Calmodulin-Dependent Regulation of Overexpressed but Not Endogenous TMEM16A Expressed in Airway Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. cDNA, siRNA-TMEM16A, RT-PCR
2.3. Patch Clamping
2.4. Ussing Chamber
2.5. YFP Quenching
2.6. Materials and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
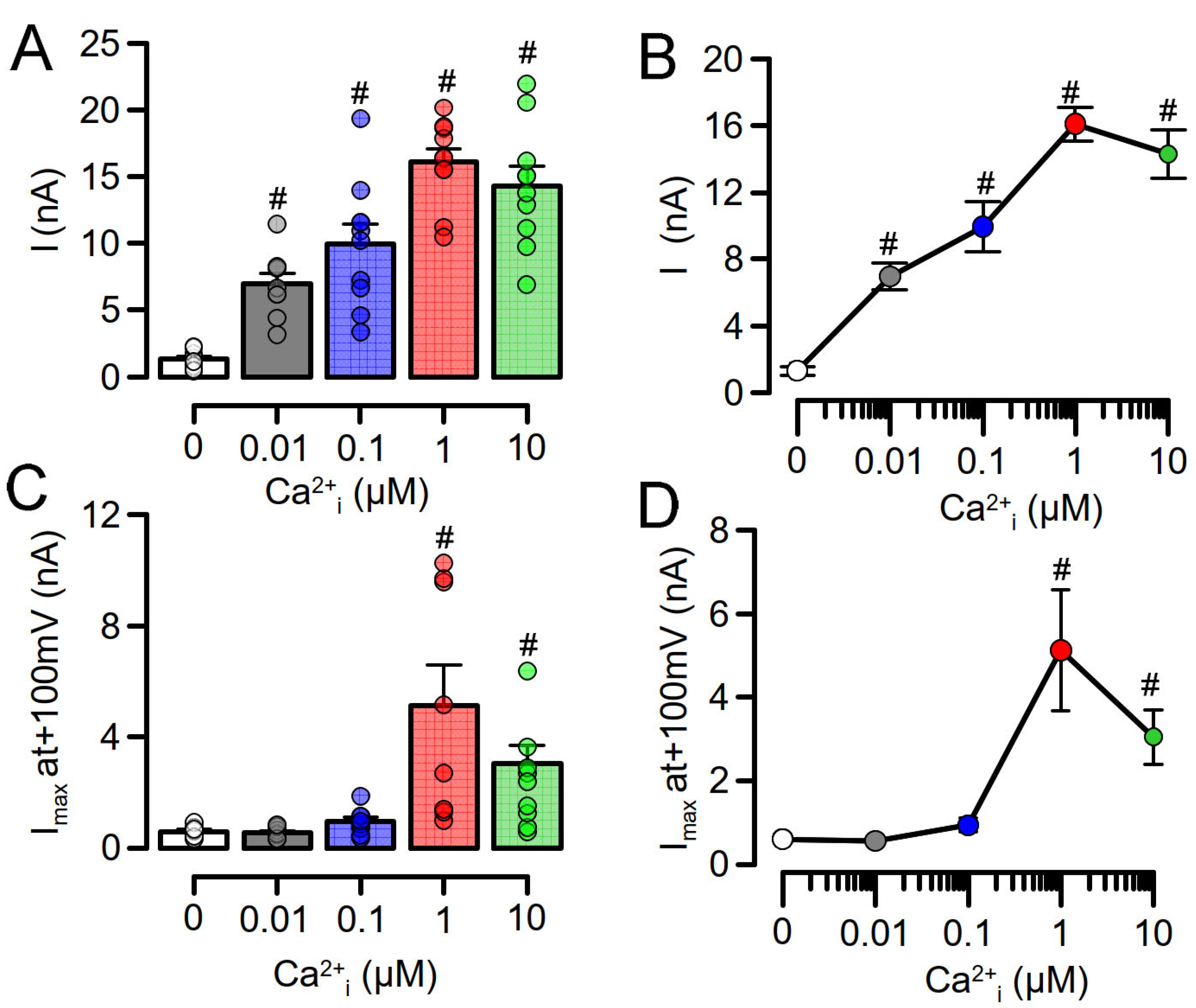
3.1. Overexpressed TMEM16A Is Spontaneously Active Due to Enhanced Ca2+ Sensitivity
3.2. Enhanced Ca2+ Sensitivity of Overexpressed TMEM16A Is Modulated by CAM
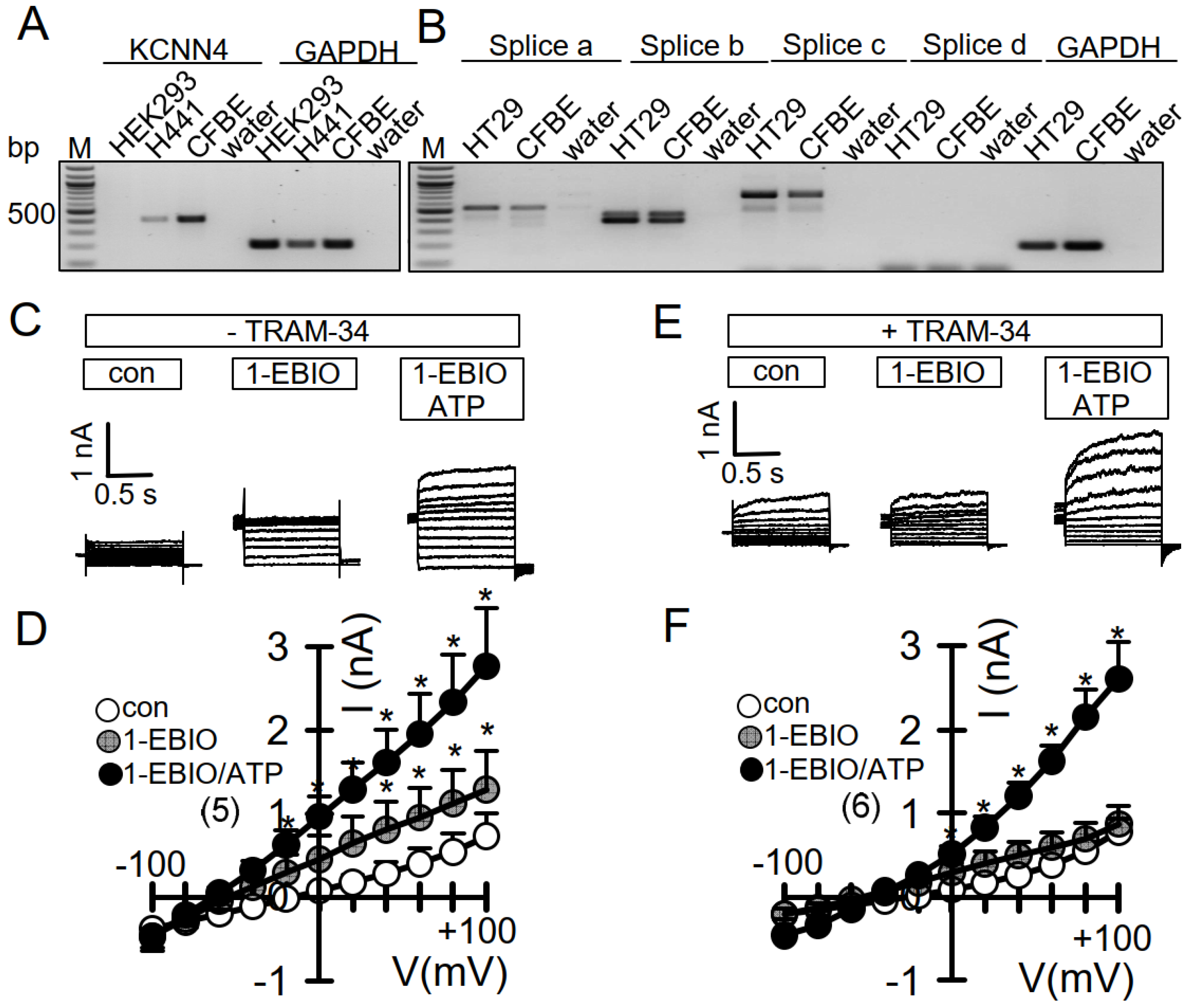
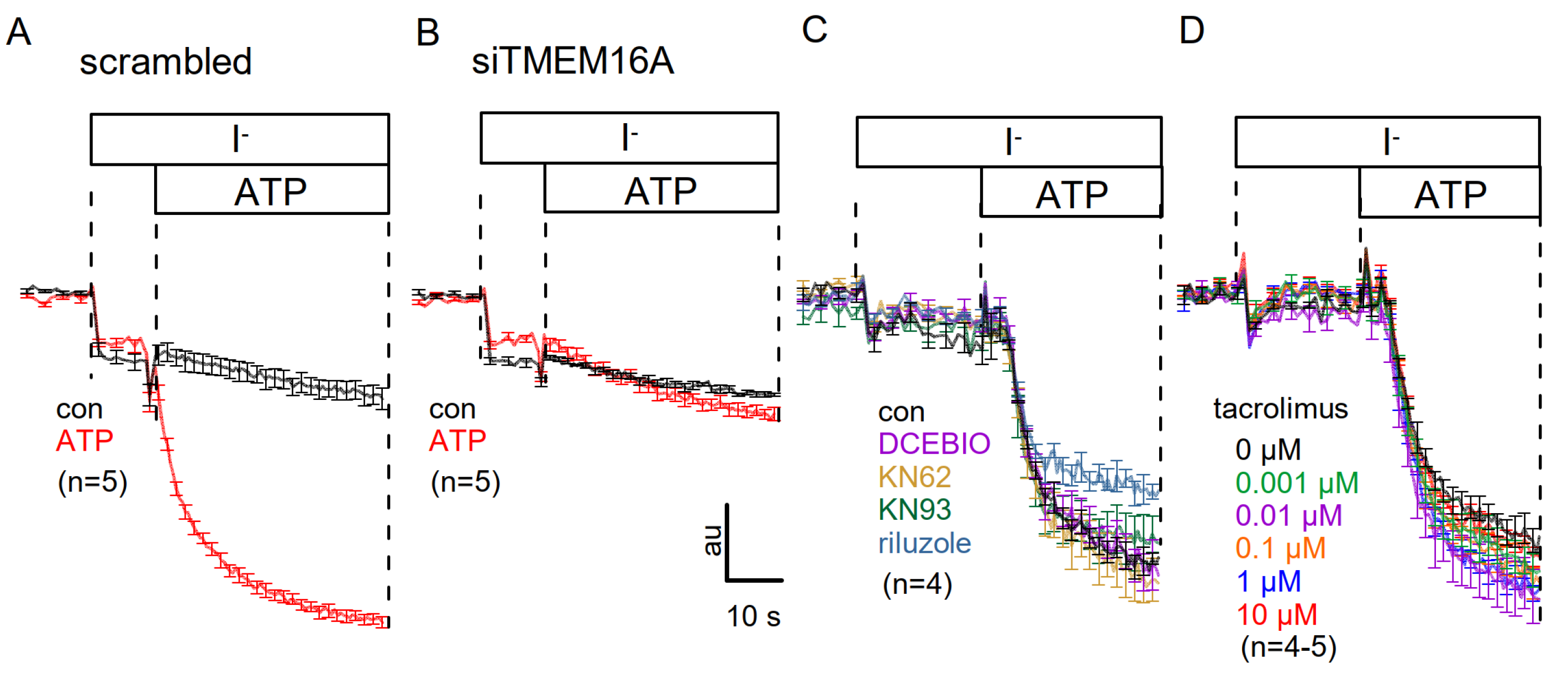
3.3. No Activation of Endogenous TMEM16A by 1-EBIO and No CAMKII-Dependent Regulation of TMEM16A in Airway Epithelial Cells
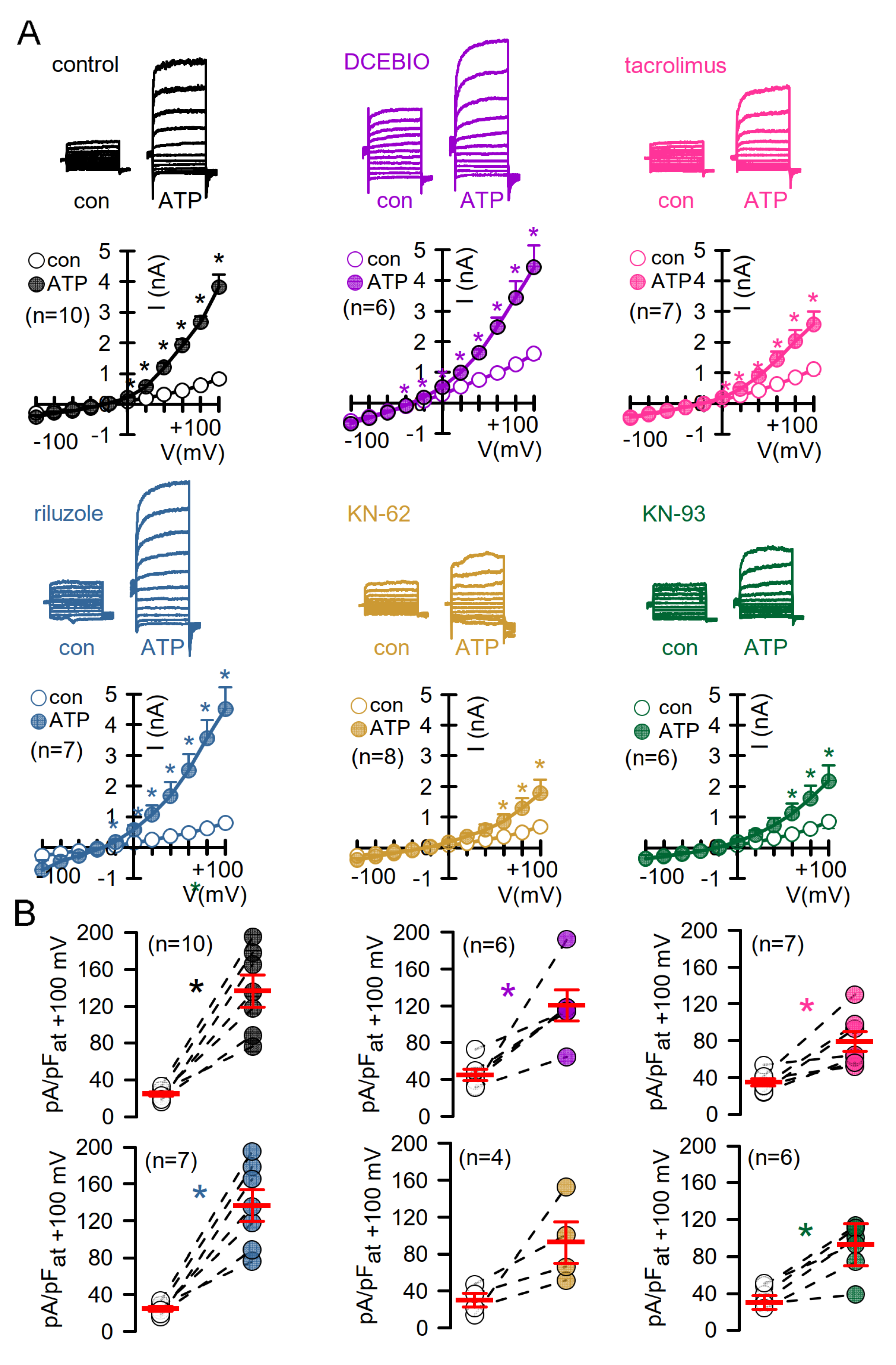
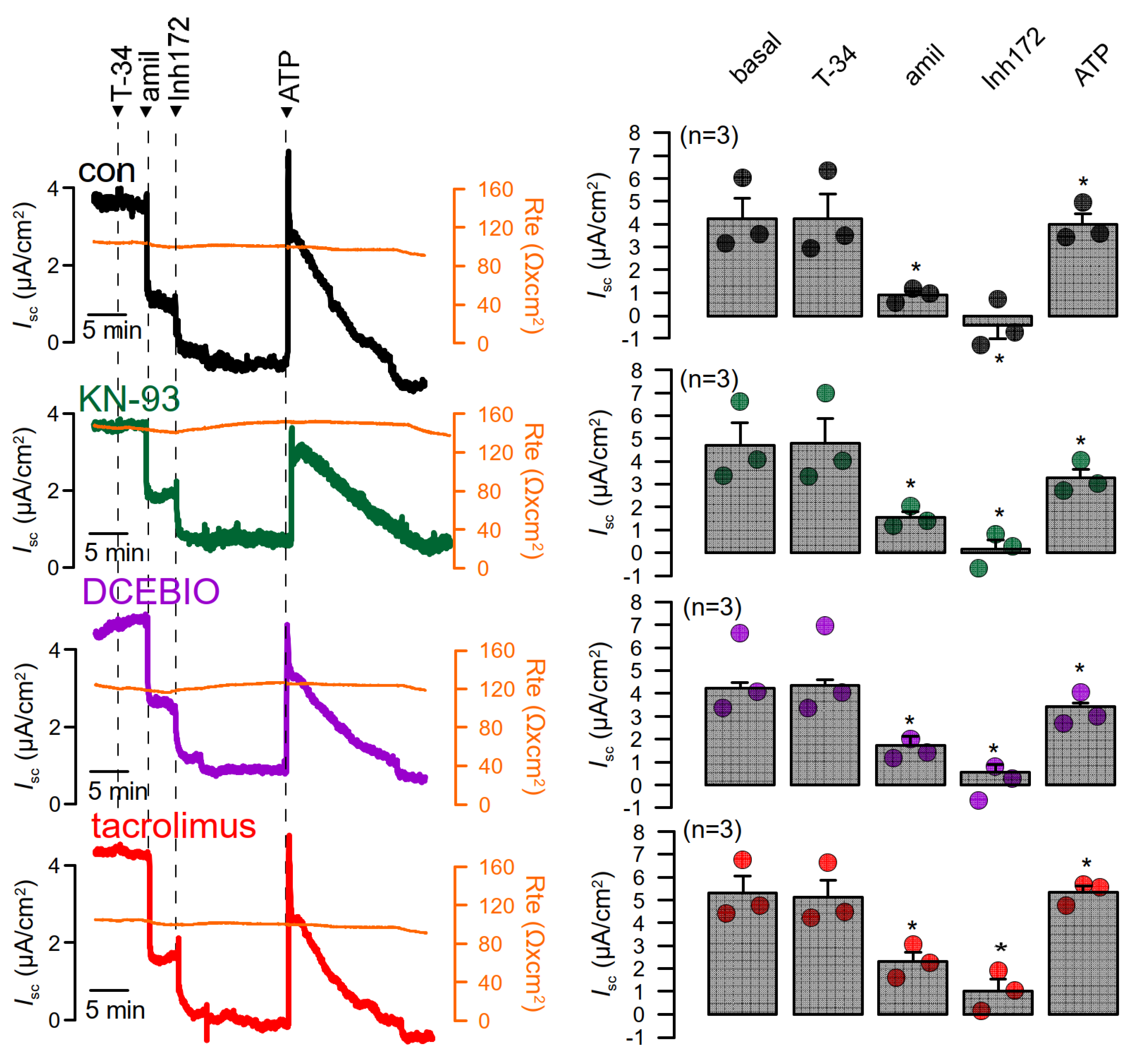
3.4. No Evidence for CAM, CAMKII, or Calcineurin-Dependent Regulation of Endogenous TMEM16A Expressed in Bci-NS1 Airway Epithelial Cells
3.5. No Evidence for CAM, CAMKII, or Calcineurin-Dependent Regulation of Endogenous TMEM16A in HT29 Colonic Epithelial Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Y.; Kongsuphol, P.; Hug, M.; Ousingsawat, J.; Witzgall, R.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Calmodulin-dependent activation of the epithelial calcium-dependent chloride channel TMEM16A. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.; Nam, J.H.; Park, H.W.; Oh, U.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, M.G. Dynamic modulation of ANO1/TMEM16A HCO3- permeability by Ca2+/calmodulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Colecraft, H.M. Preassociated apocalmodulin mediates Ca2+-dependent sensitization of activation and inactivation of TMEM16A/16B Ca2+-gated Cl−channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18213–18218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Colecraft, H.M. Calmodulin regulation of TMEM16A and 16B Ca2+-activated chloride channels. Channels 2015, 10, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vocke, K.; Dauner, K.; Hahn, A.; Ulbrich, A.; Broecker, J.; Keller, S.; Frings, S.; Möhrlen, F. Calmodulin-dependent activation and inactivation of anoctamin calcium-gated chloride channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2013, 142, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, T.-Y. Purified human brain calmodulin does not alter the bicarbonate permeability of the ANO1/TMEM16A channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2015, 145, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, K.; Zhu, J.; Qu, Z.; Cui, Y.-Y.; Hartzell, H.C. Activation of the Ano1 (TMEM16A) chloride channel by calcium is not mediated by calmodulin. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 143, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, J.A.; Cozens, A.L.; Schulman, H.; Gruenert, D.C.; Stryer, L.; Gardner, P. Activation of chloride chanels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by multifunctional calcium/calmodulin- dependent protein kinase. Nature 1991, 349, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrell, R.T.; A Frizzell, R. CaMKII mediates stimulation of chloride conductance by calcium in T84 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1991, 260, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, J.; Yen, M.; Basavappa, S.; Mangel, A.; Kwiatkowski, A. ATP-Activated Chloride Permeability in Biliary Epithelial Cells Is Regulated by Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 208, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Kaetzel, M.A.; Bruzik, K.S.; Dedman, J.R.; Shears, S.; Nelson, D.J. Inositol 3,4,5,6-Tetrakisphosphate Inhibits the Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II-activated Chloride Conductance in T84 Colonic Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14092–14097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlenker, T.; Fitz, J.G. Ca(2+)-activated C1- channels in a human biliary cell line: Regulation by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1996, 271, G304–G310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Inactivation of calcium-activated chloride channels in smooth muscle by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14918–14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, X.-D.; Goyal, R.K. CaMKII inhibition hyperpolarizes membrane and blocks nitrergic IJP by closing a Cl− conductance in intestinal smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G240–G246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-X.; Lv, X.-F.; Yuan, F.; Li, X.-Y.; Ma, M.-M.; Liu, C.-Z.; Zhou, J.-G.; Wang, G.-L.; Guan, Y.-Y. Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II γ-Dependent Serine727 Phosphorylation Is Required for TMEM16A Ca2+-Activated Cl− Channel Regulation in Cerebrovascular Cells. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayon, R.J.; Hawn, M.B.; Aoun, J.; Wiwchar, M.; Forrest, A.S.; Cunningham, F.; Singer, C.A.; Valencik, M.L.; Greenwood, I.A.; Leblanc, N. Molecular mechanism of TMEM16A regulation: Role of CaMKII and PP1/PP2A. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2019, 317, C1093–C1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Solano, A.; Corral, N.; Segura-Covarrubias, G.; Guzmán-Hernández, M.L.; Arechiga-Figueroa, I.; Cruz-Rangel, S.; Pérez-Cornejo, P.; Arreola, J. Regulation of the Ca2+-activated chloride channel Anoctamin-1 (TMEM16A) by Ca2+-induced interaction with FKBP12 and calcineurin. Cell Calcium 2020, 89, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, I.A.; LeDoux, J.; Leblanc, N. Differential regulation of Ca2+-activated Cl− currents in rabbit arterial and portal vein smooth muscle cells by Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent kinase. J. Physiol. 2001, 534, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.; Suh, B.-C. Differential regulation of Ca2+-Activated Cl− Channel TMEM16A Splice Variants by Membrane PI(4,5)P2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.; Jung, S.-R.; Kim, K.-W.; Yeon, J.-H.; Park, C.-G.; Nam, J.H.; Hille, B.; Suh, B.-C. Allosteric modulation of alternatively spliced Ca2+-activated Cl−channels TMEM16A by PI(4,5)P2and CaMKII. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30787–30798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Solomons, K.R.H.; Freeman, S.; Kaetzel, M.A.; Bruzik, K.S.; Nelson, D.J.; Shears, S.B. Regulation of Ca2+-dependent Cl−conductance in a human colonic epithelial cell line (T84): Cross-talk between Ins(3,4,5,6)P4and protein phosphatases. J. Physiol. 1998, 510, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.W.; Kaetzel, M.A.; Armstrong, D.L.; Shears, S.B. Regulation of a human chloride channel. a paradigm for integrating input from calcium, type ii calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, and inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18673–18680. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Schreiber, R.; Wanitchakool, P.; Kongsuphol, P.; Sousa, M.; Uliyakina, I.; Palma, M.; Faria, D.; E Traynor-Kaplan, A.; I Fragata, J.; et al. Control of TMEM16A by INO-4995 and other inositolphosphates. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 168, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Centeio, R.; Cabrita, I.; Benedetto, R.; Talbi, K.; Ousingsawat, J.; Schreiber, R.; Sullivan, J.K.; Kunzelmann, K. Pharmacological Inhibition and Activation of the Ca2+ Activated Cl− Channel TMEM16A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabrita, I.; Benedetto, R.; Wanitchakool, P.; Lerias, J.; Centeio, R.; Ousingsawat, J.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. TMEM16A Mediates Mucus Production in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, R.; Uliyakina, I.; Kongsuphol, P.; Warth, R.; Mirza, M.; Martins, J.R.; Kunzelmann, K. Expression and Function of Epithelial Anoctamins. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7838–7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lérias, J.; Pinto, M.; Benedetto, R.; Schreiber, R.; Amaral, M.; Aureli, M.; Kunzelmann, K. Compartmentalized crosstalk of CFTR and TMEM16A (ANO1) through EPAC1 and ADCY1. Cell. Signal. 2018, 44, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.R.; Faria, D.; Kongsuphol, P.; Reisch, B.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Anoctamin 6 is an essential component of the outwardly rectifying chloride channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18168–18172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedetto, R.; Centeio, R.; Ousingsawat, J.; Schreiber, R.; Janda, M.; Kunzelmann, K. Transport properties in CFTR-/- knockout piglets suggest normal airway surface liquid pH and enhanced amiloride-sensitive Na(+) absorption. Pflügers Arch. -Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Anoctamins are a family of Ca2+ activated Cl− channels. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4991–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedetto, R.; Ousingsawat, J.; Wanitchakool, P.; Zhang, Y.; Holtzman, M.J.; Amaral, M.; Rock, J.R.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Epithelial Chloride Transport by CFTR Requires TMEM16A. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De La Fuente, R.; Namkung, W.; Mills, A.; Verkman, A.S. Small-Molecule Screen Identifies Inhibitors of a Human Intestinal Calcium-Activated Chloride Channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Centeio, R.; Ousingsawat, J.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. CLCA1 Regulates Airway Mucus Production and Ion Secretion Through TMEM16A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedemonte, N.; Galietta, L. Structure and Function of TMEM16 Proteins (Anoctamins). Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 419–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitlock, J.M.; Hartzell, H.C. Anoctamins/TMEM16 Proteins: Chloride Channels Flirting with Lipids and Extracellular Vesicles. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, J.; Umeda, M.; Sims, P.J.; Nagata, S. Calcium-dependent phospholipid scrambling by TMEM16F. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 468, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirianant, L.; Ousingsawat, J.; Wanitchakool, P.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Cellular volume regulation by anoctamin 6: Ca2+, phospholipase A2 and osmosensing. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2015, 468, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrita, I.; Benedetto, R.; Fonseca, A.; Wanitchakool, P.; Sirianant, L.; Skryabin, B.V.; Schenk, L.K.; Pavenstädt, H.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Differential effects of anoctamins on intracellular calcium signals. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunzelmann, K.; Cabrita, I.; Wanitchakool, P.; Ousingsawat, J.; Sirianant, L.; Benedetto, R.; Schreiber, R. Modulating Ca2+ signals: A common theme for TMEM16, Ist2, and TMC. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2015, 468, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, Y.; Shibasaki, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamanaka, A.; Tominaga, M. Modulation of water efflux through functional interaction between TRPV4 and TMEM16A/anoctamin 1. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2238–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Yang, Y.D.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.; Kim, T.; Jang, Y.; Back, S.K.; Na, H.S.; Harfe, B.D.; Wang, F.; et al. The calcium-activated chloride channel anoctamin 1 acts as a heat sensor in nociceptive neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawn, M.B.; Akin, E.; Hartzell, H.; Greenwood, I.A.; Leblanc, N. Molecular Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation of ANO1-Encoded Ca2+-Activated Cl- Channels. Channels 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, R.; Leeson-Payne, A.; Jaggar, J.H.; Zhang, X. Calmodulin is responsible for Ca2+-dependent regulation of TRPA1 Channels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep45098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.; Cai, R.; Hofmann, L.; Nesin, V.; Hu, Q.; Long, W.; Fatehi, M.; Liu, X.; Hussein, S.; Kong, T.; et al. Direct Binding between Pre-S1 and TRP-like Domains in TRPP Channels Mediates Gating and Functional Regulation by PIP2. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 1560–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; A Syme, C.; Singh, A.K.; Devor, D.C.; Bridges, R.J. Benzimidazolone activators of chloride secretion: Potential therapeutics for cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 296, 600–611. [Google Scholar]
- Devor, D.C.; Singh, A.K.; A Frizzell, R.; Bridges, R.J. Modulation of Cl- secretion by benzimidazolones. I. Direct activation of a Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channel. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1996, 271, L775–L784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedarzani, P.; Mosbacher, J.; Rivard, A.; Cingolani, L.A.; Oliver, D.; Stocker, M.; Adelman, J.P.; Fakler, B. Control of Electrical Activity in Central Neurons by Modulating the Gating of Small Conductance Ca2+-activated K+ Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9762–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prado, P.Á.; Häfner, S.; Comoglio, Y.; Wdziekonski, B.; Duranton, C.; Attali, B.; Barhanin, J.; Sandoz, G. KCNE1 is an auxiliary subunit of two distinct ion channel superfamilies. Cell 2020, 184, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Accession Number | Primer | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| TMEM16A (abcd) NM_001378092.1 | ||
| Splice variant a | s: 5′-GGACCCTGATGCCGAGTGC as: 5′-GGAGAAGGGATAGGAGAGTC | 547 |
| Splice variant b | s: 5′-ACAGCAAAACCCGGAGC as: 5′-TCTCTGGTCACACATCTCC | 462 |
| Splice variant c | s: 5′-ACAGCAAAACCCGGAGC as: 5′-GGATGATCCTTGACAGCCTC | 703 |
| Splice variant d | s: 5′-GAAGAAAGAGTCCAGAAAC as: 5′-CCGATCTCTCCATGTCAGC | 136 |
| KCNN4 NM_002250.3 | s: 5′-GATTTAGGGGCGCCGCTGAC as: 5′-CTTGCCCCACATGGTGCCC | 405 |
| Gapdh NM_001289726 | s: 5′-GTATTGGGCGCCTGGTCAC as: 5′-CTCCTGGAAGATGGTGATGG | 200 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talbi, K.; Ousingsawat, J.; Centeio, R.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Calmodulin-Dependent Regulation of Overexpressed but Not Endogenous TMEM16A Expressed in Airway Epithelial Cells. Membranes 2021, 11, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090723
Talbi K, Ousingsawat J, Centeio R, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K. Calmodulin-Dependent Regulation of Overexpressed but Not Endogenous TMEM16A Expressed in Airway Epithelial Cells. Membranes. 2021; 11(9):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090723
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalbi, Khaoula, Jiraporn Ousingsawat, Raquel Centeio, Rainer Schreiber, and Karl Kunzelmann. 2021. "Calmodulin-Dependent Regulation of Overexpressed but Not Endogenous TMEM16A Expressed in Airway Epithelial Cells" Membranes 11, no. 9: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090723
APA StyleTalbi, K., Ousingsawat, J., Centeio, R., Schreiber, R., & Kunzelmann, K. (2021). Calmodulin-Dependent Regulation of Overexpressed but Not Endogenous TMEM16A Expressed in Airway Epithelial Cells. Membranes, 11(9), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090723






