Feasibility of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride) Polymeric Network Hydrogel as Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
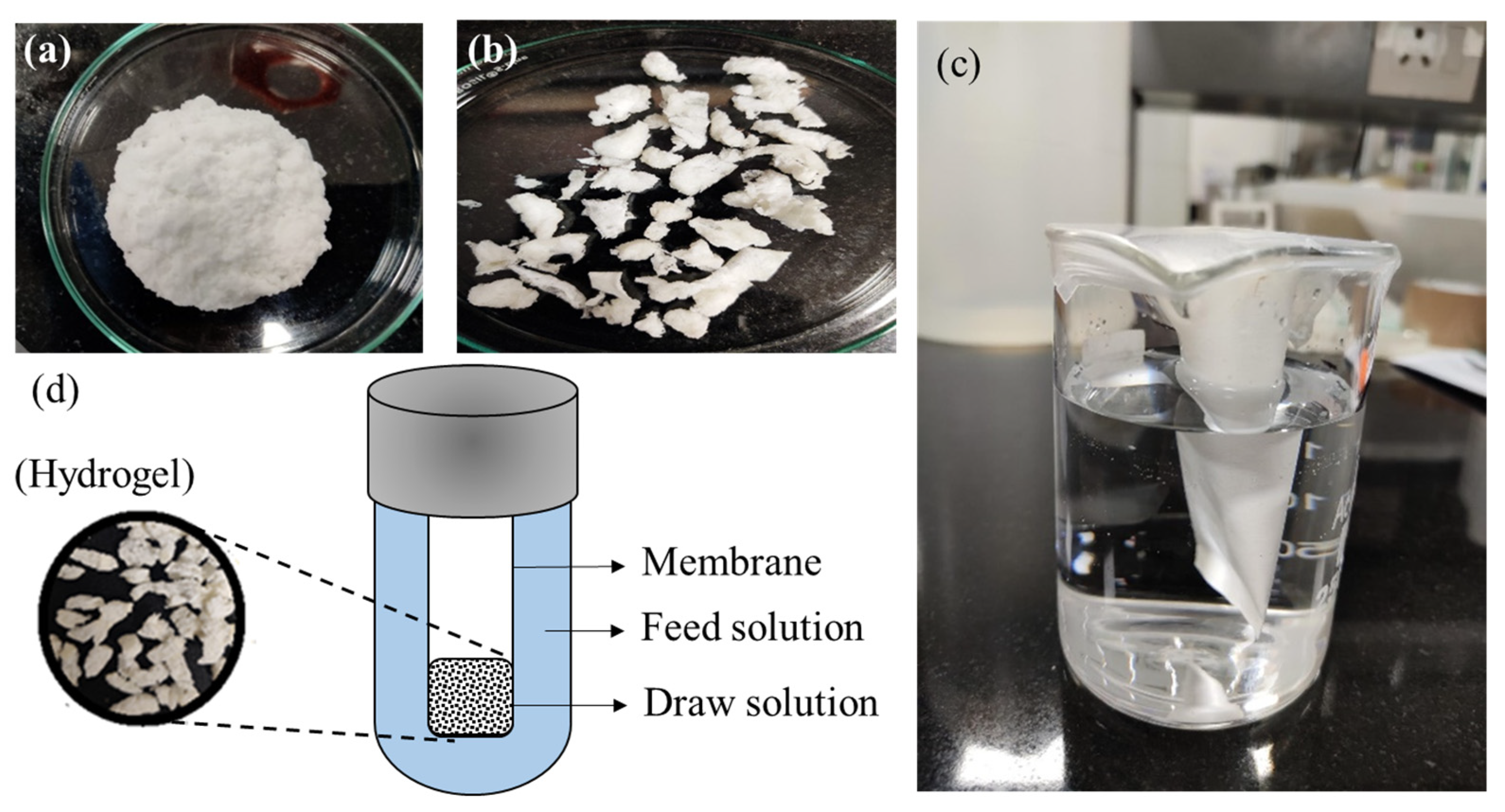
2.2. Synthesis of Hydrogel
2.3. Characterization of Hydrogel
2.4. The Swelling Ratio of Hydrogel
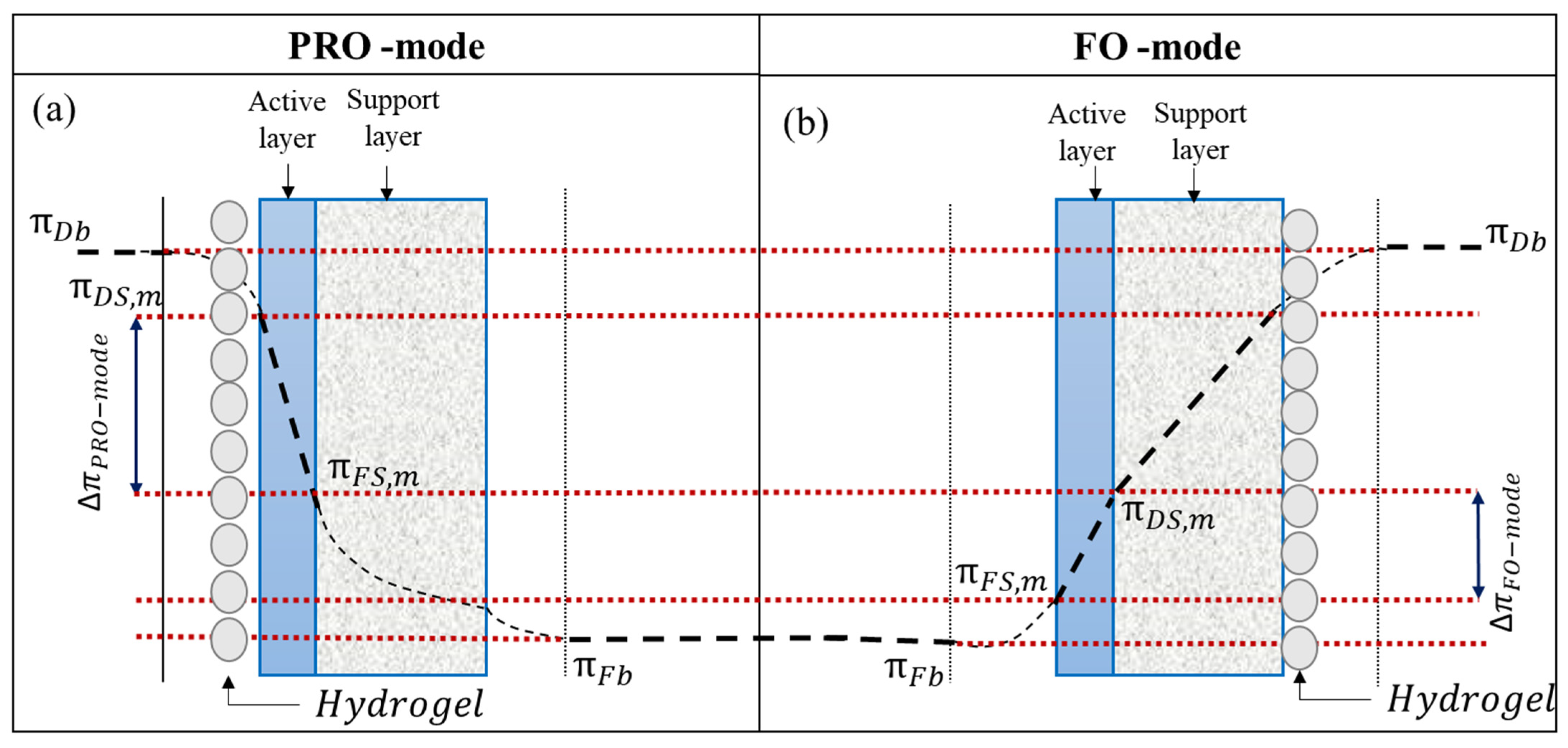
2.5. FO Performance
2.6. Hydrogel Stability Test
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.1.1. Membrane’s Characterization
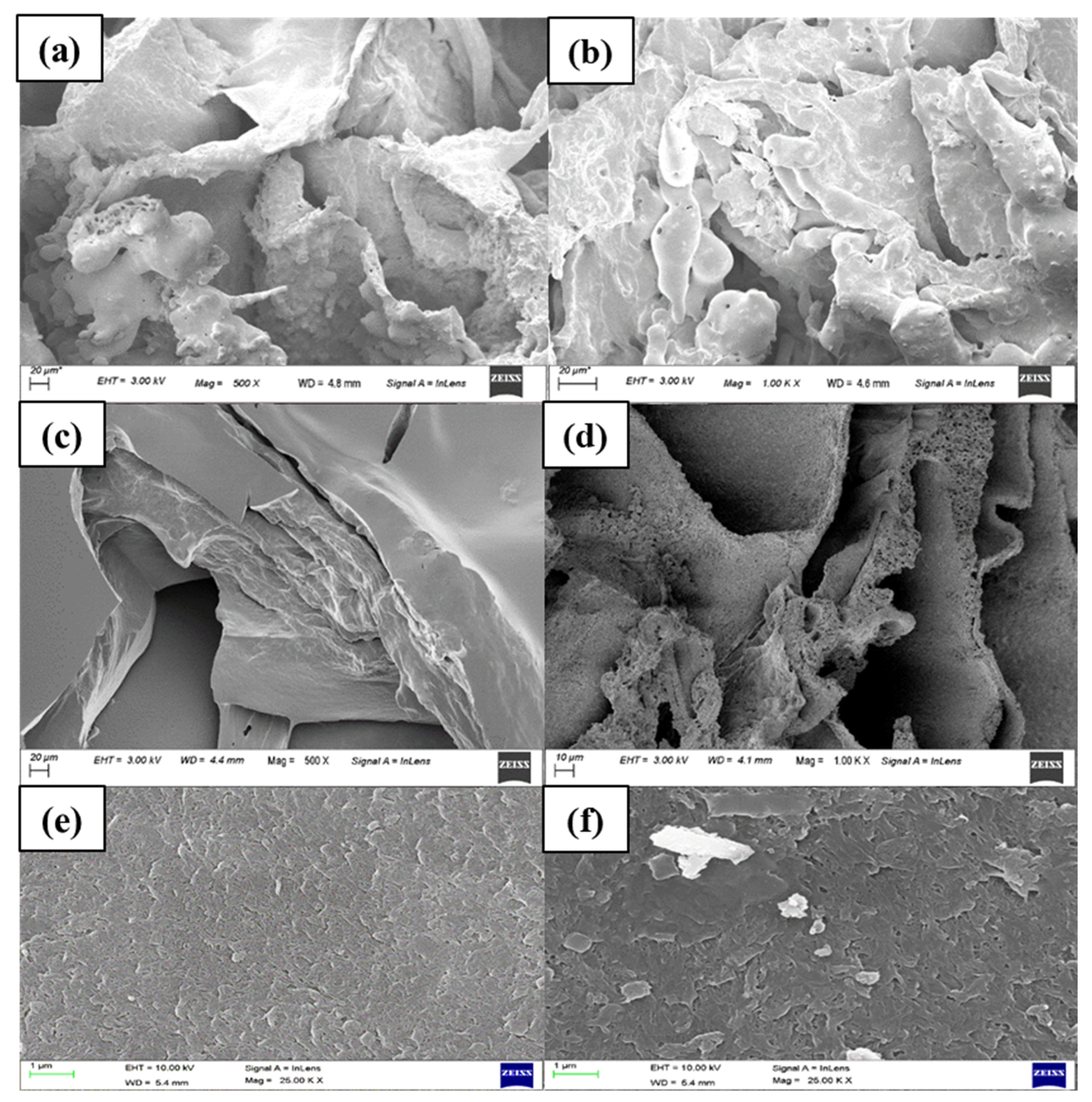
3.1.2. Morphological Characterization of the Synthesized Hydrogel
3.2. Swelling Characteristics of the Hydrogel
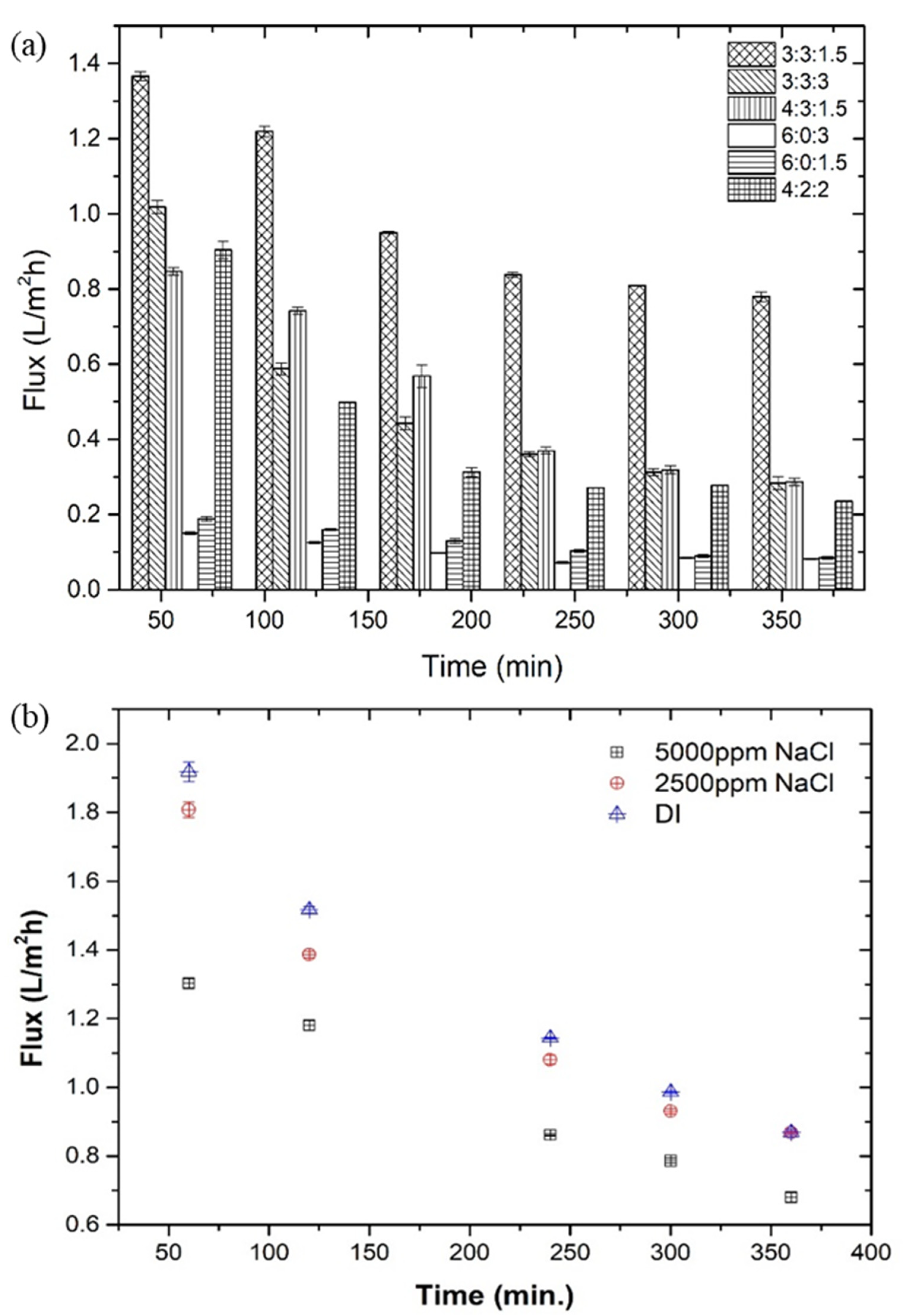
3.3. FO Performance of Hydrogel
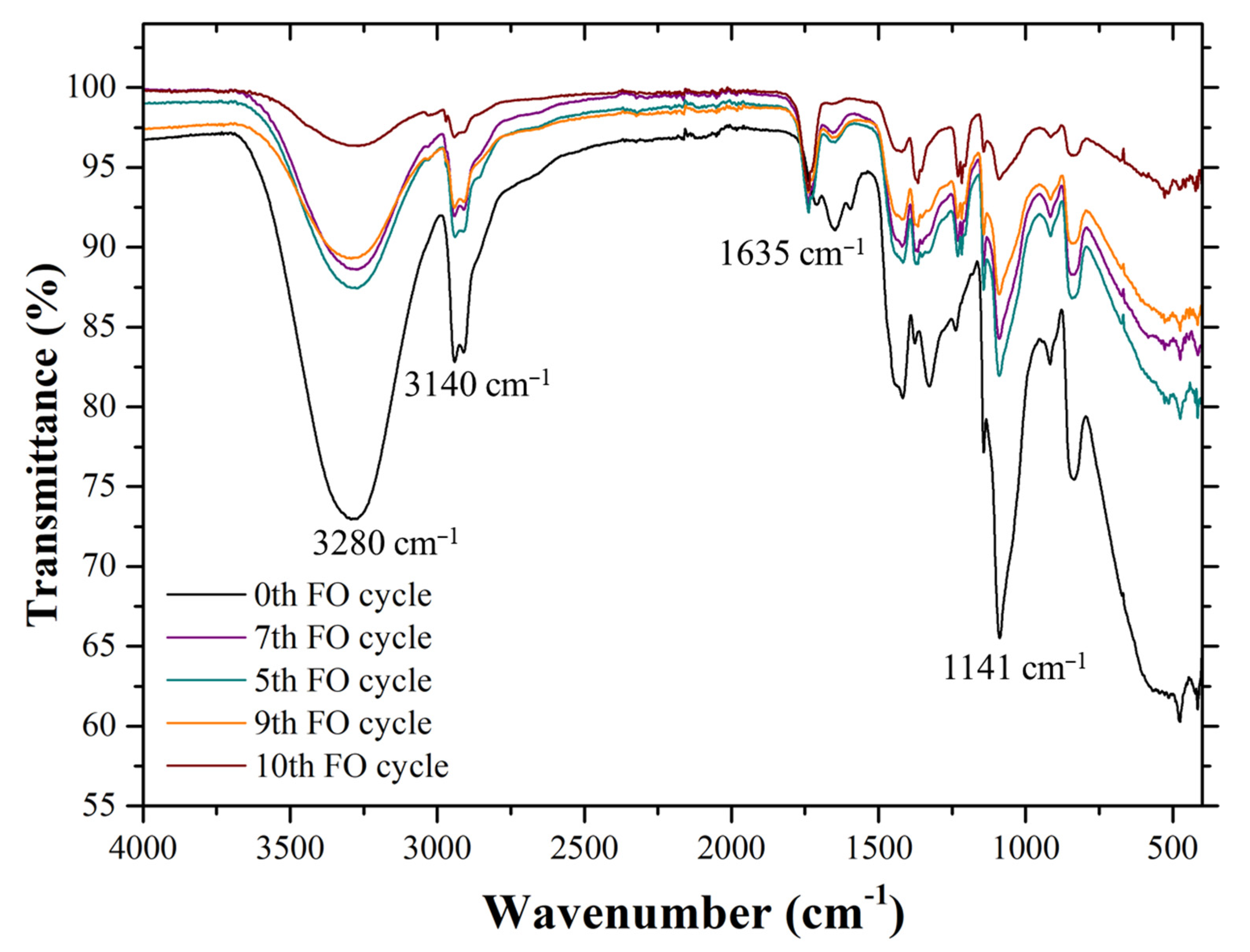
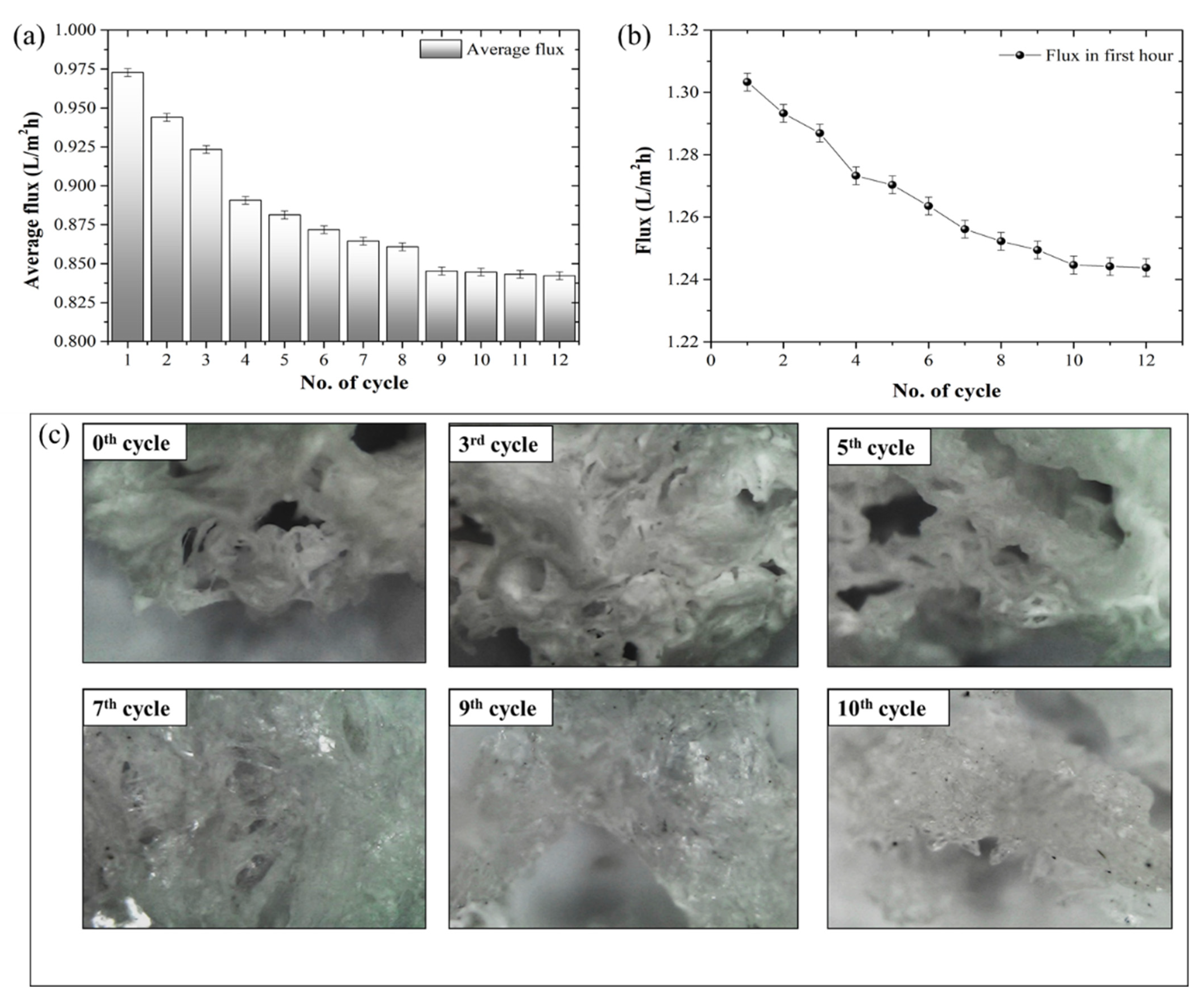
3.4. Hydrogel Stability Test
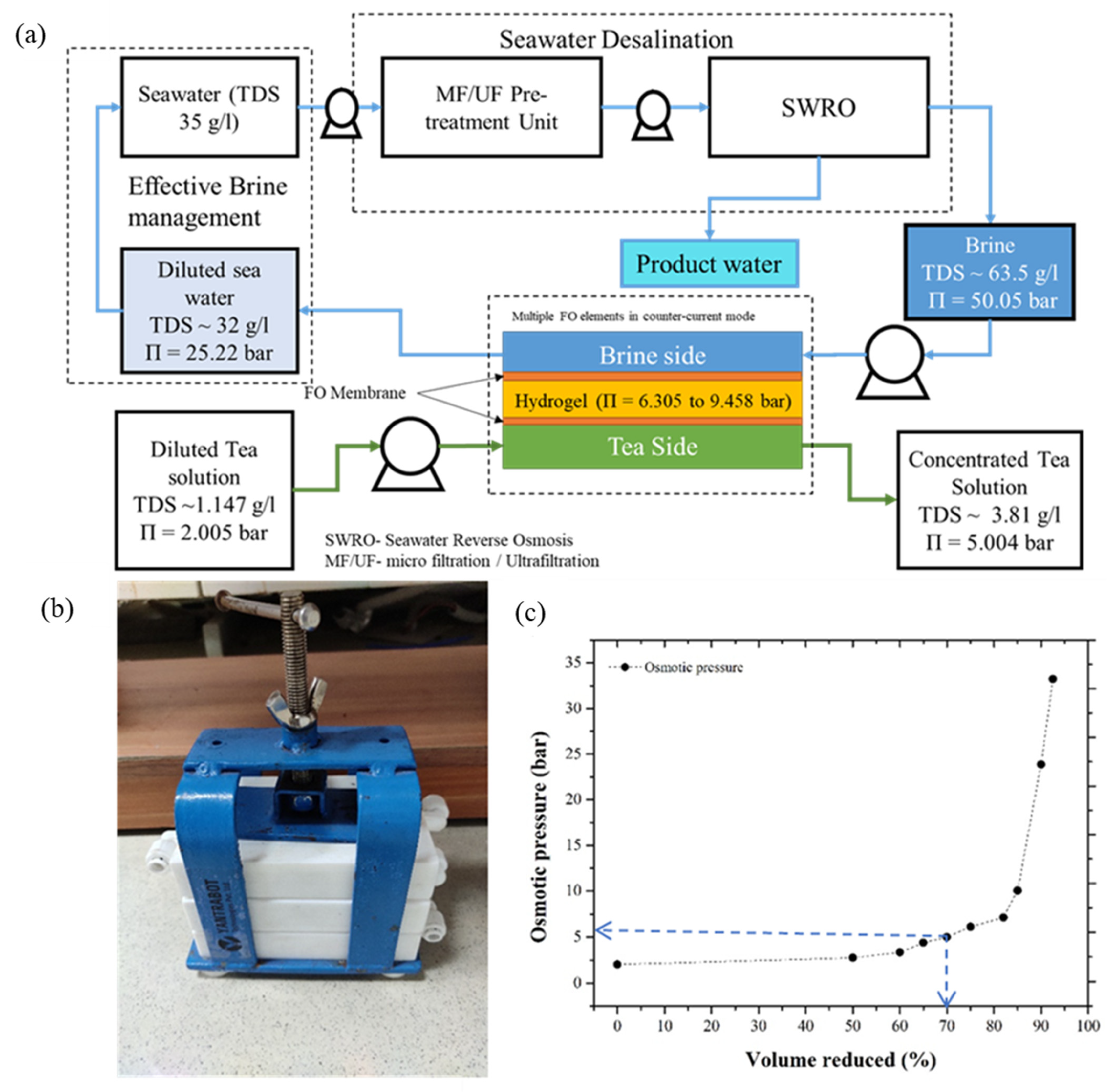
3.5. Prospects of the Synthesized Hydrogel in the Field of Liquid-Food Concentration Application
4. Conclusions
- Due to the cationic polyelectrolyte ‘polyDADMAC’, the swelling ability (13.6 g g−1) and FO performance (1.81 L m−2 h−1, against 2500 mg L−1 NaCl solution) were improved.
- Further, the saturated hydrogel after the FO process can be regenerated (>70%) by blowing hot air (at 39–50 °C).
- The study suggests that water flux can be recovered by up to 86.6% of its initial value in 12-times regeneration using the same hydrogel. Thus, the synthesized hydrogel has tremendous potential for lowering energy consumption in FO applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blandin, G.; Ferrari, F.; Lesage, G.; Le-Clech, P.; Héran, M.; Martinez-Lladó, X. Forward Osmosis as Concentration Process: Review of Opportunities and Challenges. Membranes 2020, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Hu, X.M. A Critical Review on Draw Solutes Development for Forward Osmosis. Desalination 2016, 391, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.M.; Logan, B.E.; Saikaly, P.E.; Amy, G.L. Wastewater Treatment, Energy Recovery and Desalination Using a Forward Osmosis Membrane in an Air-Cathode Microbial Osmotic Fuel Cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M. Desalination by Ammonia–Carbon Dioxide Forward Osmosis: Influence of Draw and Feed Solution Concentrations on Process Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dova, M.I.; Petrotos, K.B.; Lazarides, H.N. On the Direct Osmotic Concentration of Liquid Foods. Part I: Impact of Process Parameters on Process Performance. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Jin, X.; Tang, C.Y. Osmotic Power Production from Salinity Gradient Resource by Pressure Retarded Osmosis: Effects of Operating Conditions and Reverse Solute Diffusion. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.M.; Chung, T.-S. Novel Dual-Stage FO System for Sustainable Protein Enrichment Using Nanoparticles as Intermediate Draw Solutes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, G.; Kim, D.I.; Hong, S. Draw Solutes for FO: Model, Polymer Hydrogels, and Nanoparticles; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128167779. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Tian, J.; Cui, F.; Shi, W. Recent Developments and Future Challenges of Hydrogels as Draw Solutes in Forward Osmosis Process. Water 2020, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E. Selection of Inorganic-Based Draw Solutions for Forward Osmosis Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M. A Novel Ammonia-Carbon Dioxide Forward (Direct) Osmosis Desalination Process. Desalination 2005, 174, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Petrinic, I.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Basu, S.; Balakrishnan, M. Concentrating Molasses Distillery Wastewater Using Biomimetic Forward Osmosis (FO) Membranes. Water Res. 2018, 130, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Shen, W.; Loo, S.L.; Krantz, W.B.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Hu, X. Towards Temperature Driven Forward Osmosis Desalination Using Semi-IPN Hydrogels as Reversible Draw Agents. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, H. Smart Draw Agents for Emerging Forward Osmosis Application. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 14049–14060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, T. Thermo-Sensitive Polyelectrolytes as Draw Solutions in Forward Osmosis Process. Desalination 2013, 318, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.L.; Rae, C.; Stewart, F.F.; Wilson, A.D. Switchable Polarity Solvents as Draw Solutes for Forward Osmosis. Desalination 2013, 312, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, W.; Ge, Q. Synthetic Draw Solutes for Forward Osmosis: Status and Future. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2018, 34, 767–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, W.; Yu, S. Research on Forward Osmosis Membrane Technology Still Needs Improvement in Water Recovery and Wastewater Treatment. Water 2020, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Nakhjiri, M.T.; Salehi, H.; Ghorbani, F.; Khankeshipour, N. Preparation of Polymer-Carbon Nanotubes Composite Hydrogel and Its Application as Forward Osmosis Draw Agent. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 24, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, E.C.; Geuskens, G. Compressive Elastic Modulus of Polyacrylamide Hydrogels and Semi-IPNs with Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide). Macromolecules 2001, 34, 4480–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Barati, M.R.; Simon, G.P.; Suzuki, K.; Wang, H. Fast Deswelling of Nanocomposite Polymer Hydrogels via Magnetic Field-Induced Heating for Emerging FO Desalination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6297–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, H.; Patel, C. Effect of Crosslinker Concentration on Characteristics of Superporous Hydrogel. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2011, 1, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Yao, J.; Simon, G.P.; Wang, H. Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Hydrogels as a New Class of Draw Agent for Forward Osmosis Desalination. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1710–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Cui, H.; Li, H.; Yang, F. Forward Osmosis Using Electric-Responsive Polymer Hydrogels as Draw Agents: Influence of Freezing–Thawing Cycles, Voltage, Feed Solutions on Process Performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, H. Synthesis and Swelling Properties of a Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Based Superabsorbing Hydrogel. Curr. Chem. Lett. 2013, 2, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.C.; Edgren, D. Crosslinking Reaction of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) with Glyoxal. J. Polym. Res. 2010, 17, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, M.J.A.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Forward Osmosis for Water Recovery Using Polyelectrolyte PolyDADMAC and DADMAC Draw Solutions as a Low Pressure Energy Saving Process. Desalination 2019, 453, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, A.; Marx, C.; Lerch, A. Modelling Forward Osmosis Treatment of Automobile Wastewaters. Membranes 2019, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, A.; Lerch, A. Forward Osmosis Application in Manufacturing Industries: A Short Review. Membranes 2018, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Influence of Concentrative and Dilutive Internal Concentration Polarization on Flux Behavior in Forward Osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Mulcahy, D. Effects of Membrane Orientation on Process Performance in Forward Osmosis Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 382, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.T.; McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Internal Concentration Polarization in Forward Osmosis: Role of Membrane Orientation. Desalination 2006, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Guo, H.; Yu, H.; Wen, G.; Qu, F.; Huang, T.; He, J. Sewage Sludge Ash-Based Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel as a Novel Draw Agent towards High Performance of Water Flux and Recovery for Forward-Osmosis. Desalination 2021, 512, 115147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, P.; Verma, V.K.; Yurembam, B.; Neog, A.B.; Raidongia, K.; Subbiah, S. Performance Evaluation of Reduced Graphene Oxide Membrane Doped with Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid for Forward Osmosis Process. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 44, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, I.W.; Ngila, J.C.; Ndungu, P.; Msagati, T.A.M. Method Development for the Determination of Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride at Trace Levels by Epoxidation Process. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharazmi, A.; Faraji, N.; Hussin, R.M.; Saion, E.; Yunus, W.M.M.; Behzad, K. Structural, Optical, Opto-Thermal and Thermal Properties of ZnS-PVA Nanofluids Synthesized through a Radiolytic Approach. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, I.; Ngila, J.C.; Ndungu, P. A New Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Residual Polydiallyldimethylammonium Chloride Focculant in Treated Water Based on a Diazotization-Coupledion Pair. Water SA 2012, 38, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Madras, G. Effect of Crosslinker on the Swelling and Adsorption Properties of Cationic Superabsorbent. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, R.; Zhang, H.; Kim, S.; Simon, G.P.; Hou, H.; Wang, H. Improvement of the Swelling Properties of Ionic Hydrogels by the Incorporation of Hydrophobic, Elastic Microfibers for Forward Osmosis Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Code | PVA (wt%) | PolyDADMAC (wt%) | Glyoxal (wt%) | Swelling Capacity (g g−1) | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-3:3:1.5 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 13.59 ± 0.06 | Gel formed with spongy white color texture after drying |
| H-4:3:1.5 | 13.33 | 10 | 5 | 20.68 ± 0.06 | |
| H-6:0:1.5 | 20 | 0 | 5 | 13.45 ± 0.02 | |
| H-4:2:2 | 13.33 | 6.67 | 6.67 | 16.56 ± 0.05 | Gel formed with spongy white color texture after drying |
| H-3:3:3 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11.77 ± 0.02 | Gel formed with spongy pale-yellow texture color after drying |
| H-6:0:3 | 20 | 0 | 10 | 11.15 ± 0.06 | Strong network gel formed |
| Manufacturer | DOW Filmtech Membrane |
|---|---|
| Material | Polyamide TFC |
| pH | 2–11 |
| Pure water permeability coefficient, A (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) | 5.99 |
| Solute permeability coefficient, B (L m−2 h−1) | 3.44 |
| A/B (bar) | 0.57 |
| Structural parameter, S (µm) | 424–786 |
| Draw Solute | Feed Solution (mg L−1 NaCl) | Regeneration Method | FO Performance | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Flux (L m−2 h−1) | Water Recovery (%) | ||||
| PSA | 2000 | Heating at 50 °C | 0.96 (in, 60 min) | <5 | [23] |
| HA-PVA-5 | 2000 | Electric field (9V) | 1.20 | NA | [24] |
| HA-PVA-7 | 0.91 | ||||
| HA-PVA-9 | 0.90 | ||||
| SI-0.2PSA | 2000 | Heating at 40 °C for 10 min | 0.18 (in 60 min) | NA | [13] |
| SI-0.5PSA | 0.18 (in 60 min) | ||||
| SI-0.2PVA | 0.12 (in 60 min) | ||||
| PSA/Polyester | 2000 | Solar simulator (1 kW/m2) for 60 min | 3.50 (in 60min) | 21 | [39] |
| PVA-polyDADMAC | 2500 | Hot air at 39–50 °C | 1.81 (in 60 min) | >70% | (This study) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bardhan, A.; Subbiah, S.; Mohanty, K.; Ibrar, I.; Altaee, A. Feasibility of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride) Polymeric Network Hydrogel as Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Process. Membranes 2022, 12, 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111097
Bardhan A, Subbiah S, Mohanty K, Ibrar I, Altaee A. Feasibility of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride) Polymeric Network Hydrogel as Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Process. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111097
Chicago/Turabian StyleBardhan, Ananya, Senthilmurugan Subbiah, Kaustubha Mohanty, Ibrar Ibrar, and Ali Altaee. 2022. "Feasibility of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride) Polymeric Network Hydrogel as Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Process" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111097
APA StyleBardhan, A., Subbiah, S., Mohanty, K., Ibrar, I., & Altaee, A. (2022). Feasibility of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride) Polymeric Network Hydrogel as Draw Solute for Forward Osmosis Process. Membranes, 12(11), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111097






