Non-Solvent Influence of Hydrophobic Polymeric Layer Deposition on PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane for CO2 Gas Absorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Hydrophobic Surface
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. SEM
2.3.2. Contact Angle Measurement
2.3.3. Bulk Porosity
2.3.4. FTIR
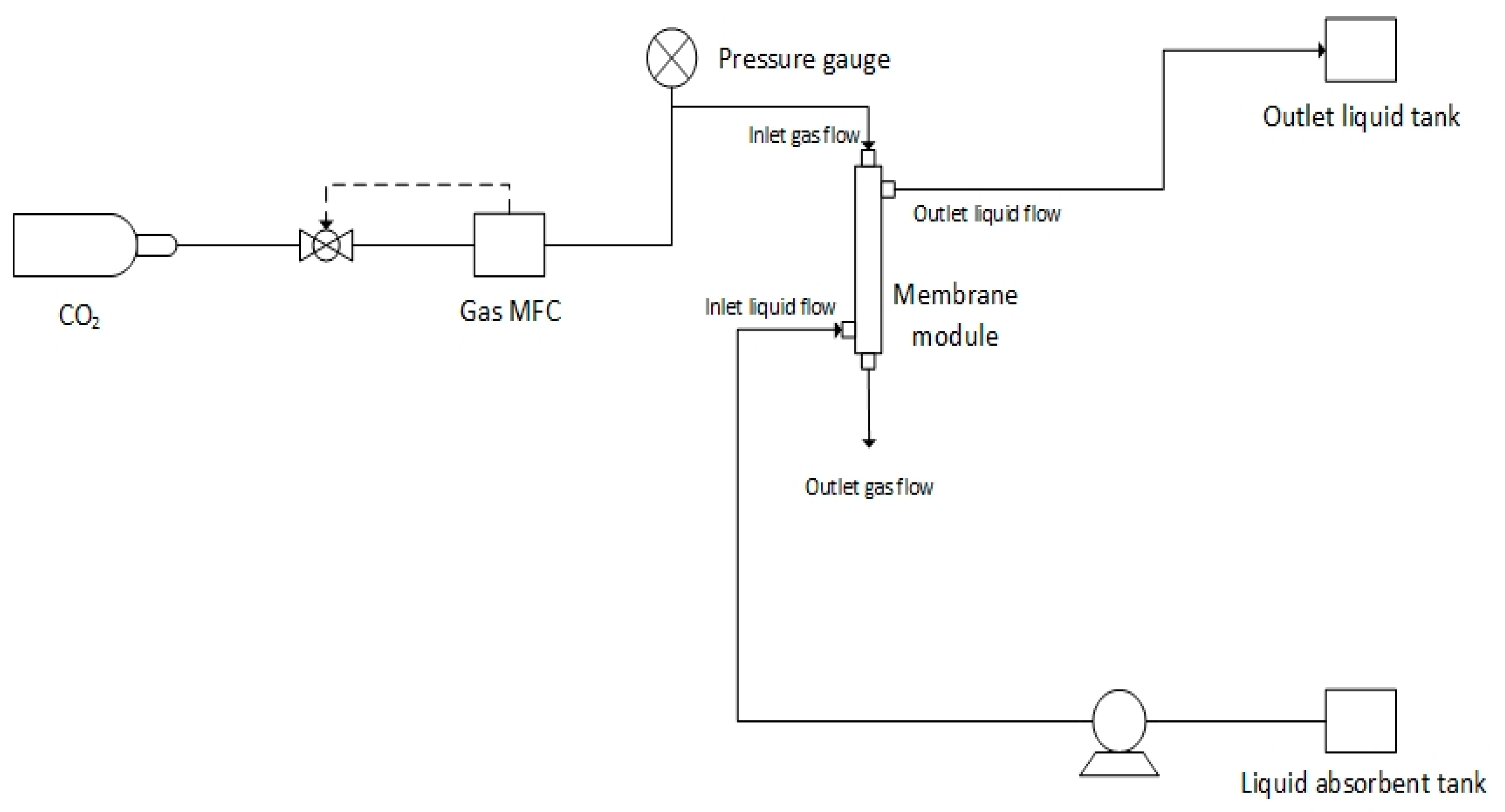
2.3.5. Experimental Setup of the MGA Process
2.3.6. Mass Transfer Rate of CO2
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PP Coating Solution Interaction with and without the Non-Solvent PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane Surface Morphology
3.2. Characterization of the Modified PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane with and without the Non-Solvent
3.2.1. Bulk Porosity and Contact Angle
3.2.2. Characterization of the FTIR Spectra of the Modified PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane with and without the Non-Solvent
3.3. CO2 Absorption Performance of the Pristine and Modified PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, Y.; Yu, X.; Tu, S.T.; Yan, J.; Dahlquist, E. Experimental studies on simultaneous removal of CO2 and SO2 in a poly-propylene hollow fiber membrane contactor. Appl. Energy 2012, 97, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongwong, W.; Jiraratananon, R.; Atchariyawut, S. Experimental study on membrane wetting in gas–liquid membrane contacting process for CO2 absorption by single and mixed absorbents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 69, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Recent Progress on Improving the Sustainability of Membrane Fabrication. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2019, 6, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- Barbe, A.M.; Hogan, P.A.; Johnson, R.A. Surface morphology changes during initial usage of hydrophobic, microporous polypropylene membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 172, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh-Sedghi, S.; Rodrigue, D.; Brisson, J.; Iliuta, M.C. Wetting phenomenon in membrane contactors—Causes and prevention. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 332–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, G.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Z. Research Progress in Gas Separation Using Hollow Fiber Membrane Contactors. Membranes 2020, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaisri, S.; Demontigny, D.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Jiraratananon, R. Comparing membrane resistance and absorption performance of three different membranes in a gas absorption membrane contactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himma, N.F.; Prasetya, N.; Anisah, S.; Wenten, I.G. Superhydrophobic membrane: Progress in preparation and its separation properties. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 211–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himma, N.F.; Wenten, I.G. Superhydrophobic Membrane Contactor for Acid Gas Removal. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 877, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajabzadeh, S.; Yoshimoto, S.; Teramoto, M.; Al-Marzouqi, M.; Matsuyama, H. CO2 absorption by using PVDF hollow fiber membrane contactors with various membrane structures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 69, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.A.; Leo, C.P.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ramli, W.K.W. Membranes with Great Hydrophobicity: A Review on Preparation and Characterization. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2015, 44, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Y.C.; Arning, A. Performance Comparison between Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Polytetrafluoroethylene Hollow Fiber Membranes for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Membranes 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.; Ramli, W.; Fernando, W.; Daud, W.R.W. Effect of ethanol concentration in water coagulation bath on pore geometry of PVDF membrane for Membrane Gas Absorption application in CO2 removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 88, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Marzooqi, F.A.; Bilad, M.R.; Arafat, H.A. Improving liquid entry pressure of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes by exploiting the role of fabrication parameters in vapor-induced phase separation VIPS and non-solvent-induced phase separation (NIPS) processes. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, A.; Ahmad, A.L.; Low, S.C. Anti-wetting polyvinylidene fluoride membrane incorporated with hydrophobic pol-yethylene-functionalized-silica to improve CO2 removal in membrane gas absorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Malaysia; Ramli, M.R.M.; Esham, M.I.M. Effect of Additives on Hydrophobicity of PVDF Membrane in Two-stage Coagulation Baths for Desalination. J. Phys. Sci. 2019, 30, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himma, N.F.; Wardani, A.K.; Wenten, I.G. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Polypropylene Membrane Using Dip-Coating Method: The Effects of Solution and Process Parameters. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, H.Y.; Demirel, A.L.; Avcı, Y.; Mert, O. Transformation of a Simple Plastic into a Superhydrophobic Surface. Science 2003, 299, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yu, X.; Jia, J.; Tu, S.-T.; Yan, J.; Dahlquist, E. Fabrication and characterization of superhydrophobic polypropylene hollow fiber membranes for carbon dioxide absorption. Appl. Energy 2012, 90, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, G.; Ma, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Wang, F. Preparation of a super-hydrophobic poly(vinyl chloride) surface via solvent–nonsolvent coating. Polymer 2006, 47, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, A.; Ahmad, A.L.; Low, S.C. Functionalization of silica nanoparticles to reduce membrane swelling in CO2 ab-sorption process. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Himma, N.F.; Wardani, A.K.; Wenten, I.G. The effects of non-solvent on surface morphology and hydrophobicity of dip-coated polypropylene membrane. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 054001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafie, Z.M.H.M.; Ahmad, A.L.; Low, S.C.; Rode, S.; Belaissaoui, B. Lithium chloride (LiCl)-modified polyethersulfone (PES) substrate surface pore architectures on thin poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) dense layer formation and the composite membrane’s performance in gas separation. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9500–9511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourizadeh, A. Experimental study of CO2 absorption/stripping via PVDF hollow fiber membrane contactor. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari-Sisakht, M.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Emadzadeh, D.; Padaki, M.; Ismail, A. Study on CO2 stripping from water through novel surface modified PVDF hollow fiber membrane contactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossno, S.K.; Kalbus, L.H.; Kalbus, G.E. Determinations of Carbon Dioxide by Titration: New Experiments for General, Physical, and Quantitative Analysis Courses. J. Chem. Educ. 1996, 73, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, R.A.; Lau, W.J.; Sakthivel, D.B.; Khademi, S.; Zulhairun, A.K.; Goh, P.S. Separation of CO2/CH4 and O2/N2 by polysulfone hollow fiber membranes: Effects of membrane support properties and surface coating materials. J. Polym. Eng. 2018, 38, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasalkova, N.S.; Slepicka, P.; Kolska, Z.; Svorcik, V. Wettability and Other Surface Properties of Modified Polymers. In Wetting and Wettability; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Sano, R.; Shimomura, A.; Matsuyama, H.; Maruyama, T. Reorganization of the surface geometry of hollow-fiber membranes using dip-coating and vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 460, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Zhenova, A.; Roberts, S.; Petchey, T.; Zhu, P.; Dancer, C.; McElroy, C.; Kendrick, E.; Goodship, V. On the Solubility and Stability of Polyvinylidene Fluoride. Polymers 2021, 13, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottino, A.; Capannelli, G.; Munari, S.; Turturro, A. Solubility parameters of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 1988, 26, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.N.; Sarip, M.N.; Zaharah, E.Z.E.; Rozana, M.D. Effect of Varying Solvents on Structural Properties of Annealed PVDF-Trfe Thin Films. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 7, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vebber, G.C.; Pranke, P.; Pereira, C.N. Calculating hansen solubility parameters of polymers with genetic algorithms. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.T.; Kim, J.F.; Wang, H.H.; di Nicolo, E.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Understanding the non-solvent induced phase sepa-ration (NIPS) effect during the fabrication of microporous PVDF membranes via thermally induced phase separation (TIPS). J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 514, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Rodrigue, D. A Review on Porous Polymeric Membrane Preparation. Part I: Production Techniques with Polysulfone and Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride). Polymers 2019, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franco, J.A.; Kentish, S.E.; Perera, J.M.; Stevens, G.W. Fabrication of a superhydrophobic polypropylene membrane by deposition of a porous crystalline polypropylene coating. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Mohammed, H.N.; Ooi, B.S.; Leo, C.P. Deposition of a polymeric porous superhydrophobic thin layer on the surface of poly(vinylidenefl uoride) hollow fiber membrane. Polish J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomar, B.S.; Shahin, A.; Tirumkudulu, M.S. Cracking in drying films of polymer solutions. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 3476–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuri, L.; Narkis, M.; Silverstein, M.S. Film formation and crack development in plasma polymerized hexamethyldisilox-ane. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1997, 37, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.A.U.R.; Khalid, M.W.; Ahmad, N.M.; Niazi, M.B.; Anwar, M.N.; Batool, M.; Cheema, W.; Rafiq, S. Polymer Concentration and Solvent Variation Correlation with the Morphology and Water Filtration Analysis of Polyether Sulfone Microfiltration Membrane. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2019, 2019, 8074626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdulKadir, W.A.F.W.; Ahmad, A.L.; Seng, O.B.; Lah, N.F.C. Biomimetic hydrophobic membrane: A review of anti-wetting properties as a potential factor in membrane development for membrane distillation (MD). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 91, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Matsui, J.; Yamamoto, S.; Miyashita, T.; Mitsuishi, M. Solvent-dependent properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) monolayers at the air–water interface. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z.; Drioli, E.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S. Enhancing wetting resistance of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes for vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2017, 415, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L. Surface modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) hollow fibre membranes for biogas purification in a gas–liquid membrane contactor system. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 171321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toh, M.J.; Oh, P.C.; Chew, T.L.; Ahmad, A.L. Preparation of polydimethylsiloxane-SiO2/PVDF-HFP mixed matrix membrane of enhanced wetting resistance for membrane gas absorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 244, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mntambo, S.A.; Mdluli, P.S.; Mahlambi, M.M.; Onwubu, S.C.; Nxumalo, N.L. Synthesis and characterisation of ultra-filtration membranes functionalised with c18 as a modifier for adsorption capabilities of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. Water SA 2019, 45, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linares, A.B.; Jiménez, J.C.; López, P.; de Gáscue, B.R. Biodegradability study by FTIR and DSC of polymers films based on polypropylene and Cassava starch. Orbital 2019, 11, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Reyes-Rodríguez, P.; Andrade-Guel, M.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Alvarez, M.P.; Cruz-Delgado, V.; Melo-López, L.; Quiñones-Jurado, Z.; Ávila-Orta, C. Melt-Mixed Thermoplastic Nanocomposite Containing Carbon Nanotubes and Titanium Dioxide for Flame Retardancy Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Mustaffar, A.; Phan, A.N.; Zivkovic, V.; Reay, D.; Law, R.; Boodhoo, K. A review of process intensification applied to solids handling. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2017, 118, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaee, A.; Ghadimi, A.; Sadatnia, B.; Ismail, A.F.; Mansourpour, Z.; Khosravi, M. Synthesis and characterization of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane containing hydrophobic silica nanoparticles for CO2 absorption from CO2/N2 using membrane contactor. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 120, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korminouri, F.; Rahbari-Sisakht, M.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F. Surface modification of polysulfone hollow fiber mem-brane spun under different air-gap lengths for carbon dioxide absorption in membrane contactor system. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahbari-Sisakht, M.; Ismail, A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Emadzadeh, D. Effect of SMM concentration on morphology and performance of surface modified PVDF hollow fiber membrane contactor for CO2 absorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 116, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourizadeh, A.; Ismail, A.F. Effect of additives on the structure and performance of polysulfone hollow fiber mem-branes for CO2 absorption. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 348, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Average pore size (µm) | 0.03 |
| Fiber inner diameter (mm) | 0.7 |
| Fiber outer diameter (mm) | 1.3 |
| Fiber surface area (m2) | 1.0 |
| Intrinsic contact angle (°) | 72.53 |
| Parameter | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Module inner diameter (mm) | 16 |
| Module length (mm) | 220 |
| Number of fibers (n) | 1 |
| Effective fiber length (mm) | 180 |
| Effective membrane area (m2) | 7.4 × 10−4 |
| Sample | (MPa) | (MPa) | (MPa) | (MPa) | RED | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | 17.2 | 12.5 | 9.2 | 23.2 | - | [31] |
| MEK | 16.0 | 9.0 | 5.1 | 19.05 | 1.2 | [33] |
| Xylene | 17.4 | 1.0 | 3.1 | 17.70 | 2.64 | [34] |
| Sample | PP Concentration (mg mL−1) | Bulk Porosity (%) | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Without MEK | 10 | 78.82 ± 3.26 | 91.97 ± 8.20 |
| 25 | 77.29 ± 1.55 | 100.78 ± 3.45 | |
| 40 | 77.25 ± 1.04 | 102.38 ± 3.96 | |
| With MEK | 10 | 83.43 ± 4.61 | 98.79 ± 1.55 |
| 25 | 80.27 ± 0.67 | 106.09 ± 2.02 | |
| 40 | 87.62 ± 1.32 | 119.85 ± 4.66 |
| Membrane Type | CO2 Absorption Flux (mol m−2 s−1) |
|---|---|
| Pristine | 3.13 × 10−4 |
| 25 mg modified | 3.33 × 10−4 |
| 40 mg modified | 2.42 × 10−4 |
| Membrane Type | CO2 Absorption Flux (mol m−2 s−1) | Remarks | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF hollow fiber | 2.3 × 10−3 | Water absorbent; = 0.9 m s−1 Number of fibers = 30 | [24] |
| Polysulfone (PSf) hollow fiber | 2 × 10−4 | Water absorbent; = 300 mL min−1 Number of fibers = 7 | [52] |
| Composite PVDF | 8.7 × 10−4 | AMP absorbent; = 100 mL min−1 | [15] |
| Surface modifying macromolecule (SMM)-modified PVDF hollow fiber membrane | 5.4 × 10−3 | Water absorbent; = 300 mL min−1 Number of fibers = 10 | [53] |
| PSf + PEG200 hollow fiber membrane | 1.09 × 10−3 | Water absorbent; = 1.4 m s−1 Number of fibers = 10 | [54] |
| PP-modified PVDF hollow fiber membrane | 3.33 × 10−4 | Water absorbent; = 100 mL min−1 Number of fibers = 1 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, A.L.; Hassan, A.I.; Peng, L.C. Non-Solvent Influence of Hydrophobic Polymeric Layer Deposition on PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane for CO2 Gas Absorption. Membranes 2022, 12, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010041
Ahmad AL, Hassan AI, Peng LC. Non-Solvent Influence of Hydrophobic Polymeric Layer Deposition on PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane for CO2 Gas Absorption. Membranes. 2022; 12(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Abdul Latif, Amir Ikmal Hassan, and Leo Choe Peng. 2022. "Non-Solvent Influence of Hydrophobic Polymeric Layer Deposition on PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane for CO2 Gas Absorption" Membranes 12, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010041
APA StyleAhmad, A. L., Hassan, A. I., & Peng, L. C. (2022). Non-Solvent Influence of Hydrophobic Polymeric Layer Deposition on PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane for CO2 Gas Absorption. Membranes, 12(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010041







