Microstructure and Hydrothermal Stability of Microporous Niobia-Silica Membranes: Effect of Niobium Doping Contents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Fabrication of Nb/SiO2 Sols
2.2. Fabrication of Nb/SiO2 Materials
2.3. Fabrication of Nb/SiO2 Membranes
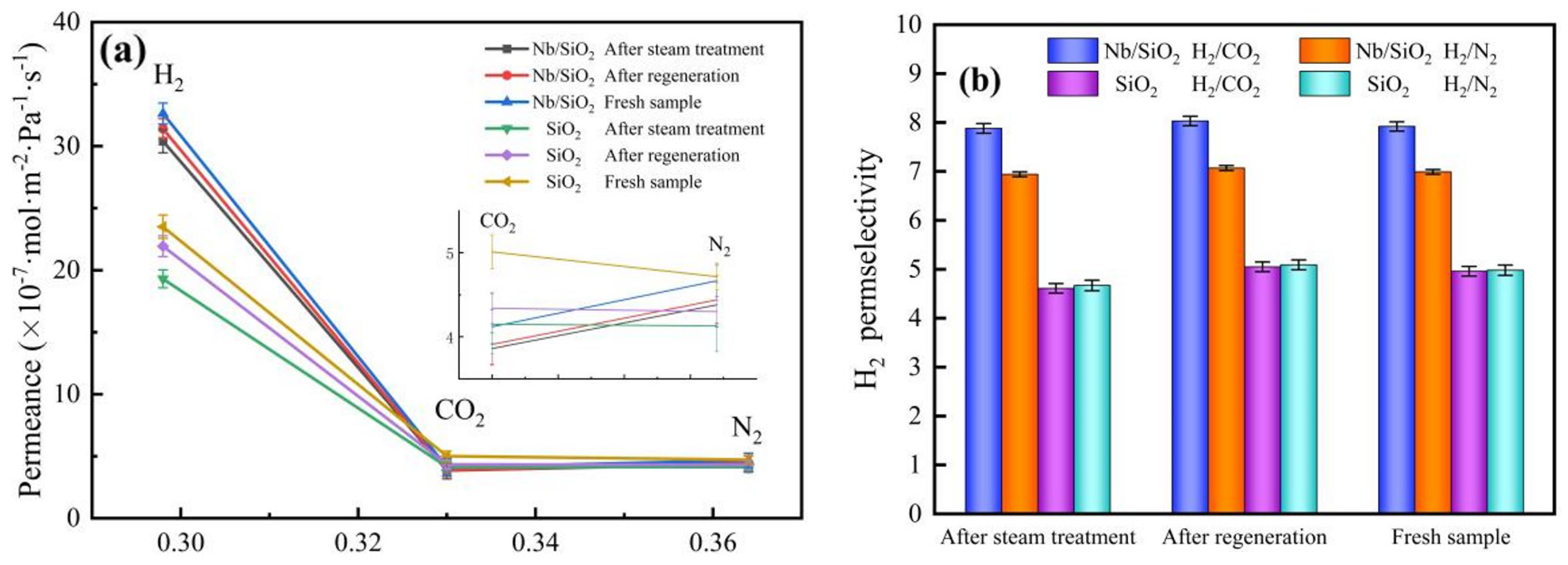
2.4. Steam-Treatment and Regeneration of Nb/SiO2 Membranes
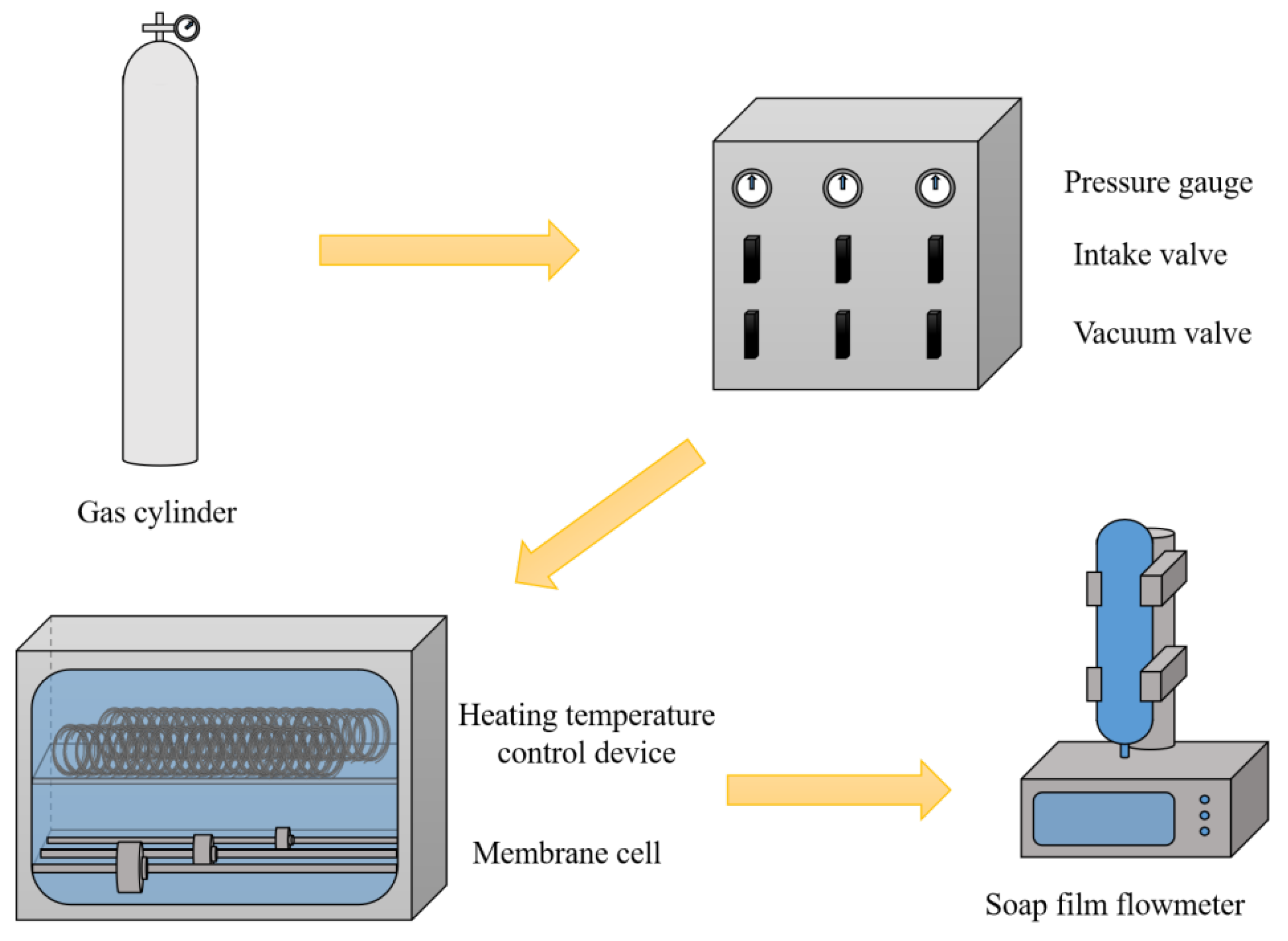
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
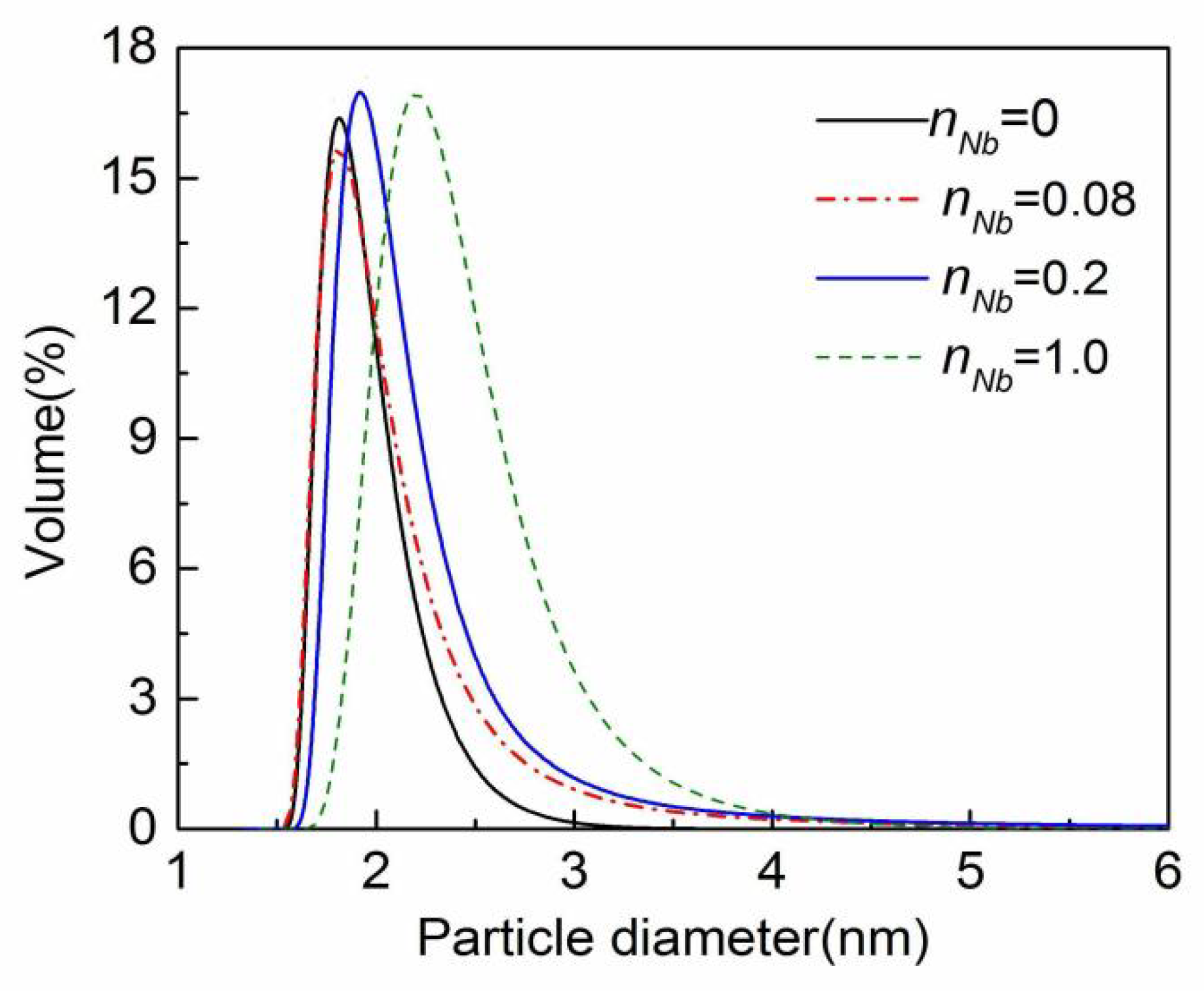
3.1. Analysis of Nb/SiO2 Sol Performance
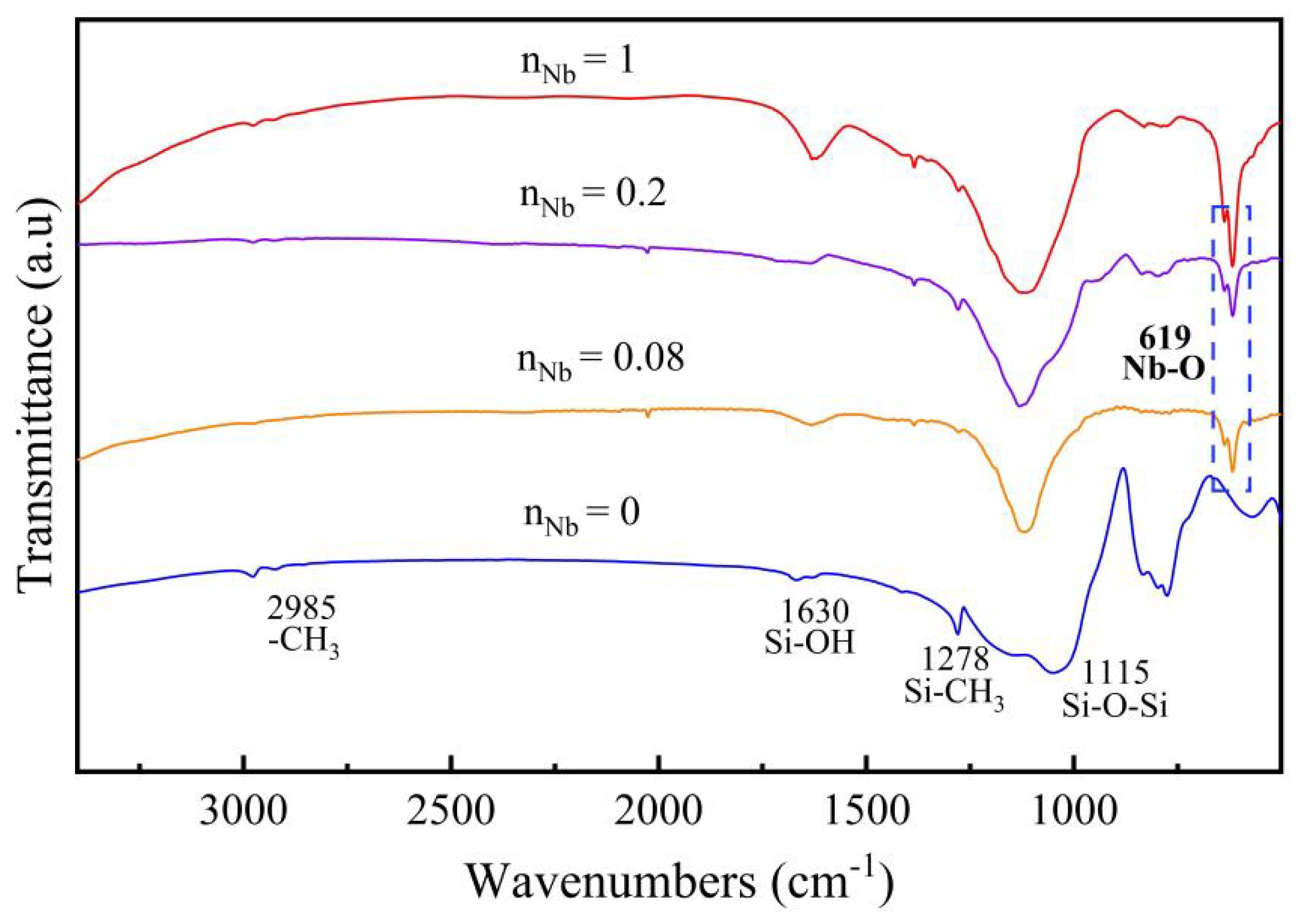
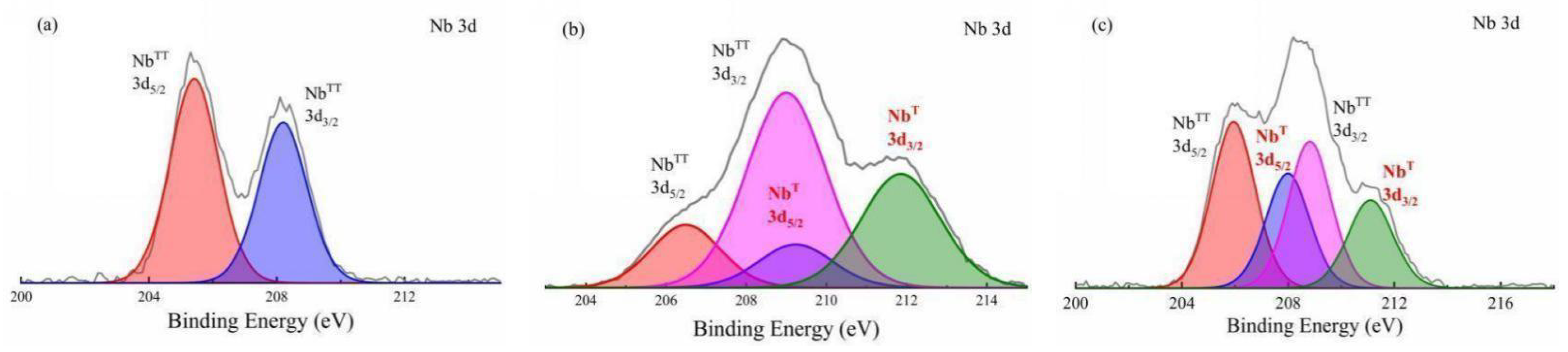
3.2. Chemical Structure Analysis
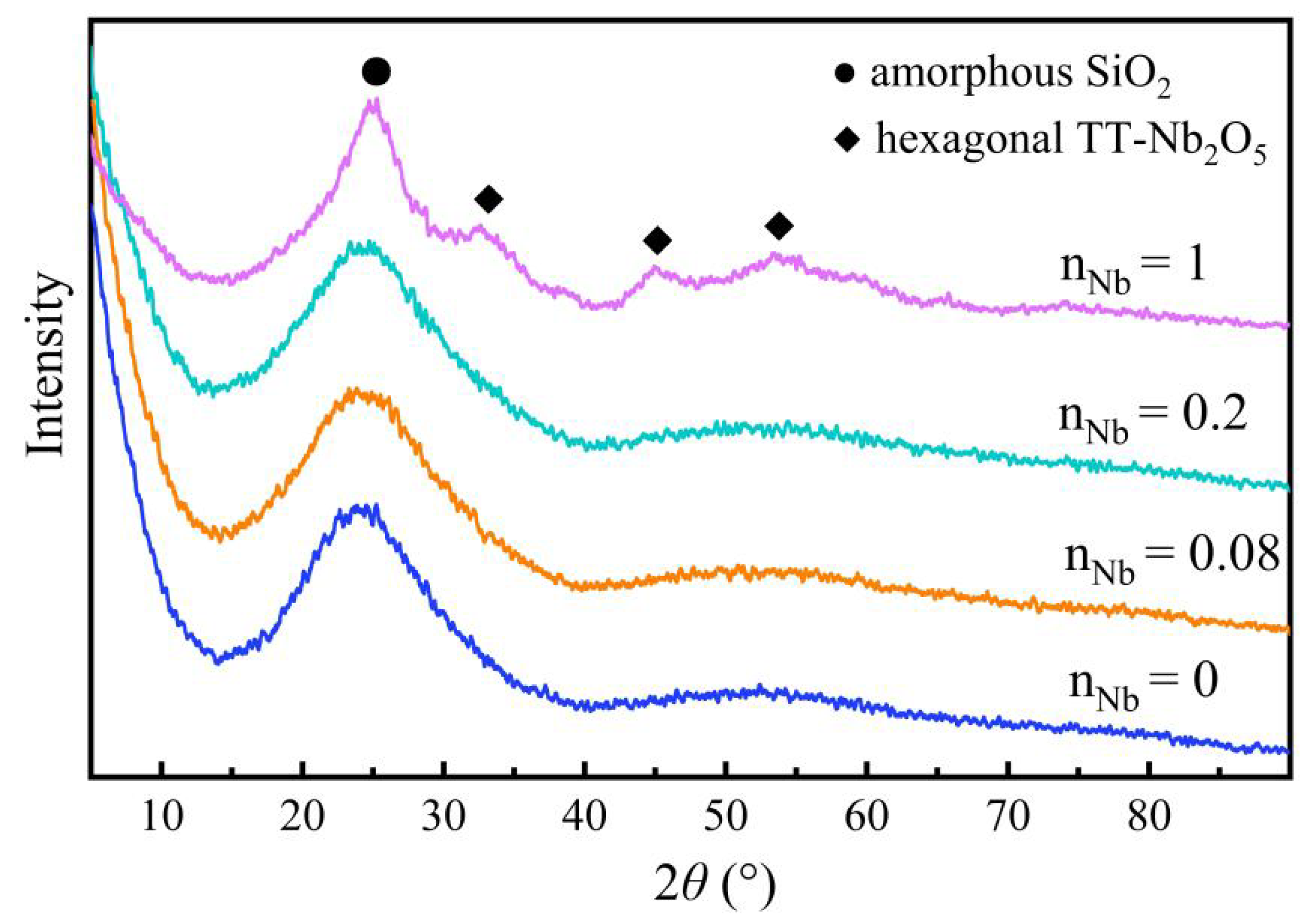
3.3. Phase Structure Analysis
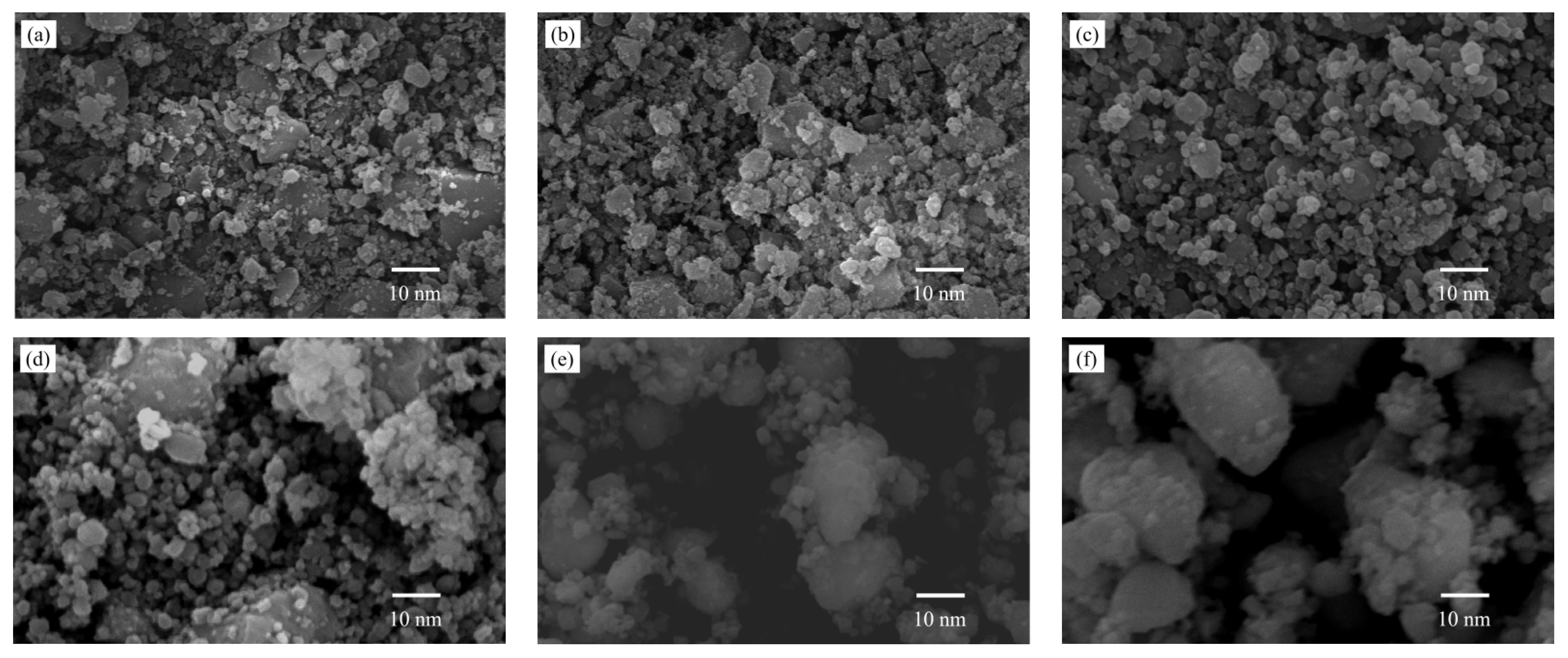
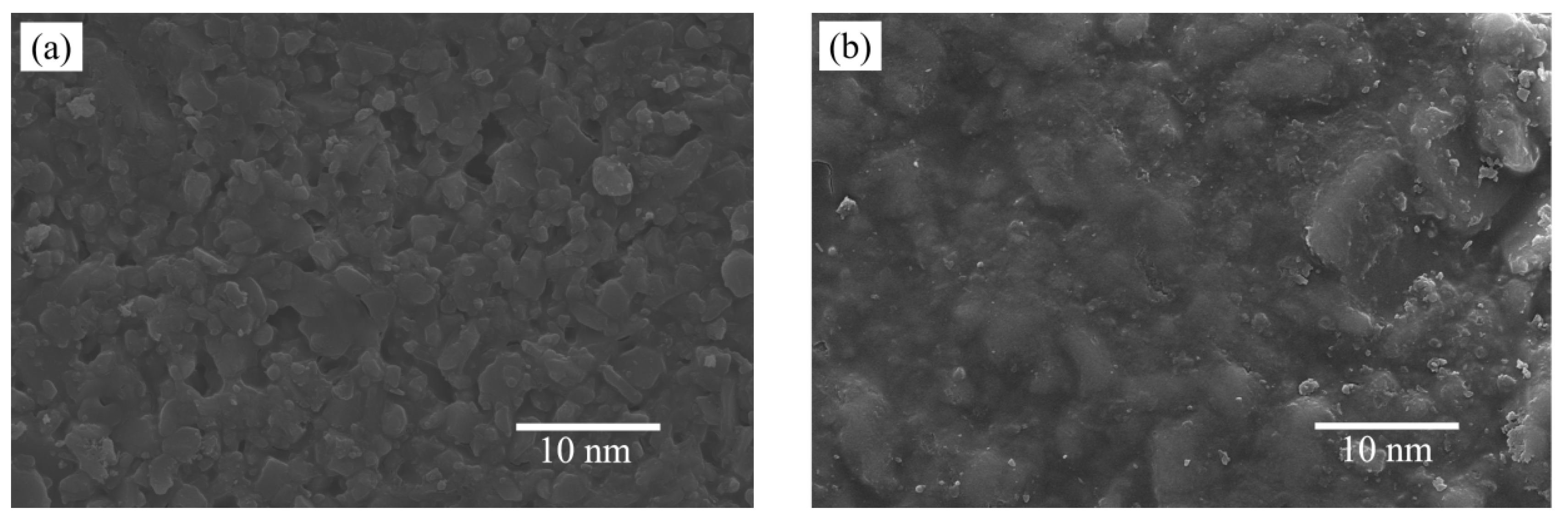
3.4. SEM Analysis
3.5. Pore Structure Analysis
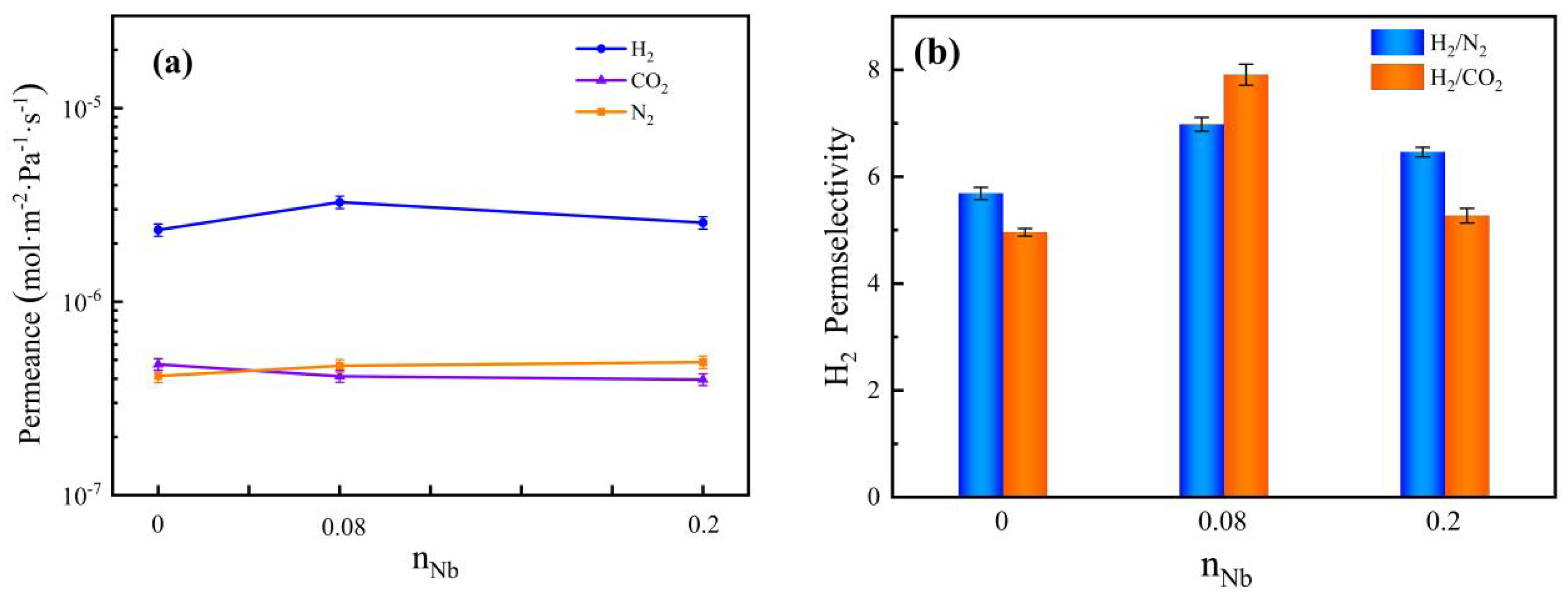
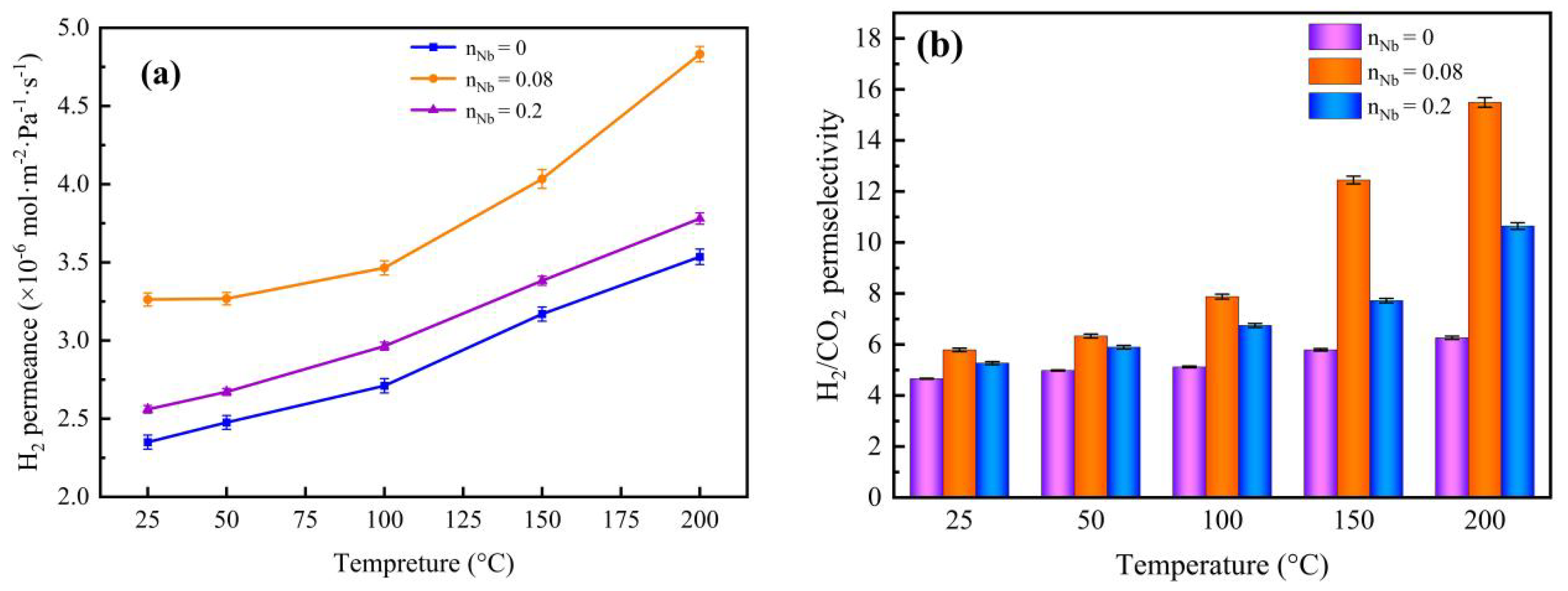
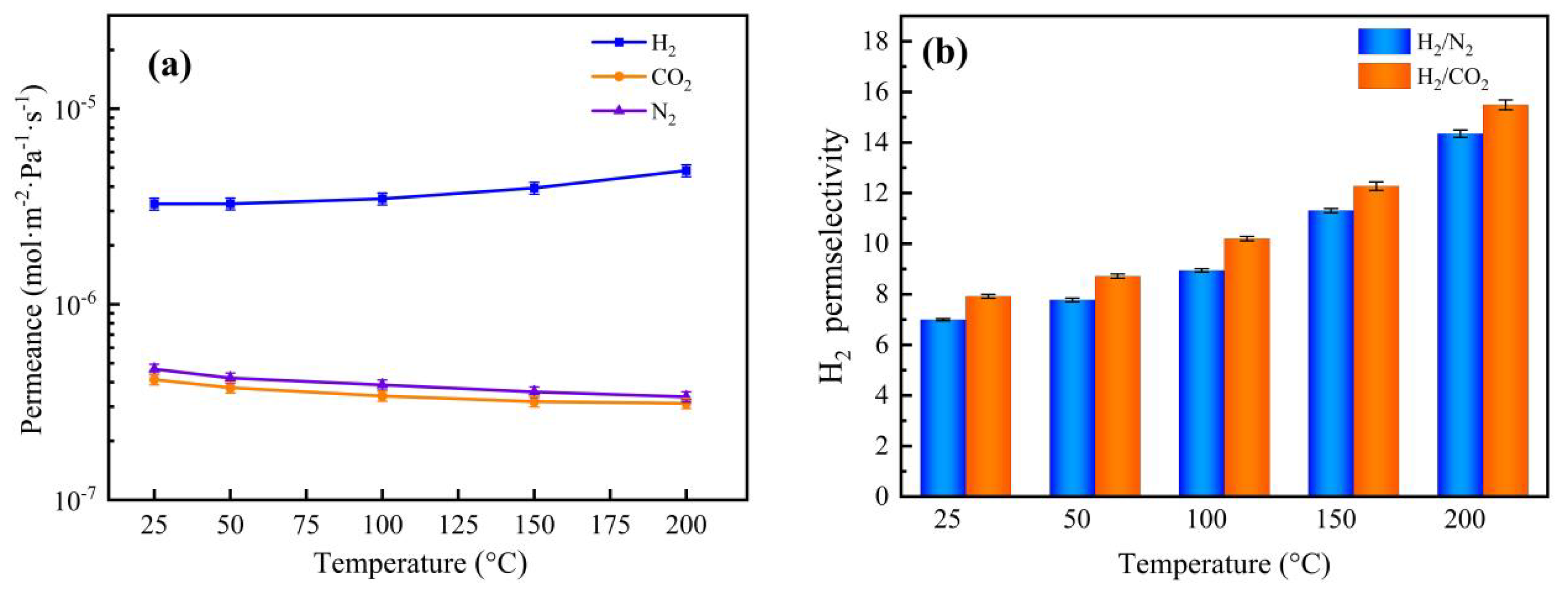
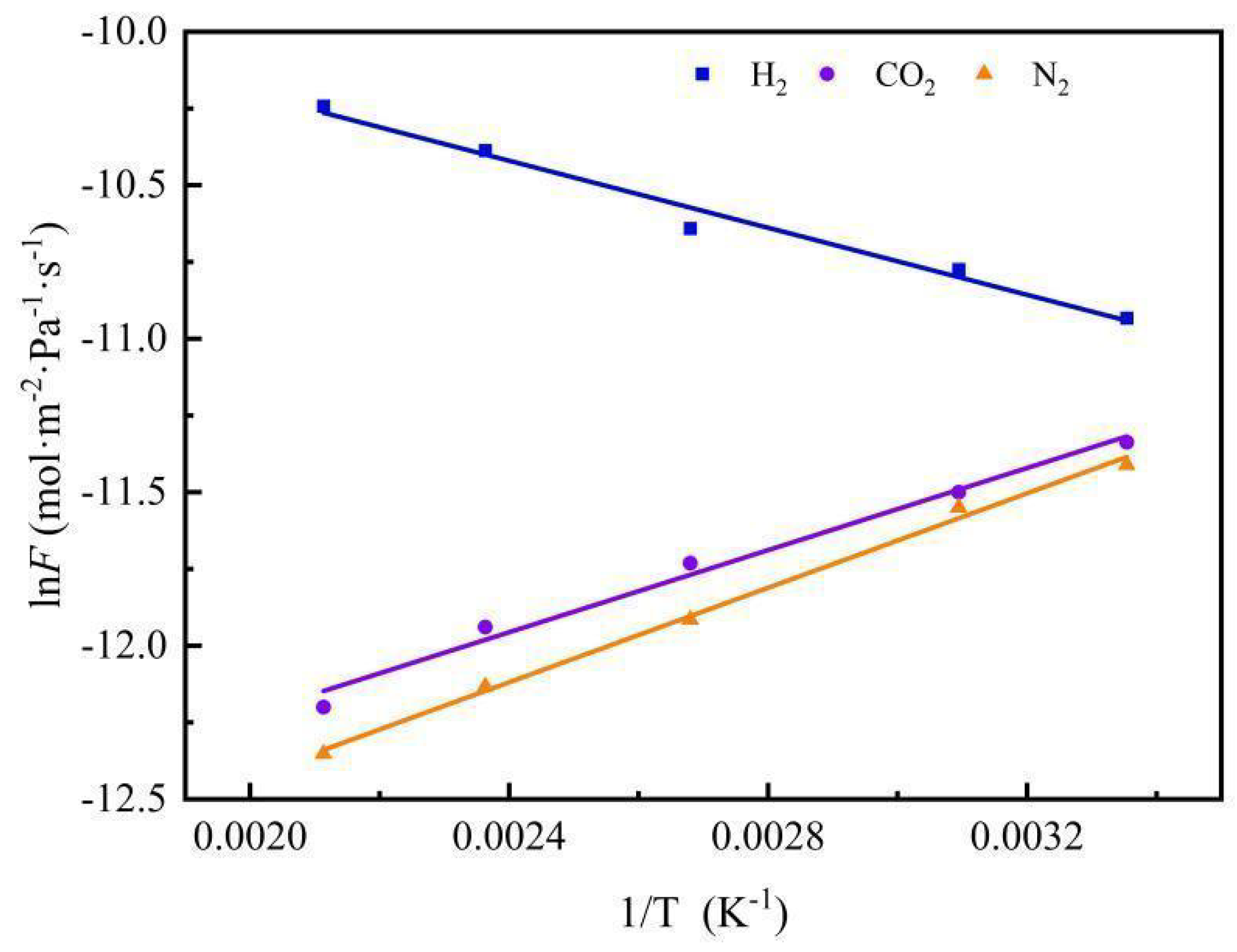
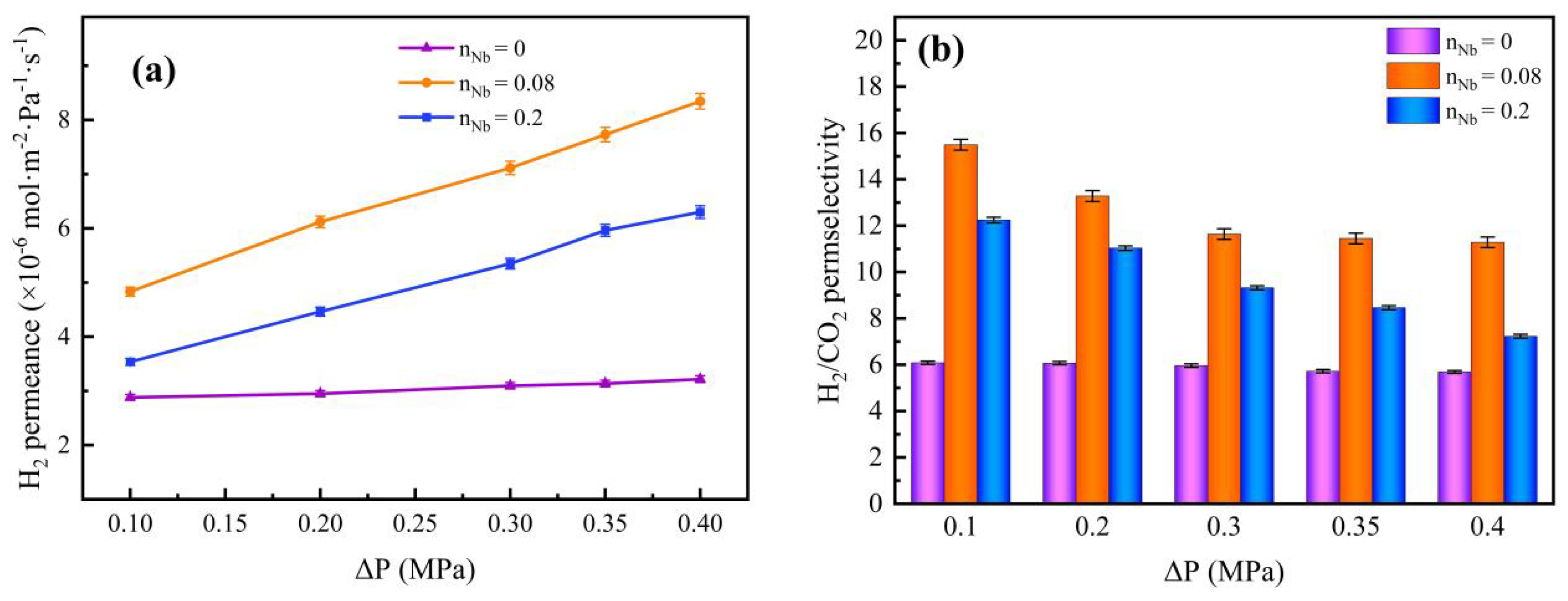
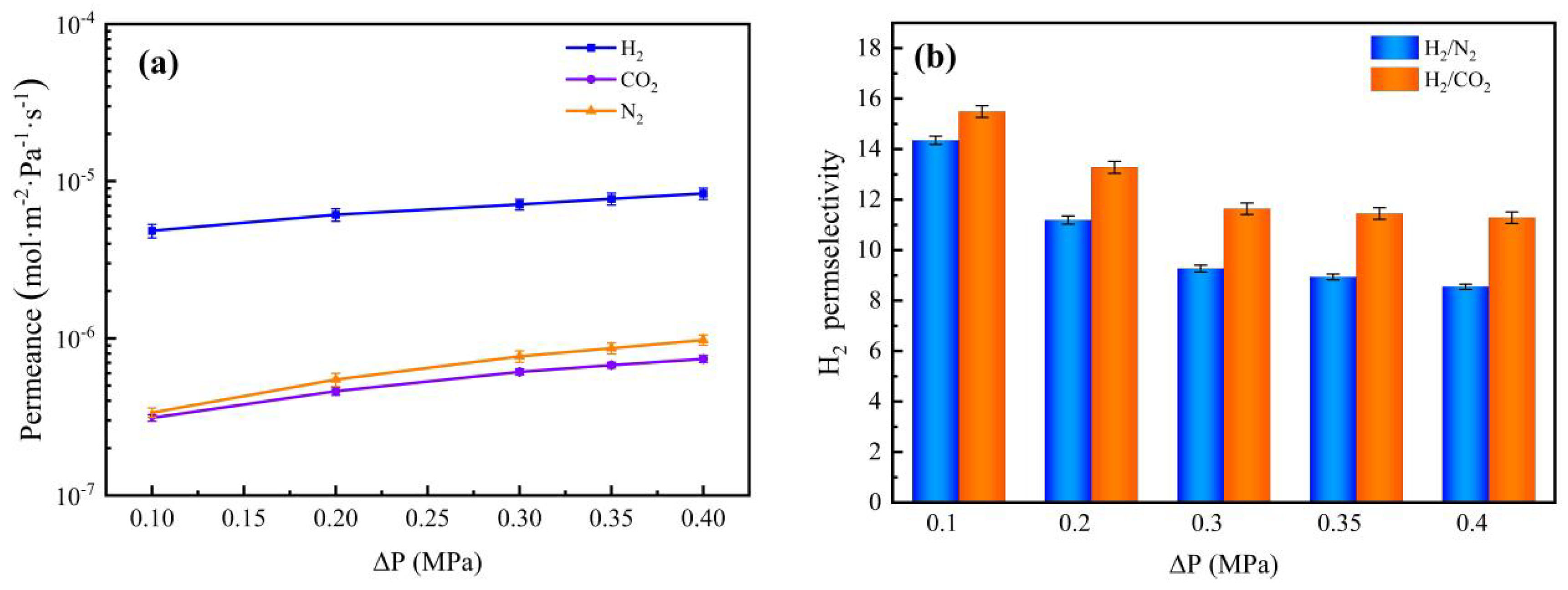
3.6. Gas Permeation and Separation Property Analysis
| Membrane Type | Temperature and Pressure | Ea of H2 (kJ·mol−1) | H2 Permeance (mol·m−2·Pa−1·s−1) | H2 Permselectivities | Mean Pore Diameter (nm) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2/CO2 | H2/N2 | ||||||
| SiO2 | 200 °C, 2 bar | - | 4.62 × 10−7 | 3.7 | 10.5 | 0.30–0.54 | [33] |
| SiO2(400) | 200 °C, 1 bar | 8 | 17.4 × 10−7 | 7.5 | 64 | 0.38–0.55 | [28] |
| SiO2(600) | 200 °C, 2 bar | 7.6 | 4.03 × 10−7 | 66 | - | 0.36–0.38 | [28] |
| Pd/SiO2 | 200 °C, 0.3 MPa | - | 7.26 × 10−7 | 4.3 | 14 | 0.57 | [34] |
| Co/SiO2 | 200 °C, 0.2 MPa | 1.98 | 1.97 × 10−5 | 10.48 | 13.08 | 2.34 | [35] |
| Nb/SiO2 * | 200 °C, 0.1 MPa | 2.53 | 4.83 × 10−6 | 15.49 | 9.54 | 2.4549 | |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnston, B.; Mayo, M.C.; Anshuman, K. Hydrogen: The energy source for the 21st century. Technovation 2005, 25, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Pothu, R.; Siyal, S.; Phulpoto, D.; Sajjad, M.; Thebo, K. Graphene-based membranes for CO2 separation. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameh, A.E.; Eze, C.P.; Antunes, E.; Cornelius, M.-L.U.; Musyoka, N.; Petrik, L.F. Stability of fly ash-based BEA-zeolite in hot liquid phase. Catal. Today 2019, 357, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodinger, S.; Derewinski, M.A. Recent Progress to Understand and Improve Zeolite Stability in the Aqueous Medium. Pet. Chem. 2020, 60, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Du, H.; Lin, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Kong, C.; Chen, L. Hybrid organosilica membrane with high CO2 permselectivity fabricated by a two-step hot coating method. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 506, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ding, Y.-L.; Nie, Z.-R.; Liu, X.-G.; Li, Q.-Y. Wettability, pore structure and performance of perfluorodecyl-modified silica membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, D.; Zheng, L.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of Nickel-Doped Silica Films and Gas Separation Performance for CH4/CO2. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 42, 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xing, X.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, R.; Guo, Y.; Hou, H. Microstructures of nickel-doped methylated silica membrane materials calcined in air: Influence of Ni content. Ferroelectrics 2020, 562, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tian, L. Preparation, Characterization and Surface Free Energy of Nickel-Doped Silica Organic Inorganic Hybrid Membrane for H2/CO2 Separation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 3180–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Song, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, S.; Qi, H. A novel strategy to enhance hydrothermal stability of Pd-doped organosilica membrane for hydrogen separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 253, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhong, S. Preparation and Application of Supported Palladium-Modified Polyimide-Silica Hybrid Membrane for Selective Separation of H2. Chin. J. Catal. 2006, 3, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hove, M.; Nijmeijer, A.; Winnubst, L. Facile synthesis of zirconia doped hybrid organic inorganic silica membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Han, J.; Xu, N. Effect of calcination temperature on carbon dioxide separation properties of a novel microporous hybrid silica membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 382, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakiliç, P.; Huiskes, C.; Luiten-Olieman, M.W.J.; Nijmeijer, A.; Winnubst, L. Sol-gel processed magnesium-doped silica membranes with improved H2/CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 543, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezashi, M.; Miyauchi, S.; Nagasawa, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Gas permeation properties through Al-doped organosilica membranes with controlled network size. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igi, R.; Yoshioka, T.; Ikuhara, Y.H.; Iwamoto, Y.; Tsuru, T. Characterization of Co-doped silica for improved hydrothermal stability and application to hydrogen separation membranes at high temperatures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ai, Y.; Fan, W.; Mu, R.; Chen, X.; Hou, H. Cobalt-Doped Silica Organic-Inorganic Materials by Sol-Gel Method: Preparation and Thermal Stability Calcined under N2 Atmosphere. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2021, 219, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffa, V.; Blank, D.; Elshof, J.E.T.; Tenelshof, J. Hydrothermal stability of microporous silica and niobia–Silica membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 319, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Song, H.; Zhu, H.; Chen, J.; Qi, H. The influence of the particle size of polymer sol on the gas separation performance of niobium-doped organic-inorganic hybrid SiO2 membrane. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Košutová, T.; Horák, L.; Pleskunov, P.; Hanuš, J.; Nikitin, D.; Kúš, P.; Cieslar, M.; Gordeev, I.; Burazer, S.; Choukourov, A.; et al. Thermally-driven morphogenesis of niobium nanoparticles as witnessed by in-situ x-ray scattering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 277, 125466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frevel, L.K.; Rinn, H.W. Powder Diffraction Standards for Niobium Pentoxide and Tantalum Pentoxide. Anal. Chem. 1955, 27, 1329–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, G. Die oxyde des niobs. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1941, 248, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Tamura, S. Die kristallstruktur von T-Nb2O5. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem. 1975, 31, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerer, P.; van Karsbergen, V.; Weinberger, N.; Strauss, G.; Neubauer, E.; Friessnegger, B.; Marsoner, S. In-situ high-temperature X-ray diffraction investigations of magnetron sputtered niobium oxide layers up to 900 °C. Thin Solid Films 2019, 674, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; Gushikem, Y. Synthesis and characterization of SiO2–Nb2O5 systems prepared by the sol–gel method: Structural stability studies. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boffa, V.; Elshof, J.E.T.; Petukhov, A.V.; Blank, D.H.A. Microporous Niobia–Silica Membrane with Very Low CO2 Permeability. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boffa, V.; Elshof, J.T.; Garcia, R.; Blank, D. Microporous niobia-silica membranes: Influence of sol composition and structure on gas transport properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 118, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, R.M.; Verweij, H. Improved performance of silica membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 143, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, B.N.; Keizer, K.; Suematsu, H.; Suma, Y.; Kaneko, N.; Ono, S.; Okubo, A.T.; Nakao, S.-I. Synthesis of Gas and Vapor Molecular Sieving Silica Membranes and Analysis of Pore Size and Connectivity. Langmuir 2000, 16, 4558–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhorn, R.; Keizer, K.; Burggraaf, A. Gas transport and separation with ceramic membranes. Part II. Synthesis and separation properties of microporous membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 66, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanezashi, M.; Fujita, T.; Asaeda, M. Nickel-Doped Silica Membranes for Separation of Helium from Organic Gas Mixtures. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Hirano, Y.; Fujii, H.; Tsuru, T.; Asaeda, M. Hydrothermal Stability and Performance of Silica-Zirconia Membranes for Hydrogen Separation in Hydrothermal Conditions. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2001, 34, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, H.F.; Nijmeijer, A.; Winnubst, L. Influence of sol–gel process parameters on the micro-structure and performance of hybrid silica membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhao, S.; Lei, J.; Wang, C.; Qi, H. Pd-doped organosilica membrane with enhanced gas permeability and hydrothermal stability for gas separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 6275–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Mu, R.; Guo, Y.; Hou, H. Sol-Gel Processed Cobalt-Doped Methylated Silica Membranes Calcined under N2 Atmosphere: Microstructure and Hydrogen Perm-Selectivity. J. Mater. 2021, 14, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| nNb | pH | Density/g·cm−3 | Solid Content/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.41 ± 0.04 | 0.8418 ± 0.0007 | 22.31 ± 0.04 |
| 0.08 | 2.93 ± 0.03 | 0.8529 ± 0.0006 | 22.58 ± 0.05 |
| 0.2 | 2.64 ± 0.02 | 0.8710 ± 0.0008 | 22.80 ± 0.06 |
| 1 | 1.02 ± 0.02 | 0.9130 ± 0.0006 | 24.46 ± 0.07 |
| nNb | BET/ m2·g−1 | Vt/ cm3·g−1 | Vmic/ cm3·g−1 | Mean Pore Width/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 386.4545 | 0.1716 | 0.1115 | 1.8759 |
| 0.08 | 778.7121 | 0.4901 | 0.0867 | 2.4549 |
| 0.2 | 535.4072 | 0.4632 | 0.0748 | 2.2591 |
| 1 | 86.1599 | 0.0762 | 0.0266 | 1.2176 |
| Gases | Ea/ kJ·mol−1 | Qst/ kJ·mol−1 [28] | Em/ kJ·mol−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | 2.53 | 6 | 8.53 |
| CO2 | −4.28 | 24 | 19.72 |
| N2 | −4.07 | 18 | 13.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, R. Microstructure and Hydrothermal Stability of Microporous Niobia-Silica Membranes: Effect of Niobium Doping Contents. Membranes 2022, 12, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050527
Xia J, Yang J, Zhang H, Guo Y, Zhang R. Microstructure and Hydrothermal Stability of Microporous Niobia-Silica Membranes: Effect of Niobium Doping Contents. Membranes. 2022; 12(5):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050527
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Jiachen, Jing Yang, Hao Zhang, Yingming Guo, and Ruifeng Zhang. 2022. "Microstructure and Hydrothermal Stability of Microporous Niobia-Silica Membranes: Effect of Niobium Doping Contents" Membranes 12, no. 5: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050527
APA StyleXia, J., Yang, J., Zhang, H., Guo, Y., & Zhang, R. (2022). Microstructure and Hydrothermal Stability of Microporous Niobia-Silica Membranes: Effect of Niobium Doping Contents. Membranes, 12(5), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050527






