Study on the Control of Membrane Fouling by Pulse Function Feed and CFD Simulation Verification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
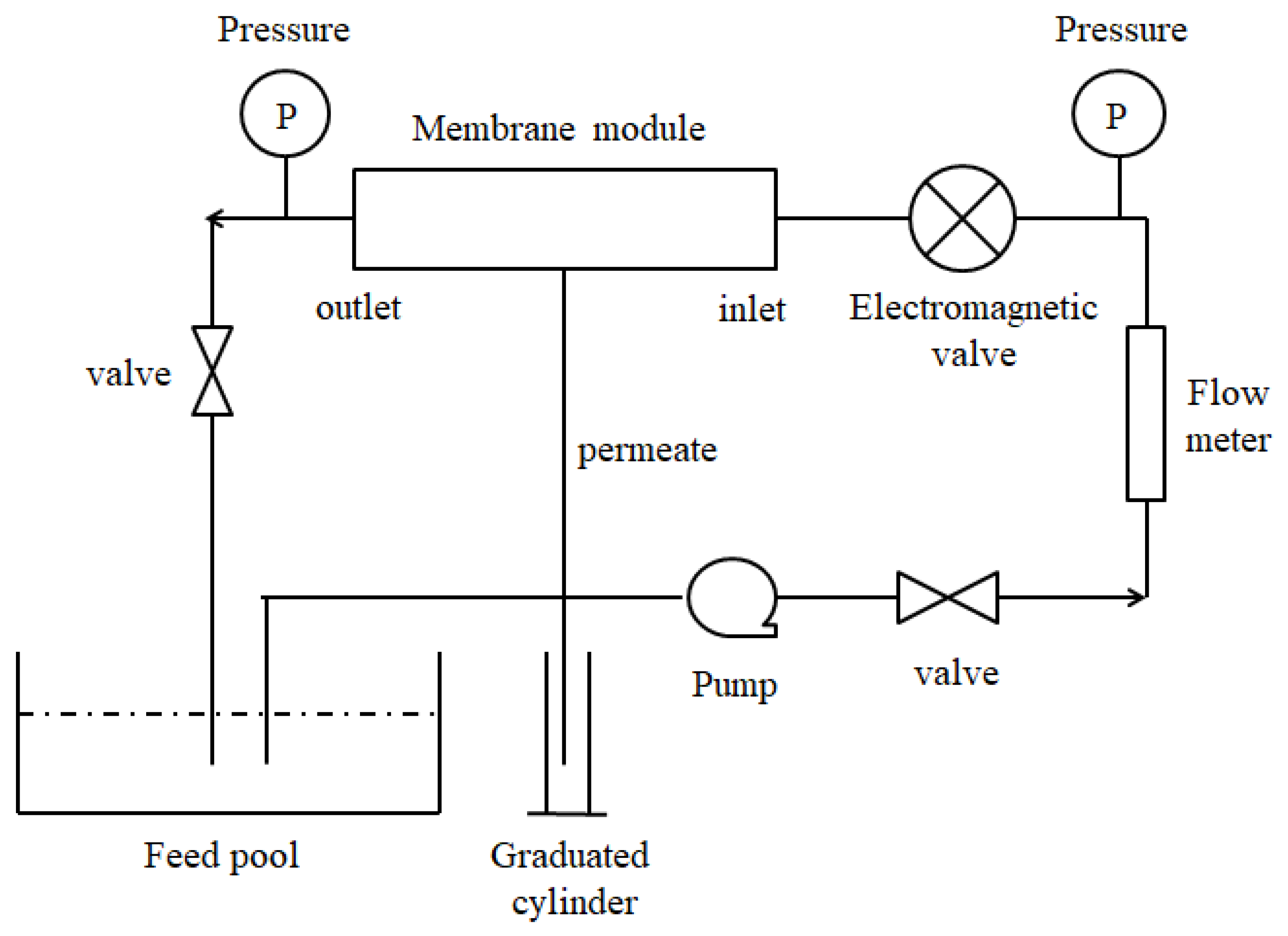
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Development of the CFD Simulation
2.3.1. Governing Equations
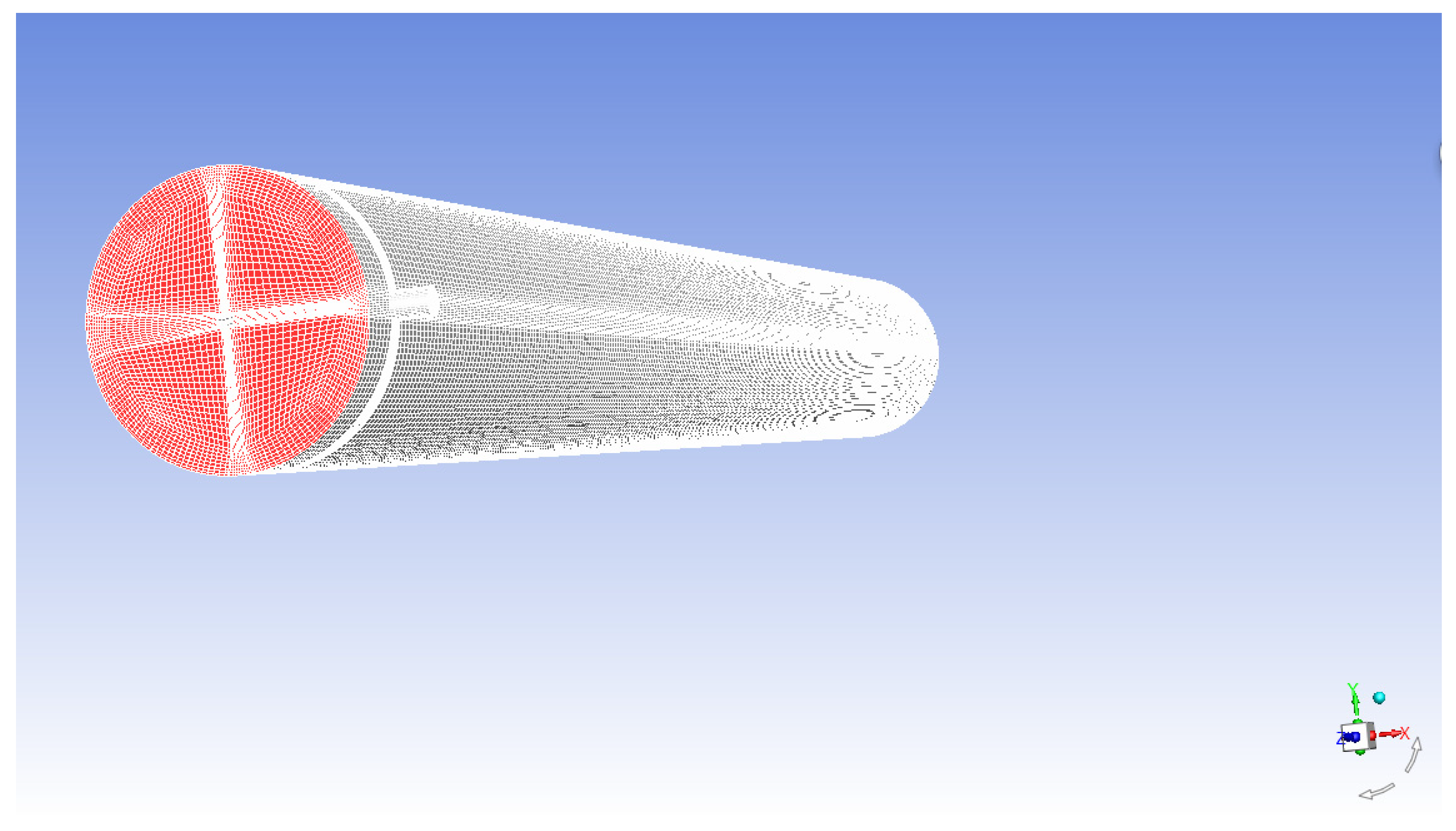
2.3.2. Model Geometry and Meshing
2.3.3. Boundary Condition and Solving Parameters
2.3.4. Numerical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Results
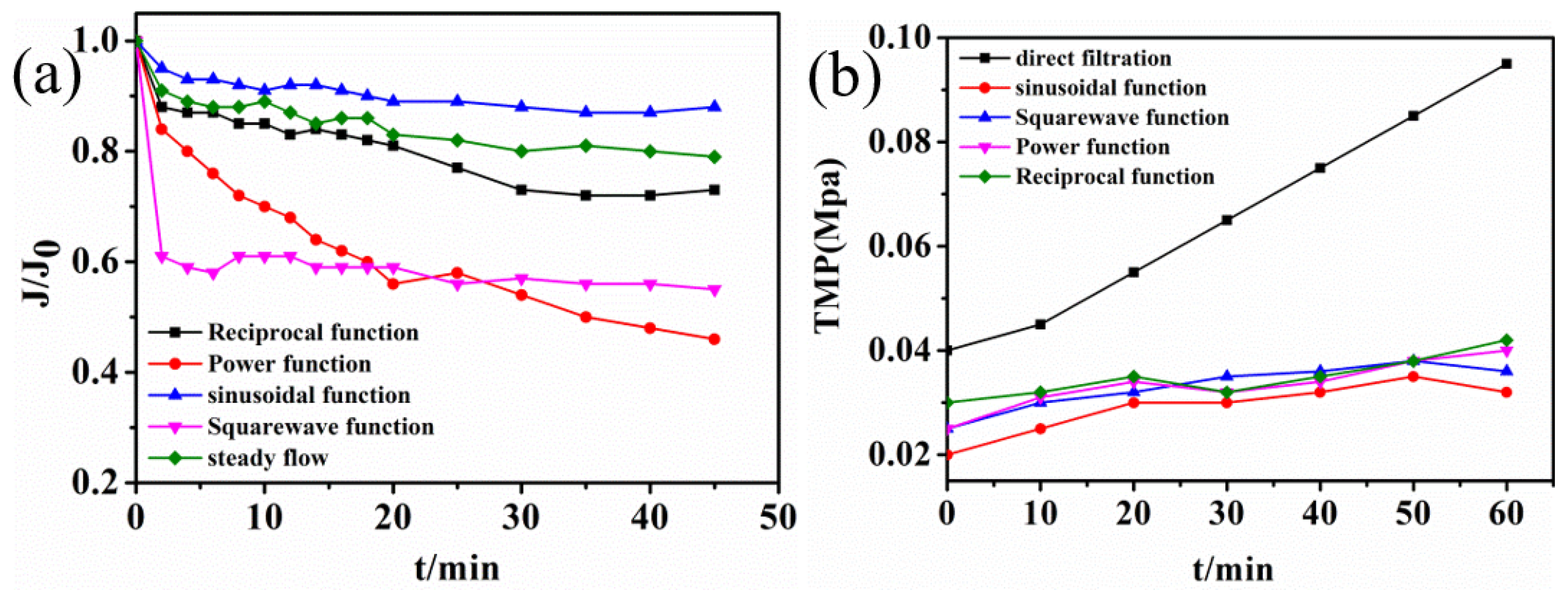
3.1.1. Effects of Different Feeding Methods on Membrane Fouling Control
3.1.2. Membrane Surface Morphology Analysis
3.2. CFD Simulation of the Membrane Separation Process with Different Feeding Modes
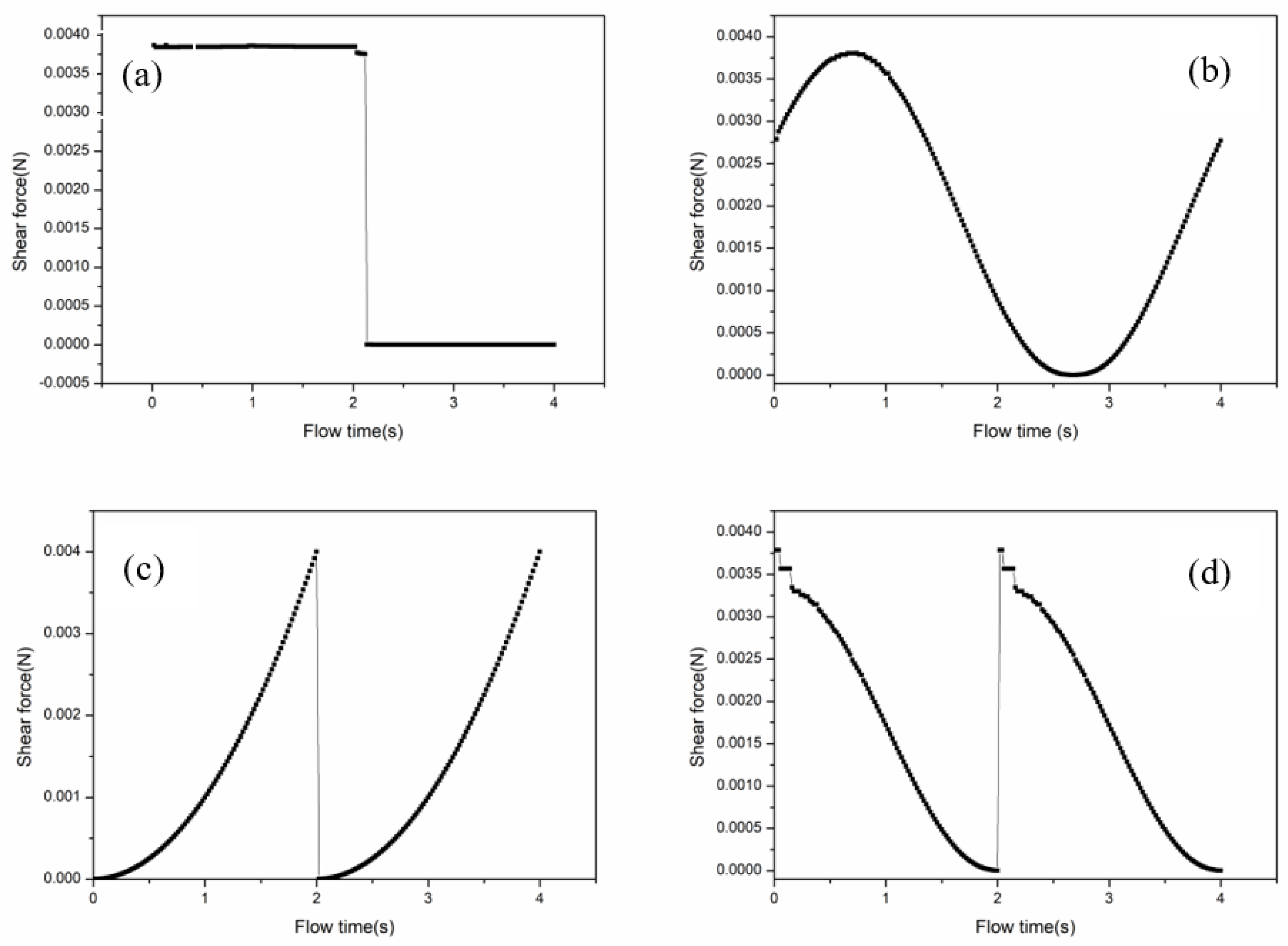
3.2.1. Effects of Feeding Modes on Shear Force
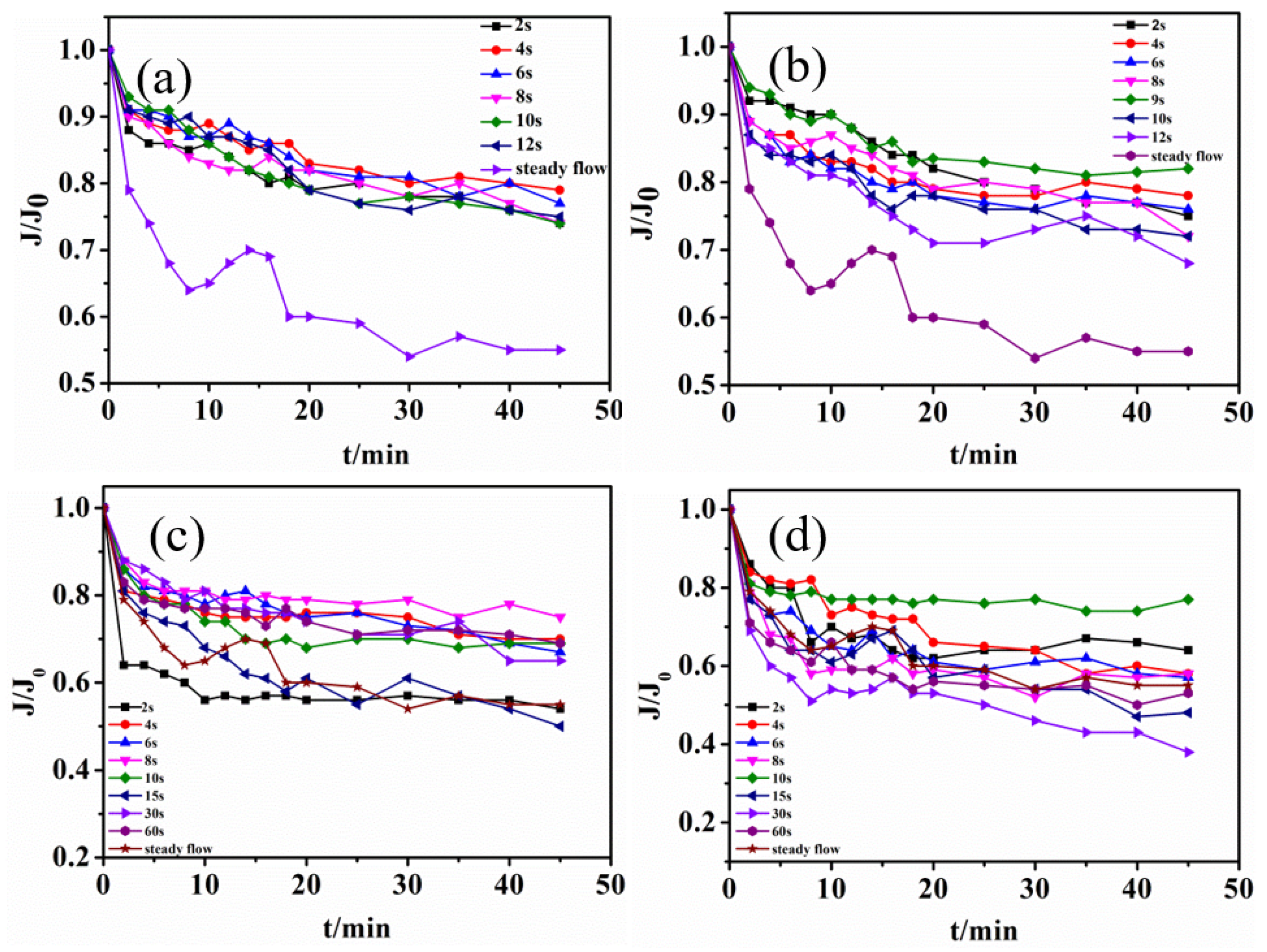
3.2.2. Effect of Feeding Modes on Membrane-Specific Flux
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Jv | Permeate flux (L/m2·h) |
| J0 | Water flux (L/m2·h) |
| ΔP | Transmembrane pressure (TMP) drop (KPa) |
| ρ | Density (Kg·m−3) |
| μ | Viscosity (Pa·s) |
| k | Turbulence kinetic energy (m2/s2) |
| ε | Turbulence dissipation rate (m2/s2) |
| x, y, z | Cylindrical coordinate (m) |
References
- Vatanpour, V.; Karami, A.; Sheydaei, M. Central composite design optimization of Rhodamine B degradation using TiO2 nanoparticles/UV/PVDF process in continuous submerged membrane photo reactor. Chem. Eng. Process. 2017, 116, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W. Enhanced antifouling performance of ZnS/GO/PVDF hybrid membrane by improving hydrophilicity and photocatalysis. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 30, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, L.; Murgolo, S.; Dzinun, H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Carballa, M.; Mascolo, G. Application of immobilized TiO2 on PVDF dual layer hollow fiber membrane to improve the photocatalytic removal of pharmaceuticals in different water matrices. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 240, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Wu, T.F.; Shi, J.; Teng, K.Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, M.J.; Li, J.; Qian, X.M.; Li, C.Y.; Fan, J.T. Photocatalytic antifouling PVDF ultrafiltration membranes based on synergy of graphene oxide and TiO2 for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Ma, J.; Han, M.; Chen, Z.L.; Han, Z.S.; Li, G.B. Membrane fouling control in ultrafiltration technology for drinking water production: A review. Desalination 2011, 272, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Q.; Bai, L.M.; Tang, X.B.; Huang, Q.J.; Xie, B.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Li, G.B.; Liang, H. Coupling continuous sand filtration to ultrafiltration for drinking water treatment: Improved performance and membrane fouling control. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 567, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.F.; Tal, G.; Hankins, N.P.; Gitis, V. Fouling and cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 1, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xiong, H.F.; Liu, F.; Yang, Q.Y.; Xu, B.J.; Zhan, C.C. Effect of UV/TiO2 Pretreatment on Fouling Alleviation and Mechanisms of Fouling Development in a Cross-flow Filtration Process Using a Ceramic UF Membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1583–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Yu, H.R.; Gao, S.S.; Li, G.B. Applying ultraviolet/persulfate (UV/PS) pre-oxidation for controlling ultrafiltration membrane fouling by natural organic matter (NOM) in surface water. Water Res. 2018, 132, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbozorg, M.; Li, T.; Law, A.W.K. Effect of turbulence on fouling control of submerged hollow fiber membrane filtration. Water Res. 2016, 99, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.J.; Mao, Z.M.; See, T.W.; Zen, T.Y.; Wei, C.J.; Haur, C.T.; Fane, A.G. Spacer Vibration for Fouling Control of Submerged Flat Sheet Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; He, G.H.; Liu, X.D.; Xiao, G.K.; Li, B.J. CFD simulations of turbulent flow in baffle-filled membrane tubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 67, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.H.; Sim, L.N.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G. Ultrafiltration with Intermittent Relaxation using Colloidal Silica and Humic Acid as Model Foulants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.F.; Li, C.; Peng, T.; Qiao, X.W.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, L.H.; Wang, X.H.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, M. CFD modeling and experimental study of pulse flow in a hollow fiber membrane for water filtration. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 79, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, R.; Bilad, M.R.; Laziz, A.M.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Jusoh, N.; Putra, Z.A.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Jaafar, J. Finned spacer for efficient membrane fouling control in produced water filtration. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agi, A.; Junin, R.; Yahya, A.; Gbadamosi, A.; Abbas, A. Comparative study of continuous and intermittent ultrasonic ultrafiltration membrane for treatment of synthetic produced water containing emulsion. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2018, 132, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, R.; Deveci, G.; Turken, T.; Sengur, R.; Guclu, S.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Koyuncu, I. Analysis of wall shear stress on the outside-in type hollow fiber membrane modules by CFD simulation. Desalination 2014, 351, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Ruan, Y.H.; Ma, Y.L.; Jiang, X.B.; Zheng, W.J.; Liu, Y.F.; He, G.H. Modeling and simulation of mitigating membrane fouling under a baffle-filled turbulent flow with permeate boundary. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Y.; Toh, K.Y.; Weihs, G.A.F. 3D CFD study of the effect of multi-layer spacers on membrane performance under steady flow. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 580, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Y.; Weihs, G.A.F.; Fletcher, D.F. CFD study of the effect of unsteady slip velocity waveform on shear stress in membrane systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 192, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.E.; Lin, Y.C.; Hwang, K.J.; Cheng, T.W.; Tung, K.L. High-efficiency hollow fiber arrangement design to enhance filtration performance by CFD simulation. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2018, 125, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Z.; Mao, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.J.; Tan, W.S.; Chong, T.H.; Wu, B.; Chew, J.W. Enhancing fouling mitigation of submerged flat-sheet membranes by vibrating 3D-spacers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, K.M.; Yang, H.Y. The relationship between size-segregated particles migration phenomenon and combined membrane fouling in ultrafiltration processes: The significance of shear stress. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 96, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; He, G.H.; Ding, L.H.; Dou, H.; Ju, J.; Li, B.J. Experimental and CFD studies on the performance of microfiltration enhanced by a turbulence promoter, separation science and engineering. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, Y.; Leslie, G.; Li, G.B.; Liang, H. Shear stress in a pressure-driven membrane system and its impact on membrane fouling from a hydrodynamic condition perspective: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Y.; Weihs, G.E.F.; Setiawan, R.; Wiley, D.E. CFD modelling of unsteady electro-osmotic permeate flux enhancement in membrane systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 146, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Su, X.; Palazzolo, A.; Ahmed, S.; Thomas, E. Reverse osmosis membrane, seawater desalination with vibration assisted reduced inorganic fouling. Desalination 2017, 417, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Y.; Weihs, G.A.F.; Wiley, D.E. CFD modelling of electro-osmotic permeate flux enhancement in spacer-filled membrane channels. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 507, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, H.E.; Andrews, R.C.; Bérubé, P.R. Surface shear stress and membrane fouling when considering natural water matrices. Desalination 2013, 330, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Function Form | Function Expression |
|---|---|
| sine functions | |
| square wave functions | |
| reciprocal functions | |
| power functions |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Xiong, H.; Sun, T.; Wu, X.; Shi, Z.; Lin, Q. Study on the Control of Membrane Fouling by Pulse Function Feed and CFD Simulation Verification. Membranes 2022, 12, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040362
Li C, Zhang D, Liu J, Xiong H, Sun T, Wu X, Shi Z, Lin Q. Study on the Control of Membrane Fouling by Pulse Function Feed and CFD Simulation Verification. Membranes. 2022; 12(4):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040362
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chen, Dashuai Zhang, Jinrui Liu, Hanyu Xiong, Tianyi Sun, Xinghui Wu, Zaifeng Shi, and Qiang Lin. 2022. "Study on the Control of Membrane Fouling by Pulse Function Feed and CFD Simulation Verification" Membranes 12, no. 4: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040362
APA StyleLi, C., Zhang, D., Liu, J., Xiong, H., Sun, T., Wu, X., Shi, Z., & Lin, Q. (2022). Study on the Control of Membrane Fouling by Pulse Function Feed and CFD Simulation Verification. Membranes, 12(4), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040362





