/dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine membranes: EPR and DSC studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 8994–9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Formation of cholesterol Bilayer Domains Precedes Formation of Cholesterol Crystals in Membranes Made of the Major Phospholipids of Human Eye Lens Fiber Cell Plasma Membranes. Curr. Eye Res. 2020, 45, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froncisz, W.; Oles, T.; Hayde, J.S. Q-band loop–gap resonator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1986, 57, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, J.S.; Yin, J.J.; Subczynski, W.K.; Camenisch, T.G.; Ratke, J.J.; Froncisz, W. Spin-label EPR T1 values using saturation recovery from 2 to 35 GHz. J. Phys. Chem. 2004, 108, 9524–9529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froncisz, W.; Hyde, J.S. The loop–gap resonator: A new micro-wave lumped circuit ESR sample structure. J. Magn. Reson. 1982, 47, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Sidabras, J.W.; Camenisch, T.G.; Ratke, J.J.; Raguz, M.; Hyde, J.S.; Subczynski, W.K. Spin-label W-band EPR with seven-loop-six-gap resonator: Application to lens membranes derived from eyes of a single donor. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2014, 45, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, D. Molecular order and T1-relaxation, cross-relaxation in nitroxide spin labels. J. Magn. Reson. 2018, 290, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailer, C.; Nielsen, R.D.; Robinson, B.H. Explanation of spin-lattice relaxation rates of spin labels obtained with multifrequency saturation recovery EPR. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 4049–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.H.; Haas, D.A.; Mailer, C. Molecular dynamics in liquids: Spin-lattice relaxation of nitroxide spin labels. Science 1994, 263, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.J.; Freed, J.H. Calculating slow motional magnetic resonance spectra: A user’s guide. In Spin Labeling: Theory and Application; Berliner, L.J., Ed.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Meirovitch, E.; Freed, J.H. Analysis of slow-motional electron spin resonance spectra in smectic phases in terms of molecular configuration, intermolecular interactions, and dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 4995–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, K.A.; Budil, D.E. Calculating slow-motion ESR spectra of spin-labeled polymers. In Advanced ESR Methods in Polymer Research; Schlick, S., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 54–82. [Google Scholar]
- Mainali, L.; Feix, J.B.; Hyde, J.S.; Subczynski, W.K. Membrane fluidity profiles as deduced by saturation-recovery EPR measurements of spin-lattice relaxation times of spin labels. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 212, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Hyde, J.S.; Subczynski, W.K. Using spin-label W-band EPR to study membrane fluidity profiles in samples of small volume. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 226, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Phases and domains in sphingomyelin-cholesterol membranes: Structure and properties using EPR spin-labeling methods. Eur. Biophys. J. 2012, 41, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Changes in the Properties and Organization of Human Lens Lipid Membranes Occurring with Age. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Properties of membranes derived from the total lipids extracted from the human lens cortex and nucleus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguz, M.; Mainali, L.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Lipid domains in intact fiber-cell plasma membranes isolated from cortical and nuclear regions of human eye lenses of donors from different age groups. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 132, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Raguz, M.; Mainali, L.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Lipid-protein interactions in plasma membranes of fiber cells isolated from the human eye lens. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 120, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccai, G.; Buldt, G.; Seelig, A.; Seelig, J. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. II. Chain conformation and segmental disorder. J. Mol. Biol. 1979, 134, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, M.J.; Small, D.M.; Shipley, G.G. Nature of the Thermal pretransition of synthetic phospholipids: Dimyristolyl- and dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 4575–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widomska, J.; Raguz, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Oxygen permeability of the lipid bilayer membrane made of calf lens lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Bridges, M.; Lerch, M.T.; Altenbach, C.; Hubbell, W.L. Saturation Recovery EPR and Nitroxide Spin Labeling for Exploring Structure and Dynamics in Proteins. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 564, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauble, H. The movement of molecules across lipid membranes: A molecular theory. J. Membr. Biol. 1971, 4, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, R.J.; Chan, S.I. Molecular motions in lipid bilayers. III. Lateral and transverse diffusion in bilayers. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 76, 4241–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windrem, D.A.; Plachy, W.Z. The diffusion-solubility of oxygen in lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 600, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, J.S.; Subczynski, W.K. Spin-Label Oximetry. In Biological Magnetic Resonance. Vol. 8. Spin Labeling. Theory and Applications; Berliner, L.J., Ed.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 399–425. [Google Scholar]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Lewis, R.N.; McElhaney, R.N.; Hodges, R.S.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Molecular organization and dynamics of 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers containing a transmembrane alpha-helical peptide. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 3156–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Wisniewska, A.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Three-dimensional dynamic structure of the liquid-ordered domain in lipid membranes as examined by pulse-EPR oxygen probing. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widomska, J.; Raguz, M.; Dillon, J.; Gaillard, E.R.; Subczynski, W.K. Physical properties of the lipid bilayer membrane made of calf lens lipids: EPR spin labeling studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raguz, M.; Widomska, J.; Dillon, J.; Gaillard, E.R.; Subczynski, W.K. Characterization of lipid domains in reconstituted porcine lens membranes using EPR spin-labeling approaches. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Properties of membranes derived from the total lipids extracted from clear and cataractous lenses of 61-70-year-old human donors. Eur. Biophys. J. 2015, 44, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikawa, I.; Yin, J.J.; Subczynski, W.K.; Kouyama, T.; Hyde, J.S.; Kusumi, A. Molecular organization and dynamics in bacteriorhodopsin-rich reconstituted membranes: Discrimination of lipid environments by the oxygen transport parameter using a pulse ESR spin-labeling technique. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 4947–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguz, M.; Widomska, J.; Dillon, J.; Gaillard, E.R.; Subczynski, W.K. Physical properties of the lipid bilayer membrane made of cortical and nuclear bovine lens lipids: EPR spin-labeling studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Raguz, M.; Widomska, J. Studying lipid organization in biological membranes using liposomes and EPR spin labeling. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 606, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plesnar, E.; Subczynski, W.K.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M. Saturation with cholesterol increases vertical order and smoothes the surface of the phosphatidylcholine bilayer: A molecular simulation study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeley, J.M.; Mitchell, T.W.; Wei, X.; Korth, J.; Nealon, J.R.; Blanksby, S.J.; Truscott, R.J. Human lens lipids differ markedly from those of commonly used experimental animals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; Subczynski, W.K. Phase-separation and domain-formation in cholesterol-sphingomyelin mixture: Pulse-EPR oxygen probing. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raguz, M.; Mainali, L.; Widomska, J.; Subczynski, W.K. Using spin-label electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) to discriminate and characterize the cholesterol bilayer domain. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2011, 164, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Vaz, W.L. Model systems, lipid rafts, and cell membranes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2004, 33, 269–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loura, L.M.; Fedorov, A.; Prieto, M. Fluid-fluid membrane microheterogeneity: A fluorescence resonance energy transfer study. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, N.K.; Timsina, R.; Rowe, E.; O’Dell, M.; Mainali, L. Mechanical properties of the high cholesterol-containing membrane: An AFM study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; Raguz, M.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Properties of fiber cell plasma membranes isolated from the cortex and nucleus of the porcine eye lens. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 97, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, L.; O’Brien, W.J.; Subczynski, W.K. Detection of cholesterol bilayer domains in intact biological membranes: Methodology development and its application to studies of eye lens fiber cell plasma membranes. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 178, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, N.; Mainali, L.; Hyde, J.S.; Subczynski, W.K. Characterization of the distribution of spin-lattice relaxation rates of lipid spin labels in fiber cell plasma membranes of eye lenses with a stretched-exponential function. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2019, 50, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, N.; Subczynski, W.K. Oxygen Transport Parameter in Plasma Membrane of Eye Lens Fiber Cells by Saturation Recovery EPR. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2021, 52, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, N.; Subczynski, W.K. Differences in the properties of porcine cortical and nuclear fiber cell plasma membranes revealed by saturation recovery EPR spin labeling measurements. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 206, 108536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subczynski, W.K.; Raguz, M.; Widomska, J. Multilamellar Liposomes as a Model for Biological Membranes: Saturation Recovery EPR Spin-Labeling Studies. Membranes 2022, 12, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070657
Subczynski WK, Raguz M, Widomska J. Multilamellar Liposomes as a Model for Biological Membranes: Saturation Recovery EPR Spin-Labeling Studies. Membranes. 2022; 12(7):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070657
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubczynski, Witold Karol, Marija Raguz, and Justyna Widomska. 2022. "Multilamellar Liposomes as a Model for Biological Membranes: Saturation Recovery EPR Spin-Labeling Studies" Membranes 12, no. 7: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070657
APA StyleSubczynski, W. K., Raguz, M., & Widomska, J. (2022). Multilamellar Liposomes as a Model for Biological Membranes: Saturation Recovery EPR Spin-Labeling Studies. Membranes, 12(7), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070657






