One-Step Fabrication of Novel Polyethersulfone-Based Composite Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Food Industry Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
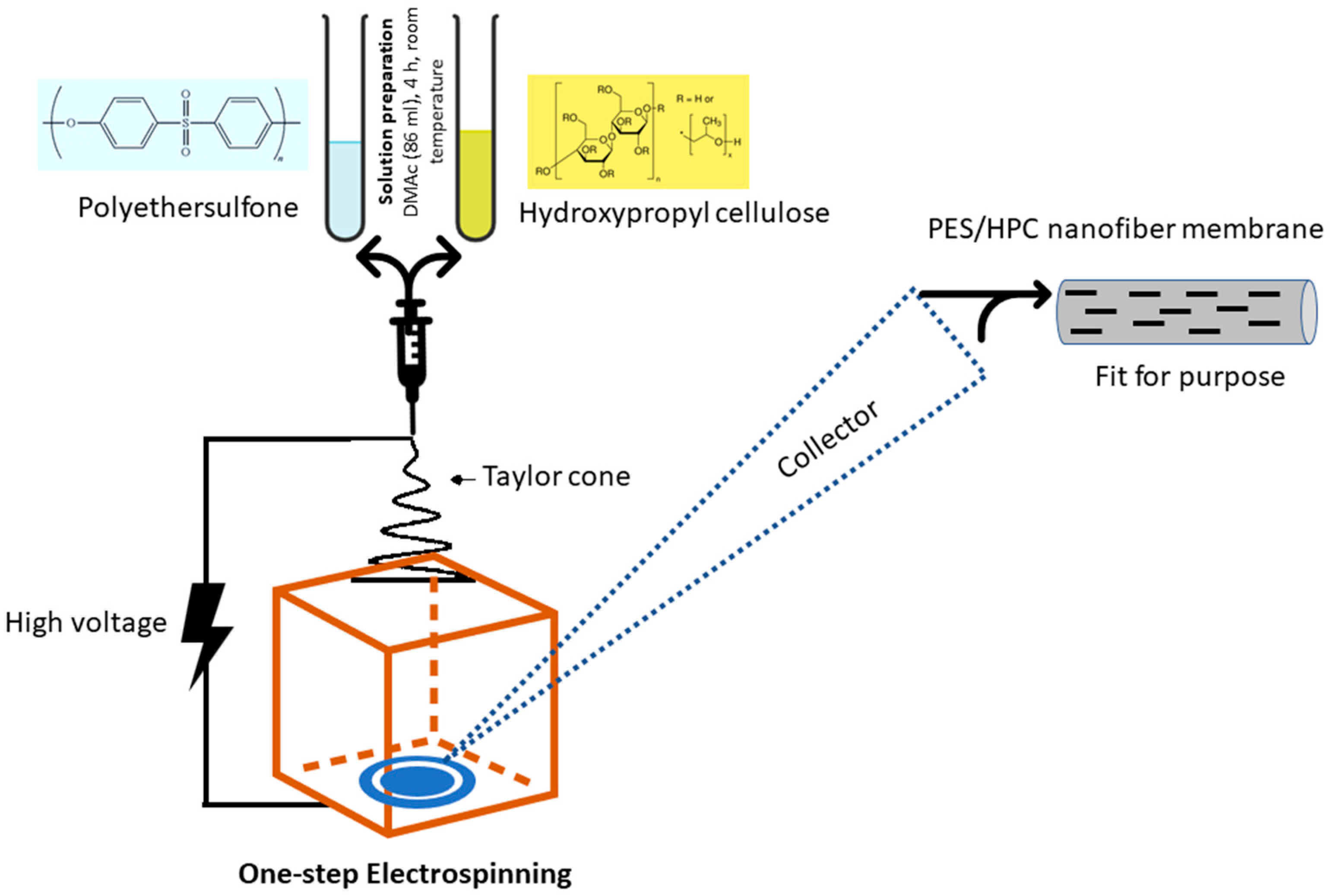
2.2. One-Step Electrospinning
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Batch Adsorption Studies
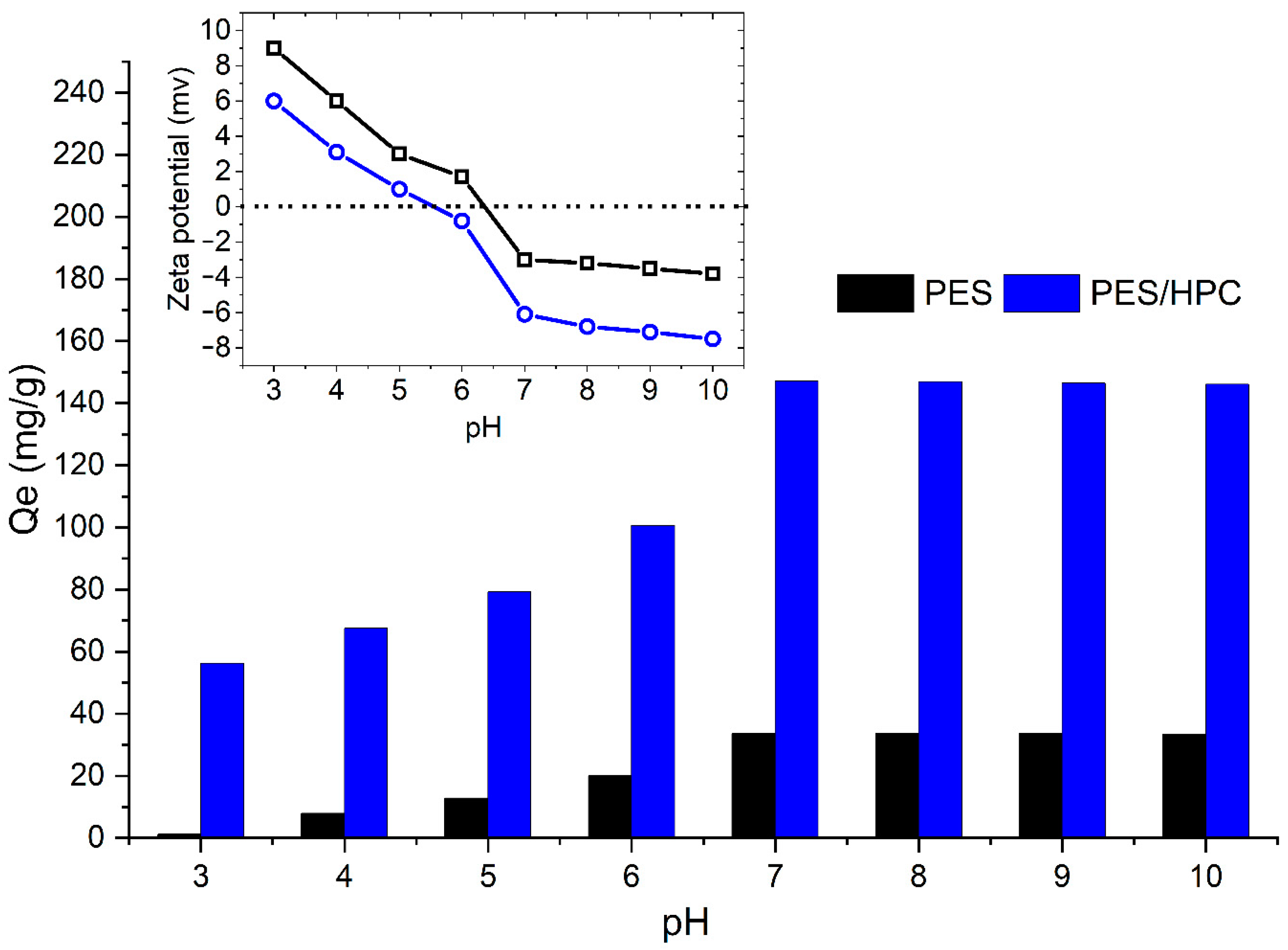
2.4.1. The Effect of the Solution pH
2.4.2. The Effect of the Initial MB Concentrations
2.4.3. The Effect of the Ionic Strength Concentration
2.5. Reusability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Properties of the Adsorbents
3.1.1. SEM
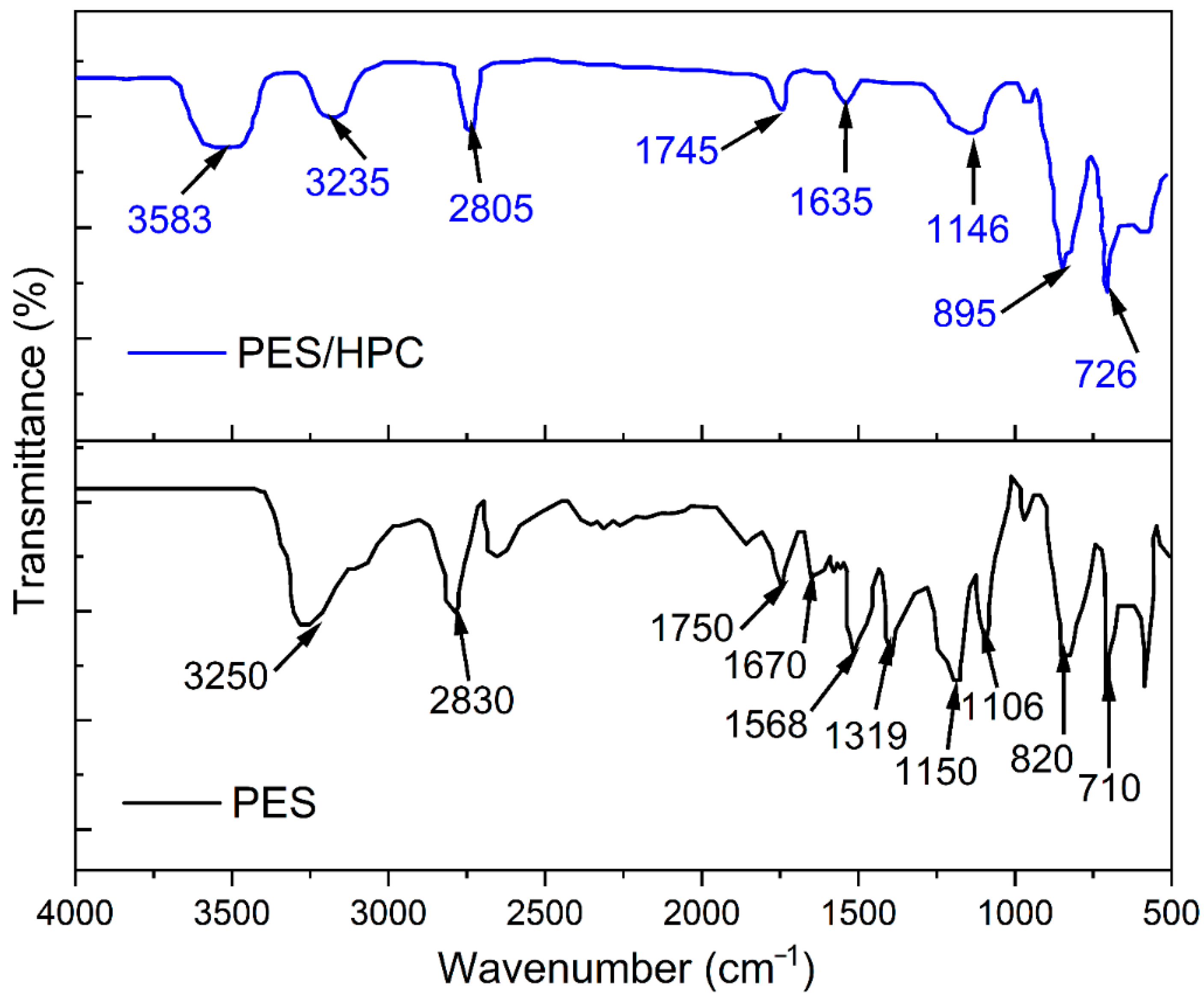
3.1.2. FTIR
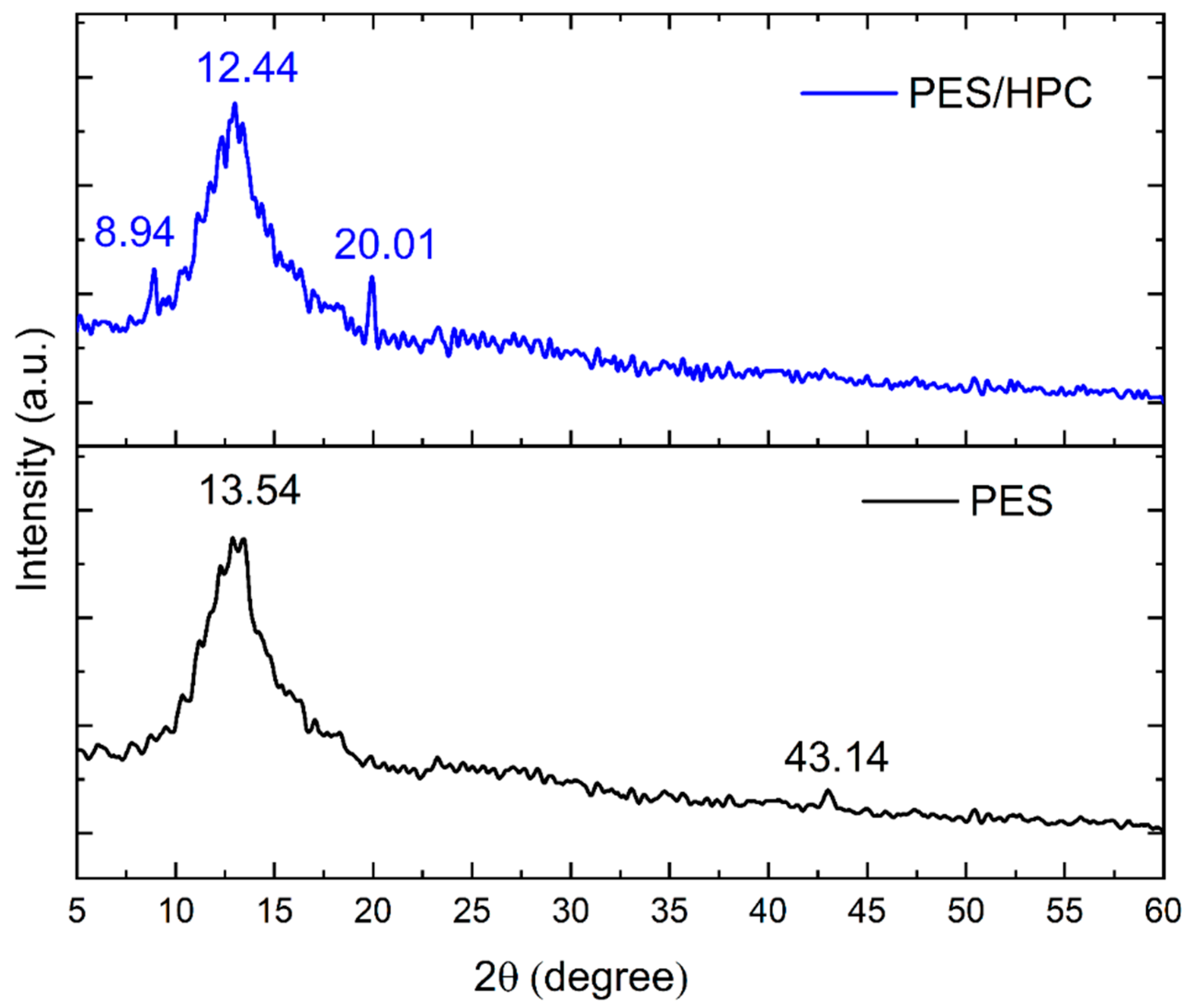
3.1.3. XRD
3.1.4. TGA
3.1.5. Mechanical Properties
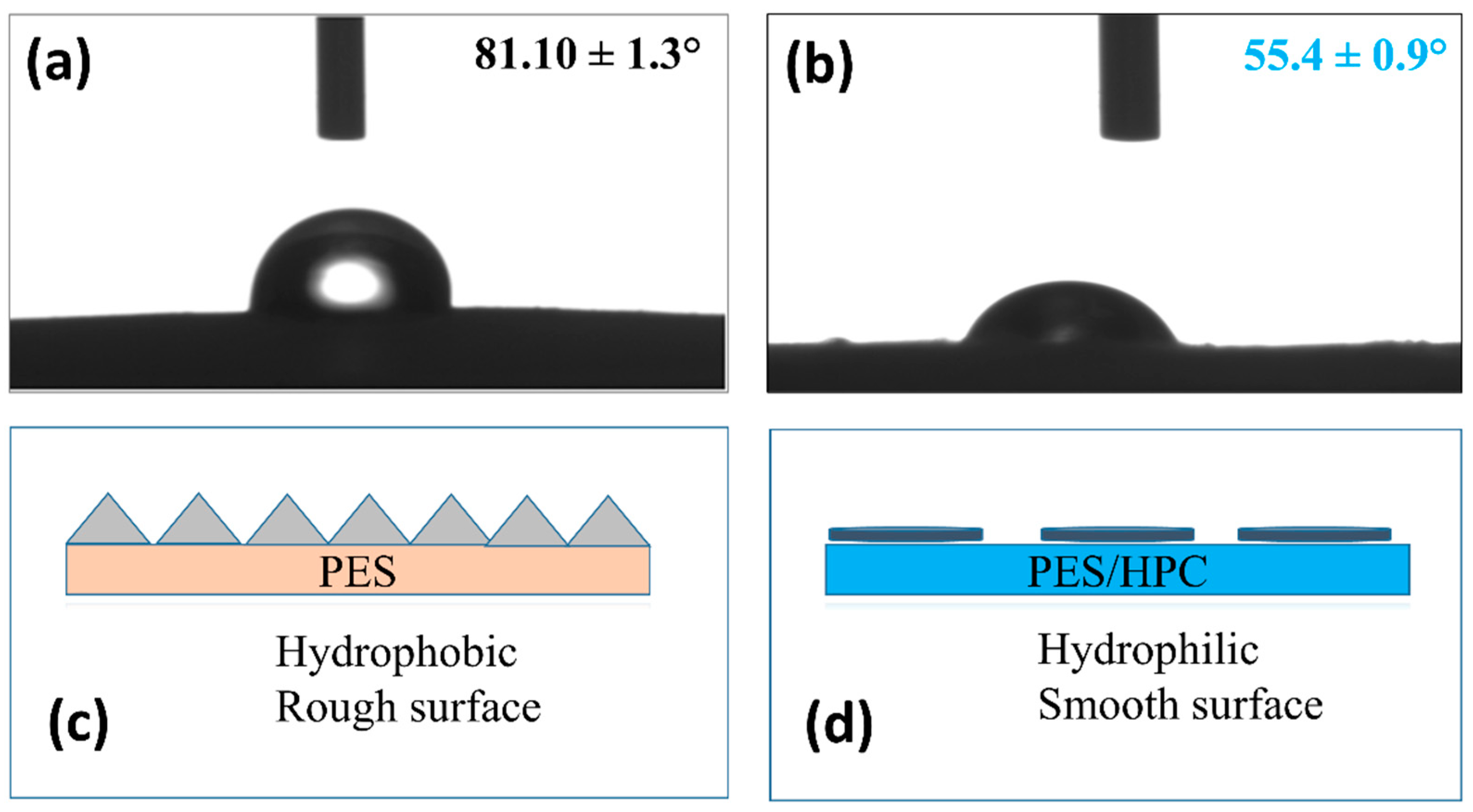
3.1.6. Hydrophilicity
3.2. MB Adsorption Studies
3.2.1. The Effect of the Initial Concentration
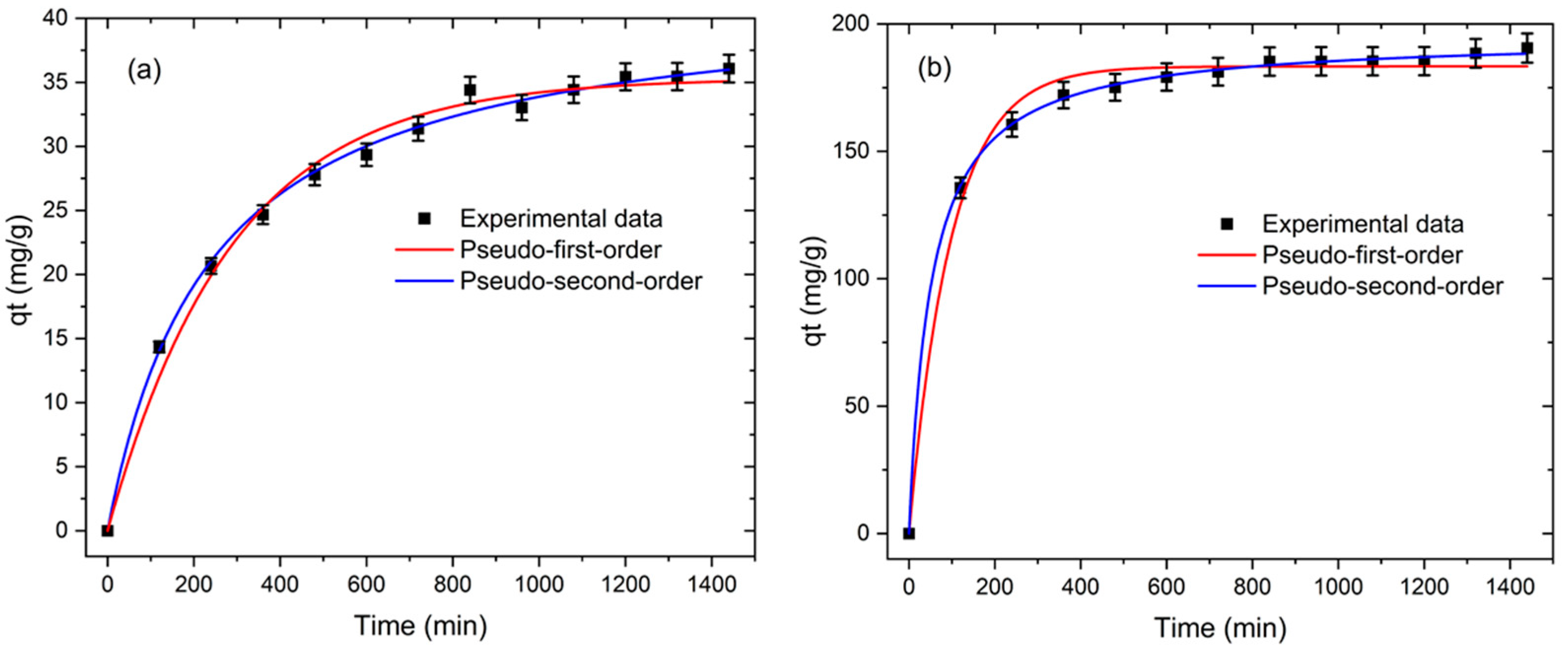
3.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.2.3. Adsorption Isotherms
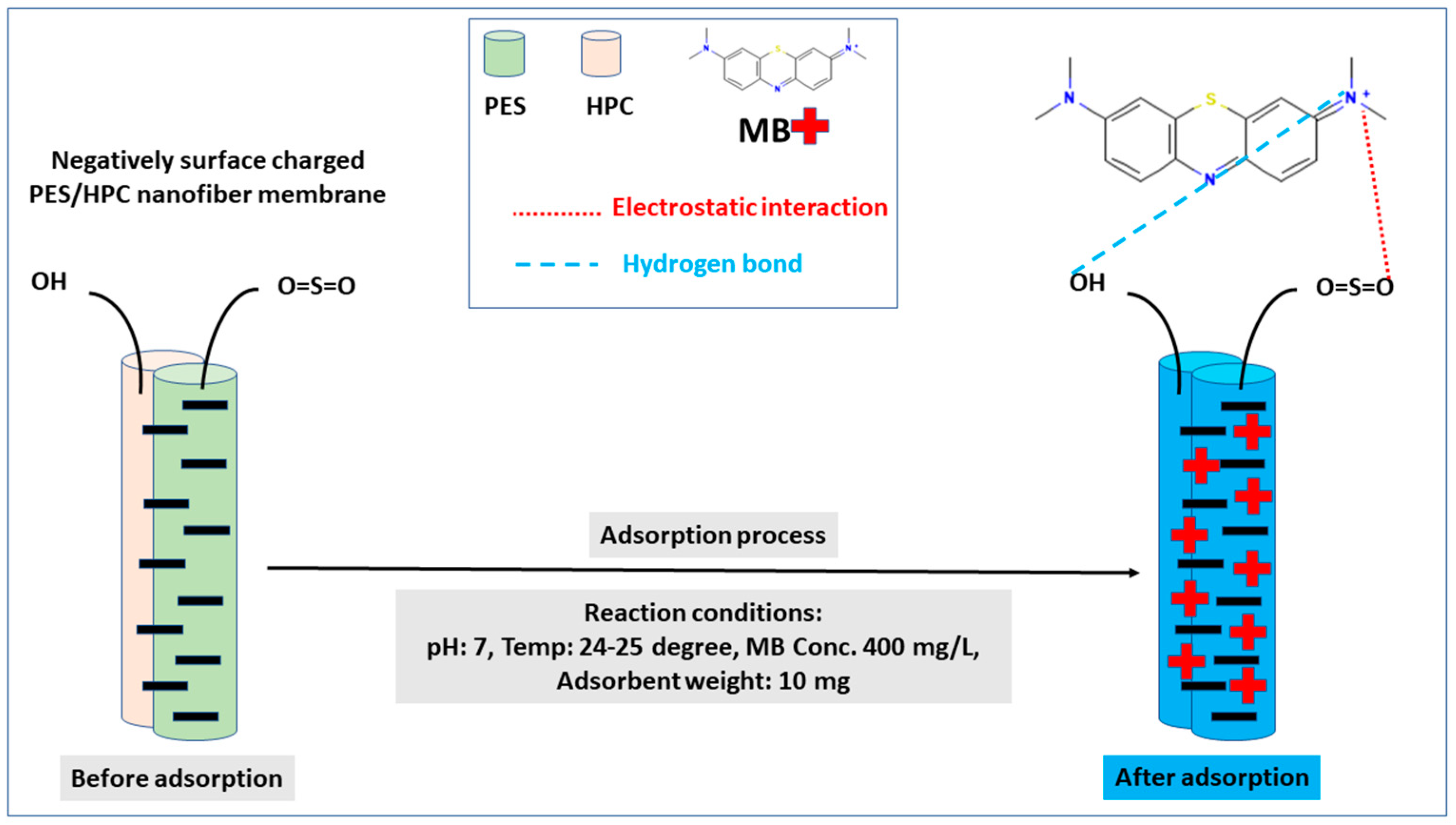
3.2.4. Adsorption Mechanism
3.3. The Effect of Ionic Strength
3.4. Reusability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pervez, M.N.; He, W.; Zarra, T.; Naddeo, V.; Zhao, Y. New sustainable approach for the production of Fe3O4/graphene oxide-activated persulfate system for dye removal in real wastewater. Water 2020, 12, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morshed, M.N.; Pervez, M.N.; Behary, N.; Bouazizi, N.; Guan, J.; Nierstrasz, V.A. Statistical modeling and optimization of heterogeneous Fenton-like removal of organic pollutant using fibrous catalysts: A full factorial design. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervez, M.N.; Telegin, F.Y.; Cai, Y.; Xia, D.; Zarra, T.; Naddeo, V. Efficient degradation of Mordant Blue 9 using the fenton-activated persulfate system. Water 2019, 11, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, C.; Sharma, P.R.; He, H.; Sharma, S.K.; McCauley-Pearl, A.; Wang, R.; Hsiao, B.S. Rice husk based nanocellulose scaffolds for highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions from contaminated water. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 3080–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Zhan, C.; Sharma, S.K.; Geng, L.; Hsiao, B.S. Lead removal from water using carboxycellulose nanofibers prepared by nitro-oxidation method. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Mishu, M.R.; Stylios, G.K.; Hasan, S.W.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zarra, T.; Belgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V. Sustainable treatment of food industry wastewater using membrane technology: A short review. Water 2021, 13, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Pervez, M.N.; Sun, P.; Cao, C.; Li, B.; Naddeo, V.; Jin, W.; Zhao, Y. Highly efficient removal of bisphenol A by a novel Co-doped LaFeO3 perovskite/PMS system in salinity water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya-Özkiper, K.; Uzun, A.; Soyer-Uzun, S. A novel alkali activated magnesium silicate as an effective and mechanically strong adsorbent for methylene blue removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Y.; Zhu, W.; Pervez, M.N.; Yang, X.; Sarker, S.; Hassan, M.M.; Hoque, M.I.U.; Naddeo, V.; Cai, Y. Adsorption, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies of cacao husk extracts in waterless sustainable dyeing of cotton fabric. Cellulose 2021, 28, 2521–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; AlGarni, T.S.; Naushad, M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Stadler, F.J. Adsorption of cationic dyes onto carrageenan and itaconic acid-based superabsorbent hydrogel: Synthesis, characterization and isotherm analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Balakrishnan, M.; Hasan, S.W.; Choo, K.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zarra, T.; Belgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V. A critical review on nanomaterials membrane bioreactor (NMs-MBR) for wastewater treatment. Npj Clean Water 2020, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Stylios, G.K.; Liang, Y.; Ouyang, F.; Cai, Y. Low-temperature synthesis of novel polyvinylalcohol (PVA) nanofibrous membranes for catalytic dye degradation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Stylios, G.K. Investigating the synthesis and characterization of a novel “green” H2O2-assisted, water-soluble chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber for environmental end uses. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pervez, M.N.; Stylios, G.K. An experimental approach to the synthesis and optimisation of a ‘green’ nanofibre. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, W.; Long, Y.; Bao, J.; He, C.; Cheng, C.; Deng, C.; et al. Superhydrophilic and polyporous nanofibrous membrane with excellent photocatalytic activity and recyclability for wastewater remediation under visible light irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.E.; Hasan, K.M.F.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Li, C.; Song, H. Novel fibrin functionalized multilayered electrospun nanofiber membrane for burn wound treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 12814–12834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghafri, B.; Bora, T.; Sathe, P.; Dobrestov, S.; Al-Abri, M. Photocatalytic microbial removal and degradation of organic contaminants of water using PES fibers. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 233, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.E.; Alam, F.; Pervez, M.N.; Jiangming, W.; Hassan, F.; Stylios, G.K.; Naddeo, V.; Song, H. New generation washable PES membrane face mask for virus filtration. Nanocomposites 2022, 8, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Mahboubi, A.; Uwineza, C.; Zarra, T.; Belgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Factors influencing pressure-driven membrane-assisted volatile fatty acids recovery and purification-A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushkbaghi, S.; Zakialamdari, A.; Pishnamazi, M.; Ramandi, H.F.; Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M. Aminated-Fe3O4 nanoparticles filled chitosan/PVA/PES dual layers nanofibrous membrane for the removal of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions in adsorption and membrane processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ni, C.; Xiao, W.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y. Ionic liquid grafted polyethersulfone nanofibrous membrane as recyclable adsorbent with simultaneous dye, heavy metal removal and antibacterial property. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Lindström, T.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose-Enabled Membranes for Water Purification: Perspectives. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 4, 1900114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.K.; Dutta, S.D.; Lim, K.-T. Nanocellulose-based polymer hybrids and their emerging applications in biomedical engineering and water purification. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19143–19162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Hsiao, B.S. Efficient Removal of UO22+ from Water Using Carboxycellulose Nanofibers Prepared by the Nitro-Oxidation Method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 13885–13893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, P.R.; Yeh, H.; Johnson, K.; Hsiao, B.S. Arsenic(III) Removal by Nanostructured Dialdehyde Cellulose–Cysteine Microscale and Nanoscale Fibers. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22008–22020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.R.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Geng, L.; Amiralian, N.; Martin, D.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose from Spinifex as an Effective Adsorbent to Remove Cadmium(II) from Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Shi, J. Preparation and characterization of all-biomass soy protein isolate-based films enhanced by epoxy castor oil acid sodium and hydroxypropyl cellulose. Materials 2016, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassanpour, S.; Azhar, F.F.; Bagheri, M. Novel nanogels based on hydroxypropyl cellulose–poly (itaconic acid) for adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution: Process modeling and optimization using response surface methodology. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 933–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, C. Adsorptive removal of phenol by single and double network composite hydrogels based on hydroxypropyl cellulose and graphene oxide. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3898–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Fu, D.; Wang, X.; Bao, Q.; Yu, T.; Naddeo, V.; Tian, H.; Cao, C.; Zhao, Y. A bifunctional α-FeOOH@GCA nanocomposite for enhanced adsorption of arsenic and photo Fenton-like catalytic conversion of As(III). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Systematic parameter study for ultra-fine fiber fabrication via electrospinning process. Polymer 2005, 46, 6128–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zheng, W.; Wang, C. A novel alcohol detector based on ZrO2-doped SnO2 electrospun nanofibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, B.S.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Radwan, E.K.; Hamouda, A.S.; El-Sheikh, M.N.; Salama, M. Fabrication, characterization, and dye adsorption capability of recycled modified polyamide nanofibers. Egypt. J. Chem. 2018, 61, 867882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Wei, Y.; Sun, P.; Qu, G.; Naddeo, V.; Zhao, Y. α-FeOOH quantum dots impregnated graphene oxide hybrids enhanced arsenic adsorption: The mediation role of environmental organic ligands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lu, S.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhang, J. Novel polysulfone hybrid ultrafiltration membrane prepared with TiO2-g-HEMA and its antifouling characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.S.; Buhr, K.; Ebert, K. Polyethersulfone electrospun nanofibrous composite membrane for liquid filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Wakil, N.A.-E.A.; Fahmy, Y.; Abou-Zeid, R.E.M.; Dufresne, A.; El-Sherbiny, S. Liquid crystalline behavior of hydroxypropyl cellulose esterified with 4-alkoxybenzoic acid. Bioresources 2010, 5, 1834–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Guirguis, O.W.; Moselhey, M.T. Optical properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)/hydroxypropyl cellulose blends. Mater. Sci. Indian J. 2013, 9, 8–23. [Google Scholar]
- Laghaei, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Ghalei, B.; Shahrooz, M. The role of compatibility between polymeric matrix and silane coupling agents on the performance of mixed matrix membranes: Polyethersulfone/MCM-41. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 513, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamus, T.; Wojciechowski, P.; Bobowska, I. Synthesis and characterization of (hydroxypropyl)cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite films. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyaru, S.; Ahn, Y.-H. Fabrication and separation performance of polyethersulfone/sulfonated TiO2 (PES–STiO2) ultrafiltration membranes for fouling mitigation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 67, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kang, H.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, R. Synthesis and photosensitivity of azobenzene functionalized hydroxypropylcellulose. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 15909–15916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Effect of lignin–cellulose nanofibrils on the hydrophilicity and mechanical properties of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes. High Perform. Polym. 2016, 28, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, R.; Haghighat Mamaghani, A.; Boluk, Y.; Hashisho, Z. Synthesis and characterization of electrospun PAN-based activated carbon nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals for adsorption of VOCs. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Baek, I.; Choi, H. Mechanically enhanced PES electrospun nanofiber membranes (ENMs) for microfiltration: The effects of ENM properties on membrane performance. Water Res. 2016, 105, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.; Deng, S.; et al. Graphene Oxide–IPDI–Ag/ZnO@Hydroxypropyl Cellulose nanocomposite films for biological wound-dressing applications. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15373–15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bui, N.-N.; McCutcheon, J.R. Hydrophilic nanofibers as new supports for thin film composite membranes for engineered osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradinaru, L.M.; Barbalata-Mandru, M.; Drobota, M.; Aflori, M.; Spiridon, M.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Bleotu, C.; Butnaru, M.; Vlad, S. Preparation and evaluation of nanofibrous hydroxypropyl cellulose and β-Cyclodextrin polyurethane composite mats. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Górecki, R.P.; Stamate, E.; Norrman, K.; Aili, D.; Zuo, M.; Guo, W.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Zhang, W. Preparation of super-hydrophilic polyphenylsulfone nanofiber membranes for water treatment. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Cui, J.; Cui, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, F. High-efficiency adsorption and regeneration of methylene blue and aniline onto activated carbon from waste edible fungus residue and its possible mechanism. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 14262–14273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.; Wang, M.; Pang, H.; Zhang, R.; Huang, J.; Liang, K.; Chen, P.; Sun, P.; Kong, B. Super-assembled highly compressible and flexible cellulose aerogels for methylene blue removal from water. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Luna, J.; Ramírez-Montes, L.E.; Martinez-Vargas, S.; Martínez, A.I.; Mijangos-Ricardez, O.F.; González-Chávez, M.d.C.A.; Carrillo-González, R.; Solís-Domínguez, F.A.; Cuevas-Díaz, M.d.C.; Vázquez-Hipólito, V. Linear and nonlinear kinetic and isotherm adsorption models for arsenic removal by manganese ferrite nanoparticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talukder, M.E.; Pervez, M.N.; Jianming, W.; Gao, Z.; Stylios, G.K.; Hassan, M.M.; Song, H.; Naddeo, V. Chitosan-functionalized sodium alginate-based electrospun nanofiber membrane for As (III) removal from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Huang, F.; Zhuang, Z.; Lin, Z. A study of the potential application of nano-Mg(OH)2 in adsorbing low concentrations of uranyl tricarbonate from water. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.; Chia, C.H.; Zakaria, S.; Sajab, M.S.; Chin, S.X. Cellulose nanofibrils: A rapid adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 18204–18212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhan, C.; Wu, J.; Cui, Z.; Si, J.; Wang, Q.; Peng, X.; Turng, L.-S. Highly efficient removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous solution using cellulose acetate nanofibrous membranes modified by polydopamine. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5389–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xue, F.; Chen, Y.; Bin Aftab, T.; Li, D. Hybrid monolith of graphene/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofiber as mechanically robust, highly functional, and recyclable adsorbent of methylene blue dye. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 5963982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivito, F.; Algieri, V.; Jiritano, A.; Tallarida, M.A.; Tursi, A.; Costanzo, P.; Maiuolo, L.; De Nino, A. Cellulose citrate: A convenient and reusable bio-adsorbent for effective removal of methylene blue dye from artificially contaminated water. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 34309–34318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, W.; Song, L.; Chen, P. Fabrication of hydrogel of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) composited with graphene oxide and its application for methylene blue removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 6113–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tan, F.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cai, W. Effective removal of cation dyes from aqueous solution using robust cellulose sponge. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Zillohu, A.U.; Abdelaziz, R.; Hedayati, M.K.; Elbahri, M. A novel nanohybrid nanofibrous adsorbent for water purification from dye pollutants. Materials 2016, 9, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, F.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose-based adsorbent for removal of anionic and cationic dyes. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14, 1558925019828194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Li, K.; Hang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, P.; Wei, L.; Xie, C. Efficient removal of methylene blue by activated hydrochar prepared by hydrothermal carbonization and NaOH activation of sugarcane bagasse and phosphoric acid. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N.; Shetty, S.; Moustafa, M.S.; Al-Mousawi, S.; Alameddine, B. Selective removal of toxic organic dyes using Trӧger base-containing sulfone copolymers made from a metal-free thiol-yne click reaction followed by oxidation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 21170–21178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gao, Z.Y.; Su, X.P.; Chen, X.; Jiang, L.; Yao, J.M. Adsorption removal of dyes from single and binary solutions using a cellulose-based bioadsorbent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
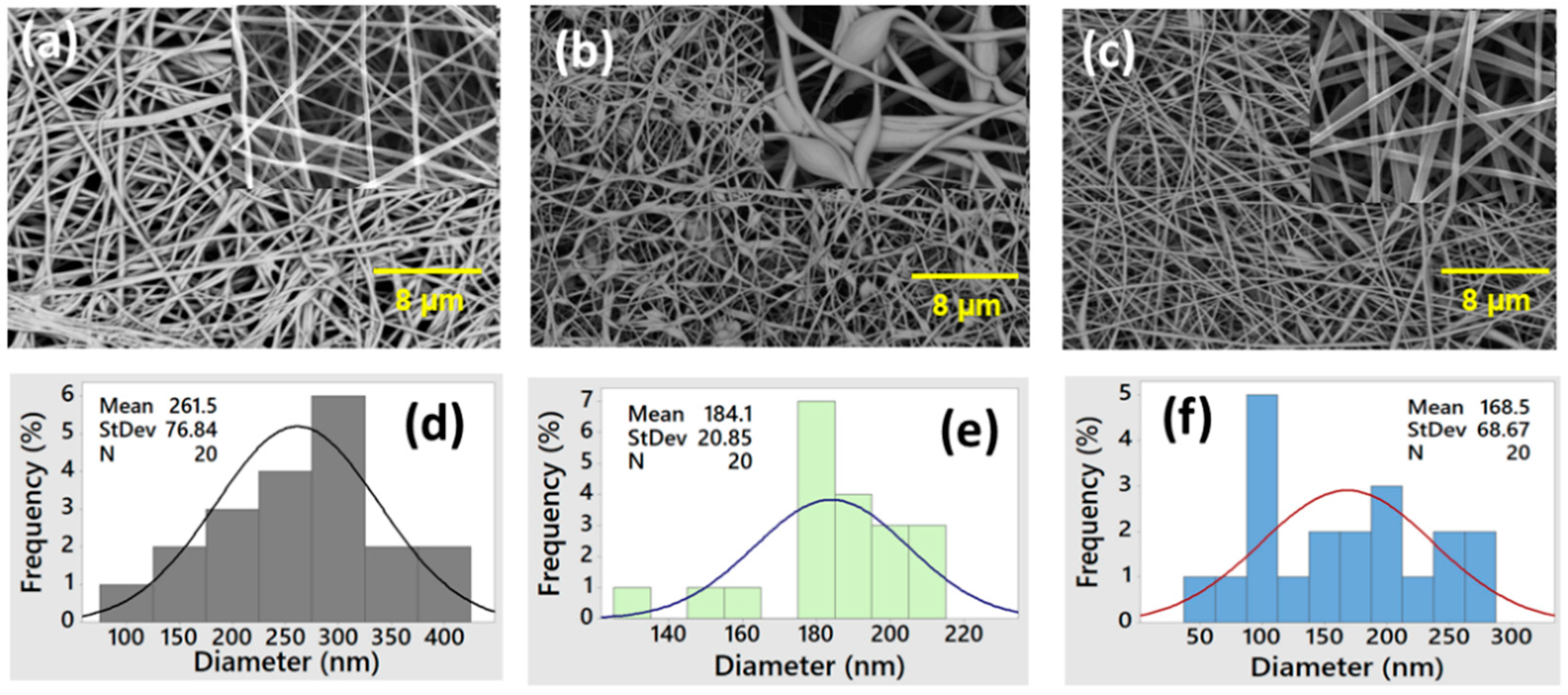




| Sample Type | Polymer Concentrations (wt%) | Voltage (kV) | Flow Rate (mL/h) | Viscosity (mPa/s) | Conductivity (mS/cm) | Fiber Morphology | Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | 10 | 7.5 | 1.0 | 2268 | 1.6 | Continuous fibers | 261.5 |
| HPC | 2 | 12 | 1.5 | 320 | 0.002 | No fibers | - |
| PES/HPC | 10/2 | 7.5 | 1.0 | 1845 | 1.9 | Beads with fibers | 184.1 |
| PES/HPC | 10/4 | 7.5 | 1.0 | 1543 | 2.2 | Continuous fibers | 168.5 |
| Samples | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | K2 (g/mg/min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | |
| PES | 0.0034 | 35.3161 | 0.9893 | 0.0001 | 41.9531 | 0.9960 |
| PES/HPC | 0.0101 | 183.3293 | 0.9908 | 0.0004 | 195.0212 | 0.9995 |
| Samples | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF (mg/g) | 1/n | R2 | |
| PES | 48.0076 | 0.0026 | 0.9913 | 1.0012 | 0.5211 | 0.9747 |
| PES/HPC | 259.7402 | 0.0049 | 0.9984 | 10.1847 | 0.4593 | 0.9693 |
| Adsorbent | Optimum MB Conc. (mg/L) | Optimum pH | Kinetics | Isotherm | qmax (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose nanofibrils | 100 | 9 | - | Langmuir | 122 | [55] |
| Deacetylated cellulose acetate (DA)@polydopamine (PDA) nanofibers | 50 | 6.5 | 2nd order | Langmuir | 88.2 | [56] |
| Graphene/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrous | 100 | 6.5 | 2nd order | Langmuir | 227.27 | [57] |
| Cellulose citrate | 100 | 3 | 2nd order | Langmuir | 96.2 | [58] |
| Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC)/graphene oxide hydrogels | - | - | 2nd order | Freundlich | 118.4 | [59] |
| Cellulose sponge | 30 | 7 | 2nd order | Langmuir | 123.46 | [60] |
| Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) nanoparticles/PES | 1 | 10 | 2nd order | Freundlich | 85% | [61] |
| PES nanofibers | 400 | 7 | 2nd order | Langmuir | 48.0 | Present work |
| PES/HPC nanofibers | 400 | 7 | 2nd order | Langmuir | 259.74 | Present work |
| Samples | Control, qe (mg/g) | NaCl Concentrations (M), qe (mg/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | ||
| PES | 32.47 | 29.44 | 27.34 | 23.77 | 21.88 | 20.44 |
| PES/HPC | 185.45 | 182.32 | 180.21 | 179.15 | 178.05 | 177.25 |
| Cycles, qe (mg/g) | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| PES | 32.47 | 30.17 | 27.14 | 24.05 | 22.13 | 20.45 |
| PES/HPC | 185.45 | 183.12 | 181.88 | 178.18 | 176.21 | 174.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pervez, M.N.; Talukder, M.E.; Mishu, M.R.; Buonerba, A.; Del Gaudio, P.; Stylios, G.K.; Hasan, S.W.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Figoli, A.; et al. One-Step Fabrication of Novel Polyethersulfone-Based Composite Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Food Industry Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040413
Pervez MN, Talukder ME, Mishu MR, Buonerba A, Del Gaudio P, Stylios GK, Hasan SW, Zhao Y, Cai Y, Figoli A, et al. One-Step Fabrication of Novel Polyethersulfone-Based Composite Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Food Industry Wastewater Treatment. Membranes. 2022; 12(4):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040413
Chicago/Turabian StylePervez, Md. Nahid, Md Eman Talukder, Monira Rahman Mishu, Antonio Buonerba, Pasquale Del Gaudio, George K Stylios, Shadi W. Hasan, Yaping Zhao, Yingjie Cai, Alberto Figoli, and et al. 2022. "One-Step Fabrication of Novel Polyethersulfone-Based Composite Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Food Industry Wastewater Treatment" Membranes 12, no. 4: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040413
APA StylePervez, M. N., Talukder, M. E., Mishu, M. R., Buonerba, A., Del Gaudio, P., Stylios, G. K., Hasan, S. W., Zhao, Y., Cai, Y., Figoli, A., Zarra, T., Belgiorno, V., Song, H., & Naddeo, V. (2022). One-Step Fabrication of Novel Polyethersulfone-Based Composite Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Food Industry Wastewater Treatment. Membranes, 12(4), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040413














