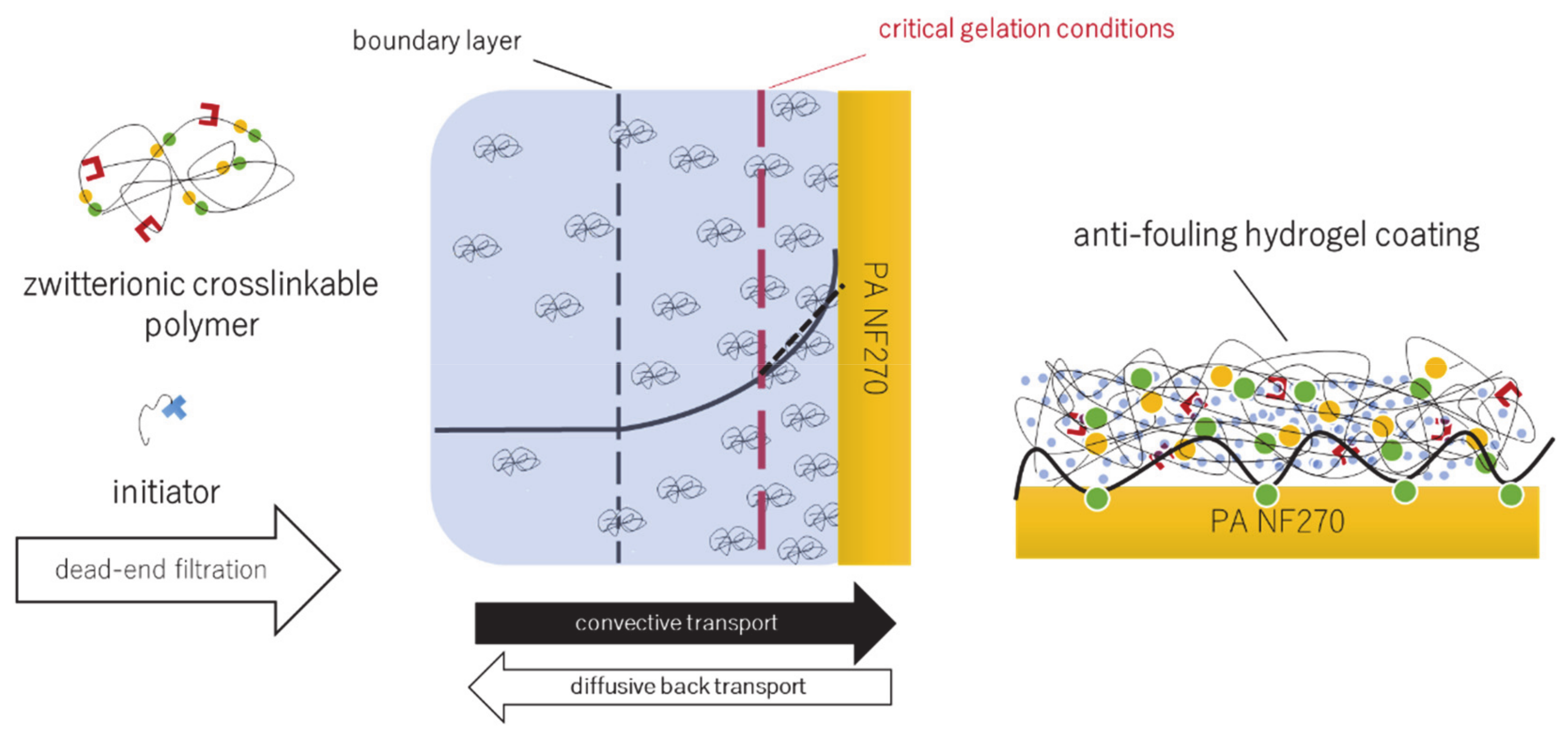
Concentration Polarization Enabled Reactive Coating of Nanofiltration Membranes with Zwitterionic Hydrogel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
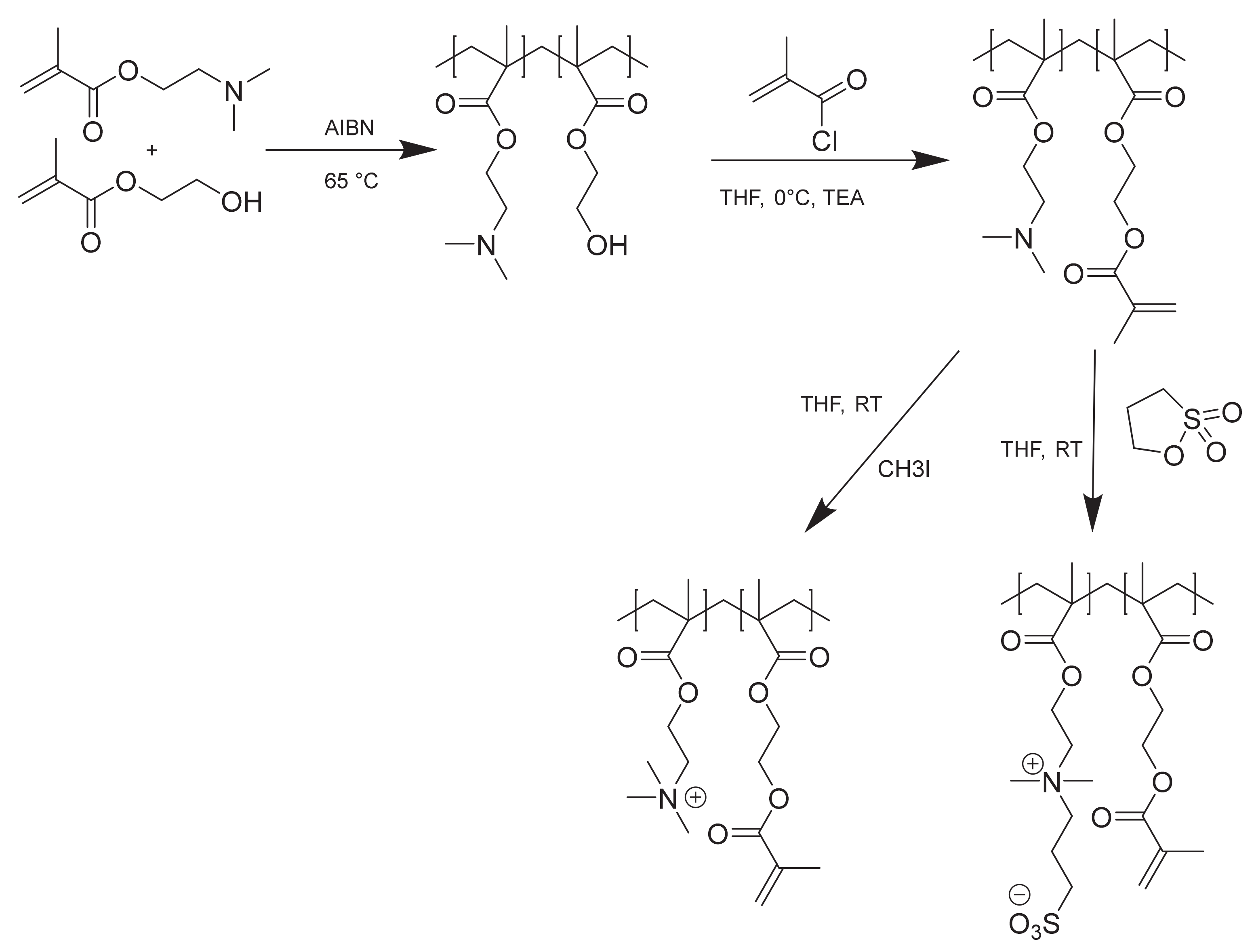
2.2. Polymer Synthesis
2.3. Polymer Characterization
2.3.1. Copolymer Composition
2.3.2. Molecular Weight
2.3.3. Hydrodynamic Size of Copolymer in Solution
2.3.4. Viscosity and Overlap Concentration of Copolymer Solutions
2.4. Rheological Investigation of Hydrogel Formation in Free Bulk
2.5. Concentration Polarization-Enabled Reactive Coating of NF270 Membranes
2.5.1. Membrane Performance Characterization
2.5.2. CP-Enabled Membrane Modification
2.5.3. Membrane Characterization
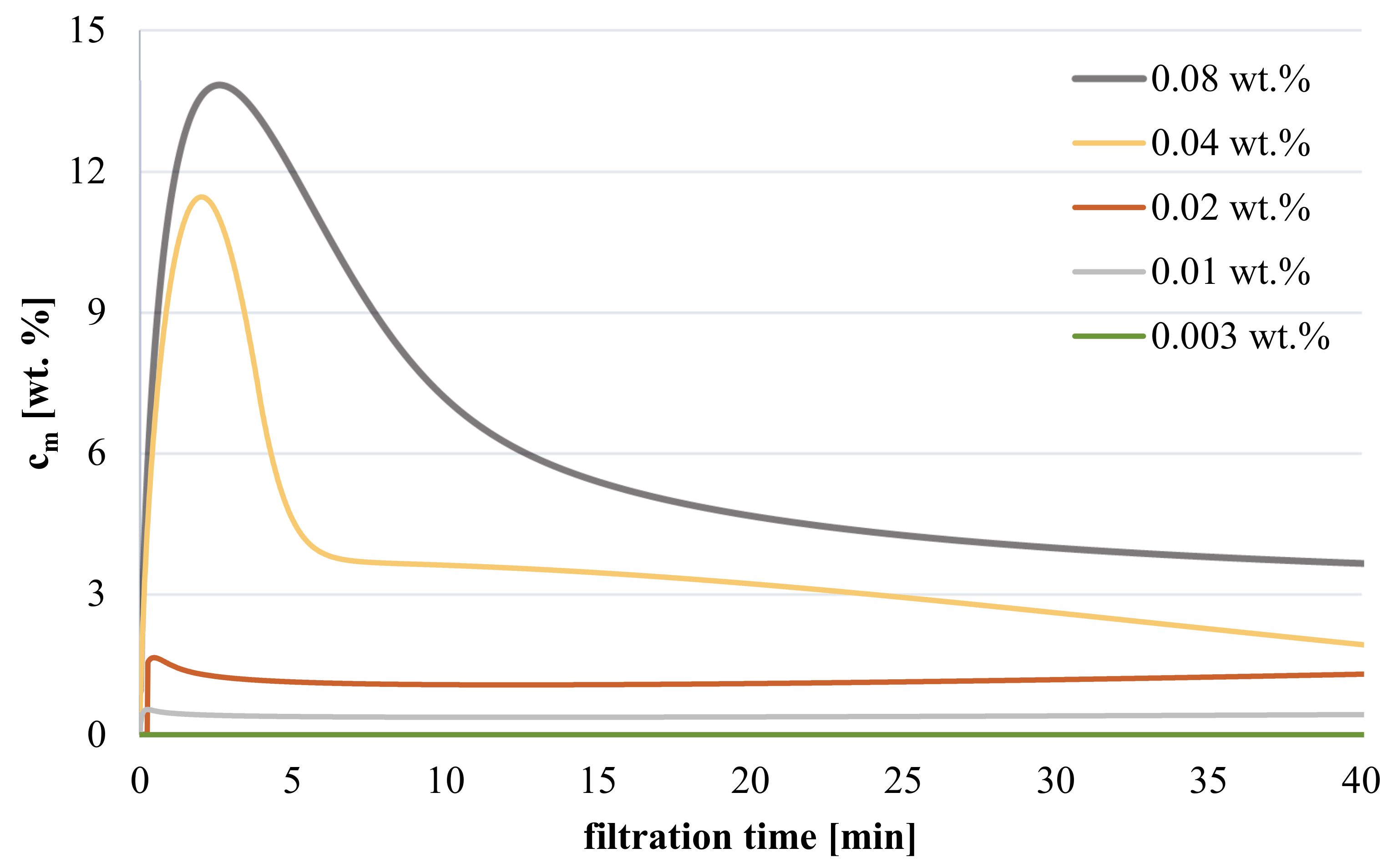
2.6. Estimation of Concentration Polarization
2.6.1. Approach
- (i)
- concentration polarization increases linearly within the boundary layer δ;
- (ii)
- boundary layer thickness δ is constant during entire modification procedure;
- (iii)
- back diffusion is dependent on macromolecule size and solution viscosity.
- (i)
- boundary layer thickness δ, which was estimated during a separate experiment (see Section 2.6.2), along with A as effective membrane area yielding the volume of the boundary layer;
- (ii)
- flux J(tn) and initial feed concentration cf(t0), which allow to calculate the permeate volume in the time interval V(tn) and thus also the convectively transported mass towards membrane surface mC(tn) and subsequently also cf(tn);
- (iii)
- single macromolecule radius rpolymer, which was obtained by DLS measurement (see Section 2.3.3), required to calculate the diffusion coefficient of the polymer and thus diffusive mass transport back toward feed mD(tn);
- (iv)
- average viscosity of copolymer solution in boundary layer η(cpolymer), using a relationship derived from rheological measurements (see Section 2.3.4) and calculated values for cf(tn) and cm(tn), also required to calculate mD(tn).
2.6.2. Estimation of Boundary Layer Thickness
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polymer Synthesis and Characterization
3.1.1. Molecular Weight and Composition of P(SBMA-co-MAHEMA)
3.1.2. Hydrodynamic Size of P(SBMA-co-MAMMA)
3.1.3. Viscosity of Aqueous Solutions Containing P(SBMA-co-MAMMA)
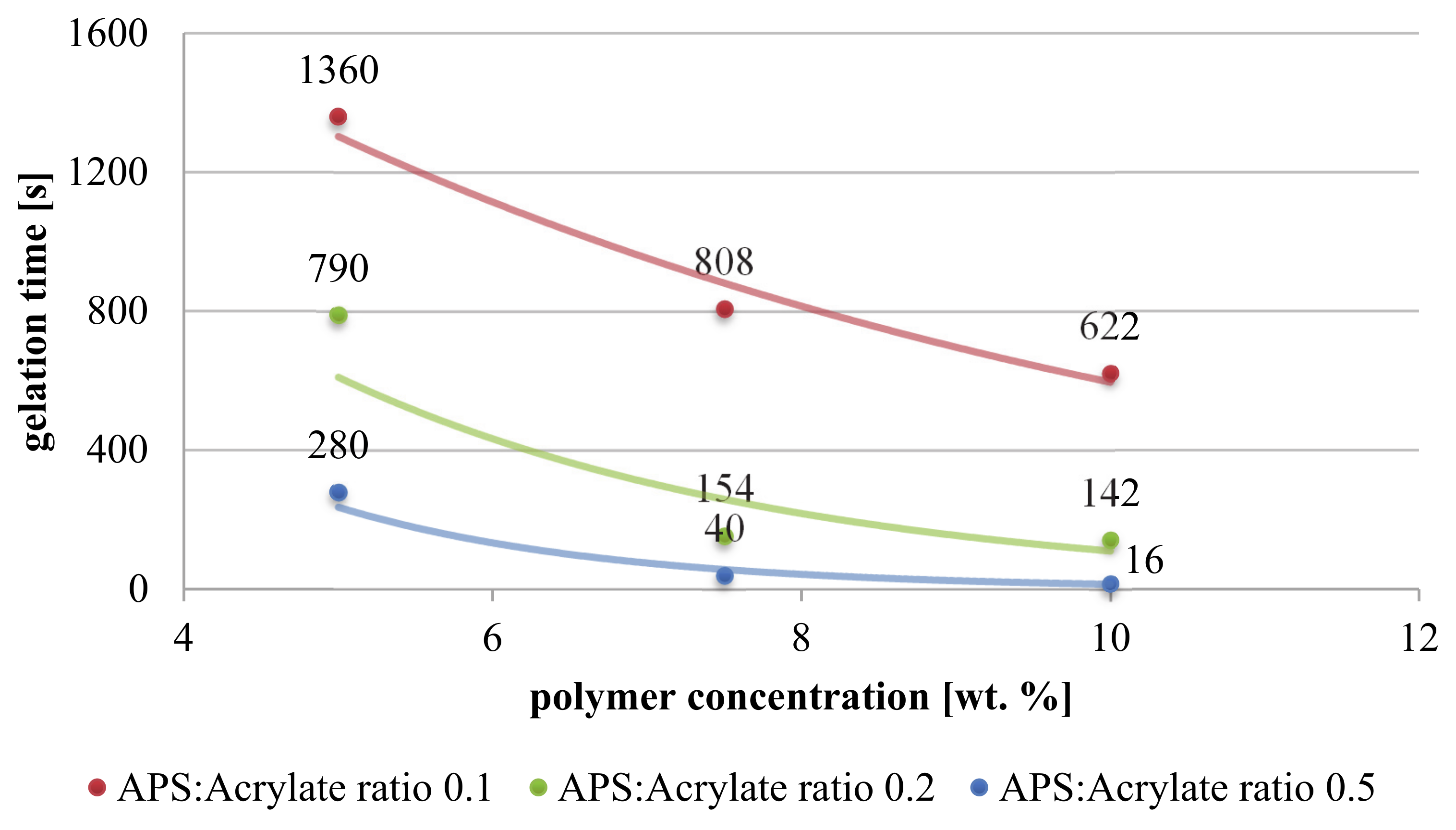
3.2. Bulk Gelation
Gelation Kinetics
3.3. Concentration Polarization-Enabled Hydrogel Coating of a Polyamide Nanofiltration Membrane
3.3.1. NF270 Membrane Characteristics
3.3.2. Influence of Polymer Concentration on Hydrogel Coating during Filtration
3.3.3. Influence of Redox Initiator
3.3.4. Influence of Filtration Time
3.3.5. Other Membrane Properties
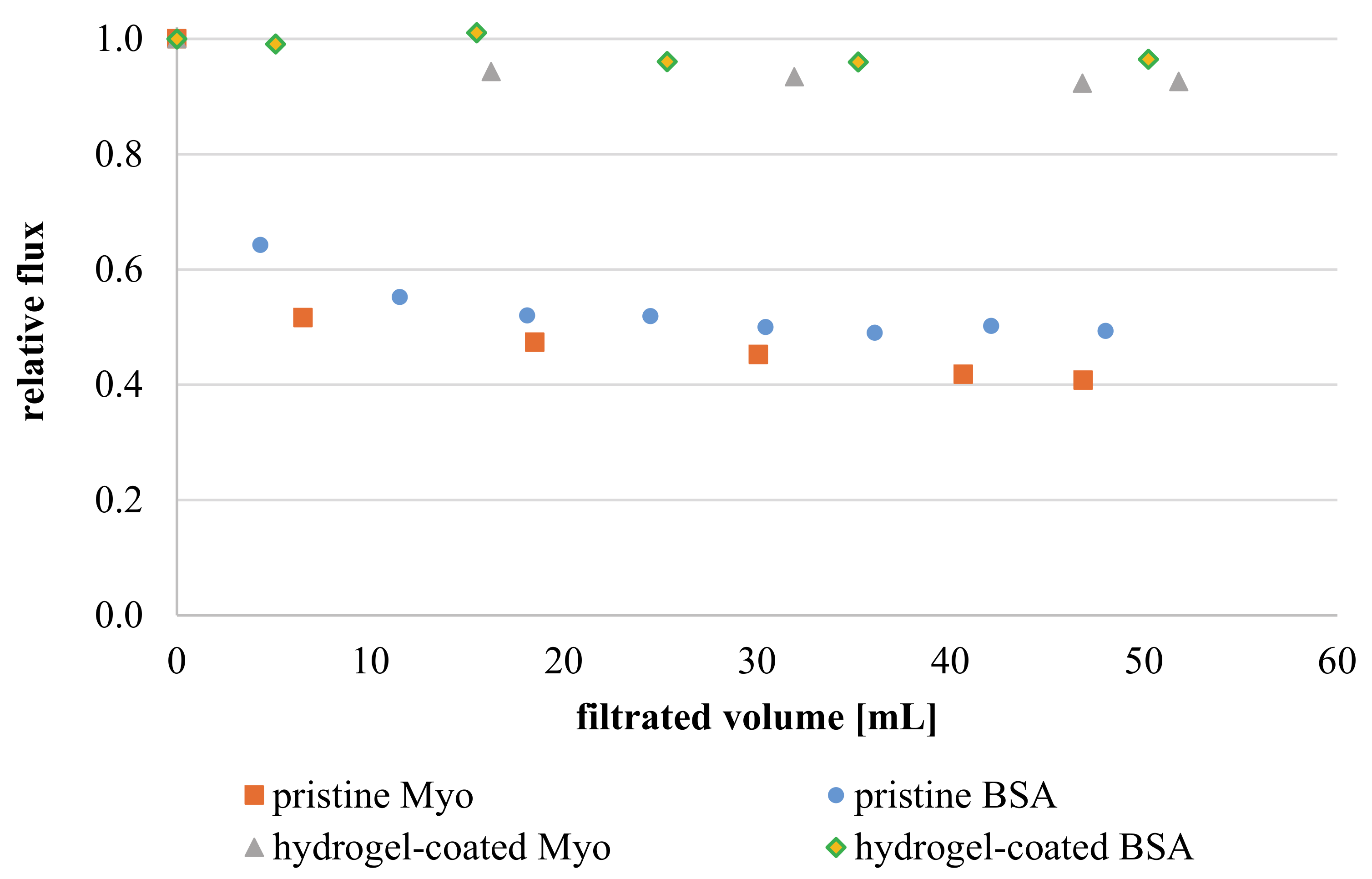
3.3.6. Membrane Fouling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorosmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Marinas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The Future of Seawater Desalination: Energy, Technology, and the Environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werber, J.R.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Gao, K.; Zhou, L.; Jiao, Z.; Wu, M.; Cao, J.; You, X.; Cai, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhongyi, J. Zwitterionic materials for antifouling membrane surface construction. Acta Biomater. 2016, 40, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Dreyer, D.; Bielawski, C.; Paul, D.; Freeman, B. Surface Modification of Water Purification Membranes: A Review. Angew. Chem. 2017, 56, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Su, Y.; Gao, C.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling membrane surface construction: Chemistry plays a critical role. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 551, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, H.Z.; Matin, A.; Khan, Z.; Khalil, A.; Gleason, K.K. Surface modification of reverse osmosis membranes with zwitterionic coatings: A potential strategy for control of biofouling. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 279, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, J. Surface hydration: Principles and applications toward low-fouling/nonfouling biomaterials. Polymer 2010, 51, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Sundaram, H.S.; Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Applications of zwitterionic polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 118, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-F.; Zhu, L.-P.; Yi, Z.; Zhu, B.-K.; Xu, Y.-Y. Zwitterionic hydrogel thin films as antifouling surface layers of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes anchored via reactive copolymer additive. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Kaufman, Y.; Bernstein, R. Surface and anti-fouling properties of a polyampholyte hydrogel grafted onto a polyethersulfone membrane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 517, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenoff, J.B. Zwitteration: Coating surfaces with zwitterionic functionality to reduce nonspecific adsorption. Langmuir 2014, 30, 9625–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschewsky, A. Structures and Synthesis of Zwitterionic Polymers. Polymers 2014, 6, 1544–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Ulbricht, M. Macroinitiator-mediated photoreactive coating of membrane surfaces with antifouling hydrogel layers. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, H.; Ulbricht, M. Photografted Thin Polymer Hydrogel Layers on PES Ultrafiltration Membranes: Characterization, Stability, and Influence on Separation Performance. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7818–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Du, M.; Wu, Z.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Strategy to construct polyzwitterionic hydrogel coating with antifouling, drag-reducing and weak swelling performance. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daumann, K.; May, P.; Brückerhoff, J.; Ulbricht, M. Synthesis of well-defined cross-linkable zwitterionic macromolecular building blocks for hydrogels. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 131, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.P.; Culfaz-Emecen, P.Z.; Ramon, G.Z.; Visser, T.; Koops, G.H.; Jin, W.; Ulbricht, M. Thinking the future of membranes: Perspectives for advanced and new membrane materials and manufacturing processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilitzsch, M.; Osmond, R.; Krug, M.; Heijnen, M.; Ulbricht, M. Macro-initiator mediated surface selective functionalization of ultrafiltration membranes with anti-fouling hydrogel layers applicable to ready-to-use capillary membrane modules. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 518, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, R.; Belfer, S.; Freger, V. Surface Modification of Dense Membranes Using Radical Graft Polymerization Enhanced by Monomer Filtration. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12358–12365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baransi-Karkaby, K.; Bass, M.; Freger, V. In Situ Modification of Reverse Osmosis Membrane Elements for Enhanced Removal of Multiple Micropollutants. Membranes 2019, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, R.; Belfer, S.; Freger, V. Improving performance of spiral wound RO elements by in situ concentration polarization-enhanced radical graft polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 405–406, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakizeh, M.; May, P.; Matthias, M.; Ulbricht, M. Preparation and characterization of polyzwitterionic hydrogel coated polyamide-based mixed matrix membrane for heavy metal ions removal. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, e49595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P.G. Some physical properties of polymer solutions and melts. Die Makromol. Chem. 1979, 3 (Suppl. S19791), 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Panglisch, S.; Gimbel, R. Measuring hydraulic layer resistance and correlated effects in colloidal fouling of salt-retaining membranes. Water Supply 2017, 17, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Fane, A.; Waite, T. Nanofiltration; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Koyuncu, I.; Topacik, D. Effect of organic ion on the separation of salts by nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 195, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opong, W.S.; Zydney, A.L. Diffusive and convective protein transport through asymmetric membranes. AIChE J. 1991, 37, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Urban, G.; Moser, I.; Jobst, G.; Gruber, H. Photolithographically patternable modified poly(HEMA) hydrogel membrane. Polym. Bull. 1995, 35, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.P.; Podgórski, M.; Chatani, S.; Gong, T.; Xi, W.; Fenoli, C.R.; Bowman, C.N. The Thiol-Michael Addition Click Reaction: A Powerful and Widely Used Tool in Materials Chemistry. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 724–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Li, J.; Cui, M.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, L.; Wei, Y.; Ye, L.; Sun, H.; Yao, F. In Situ “Clickable” Zwitterionic Starch-Based Hydrogel for 3D Cell Encapsulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4442–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, A.B.; McCormick, C.L. Synthesis and Solution Properties of Zwitterionic Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4177–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, G.S.; Kamenska, E.B.; Vassileva, E.D.; Kamenova, I.P.; Georgieva, V.T.; Iliev, S.B.; Ivanov, I.A. Self-Assembly, Antipolyelectrolyte Effect, and Nonbiofouling Properties of Polyzwitterions. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Fredrickson, G.H. Theory of polyzwitterion conformations. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grooth, J.; Ogieglo, W.; de Vos, W.M.; Girones, M.; Nijmeijer, K.; Benes, E. Swelling dynamics of zwitterionic copolymers: The effects of concentration and type of anion and cation. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 55, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Suo, Z.; Vlassak, J.J. Stiff, strong, and tough hydrogels with good chemical stability. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 39, 6708–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, H.; Ulbricht, M. High-performance thin-layer hydrogel composite membranes for ultrafiltration of natural organic matter. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiao, A.; Schaefer, A. Estrogenic micropollutant adsorption dynamics onto nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, B.; Matějka, L.; Zhigunov, A.; Konefał, R.; Spěváček, J.; Dybal, J.; Puffr, R. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)–clay based hydrogels controlled by the initiating conditions: Evolution of structure and gel formation. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 9291–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.-S.; Kim, J.-H. An experimental and theoretical study on the initial period of cake filtration. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2000, 17, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Hong, S. Effect of cake layer structure on colloidal fouling in reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2008, 220, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freger, V.; Gilron, J.; Belfer, S. TFC polyamide membranes modified by grafting of hydrophilic polymers: An FT-IR/AFM/TEM study. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 209, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Meng, J.; Geise, G.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. Water and salt transport properties of zwitterionic polymers film. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 491, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, C.; Taylor, J.; Hong, S. Effect of surface roughness on fouling of RO and NF membranes during filtration of a high organic surficial groundwater. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2006, 55, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mänttäri, M.; Pekuri, T.; Nyström, M. NF270, a new membrane having promising characteristics and being suitable for treatment of dilute effluents from the paper industry. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 242, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




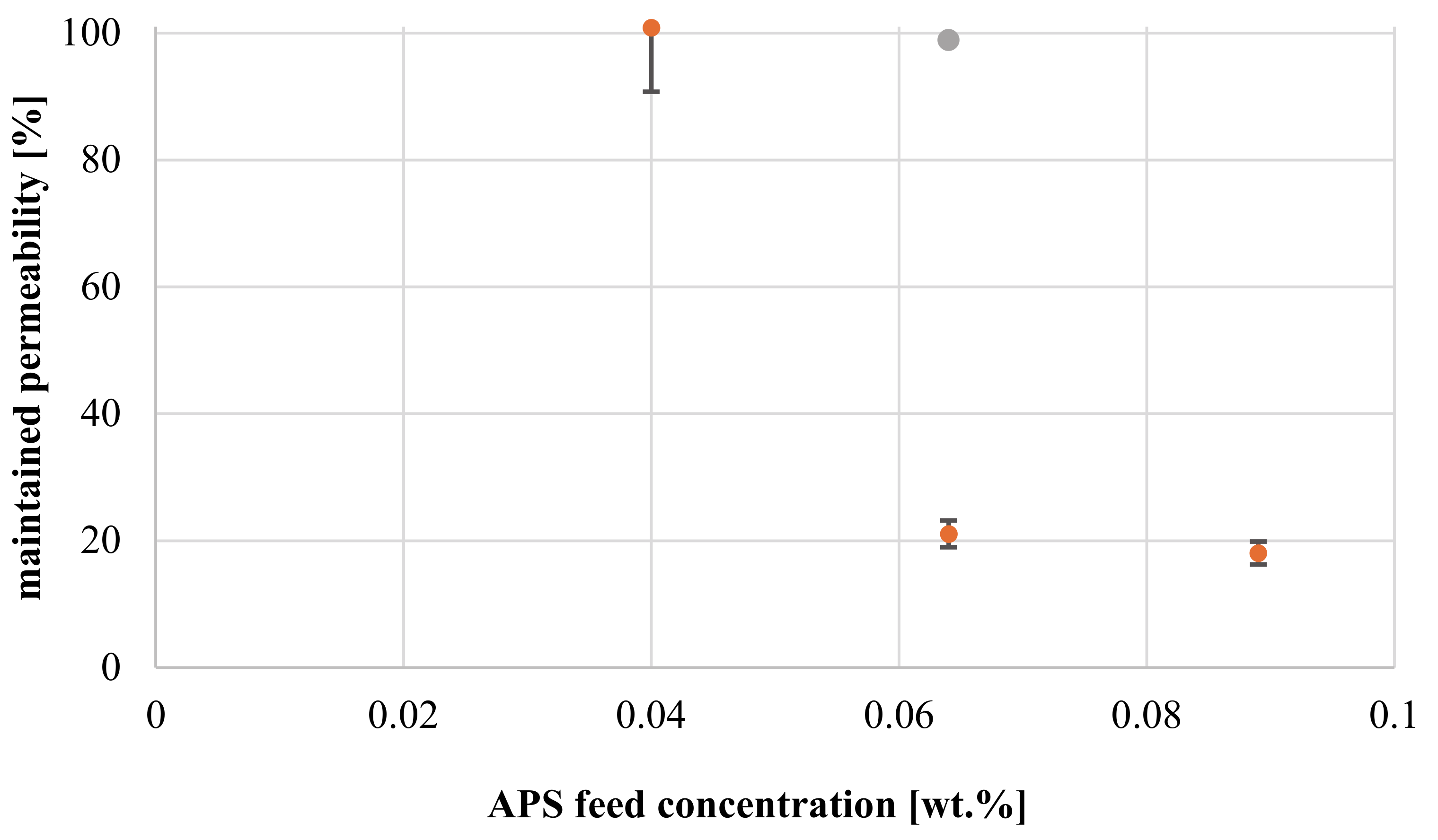
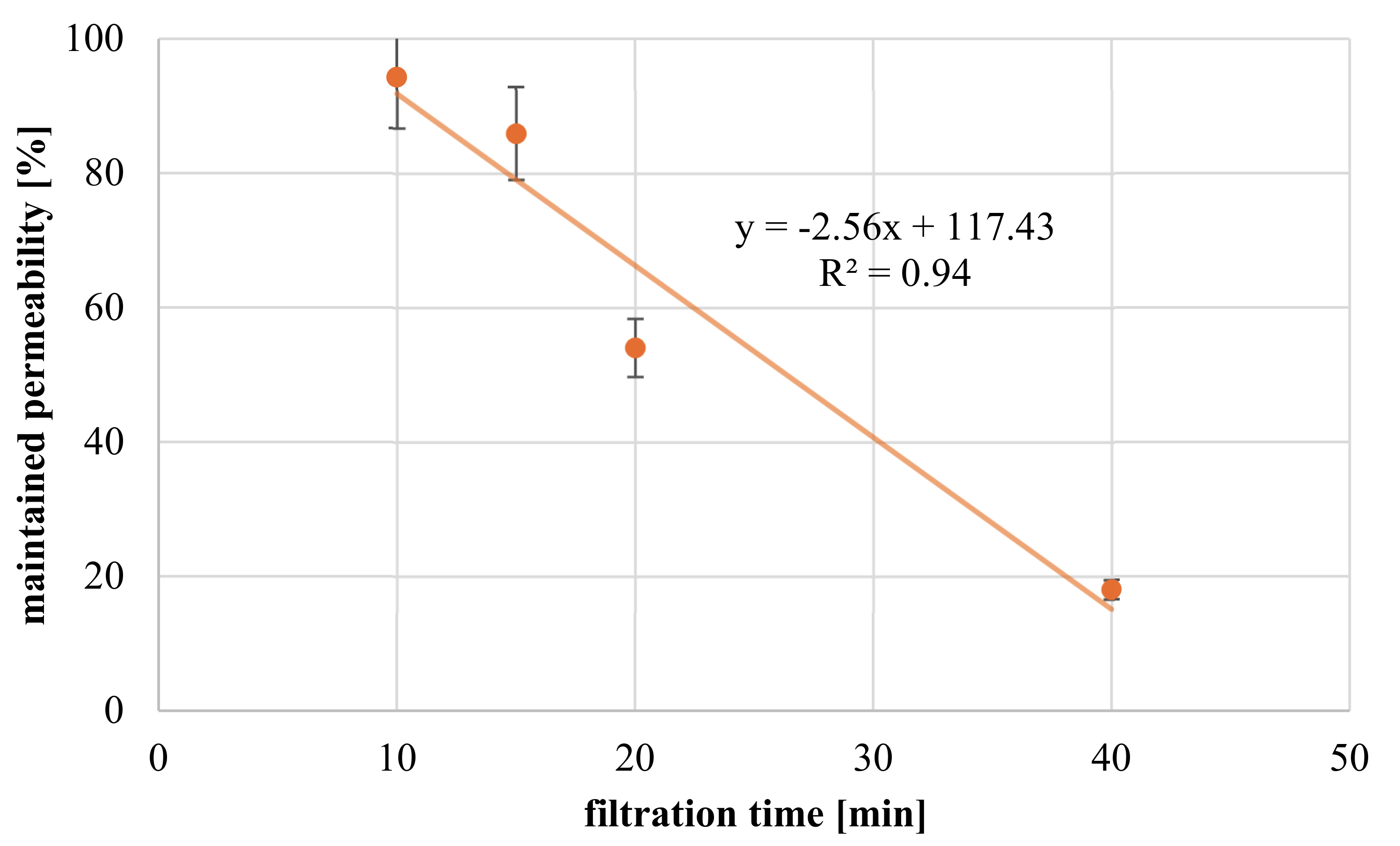

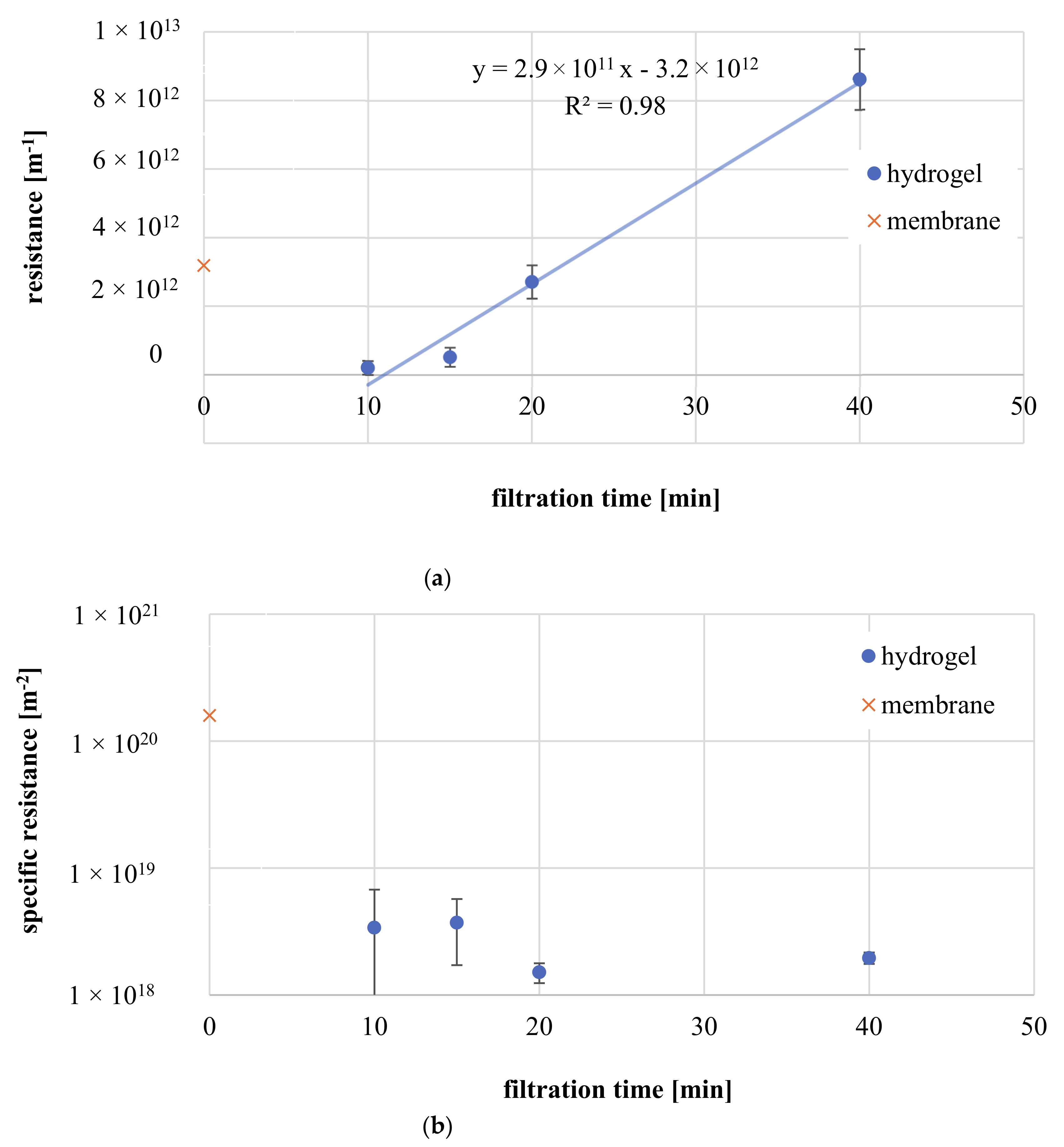
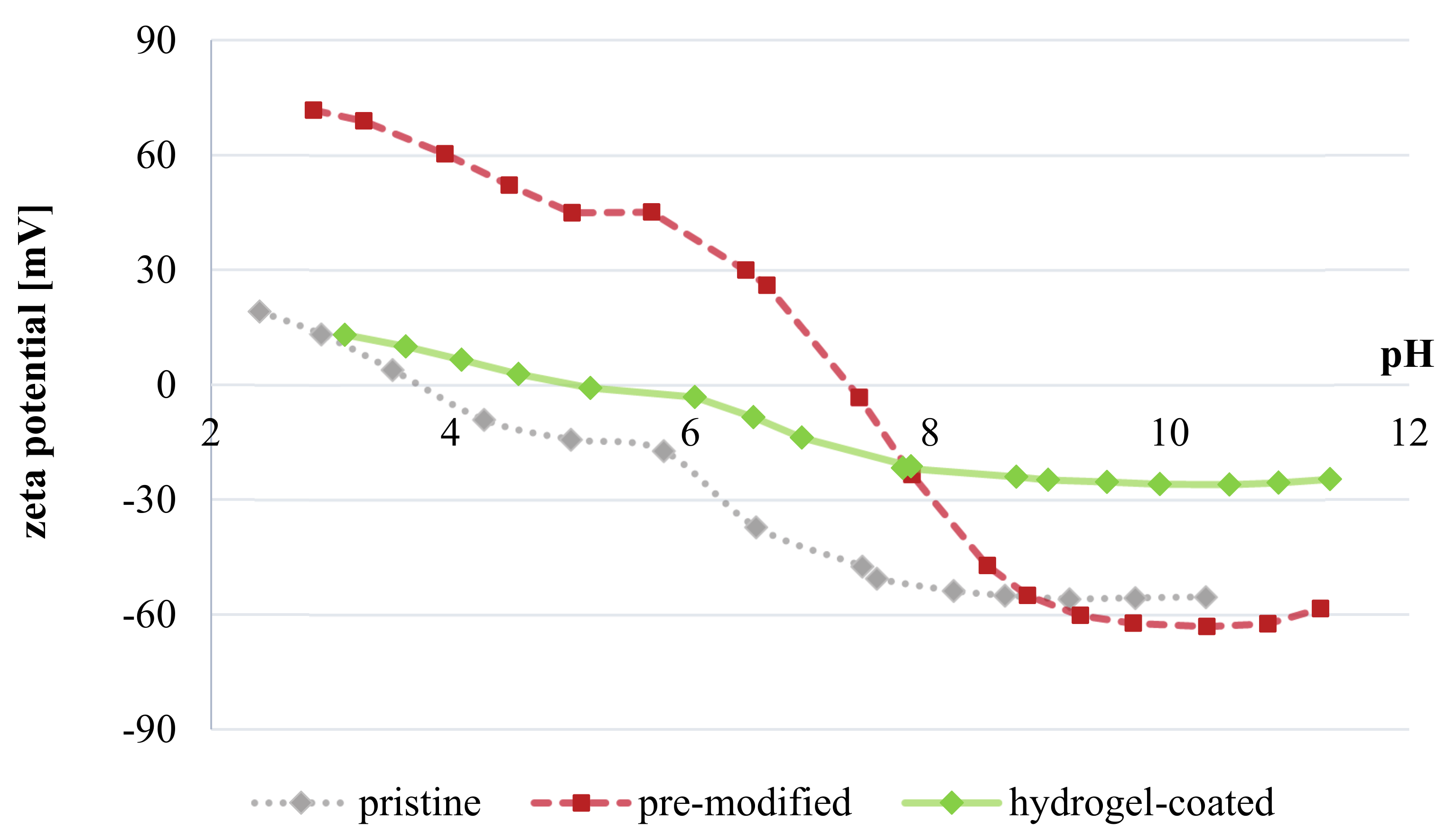
| Polymer Feed Concentration [wt.%] | APS Feed Concentration [wt.%] | Reaction Time [min] | No. of Repetitions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.08 | 0.06 | 40 | 4 |
| 0.04 | 0.06 | 40 | 2 |
| 0.02 | 0.06 | 40 | 2 |
| 0.01 | 0.06 | 40 | 1 |
| 0.005 | 0.06 | 40 | 1 |
| 0.003 | 0.06 | 40 | 1 |
| 0.001 | 0.06 | 40 | 1 |
| 0.08 | 0.09 | 40 | 1 |
| 0.08 | 0.04 | 40 | 1 |
| 0.08 | 0.06 * | 40 | 2 |
| 0.08 | 0.06 | 10 | 2 |
| 0.08 | 0.06 | 15 | 2 |
| 0.08 | 0.06 | 20 | 2 |
| Methacrylate [%] | Hydroxyl [%] | Sulfobetaine [%] | Dimethylamino [%] | Mn (univ.) [kDa] | PDI (univ.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ~20 | <1 | ~79 | <1 | 122.2 | 2.6 |
| Characteristics | Hydrogel Coated | Pristine |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl rejection [%] | 39.3 ± 8.8 | 37.7 ± 7.8 |
| NaSO4 rejection [%] | 89.9 ± 7.7 | 89.7 ± 2.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
May, P.; Laghmari, S.; Ulbricht, M. Concentration Polarization Enabled Reactive Coating of Nanofiltration Membranes with Zwitterionic Hydrogel. Membranes 2021, 11, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030187
May P, Laghmari S, Ulbricht M. Concentration Polarization Enabled Reactive Coating of Nanofiltration Membranes with Zwitterionic Hydrogel. Membranes. 2021; 11(3):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030187
Chicago/Turabian StyleMay, Patrick, Soraya Laghmari, and Mathias Ulbricht. 2021. "Concentration Polarization Enabled Reactive Coating of Nanofiltration Membranes with Zwitterionic Hydrogel" Membranes 11, no. 3: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030187
APA StyleMay, P., Laghmari, S., & Ulbricht, M. (2021). Concentration Polarization Enabled Reactive Coating of Nanofiltration Membranes with Zwitterionic Hydrogel. Membranes, 11(3), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030187







