Effect of Different Hot-Pressing Pressure and Temperature on the Performance of Titanium Mesh-Based MEA for DMFC
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation Methods of Titanium Mesh-Based MEA
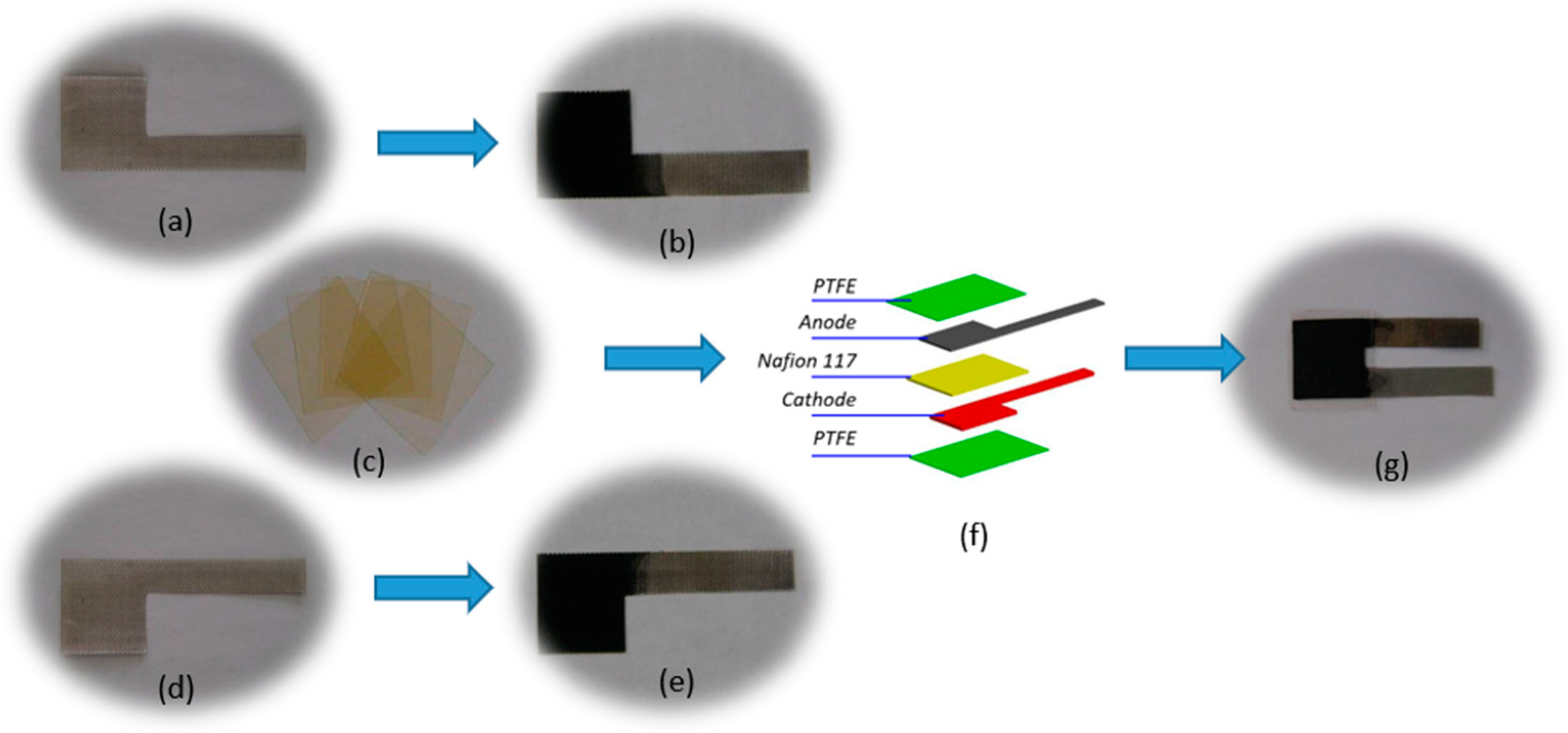
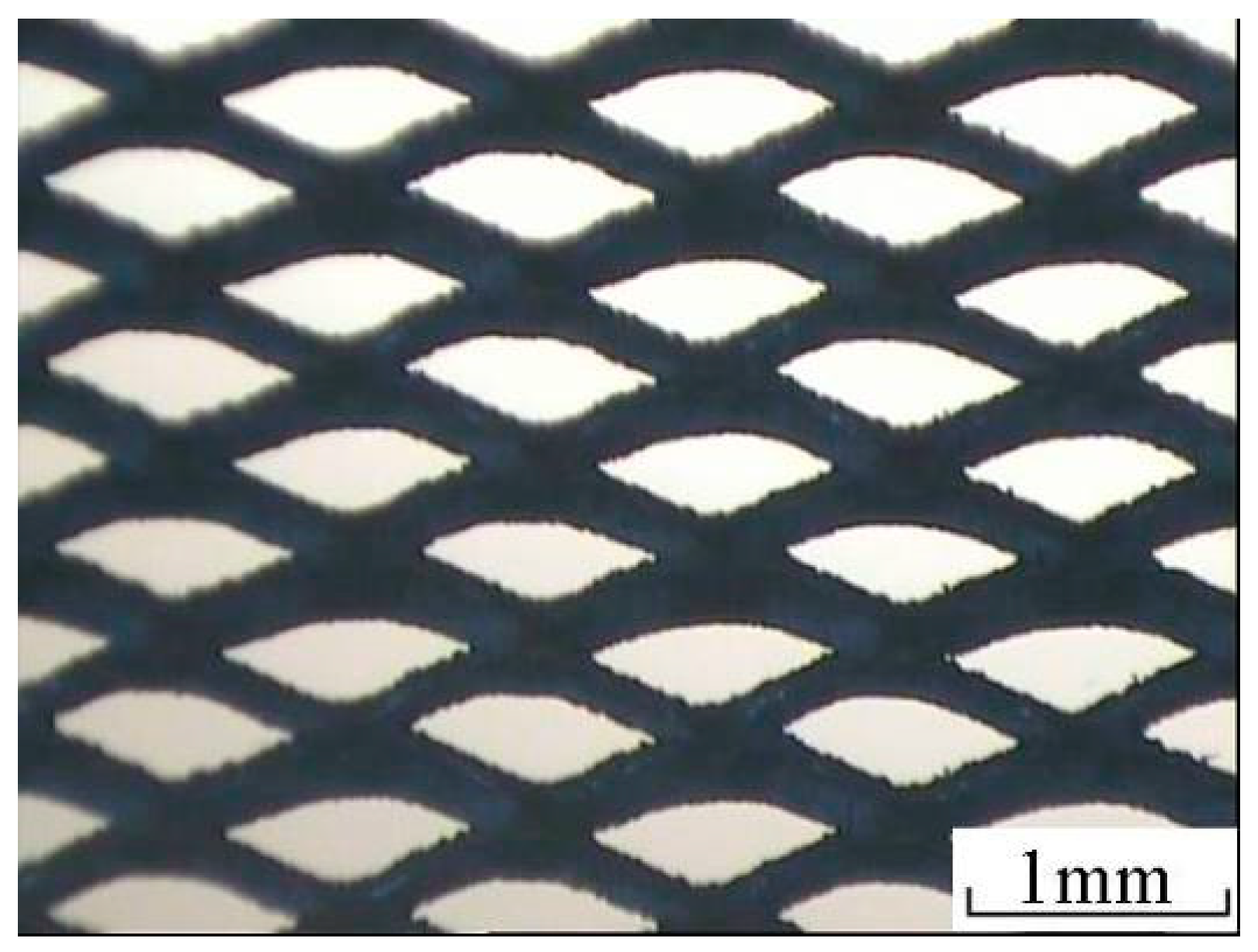
2.2.1. Titanium Mesh Pretreatment
2.2.2. Nafion 117 Membrane Pretreatment
2.2.3. Cathode Preparation
2.2.4. Anode Preparation
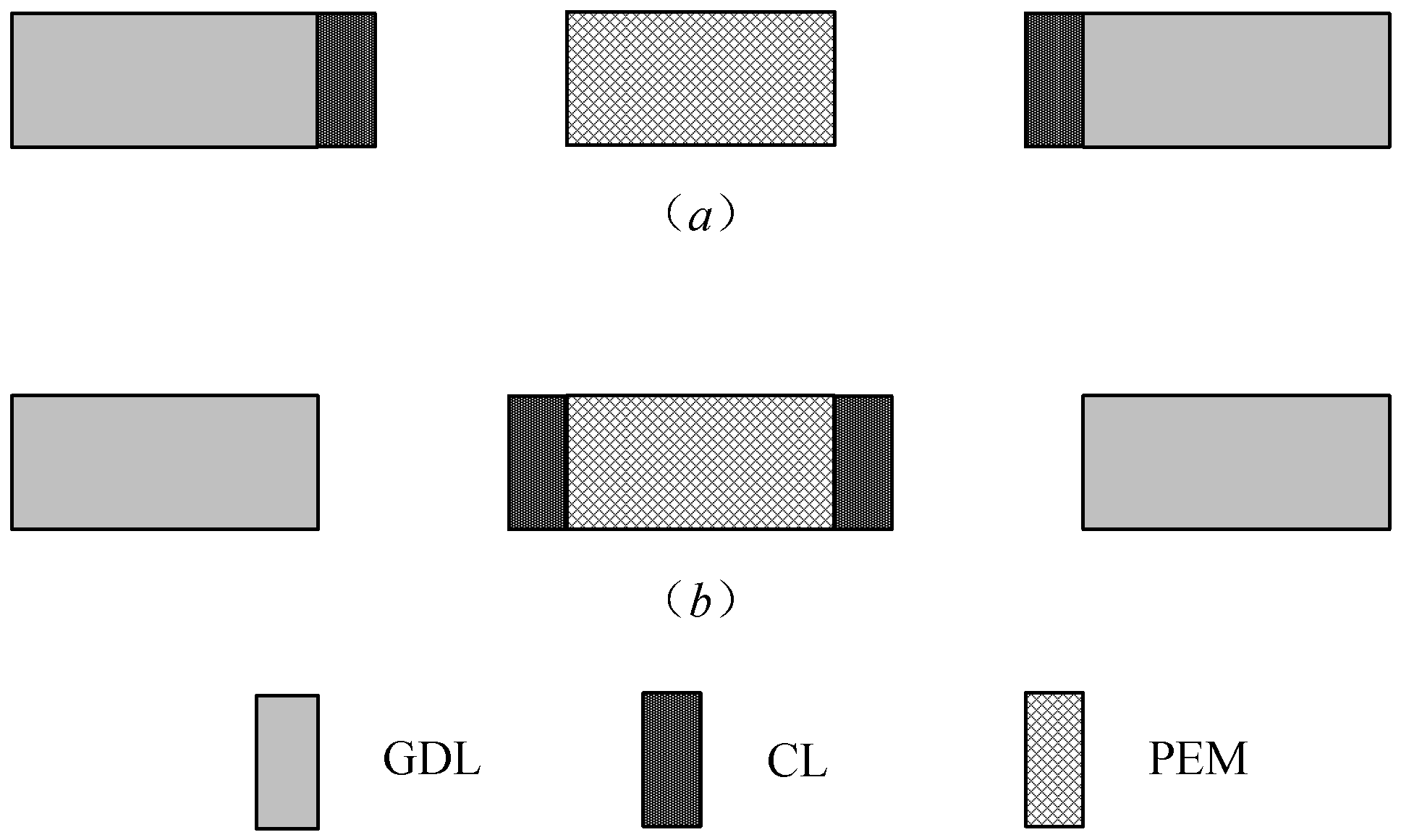
2.2.5. MEA Hot-Pressing
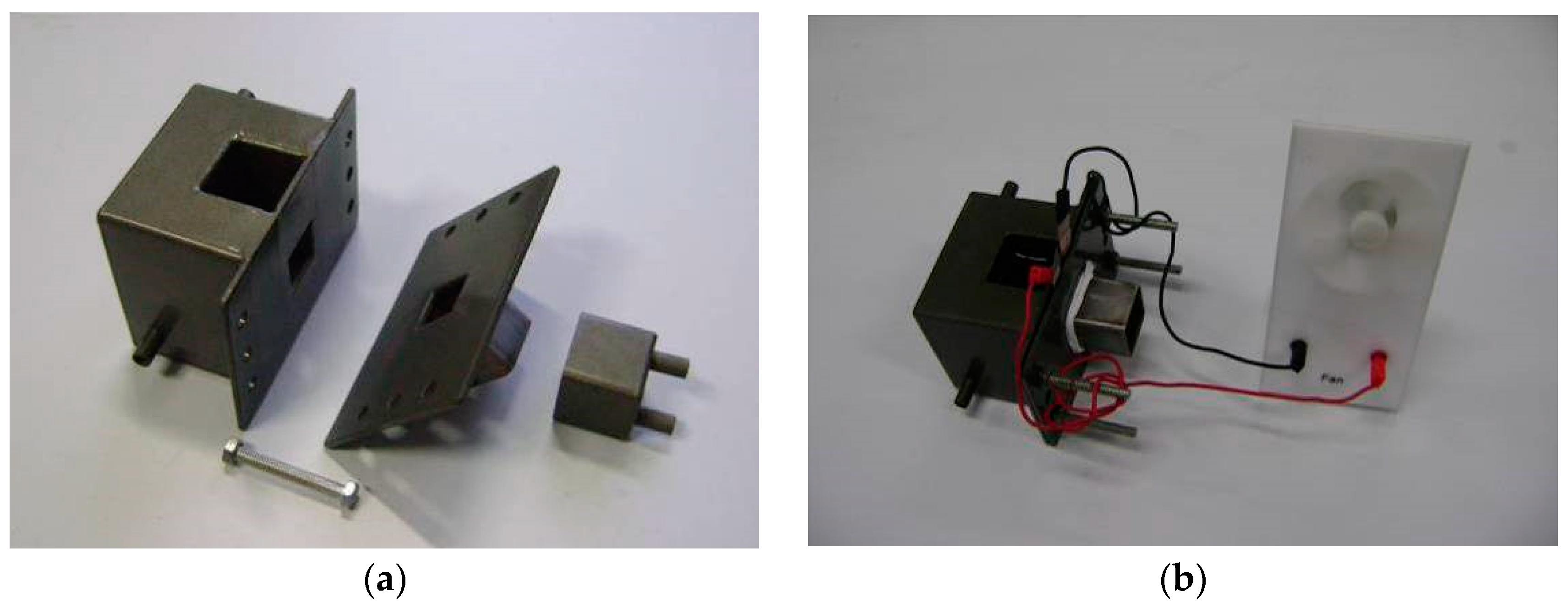
2.3. Performance Testing Device and Characterization Methods
3. Results
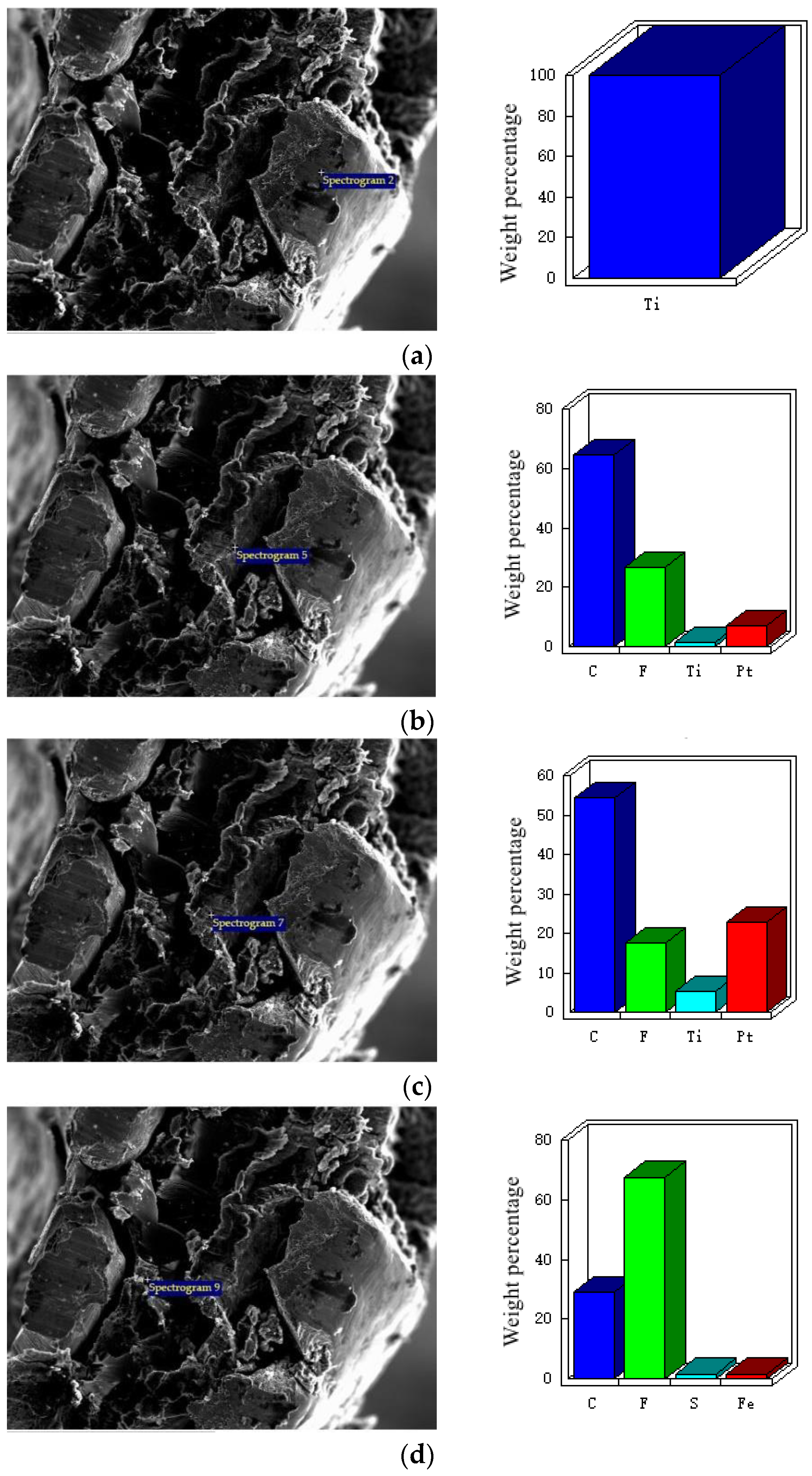
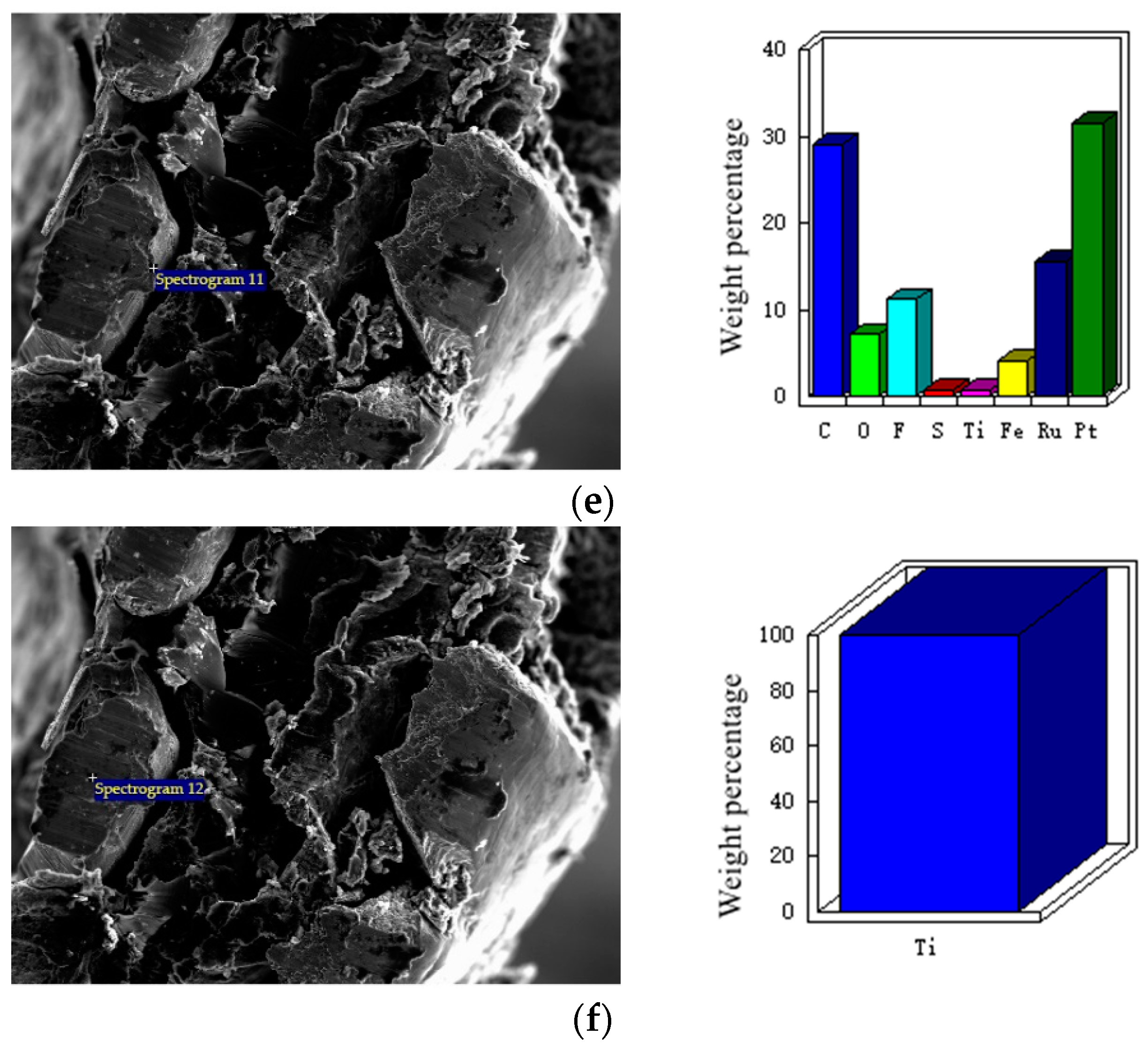
3.1. Morphology Observation and Elemental Analysis of Electrode
3.1.1. Micro Morphology of Electrode Preparation Process
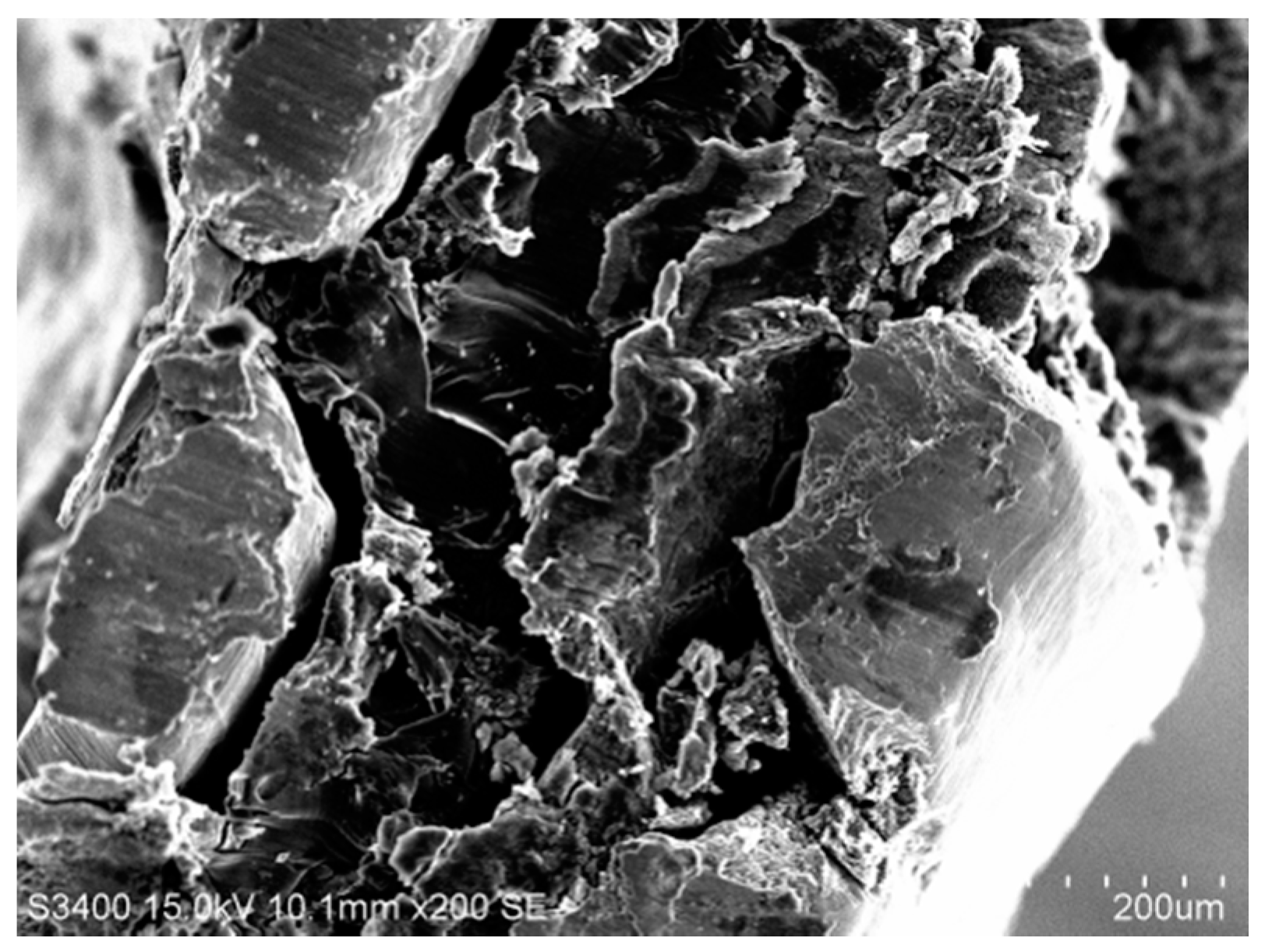
3.1.2. Micro Morphology of Electrode Section
3.1.3. Element Analysis of Electrode Cross-Section
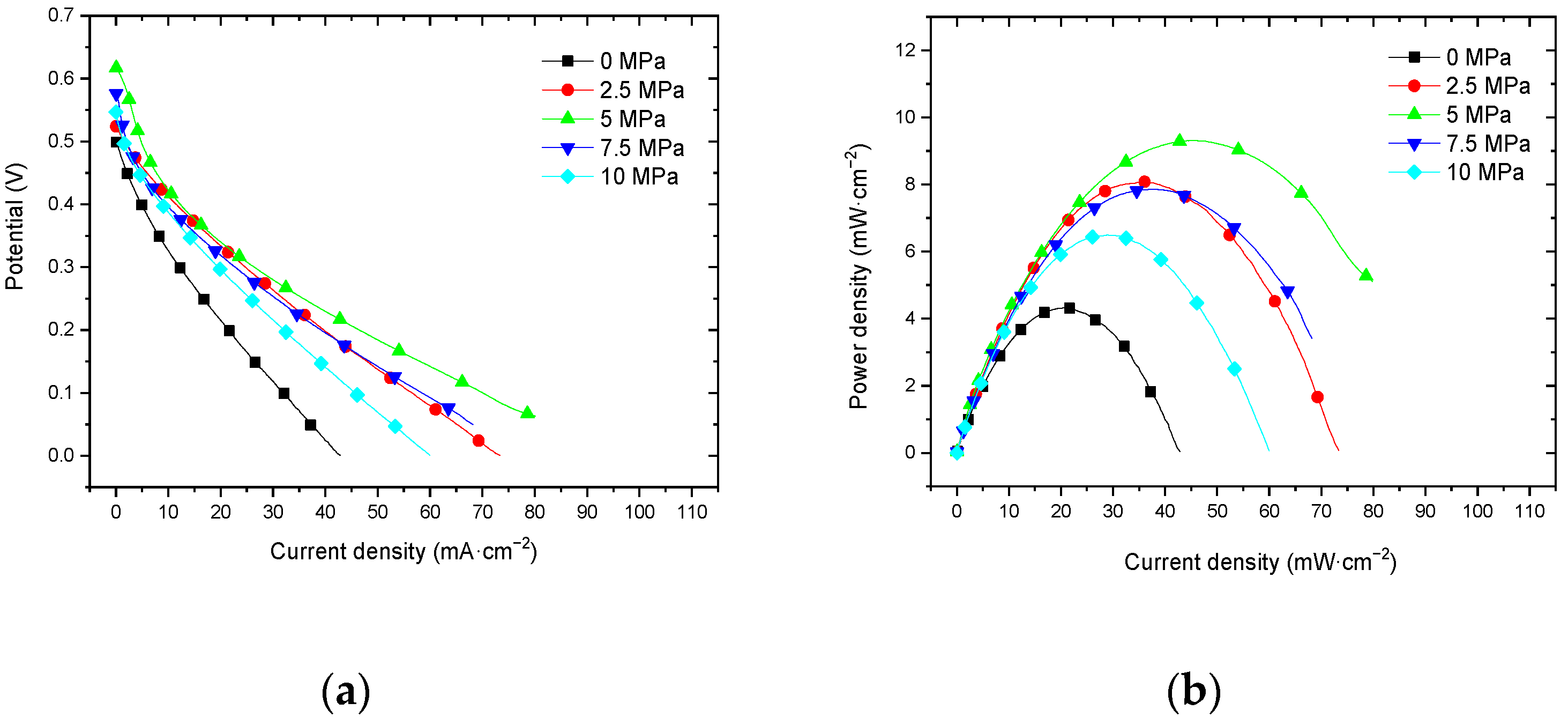
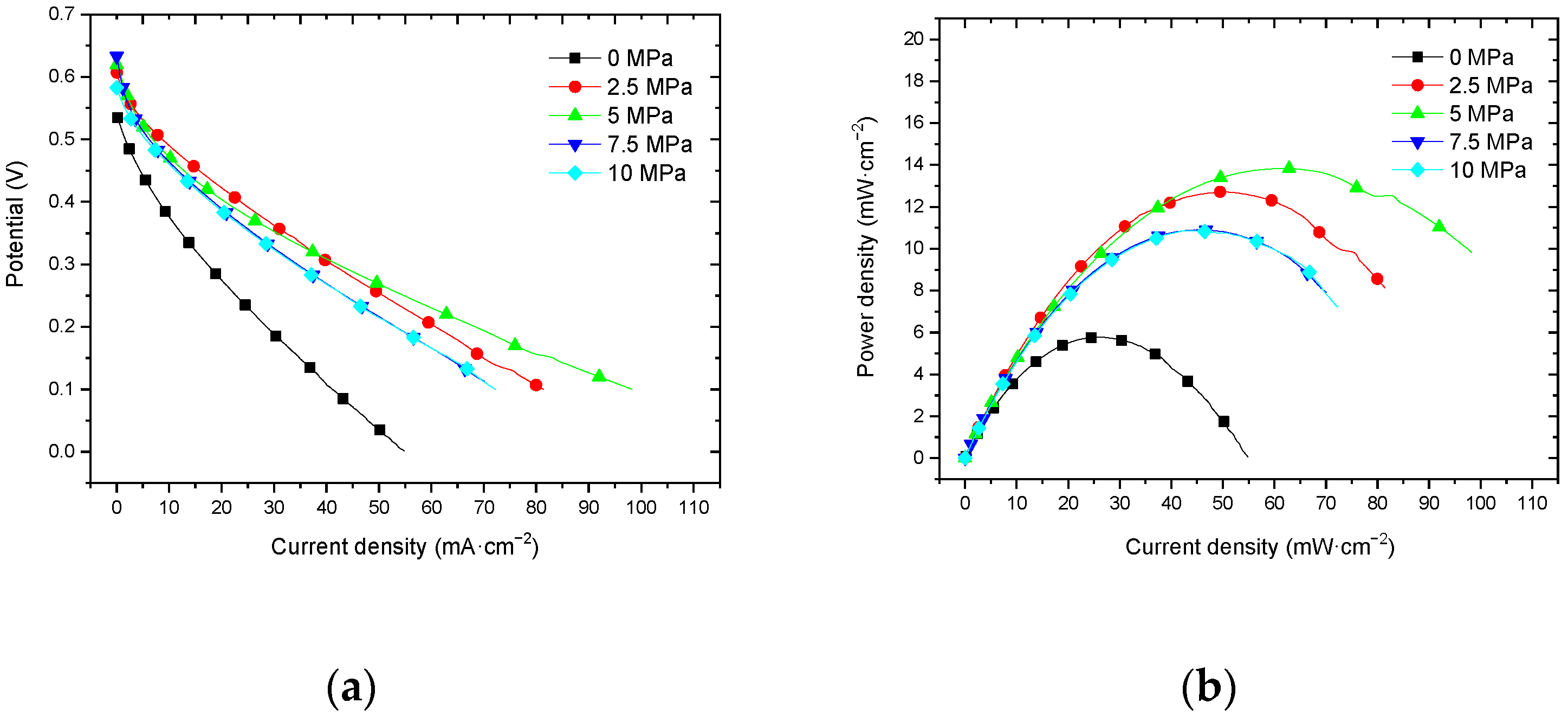
3.2. Effect of Hot-Pressing Pressure on the Performance of Titanium Mesh-Based MEA
3.2.1. Performance at Room Temperature with Air Self-Breathing Environment
3.2.2. Performance at Room Temperature with Oxygen Environment
3.2.3. Performance at 60 °C with Air Self-Breathing Environment
3.2.4. Performance at 60 °C with Oxygen Environment
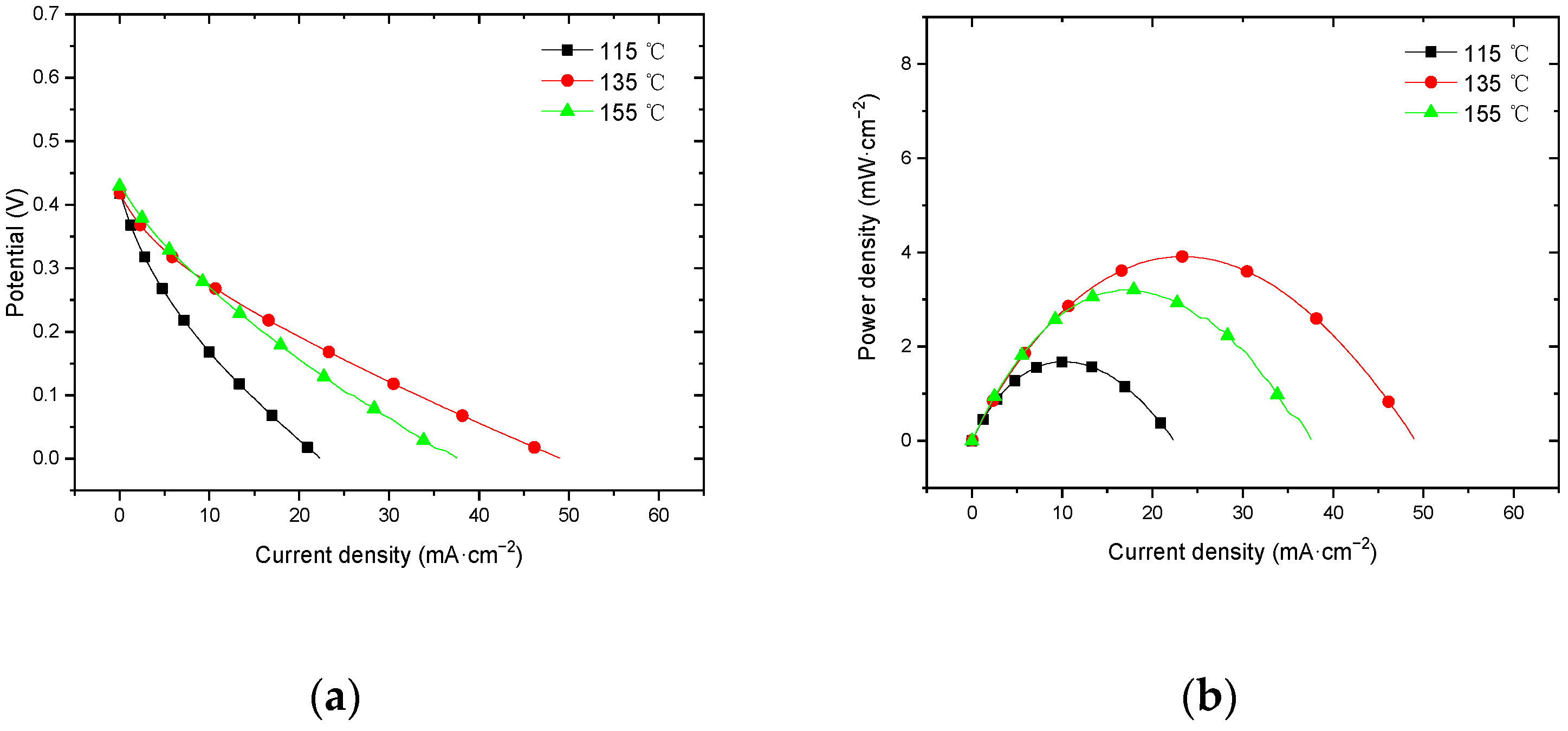
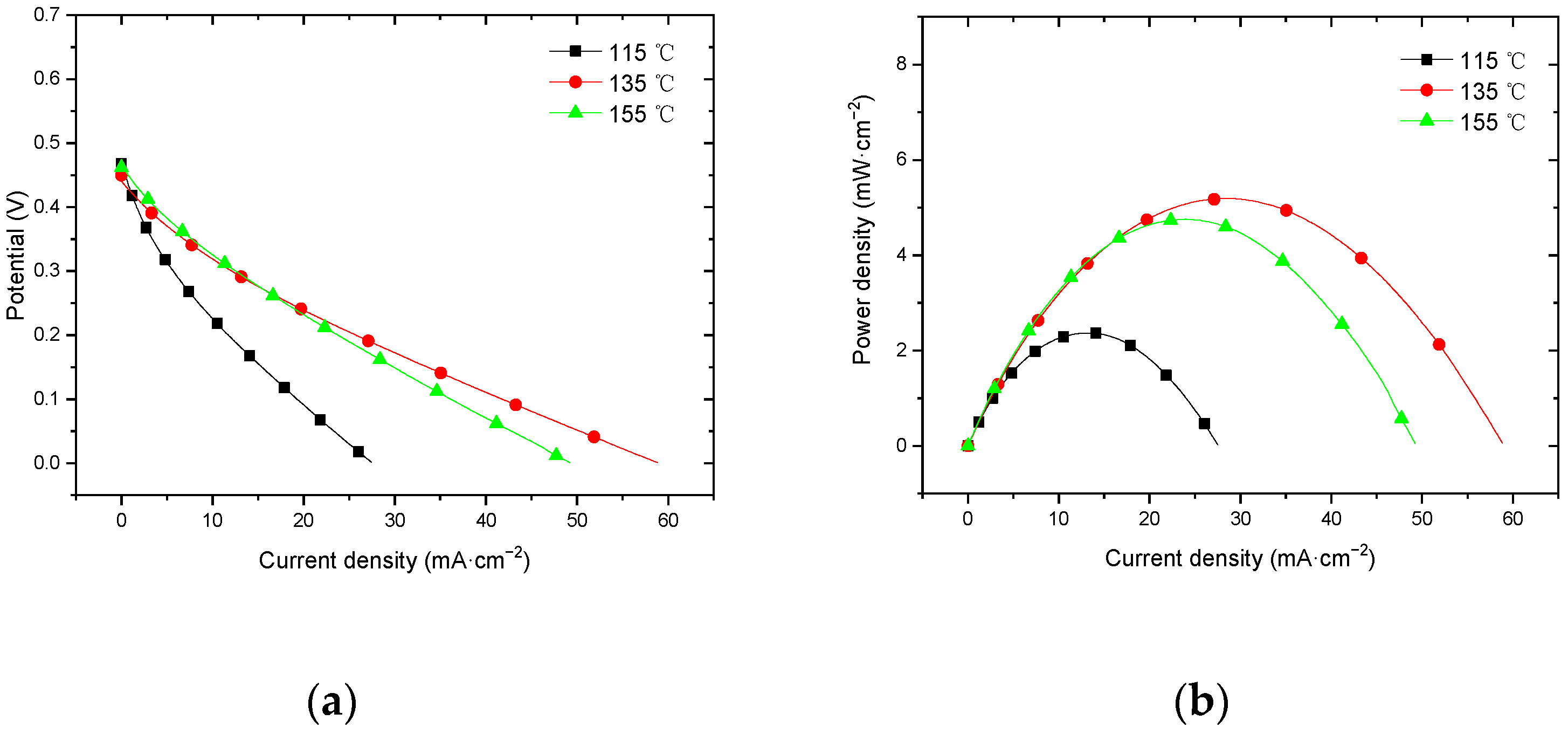
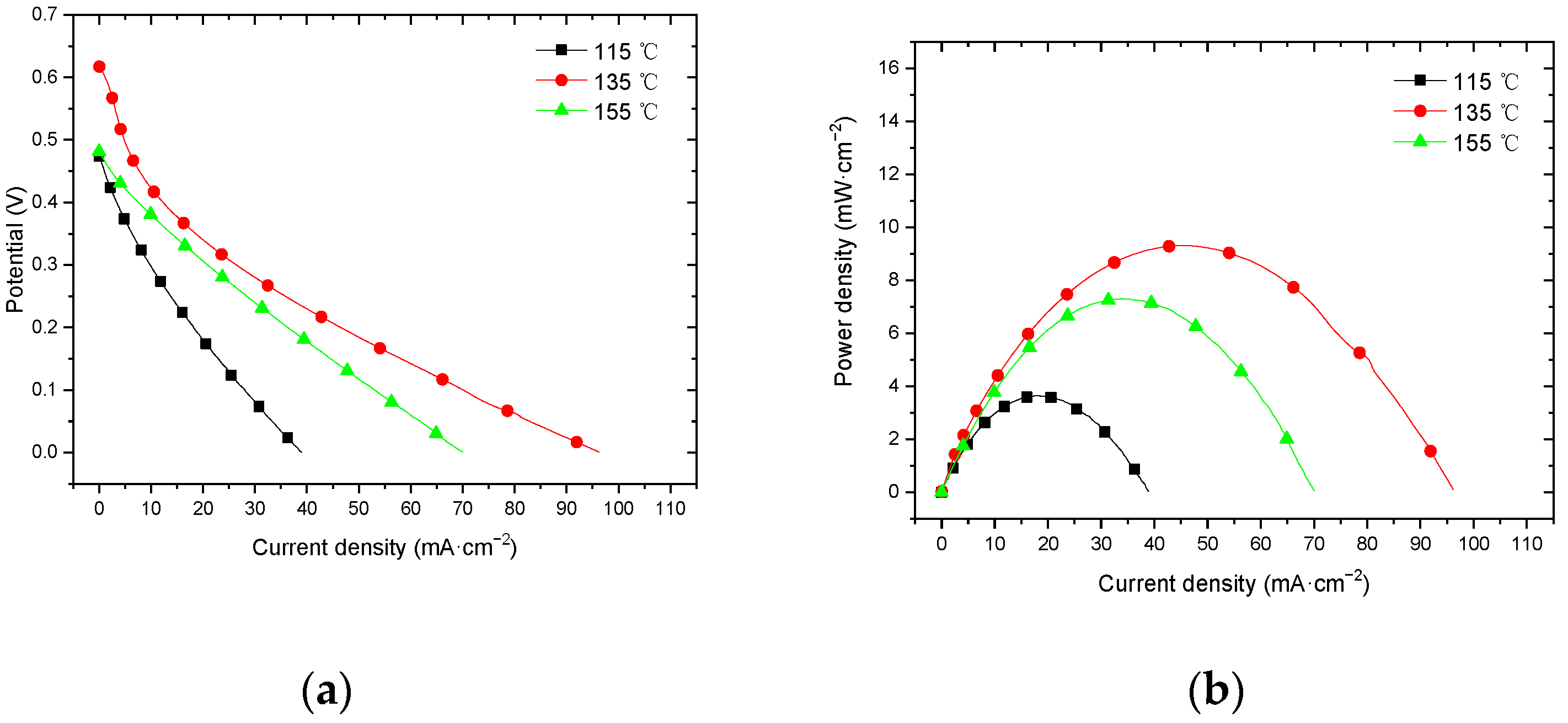
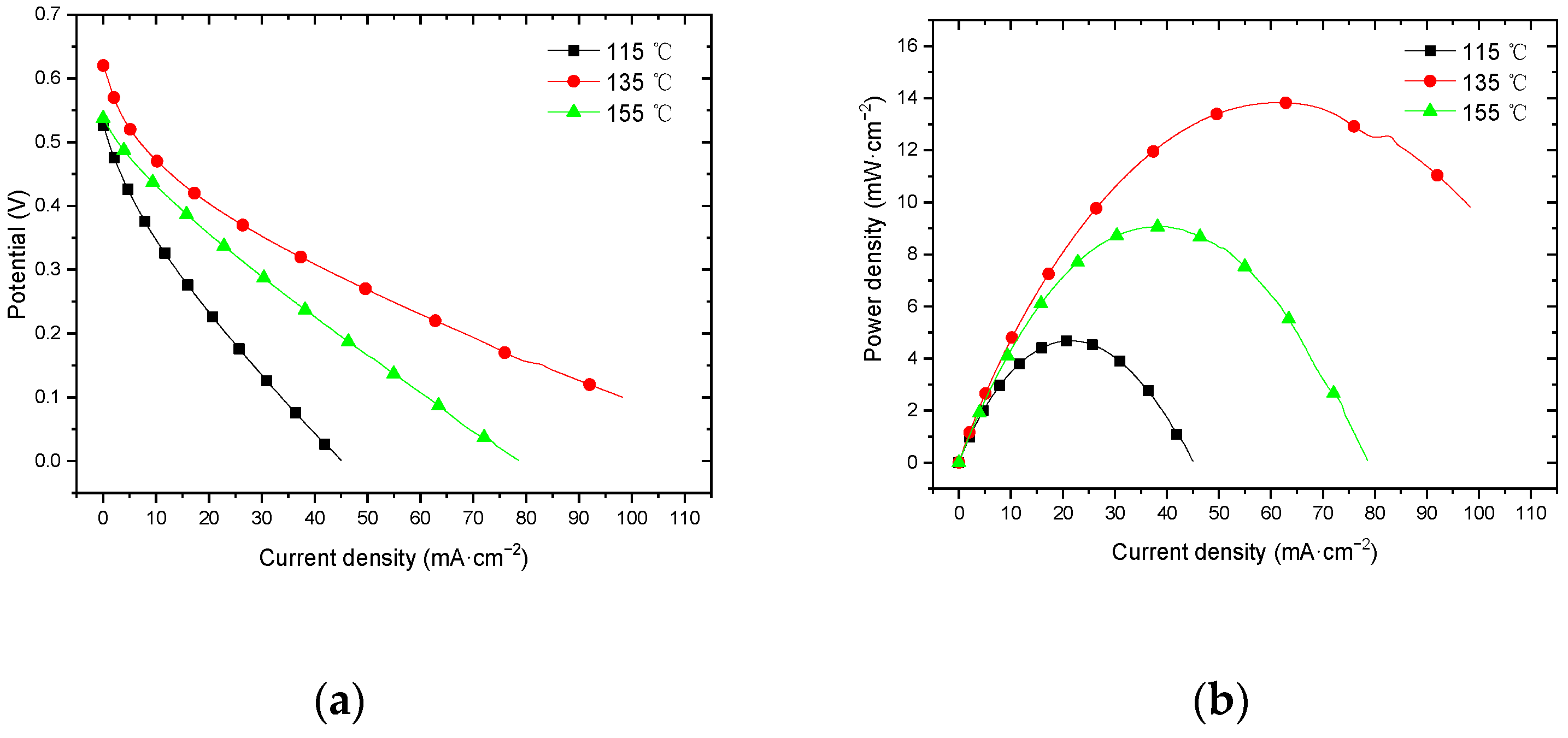
3.3. Effect of Hot-Pressing Temperature on the Performance of Titanium Mesh-Based MEA
3.3.1. Performance at Room Temperature with Air Self-Breathing Environment
3.3.2. Performance at Room Temperature with Oxygen Environment
3.3.3. Performance at 60 °C with Air Self-Breathing Environment
3.3.4. Performance at 60 °C with Oxygen Environment
4. Discussion
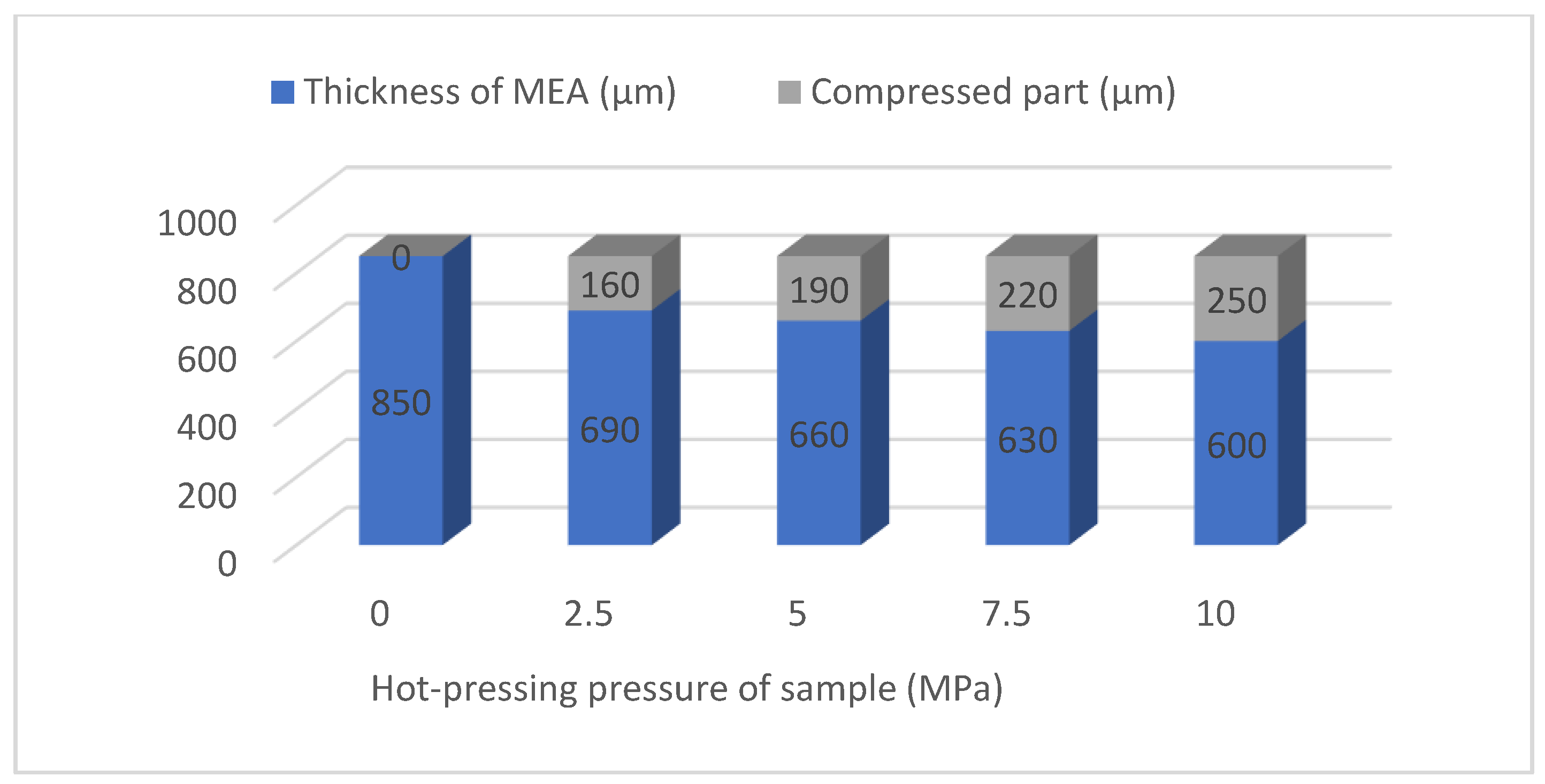
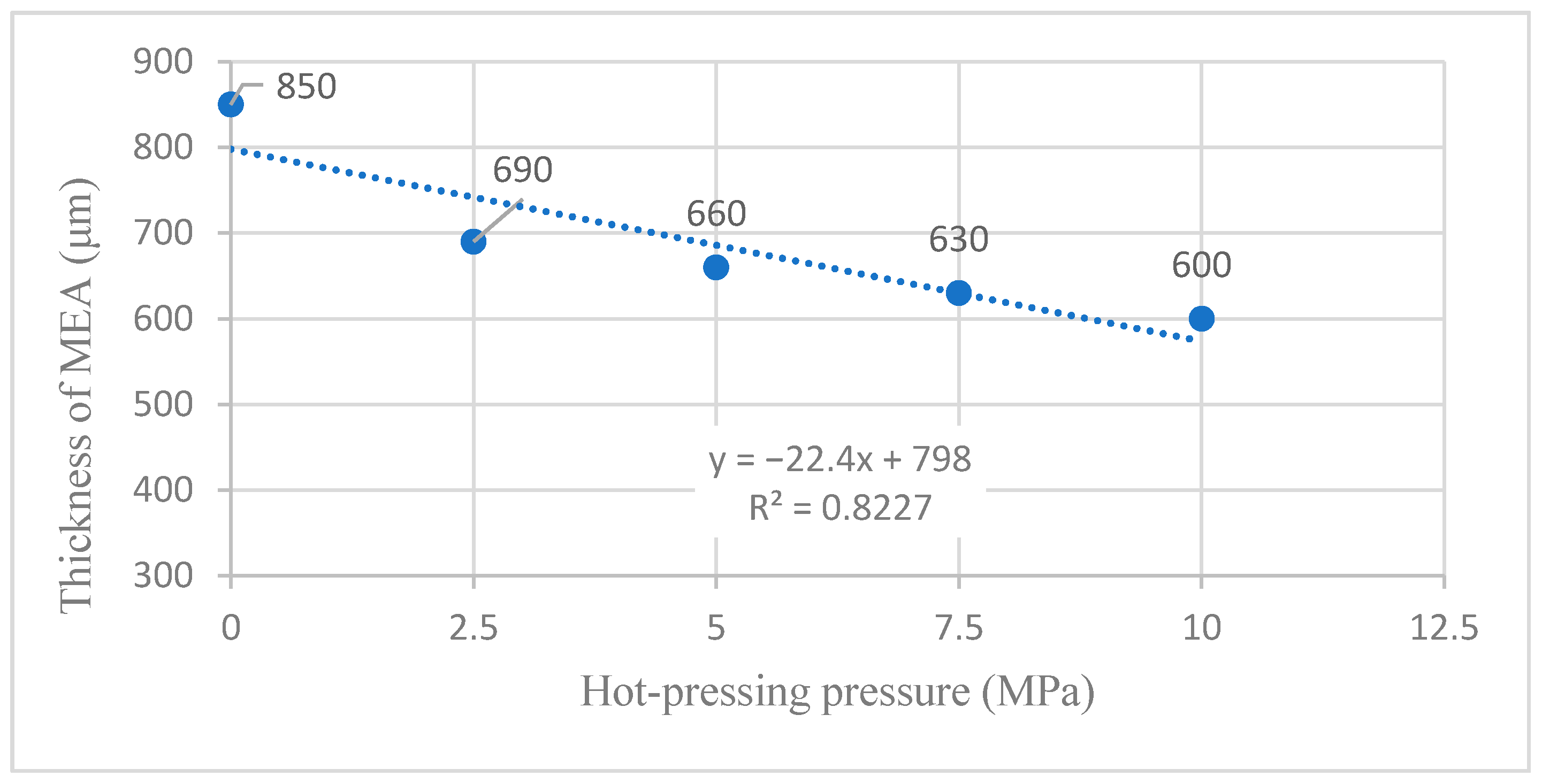
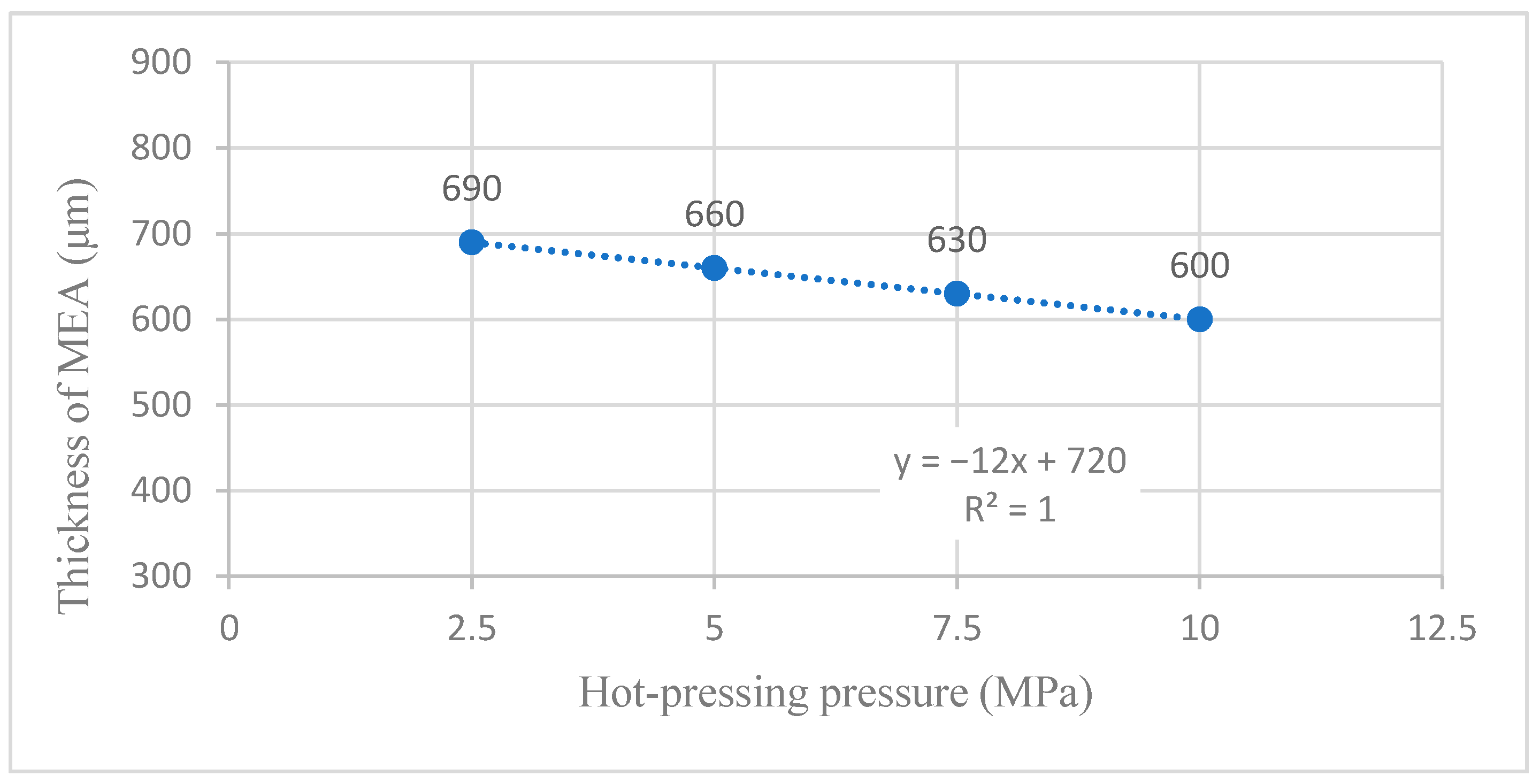
4.1. Influence of Hot-Pressing Pressure on the Forming Thickness of MEA
4.1.1. Linear Fitting Analysis with Full Parameters
4.1.2. Linear Fitting Analysis without 0 MPa Sample
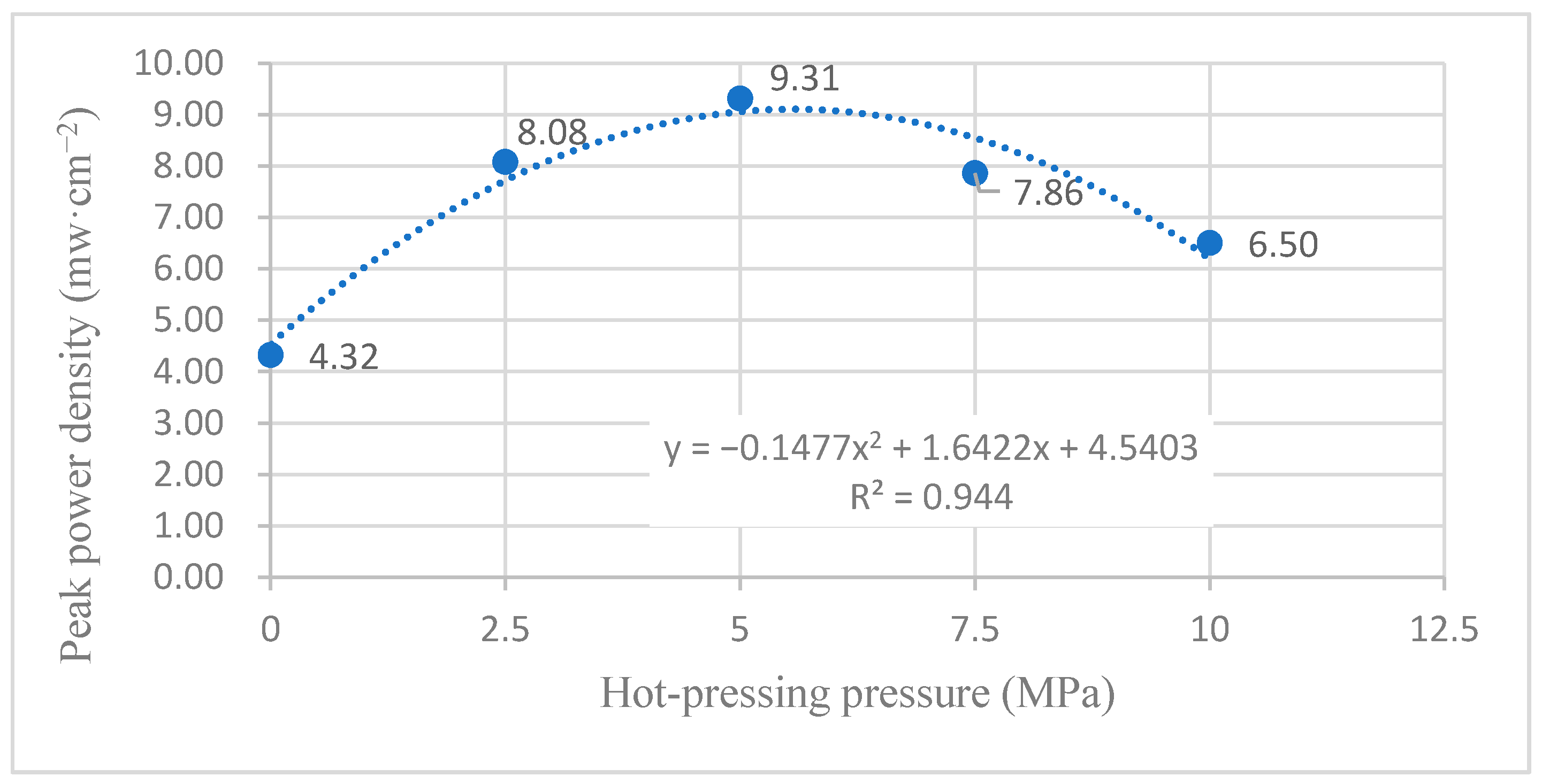
4.2. Influence of Hot-Pressing Pressure on the Peak Power Density
4.2.1. Performance Comparison at Room Temperature
4.2.2. Performance Comparison at 60 °C
4.2.3. Comparison of the Comprehensive Properties
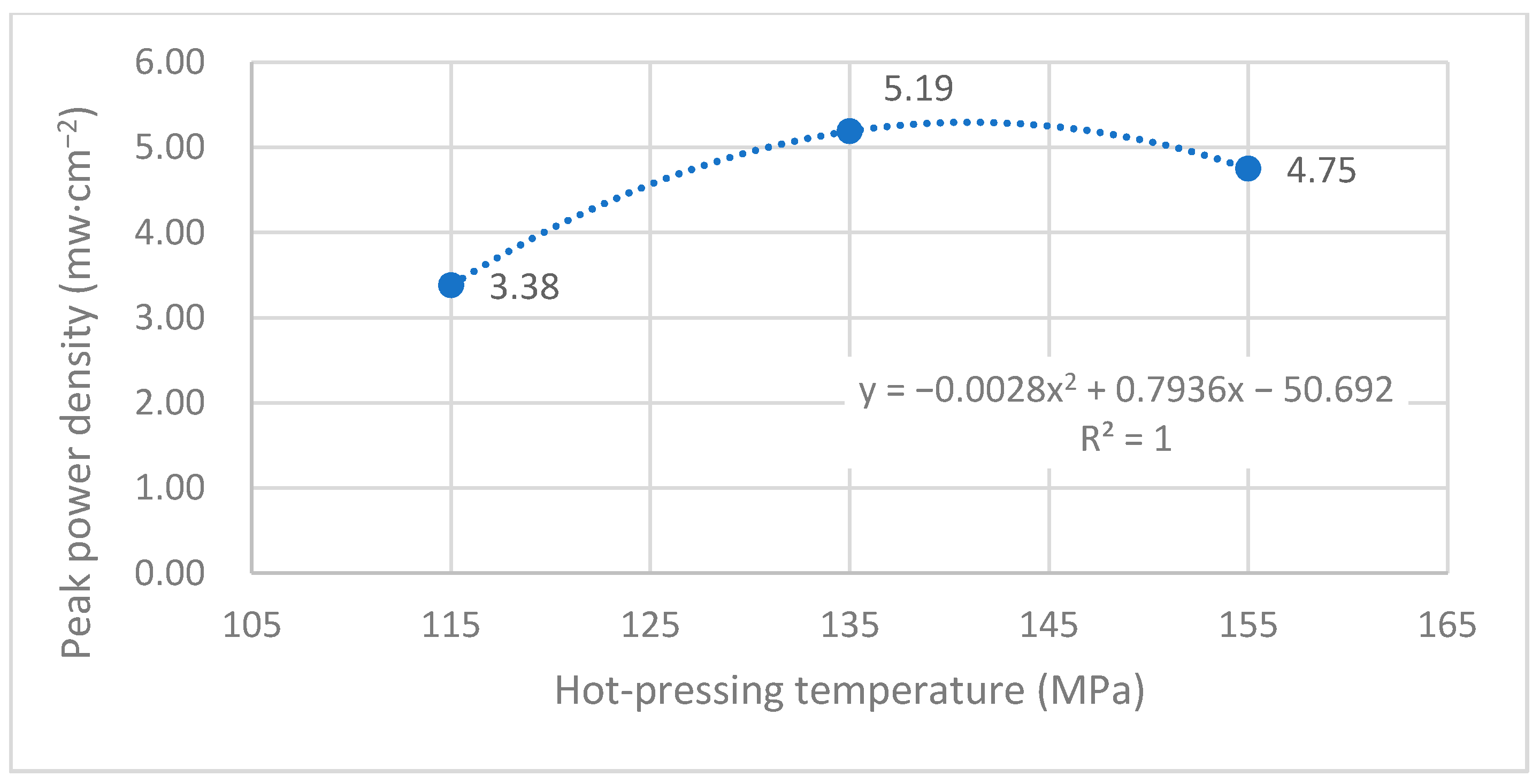
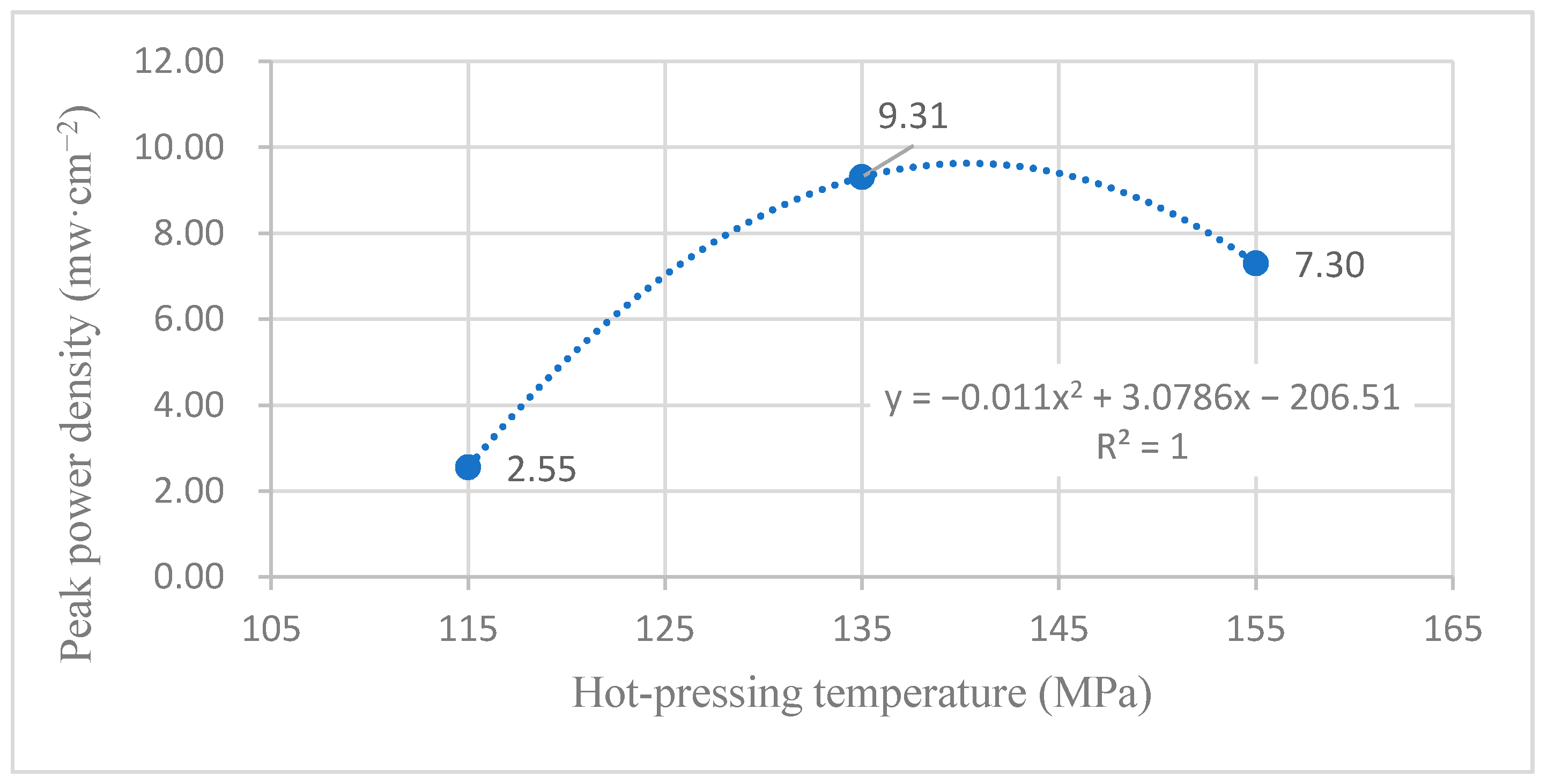
4.3. Influence of Hot-Pressing Temperature on the Peak Power Density
4.3.1. Performance Comparison at Room Temperature
4.3.2. Performance Comparison at 60 °C
4.3.3. Comparison of the Comprehensive Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sazali, N.; Wan Salleh, W.N.; Jamaludin, A.S.; Mhd Razali, M.N. New perspectives on fuel cell technology: A brief review. Membranes 2020, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajanovic, A.; Haas, R. Economic prospects and policy framework for hydrogen as fuel in the transport sector. Energy Policy 2018, 123, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chu, T.; Wang, T.; Wan, K.; Yang, D.; Li, B.; Ming, P.; Zhang, C. Preparation, performance and challenges of catalyst layer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Membranes 2021, 11, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Reddi, K.; Elgowainy, A.; Lohse-Busch, H.; Wang, M.; Rustagi, N. Comparison of well-to-wheels energy use and emissions of a hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicle relative to a conventional gasoline-powered internal combustion engine vehicle. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inci, M.; Turksoy, O. Review of fuel cells to grid interface: Configurations, technical challenges and trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 1353–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Diaz, D.F.R.; Chen, K.S.; Wang, Z.; Adroher, X.C. Materials, technological status, and fundamentals of PEM fuel cells—A review. Mater. Today 2020, 32, 178–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaswad, A.; Omran, A.; Sodre, J.R.; Wilberforce, T.; Pignatelli, G.; Dassisti, M.; Baroutaji, A.; Olabi, A.G. Technical and commercial challenges of proton-exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells. Energies 2021, 14, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junoh, H.; Jaafar, J.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Rahman, M.A.; Aziz, F.; Yusof, N. Performance of polymer electrolyte membrane for direct methanol fuel cell application: Perspective on morphological structure. Membranes 2020, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinodh, R.; Atchudan, R.; Kim, H.J.; Yi, M. Recent advancements in polysulfone based membranes for fuel cell (PEMFCs, DMFCs and AMFCs) applications: A critical review. Polymers 2022, 14, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, S.K.; Daud, W.R.W.; Ho, S.L.; Hasran, U.A. Overview on the challenges and developments of micro-direct methanol fuel cells (DMFC). J. Power Sources 2007, 163, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafidah, R.S.R.; Rashmi, W.; Khalid, M.; Wong, W.Y.; Priyanka, J. Recent progress in the development of aromatic polymer-based proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Kolb, S.; Sata, N.; Fallisch, A.; Zielke, L.; Thiele, S.; Gago, A.S.; Friedrich, K.A. Comprehensive investigation of novel pore-graded gas diffusion layers for high-performance and cost-effective proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 2521–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, G.P.; Wang, Z.B.; Lai, Q.Z.; Cai, K.D. Effects of hot pressing conditions on the performances of MEAs for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Tsao, C.S. Characterization of electrode structures and the related performance of direct methanol fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2006, 31, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.H.; Stamatialis, D.; Wessling, M. Dimensionally stable Nafion–polyethylene composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 321, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.Y.; Cho, K.Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Park, J.K.; Choi, J.H.; Sung, Y.E. Influence of annealing of membrane electrode assembly (MEA) on performance of direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC). J. Power Sources 2007, 163, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.X.; Zhao, T.S.; Xu, C.; Xu, J.B. Microscopic characterizations of membrane electrode assemblies prepared under different hot-pressing conditions. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 53, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oedegaard, A.; Hebling, C.; Schmitz, A.; Moller-Holst, S.; Tunold, R. Influence of diffusion layer properties on low temperature DMFC. J. Power Sources 2004, 127, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahler, M.; Stahler, A.; Scheepers, F.; Carmo, M.; Stolten, D. A completely slot die coated membrane electrode assembly. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 7053–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.H.; Chen, H.L.; Tian, A.H. Effect of MEA hot-pressing on the performance of direct methanol fuel cells. Top. Chem. Mater. Eng. 2018, 1, 402–404. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, M.Y.; Ni, H.J. Effect of molding temperature conditions upon titanium mesh MEA performance for direct methanol fuel cell. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 684, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.J.; Cao, G.Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Li, Z.F. Development of tubular air-breathing direct methanol fuel cell. Chin. J. Power Sources 2005, 29, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, K.; Okada, T.; Ishida, M. Micro-tubular direct methanol fuel cells for portable applications. Electrochemistry 2002, 70, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Kunimatsu, M.; Okada, T. Pt catalyst configuration by a new plating process for a micro tubular DMFC cathode. J. Power Sources 2005, 139, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, M.S.; Azder, M.A.; Salihoglu, O.; San, F.G.B. Ultralow Pt loading on CVD graphene for acid electrolytes and PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 18572–18577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.G.; Lin, W.F.; Zhu, F.Y.; Christensen, P.A.; Zhang, H.M.; Yi, B.L. A tubular direct methanol fuel cell with Ti mesh anode. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.J.; Li, F.; Tang, D.; Wang, X.X.; Lin, W.F.; Christensen, P.A. Preparation and cell performance of tubular cathode for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Jiangsu Univer. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 30, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, M.B.; Mohammadi, F.; Hooshyari, K. Recent approaches to improve Nafion performance for fuel cell applications: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 28919–28938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Ni, H.J.; Zhang, C.J.; Wang, X.X.; Huang, M.Y.; Zhu, Y. Direct methanol Fuel Cell Test Device: Chinese patent. Chinese Patent CN200910182793.2, 27 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.X.; Ni, H.J.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, S.Q.; Wan, X.F.; Ma, J. Study on the passive direct methanol fuel cell based on titanium mesh membrane electrode assembly. J. Nantong Univer. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 12, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, H.J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Lv, S.S.; Wang, X.X.; Pei, Y.; Li, F. Coating process parameters and structural properties of the tubular electrodes of fuel cells based on a self-made coating device. Coatings 2020, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, C.; Fahy, K.F.; Shrestha, P.; Krause, K.; Shafaque, H.W.; Bazylak, A. Tailoring catalyst layer interface with titanium mesh porous transport layers. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 373, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.K.; Zhao, B.; Fahy, K.F.; Lamanna, J.M.; Baltic, E.; Hussey, D.S.; Jacobson, D.L.; Schulz, V.P.; Bazylak, A. Temperature-dependent gas accumulation in polymer electrolyte membrane electrolyzer porous transport layers. J. Power Sources 2020, 446, 227–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.Y.; Xia, Z.X.; Sun, R.L.; Wang, S.L.; Sun, G.Q. Nanostructured ultrathin catalyst layer with ordered platinum nanotube arrays for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 43, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Chu, A.H.; Li, D.; Yuan, Y.N.; Fan, X.L.; Deng, Y.L. Development of the cycling life model of Ni-MH power batteries for hybrid electric vehicles based on real-world operating conditions. J. Energy Storage 2021, 34, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.S.; Wang, X.X.; Lu, W.F.; Zhang, J.Q.; Ni, H.J. The influence of temperature on the capacity of lithium ion batteries with different anodes. Energies 2021, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B.G.; Chetty, R. Design and fabrication of a quick-fit architecture air breathing direct methanol fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 6845–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Name | Model/Quality Score | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium mesh | 0.5 × 1.2 diamond hole | Anping County Wire and Wire Mesh FACTORY, Henan, China |
| PtRu/XC-72R | 40 wt.% Pt, 20 wt.% Ru | Johnson Matthey, London UK |
| Nafion membrane | 117 | Dupont, Wilmington, DE, USA |
| Pt/XC-72R | 40 wt.% Pt | Johnson Matthey, London, UK |
| Nafion solution | 5% | Dupont, Wilmington, DE, USA |
| XC-72 | Vulcan XC-72 | Cabot, Boston, MA, USA |
| PTFE solution | 60% | Dupont, Wilmington, DE, USA |
| CH3CH2OH | ≥99.7 wt.% | Shanghai Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| H2SO4 | ≥98 wt.% | Shanghai Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| H2O2 | 30 wt.% | Shanghai Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Deionized Water | 18.25 MΩ·cm | Self-made |
| Sample | Hot-Pressing Pressure (MPa) | Thickness of MEA (μm) | Compression Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 850 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 2.5 | 690 | 18.82 |
| 3 | 5 | 660 | 22.35 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 630 | 25.88 |
| 5 | 10 | 600 | 29.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, S.; Ni, H.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, Y. Effect of Different Hot-Pressing Pressure and Temperature on the Performance of Titanium Mesh-Based MEA for DMFC. Membranes 2022, 12, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040431
Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Lv S, Ni H, Deng Y, Yuan Y. Effect of Different Hot-Pressing Pressure and Temperature on the Performance of Titanium Mesh-Based MEA for DMFC. Membranes. 2022; 12(4):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040431
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xingxing, Yujie Zhang, Yu Zhu, Shuaishuai Lv, Hongjun Ni, Yelin Deng, and Yinnan Yuan. 2022. "Effect of Different Hot-Pressing Pressure and Temperature on the Performance of Titanium Mesh-Based MEA for DMFC" Membranes 12, no. 4: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040431
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, Y., Zhu, Y., Lv, S., Ni, H., Deng, Y., & Yuan, Y. (2022). Effect of Different Hot-Pressing Pressure and Temperature on the Performance of Titanium Mesh-Based MEA for DMFC. Membranes, 12(4), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040431







