Comparative Study of 4-Aminophenol Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Emulsion Liquid Membranes Using Acid and Basic Type 1 Facilitations: Optimisation and Kinetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Optimisation of 4-Aminophenol Removal
2.4. Kinetic Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimisation of 4-Aminophenol Removal Removal Using Acid and Basic Type 1 Facilitations
3.2. Comparison of Acid and Basic Type 1-Facilitated Transports of 4-Aminophenol
3.3. 4-Aminophenol Removal Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; Meyer, M.T.; Thurman, E.M.; Zaugg, S.D.; Buxton, B.H.T. Pharmaceuticals, hormones and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams 1999–2000: A national reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, J.V.; Karthik, R.; Chen, S.M.; Saravanakumar, K.; Govindasamy, M.; Muthuraj, V. Novel hydrothermal synthesis of MoS2 nanocluster structure for sensitive electrochemical detection of human and environmental hazardous pollutant 4-aminophenol. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 40399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Hamayun, M.; Ahmed, S. Degradation of 4-aminophenol by newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. strain ST-4. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Paliwal, M.; Ameta, R.; Khandelwal, R.C. Degradation of organic effluents containing wastewater by photo-Fenton oxidation process. Ind. J. Chem. 2008, 47, 1681–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, J.F.; Kuo, C.H.; Deshore, G.M.; Hoefle, D.; Bernstein, J.; Hook, J.B. The role of p-aminophenol in acetaminophen induced nephrotoxicity: Effect of bis(p-nitrophenyl)phosphate on acetaminophen and p-aminophenol nephrotoxicity and metabolism. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1985, 69, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, R.C.; Terneus, M.V.; Kiningham, K.K.; Valentovic, M. Time-dependent effect of p-Aminophenol (PAP) toxicity in renal slices and development of oxidative stress. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 209, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, D.A.; Cordova, J.S.; Smith, L.G.; Son, H.J.; Biris, A.S. Characterization of aminophenol isomer adsorption on silver nanostructures. Vibrat. Spectr. 2011, 55, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, T.; Ahsin, A.; Ullah, F.; Mahmood, T.; Ayub, K. Adsorption mechanism of p- aminophenol over silver-graphene composite: A first principles study. J. Molec. Liquids 2021, 341, 117415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, K.; Dixit, U.; Agarwal, A.; Bhat, R.A. Effective removal of 4-Aminophenol from aqueous environment by pea (Pisum sativum) shells activated with sulfuric acid: Characterization, isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.; Yu, X. Electrochemical oxidation of para-aminophenol with rare earth doped lead dioxide electrodes: Kinetics modeling and mechanism. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, S.; Risheng, Y.; Yahua, Y.; Shengsong, D.; Wenxia, G. Degradation of 4-aminophenol by hydrogen peroxide oxidation using enzyme from Serratia marcescens as catalyst. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2007, 1, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Amiri, M. CuO supported Clinoptilolite towards solar photocatalytic degradation of p-aminophenol. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Ghime, D.; Lunia, D. Degradation of p-aminophenol by Fenton’s process. Influence of operational parameters. Environ. Protec. Eng. 2017, 43, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratiu, C.; Manea, F.; Lazau, C.; Grozescu, I.; Radovan, C.; Schoonman, J. Electrochemical oxidation of p-aminophenol from water with boron-doped diamond anodes and assisted photocatalytically by TiO2-supported zeolita. Desalination 2010, 260, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Song, S.; Ying, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, J. p-Aminophenol degradation by ozonation combined with sonolysis: Operating conditions influence and mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajerani, M.; Mehrvar, M.; Ein-Mozaffari, E. Optimization of aqueous p-aminophenol degradation by external-loop airlift sonophotoreactor using response surface methodology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.B.; Bhandari, V.M. Solvent-assisted cavitation for enhanced removal of organic pollutants—Degradation of 4-aminophenol. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehtash, M.; Fournier-Salaün, M.C.; Dimitrov, K.; Salaün, P.; Saboni, A. Phenol removal from aqueous media by pertraction using vegetable oil as a liquid membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 15, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Duan, H.; Shi, D.; Yang, R.; Wang, S.; Guo, H. Facilitated transport of phenol through supported liquid membrane containing bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfoxide (BESO) as the carrier. Chem. Eng. Process. Proc. Intens. 2015, 93, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devulapalli, R.; Jones, F. Separation of aniline from aqueous solutions using emulsion liquid membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 1999, 70, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J. Removal of aniline from wastewater using hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 22, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislik, V.S. Introduction, general description, definitions and classification. Overview. In Liquid Membranes, 1st ed.; Kislik, V.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- León, G. Facilitated transport. In Encyclopedia of Membranes, 1st ed.; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 763–764. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, N.; Shi, Y.; Su, Y.F. A mass transfer model for type I facilitated transport in liquid membranes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 4365–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Long, R.L., Jr. Phenol removal by emulsion liquid membrane: A modified diffusion model. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1997, 156, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Jiang, Y.; Kun, S.C. A general mass transfer model for liquid surfactant membrane. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 433–441. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P. Science and statistics. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1976, 71, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, I.N. Physical Chemistry, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 515–589. [Google Scholar]
- Behnajady, M.A.; Modirshahla, N.; Ghanbary, F. A kinetic model for the decolorization of C.I. Acid Yellow 23 by Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of phase change. I General theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1940, 7, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laki, S.; Kargari, A. Extraction of silver ions from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2016, 2, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Abbassian, K.; Kargari, A. Modification of membrane formulation for stabilization of emulsion liquid membrane for extraction of phenol from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3926–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Kusumastuti, A.; Derek, C.J.C.; Ooi, B.S. Emulsion liquid membrane for heavy metal removal: An overview on emulsion stabilization and destabilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargari, A.; Kaghazchi, T.; Soleimani, M. Role of emulsifier in the extraction of gold (III) ions from aqueous solutions using the emulsion liquid membrane technique. Desalination 2004, 162, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebizadeh, P.; Javanshir, S.; Ahmadi, A. Zinc extraction from a bioleaching solution by emulsion liquid membrane technique. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Mahajani, V.V. Application of liquid emulsion membrane (LEM) process for enrichment of Molybdenum from aqueous solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 201, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Kim, H.C. Batch and continuous separation of acetic acid from succinic acid in a feed solution with high concentrations of carboxylic acids by emulsion liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 367, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouchi, S.; Hamdaoui, O. Acetaminophen extraction by emulsion liquid membrane using Aliquat 336 as extractant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 129, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguel, S.; Samar, M.H. Removal of Europium(III) from water by emulsion liquid membrane using Cyanex 302 as a carrier. Desal. Water Treat. 2019, 165, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikes, P. A Guide Book to Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Longman Publishing Group: London, UK, 1981; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Caroll, F.A. Perspectives on Structure and Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 385–404. [Google Scholar]

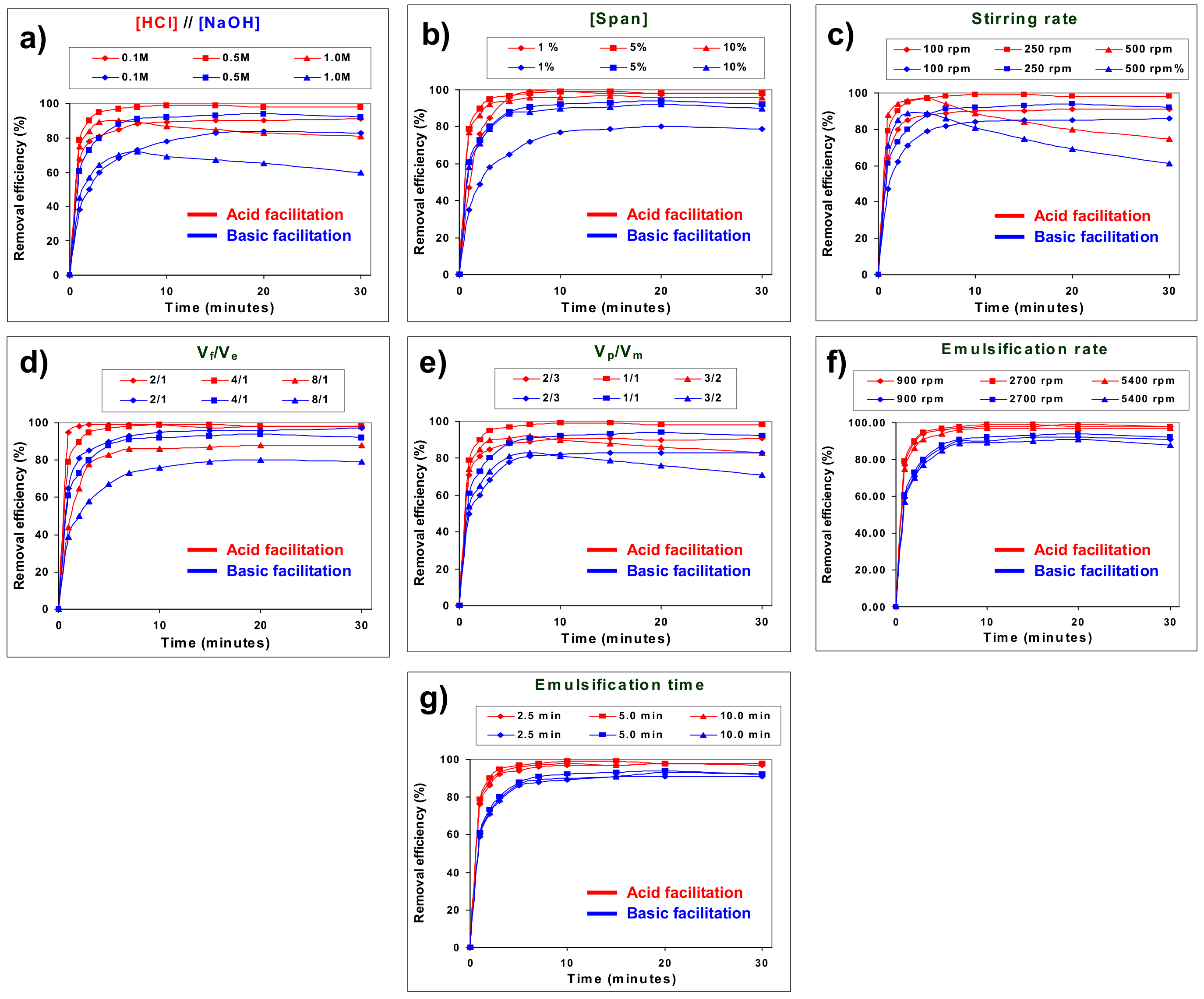
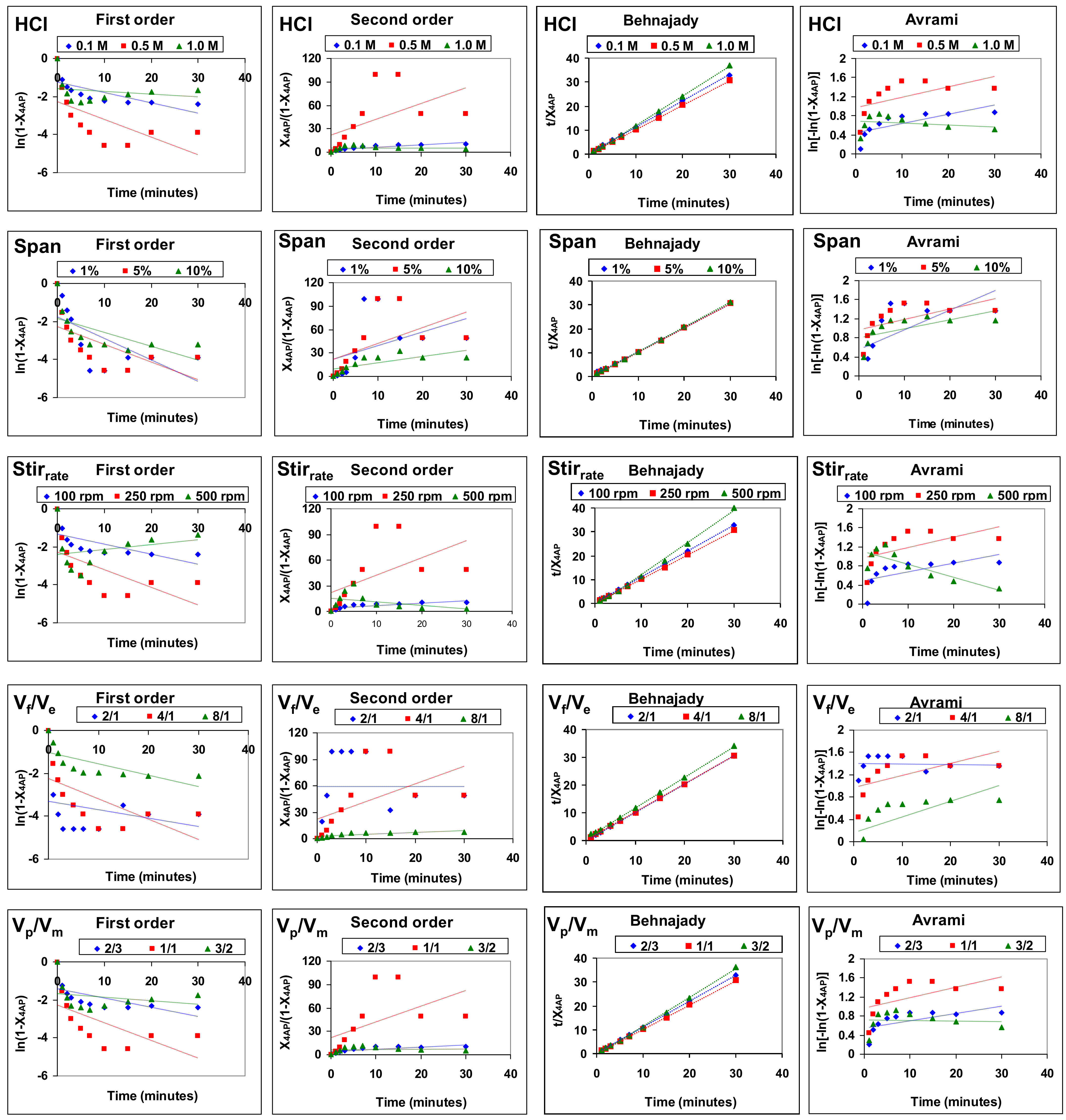
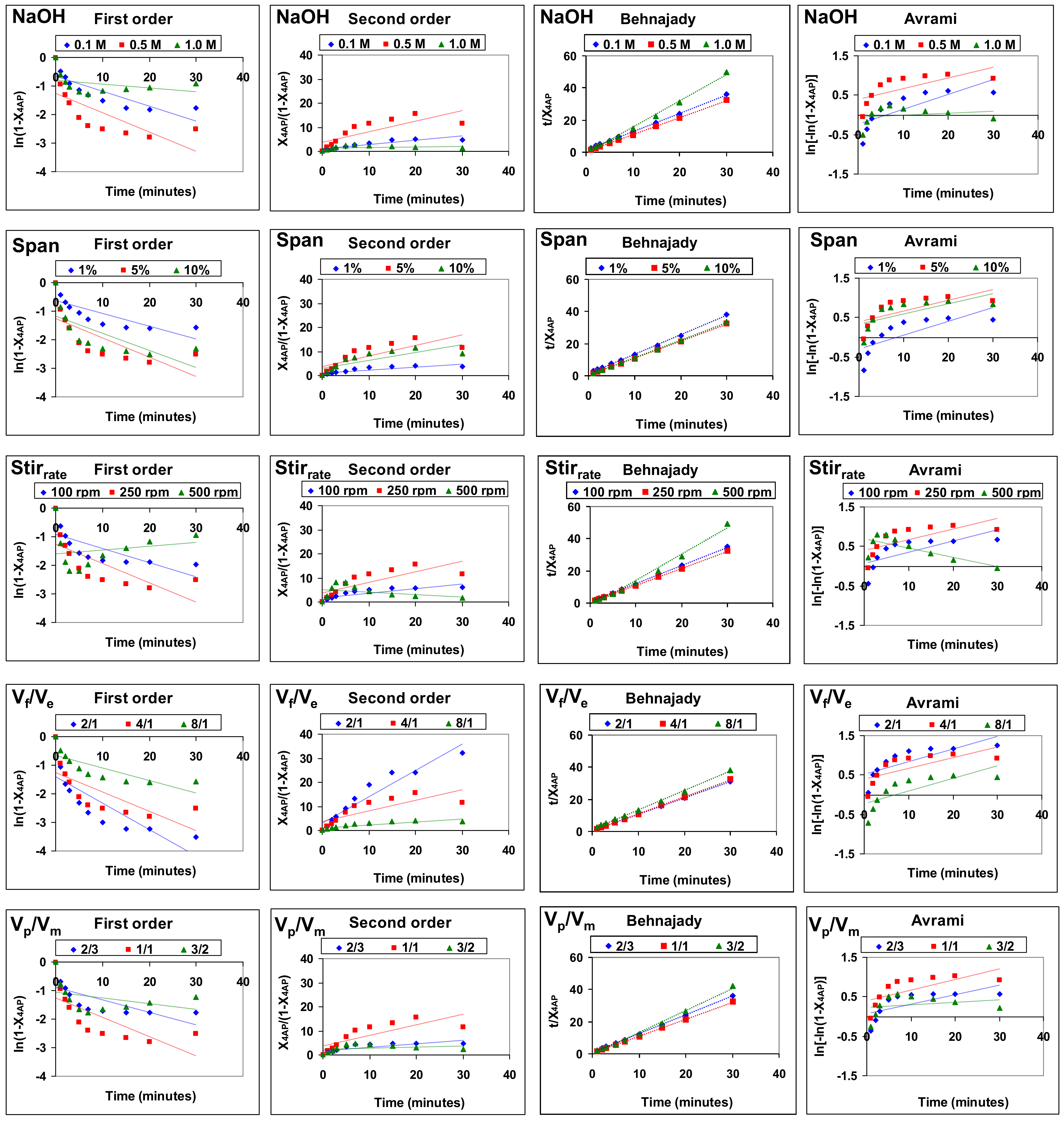
| Acid Type 1 Facilitation | Basic Type 1 Facilitation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter/Value | First Order | Second Order | Behnajady | Avrami | Parameter/Value | First Order | Second Order | Behnajady | Avrami | ||
| [HCl] | 0.1 M | 0.4911 | 0.7335 | 1.0000 | 0.5641 | [HCl] | 0.1 M | 0.6871 | 0.8072 | 0.9992 | 0.6190 |
| 0.5 M | 0.3873 | 0.2958 | 0.9999 | 0.3466 | 0.5 M | 0.5160 | 0.6315 | 0.9995 | 0.4845 | ||
| 1.0 M | 0.0408 | 0.0006 | 0.9990 | 0.0472 | 1.0 M | 0.1249 | 0.0913 | 0.9943 | 0.0365 | ||
| [Span 80] | 1% | 0.4265 | 0.2001 | 0.9999 | 0.3540 | [Span 80] | 1 % | 0.6274 | 0.7368 | 0.9990 | 0.5569 |
| 5% | 0.3873 | 0.2958 | 0.9999 | 0.3466 | 5 % | 0.5160 | 0.6315 | 0.9995 | 0.4845 | ||
| 10% | 0.4119 | 0.5281 | 0.9999 | 0.4079 | 10 % | 0.4970 | 0.6252 | 0.9995 | 0.4633 | ||
| Stirrate | 100 rpm | 0.4224 | 0.6262 | 0.9999 | 0.4127 | Stirrate | 100 rpm | 0.5444 | 0.70386 | 0.9998 | 0.4928 |
| 250 rpm | 0.3873 | 0.2958 | 0.9999 | 0.3466 | 250 rpm | 0.5160 | 0.6315 | 0.9995 | 0.4845 | ||
| 500 rpm | 0.0606 | 0.1611 | 0.9959 | 0.7028 | 500 rpm | 0.0342 | 0.1240 | 0.9883 | 0.5758 | ||
| Vf/Vemul | 2/1 | 0.0738 | 0.0001 | 0.9999 | 0.0034 | Vf/Vemul | 2/1 | 0.6540 | 0.9250 | 1.0000 | 0.6125 |
| 4/1 | 0.3873 | 0.2958 | 0.9999 | 0.3466 | 4/1 | 0.5160 | 0.6315 | 0.9995 | 0.4845 | ||
| 8/1 | 0.4998 | 0.6572 | 0.9995 | 0.4036 | 8/1 | 0.6171 | 0.7364 | 0.9993 | 0.5730 | ||
| Vm/Vp | 2/3 | 0.3898 | 0.5691 | 0.9999 | 0.4446 | Vm/Vp | 2/3 | 0.4968 | 0.6161 | 0.9996 | 0.4792 |
| 1/1 | 0.3873 | 0.2958 | 0.9999 | 0.3466 | 1/1 | 0.5160 | 0.6315 | 0.9995 | 0.4845 | ||
| 3/2 | 0.0589 | 0.0058 | 0.9986 | 0.0043 | 3/2 | 0.1387 | 0.0852 | 0.9950 | 0.0571 | ||
| Acid type 1 Facilitation | Basic Type 1 Facilitation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter/Value | Parameter a | V0 (1/a) | Parameter b | Xmax (1/b) | Parameter/Value | Parameter a | V0 (1/a) | Parameter b | Xmax (1/b) | ||
| [HCl] | 0.1 M | 0.4076 | 2.4534 | 1.0862 | 0.9206 | [HCl] | 0.1 M | 1.5158 | 0.6597 | 1.1374 | 0.8792 |
| 0.5 M | 0.1107 | 9.0334 | 1.0131 | 0.9871 | 0.5 M | 0.4240 | 2.3585 | 1.0559 | 0.9435 | ||
| 1.0 M | 0.4290 | 2.3310 | 1.2327 | 0.8112 | 1.0 M | 0.7368 | 1.3572 | 1.6297 | 0.6136 | ||
| [Span 80] | 1% | 0.1125 | 8.8889 | 1.0141 | 0.9861 | [Span 80] | 1% | 1.4534 | 0.6880 | 1.1198 | 0.8349 |
| 5% | 0.1107 | 9.0334 | 1.0131 | 0.9871 | 5% | 0.4240 | 2.3585 | 1.0559 | 0.9435 | ||
| 10% | 0.1578 | 6.3371 | 1.0327 | 0.9683 | 10% | 0.4442 | 2.2512 | 1.0829 | 0.9234 | ||
| Stirrate | 100 rpm | 0.3129 | 3.1959 | 1.0865 | 0.9204 | Stirrate | 100 rpm | 0.7832 | 1.2678 | 1.1329 | 0.8827 |
| 250 rpm | 0.1107 | 9.0334 | 1.0131 | 0.9871 | 250 rpm | 0.4240 | 2.3585 | 1.0559 | 0.9435 | ||
| 500 rpm | −1.2361 | - | 1.3356 | 0.7487 | 500 rpm | −2.1923 | - | 1.6251 | 0.6153 | ||
| Vf/Vemul | 2/1 | 0.0242 | 41.3223 | 1.0021 | 0.9979 | Vf/Vemul | 2/1 | 0.4565 | 2.1906 | 1.0153 | 0.9849 |
| 4/1 | 0.1107 | 9.0334 | 1.0131 | 0.9871 | 4/1 | 0.4240 | 2.3585 | 1.0559 | 0.9435 | ||
| 8/1 | 0.6780 | 1.4749 | 1.1069 | 0.9034 | 8/1 | 1.3214 | 0.7456 | 0.2945 | 0.830. | ||
| Vm/Vp | 2/3 | 0.2410 | 1.0908 | 1.0908 | 0.9168 | Vm/Vp | 2/3 | 0.6886 | 1.4522 | 1.1732 | 0.8524 |
| 1/1 | 0.1107 | 9.0334 | 1.0131 | 0.9871 | 1/1 | 0.4240 | 2.3585 | 1.0559 | 0.9435 | ||
| 3/2 | 0.4028 | 2.4826 | 1.1970 | 0.8354 | 3/2 | 0.5052 | 1.9794 | 1.3774 | 0.7260 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
León, G.; Otón, J.; Hidalgo, A.M.; Saavedra, M.I.; Miguel, B. Comparative Study of 4-Aminophenol Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Emulsion Liquid Membranes Using Acid and Basic Type 1 Facilitations: Optimisation and Kinetics. Membranes 2022, 12, 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121213
León G, Otón J, Hidalgo AM, Saavedra MI, Miguel B. Comparative Study of 4-Aminophenol Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Emulsion Liquid Membranes Using Acid and Basic Type 1 Facilitations: Optimisation and Kinetics. Membranes. 2022; 12(12):1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121213
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón, Gerardo, Juliana Otón, Asunción María Hidalgo, María Isabel Saavedra, and Beatriz Miguel. 2022. "Comparative Study of 4-Aminophenol Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Emulsion Liquid Membranes Using Acid and Basic Type 1 Facilitations: Optimisation and Kinetics" Membranes 12, no. 12: 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121213
APA StyleLeón, G., Otón, J., Hidalgo, A. M., Saavedra, M. I., & Miguel, B. (2022). Comparative Study of 4-Aminophenol Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Emulsion Liquid Membranes Using Acid and Basic Type 1 Facilitations: Optimisation and Kinetics. Membranes, 12(12), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121213







