A Review of Recent Developments of Pervaporation Membranes for Ethylene Glycol Purification
Abstract
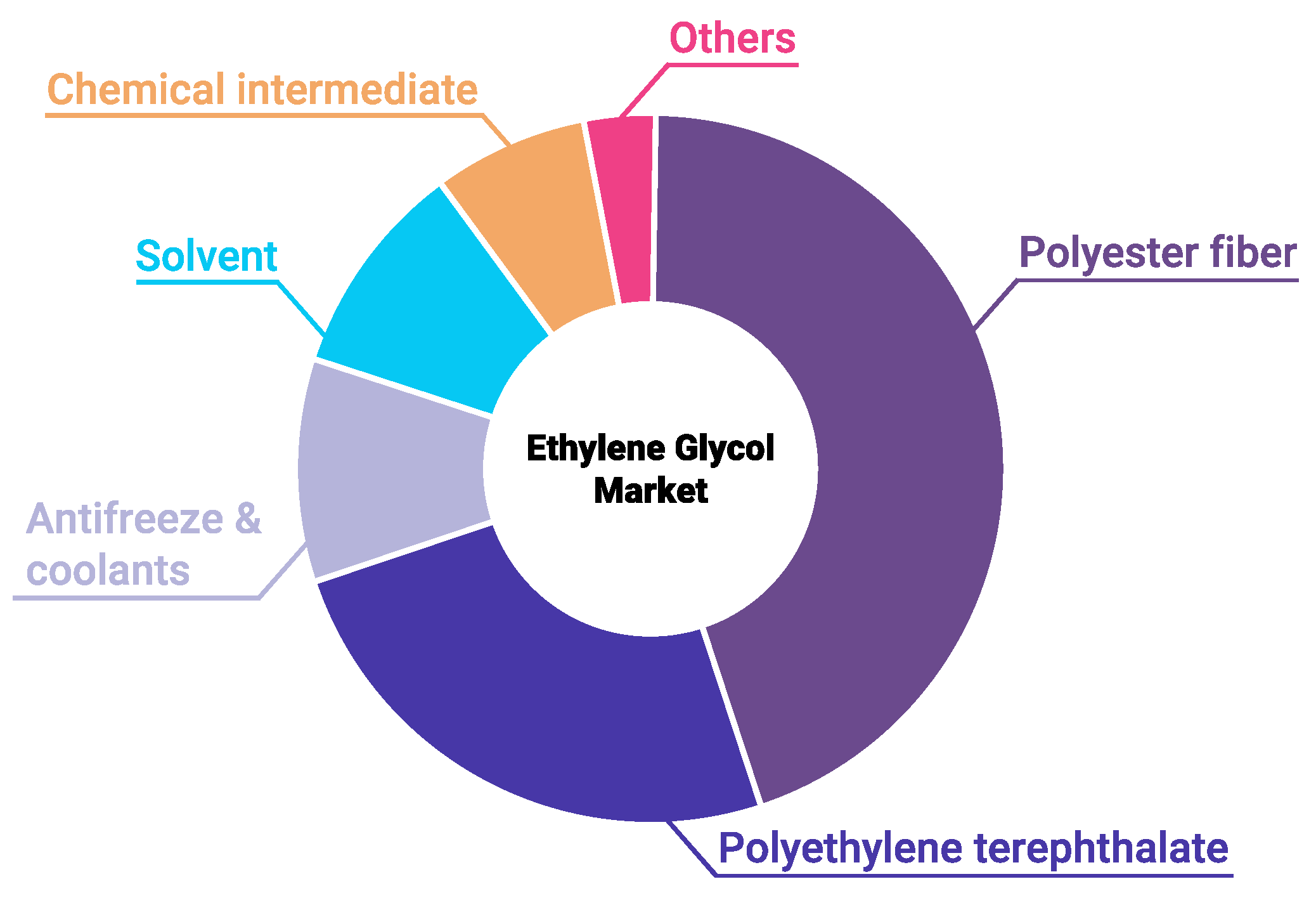
1. Introduction
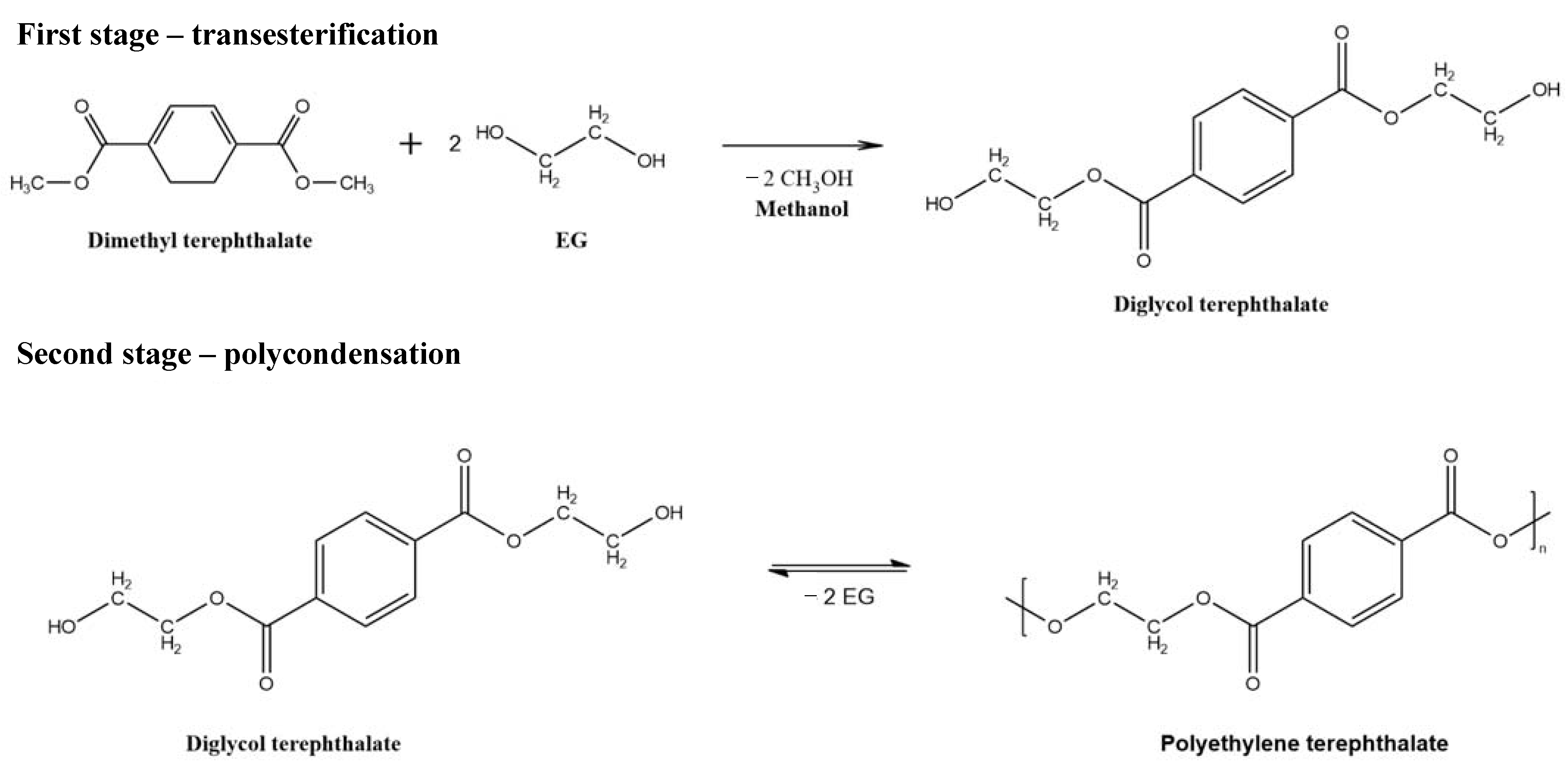
2. Properties of Ethylene Glycol
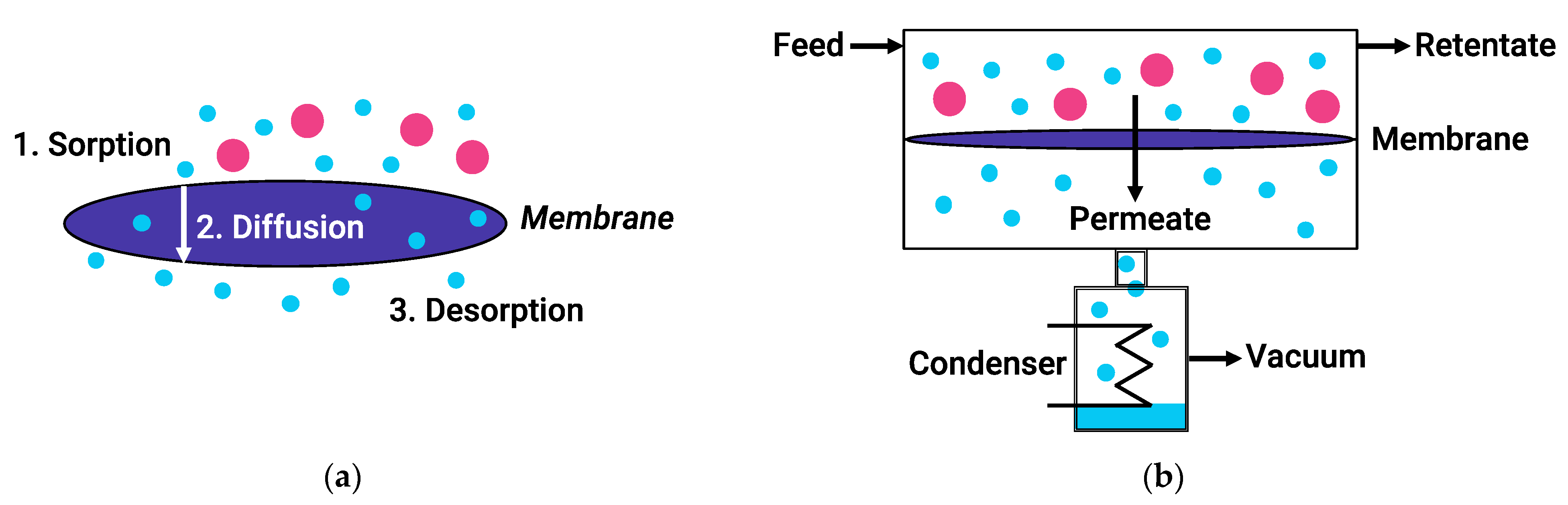
3. Pervaporation
4. Membranes for EG Dehydration
4.1. Hydrophilic Membranes
4.1.1. Poly(vinyl) Alcohol
4.1.2. Chitosan
4.2. Miscellaneous Polymers
5. Membranes for Methanol/EG Separation
6. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | acrylic acid |
| AM | acrylamide |
| AN | acrylonitrile |
| ATR-FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy with attenuated total reflectance |
| bis-MPA | 2,2-bis (hydroxymethyl) propionic acid |
| BTEE | 2-bis(triethoxysilyl)-ethane |
| CA | calcium alginate |
| CMS-3 | perfluoropolymer |
| CNT | carbon nanotube |
| cPIM-1 | carboxylated PIM-1 |
| CS | chitosan |
| DMO | dimethyl oxalate |
| DSC | differential scanning microscopy |
| EG | ethylene glycol |
| EO | ethylene oxide |
| FIPN | full interpenetrating network |
| FPS | fullerene-containing polystyrene |
| GA | glutaraldehyde |
| GO | graphene oxide |
| GPTMS | γ-glycidyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane |
| HAS | heteroarm star |
| HBPE | hyperbranched polyester |
| HEMA | hydroxy ethyl methacrylate |
| HSM | hybrid star-shaped macromolecules |
| IPN | interpenetrating network |
| MAC | methacrylic acid |
| MBA | methylene-bis-acrylamide |
| MMM | mixed matrix membrane |
| MOF | metal–organic frameworks |
| MPTMS | γ-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane |
| p-TSA | p-toluenesulfonic acid |
| PA | polyamide |
| PAA | polyacrylic acid |
| PAAM | polyacrylamide |
| PBI | polybenzimidazole |
| PD | polydopamine |
| PDMAEMA | poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) |
| Pebax | poly(ether-block-amide) |
| PEC NP | polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticle |
| PECM | polyelectrolyte complex membrane |
| PEI | polyetherimide |
| PEIm | polyethyleneimine |
| PES | polyethersulfone |
| PET | polyethylene terephthalate |
| PIM | polymers with intrinsic microporosity |
| PP | polypropylene |
| PPO | poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) |
| PS | polystyrene |
| PSF | polysulfone |
| PTBMA | poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) |
| PV | pervaporation |
| PVA | poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| P2VP | poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) |
| PVSM | polyvinylamine |
| SPEEK | sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) |
| TEOS | tetraethoxysilane |
| TFC | thin-film composite |
| TMP | 1,1,1-trimethylolpropane |
| TMS | trimesoyl chloride |
| VP | vinyl pyrrolidone |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| Symbols and Units | |
| J | total flux (kg/m2·h) |
| M | weight of permeate (kg) |
| S | membrane area (m2) |
| t | test period (h) |
| T | temperature (°C) |
| x | weight percentage of components in the feed |
| y | weight percentage of components in the feed |
| β | separation factor |
References
- Forkner, M.W.; Robson, J.H.; Snellings, W.M.; Martin, A.E.; Murphy, F.H.; Parsons, T.E. Glycols. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 544–582. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Gong, J. Ethylene glycol: Properties, synthesis, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carney, E.W.; Stice, S.A. Ethylene Glycol. In Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology, 2nd ed.; Gupta, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 797–809. ISBN 97801280-42397. [Google Scholar]
- Knifton, J.F. Ethylene glycol from synthesis gas via ruthenium melt catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 3959–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, R.F. Ethylene glycols technology. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2001, 18, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.M.; Shao, P.; Feng, X.; Anderson, W.A. Separation of ethylene glycol-water mixtures using sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) pervaporation membranes: Membrane relaxation and separation performance analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 2957–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, G.; Keshav, A.; Anandkumar, J. Review on Pervaporation: Theory, Membrane Performance, and Application to Intensification of Esterification Reaction. J. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlaskin, A.A.; Trubyanov, M.M.; Yanbikov, N.R.; Vorotyntsev, A.V.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Comprehensive experimental study of membrane cascades type of “continuous membrane column” for gases high-purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pientka, Z.; Brozova, L.; Pulyalina, A.Y.; Goikhman, M.Y.; Podeshvo, I.V.; Gofman, I.V.; Saprykina, N.N.; Polotskaya, G.A. Synthesis and characterization of polybenzoxazinone and its prepolymer using gas separation. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulyalina, A.Y.; Polotskaya, G.A.; Kalyuzhnaya, L.M.; Saprykina, N.N.; Sushchenko, I.G.; Meleshko, T.K.; Toikka, A.M. The study of sorption and transport properties of membranes containing polyaniline. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2010, 52, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.K.; Shi, G.M.; Le, N.L.; Tang, Y.P.; Zuo, J.; Nunes, S.P.; Chung, T.S. Recent membrane development for pervaporation processes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 57, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulyalina, A.Y.; Polotskaya, G.A.; Kalyuzhnaya, L.M.; Sushchenko, I.G.; Meleshko, T.K.; Yakimanskii, A.V.; Chislov, M.V.; Toikka, A.M. Sorption and transport of aqueous isopropanol solutions in polyimide-poly(aniline-co-anthranilic acid) composites. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2011, 84, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xie, Z.; Cran, M.; Wu, C.; Gray, S. Dimensional Nanofillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Pervaporation Separations: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, P.; Sundarrajan, S.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Mixed Matrix Membranes for Solvent Dehydration and Recovery Process. Membranes 2021, 11, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Jin, W. Pervaporation membrane materials: Recent trends and perspectives. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulyalina, A.Y.; Toikka, A.M.; Polotskaya, G.A. Investigation of pervaporation membranes based on polycarbamide: Effect of residual solvent. Pet. Chem. 2014, 54, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, D.; Shiu, W.-Y.; Lee, S.C. Handbook of Physical-Chemical Properties and Environmental Fate for Organic Chemicals, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; ISBN 97804291-50074. [Google Scholar]
- Böddeker, K.W. Terminology in pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 51, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulyalina, A.; Rostovtseva, V.; Faykov, I.; Toikka, A. Application of Polymer Membranes for a Purification of Fuel Oxygenated Additive. Methanol/Methyl Tert-butyl Ether (MTBE) Separation via Pervaporation: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 72, ISBN 07923-4247X. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, H.L. Membrane pervaporation: Separation of organic/aqueous mixtures. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1990, 25, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Huang, R.Y.M. Polymeric membrane pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.; Tran, T.; Hoang, M.; Xie, Z. Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.R.; Chen, H.F. A diffusion model of the pervaporation separation of ethylene glycol-water mixtures through crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 139, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, H. Pervaporation separation of ethylene glycol/water mixtures using crosslinked PVA/PES composite membranes. Part II. The swelling equilibrium model of the dense active layer in ethylene glycol/water mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 118, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Shahverdi, M.; Shirazian, S.; Mohammadi, T.; Pak, A. CFD simulation of water removal from water/ethylene glycol mixtures by pervaporation. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmgar, K.; Nasiraee, M. Polyvinyl alcohol-based membranes for filtration of aqueous solutions: A comprehensive review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 62, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuila, S.B.; Ray, S.K.; Das, P.; Singha, N.R. Synthesis of full interpenetrating network membranes of poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) in the matrix of polyvinyl alcohol for dehydration of ethylene glycol by pervaporation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2011, 50, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burshe, M.C.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Dehydration of ethylene glycol by pervaporation using hydrophilic IPNs of PVA, PAA and PAAM membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 1998, 13, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, M.N.; Chen, P. Pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol with chitosan-poly(vinyl alcohol) blend membranes: Effect of CS-PVA blending ratios. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Hu, C.; Li, B.; Jiang, Z. Pervaporation separation of ethylene glycol/water mixtures through surface crosslinked PVA membranes: Coupling effect and separation performance analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 289, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, H.K.; Nath, K. Synthesis, characterization and application of disodium tetraborate cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol membranes for pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol. Acta Chim. Slov. 2018, 65, 902–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Pak, A. Separation of ethylene glycol-water mixtures with composite poly(vinyl alcohol)-polypropylene membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Fang, X.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Preparation and pervaporation performance of surface crosslinked PVA/PES composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 322, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.R.; Chen, H.F. Pervaporation separation of ethylene glycol-water mixtures using crosslinked PVA-PES composite membranes. Part I. Effects of membrane preparation conditions on pervaporation performances. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 109, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, M.N.; Huang, R.Y.M.; Chen, P. Composite poly(vinyl alcohol)-poly(sulfone) membranes crosslinked by trimesoyl chloride: Characterization and dehydration of ethylene glycol-water mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, C.; Leak, D.; Patterson, D. Hybrid and Mixed Matrix Membranes for Separations from Fermentations. Membranes 2016, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penkova, A.V.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Ermakov, S.S.; Toikka, A.M.; Roizard, D. Novel green PVA-fullerenol mixed matrix supported membranes for separating water-THF mixtures by pervaporation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20354–20362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šupová, M.; Martynková, G.S.; Barabaszová, K. Effect of nanofillers dispersion in polymer matrices: A review. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2011, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N. Some basic aspects of polymer nanocomposites: A critical review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Hojjati, M.; Okamoto, M.; Gorga, R.E. Review article: Polymer-matrix nanocomposites, processing, manufacturing, and application: An overview. J. Compos. Mater. 2006, 40, 1511–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algieri, C.; Drioli, E. Zeolite membranes: Synthesis and applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Boczkaj, G. Pervaporation Zeolite-Based Composite Membranes for Solvent Separations. Molecules 2021, 26, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baheri, B.; Shahverdi, M.; Rezakazemi, M.; Motaee, E.; Mohammadi, T. Performance of PVA/NaA Mixed Matrix Membrane for Removal of Water from Ethylene Glycol Solutions by Pervaporation. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2015, 202, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjani, A. Separation of Water from Ethylene Glycol Using Polyvinyl Alcohol–Zeolite Composite Membrane. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2018, 42, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, M.; Baheri, B.; Rezakazemi, M.; Motaee, E.; Mohammadi, T. Pervaporation study of ethylene glycol dehydration through synthesized (PVA-4A)/polypropylene mixed matrix composite membranes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Composite membranes comprising of polyvinylamine-poly(vinyl alcohol) incorporated with carbon nanotubes for dehydration of ethylene glycol by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Ma, X.; Hu, C.; Jiang, Z. Novel PVA-silica nanocomposite membrane for pervaporative dehydration of ethylene glycol aqueous solution. Polymer 2007, 48, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Hu, C.; Pan, F.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. PVA-GPTMS/TEOS hybrid pervaporation membrane for dehydration of ethylene glycol aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Yang, P.; Sun, H.L.; Li, B.B. Preparation and characterization of cross-linked poly (vinyl alcohol)/hyperbranched polyester membrane for the pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol solution. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 62, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Nikolaeva, D.; Hartanto, Y.; Luis, P. MOF-based membranes for pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ying, Y.; Ma, J.; Guo, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. Mixed matrix membranes incorporated with polydopamine-coated metal-organic framework for dehydration of ethylene glycol by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari Sanjari, A.; Asghari, M. A Review on Chitosan Utilization in Membrane Synthesis. ChemBioEng Rev. 2016, 3, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hein, S.; Wang, K. Chitosan membrane in separation applications. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Sridhar, S.; Ming, Y.W.; Krishnaiah, A. Pervaporative separation of ethylene glycol/water mixtures by using cross-linked chitosan membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.; Kumar, N.S.; Subbaiah, M.V.; Suguna, M.; Krishnaiah, A. Maleic anhydride crosslinked alginate-chitosan blend membranes for pervaporation of ethylene glycol-water mixtures. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 46, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong Nam, S.; Moo Lee, Y. Pervaporation of ethylene glycol-water mixtures. I. Pervaporation performance of surface crosslinked chitosan membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 153, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, B.; Guo, R.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Pervaporation performance of chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) polyelectrolyte complex membranes for dehydration of ethylene glycol aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 55, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Guo, R.; Li, B.; Ma, X.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Development of novel mordenite-filled chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) polyelectrolyte complex membranes for pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 293, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, H.; Durmaz Hilmioglu, N. Chitosan coated zeolite filled regenerated cellulose membrane for dehydration of ethylene glycol/water mixtures by pervaporation. Desalination 2010, 258, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Sirkar, K.K.; Majumdar, S. Pervaporative dehydration of concentrated aqueous solutions of selected polar organics by a perfluoropolymer membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 175, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Soyekwo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, R.; Zhu, A.; Liu, Q. Toward improved hydrophilicity of polymers of intrinsic microporosity for pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Huang, R.Y.M.; Feng, X.; Anderson, W.; Pal, R.; Burns, C.M. Composite membranes with an integrated skin layer: Preparation, structural characteristics and pervaporation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 254, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gruender, M.; Chung, T.S. Pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol through polybenzimidazole (PBI)-based membranes. 1. Membrane fabrication. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chung, T.S.; Neo, B.W.; Gruender, M. Processing and engineering of pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol via dual-layer polybenzimidazole (PBI)/polyetherimide (PEI) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Kalyani, S.; Ravikumar, Y.V.L.; Muralikrishna, T.S.V.N. Performance of composite membranes of poly(ether-block-amide) for dehydration of rthylene glycol and ethanol. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gao, C.; Feng, X. Thin-film-composite membranes comprising of self-assembled polyelectrolytes for separation of water from ethylene glycol by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 352, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rhim, J.W.; Feng, X. Improving the stability of layer-by-layer self-assembled membranes for dehydration of alcohol and diol. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chakma, A.; Feng, X. Dehydration of ethylene glycol by pervaporation using poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)/polysulfone composite membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 64, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Martin, J.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Thin film composite membranes comprising of polyamide and polydopamine for dehydration of ethylene glycol by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.K.; Ye, C.C.; Zhang, W.H.; Wang, N.X.; Lee, K.R.; An, Q.F. Construction of well-arranged graphene oxide/polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles membranes for pervaporation ethylene glycol dehydration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 577, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halakoo, E.; Feng, X. Self-assembled membranes from polyethylenimine and graphene oxide for pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 616, 118583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulyalina, A.; Rostovtseva, V.; Polotskaya, G.; Vinogradova, L.; Zoolshoev, Z.; Simonova, M.; Hairullin, A.; Toikka, A.; Pientka, Z. Hybrid macromolecular stars incorporated poly(phenylene oxide) membranes: Organization, physical, and gas separation properties. Polymer 2019, 172, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulyalina, A.Y.; Shugurov, S.M.; Larkina, A.A.; Faikov, I.I.; Tataurov, M.V.; Rostovtseva, V.A.; Nesterova, V.P.; Saprykina, N.N.; Vinogradova, L.V.; Polotskaya, G.A. Effect of Star-Shaped Modifiers on the Transport Properties of Polymer Composites in the Butan-1-ol Dehydration Process. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2019, 89, 2082–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulyalina, A.Y.; Tataurov, M.V.; Larkina, A.A.; Faykov, I.I.; Rostovtseva, V.A.; Vinogradova, L.V.; Polotskaya, G.A. Pervaporation Desulfurization of a Thiophene/n-Octane Mixture Using PPO Membranes Modified with Hybrid Star-Shaped Macromolecules. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovtseva, V.; Pulyalina, A.; Rudakova, D.; Vinogradova, L.; Polotskaya, G. Strongly selective polymer membranes modified with heteroarm stars for the ethylene glycol dehydration by pervaporation. Membranes 2020, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabzevari, O.; Marjani, A.; Daripour, A. Polyamide/nano mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration Ethylene glycols. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Villaluenga, J.P.G.; Godino, M.P.; Mengual, J.I.; Seoane, B.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T. Preparation and application of dense poly(phenylene oxide) membranes in pervaporation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 278, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotskaya, G.A.; Krasnopeeva, E.L.; Kalyuzhnaya, L.M.; Saprykina, N.N.; Vinogradova, L.V. Mixed matrix membranes with hybrid star-shaped macromolecules for mono- and dihydric alcohols pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 143, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotskaya, G.A.; Lebedev, V.T.; Pulyalina, A.Y.; Vinogradova, L.V. Structure and transport properties of pervaporation membranes based on polyphenylene oxide and heteroarm star polymers. Pet. Chem. 2016, 56, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
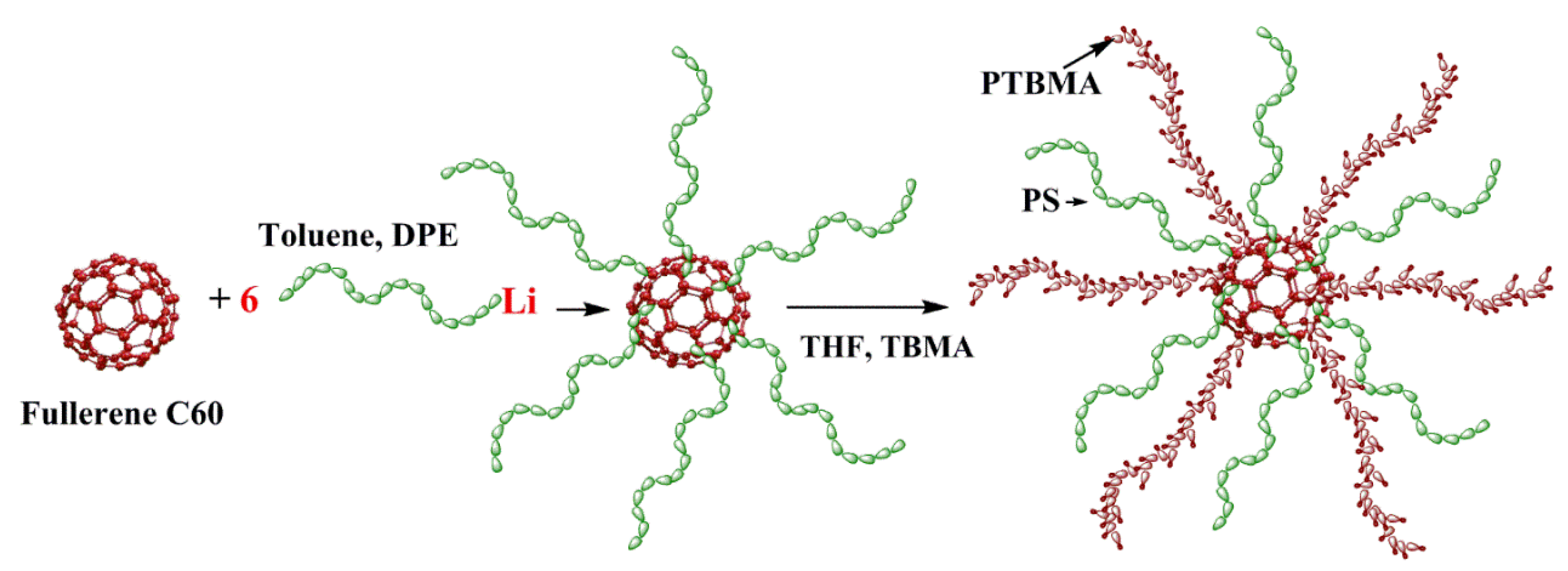
- Polotskaya, G.A.; Pulyalina, A.Y.; Rostovtseva, V.A.; Toikka, A.M.; Saprykina, N.N.; Vinogradova, L. V Effect of polystyrene stars with fullerene C 60 cores on pervaporation properties of poly(phenylene oxide) membrane. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, L.V.; Pulyalina, A.Y.; Rostovtseva, V.A.; Toikka, A.M.; Polotskaya, G.A. C60 fullerene-containing polymer stars in mixed matrix membranes. Nanosyst. Phys. Chem. Math. 2016, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Hu, W.W.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q.L. UV-crosslinked chitosan/polyvinylpyrrolidone blended membranes for pervaporation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Han, G.L.; Hu, W.W.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q.L. Pervaporation of methanol-ethylene glycol mixture over organic-inorganic hybrid membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 7541–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Hu, W.W.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhu, A.M. Chitosan/polyvinylpyrrolidone-silica hybrid membranes for pervaporation separation of methanol/ethylene glycol azeotrope. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 3178–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Guo, H.; Soyekwo, F.; Zhang, Q.G.; Lin, C.X.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhu, A.M. Pervaporation Purification of Ethylene Glycol Using the Highly Permeable PIM-1 Membrane. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, L.; Sanyal, S.K.; Mukherjea, R.N. Pervaporation of Methanol-Ethylene Glycol with Cellophane Membranes: Performance of Conditioned Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1989, 28, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.K.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Methanol selective membranes for separation of methanol-ethylene glycol mixtures by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Property | |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 62 g/mol |
| Boiling point at 760 mmHg | 197.6 °C |
| Density at 40 °C | 1099 kg/m3 |
| Viscosity at 20 °C | 19.8 × 10−3 Pa·s |
| Normal freezing point | −13.0 °C |
| Vapor pressure at 20 °C | 7.5 Pa |
| Flash point, Cleveland open-cup method | 115.0 °C |
| Surface tension at 25 °C | 48.0 × 10−3 N/m |
| Water solubility at 20 °C | 100% |
| Critical specific volume | 19.1 × 10−2 L·mol/g |
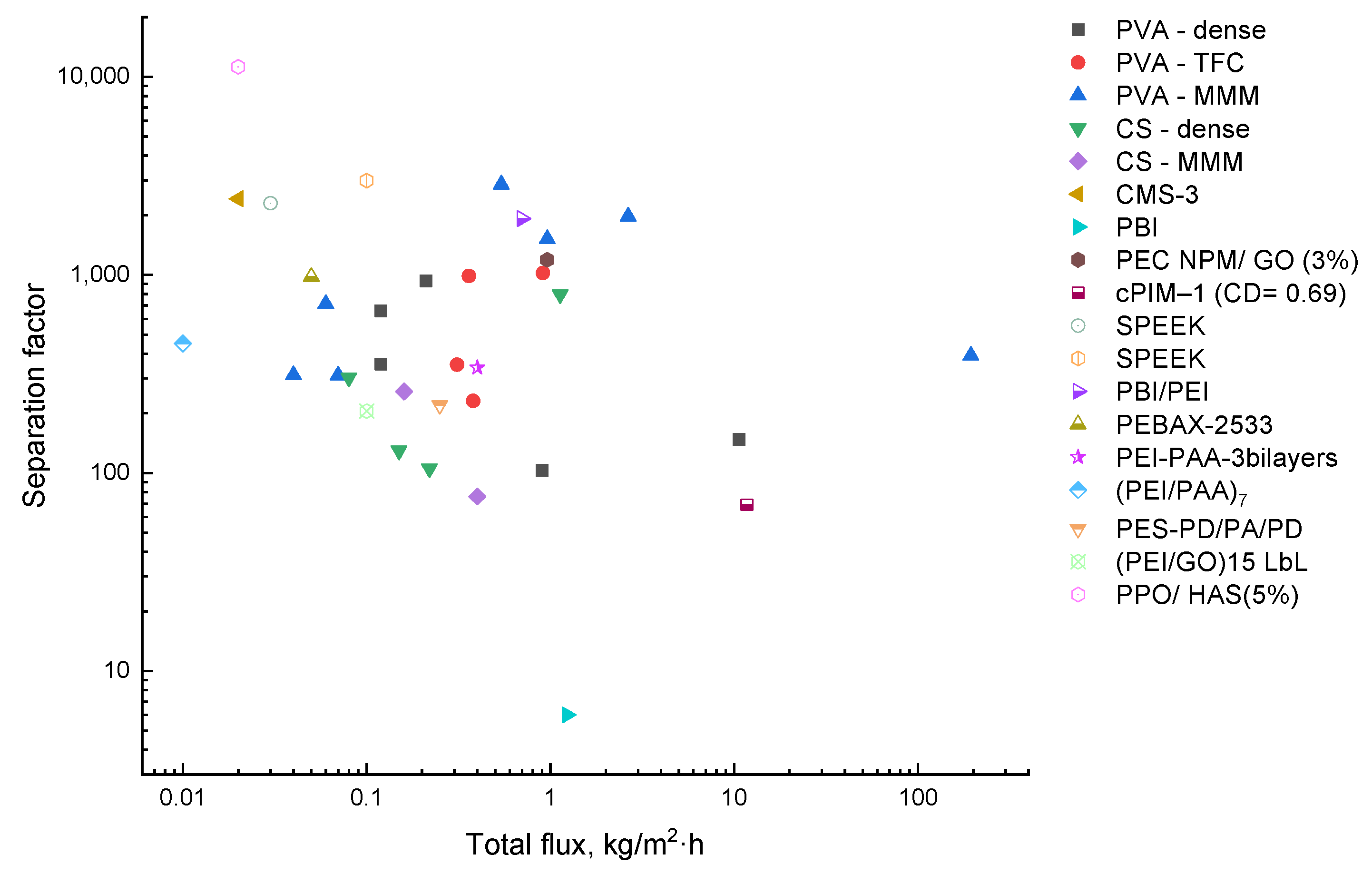
| Polymer | EG in Feed, wt.% | T, °C | Membrane Performance | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Separation Factor | Total Flux, kg/m2·h | ||||
| PVA | 90 | 60 | - | 66.70 | [24] |
| FIPN50 | 97.1 | 75 | 148 | 10.63 | [28] |
| PAA/PVA = 30/70 | 90 | 30 | 103 | 0.90 | [29] |
| CS–PVA2 | 90 | 25 | 659 | 0.12 | [30] |
| PVA | 90 | 25 | 354 | 0.12 | [30] |
| PVA(GA15) | 80 | 70 | 933 | 0.21 | [31] |
| PVA–PES 0.2% Borax | 80 | 45 | 3.5 | 6 m3 (stp)/m2·h | [32] |
| PVA/PP | 80 | 60 | 1021 | 0.91 | [33] |
| PVA/PES (0.5 wt.% borax) | 80 | 70 | 352 | 0.31 | [34] |
| PVA–PES | 82.5 | 80 | 231 | 0.38 | [35] |
| PVA4 (TMC) | 90 | 60 | 987 | 0.36 | [36] |
| PVA/NaA (5%) | 80 | 70 | 1520 | 0.96 | [44] |
| PVA/NaA | 90 | 60 | - | 0.35 | [45] |
| PVA/PP/Zeolite 4A (5%) | 80 | 70 | 1972 | 2.65 | [46] |
| PVAm–PVA on PSf support/ CNT (0.5) | 97 | 70 | 391 | 194.00 | [47] |
| PVA/MPTMS 50 | 80 | 70 | 311 | 0.07 | [48] |
| PVA–GPTMS/TEOS 1:1 | 80 | 70 | 714 | 0.06 | [49] |
| PVA10 wt.% HBPE | 90 | 25 | 312 | 0.04 | [50] |
| PVA (SO3H-MIL-101-Cr) | 90 | 70 | 2864 | 0.54 | [52] |
| Polymer | EG in Feed, wt.% | T, °C | Membrane Performance | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Separation Factor | Total Flux, kg/m2·h | ||||
| CS | 90 | 30 | 129.5 | 0.15 | [55] |
| M-CA/CS | 96.8 | 30 | 302 | 0.08 | [56] |
| Surface crosslinked CS/PES | 80 | 80 | 796 | 1.13 | [57] |
| PECM60/40 | 80 | 70 | 105 | 0.22 | [58] |
| Chitosan–poly(acrylic acid) polyelectrolyte complex/mordenite | 80 | 70 | 258 | 0.16 | [59] |
| Chitosan-coated zeolite-filled cellulose membrane | 95 | 30 | 76 | 0.4 | [60] |
| Polymer | EG in Feed, wt.% | T, °C | Membrane Performance | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Separation Factor | Total Flux, kg/m2·h | ||||
| CMS-3 | 95 | 30 | 2419 | 0.02 | [61] |
| cPIM–1 (CD = 0.69) | 80 | 30 | 69 | 11.73 | [62] |
| SPEEK | 90 | 32 | 2300 | 0.03 | [6] |
| SPEEK | 90 | 30 | 2991 | 0.10 | [63] |
| PBI | 50 | 25 | 6 | 1.23 | [64] |
| PBI/PEI | 80 | 50 | 1925 | 0.70 | [65] |
| PEBAX-2533 | 94.7 | 30 | 978 | 0.05 | [66] |
| PEI–PAA 3 bilayers | 97 | 40 | 340 | 0.40 | [67] |
| (PEI/PAA)7 | 95 | 22 | 450 | 0.01 | [68] |
| PDMAEMA/PSF | 99.7 | 30 | 32,901 | 1 mol/(m2·h) | [69] |
| PES–PD/PA/PD | 89.5 | 38 | 220 | 0.25 | [70] |
| PEC NPM/GO (3%) | 90 | 60 | 1191 | 0.96 | [71] |
| (PEI/GO) 15 LbL | 95 | 35 | 205 | 0.10 | [72] |
| PPO/ HAS (5%) | 90 | 50 | 11,240 | 0.02 | [76] |
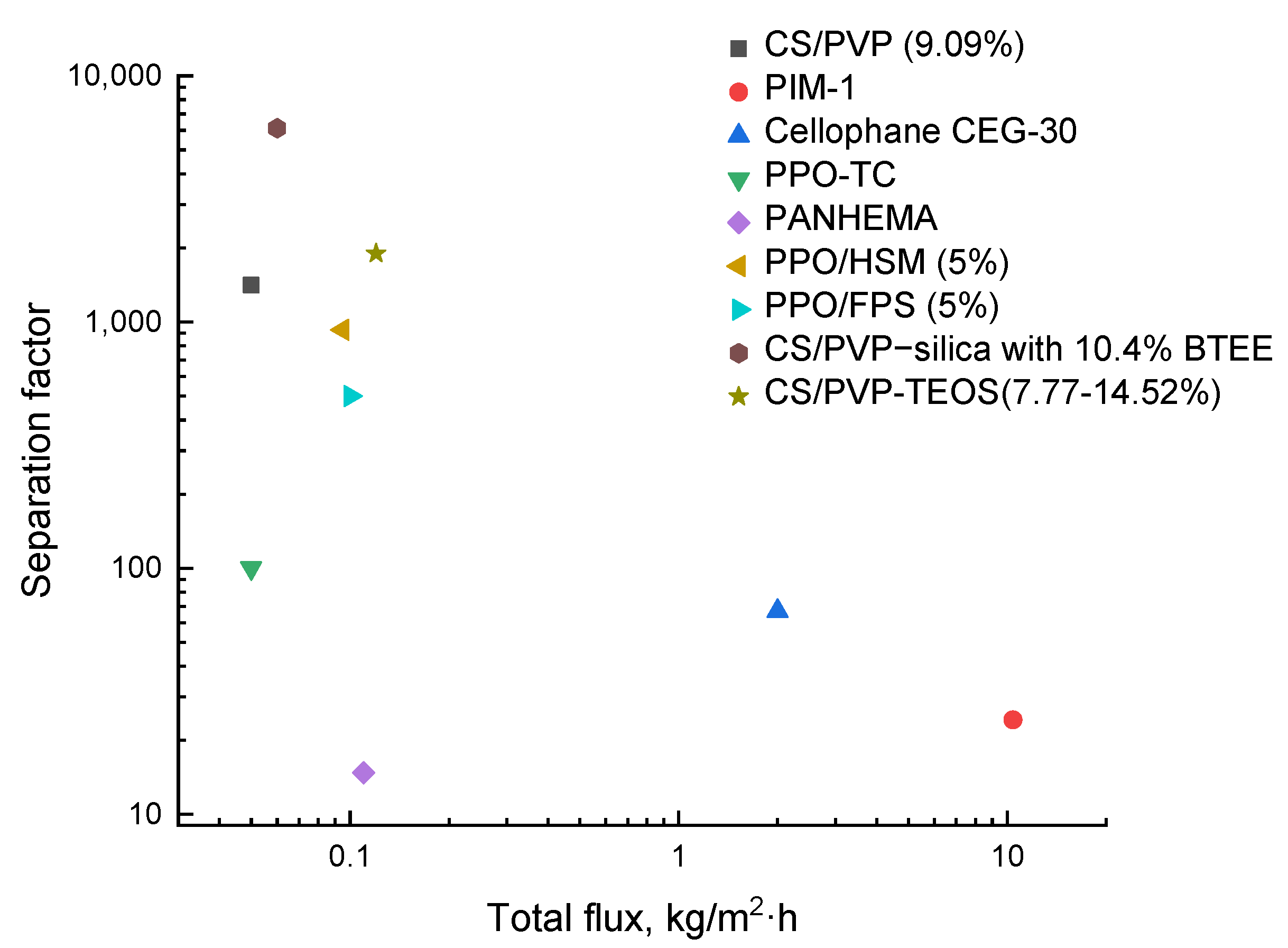
| Polymer | EG in Feed, wt.% | T, °C | Membrane Performance | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Separation Factor | Total Flux, kg/m2·h | ||||
| CS/PVP (9.09%) | 94 | 25 | 1410 | 0.05 | [83] |
| PIM-1 | 71.5 | 30 | 24.2 | 10.40 | [86] |
| Cellophane CEG-30 | 85 | 30 | 67 | 2.00 | [87] |
| PPO-TC | 90 | 30 | 100 | 0.05 | [78] |
| PANHEMA | 50 | 30 | 14.74 | 0.11 | [88] |
| PPO/HSM (5%) | 95 | 50 | 930 | 0.095 | [79,80] |
| PPO/FPS (5%) | 95 | 50 | 500 | 0.10 | [81] |
| CS/PVP−silica hybrid membrane with 10.4% BTEE | 94 | 60 | 6129 | 0.06 | [84] |
| CS/PVP–TEOS (7.77–14.52%) | 94 | 60 | 1899 | 0.12 | [85] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rostovtseva, V.; Faykov, I.; Pulyalina, A. A Review of Recent Developments of Pervaporation Membranes for Ethylene Glycol Purification. Membranes 2022, 12, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030312
Rostovtseva V, Faykov I, Pulyalina A. A Review of Recent Developments of Pervaporation Membranes for Ethylene Glycol Purification. Membranes. 2022; 12(3):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030312
Chicago/Turabian StyleRostovtseva, Valeriia, Ilya Faykov, and Alexandra Pulyalina. 2022. "A Review of Recent Developments of Pervaporation Membranes for Ethylene Glycol Purification" Membranes 12, no. 3: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030312
APA StyleRostovtseva, V., Faykov, I., & Pulyalina, A. (2022). A Review of Recent Developments of Pervaporation Membranes for Ethylene Glycol Purification. Membranes, 12(3), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030312







