Molecular Modeling of Cardiac Sodium Channel with Mexiletine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussions
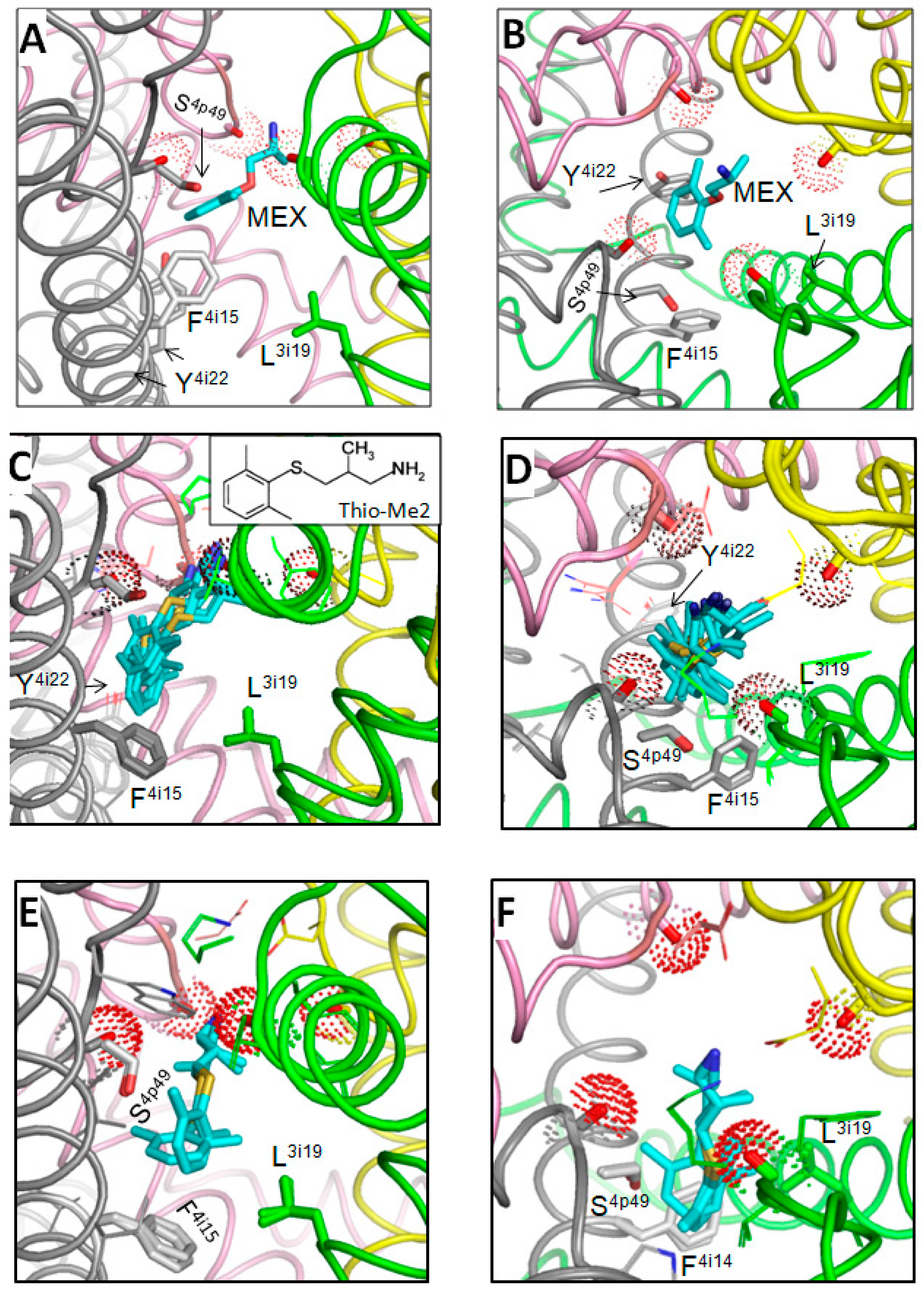
3.1. Docking MEX and Its More Potent Analog
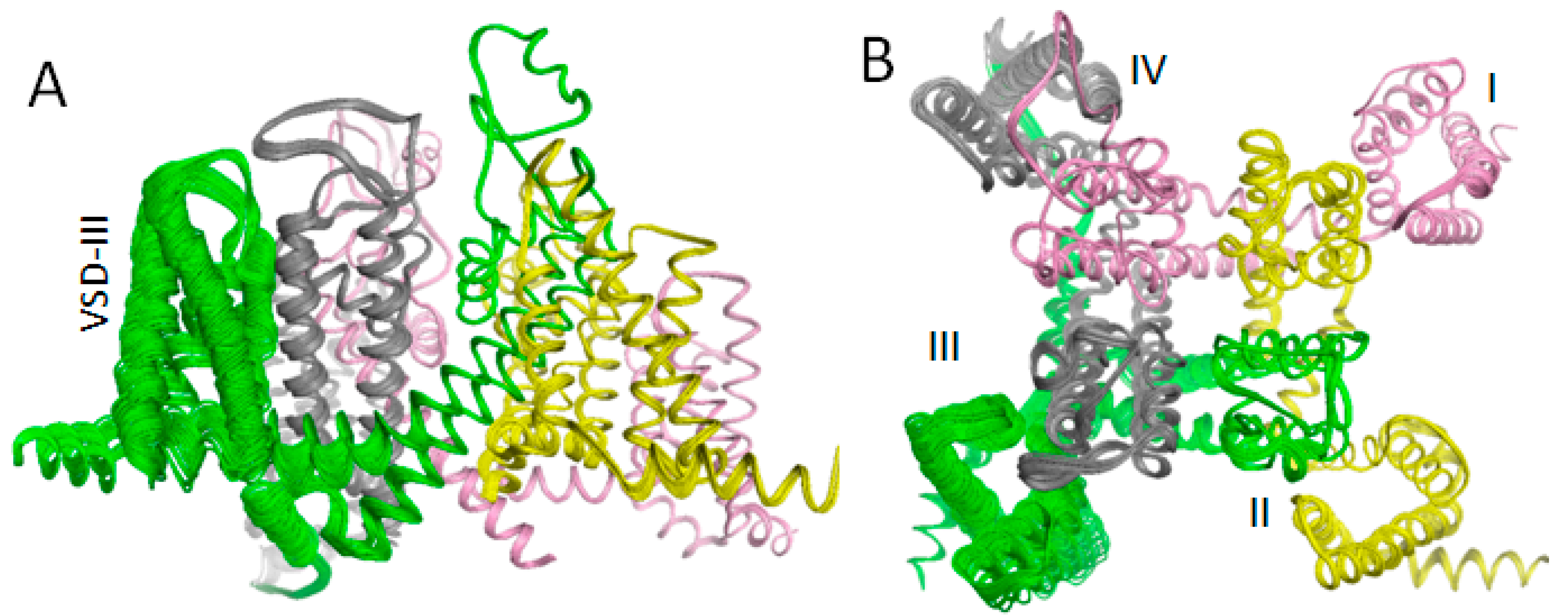
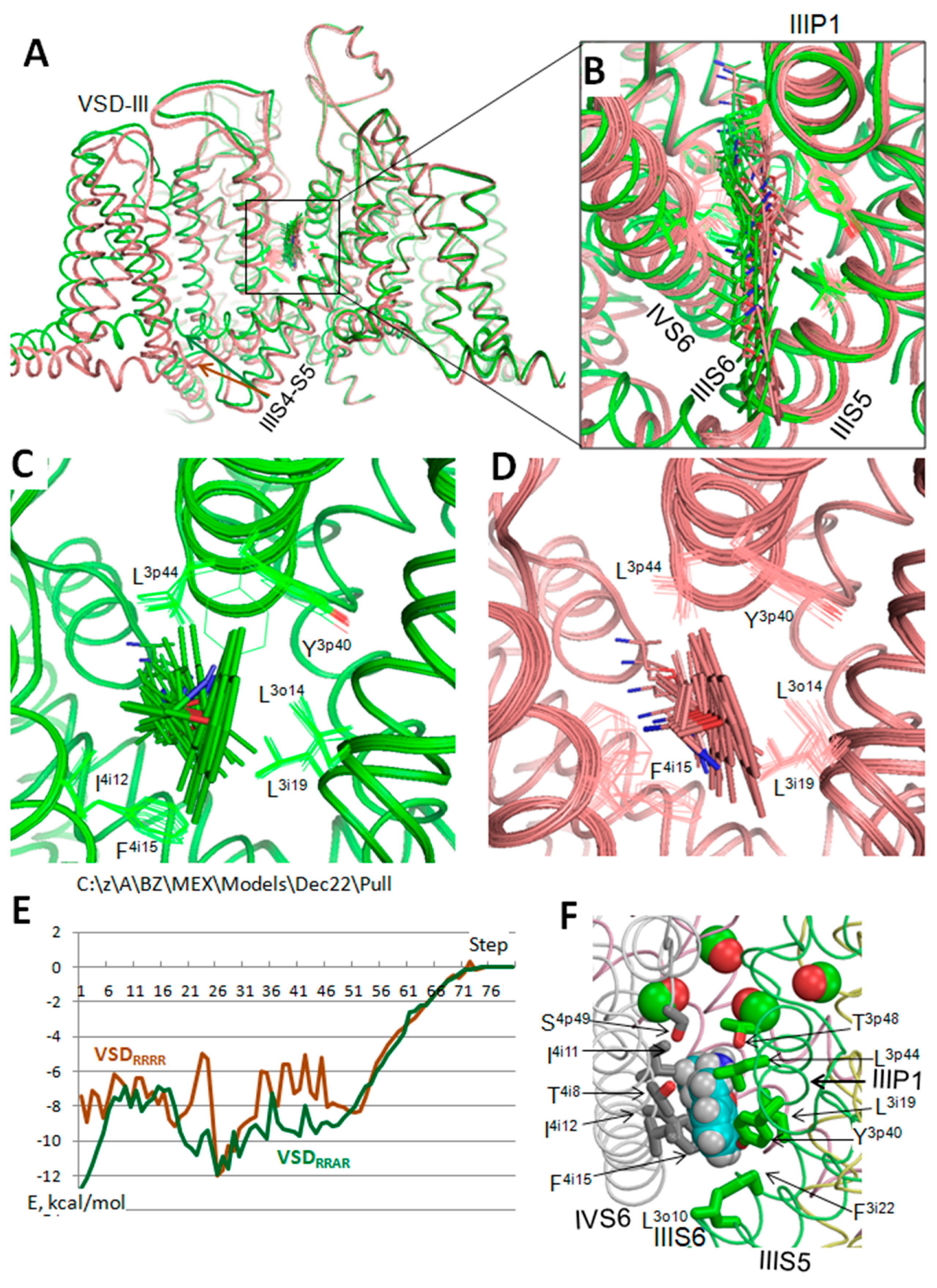
3.2. In Silico Deactivation of VSDIII
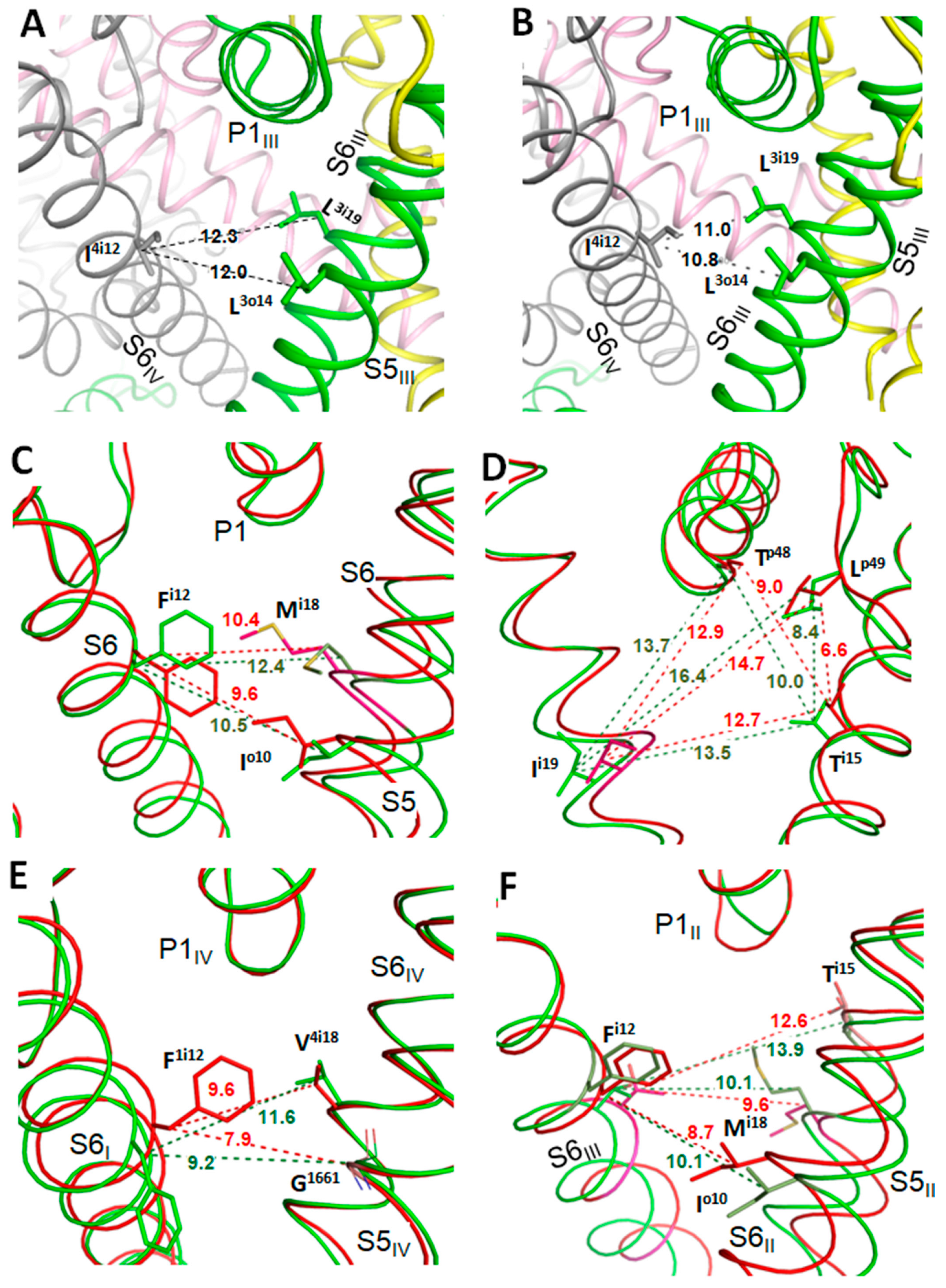
3.3. State-Dependent Geometry of Fenestration in Experimental Structures
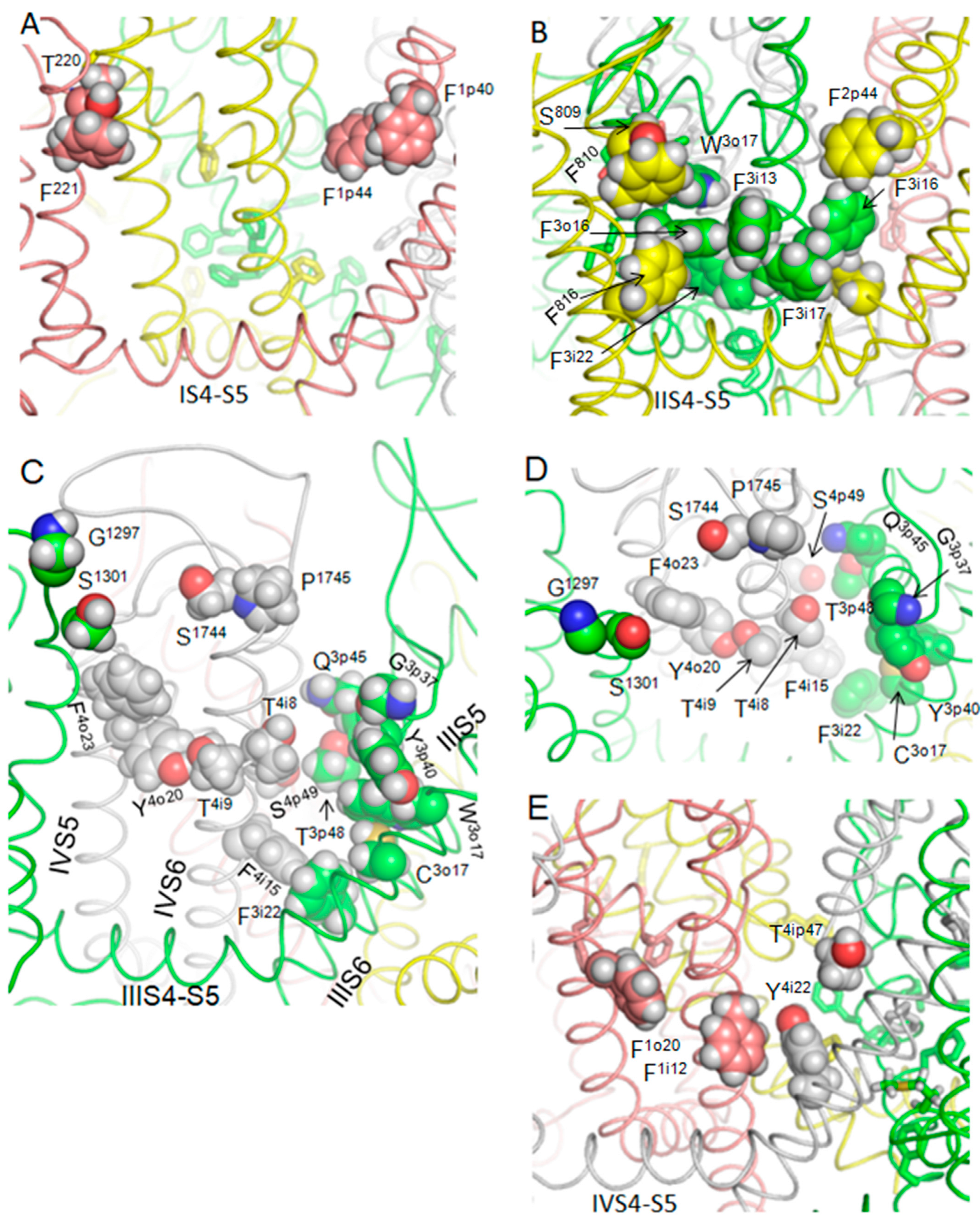
3.4. Hydrophobic Access Pathway to the Nav1.5 Inner Pore through III/IV Fenestrations Is Paved by Aromatic and Polar Residues
3.5. State-Dependent Energy Barrier for TB-Bound MEX Egress through Fenestration III/IV
3.6. Relations between the Half-Voltage of VSDIII Activation (aV0.5) and TB by MEX
3.7. Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rudy, Y.; Silva, J.R. Computational biology in the study of cardiac ion channels and cell electrophysiology. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2006, 39, 57–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Tonggu, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Banh, R.; Pomes, R.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structural basis for voltage-sensor trapping of the cardiac sodium channel by a deathstalker scorpion toxin. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Shi, H.; Tonggu, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Lenaeus, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Yoshioka, C.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structure of the Cardiac Sodium Channel. Cell 2020, 180, 122–134.e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Wu, T.; Huang, G.; Wu, K.; Lei, J.; Pan, X.; Yan, N. Structural Basis for Pore Blockade of the Human Cardiac Sodium Channel Nav 1.5 by the Antiarrhythmic Drug Quinidine*. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11474–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, G.; Huang, X.; Shen, Z.; Cao, Y.; Dong, M.; Lei, J.; et al. Comparative structural analysis of human Na(v)1.1 and Na(v)1.5 reveals mutational hotspots for sodium channelopathies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100066118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes, 3rd ed.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderlamd, MA, USA, 2001; p. 814. [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale, D.S.; McPhee, J.C.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A. Molecular determinants of state-dependent block of Na+ channels by local anesthetics. Science 1994, 265, 1724–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragsdale, D.S.; McPhee, J.C.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A. Common molecular determinants of local anesthetic, antiarrhythmic, and anticonvulsant block of voltage-gated Na+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9270–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.K.; Quan, C.; Wang, S.Y. Local anesthetic block of batrachotoxin-resistant muscle Na+ channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.K.; Russell, C.; Wang, S.Y. Mexiletine block of wild-type and inactivation-deficient human skeletal muscle hNav1.4 Na+ channels. J. Physiol. 2004, 554, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; Brown, J.; Sharp, E.M.; Clare, J.J.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A. Molecular determinants of voltage-dependent gating and binding of pore-blocking drugs in transmembrane segment IIIS6 of the Na(+) channel alpha subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; McPhee, J.C.; Idsvoog, D.; Pate, C.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A. Role of amino acid residues in transmembrane segments IS6 and IIS6 of the Na+ channel alpha subunit in voltage-dependent gating and drug block. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35393–35401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahern, C.A.; Eastwood, A.L.; Dougherty, D.A.; Horn, R. Electrostatic contributions of aromatic residues in the local anesthetic receptor of voltage-gated sodium channels. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, B. Local anesthetics: Hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J. Gen. Physiol. 1977, 69, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhova, I.; Tikhonov, D.B.; Zhorov, B.S. Access and binding of local anesthetics in the closed sodium channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Zhorov, B.S. Mechanism of sodium channel block by local anesthetics, antiarrhythmics, and anticonvulsants. J. Gen. Physiol. 2017, 149, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Lenaeus, M.J.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Fenestrations control resting-state block of a voltage-gated sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13111–13116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Munakata, T.; Sunami, A. Mexiletine Block of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Isoform- and State-Dependent Drug-Pore Interactions. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 95, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Mazzanti, A.; Voelker, T.L.; Hou, P.; Moreno, J.D.; Angsutararux, P.; Naegle, K.M.; Priori, S.G.; Silva, J.R. Predicting Patient Response to the Antiarrhythmic Mexiletine Based on Genetic Variation. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Makita, N.; Sunami, A.; Sakurada, H.; Shirai, N.; Yokoi, H.; Kimura, A.; Tohse, N.; Hiraoka, M.; Kitabatake, A. Unexpected mexiletine responses of a mutant cardiac Na+ channel implicate the selectivity filter as a structural determinant of antiarrhythmic drug access. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisedchaisri, G.; Tonggu, L.; McCord, E.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Wang, L.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Resting-State Structure and Gating Mechanism of a Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel. Cell 2019, 178, 993–1003.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, T.; Rohou, A.; Arthur, C.P.; Tzakoniati, F.; Wong, E.; Estevez, A.; Kugel, C.; Franke, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Structural Basis of Nav1.7 Inhibition by a Gating-Modifier Spider Toxin. Cell 2019, 176, 1238–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garden, D.P.; Zhorov, B.S. Docking flexible ligands in proteins with a solvent exposure- and distance-dependent dielectric function. J. Comput. Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Zhorov, B.S. Architecture and pore block of eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channels in view of NavAb bacterial sodium channel structure. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Scheraga, H.A. Monte Carlo-minimization approach to the multiple-minima problem in protein folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6611–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, S.J.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A.; Singh, U.C.; Chio, C.; Alagona, G.; Profeta, S.; Weiner, P.K. A new force field for molecular mechanical simulation of nucleic acids and proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 765–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, S.J.; Kollman, P.A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Case, D.A. An All Atom Force-Field for Simulations of Proteins and Nucleic-Acids. J. Comput. Chem. 1986, 7, 230–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, M.J.S.; Zoebisch, E.G.; Healy, E.F.; Stewart, J.J.P. AM1: A New General Purpose Quantum Mechanical Model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 3902–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.L.; Pettitt, M.; Karplus, M. Structural and energetic effects of truncating long ranged interactions in ionic and polar fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83, 5897–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Natuzzi, F.; Lentini, G.; Franchini, C.; Tortorella, V.; Conte Camerino, D. Stereoselective effects of mexiletine enantiomers on sodium currents and excitability characteristics of adult skeletal muscle fibers. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1995, 352, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhorov, B.S.; Du, Y.; Song, W.; Luo, N.; Gordon, D.; Gurevitz, M.; Dong, K. Mapping the interaction surface of scorpion beta-toxins with an insect sodium channel. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 2843–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaytseva, A.K.; Boitsov, A.S.; Kostareva, A.A.; Zhorov, B.S. Possible Interactions of Extracellular Loop IVP2-S6 With Voltage-Sensing Domain III in Cardiac Sodium Channel. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 742508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevitz, M.; Zhorov, B.S.; Dong, K. Allosteric interactions among voltage-sensor modules of sodium channels probed by scorpion toxin modifiers. J. Neurobiol. Physiol. 2022, 4, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhorov, B.S.; Tikhonov, D.B. Potassium, sodium, calcium and glutamate-gated channels: Pore architecture and ligand action. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 782–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaeus, M.J.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Ing, C.; Ramanadane, K.; Pomes, R.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structures of closed and open states of a voltage-gated sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3051–E3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Zhorov, B.S. Predicting Structural Details of the Sodium Channel Pore Basing on Animal Toxin Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.B.; Tao, X.; Campbell, E.B.; MacKinnon, R. Atomic structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel in a lipid membrane-like environment. Nature 2007, 450, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhova, I.; Zhorov, B.S. A homology model of the pore domain of a voltage-gated calcium channel is consistent with available SCAM data. J. Gen. Physiol. 2010, 135, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Satar, G.; Hu, Z.; Nauen, R.; He, S.Y.; Zhorov, B.S.; Dong, K. Molecular evidence for dual pyrethroid-receptor sites on a mosquito sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11785–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Bruhova, I.; Zhorov, B.S. Atomic determinants of state-dependent block of sodium channels by charged local anesthetics and benzocaine. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 6027–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhorov, B.S. Possible Mechanism of Ion Selectivity in Eukaryotic Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 2074–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, A.O.; Eberhardt, E.; Weidner, C.; Alzheimer, C.; Wallace, B.A.; Lampert, A. Bisphenol A binds to the local anesthetic receptor site to block the human cardiac sodium channel. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mi, J.; Lu, K.; Lu, Y.; Wang, K. Comparison of Gating Properties and Use-Dependent Block of Nav1.5 and Nav1.7 Channels by Anti-Arrhythmics Mexiletine and Lidocaine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.L.; Galue, A.; Meadows, L.; Ragsdale, D.S. A molecular basis for the different local anesthetic affinities of resting versus open and inactivated states of the sodium channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 55, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, A.; Budriesi, R.; Bruno, C.; Di Mola, A.; Defrenza, I.; Cavalluzzi, M.M.; Micucci, M.; Carocci, A.; Franchini, C.; Lentini, G. Searching for new antiarrhythmic agents: Evaluation of meta-hydroxymexiletine enantiomers. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 65, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Woltz, R.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Ren, L.; He, P.X.; Yu, S.D.; Liu, X.Q.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; Hu, D.; Chiamvimonvat, N.; et al. Gating Properties of Mutant Sodium Channels and Responses to Sodium Current Inhibitors Predict Mexiletine-Sensitive Mutations of Long QT Syndrome 3. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, V.; Harris, J.; Adams, R.; Nguyen, D.; Spiers, J.; Baudry, J.; Howell, E.E.; Hinde, R.J. A survey of aspartate-phenylalanine and glutamate-phenylalanine interactions in the protein data bank: Searching for anion-pi pairs. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Bruhova, I.; Garden, D.P.; Zhorov, B.S. State-dependent inter-repeat contacts of exceptionally conserved asparagines in the inner helices of sodium and calcium channels. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2015, 467, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Tikhonov, D.B.; Nomura, Y.; Dong, K.; Zhorov, B.S. Mutational analysis of state-dependent contacts in the pore module of eukaryotic sodium channels. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 652, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Talon, S.; De Bellis, M.; Desaphy, J.F.; Franchini, C.; Lentini, G.; Catalano, A.; Corbo, F.; Tortorella, V.; Conte-Camerino, D. Inhibition of skeletal muscle sodium currents by mexiletine analogues: Specific hydrophobic interactions rather than lipophilia per se account for drug therapeutic profile. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2003, 367, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroi, Y.; Chanda, B. Local anesthetics disrupt energetic coupling between the voltage-sensing segments of a sodium channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2009, 133, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisedchaisri, G.; Tonggu, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; McCord, E.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structural Basis for High-Affinity Trapping of the NaV1.7 Channel in Its Resting State by Tarantula Toxin. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 38–48.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheets, M.F.; Hanck, D.A. Molecular action of lidocaine on the voltage sensors of sodium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2003, 121, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcisio-Miranda, M.; Muroi, Y.; Chowdhury, S.; Chanda, B. Molecular mechanism of allosteric modification of voltage-dependent sodium channels by local anesthetics. J. Gen. Physiol. 2010, 136, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagneris, C.; DeCaen, P.G.; Naylor, C.E.; Pryde, D.C.; Nobeli, I.; Clapham, D.E.; Wallace, B.A. Prokaryotic NavMs channel as a structural and functional model for eukaryotic sodium channel antagonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8428–8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkosh, V.S.; Zhorov, B.S.; Tikhonov, D.B. Modeling interactions between blocking and permeant cations in the NavMs channel. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 780, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, E.J.; Zhu, W.; Schubert, A.R.; Voelker, T.; Varga, Z.; Silva, J.R. Regulation of Na(+) channel inactivation by the DIII and DIV voltage-sensing domains. J. Gen. Physiol. 2017, 149, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Liu, N.; Bloise, R.; Napolitano, C.; Priori, S.G. Gating properties of SCN5A mutations and the response to mexiletine in long-QT syndrome type 3 patients. Circulation 2007, 116, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschen-Ohm, M.P.; Capes, D.L.; Oelstrom, K.M.; Chanda, B. Multiple pore conformations driven by asynchronous movements of voltage sensors in a eukaryotic sodium channel. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capes, D.L.; Goldschen-Ohm, M.P.; Arcisio-Miranda, M.; Bezanilla, F.; Chanda, B. Domain IV voltage-sensor movement is both sufficient and rate limiting for fast inactivation in sodium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2013, 142, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Channel | Segment | Residue # |  |
| NavAb b | S4-S5, SS | 113 |  |
| hNav1.5 c | IS4-S5, IS5 | 232 | |
| IIS4-S5, IIS5 | 822 | ||
| IIIS4-S5, IIIS5 | 1317 | ||
| IVS4-S5, IVS5 | 1640 | ||
 | |||
| NavAb | P | 163 |  |
| hNav1.5 | IP | 358 | |
| IIP | 884 | ||
| IIIP | 1405 | ||
| IVP | 1697 | ||
 | |||
| NavAb | S6 | 192 |  |
| hNav1.5 | IS6 | 387 | |
| IIS6 | 913 | ||
| IIIS6 | 1444 | ||
| IVS6 | 1746 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhorov, B.S. Molecular Modeling of Cardiac Sodium Channel with Mexiletine. Membranes 2022, 12, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121252
Zhorov BS. Molecular Modeling of Cardiac Sodium Channel with Mexiletine. Membranes. 2022; 12(12):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121252
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhorov, Boris S. 2022. "Molecular Modeling of Cardiac Sodium Channel with Mexiletine" Membranes 12, no. 12: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121252
APA StyleZhorov, B. S. (2022). Molecular Modeling of Cardiac Sodium Channel with Mexiletine. Membranes, 12(12), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121252






