Effects of Pressurized Aeration on the Biodegradation of Short-Chain Chlorinated Paraffins by Escherichia coli Strain 2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. The Pressurized Bioreactor
2.3. Preparation of SCCP Stock Solution and Culture Medium
2.4. Biodegradation Experiments
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.5.1. Determination of Bacterial Indices
2.5.2. SCCPs, EPS, and CSH Determination
2.5.3. SEM and Metabolite Identification
2.6. Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Rotation Speed on SCCP Removal
3.2. Effect of Initial Concentration on Bacterial SCCP Removal
3.3. Effect of Pressurization on Bacterial SCCP Removal
3.3.1. Pure Oxygen Pressurization
- (1)
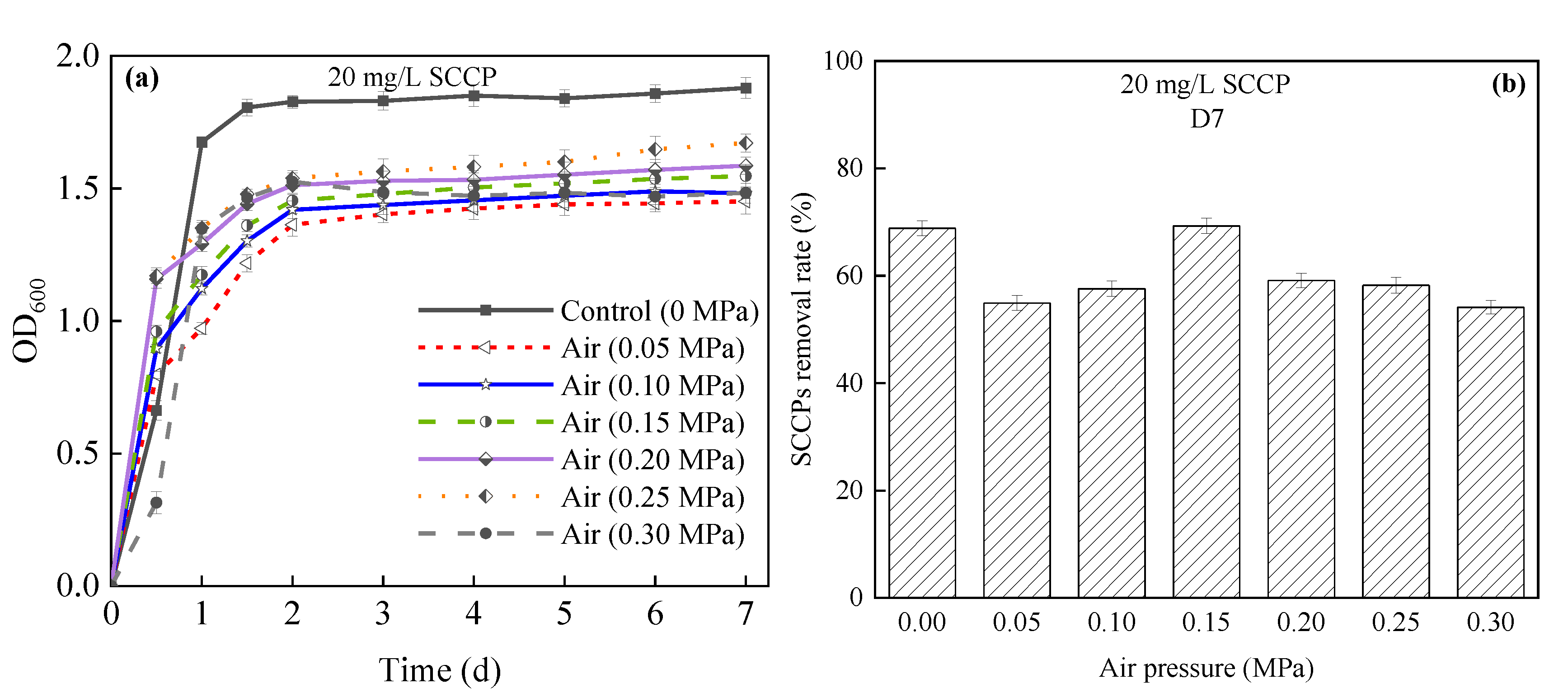
- Effects on bacterial growth and SCCP removal
- (2)
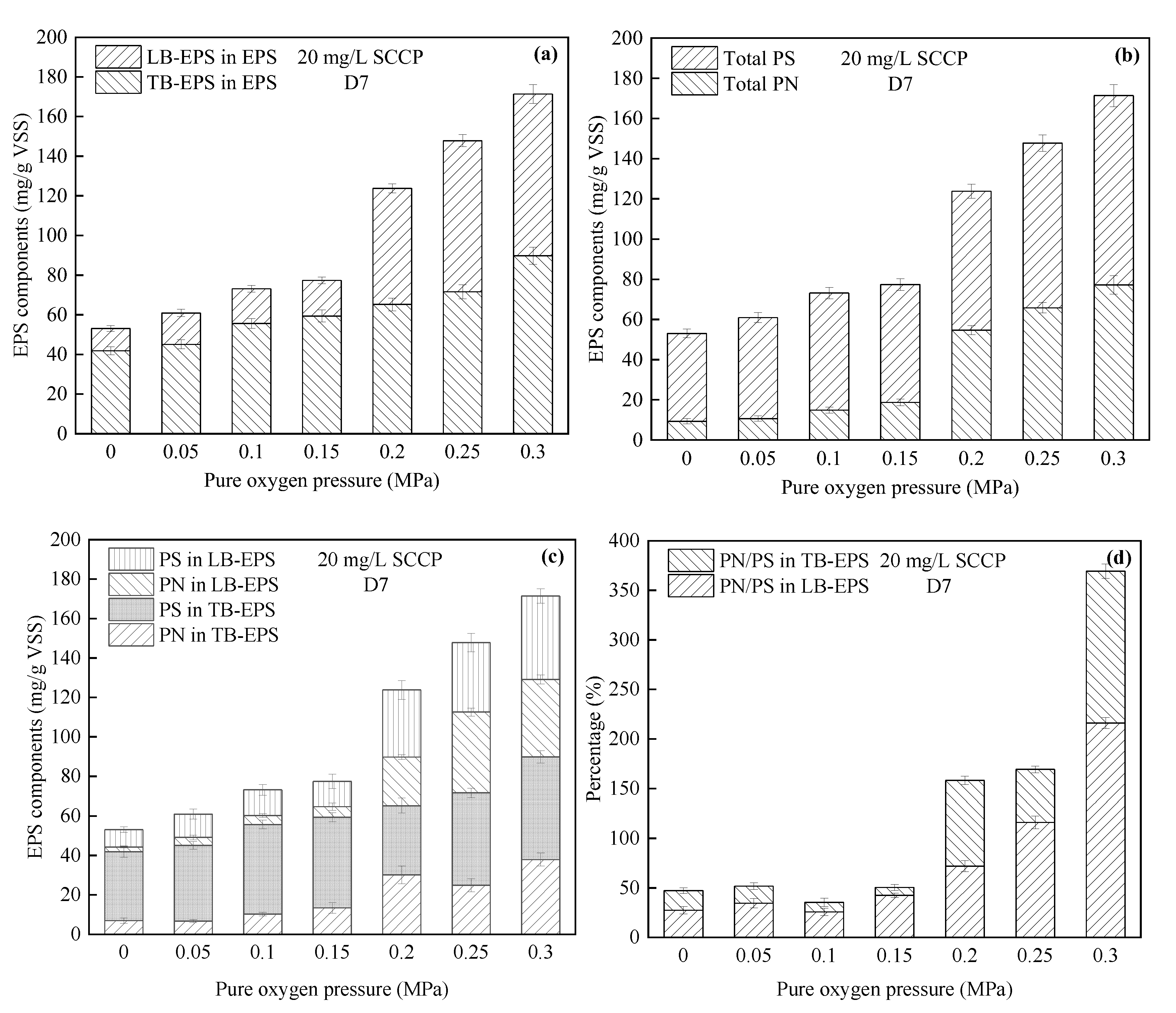
- Variations in EPS
- (3)
- Variations in DHA
3.3.2. Air Pressurization
- (1)
- Effects on bacterial growth and SCCP removal
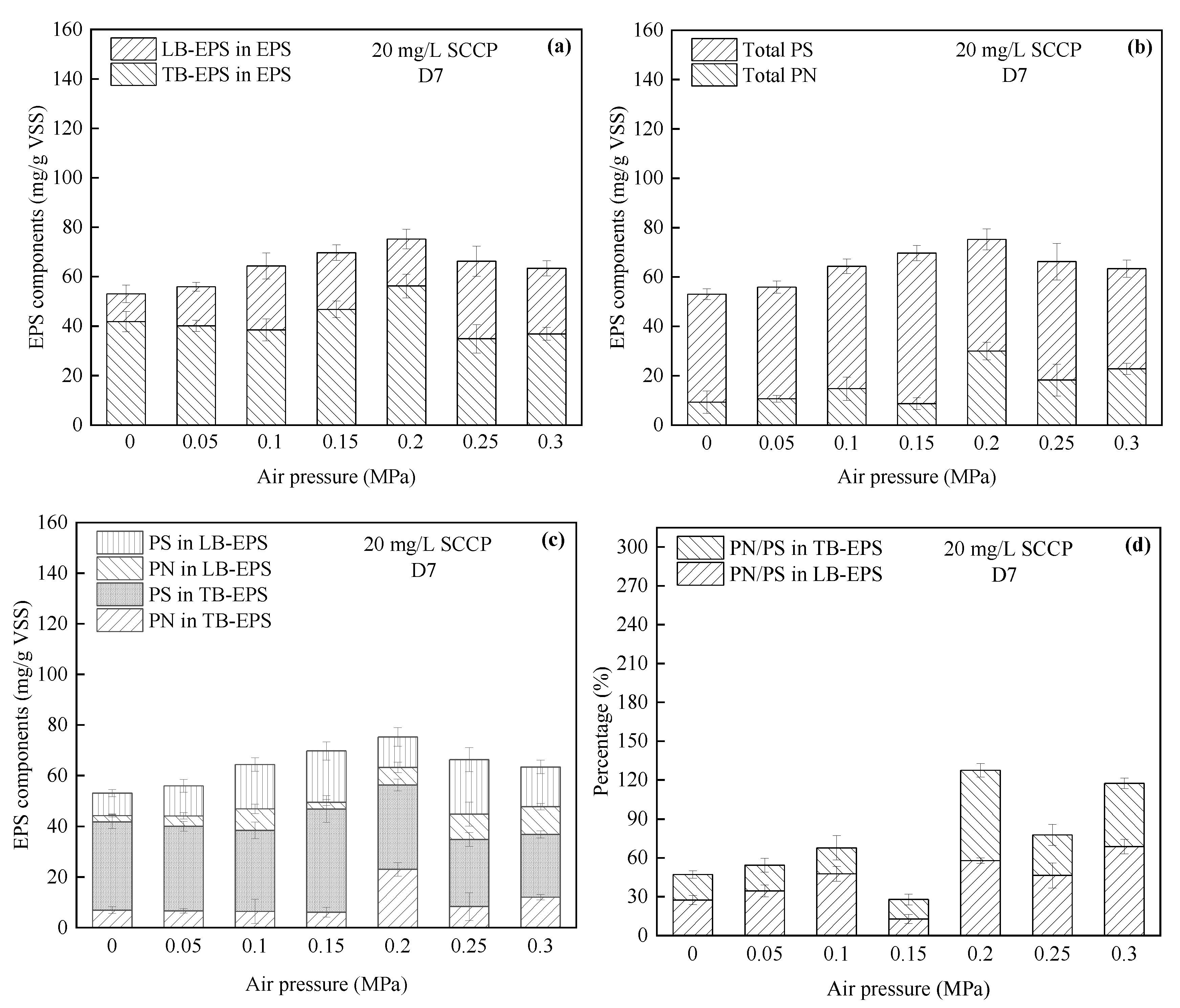
- (2)
- Variations in EPS
- (3)
- Variations in DHA
3.3.3. Summary of Pressurized Gas Type Comparison
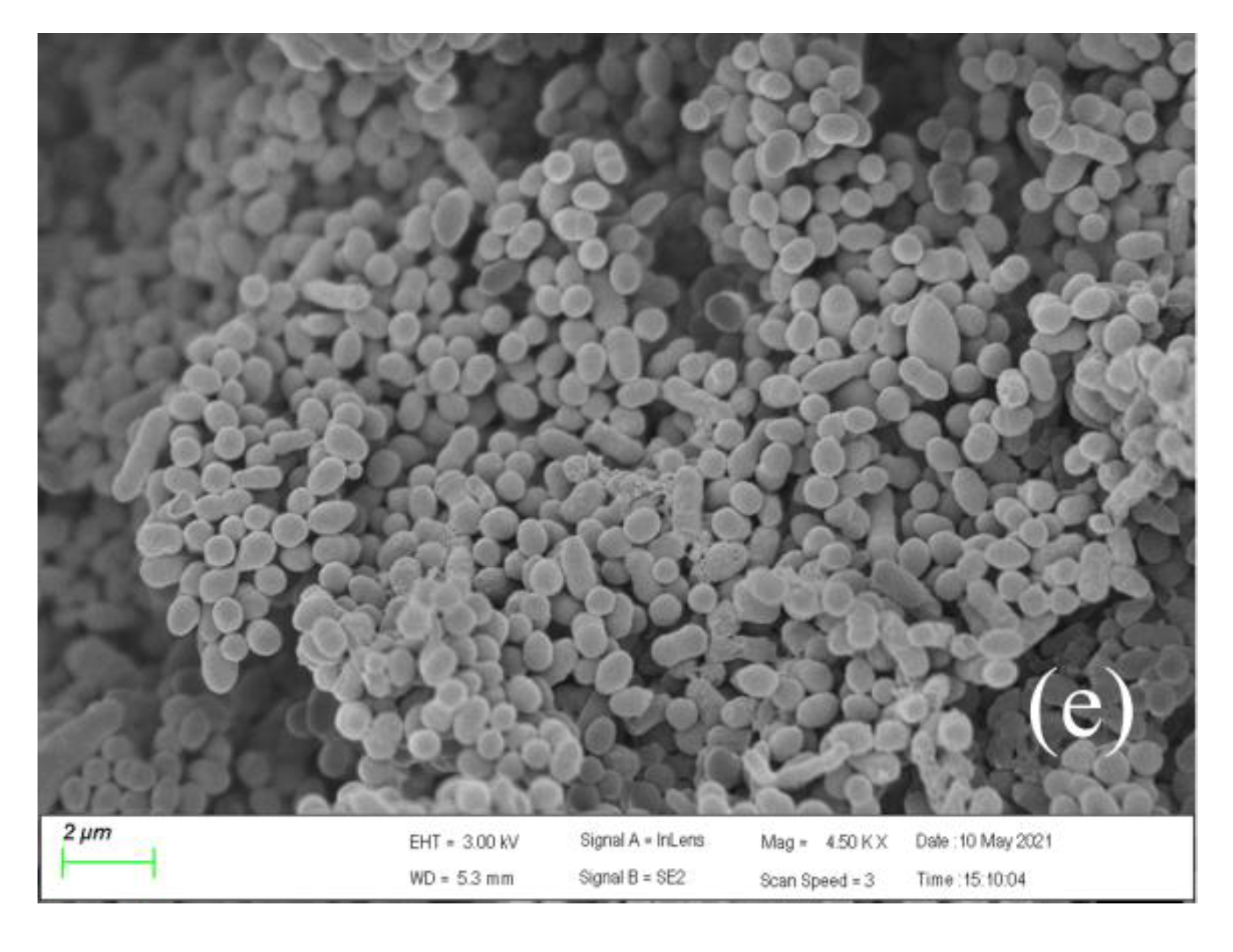
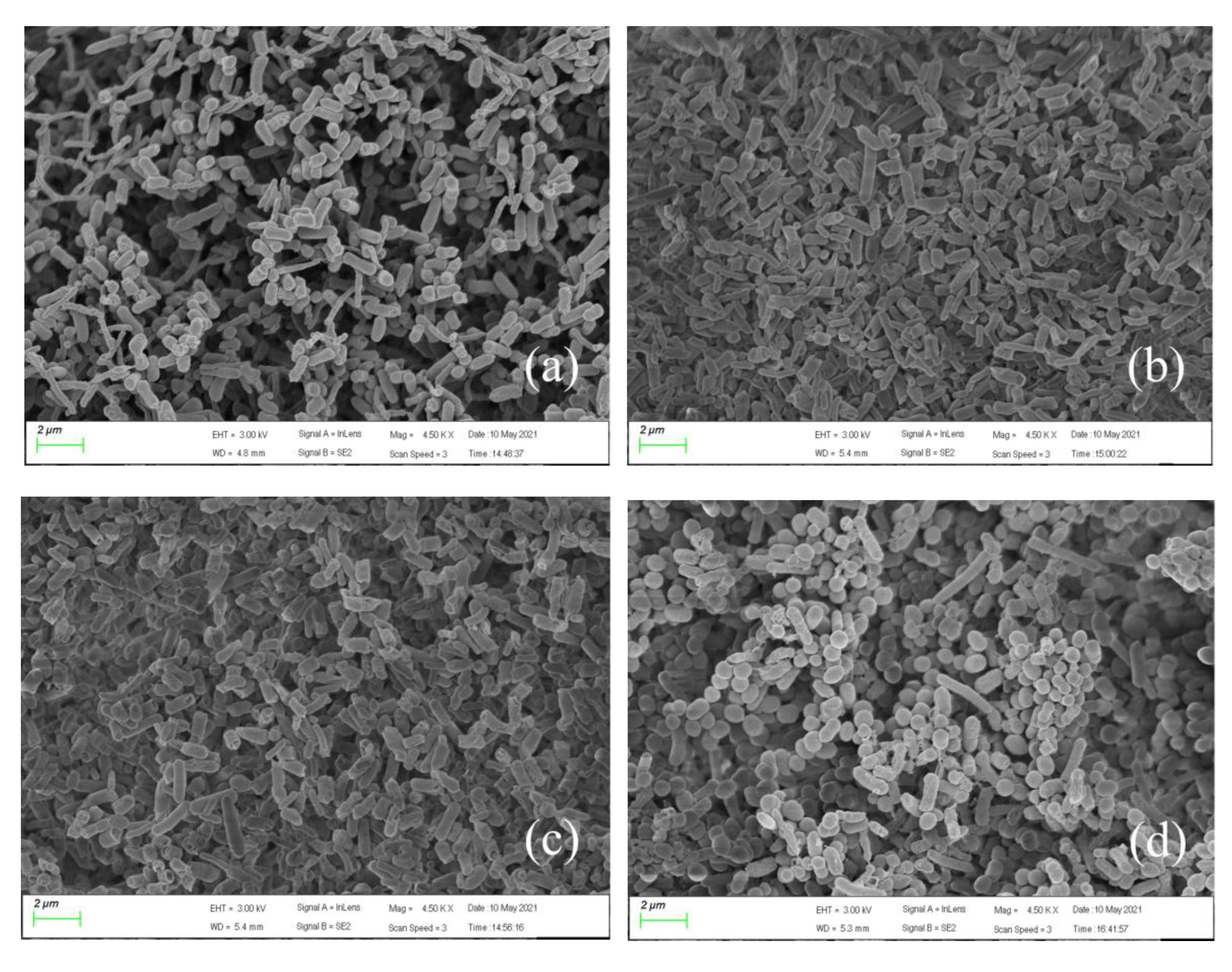
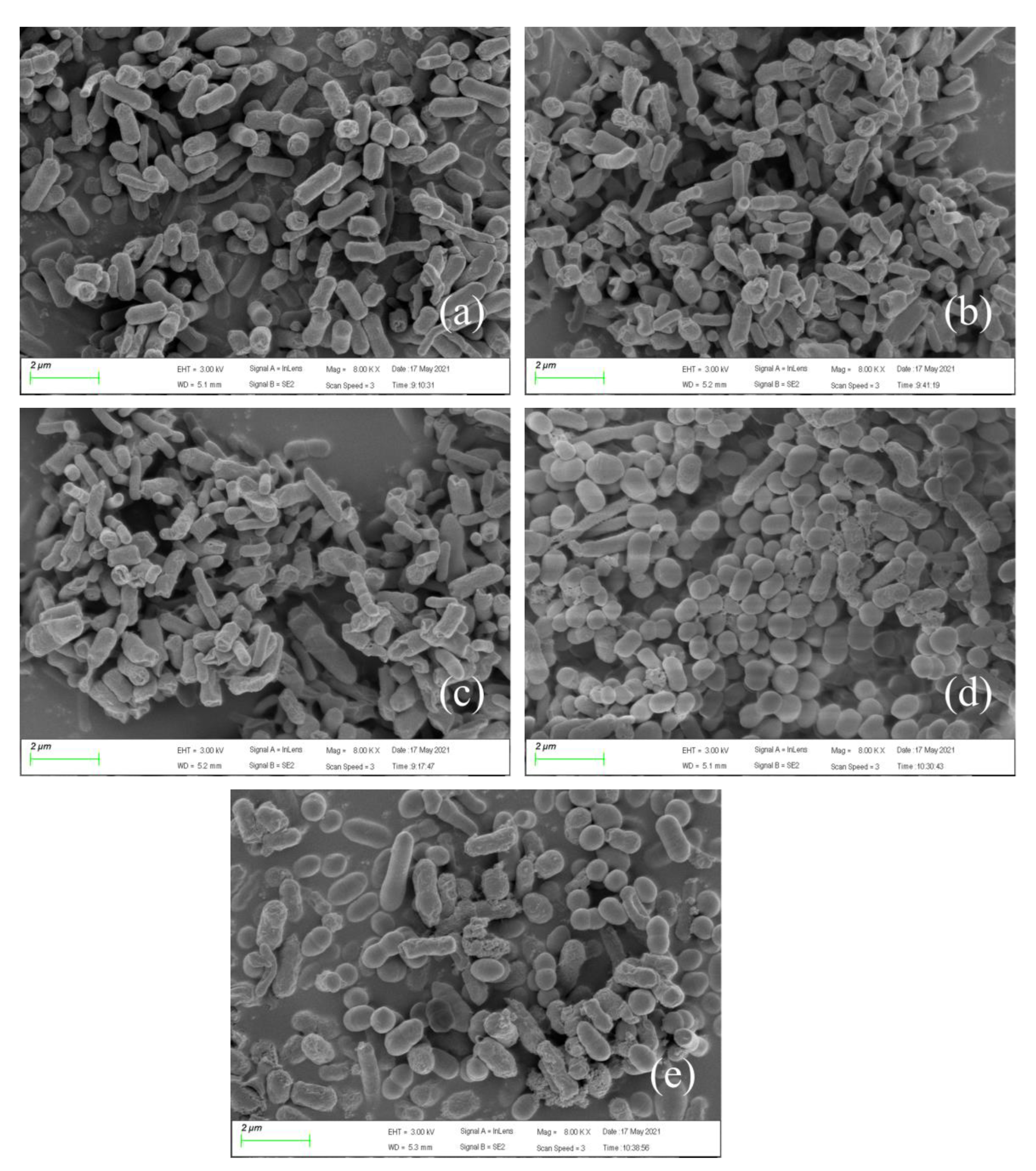
3.4. Micromorphological Changes of Bacteria under Pressure Conditions
3.5. Effects of Different Bacterial Structures on SCCP Removal
3.5.1. Cell Surface Hydrophobicity Analysis
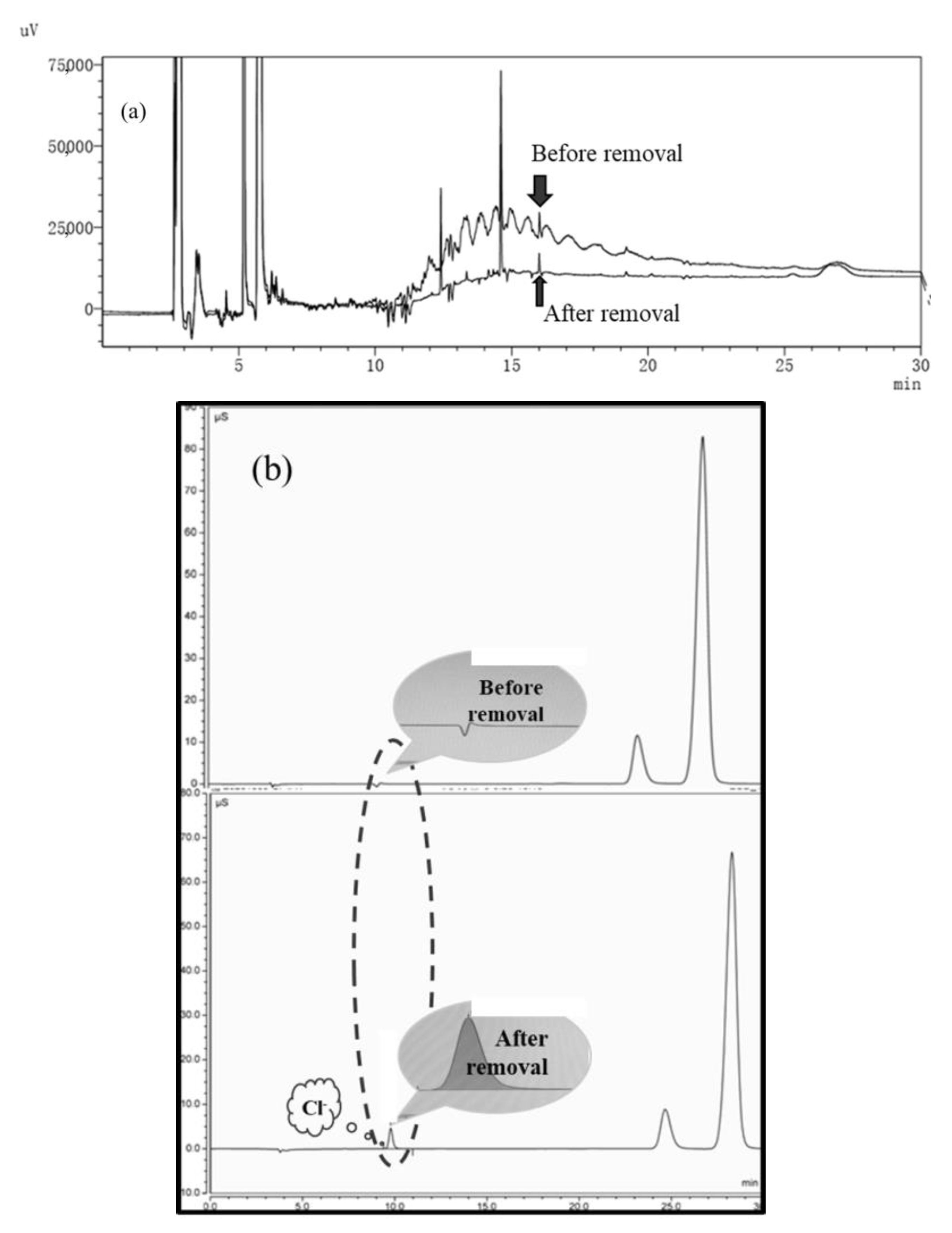
3.5.2. Adsorption of SCCPs before and after Bacterial Extraction of EPS
3.6. Possible Degradation Mechanism of Bacterial SCCP Removal
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiedler, H. Short-chain chlorinated paraffins: Production, use and international regulations. In Chlorinated Paraffins; Boer, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Van Mourik, L.M.; Gaus, C.; Leonards, P.E.G.; de Boer, J. Chlorinated paraffins in the environment: A review on their production, fate, levels and trends between 2010 and 2015. Chemosphere 2016, 155, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, A.; Li, L.; Peng, W.; Weber, R.; Liu, J. Distribution and emission estimation of short- and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in Chinese products through detection-based mass balancing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7335–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Z. The development direction of chlorinated paraffin production under the new situations. Chlor-Alkali Ind. 2019, 55, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Huang, T.; Mao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Ma, J. Gridded emission inventory of short-chain chlorinated paraffins and its validation in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, T.; Ogura, M.; Eguchi, A.; Takaoka, M. Dechlorination of short-chain chlorinated paraffins by the metal sodium dispersion method. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131201–131208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, M. Dechlorination of short chain chlorinated paraffins by nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 243, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, I.O.; Thiemann, W. Study of photochemical oxidation of standard chlorinated paraffins and identification of degradation products. J. Photoch. Photobio. A Chem. 2001, 139, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, K.J.; El-Morsi, T.M.; Abd-El-Aziz, A.S. Photochemical oxidation of short-chain polychlorinated n-alkane mixtures using H2O2/UV and the photo-Fenton reaction. Int. J. Photoenergy. 2004, 6, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiMento, B.P.; Tusei, C.L.; Aeppli, C. Photochemical degradation of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in aqueous solution by hydrated electrons and hydroxyl radicals. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134732–134740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allpress, J.D.; Gowland, P.C. Biodegradation of chlorinated paraffins and long-chain chloroalkanes by Rhodococcus sp. S45-1. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1999, 43, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, E.; Brown, W.A.; Jensen, S.R.; Bratty, M.P. Biodegradation of chlorinated alkanes and their commercial mixtures by Pseudomonas sp. strain 273. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M. Degradation of short chain polychlorinated paraffins by a new isolate: Tests in pure culture and sewage sludge. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, R.X.; Wang, G.X.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, B. Effects of pressurized aeration on organic degradation efficiency and bacterial community structure of activated sludge treating saline wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Pan, Z.; Yu, S.; Lin, C. Experimental study on pressurized activated sludge process for high concentration pesticide wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Lian, M.; Li, B. Oil-field wastewater treatment by hybrid membrane-aerated biofilm reactor (MABR) system. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, F.; Lu, S. Bioreactor consisting of pressurized aeration and dissolved air flotation for domestic wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 138, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xia, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, A.; Xu, B.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Leonard, D. A novel biosorbent for dye removal: Extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) of Proteus mirabilis TJ-1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, X. Extracellular polymeric substances govern the development of biofilm and mass transfer of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons for improved biodegradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Fang, L.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Liang, W.; Rong, X. Influence of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on Cd adsorption by bacteria. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Christensen, H.E.M.; Ulstrup, J.; Zhao, F. Extracellular polymeric substances are transient media for microbial extracellular electron transfer. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Gu, C.; Kengara, F.O.; Hong, Q.; Lv, Z.; Jiang, X. Extracellular polymeric substances enhanced mass transfer of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the two-liquid-phase system for biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, M.L.; Zhou, X.W.; Fu, H.Y.; Qu, X.L.; Zhu, D.Q. Sorption fractionation of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on mineral surfaces and associated effects on phenanthrene sorption to EPS-mineral complexes. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128264–128273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L. Exploiting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) controlling strategies for performance enhancement of biological wastewater treatments: An overview. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Jung, J.Y.; Chung, Y.C. Measurement of ammonia inhibition of microbial activity in biological wastewater treatment process using dehydrogenase assay. Biotechnol. Lett. 2000, 22, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, Y.G. Solid-phase extraction for analysis of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in water samples. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 46, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, S.F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, H.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Zeng, G.; Xia, X.; Yang, C. Effect of salinity on removal performance and activated sludge characteristics in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromans, D. Temperature and pressure dependent solubility of oxygen in water: A thermodynamic analysis. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 48, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Gutnick, D.; Rosenberg, E. Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: A simple method for measuring cell-surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1980, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, J.C.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G.; Lema, J.M. Screening of white rot fungal species for their capacity to degrade lindane and other isomers of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH). Cien. Inv. Agr. 2008, 35, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabert, R.; Boopathy, R.; Nathaniel, R.; LaFleur, G. Effect of tetracycline on ammonia and carbon removal by the facultative bacteria in the anaerobic digester of a sewage treatment plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Qi, R. Investigation for filamentous bacteria community diversity in activated sludge under various kinds and concentration conditions of nntibiotics. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Duan, B.; Jiang, S. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole in water by a combined system of ultrasound/PW12/KI/H2O2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118790–118797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoma, A.; Barbato, M.; Hernandez-Sanabria, E.; Mapelli, F.; Daffonchio, D.; Borin, S.; Boon, N. Microbial oil-degradation under mild hydrostatic pressure (10 MPa): Which pathways are impacted in piezosensitive hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23526–23539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Dasgupta, S.; Zhang, L.; Golovko, M.Y.; Golovko, S.A.; Fang, J. Alterations in membrane phospholipid fatty acids of gram-positive piezotolerant bacterium Sporosarcina sp. DSK25 in response to growth pressure. Lipids 2014, 49, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.X.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Si, L.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xie, B. Response of biodegradation characteristics of unacclimated activated sludge to moderate pressure in a batch reactor. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamaleki, A.; Miranzadeh, M.B.; Mostafaii, G.R.; Akbari, H.; Iranshahi, L.; Ghanbari, F.; Salem, A. Effect of coagulation and sonication on the dissolved air flotation (DAF) process for thickening of biological sludge in wastewater treatment. Environ. Health Eng. Manage. J. 2020, 7, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, H.; Hong, X.; Han, H.; Shan, S. Effect of pure oxygen fine bubbles on the organic matter removal and bacterial community evolution treating coal gasification wastewater by membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. Relevance of microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs)-Part I: Structural and ecological aspects. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Jie, M.; Zhang, K.; Qian, Y.; Ma, J. Performance and microbial communities of different biofilm membrane bioreactors with pre-anoxic tanks treating mariculture wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122303–122313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, M.H. Fouling characteristics in pure oxygen MBR process according to MLSS concentrations and COD loadings. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, K.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A.; Lagasse, P. Nitrification in pure oxygen activated sludge systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I.W. Biofilm exopolysaccharides: A strong and sticky framework. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, F.; Fang, F.; Guo, J.; Long, M.; Shen, Y. Differences in exopolysaccharides of three microbial aggregates. Environ. Technol. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.W.; Fu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Li, X.X.; Xing, M.; Gao, X.H.; Ren, N.Q. Linking microbial community structure to membrane biofouling associated with varying dissolved oxygen concentrations. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5626–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.W.; Liu, Y.; Tay, J.H. Biodegradability of extracellular polymeric substances produced by aerobic granules. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.H. Pressure effects on in vivo microbial processes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1595, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, A.; Daniel, I. Pressure as an environmental parameter for microbial life—A review. Biophys. Chem. 2013, 183, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.K.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, S.Y.; Bian, D.J.; Huo, M.X.; Zhou, D.D.; Huo, H.L. Characterization of a novel micro-pressure swirl reactor for removal of chemical oxygen demand and total nitrogen from domestic wastewater at low temperature. Biodegradation 2017, 28, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.H.; Wu, M.F.; Chen, J.R.; Lin, H.J.; He, Y.M. Different fouling propensities of loosely and tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) and the related fouling mechanisms in a membrane bioreactor. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126953–126963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, E.; Liu, X.R.; Judd, S.J. Effect of high salinity on activated sludge characteristics and membrane permeability in an immersed membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.H.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.G.; Price, W.E.; Guo, W.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Yamamoto, K.; Nghiem, L.D. Effects of salinity build-up on biomass characteristics and trace organic chemical removal: Implications on the development of high retention membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.P.; Peng, M.W.; Guo, J.S.; Shen, Y.; Yan, P.; Zhou, Q.H.; Jiang, J.; Fang, F. Extracellular polymeric substances dependence of surface interactions of Bacillus subtilis with Cd2+ and Pb2+: An investigation combined with surface plasmon resonance and infrared spectra. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 154, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, J.C.; Qiu, K.X.; Liu, M.Z.; Huang, L.; Liu, J.B. Cell surface hydrophobicity and degradation characteristics of high efficiency diesel degrading bacteria. J. Environ. Health 2018, 12, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.C.; Zhou, H.T.; Qiu, Z.Q.; Liu, T.T.; Yuan, Y.N.; Guan, R.N.; Li, N.Q.; Wang, W.L.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.Y. Effect of short-chain chlorinated paraffins (SCCPs) on lipid membranes:Combination of molecular dynamics and membrane damage experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 144906–144913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.Z.; Jiang, N.X.; Ye, J.X.; Cheng, Z.W.; Zhang, S.H.; Chen, J.M. Comparative investigation on a hexane-degrading strain with different cell surface hydrophobicities mediated by starch and chitosan. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3829–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Morsi, T.M.; Budakowski, W.R.; Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Friesen, K.J. Photocatalytic degradation of 1,10-dichlorodecane in aqueous suspensions of TiO2: A reaction of adsorbed chlorinated alkane with surface hydroxyl radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; An, T. Photochemical degradation kinetics and mechanism of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in aqueous solution: A case of 1-chlorodecane. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Pressurization (0–0.3 MPa) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Oxygen Pressurization | Air Pressurization | |
| SCCP removal rate | The maximum removal rate was 85.61% (0.15 MPa), which was greater than 0.05 and 0.1 MPa, while the removal rate decreased (>0.15 MPa). | The removal rate reached the highest value of 69.28% (0.15 MPa), and the removal rate decreased (>0.15 MPa). |
| OD600 | In the range of 0.05–0.15 MPa, the pressure did not affect the growth of microorganisms, but it was severely inhibited (>0.15 MPa). | Pressure did not promote bacterial growth (compared with 0 MPa). |
| EPS | Upon increasing the pressure, the EPS content increased significantly, among which TB-EPS was the main EPS type. A high pressure promoted the secretion of PN in LB-EPS. | The EPS content under pressurization increased compared with EPS under atmospheric pressure. TB-EPS accounted for more than 50% of the total EPS, and more PS was always generated than PN. |
| DHA | The DHA was promoted by an appropriate low pressure but inhibited by a high pressure (>0.15 MPa). | The DHA was lower than at atmospheric pressure. |
| Sample | Cell Surface Hydrophobicity of Bacteria |
|---|---|
| E. coli strain 2 before extraction of EPS | 12.0 ± 0.4% |
| E. coli strain 2 after extraction of EPS | 15.2 ± 0.2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Y.; Han, W.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K. Effects of Pressurized Aeration on the Biodegradation of Short-Chain Chlorinated Paraffins by Escherichia coli Strain 2. Membranes 2022, 12, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060634
Qian Y, Han W, Zhou F, Ji B, Zhang H, Zhang K. Effects of Pressurized Aeration on the Biodegradation of Short-Chain Chlorinated Paraffins by Escherichia coli Strain 2. Membranes. 2022; 12(6):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060634
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Yongxing, Wanling Han, Fuhai Zhou, Bixiao Ji, Huining Zhang, and Kefeng Zhang. 2022. "Effects of Pressurized Aeration on the Biodegradation of Short-Chain Chlorinated Paraffins by Escherichia coli Strain 2" Membranes 12, no. 6: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060634
APA StyleQian, Y., Han, W., Zhou, F., Ji, B., Zhang, H., & Zhang, K. (2022). Effects of Pressurized Aeration on the Biodegradation of Short-Chain Chlorinated Paraffins by Escherichia coli Strain 2. Membranes, 12(6), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060634








