γ-Valerolactone as Bio-Based Solvent for Nanofiltration Membrane Preparation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
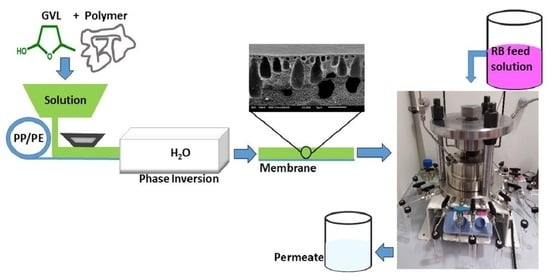
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. Viscosity Measurements
2.4. Cloudpoint Determination
2.5. Filtrations
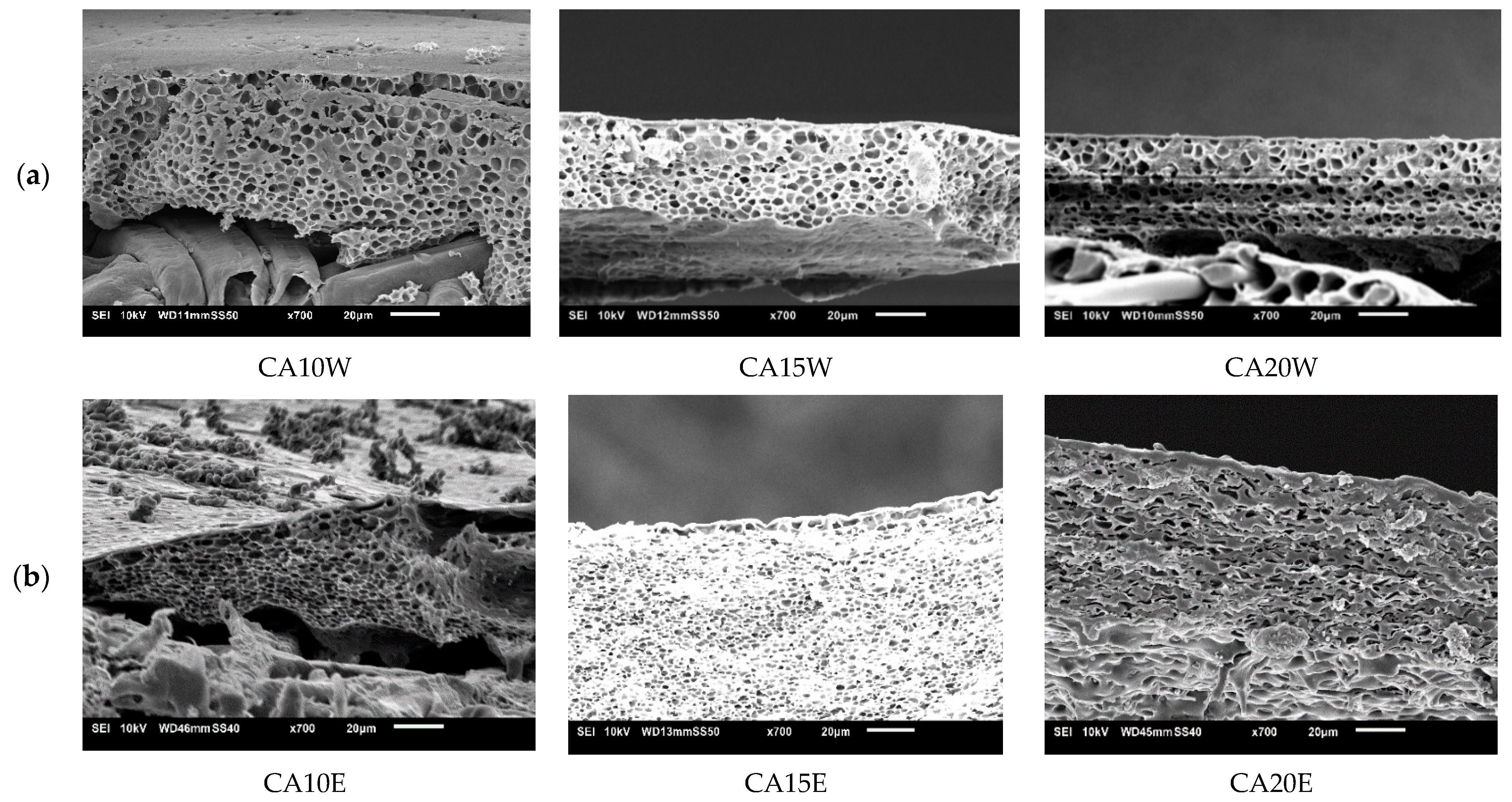
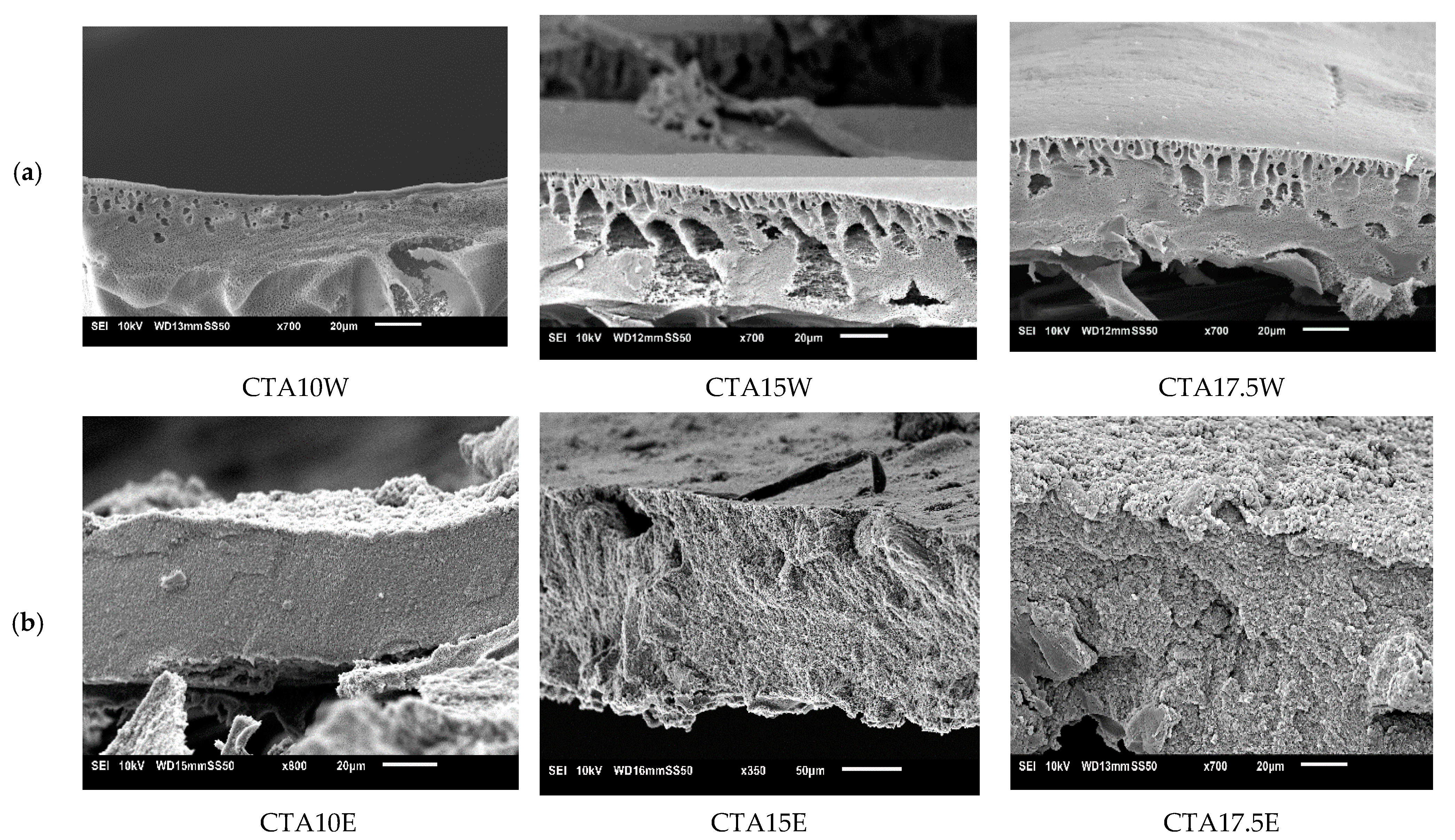
2.6. Membrane Morphology
2.7. Solubility Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Inversion Behavior of Polymer/-Valerolactone (GVL) Systems
3.1.1. Introduction
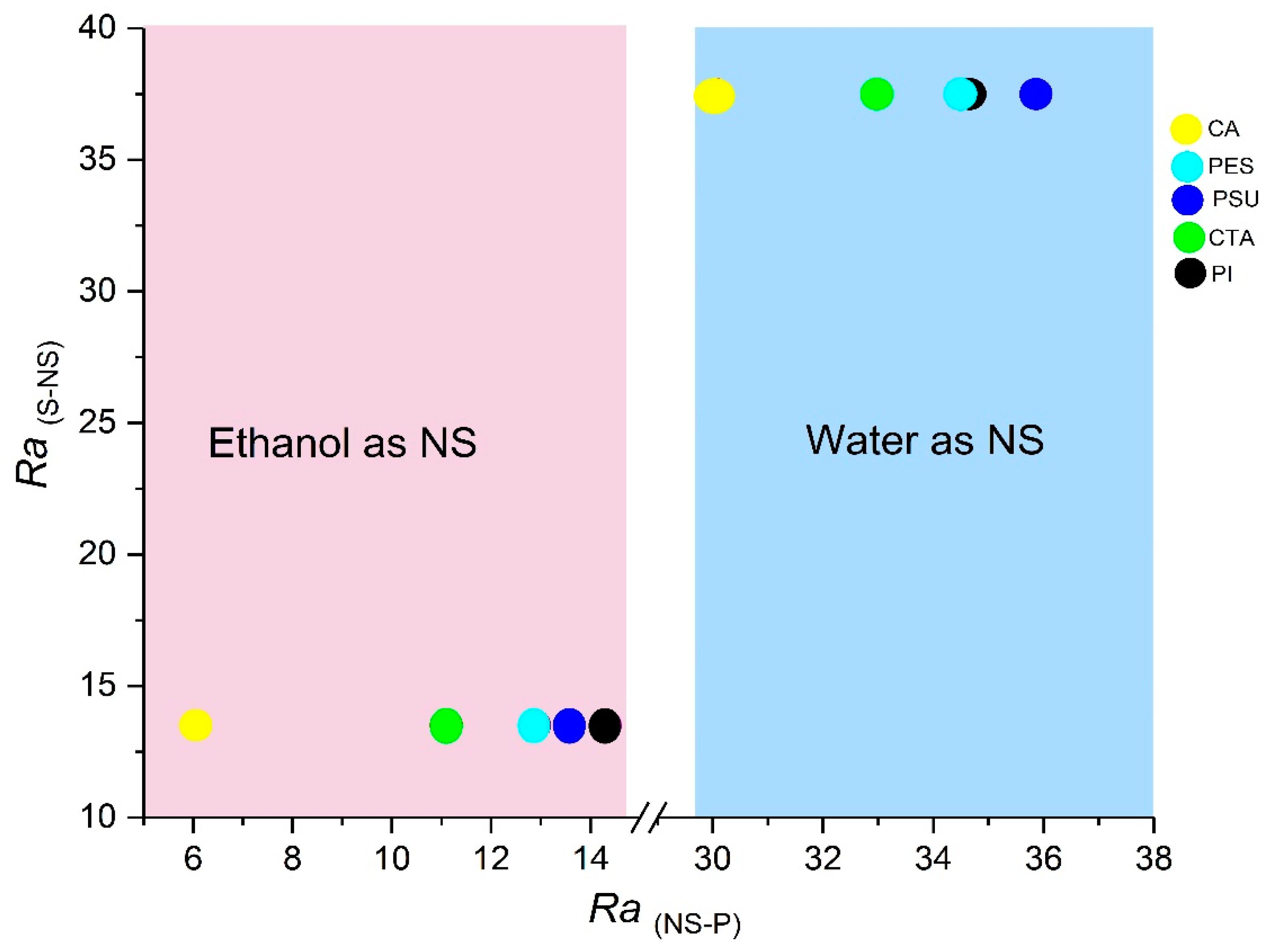
3.1.2. S-NS (Solvent and Non-Solvent) and NS-P (Non-Solvent and Polymer) Interaction Distance Parameters
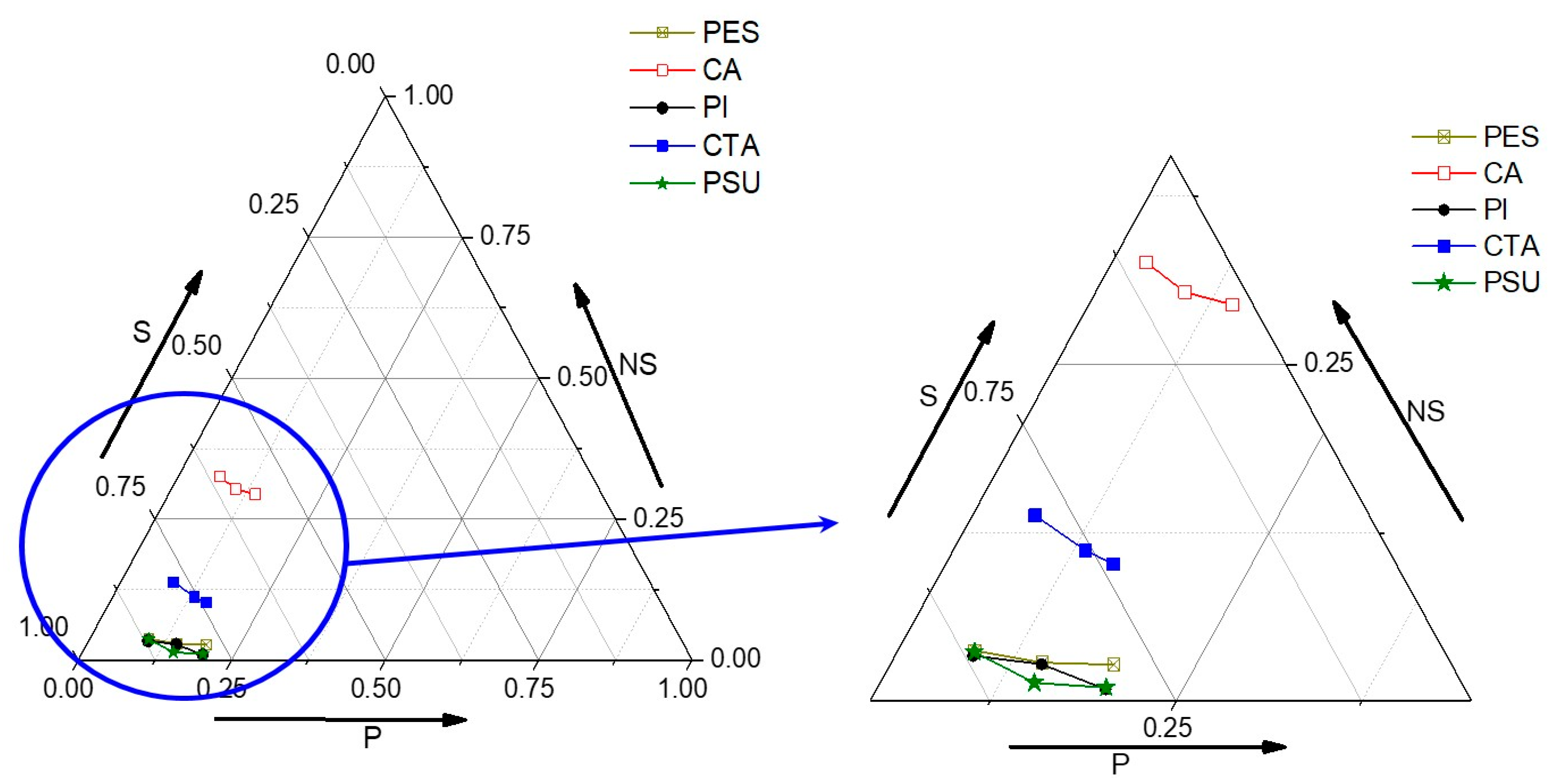
3.2. Phase Diagrams
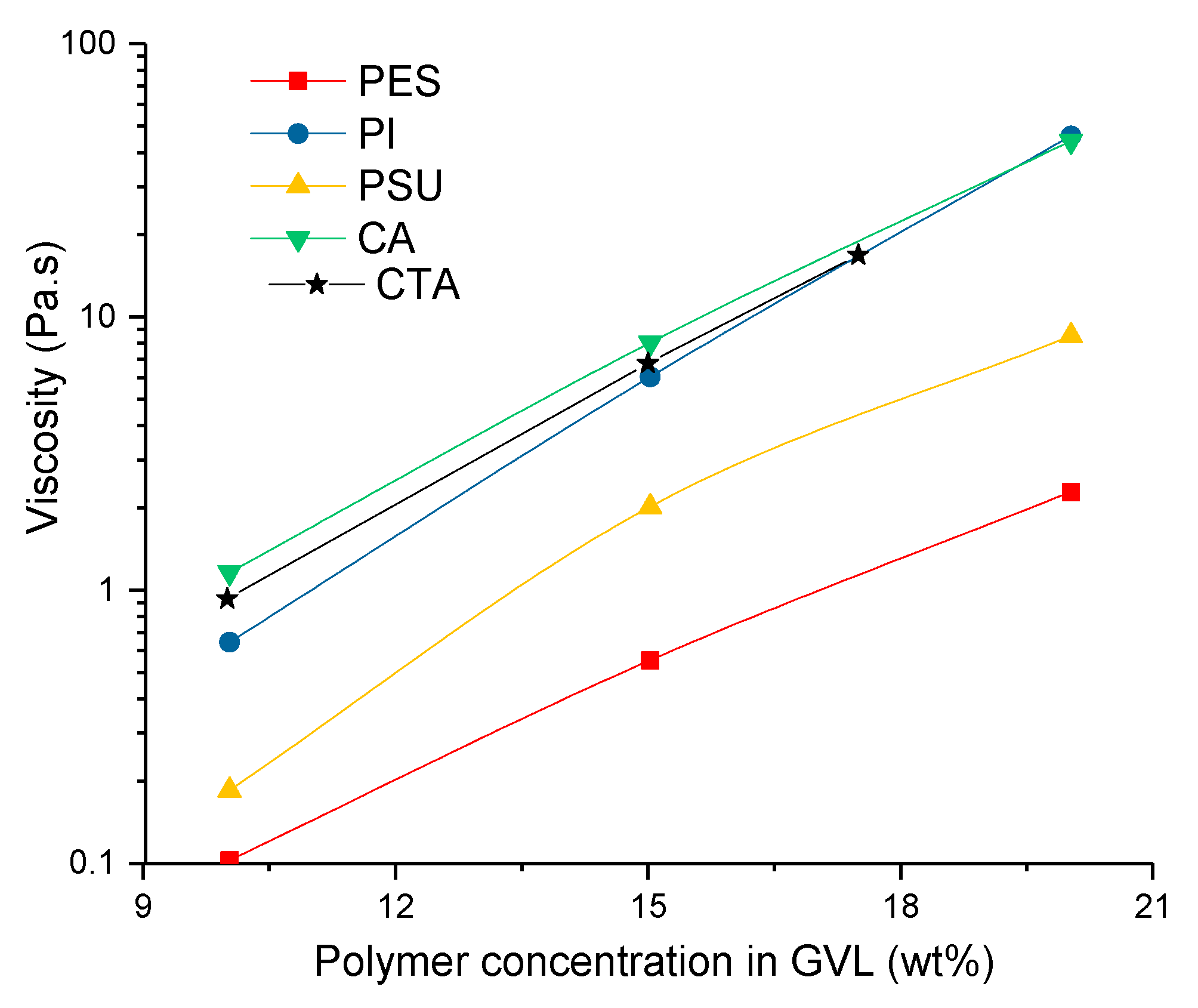
3.3. Kinetic Aspects of Non-Solvent Induced Phase Separation (NIPS) Process
3.4. Membrane Performance and Morphology
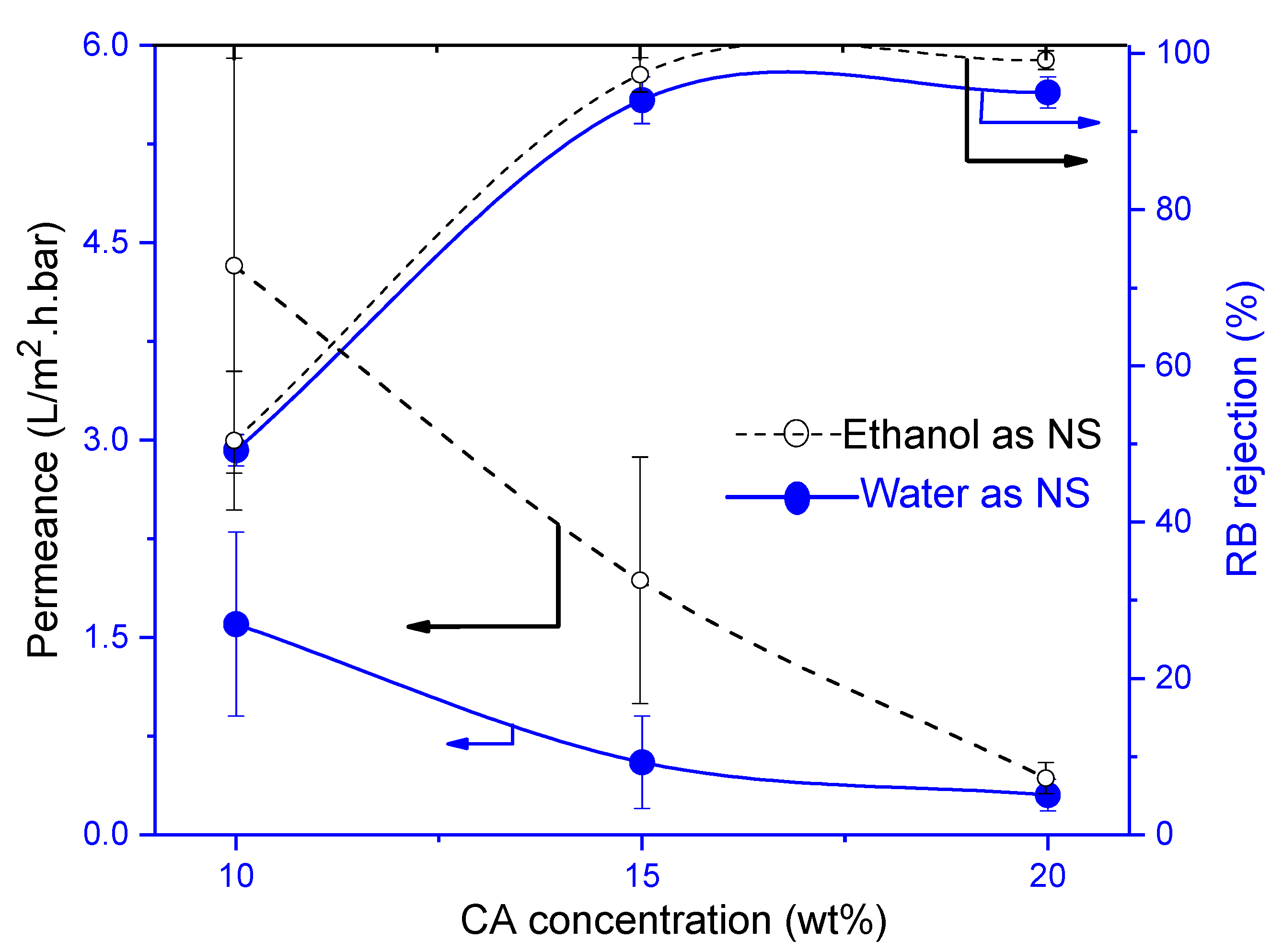
3.4.1. Influence of Cellulose Acetate (CA)
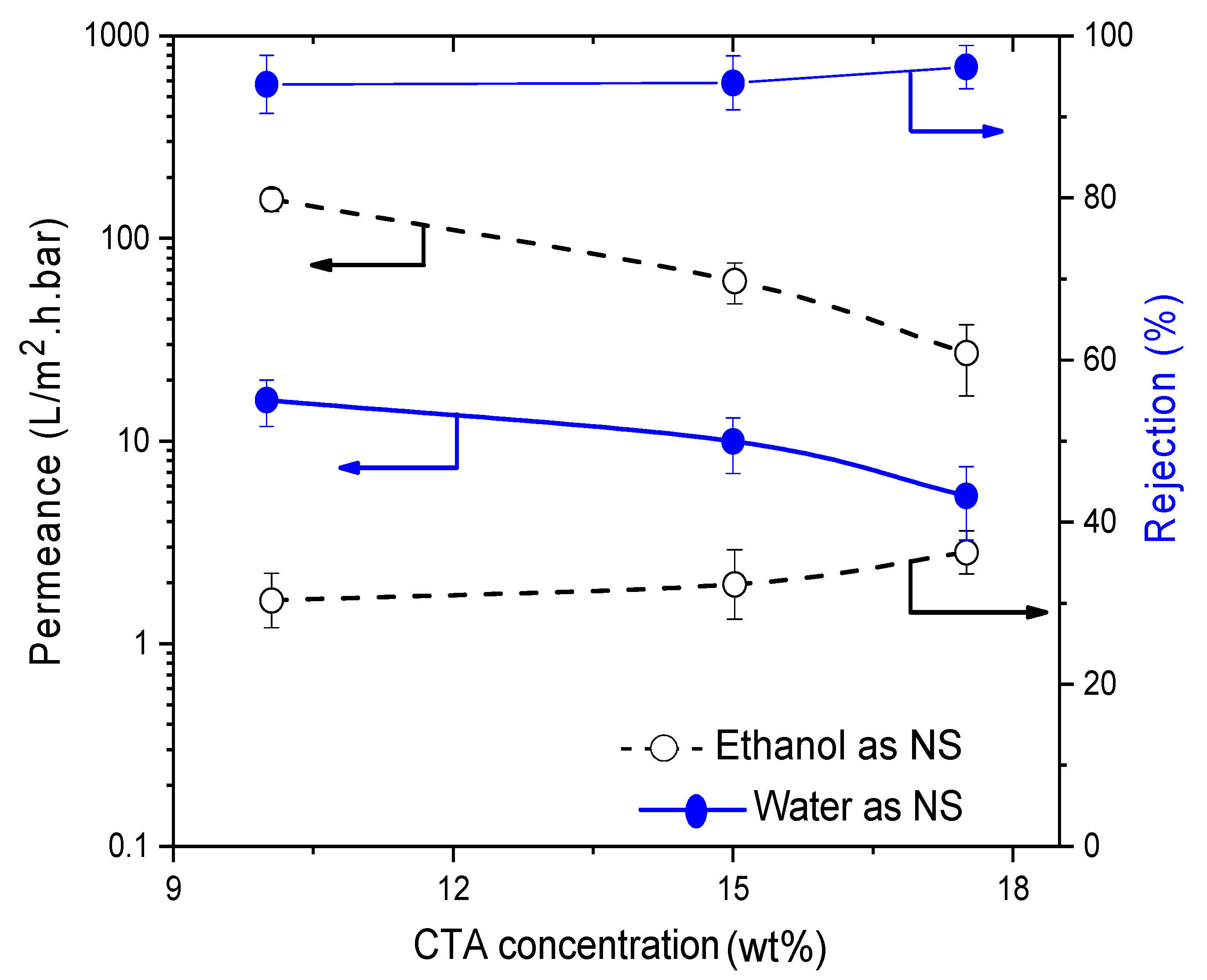
3.4.2. Influence of Cellulose Triacetate (CTA)
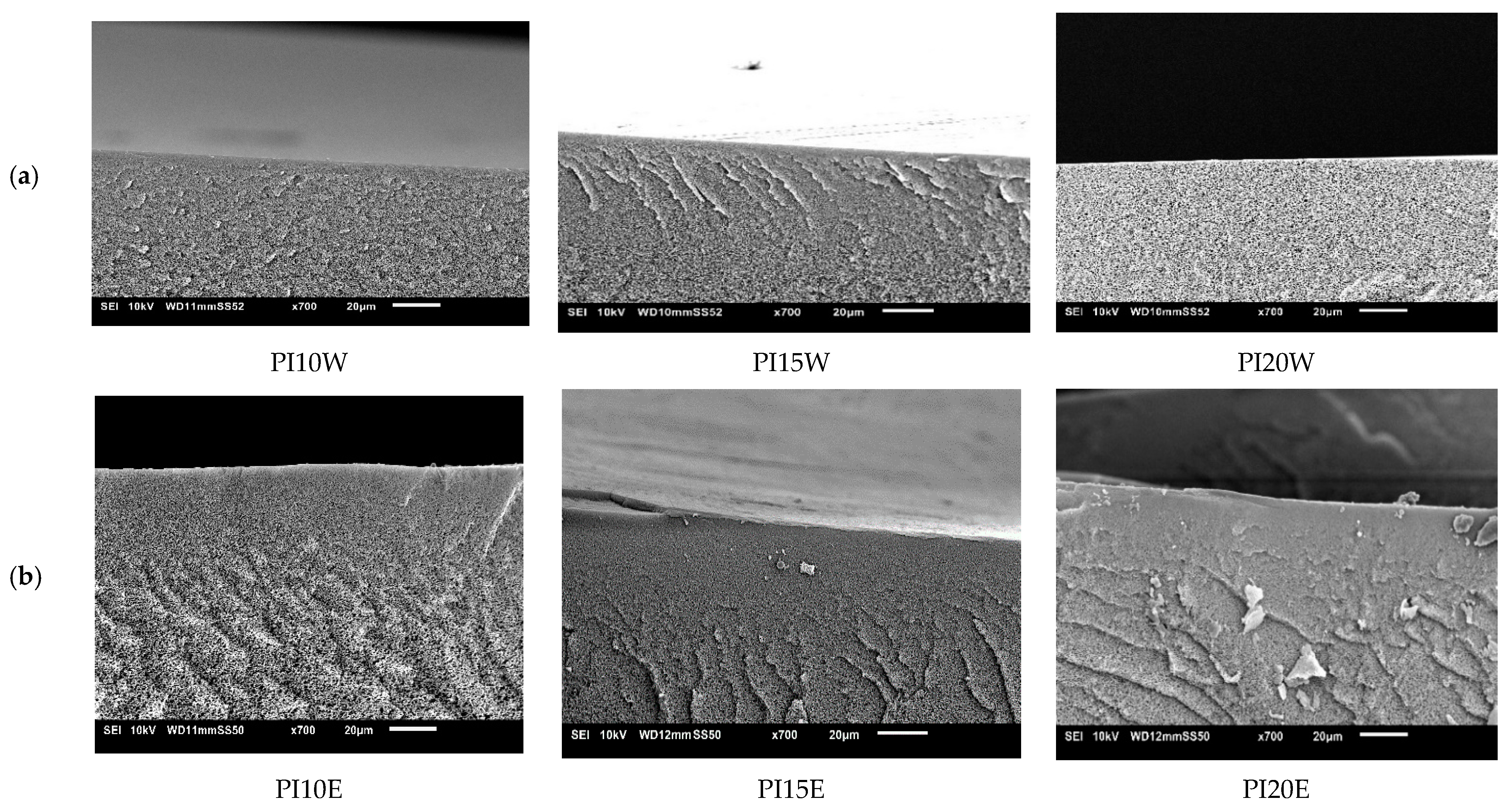
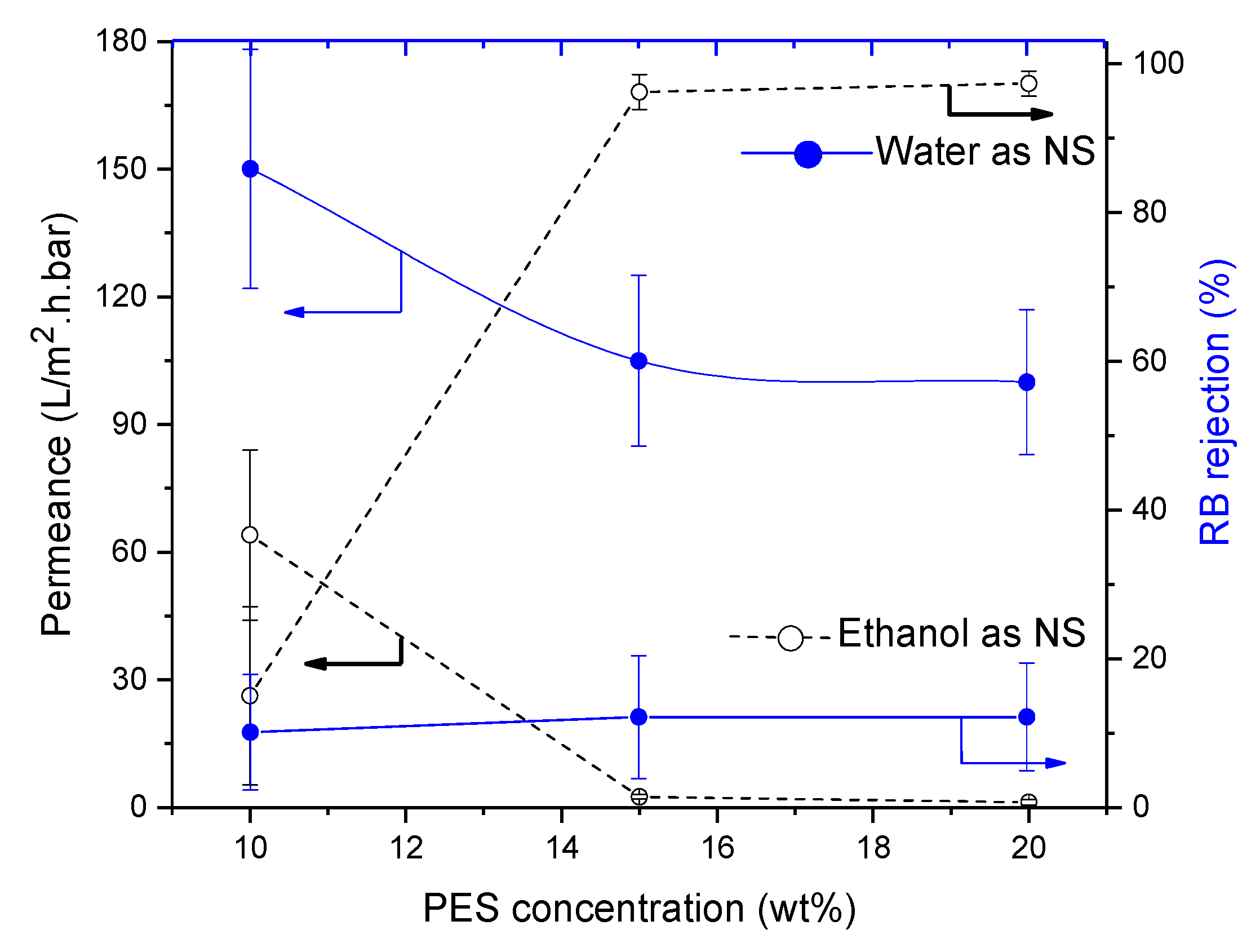
3.4.3. Influence of Polyimide (PI)
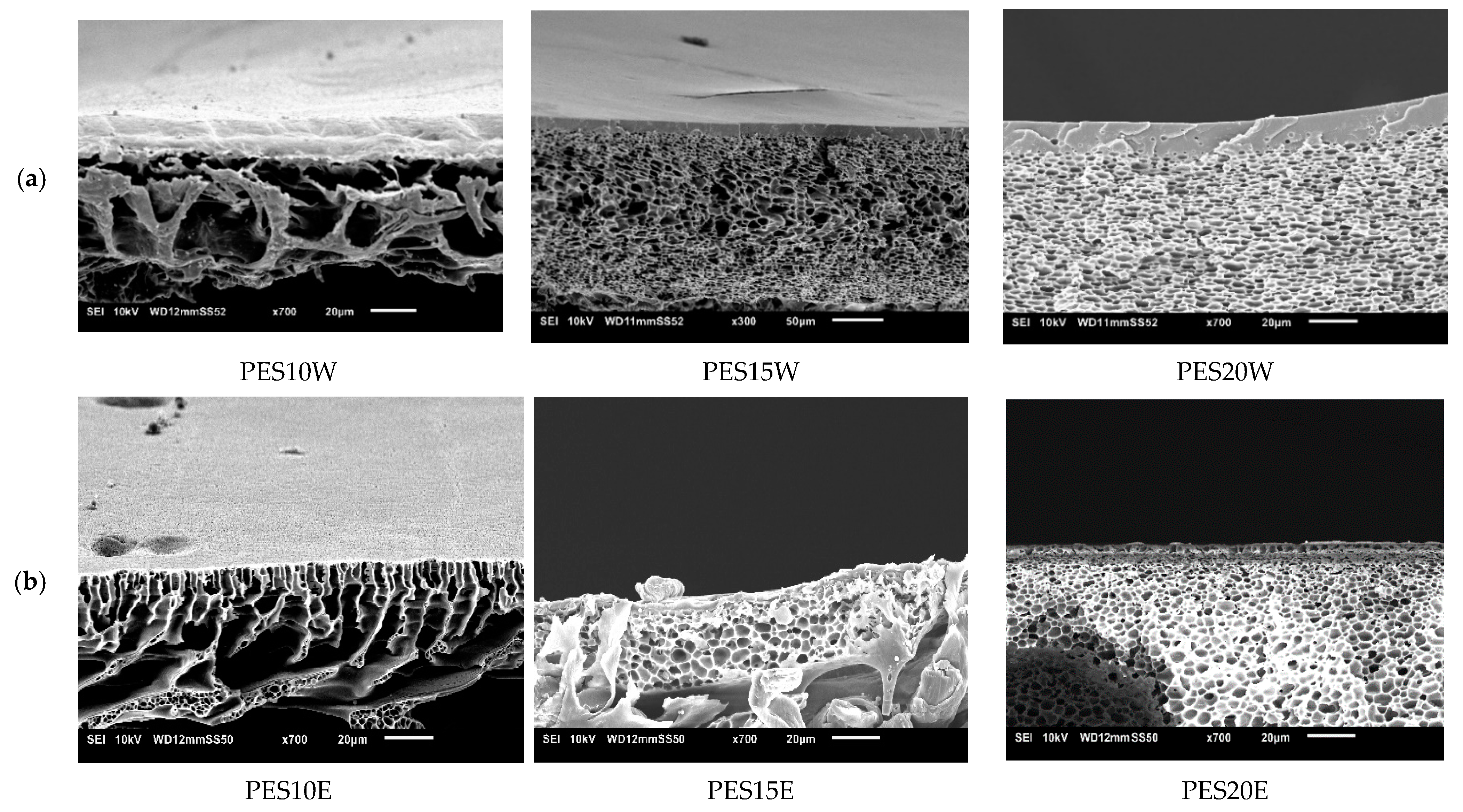
3.4.4. Influence of Polyethersulfone (PES)
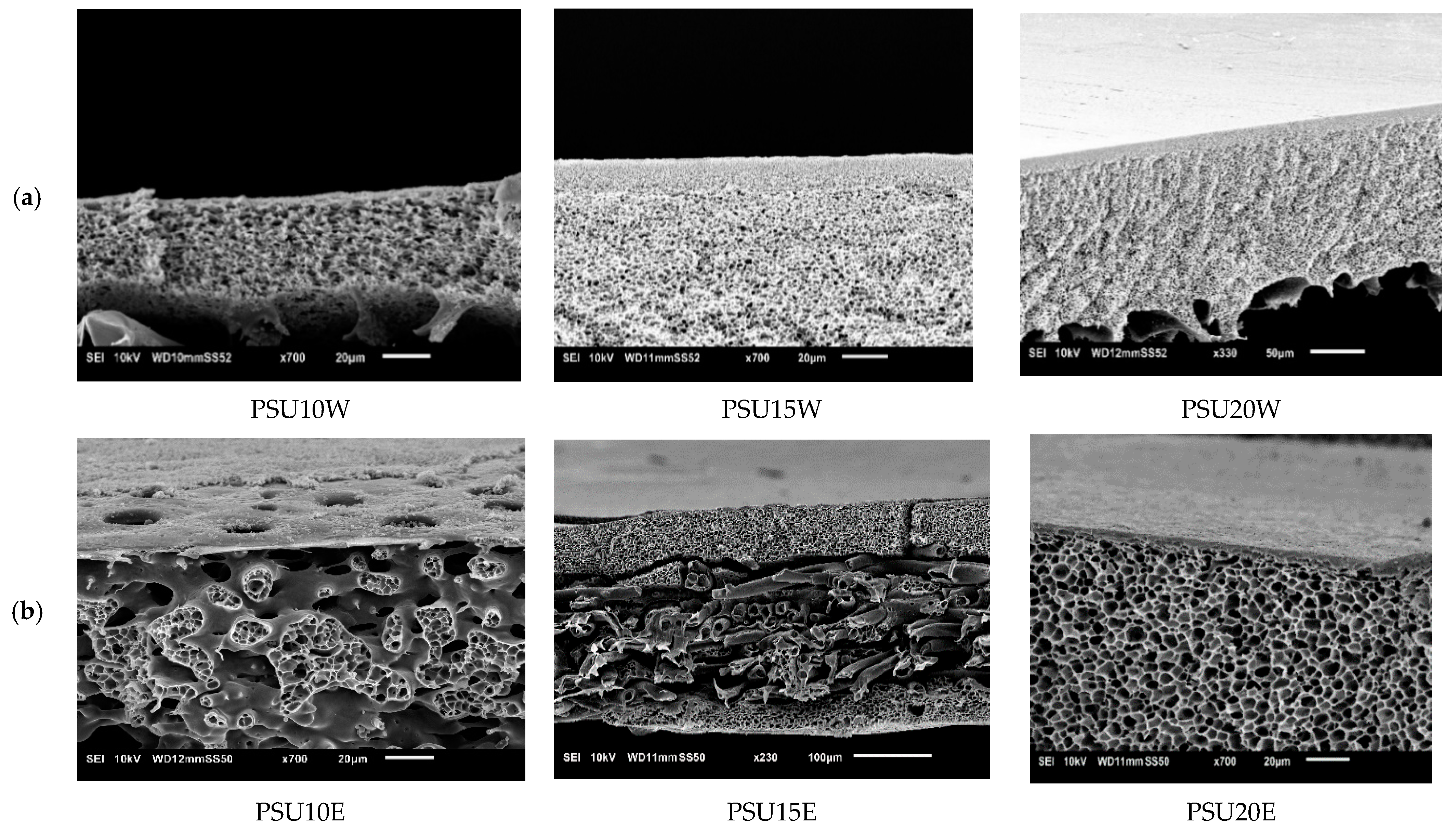
3.4.5. Influence of Polysulfone (PSU)
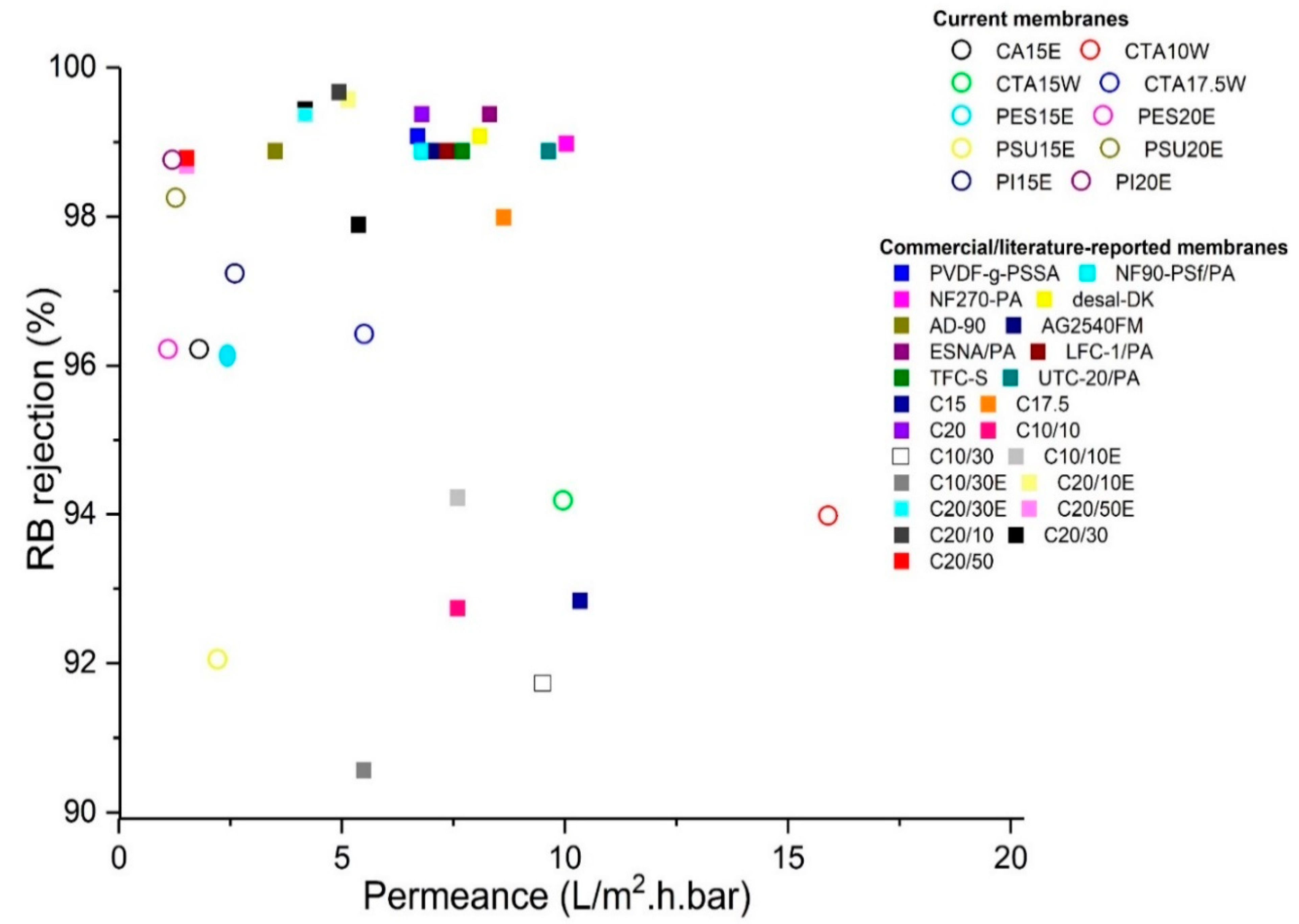
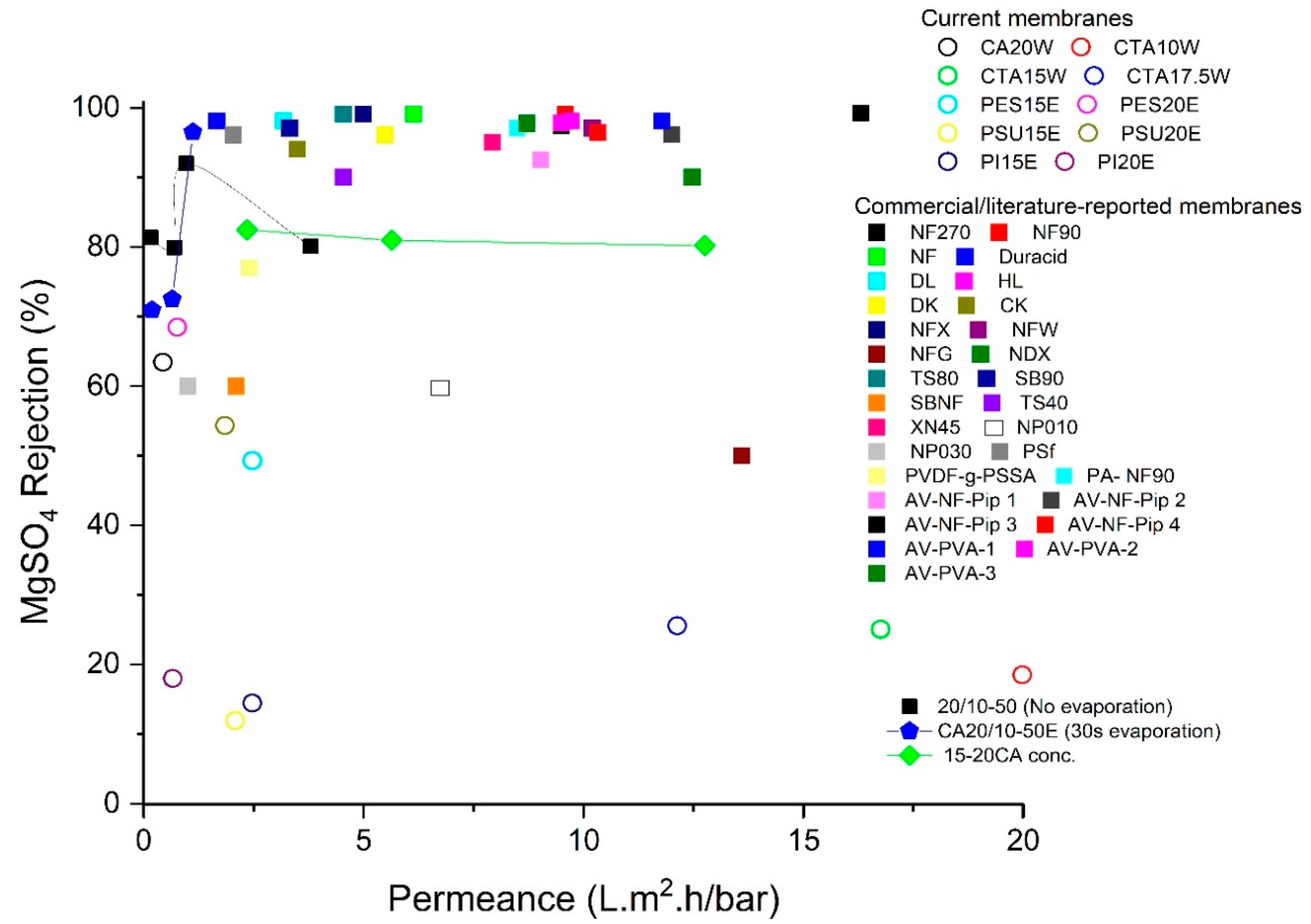
3.5. Overall Comparison
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarke, C.J.; Tu, W.-C.; Levers, O.; Bröhl, A.; Hallett, J.P. Green and Sustainable Solvents in Chemical Processes. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 747–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.; Macquarrie, D. Handbook of Green Chemistry and Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, S. Sea Water Demineralization by Means of a Semipermeable Membrane. UCLA Dept. Eng. Rep. 1960, 1–45. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/water-demineralization-means-semipermeable-membrane/dp/B0007GUWZ0 (accessed on 30 April 2021).
- Apel, P. Track etching technique in membrane technology. Radiat. Meas. 2001, 34, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A.; Marino, T.; Simone, S.; Di Nicolò, E.; Li, X.-M.; He, T.; Tornaghi, S.; Drioli, E. Towards non-toxic solvents for membrane preparation: A review. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4034–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Integrally skinned PSf-based SRNF-membranes prepared via phase inversion—Part B: Influence of low molecular weight additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Understanding and guiding the phase inversion process for synthesis of solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; Aernouts, B.; Saeys, W.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Study of polymer concentration and evaporation time as phase inversion parameters for polysulfone-based SRNF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, R.; Chen, L.; Lin, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, K.; Cao, S.; Huang, L. Preparation and characterization of antibacterial cellulose/chitosan nanofiltration membranes. Polymers 2017, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strużyńska-Piron, I.; Bilad, M.R.; Loccufier, J.; Vanmaele, L.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Influence of UV curing on morphology and performance of polysulfone membranes containing acrylates. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 462, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, K.; Koeckelberghs, G.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Study of phase inversion parameters for PEEK-based nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See-Toh, Y.H.; Ferreira, F.C.; Livingston, A.G. The influence of membrane formation parameters on the functional performance of organic solvent nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandezande, P.; Gevers, L.E.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Solvent resistant nanofiltration: Separating on a molecular level. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 37, 365–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Odena, A.; Vandezande, P.; Hendrix, K.; Zaman, R.; Mostafa, K.; Egger, W.; Sperr, P.; De Baerdemaeker, J.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Probing the Molecular Level of Polyimide-Based Solvent Resistant Nanofiltration Membranes with Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 10170–10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, M.A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Preparation of full-bio-based nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Burgal, J.; Peeva, L.; Livingston, A. Towards improved membrane production: Using low-toxicity solvents for the preparation of PEEK nanofiltration membranes. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2374–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, G.; Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Marchetti, P.; Kim, J.F.; Livingston, A.G. Sustainability assessment of organic solvent nanofiltration: From fabrication to application. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4440–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Jung, J.T.; Kim, J.F.; Kim, S.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. A novel green solvent alternative for polymeric membrane preparation via nonsolvent-induced phase separation (NIPS). J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 574, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Lu, D.; Harris, T.A.L. Polymers and Solvents Used in Membrane Fabrication: A Review Focusing on Sustainable Membrane Development. Membranes 2021, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.F.; Jung, J.T.; Wang, H.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. 1.15 Effect of Solvents on Membrane Fabrication via Thermally Induced Phase Separation (TIPS): Thermodynamic and Kinetic Perspectives. In Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 386–417. [Google Scholar]
- Razali, M.; Kim, J.F.; Attfield, M.; Budd, P.M.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, J.F.; Maginn, E.J. Ionic liquids: Innovative fluids for chemical processing. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REACH Legislation—ECHA. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/regulations/reach/legislation (accessed on 4 April 2019).
- Marchetti, P.; Solomon, M.F.J.; Szekely, G.; Livingston, A.G. Molecular separation with organic solvent nanofiltration: A critical review. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10735–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECA. How to Comply with REACH Restriction 71, Guideline for Users of NMP (1-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone); ECA: Helsinki, Finland, 2019; ISBN 9789294812148. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Salazar, O.R.; Nunes, S.P. Membrane manufacture for peptide separation. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5151–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; ISBN 9780198502340. [Google Scholar]
- Anastas, P.T. Green Chemistry as Applied to Solvents. Clean Solvents 2002, 1991, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A. Green Chemistry and Sustainable Technology Sustainable Membrane Technology for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Springer: Singapore, 2017; ISBN 9789811056215. [Google Scholar]
- Soroko, I.; Bhole, Y.; Livingston, A.G. Environmentally friendly route for the preparation of solvent resistant polyimide nanofiltration membranes. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Gonzalez, Y.; Aimar, P.; Lahitte, J.-F.; Remigy, J.-C. Towards green membranes: Preparation of cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes using methyl lactate as a biosolvent. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2011, 4, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Vovusha, H.; Schwingenschlögl, U.; Nunes, S.P. Polyethersulfone flat sheet and hollow fiber membranes from solutions in ionic liquids. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 539, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nunes, S.P. Green solvents for membrane manufacture: Recent trends and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Le, N.L.; Nunes, S.P. The effects of a co-solvent on fabrication of cellulose acetate membranes from solutions in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.-M.; Liu, F.; Ma, B.-R.; Xue, L.-X. Effect of solvent power on PVDF membrane polymorphism during phase inversion. Desalination 2013, 316, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bey, S.; Criscuoli, A.; Simone, S.; Figoli, A.; Benamor, M.; Drioli, E. Hydrophilic PEEK-WC hollow fibre membrane contactors for chromium (Vi) removal. Desalination 2011, 283, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.P.; Athanaselis, S.A. Handbook of Forensic Drug Analysis; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 9780080472898. [Google Scholar]
- Andresen-Streichert, H.; Jungen, H.; Gehl, A.; Müller, A.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S. Uptake of gamma-valerolactone-detection of gamma-hydroxyvaleric acid in human urine samples. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, M.A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Use of γ-Valerolactone and Glycerol Derivatives as Bio-based Renewable Solvents for Membrane Preparation. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.W.; Iborra, S.; Corma, A. Synthesis of Transportation Fuels from Biomass: Chemistry, Catalysts, and Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J. PVDF membrane formation via thermally induced phase separation. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2007, 44, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.A.; Van Goethem, C.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Green Preparation Process Using Methyl lactate for Cellulose-acetate-based Nanofiltration Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 232, 115903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandezande, P.; Li, X.; Gevers, L.E.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. High throughput study of phase inversion parameters for polyimide-based SRNF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 330, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Vandezande, P.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Polypyrrole modified solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.A.; Pescarmona, P.P.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Applicability of Organic Carbonates as Green Solvents for Membrane Preparation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13774–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.F.M. CRC Handbook of Solubility Parameters and Other Cohesion Parameters; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991; ISBN 0849301769. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 1420049313. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanis, E.; Panayiotou, C. Prediction of hansen solubility parameters with a new group-contribution method. Int. J. Thermophys. 2008, 29, 568–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, C.S.; Mchugh, A.J. Mass transfer modeling of asymmetric membrane formation by phase inversion. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1990, 28, 1327–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abetz, V.; Brinkmann, T.; Dijkstra, M.; Ebert, K.; Fritsch, D.; Ohlrogge, K.; Paul, D.; Peinemann, K.-V.; Pereira-Nunes, S.; Scharnagl, N.; et al. Developments in Membrane Research: From Material via Process Design to Industrial Application. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 328–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishmanesh, S.; Jansen, J.C.; Tasselli, F.; Tocci, E.; Luis, P.; Degrève, J.; Drioli, E.; Van der Bruggen, B. Novel polyphenylsulfone membrane for potential use in solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; ISBN 978-0-7923-4248-9. [Google Scholar]
- Boom, R.M.; Van Den Boomgaard, T.; Van Den Berg, J.W.A.; Smolders, C.A. Linearized cloudpoint curve correlation for ternary systems consisting of one polymer, one solvent and one non-solvent. Polymer (Guildf) 1993, 34, 2348–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.W.Y.; Guiver, M.D.; Matsuura, T. Phase separation in polysulfone/solvent/water and polyethersulfone/solvent/water systems. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 59, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ismail, A.F.; Yean, L.P. Review on the development of defect-free and ultrathin-skinned asymmetric membranes for gas separation through manipulation of phase inversion and rheological factors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koningsveld, R.; Staverman, A.J. Liquid-liquid phase separation in multicomponent polymer solutions. Kolloid Zeitschrift Zeitschrift Polym. 1967, 220, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.; Kafchinski, E.R. The effects of spinning conditions on asymmetric 6FDA/6FDAM polyimide hollow fibers for air separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fatah, M.A. Nanofiltration systems and applications in wastewater treatment: Review article. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 3077–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Polymer/Solvent | MW (kDa) | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Polyimide (PI) | 90–134 | 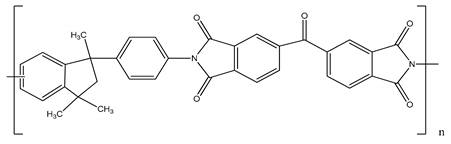 |
| Cellulose acetate (CA) | ∼30 |  |
| Polysulfone (PSU) | 21 | 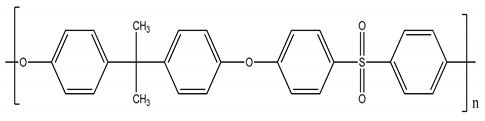 |
| Cellulose triacetate (CTA) | 278–282 | 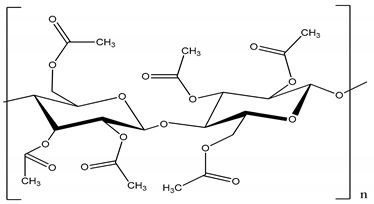 |
| Polyethersulfone (PES) | ∼35 | 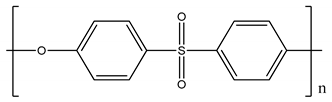 |
| Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) | 0.12 | 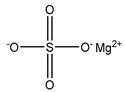 |
| Rose Bengal (RB) | 1.017 |  |
| -Valerolactone (GVL) | 0.100 | 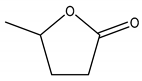 |
| Membrane ID | Polymer Type and Concentration | Non-Solvent |
|---|---|---|
| CA10W | 10 wt% CA | water |
| CA15W | 15 wt% CA | water |
| CA20W | 20 wt% CA | water |
| CA10E | 10 wt% CA | ethanol |
| CA15E | 15 wt% CA | ethanol |
| CA20E | 20 wt% CA | ethanol |
| CTA10W | 10 wt% CTA | water |
| CTA15W | 15 wt% CTA | water |
| CTA17.5W | 17.5 wt% CTA | water |
| CTA10E | 10 wt% CTA | ethanol |
| CTA15E | 15 wt% CTA | ethanol |
| CTA17.5E | 17.5 wt% CTA | ethanol |
| PI10W | 10 wt% PI | water |
| PI15W | 15 wt% PI | water |
| PI20W | 20 wt% PI | water |
| PI10E | 10 wt% PI | ethanol |
| PI15E | 15 wt% PI | ethanol |
| PI20E | 20 wt% PI | ethanol |
| PES10W | 10 wt% PES | water |
| PES15W | 15 wt% PES | water |
| PES20W | 20 wt% PES | water |
| PES10E | 10 wt% PES | ethanol |
| PES15E | 15 wt% PES | ethanol |
| PES20E | 20 wt% PES | ethanol |
| PSU10W | 10 wt% PSU | water |
| PSU15W | 15 wt% PSU | water |
| PSU20W | 20 wt% PSU | water |
| PSU10E | 10 wt% PSU | ethanol |
| PSU15E | 15 wt% PSU | ethanol |
| PSU20E | 20 wt% PSU | ethanol |
| Polymers/Solvent | HSP Values | Ra (MPa1/2) | Ra (MPa1/2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MPa1/2 | MPa1/2 | MPa1/2 | H2O | C2H5OH | GVL | |
| CA | 18.6 | 12.7 | 11.0 | 30.1 | 6.1 | 11.0 |
| CTA | 18.4 | 11.9 | 10.1 | 32.9 | 11.1 | 9.9 |
| PI | 20.9 | 11.3 | 9.7 | 34.7 | 14.2 | 13.0 |
| PSU | 19.7 | 8.3 | 8.3 | 35.9 | 13.6 | 9.3 |
| PES | 19.6 | 10.8 | 9.2 | 34.5 | 12.9 | 10.5 |
| GVL | 15.5 | 4.7 | 6.6 | |||
| H2O | 15.5 | 16.0 | 42.3 | |||
| C2H5OH | 15.8 | 8.8 | 19.4 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasool, M.A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. γ-Valerolactone as Bio-Based Solvent for Nanofiltration Membrane Preparation. Membranes 2021, 11, 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060418
Rasool MA, Vankelecom IFJ. γ-Valerolactone as Bio-Based Solvent for Nanofiltration Membrane Preparation. Membranes. 2021; 11(6):418. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060418
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasool, Muhammad Azam, and Ivo F. J. Vankelecom. 2021. "γ-Valerolactone as Bio-Based Solvent for Nanofiltration Membrane Preparation" Membranes 11, no. 6: 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060418
APA StyleRasool, M. A., & Vankelecom, I. F. J. (2021). γ-Valerolactone as Bio-Based Solvent for Nanofiltration Membrane Preparation. Membranes, 11(6), 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060418