Formation of Organic Fouling during Membrane Desalination: The Effect of Divalent Cations and the Use of an Online Visual Monitoring Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Setup of the Lab-Scale RO System
2.3. Fouling Experiments
2.4. Image Processing and Analysis
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formation of Membrane Fouling
3.1.1. The Effect of DOM Concentration on Fouling Formation
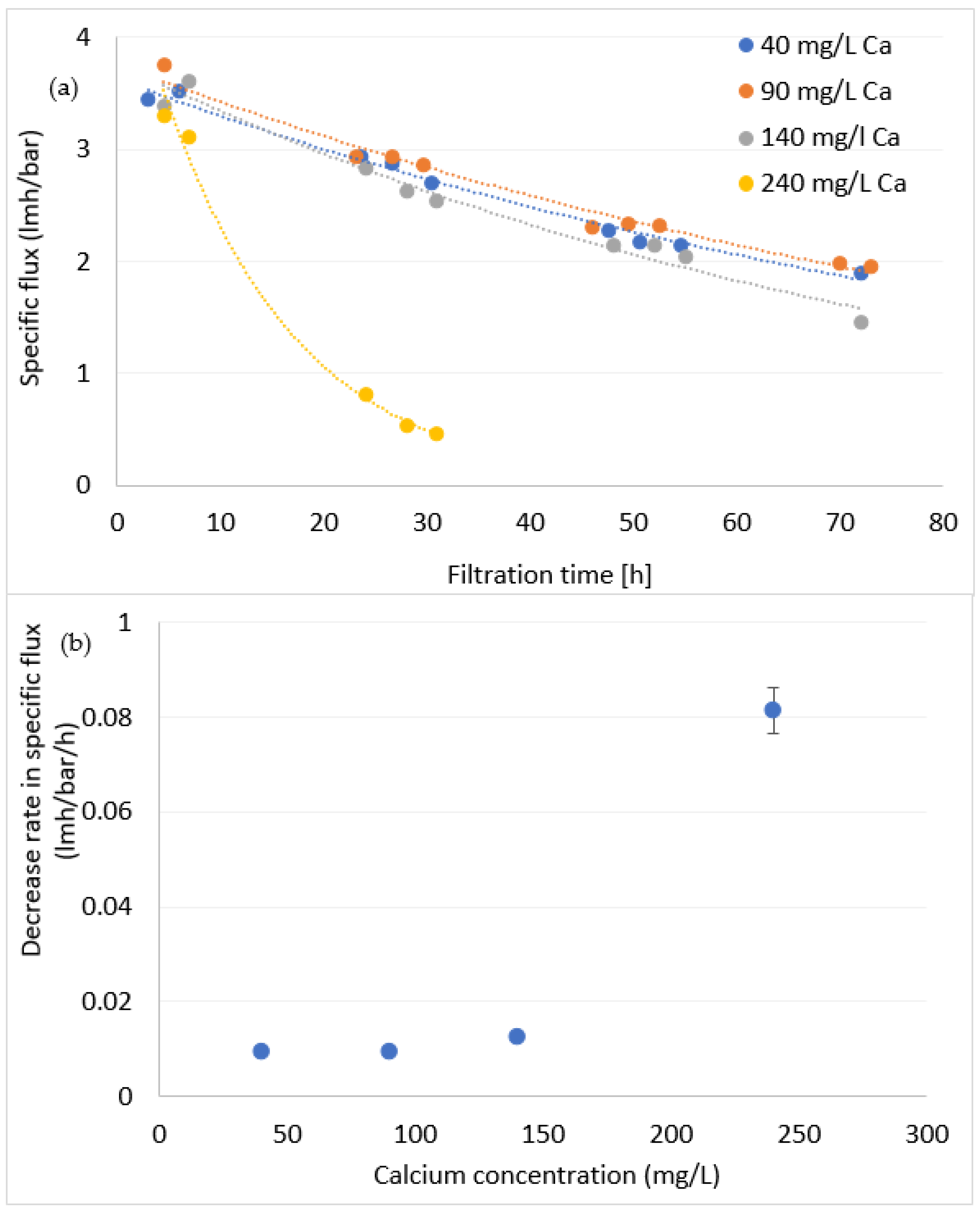
3.1.2. The Combined Effect of DOM and Calcium on Fouling Formation
3.1.3. The Effect of Strontium, Barium and Iron on Formation of Organic Fouling
3.2. Online Visual Monitoring of Fouling Formation
4. Conclusions
- When divalent ions are at low concentrations, organic fouling is insignificant, even when DOM is at the upper range of groundwater concentrations (3.5 mgC/L).
- Of the divalent ions tested, calcium, iron and strontium were shown to enhance the formation of organic fouling, whereas barium did not affect fouling formation, likely due to its low affinity to dicarboxylate moieties in the DOM.
- Visual online monitoring of fouling formation was successful, using reference color-dots positioned on the spacer. In this system, membrane color change was continuously recorded and normalized to the reference color dots, thus eliminating interferences from lightning and other environmental factors.
- The normalized color showed high correlation to the decrease in specific flux and can be used in the future to monitor and predict fouling formation during membrane desalination at full-scale.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honarparvar, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Alborzi, A.; Afroz, K.; Reible, D. Frontiers of membrane desalination processes for brackish water treatment: A review. Membranes 2021, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutchkov, N. Desalination Engineering Planning and Design; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780071777162. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane fouling in desalination and its mitigation strategies. Desalination 2018, 425, 130–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Wallace, A.F.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. Mineral scaling in membrane desalination: Mechanisms, mitigation strategies, and feasibility of scaling-resistant membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Huang, C.; Pan, J.R. Characteristics of RO foulants in a brackish water desalination plant. Desalination 2008, 220, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karime, M.; Bouguecha, S.; Hamrouni, B. RO membrane autopsy of Zarzis brackish water desalination plant. Desalination 2008, 220, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-garcía, A.; Melián-martel, N.; Mena, V. Fouling characterization of RO membranes after 11 years of operation in a brackish water desalination plant. Desalination 2018, 430, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xu, X.; Johnson, D.; Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, P. Effectiveness and mechanisms of electromagnetic field on reverse osmosis membrane scaling control during brackish groundwater desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Nuez, I.; Carrascosa-Chisvert, M.D.; Santana, J.J. Simulations of BWRO systems under different feedwater characteristics. Analysis of operation windows and optimal operating points. Desalination 2020, 491, 114582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshami, A.; Taylor, T.; Ismail, N.; Buelke, C.; Schultz, L. RO system scaling with focus on the concentrate line: Current challenges and potential solutions. Desalination 2021, 520, 115370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, M.N.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Dusseldorp, J.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D.; van der Meer, W.G.J. Effectiveness of antiscalants in preventing calcium phosphate scaling in reverse osmosis applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 623, 119090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanasiou, A.; Karabelas, A.J.; Mitrouli, S.T. Incipient membrane scaling in the presence of polysaccharides during reverse osmosis desalination in spacer-filled channels. Desalination 2021, 500, 114821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geluwe, S.; Braeken, L.; Van der Bruggen, B. Ozone oxidation for the alleviation of membrane fouling by natural organic matter: A review. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3551–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Ang, W.S.; Elimelech, M. Fouling of reverse osmosis membranes by hydrophilic organic matter: Implications for water reuse. Desalination 2006, 187, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tong, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Ikuno, N.; Ishii, K.; Hu, H. Ozonation as an efficient pretreatment method to alleviate reverse osmosis membrane fouling caused by complexes of humic acid and calcium ion. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; He, D.Q.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.Q. Probing the roles of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in humic acids-induced ultrafiltration membrane fouling using an integrated approach. Water Res. 2015, 81, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Elimelech, M. Natural organic matter fouling and chemical cleaning of nanofiltration membranes. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2004, 4, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.S. Factors affecting natural organic matter (NOM) and scaling fouling in NF membranes: A review. Desalination 2010, 259, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Carvajal, T.; Bovet, N.; Bechgaard, K.; Stipp, S.L.S.; Hassenkam, T. Effect of divalent cations on the interaction of carboxylate self-assembled monolayers. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16153–16163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musgrove, M.L. The occurrence and distribution of strontium in U.S. groundwater. Appl. Geochemistry 2021, 126, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.B.; Staubitz, W.W. Distribution and Source of Barium in Ground Water at Cattaraugus Indian Reservation, Southwestern New York; Water-Resources Investigations Report 84-4129; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1984.
- Weinrich, L.; Haas, C.N.; Lechevallier, M.W. Recent advances in measuring and modeling reverse osmosis membrane fouling in seawater desalination: A review. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2013, 3, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sim, L.N.; Chong, T.H.; Taheri, A.H.; Sim, S.T.V.; Lai, L.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G. A review of fouling indices and monitoring techniques for reverse osmosis. Desalination 2018, 434, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Rahardianto, A.; Gao, L.X.; Caro, X.P.; Giralt, J.; Rallo, R.; Christofides, P.D.; Cohen, Y. Fouling indicators for field monitoring the effectiveness of operational strategies of ultrafiltration as pretreatment for seawater desalination. Desalination 2018, 431, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, N.W.; Vogt, S.J.; Bucs, S.S.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Johns, M.L.; Fridjonsson, E.O. Novel magnetic resonance measurements of fouling in operating spiral wound reverse osmosis membrane modules. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.S.; Low, J.H.; Sim, L.N.; Webster, R.D.; Rice, S.A.; Fane, A.G.; Coster, H.G.L. In-situ monitoring of biofouling on reverse osmosis membranes: Detection and mechanistic study using electrical impedance spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 518, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushaban, A.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Kapala, M.; Pastorelli, D.; Schippers, J.C.; Mondal, S.; Goueli, S.; Kennedy, M.D. Monitoring biofouling potential using ATP-based bacterial growth potential in SWRO pre-treatment of a full-scale plant. Membranes 2020, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchymiak, M.; Bartman, A.R.; Daltrophe, N.; Weissman, M.; Gilron, J.; Christofides, P.D.; Kaiser, W.J.; Cohen, Y. Brackish water reverse osmosis ( BWRO ) operation in feed flow reversal mode using an ex situ scale observation detector (EXSOD). J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 341, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdue, E.M.; Ritchie, J.D. Dissolved organic matter in freshwaters. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 5–9, 273–318. [Google Scholar]
- Rutlidge, H.; McDonough, L.K.; Oudone, P.; Andersen, M.S.; Meredith, K.; Chinu, K.; Peterson, M.; Baker, A. Characterisation of groundwater dissolved organic matter using LC[sbnd]OCD: Implications for water treatment. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehant, A.; Bonnelye, V.; Perez, M. Assessment of ultrafiltration as a pretreatment of reverse osmosis membranes for surface seawater desalination. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Hayashi, M.; Shimamura, K.; Matsuyama, H. Important fractions of organic matter causing fouling of seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) membranes. Desalination 2016, 390, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, I.; Wiesner, M.R.; Bele, C.; Coriton, G.; Djafer, M.; Cavard, J. Bench-scale assessment of pretreatment to reduce fouling of salt-rejecting membranes. Desalination 2006, 197, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. Chemical and physical aspects of natural organic matter (NOM) fouling of nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 132, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirbahman, A.; Olson, T.M. Deposition kinetics of humic matter-coated hematite in porous media in the presence of Ca2+. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Elimelech, M. Organic fouling and chemical cleaning of nanofiltration membranes: Measurements and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4683–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedd, K.; Coxon, C.; Misstear, B.; Daly, D.; Craig, M.; Mannix, A.; Hunter Williams, T. Assessing and Developing Natural Background Levels for Chemical Parameters in Irish Groundwater Identifying Pressures Developing Solutions; EPA Research Programme 2014–2020; Environmental Protection Agency: Wexford, Ireland, 2017.
- Rosenthal, E.; Weinberger, G.; Berkowitz, B.; Flexer, A.; Kronfeld, J. The Nubian Sandstone aquifer in the central and northern Negev, Israel: Delineation of the hydrogeological model under conditions of scarce data. J. Hydrol. 1992, 132, 107–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lester, Y.; Hazut, A.; Spanier, A. Formation of Organic Fouling during Membrane Desalination: The Effect of Divalent Cations and the Use of an Online Visual Monitoring Method. Membranes 2022, 12, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121177
Lester Y, Hazut A, Spanier A. Formation of Organic Fouling during Membrane Desalination: The Effect of Divalent Cations and the Use of an Online Visual Monitoring Method. Membranes. 2022; 12(12):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121177
Chicago/Turabian StyleLester, Yaal, Amit Hazut, and Assaf Spanier. 2022. "Formation of Organic Fouling during Membrane Desalination: The Effect of Divalent Cations and the Use of an Online Visual Monitoring Method" Membranes 12, no. 12: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121177
APA StyleLester, Y., Hazut, A., & Spanier, A. (2022). Formation of Organic Fouling during Membrane Desalination: The Effect of Divalent Cations and the Use of an Online Visual Monitoring Method. Membranes, 12(12), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121177







