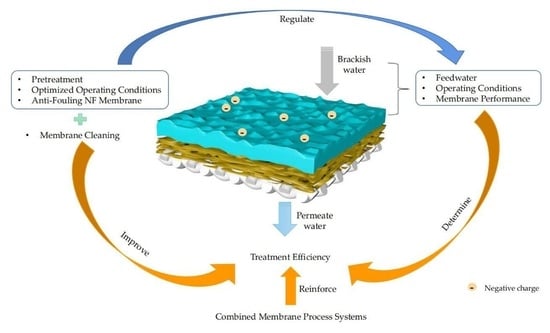
Progress in Research and Application of Nanofiltration (NF) Technology for Brackish Water Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Brackish Water
3. Factors Influencing the Efficiency of Brackish Water Treatment with NF
3.1. Characteristics of Feed Water
3.2. Operating Conditions
3.3. Properties of NF Membrane
4. Membrane Fouling Control during the Treatment of Brackish Water with NF
4.1. Pretreatment
4.2. Optimization of Operating Conditions
4.3. Selection of NF Membranes with Anti-Fouling Ability
5. Membrane Cleaning
5.1. Physical Cleaning
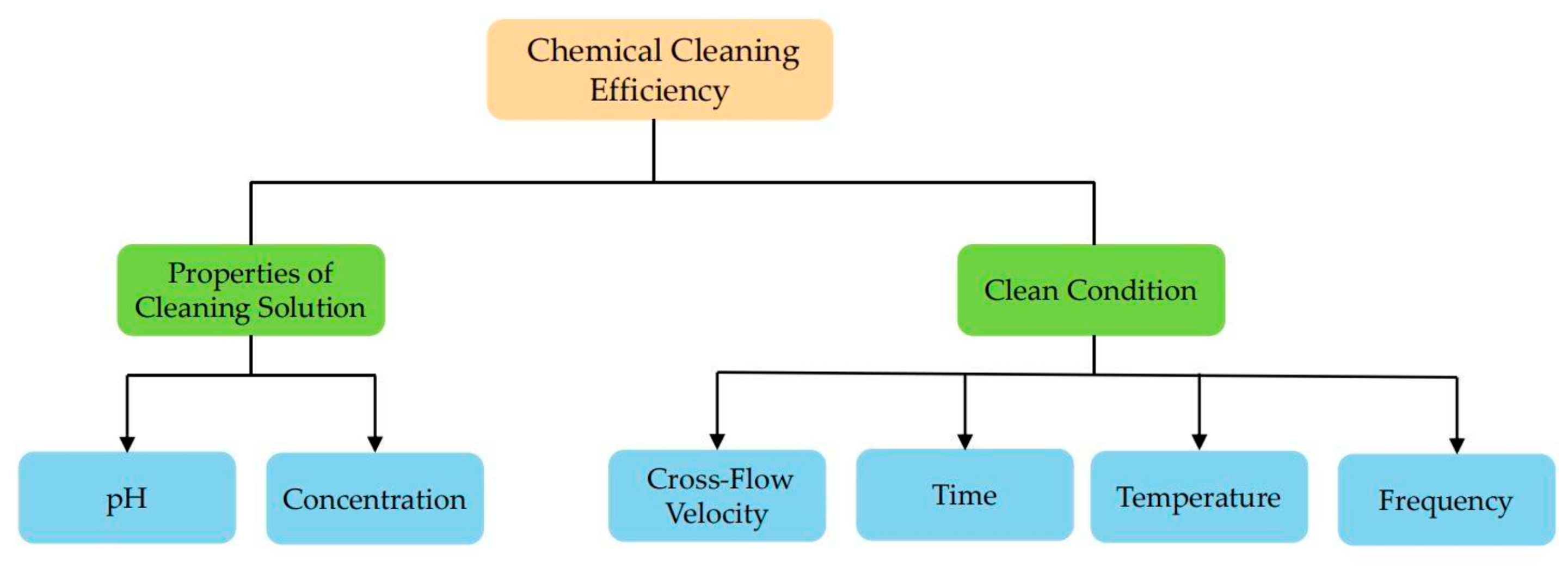
5.2. Chemical Cleaning
6. Combined Utilization of NF with Other Membrane Technology
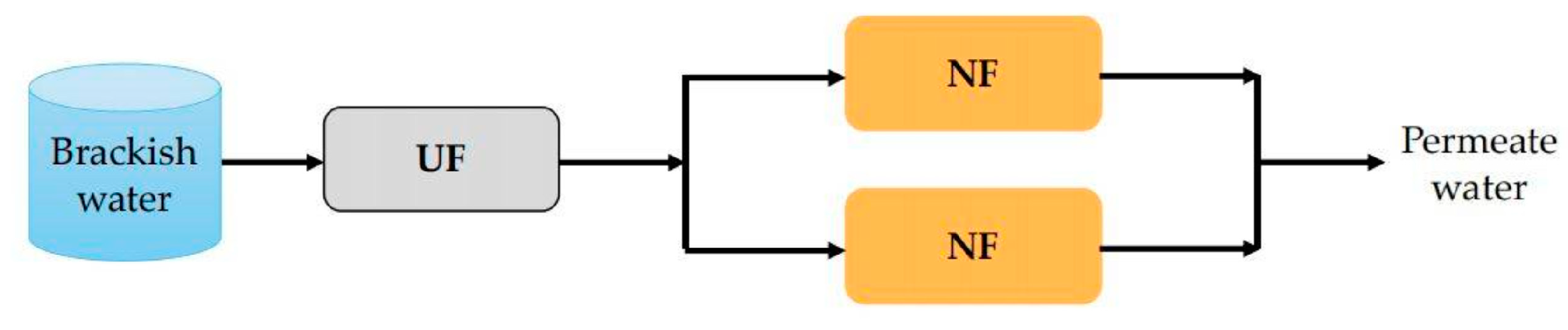
6.1. Combined Application of NF and UF
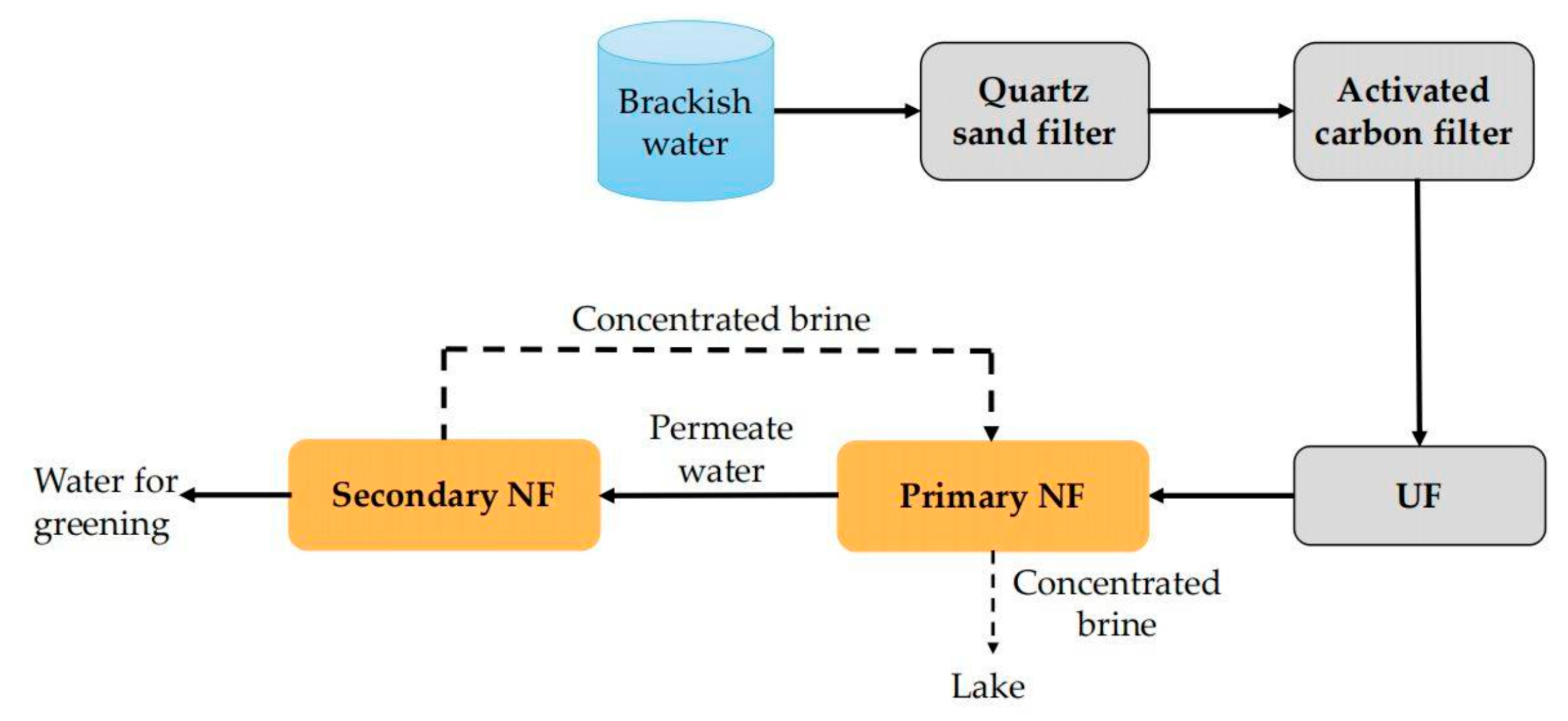
6.2. Combined Application of NF and NF
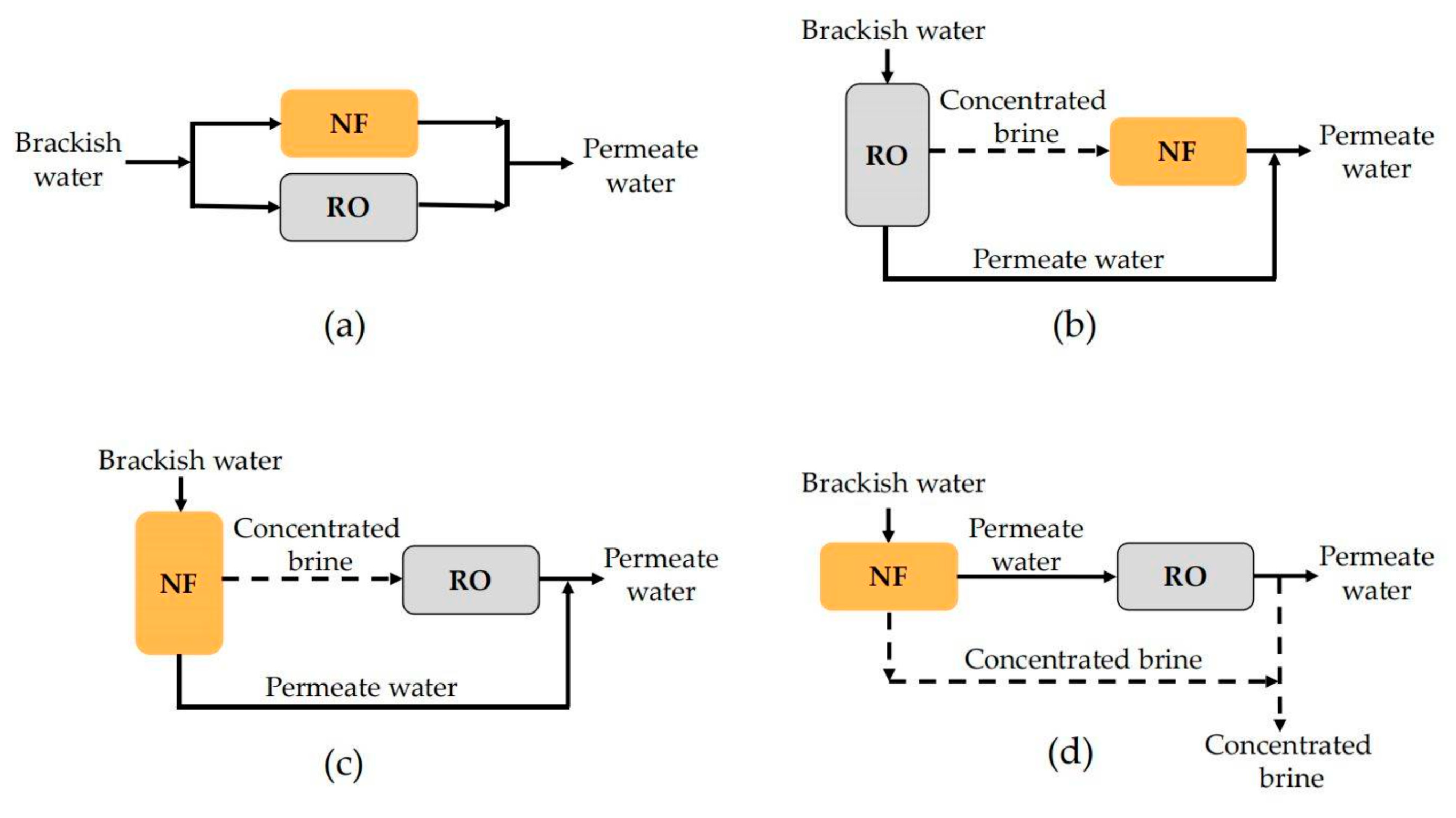
6.3. Combined Application of NF and RO
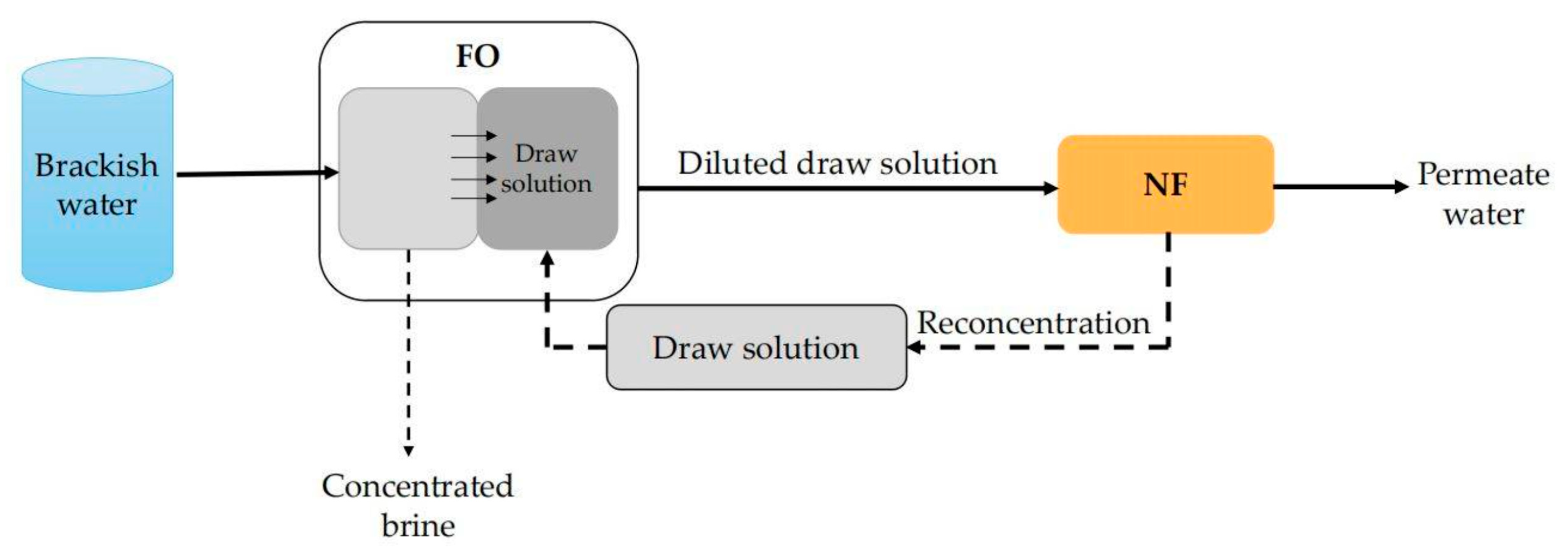
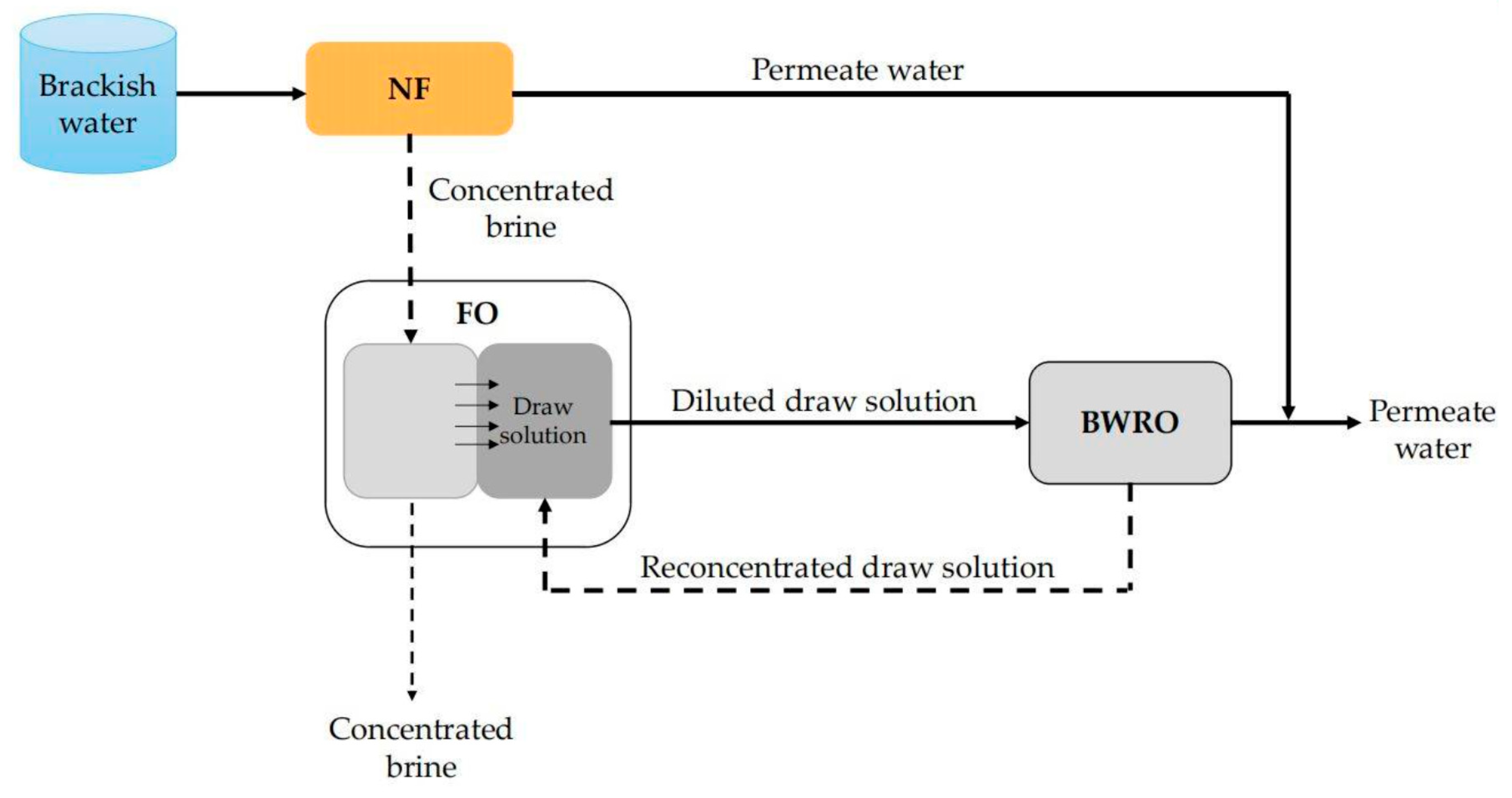
6.4. Combined Application of NF and FO
6.5. Other Combinations
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
- (1)
- The characteristics of specific brackish water and the difference in purification objectives should be taken into account first, when selecting the treatment process. Moreover, a comprehensive comparison is needed from the perspectives of economy, technology and environment;
- (2)
- Understanding the membrane fouling mechanism is the foundation of membrane fouling control, but most of the reported research related to the desalination of brackish water with NF only concerns the treatment efficiency; the analysis of the fouling mechanism is not sufficient. So, more microscopic membrane characterizations are necessary to be adopted to promote the deep understanding of membrane fouling;
- (3)
- As the core of NF membrane technology, membrane material should be given more attention to further improve the permeability, selectivity and stability, as well as reducing manufacture costs. In addition, membrane fabrication should be “fitting for purpose” according to the specific brackish water quality and treatment requirements;
- (4)
- The application of NF technology integrated with other emerging water treatment technologies is expected to further improve the performance of brackish water treatment. For instance, an integrated NF-calcite contactor process proposed by Haddad et al. was proved to be a feasible method to effectively remove the undesirable compounds (particularly manganese (Mn), iron (Fe) and hardness) from groundwater [139]. Therefore, more novel hybrid brackish water treatment process combination with NF as core should be explored.
- (5)
- In the process of treating brackish water, a large amount of concentrated brine is produced. Up to now, most of the concentrated brine has been directly discharged into the environment, which brings a great potential harm to ecology. So, subsequent treatment of concentrated brine is an important issue to be focused on in future research. The high concentration of salt in the brine should be regarded as a resource, rather than a contaminant.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, J.R.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, F.; Ali, M.E.A. Desalination of high salinity brackish water by an NF-RO hybrid system. Desalination 2020, 491, 114445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.A.; Chellam, S. Relative contributions of organic and inorganic fouling during nanofiltration of inland brackish surface water. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, S.; Allen, A.; Koutsos, V.; Semião, A.J.C. Influence of organic fouling layer characteristics and osmotic backwashing conditions on cleaning efficiency of RO membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 616, 118604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffour, N.; Missimer, T.M.; Amy, G.L. Technical review and evaluation of the economics of water desalination: Current and future challenges for better water supply sustainability. Desalination 2013, 309, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altmann, T.; Das, R. Process improvement of sea water reverse osmosis (SWRO) and subsequent decarbonization. Desalination 2021, 499, 114791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Torres, A.M.; García-Rodríguez, L.; Moral, M.J. Preliminary assessment of innovative seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) desalination powered by a hybrid solar photovoltaic (PV)-Tidal range energy system. Desalination 2020, 477, 114247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.; Shin, K.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.; Park, J.; Roh, H. Process modeling and simulation of an SWRO desalination plant: Case study of Gijang SWRO desalination plant in Korea. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 157, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, M.; Sasaki, T.; Nakatsuji, K.; Kimura, M.; Henmi, M. Low pressure SWRO membrane for desalination in the Mega-ton Water System. Desalination 2015, 368, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.; Hajjaj, M. Impact of desalination plants fluid effluents on the integrity of seawater, with the Arabian Gulf in perspective. Desalination 2005, 182, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Reducing the environmental impacts of reverse osmosis desalination by using brackish groundwater resources. Water Res. 2008, 42, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachit, D.E.; Veenstra, J.N. Analysis of reverse osmosis membrane performance during desalination of simulated brackish surface waters. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porada, S.; Zhao, R.; Wal, A.; Presser, V.; Biesheuvel, P.M. Review on the science and technology of water desalination by capacitive deionization. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 1388–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeshima, A.; Kim, H.; Shiogama, H.; Lierhammer, L.; Scinocca, J.F.; Seland, Y.; Mitchell, D. Global aridity changes due to differences in surface energy and water balance between 1.5 °C and 2 °C warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 0940a7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jude, P.J.; Dharshini, S.; Vinobaba, M.; Surendran, S.N.; Ramasamy, R. Anopheles culicifacies breeding in brackish waters in Sri Lanka and implications for malaria control. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrera, C.; Gamboa, C.; Custodio, E.; Jordan, T.; Godfrey, L.; Jódar, J.; Luque, J.A.; Vargas, J.; Sáez, A. Groundwater origin and recharge in the hyperarid Cordillera de la Costa, Atacama Desert, northern Chile. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrides, B.; Cartwright, I.; Weaver, T.R. The evolution of groundwater in the Tyrrell catchment, south-central Murray Basin, Victoria, Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1522–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypek, G.; Dogramaci, S.; Grierson, P.F. Geochemical and hydrological processes controlling groundwater salinity of a large inland wetland of northwest Australia. Chem. Geol. 2013, 357, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Tan, H.; Brusseau, M.L. Significance of isotopic and geochemical methods to determine the evolution of inland brackish and bitter water: An example from the Zuli river in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q. Enrichment of fluoride in groundwater under the impact of saline water intrusion at the salt lake area of Yuncheng basin, northern China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Nuez, I. Long-term intermittent operation of a full-scale BWRO desalination plant. Desalination 2020, 489, 114526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C.; Ho, W.S.W. High-flux reverse osmosis membranes incorporated with NaY zeolite nanoparticles for brackish water desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Optimal plant operation of brackish water reverse osmosis (BWRO) desalination. Desalination 2012, 293, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zou, L. Ion-exchange membrane capacitive deionization: A new strategy for brackish water desalination. Desalination 2011, 275, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larchet, C.; Zabolotsky, V.I.; Pismenskaya, N.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Tskhay, A.; Tastanov, K.; Pourcelly, G. Comparison of different ED stack conceptions when applied for drinking water production from brackish waters. Desalination 2008, 222, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, A.; DeCarolis, J.; Pearce, W.; Jacangelo, J.G. Vibratory shear enhanced process (VSEP) for treating brackish water reverse osmosis concentrate with high silica content. Desalination 2012, 291, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, E.R.; Gotor, A.G.; Báez, S.O.P.; Martín, A.R.; Ruiz-García, A.; González, A.C. Evaluation of the five years operating data of a RO brackish water desalination plant in Las Palmas, Canary Islands, Spain: A historic case. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 4785–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Ruiz-Saavedra, E. 80,000 h operational experience and performance analysis of a brackish water reverse osmosis desalination plant. Assessment of membrane replacement cost. Desalination 2015, 375, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Nuez, I.; Carrascosa-Chisvert, M.D.; Santana, J.J. Simulations of BWRO systems under different feedwater characteristics. Analysis of operation windows and optimal operating points. Desalination 2020, 491, 114582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabelas, A.J.; Mitrouli, S.T.; Kostoglou, M. Scaling in reverse osmosis desalination plants: A perspective focusing on development of comprehensive simulation tools. Desalination 2020, 474, 114193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoul, M.A.; Poovanaesvaran, P.; Sopian, K.; Sulaiman, M.Y. Review of brackish water reverse osmosis (BWRO) system designs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Drewes, J.E.; Heil, D.; Wang, G. Treatment of brackish produced water using carbon aerogel-based capacitive deionization technology. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2605–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaeipour, M.; Nouri, J.; Hassani, A.H.; Mahvi, A.H. An investigation of desalination by nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and integrated (hybrid NF/RO) membranes employed in brackish water treatment. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Lin, S. Pore model for nanofiltration: History, theoretical framework, key predictions, limitations, and prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.W.; Teow, Y.H.; Ang, W.L.; Chung, Y.T.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D.L.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membranes review: Recent advances and future prospects. Desalination 2015, 356, 226–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, M.; Qi, P.; Bai, X.; Jiang, K. Exploring and comparing the roles of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in small-sized natural organics-induced charged nanofiltration membrane fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Lovitt, R.W. Fouling strategies and the cleaning system of NF membranes and factors affecting cleaning efficiency. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhassani, A.; Rumeau, M.; Benjelloun, D.; Pontie, M. Selective demineralization of water by nanofiltration Application to the defluorination of brackish water. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3260–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cho, J.; Elimelech, M. Combined influence of natural organic matter (NOM) and colloidal particles on nanofiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 262, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, S.; Dong, B.; Chu, H.; Liu, J. Study on surface water treatment by hybrid sand filtration and nanofiltration. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 5327–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaep, J.; Bruggen, B.V.; Uytterhoeven, S.; Croux, R.; Vanlerberghe, F.; Vandecasteele, C.; Wilms, D.; Houtte, E.V.; Vanlerberghe, F. Removal of hardness from groundwater by nanofiltration. Desalination 1998, 119, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddada, R.; Ferjani, E.; Roudesli, M.S.; Deratani, A. Properties of cellulose acetate nanofiltration membranes. Application to brackish water desalination. Desalination 2004, 167, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Rui, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z. A Review on Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes for Water Purification. Polymers 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruggen, B.V.; Mänttäri, M.; Nyström, M. Drawbacks of applying nanofiltration and how to avoid them: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatley-Radcliffe, D.L.; Walters, M.; Ainscough, T.J.; Williams, P.M.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membranes and processes: A review of research trends over the past decade. J. Water Process. Eng. 2017, 19, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Tian, J.; Gao, S.; Bruggen, B.V. How to coordinate the trade-off between water permeability and salt rejection in nanofiltration? J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 8831–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Al-Zoubi, H.; Darwish, N.A.; Mohamma, A.W.; Arabi, M.A. A comprehensive review of nanofiltration membranes: Treatment, pretreatment, modelling, and atomic force microscopy. Desalination 2004, 170, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diawara, C.K. Nanofiltration Process Efficiency in Water Desalination. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2008, 37, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarparvar, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Alborzi, A.; Afroz, K.; Reible, D. Frontiers of Membrane Desalination Processes for Brackish Water Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badruzzaman, M.; Subramani, A.; DeCarolis, J.; Pearce, W.; Jacangelo, J.G. Impacts of silica on the sustainable productivity of reverse osmosis membranes treating low-salinity brackish groundwater. Desalination 2011, 279, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, C.Y.C.; Zerwekh, J.E.; Antich, P. Anabolic effects of fluoride on bone. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 6, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.M.; Sotoca, J.A.; Expósito, E.; Gallud, F.; García-García, V.; Montiel, V.; Aldaz, A. Brackish water desalination by electrodialysis: Batch recirculation operation modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 252, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, Q.; Liu, X.; Gao, F. HYDRUS Simulation of Sustainable Brackish Water Irrigation in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain. Water 2017, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, G.; Li, T.; Qin, W. Influence of feedwater quality on nanofiltration membrane softening efficiencies for brackish water in long-term operation. CIESC J. 2017, 68, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Song, Y.; Li, T.; Gao, C. Effect of feed water characteristics on nanofiltration separating performance for brackish water treatment in the Huanghuai region of China. J. Water Process. Eng. 2017, 19, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G.; Morel, F.M.M. Humic acid complexation of calcium and copper. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1988, 22, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Combe, C.; Clark, M.M. The effects of pH and calcium on the diffusion coefficient of humic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 183, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, V.S.; Teixeira, M.R. Silver nanoparticles separation from the water using nanofiltration membranes: The role of mono-divalent salts and NOM. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Kwon, Y.N.; Leckie, J.O. The role of foulant-foulant electrostatic interaction on limiting flux for RO and NF membranes during humic acid fouling—Theoretical basis, experimental evidence, and AFM interaction force measurement. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiller, C.L.; O’Melia, C.R. Natural organic matter and colloidal stability: Models and measurements. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 73, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. Chemical and physical aspects of natural organic matter (NOM) fouling of nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 132, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Kwon, Y.N.; Leckie, J.O. Fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes by humic acid-Effects of solution composition and hydrodynamic conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 290, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, D.; Tung, K.L.; Li, Y.L.; Lin, N.J.; Chuang, C.J. Effect of pH on membrane morphology, fouling potential, and filtration performance of nanofiltration membrane for water softening. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wan, Y. Effects of pH and salt on nanofiltration—A critical review. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 438, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, T.O.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Mamba, B.B.; Verliefde, A.R.D. Influence of organic, colloidal and combined fouling on NF rejection of NaC1 and carbamazepine: Role of solute-foulant-membrane interactions and cake-enhanced concentration polarisation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Sarper, S.; Kim, C.H.; Cho, J. Enhanced or reduced concentration polarization by membrane fouling in seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) processes. Desalination 2009, 247, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Du, C.; Yan, W.; Wang, J.; Du, R. Study on desalination of high salinity brackish water for drinking water production with a domestic nanofiltration membrane. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 87–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, C. Analysis of nanofiltration membrane performance during softening process of simulated brackish groundwater. Desalination 2016, 399, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, H.; Dickson, J.M.; Eriksson, P.K. Temperature effects on the performance of thin-film composite, aromatic polyamide membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1989, 28, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventresque, C.; Turner, G.; Bablon, G. Nanofiltration: From prototype to full scale. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1997, 89, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Chellam, S. Temperature Effects on the Morphology of Porous Thin Film Composite Nanofiltration Membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5022–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchin, P.; Aimar, P.; Sanchez, V. Model for Colloidal Fouling of Membranes. AIChE J. 1995, 41, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.H.; Aguiar, A.O.; Pires, W.L.; Grossi, L.B.; Amaral, M.C.S. Comprehensive bench-and pilot-scale investigation of NF for gold mining effluent treatment: Membrane performance and fouling control strategies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paugam, L.; Diawara, C.K.; Schlumpf, J.P.; Jaouen, P.; Quéméneur, F. Transfer of monovalent anions and nitrates especially through nanofiltration membranes in brackish water conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 40, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Sheng, M.; Cao, G.; Cai, L.; Meng, S.; Tang, C.Y. Degradation of Polyamide Nanofiltration Membranes by Bromine: Changes of Physiochemical Properties and Filtration Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6329–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Al-Zoubi, H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Darwish, N.A. Nanofiltration of highly concentrated salt solutions up to seawater salinity. Desalination 2005, 184, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, A.; Deratani, A.; Taleb, S.; Drouiche, N.; Lounici, H. Desalination and Water Treatment Performance of NF90 and NF270 commercial nanofiltration membranes in the defluoridation of Algerian brackish water. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 212, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Jons, S.D. Chemistry and fabrication of polymeric nanofiltration membranes: A review. Polymer 2016, 103, 417–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayed, A.F.M.; Ashraf, M.A. Modified nanofiltration membrane treatment of saline water: A review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 187, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaysom, C.; Cath, T.Y.; Depuydt, T.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Forward and pressure retarded osmosis: Potential solutions for global challenges in energy and water supply. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6959–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, C.R.; Wilf, M.; Andes, K.; Iong, J. Design considerations for wastewater treatment by reverse osmosis. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, S.; Amirinejad, M.; Mirzadeh, S.S.; Wood, D.A. Insights into colloidal membrane fouling mechanisms for nanofiltration of surface water using single and hybrid membrane processes. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 2517–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W.; Benamor, A.; Hilal, N.; Leo, C.P. Hybrid coagulation-NF membrane process for brackish water treatment: Effect of antiscalant on water characteristics and membrane fouling. Desalination 2016, 393, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elazhar, F.; Elazhar, M.; Filali, N.E.; Belhamidi, S.; Elmidaoui, A.; Taky, M. Potential of hybrid NF-RO system to enhance chloride removal and reduce membrane fouling during surface water desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 261, 118299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Li, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, S.; Shang, H.; Lin, H.; Chang, H. Operating parameters optimization of combined UF/NF dual-membrane process for brackish water treatment and its application performance in municipal drinking water treatment plant. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Hybrid UF/NF process treating secondary effluent of wastewater treatment plants for potable water reuse: Adsorption vs. coagulation for removal improvements and membrane fouling alleviation. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, J.; Hao, X.; Liu, D.; Cui, F. Investigations on the fouling characteristic of humic acid and alginate sodium in capacitive deionization. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2021, 11, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicini, S.; Mauri, M.; Wichert, J.; Castellano, M. Alginate gelling process: Use of bivalent ions rich microspheres. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017, 57, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.R.; Rosa, M.J.; Nyström, M. The role of membrane charge on nanofiltration performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 265, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mänttäri, M.; Pihlajamäki, A.; Nyström, M. Effect of pH on hydrophilicity and charge and their effect on the filtration efficiency of NF membranes at different pH. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.S.; Lee, S.; Elimelech, M. Chemical and physical aspects of cleaning of organic-fouled reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 272, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.S.; Elimelech, M. Protein (BSA) fouling of reverse osmosis membranes: Implications for wastewater reclamation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.; Tay, K.G.; Ng, H.Y. Fouling of reverse osmosis membrane by protein (BSA): Effects of pH, calcium, magnesium, ionic strength and temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, S.; Boch, R.; Leis, A.; Koraimann, G.; Grengg, C.; Domberger, G.; Nachtnebel, M.; Schwab, C.; Dietzel, M. Scale deposits in tunnel drainage systems—A study on fabrics and formation mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, M.A.; Gil, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Dammak, L.; Kononenko, N.A.; Larchet, C.; Grande, D.; Nikonenko, V.V. Mitigation of membrane scaling in electrodialysis by electroconvection enhancement, pH adjustment and pulsed electric field application. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.W.; Pearce, G.K. Critical, sustainable and threshold fluxes for membrane filtration with water industry applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchin, P.; Aimar, P.; Field, R.W. Critical and sustainable fluxes: Theory, experiments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 42–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, W.J.T.; Mattsson, T.; Chew, Y.M.J.; Bird, M.R. Investigation of cake fouling and pore blocking phenomena using fluid dynamic gauging and critical flux models. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 533, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Field, R.W.; Wu, D.; Howell, J.A.; Gupta, B.B. Critical flux concept for microfiltration fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braghetta, B.A.; DiGiano, F.A.; Ball, W.P. NOM Accumulation at NF Membrane Surface: Impact of Chemistry and Shear. J. Environ. Eng. 1998, 124, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitko, K.; Laskowska, E.; Turek, M.; Dydo, P.; Piotrowski, K. Scaling Risk Assessment in Nanofiltration of Mine Waters. Membranes 2020, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.L.; O’Melia, C.R. Protein and humic acid adsorption onto hydrophilic membrane surfaces: Effects of pH and ionic strength. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Khan, Z.; Zaidi, S.M.; Boyce, M.C. Biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes for seawater desalination: Phenomena and prevention. Desalination 2011, 281, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Fu, Q.S.; Criddle, C.S.; Leckie, J.O. Effect of Flux (Transmembrane Pressure) and Membrane Properties on Fouling and Rejection of Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes Treating Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Containing Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrijenhoek, E.M.; Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. Influence of membrane surface properties on initial rate of colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 188, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H. Preparation of rGO/ZIF-8 Modified Nanofiltration Membrane and Experimental Study on Desalination of Brackish Water. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ayyavoo, J.; Nguyen, T.P.N.; Jun, B.M.; Kim, I.C.; Kwon, Y.N. Protection of polymeric membranes with antifouling surfacing via surface modifications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 506, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, W.; Sun, J.; Tang, H. Developing composite nanofiltration membranes with highly stable antifouling property based on hydrophilic roughness. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 256, 117799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seman, M.N.A.; Hilal, N.; Khayet, M. UV-photografting modification of NF membrane surface for NOM fouling reduction. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 4855–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
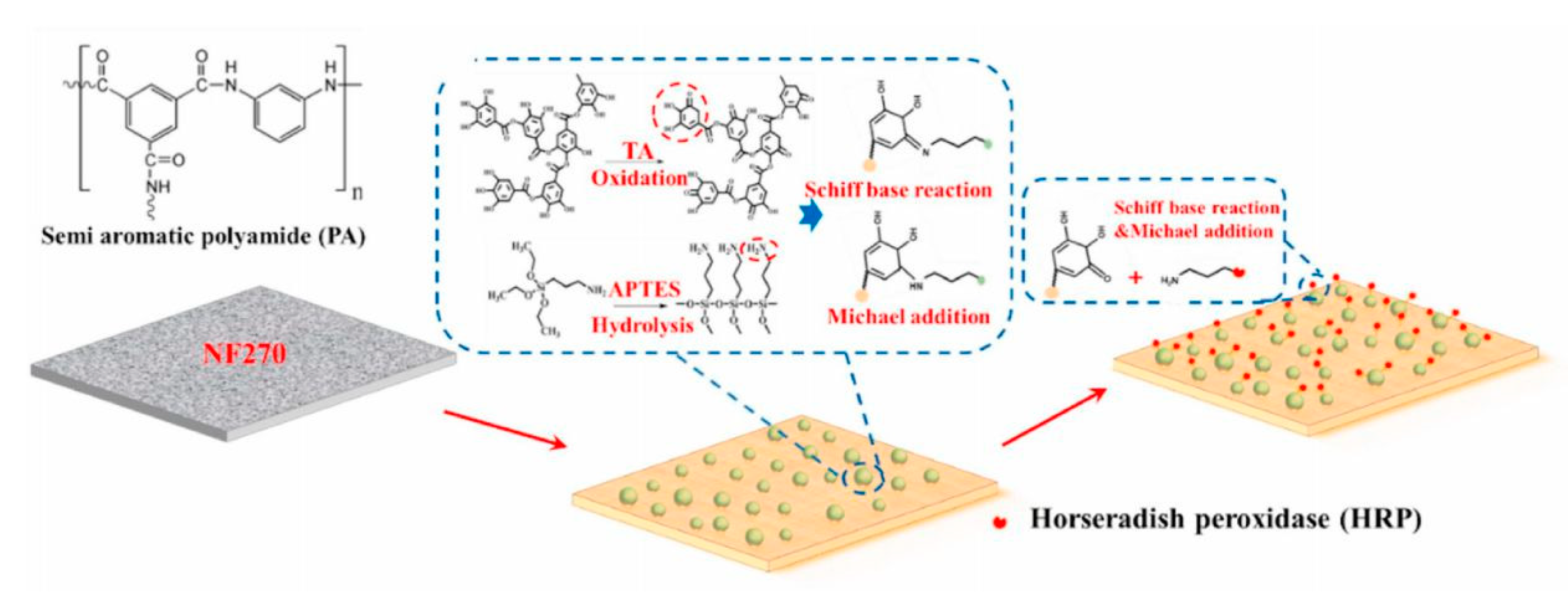
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Li, S.; Wan, Y.; Luo, J. Surface functionalization of nanofiltration membrane by catechol-amine codeposition for enhancing antifouling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Su, B.; Gao, X.; Gao, C. The performance of polyamide nanofiltration membrane for long-term operation in an integrated membrane seawater pretreatment system. Desalination 2012, 296, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, T.H.; Wong, F.S.; Fane, A.G. Enhanced concentration polarization by unstirred fouling layers in reverse osmosis: Detection by sodium chloride tracer response technique. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Study on the Performance of Nanofiltration Membrane Fouling by Natural Organic Matter. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
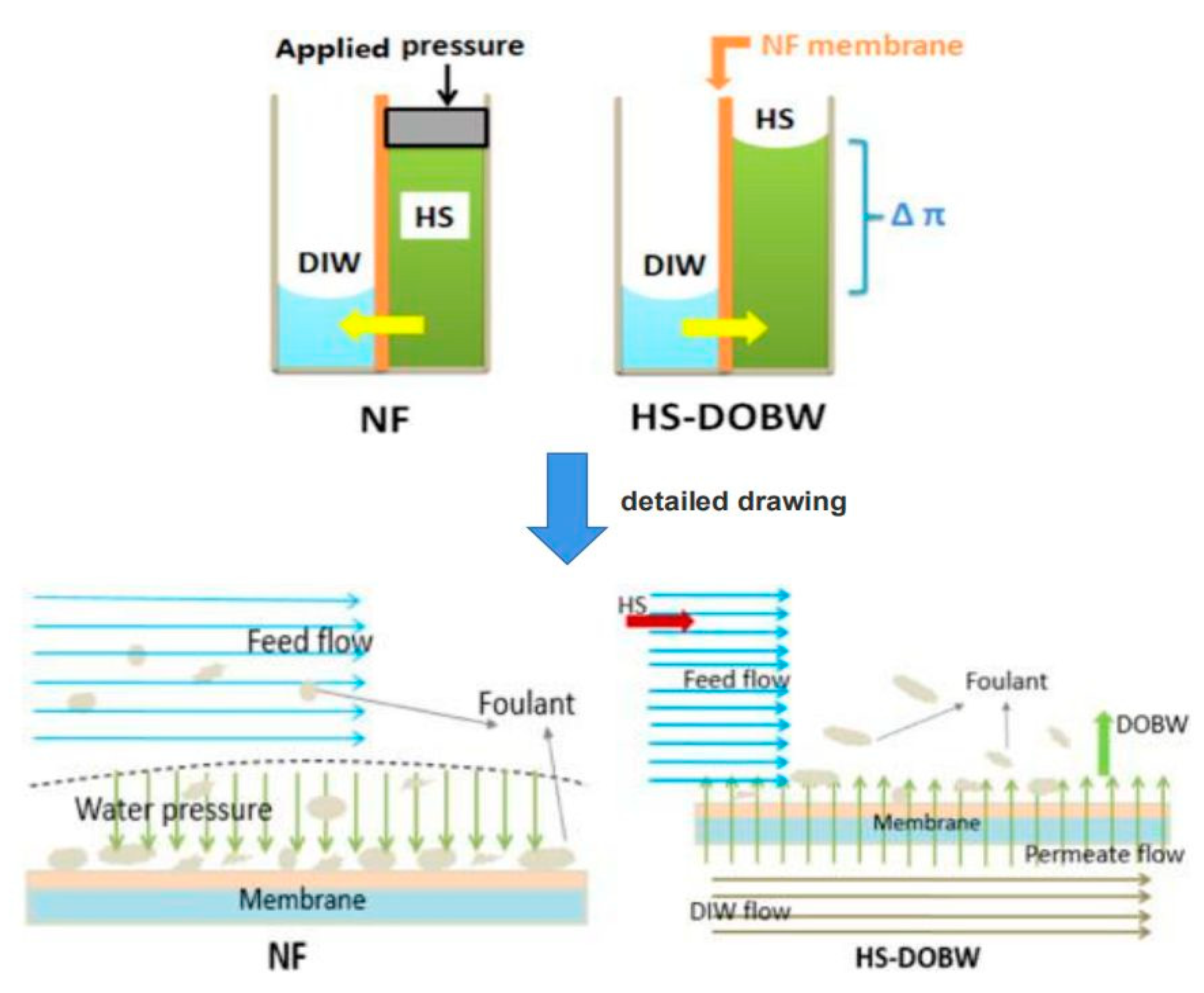
- Dana, A.; Hadas, S. Ramon, G.Z. Potential application of osmotic backwashing to brackish water desalination membranes. Desalination 2019, 468, 114029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wei, Y.; Gao, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y. An innovative backwash cleaning technique for NF membrane in groundwater desalination: Fouling reversibility and cleaning without chemical detergent. Desalination 2015, 359, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Meng, L.; Zhao, Q.B.; Shi, Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Lu, Y. Effects of chemical cleaning on RO membrane inorganic, organic and microbial foulant removal in a full-scale plant for municipal wastewater reclamation. Water Res. 2017, 113, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tin, M.M.M.; Anioke, G.; Nakagoe, O.; Tanabe, S.; Kodamatani, H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Fujioka, T. Membrane fouling, chemical cleaning and separation performance assessment of a chlorine-resistant nanofiltration membrane for water recycling applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Khan, M.T.; Cao, X.; Croue, J.P. Importance of origin and characteristics of biopolymers in reversible and irreversible fouling of ultrafiltration membranes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, N.; Amy, G.; Plottu-Pecheux, A.; Yoon, Y. Identification of nanofiltration membrane foulants. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3936–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Bolto, B.; Gray, S.; Hoang, M.; Ostarcevic, E. An autopsy study of a fouled reverse osmosis membrane element used in a brackish water treatment plant. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3915–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.; Amy, G.; Pellegrino, J.; Yoon, Y. Characterization of clean and natural organic matter (NOM) fouled NF and UF membranes, and foulants characterization. Desalination 1998, 118, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
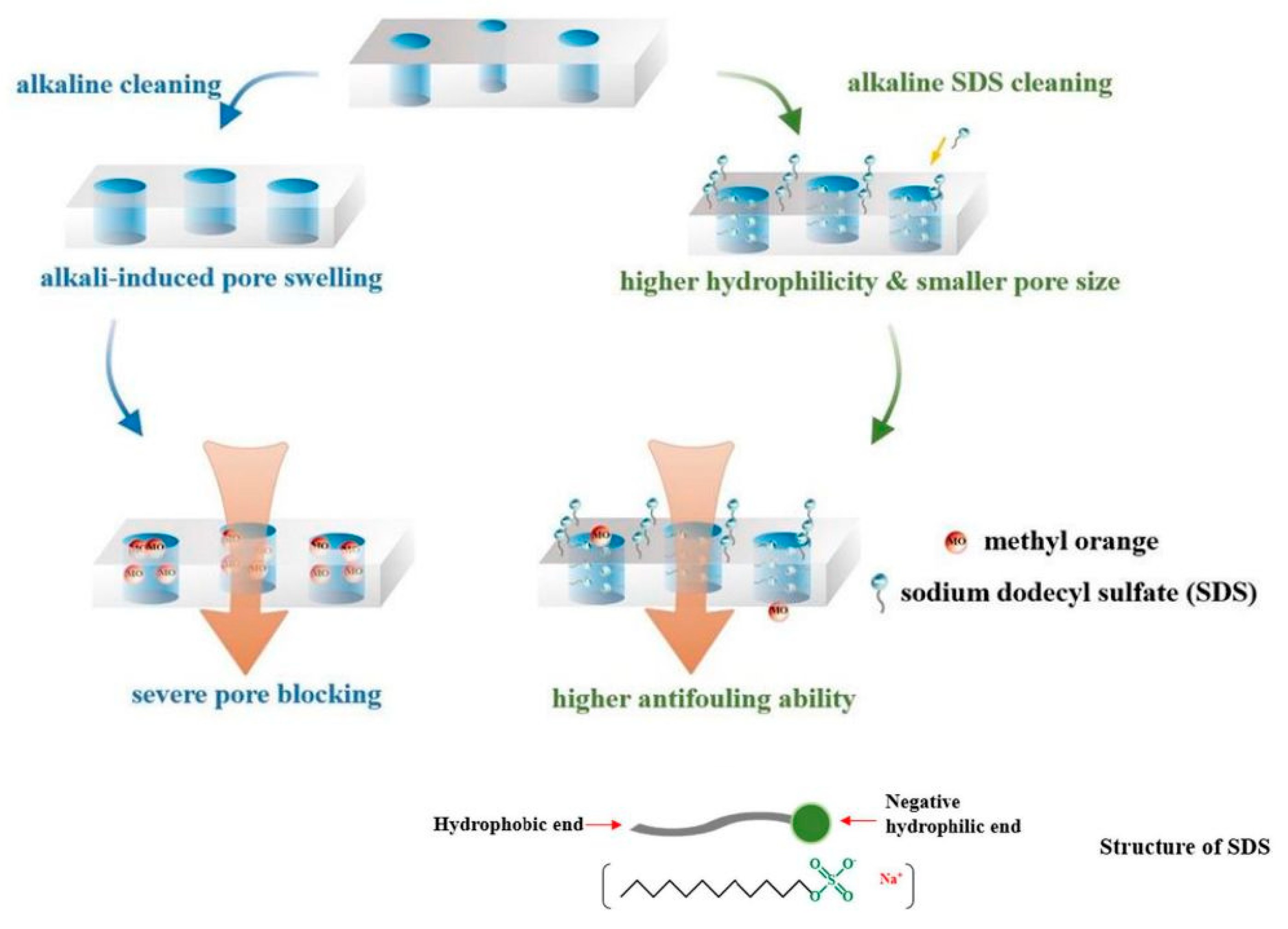
- Huang, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, S.; Wan, Y. New insights into effect of alkaline cleaning on fouling behavior of polyamide nanofiltration membrane for wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, J.; Li, C.; Meng, H. A review on cleaning of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes used for water treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 87, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, C. Ultrasonic-assisted acid cleaning of nanofiltration membranes fouled by inorganic scales in arsenic-rich brackish water. Desalination 2016, 377, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, B.; Bodzek, M. Desalination of geothermal waters using a hybrid UF-RO process. Part II: Membrane scaling after pilot-scale tests. Desalination 2013, 319, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Gao, C. Performance of UF-NF integrated membrane process for seawater softening. Desalination 2011, 276, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Mao, J.Y.; Lin, H.J.; Huang, C.C. Graphene-based nanofiltration membranes for improving salt rejection, water flux and antifouling—A review. Desalination 2018, 429, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; He, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yu, S.; Gao, C. Composite reverse osmosis membrane with a selective separation layer of double-layer structure for enhanced desalination, anti-fouling and durability properties. Desalination 2021, 499, 114838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Fu, X. Application of two stages nanofiltration in desalting of high degree brackish water. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 63–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, X.; Schäfer, A.I. Removal of Naturally Occurring Strontium by Nanofiltration/Reverse Osmosis from Groundwater. Membranes 2020, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Aghilesh, K.; Nair, A.; Ram, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ali, J.; Singh, R.; Garg, M.C. Response surface methodology and artificial neural network modelling for the performance evaluation of pilot-scale hybrid nanofiltration (NF) & reverse osmosis (RO) membrane system for the treatment of brackish ground water. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111497. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Dimitriou, E.; Nuez, I. Retrofitting assessment of a full-scale brackish water reverse osmosis desalination plant with a feed capacity of 600 m3/d. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 144, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, G.; Hong, S. New approach for scaling control in forward osmosis (FO) by using an antiscalant-blended draw solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Lee, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; Elimelech, M. Role of pressure in organic fouling in forward osmosis and reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chun, Y.; Zaviska, F.; Kim, S.J.; Mulcahy, D.; Yang, E.; Kim, I.S.; Zou, L. Fouling characteristics and their implications on cleaning of a FO-RO pilot process for treating brackish surface water. Desalination 2016, 394, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Mulcahy, D. Brackish water desalination by a hybrid forward osmosis-nanofiltration system using divalent draw solute. Desalination 2012, 284, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaee, A.; Hilal, N. High recovery rate NF-FO-RO hybrid system for inland brackish water treatment. Desalination 2015, 363, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Barbeau, B. Hybrid Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration-Calcite Contactor: A Novel Point-of-Entry Treatment for Removal of Dissolved Mn, Fe, NOM and Hardness from Domestic Groundwater Supplies. Membranes 2019, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Indicators | Values |
|---|---|
| Arsenic (mg/L) | 0.01 |
| Cadmium (mg/L) | 0.005 |
| Chromium (hexavalent, mg/L) | 0.05 |
| Fluoride (mg/L) | 1.0 |
| Nitrate (in N, mg/L) | 10 |
| Aluminum (mg/L) | 0.2 |
| Manganese (mg/L) | 0.1 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 250 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | 250 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 1000 |
| Total hardness (in CaCO3, mg/L) | 450 |
| Items | NF90 | NF270 |
|---|---|---|
| Surface layer material | fully aromatic polyamide | semi-aromatic polyamide |
| Water permeability (L/(m2·h·bar)) a | 9.0 | 17.5 |
| Salt rejection (%) b | 87.4 | 56.3 |
| Zeta potential (mV) c | −13 | −53 |
| Contact angle (°) d | 55.2 ± 2.5 | 18.3 ± 2.6 |
| Surface roughness (nm) | 64.9 ± 8.1 | 5.1 ± 0.5 |
| Pore radius (nm) e | 0.31 | 0.40 |
| NF Membrane | Feedwater | Cleaning Method | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DK | Synthetic brackish water | 2.0 wt.% citric acid + NaOH solution (pH = 10) | FR = 97.80% | [55] |
| RR = 61.63% | ||||
| DL | FR = 95.40% | |||
| RR = 49.35% | ||||
| NF3A | Synthetic arsenic-rich brackish water | Citric acid (pH = 3) + ultrasound (with the power intensity of 1 W/cm2) | FR = 99.99% | [124] |
| NF-1812 | Synthetic brackish water | Hydraulic cleaning + 0.1% NaOH + 0.025 Na-SDS | FR = 99.20% | [113] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Zhao, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Progress in Research and Application of Nanofiltration (NF) Technology for Brackish Water Treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090662
Tian J, Zhao X, Gao S, Wang X, Zhang R. Progress in Research and Application of Nanofiltration (NF) Technology for Brackish Water Treatment. Membranes. 2021; 11(9):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090662
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jiayu, Xingrui Zhao, Shanshan Gao, Xiaoying Wang, and Ruijun Zhang. 2021. "Progress in Research and Application of Nanofiltration (NF) Technology for Brackish Water Treatment" Membranes 11, no. 9: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090662
APA StyleTian, J., Zhao, X., Gao, S., Wang, X., & Zhang, R. (2021). Progress in Research and Application of Nanofiltration (NF) Technology for Brackish Water Treatment. Membranes, 11(9), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090662