Formulation and Bioavailability of Novel Mucoadhesive Buccal Films for Candesartan Cilexetil in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment
2.2. Preparation of CC Bioadhesive Buccal Film
2.3. Evaluation of the Prepared Buccal Film
2.3.1. Instrumental Assessments of the Bioadhesive Films
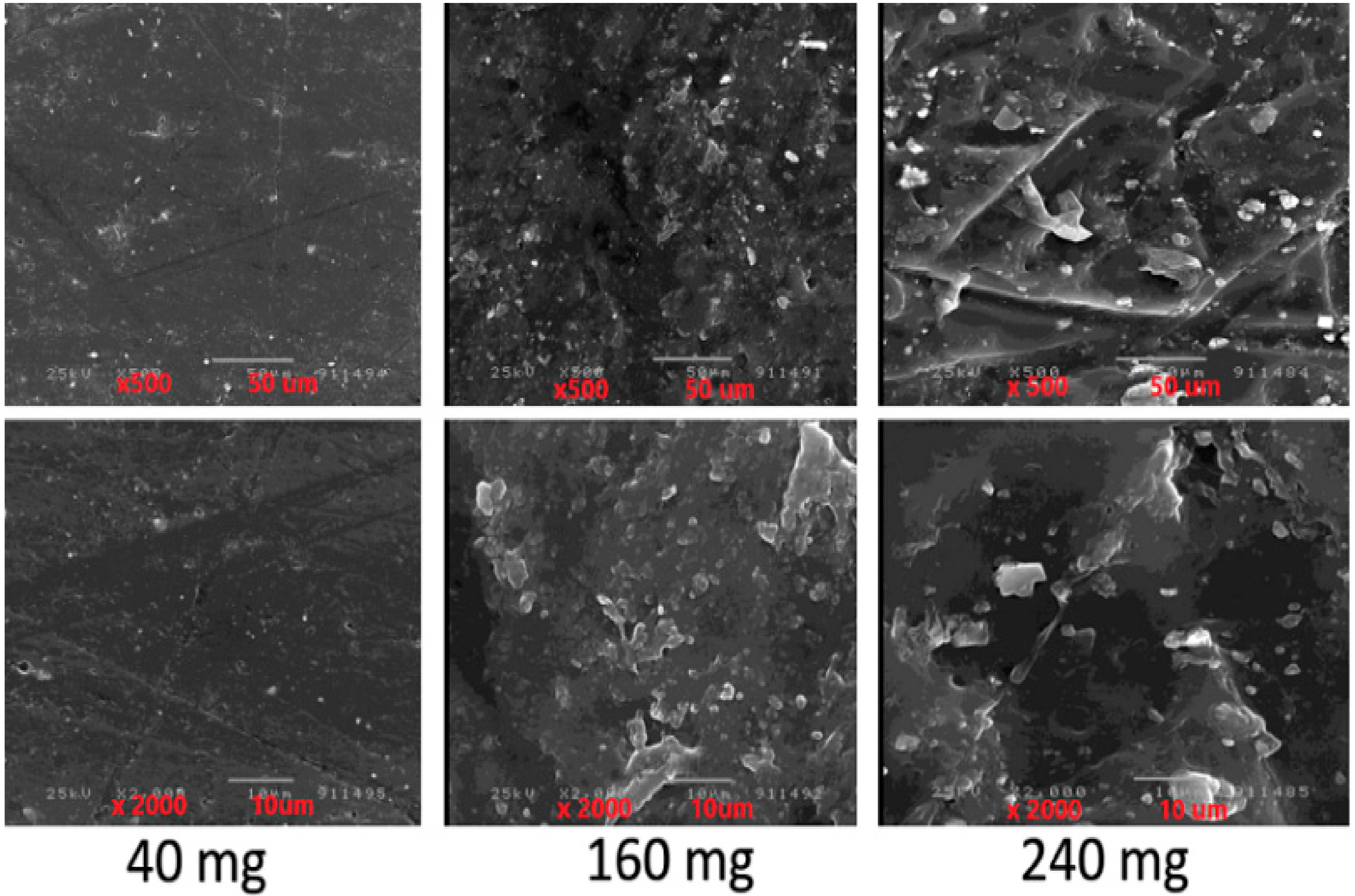
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
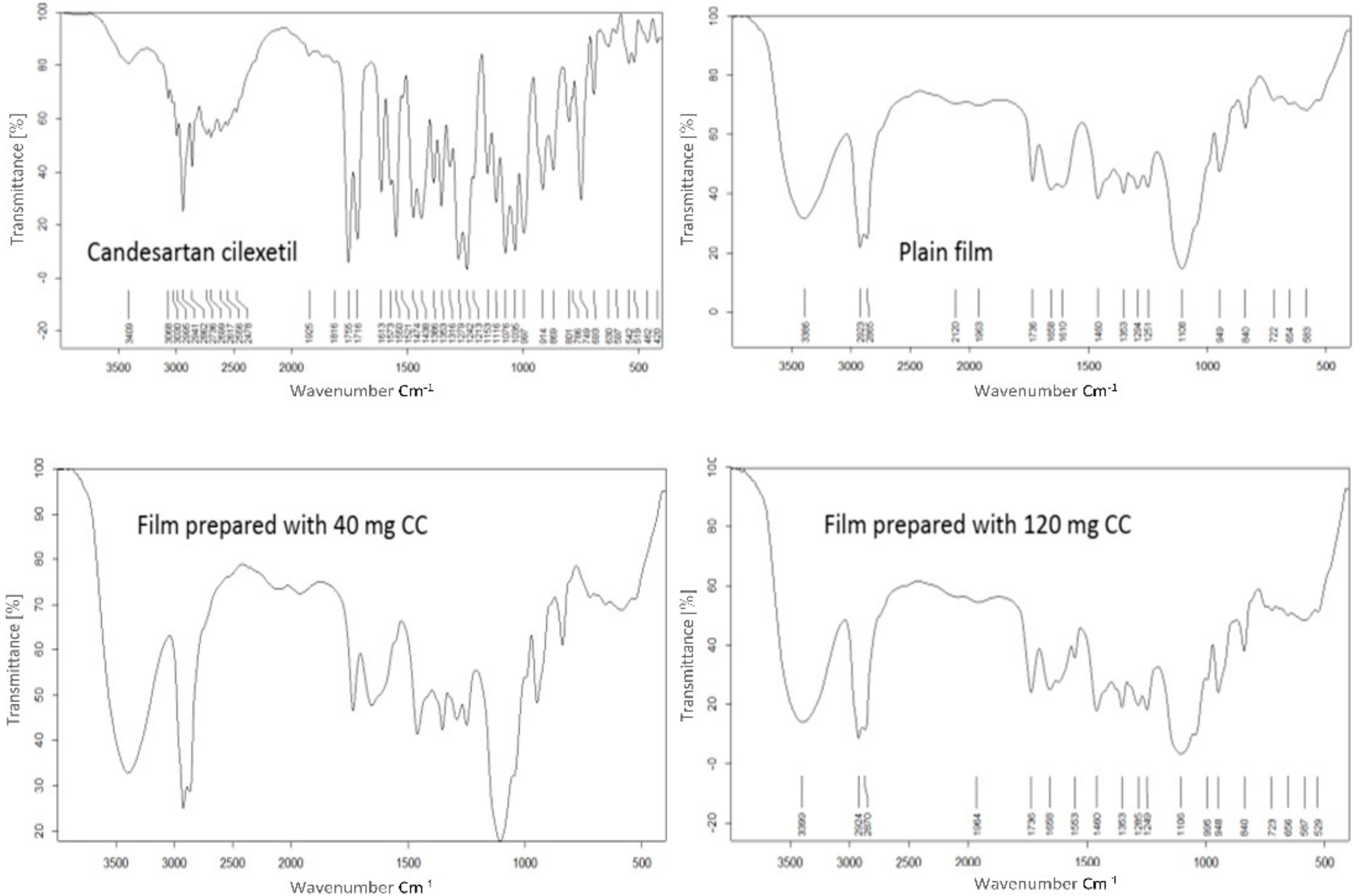
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Microenvironment pH
2.3.2. Physical Properties Assessments of the Bioadhesive Films
Weight Uniformity
Thickness Uniformity
Folding Endurance
2.3.3. Drug Content Uniformity
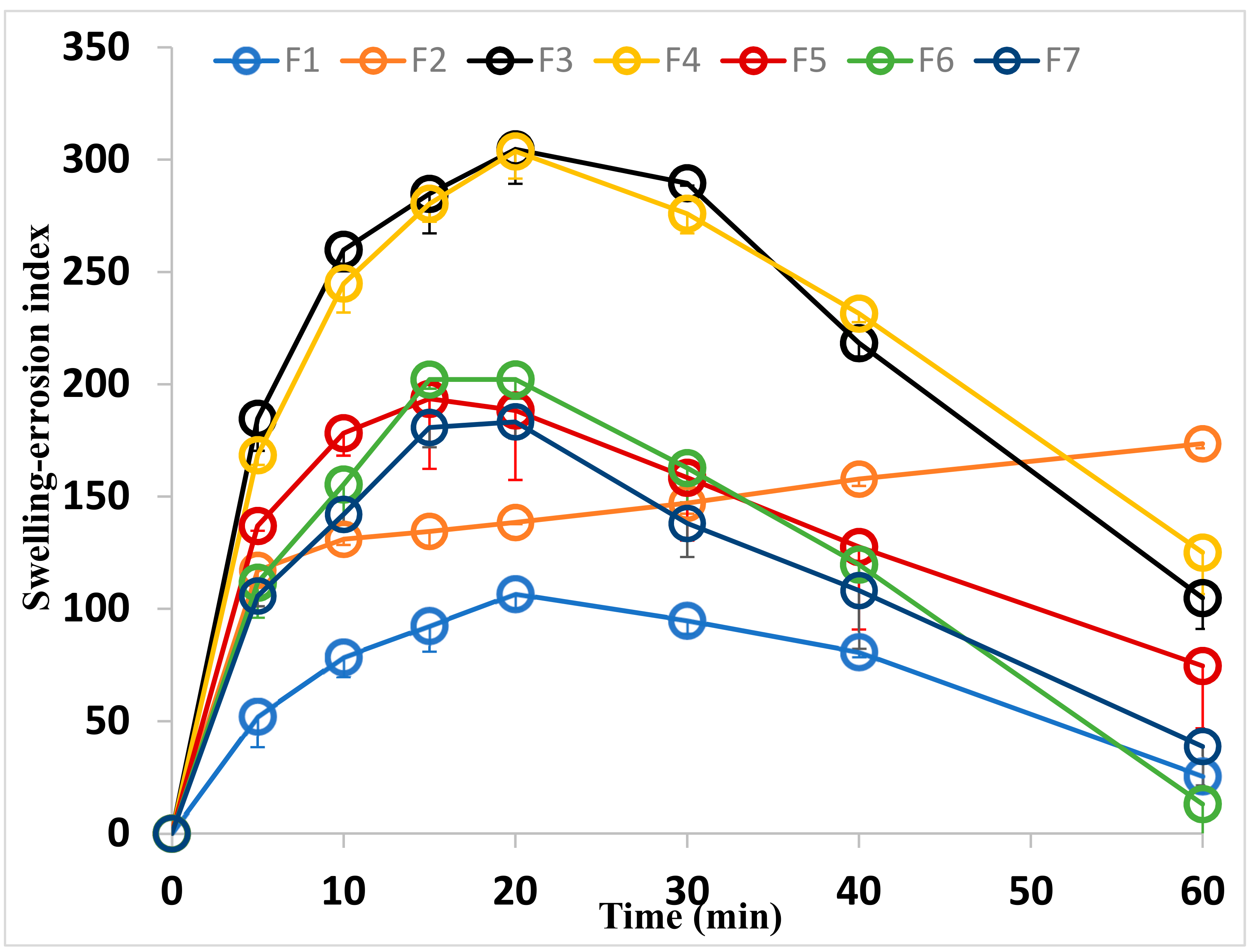
2.3.4. Swelling Index
2.3.5. In Vitro Bioadhesion Strength
2.3.6. In Vitro Bioadhesion Time
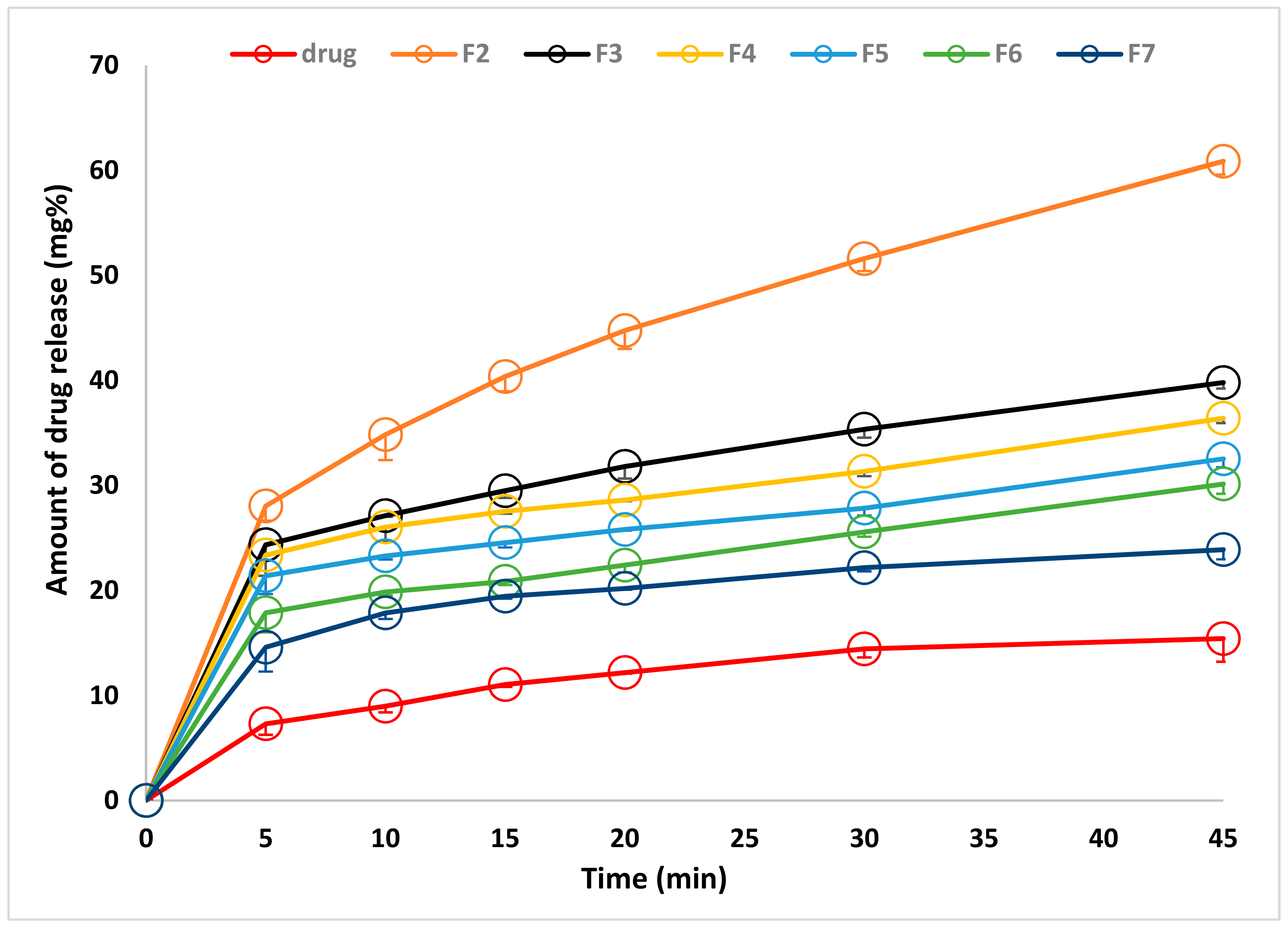
2.3.7. In Vitro Release Study
2.4. Bioavailability Study in Rats
2.4.1. Rats
2.4.2. Surgical Procedures
2.4.3. Dosage and Blood Sampling
2.4.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Assay
2.4.5. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Formulation
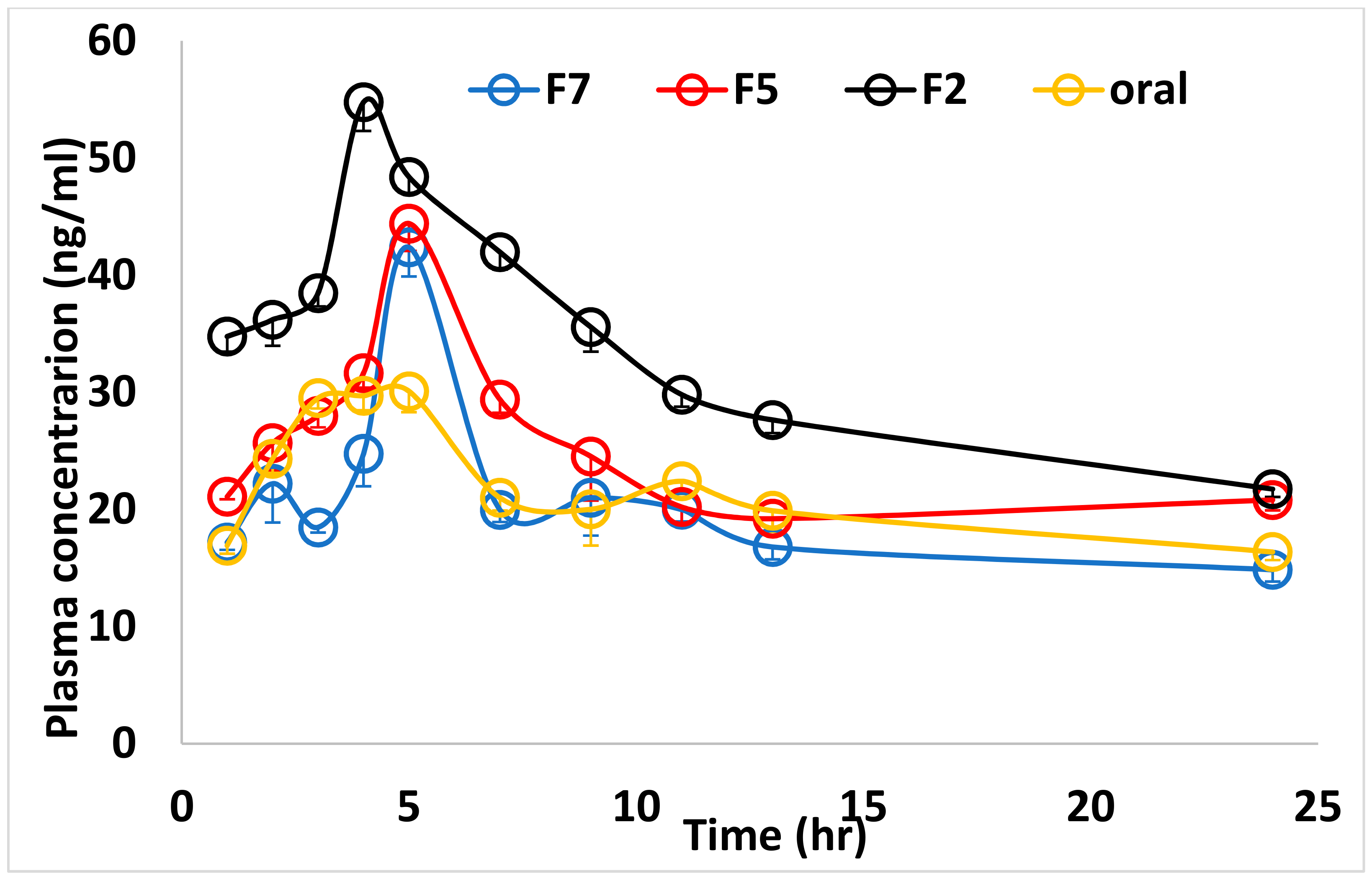
3.2. Bioavailability Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sweetman, S.C. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, 36th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Darwhekar, G.N.; Jain, D.K.; Chouhan, J. Biopharmaceutical classification of candesartan and candesartan cilexetil. Asian J. Pharm. Life Sci. 2012, 2, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Moffat, A.C.; Osselton, M.D.; Widdop, B. Clarke’s Analysis of Drugs and Poisons, 4th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.K. Effective surfactants blend concentration determination for o/w emulsion stabilization by two nonionic surfactants by simple linear regression. Ind. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhipala, N.; Veerabrahma, K. Candesartan cilexetil loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery: Characterization, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudhipala, N.; Veerabrahma, K. Candesartan cilexetil loaded nano-delivery systems for improved oral bioavailability. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, J.; Bhatia, V. Novel lipid carriers for oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2012, 15, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, U.F.; Sarhan, H.A.; Ali, T.; Sharkawy, H.A. Applying different techniques to improve the bioavailability of candesartan cilexetil antihypertensive drug, drug design. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1851–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakar, Y.; Kuotsu, K.; Bandyopadhyay, A.K. Buccal bioadhesive drug delivery—A promising option for orally less efficient drugs. J. Contr. Rel. 2006, 114, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Wilson, C.G.; Koosha, F.; Uchegbu, I.F. Sustained buccal delivery of hydrophobic drug denbufylline using physically cross linked palmitoyl chitosan hydrogels. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, Y.V.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Ramesh, G.; Madhusudan Rao, Y. Development of mucoadhesive patches for buccal administration of carvedilol. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.M.; Prajapati, B.G.; Patel, M.M. Design and characterization of chitosan-containing mucoadhesive buccal patches of propranolol hydrochloride. Acta Pharm. 2007, 57, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.S.; Jung, J.H.; Rhee, J.D.; Kim, C.K.; Choi, H.G. Physiochemical characterization and evaluation of buccal adhesive tablets containing omeprazole. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2001, 27, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Kaul, M.; Rawat, A.; Saini, S. An overview on buccal drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 1303–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Mady, O.Y.; Donia, A.A.; Al-Madboly, L. Miconazole-urea in a buccal film as a news trend for treatment of resistant mouth fungal mouth white patches. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albougy, H.A.; Naidoo, S.A. Systematic review of the management of oral candidiasis associated with HIV/AIDS. J. S. Afr. Dent. Assoc. 2002, 57, 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, A.S.; Vandana, K.L.; Priyanka, J.D. Azithromycin buccal patch in treatment of chronic periodontitis. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thimmasetty, J.; Pandey, G.; Babu, P. Design and in vivo evaluation of carvedilol buccal mucoadhesive patches. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 21, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, A.; Chhabra, N.; Aggarwal, G. Formulation and characterization of fast dissolving buccal films: A review. Der Pharm. Lett. 2011, 3, 152–165. [Google Scholar]
- Khairnar, A.; Jain, P.; Baviskar, D.; Jain, D. Development of mucoadhesive buccal patch containing aceclofenac: In vitro evaluations. Int. J. PharmTech. Res. 2009, 1, 978–981. [Google Scholar]
- Semalty, M.; Semalty, A.; Kumar, G.; Juyal, V. Development of mucoadhesive buccal films of glipizide. Ind. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 1, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giradkar, K.P.; Channawar, M.A.; Kajale, A.D.; Sirdhar, E.; Kambel, R.S.; Bakde, B.V.; Chandewar, A.V. Design, development and in vitro evaluation of bioadhesive dosage form for buccal route. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 2010, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Koland, M.; Charyulu, R.N.; Vijayanarayana, K.; Prabhu, P. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of chitosan buccal films of ondansetron hydrochloride. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 1, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafee, N.A.; Boraie, N.A.; Ismail, F.A.; Mortada, L.M. Design and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal patches containing cetylpyridinium chloride. Acta Pharm. 2003, 53, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Alanazi, F.K.; Abdel Rahman, A.A.; Mahrous, G.M.; Alsarra, I.A. Formulation and physicochemical characterization of buccoadhesive films containing ketorolac. J. Drug Del. Sci. 2007, 17, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, F.; Abdel Azeem, M.; Fetih, G.; Safwat, M. Mucoadhesive buccal patches of lornoxicam. Bull. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 33, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Jain, S.; Muthu, M.S.; Tiwari, S.; Tilak, R. Preparation and evaluation of buccal bioadhesive films containing clotimazole. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2008, 9, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Barakat, N.S.; El-Badry, M.; Shehata, M.S. Formulation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of naproxen mucoadhesive buccal patches for local effect. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tech. 2011, 21, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, J.G.; Sarfaraz, M.D.; Hiremath, D.; Sarudkar, S.A. Prearation and hysicochemical characterization of simvastatin loaded mucoadhesive bilayerd tablet. Indian J. Nov. Drug Deliv. 2009, 1, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ritschl, L.M.; Fichter, A.M.; Haberles, S.; Von-Bomhard, A.; Mitchell, D.A.; Wolff, K.D.; Mucke, T. Ketamine-xylazine anesthesia in rats: Intraperitoneal versus Intravenous administration using a microsurgical femoral vein access. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2015, 31, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Fitz, Y.; Li, Y.; Femandez, M.; Puch, I.C.; Wang, D.; Pazniokas, S.; Bucher, B.; Cui, X.; Solomon, S.B. Catheterization of the carotid artery and jugular vein to perform hemodynamic measures, infusions and blood sampling in a conscious rat model. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 95, e51881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrudan, M.B.; Muntean, D.M.; Gheldiu, A.M.; Neag, M.A.; Vlase, L. The pharmacokinetic interaction study between carvedilol and bupropion in rats. Pharmacology 2017, 99, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, J. The use of spreadsheets for pharmacokinetic simulations. Sci. World J. 2003, 3, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Hu, M. A useful microsoft excel add-in program for pharmacokinetic analysis. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2011, S11, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meineke, I.; Feltkamp, H.; Högemann, A.; Gundert-Remy, U. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of candesartan after administration of its pro-drug candesartan cilexetil in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension—A population analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 53, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, D.; Patel, U.; Bhimani, B.; Daslaniya, D.; Patel, G. Formulation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of candesartan cilexetil. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Bio. Sci. 2012, 1, 75–101. [Google Scholar]
- Halah, H.A.; Hussein, A.A. Oral solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems of candesartan cilexetil: Formulation, characterization and in vitro drug release studies. AAPS Open 2017, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gurunath, S.; Nanjwade, B.K.; Patila, P.A. Enhanced solubility and intestinal absorption of candesartan cilexetil solid dispersions using everted rat intestinal sacs. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghad, A.N.; Hind, E.Z. Enhancement of candesartan cilexetil dissolution rate by using different methods. Asia J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2015, 8, 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Sathali, A.A.; Varun, J. Formulation, development, and in vitro evaluation of candesartan cilexetil mucoadhesive microbeads. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2012, 4, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Tjandrawinata, R.R.; Setiawati, E.; Yunaidi, D.A.; Simanjuntak, R.; Santoso, I.D.; Susanto, L.W. Bioequivalence study of two formulations of candesartan cilexetil tablet in healthy subjects under fasting conditions. Drug Des. Dev. Therapy 2013, 7, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, C.H.; Mörike, K.E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of candesartan. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Bu, H.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y. Solid lipid nanoparticles loading candesartan cilexetil enhance oral bioavailability: In vitro characteristics and absorption mechanism in rats. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramineni, S.K.; Cunningham, L.L.; Dziubla, T.D.; Puleo, D.D. Competing properties of mucoadhesive films designed for localized delivery of imiquimod. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mireles, L.K.; Wu, M.R.; Saadeh, N.; Yahia, L.H.; Sacher, E. Physicochemical characterization of polyvinyl pyrrolidone: A tale of two polyvinyl pyrrolidones. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30461–30467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chan, K.; Jasti, B.R.; Upadrashta, B.; Li, X. Expression of P-glycoprotein and CYP3A4 along the porcine oral-gastrointestinal tract: Implications on oral mucosal drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, O.Y.; Ebeid, E.M.; Donia, A.A.; Qasim, W. A new trend in the formulation of the solid dosage form to increase candesartan cilexetil solubility in a simulation media to gastrointestinal tract. Eur. J. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 7, 410–424. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, W.; Dawaba, H.M.; Afouna, M.I.; Samy, A.M.; Rashed, M.H.; Abdelaziz, A.E. Enhancing the oral bioavailability of candesartan cilexetil loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: In vitro characterization and absorption in rats after oral administration. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.L.; Duong, V.A.; Maeng, H.-J. Pharmaceutical formulations with P-glycoprotein inhibitory effect as promising approaches for enhancing oral drug absorption and bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulal, N.A.; Lakshmi, P.K. Enhancement of solubility and bioavailability of candesartan cilexetil using natural p-glycoprotein inhibitors. Tropical J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AboulFotouh, K.; Allam, A.A.; El-Badry, M.; El-Sayed, A.M. A self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for enhancing the oral bioavailability of candesartan cilexetil: Ex Vivo and in vivo evaluation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3599–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, Y.; Gopalakrishna-Murthy, T.E. Design and development and evaluation of candesartan cilexetil liquid fi lling formulations. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formulae | CC (mg/Film) | CMC * (mg/cm2) | PVP * (mg/cm2) | Tween (mg/cm2) | PG * (mg/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 1.30 | 2 |
| F2 | 40 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 1.30 | 2 |
| F3 | 80 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 1.30 | 2 |
| F4 | 120 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 1.30 | 2 |
| F5 | 160 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 1.30 | 2 |
| F6 | 200 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 1.30 | 2 |
| F7 | 240 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 1.30 | 2 |
| F8 | 240 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 1.95 | 2 |
| F9 | 240 | 7.50 | 2.50 | 2.60 | 2 |
| F10 | 240 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 1.30 | 2 |
| F11 | 240 | 2.50 | 7.50 | 1.30 | 2 |
| Formulae | Weight/cm2 | * ADC/cm2 | * F. Endurance | Thickness | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 28.33 (±2.36) | --------------- | 100 | 0.30 (±0.00) | 6.680 |
| F2 | 30.49 (±1.75) | 0.58 (±0.017) | 100 | 0.47 (±0.02) | 6.740 |
| F3 | 35.32 (±2.05) | 1.04 (±0.029) | 100 | 0.49 (±0.01) | 6.760 |
| F4 | 39.75 (±2.56) | 1.43 (±0.080) | 100 | 0.50 (±0.00) | 6.790 |
| F5 | 41.48 (±1.93) | 1.92 (±0.075) | 100 | 0.50 (±0.02) | 6.900 |
| F6 | 41.90 (±2.50) | 1.73 (±0.045) | 100 | 0.52 (±0.02) | 7.160 |
| F7 | 42.34 (±2.45) | 1.63 (±0.075) | 100 | 0.52 (±0.03) | 7.230 |
| Bioadhesion Strength (g) | Adhesion Force (N) | Bond Strength (Nm2) | Bioadhesion Time (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 31.144 (2.40) | 0.306(0.01) | 0.076 | 55(2.10) |
| F2 | 32.437 (1.80) | 0.318(0.03) | 0.080 | 58(3.40) |
| F3 | 32.504 (2.02) | 0.319(0.03) | 0.080 | 59(2.20) |
| F4 | 36.147 (3.12) | 0.355(0.02) | 0.089 | 61(2.90) |
| F5 | 36.934 (1.15) | 0.363(0.04) | 0.092 | 64(3.60) |
| F6 | 39.932 (4.20) | 0.392(0.02) | 0.098 | 66(1.50) |
| F7 | 42.396 (3.12) | 0.416(0.03) | 0.104 | 70(1.90) |
| Parameters | Oral | F2 (40 mg) | F5 (160 mg) | F7 (240 mg) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0–∞ (ng * h/mL) | 547.39 ± 7.30 a | 972.89 ± 7.29 b | 544.16 ± 7.62 a | 509.98 ± 6.53 c | <0.001 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 30.03 ± 1.57 a | 54.47 ± 3.13 b | 44.40 ± 2.55 c | 42.37 ± 1.66 c | <0.001 |
| Tmax (h) | 5.00 ± 0.24 a | 4.00 ± 0.16 b | 5.00 ± 0.30 a | 5.00 ± 0.29 a | <0.001 |
| Kel (h−1) | 0.29 ± 0.02 a | 0.10 ± 0.02 b | 0.29 ± 0.03 a | 0.29 ± 0.01 a | <0.001 |
| Kab (h−1) | 0.30 ± 0.01 a | 0.66 ± 0.02 b | 0.30 ± 0.02 a | 0.31 ± 0.02 a | <0.001 |
| t1/2 (h) | 2.22 ± 0.16 a | 1.05 ± 0.03 b | 2.17 ± 0.97 a | 2.18 ± 0.22 a | <0.001 |
| Frel | Reference | 177.73% | 99.41% | 93.17% | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mady, O.Y.; Abulmeaty, M.M.A.; Donia, A.A.; Al-Khureif, A.A.; Al-Shoubki, A.A.; Abudawood, M.; Abdel Moety, D.A. Formulation and Bioavailability of Novel Mucoadhesive Buccal Films for Candesartan Cilexetil in Rats. Membranes 2021, 11, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090659
Mady OY, Abulmeaty MMA, Donia AA, Al-Khureif AA, Al-Shoubki AA, Abudawood M, Abdel Moety DA. Formulation and Bioavailability of Novel Mucoadhesive Buccal Films for Candesartan Cilexetil in Rats. Membranes. 2021; 11(9):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090659
Chicago/Turabian StyleMady, Omar Y., Mahmoud M. A. Abulmeaty, Ahmed A. Donia, Abdulaziz A. Al-Khureif, Adam A. Al-Shoubki, Manal Abudawood, and Doaa A. Abdel Moety. 2021. "Formulation and Bioavailability of Novel Mucoadhesive Buccal Films for Candesartan Cilexetil in Rats" Membranes 11, no. 9: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090659
APA StyleMady, O. Y., Abulmeaty, M. M. A., Donia, A. A., Al-Khureif, A. A., Al-Shoubki, A. A., Abudawood, M., & Abdel Moety, D. A. (2021). Formulation and Bioavailability of Novel Mucoadhesive Buccal Films for Candesartan Cilexetil in Rats. Membranes, 11(9), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11090659








