Membrane Protein Stabilization Strategies for Structural and Functional Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Membrane Protein Mutagenesis
Systematic vs. Random Mutagenesis Approach
3. Detergent Selection
Classification of Detergents
4. Lipid Membrane Mimics
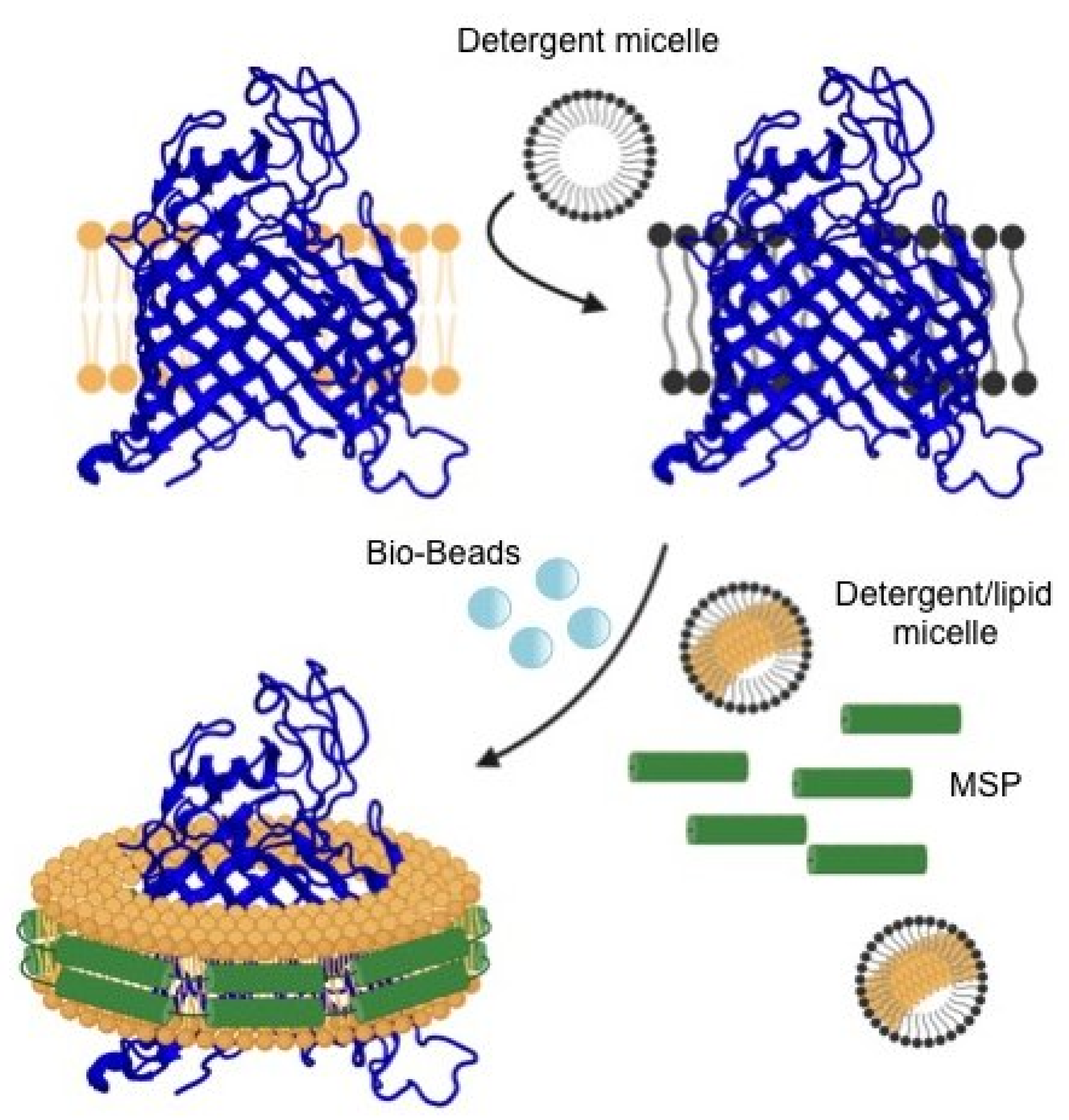
Nanodisc Applications in Membrane Protein Biophysics
5. Antibodies
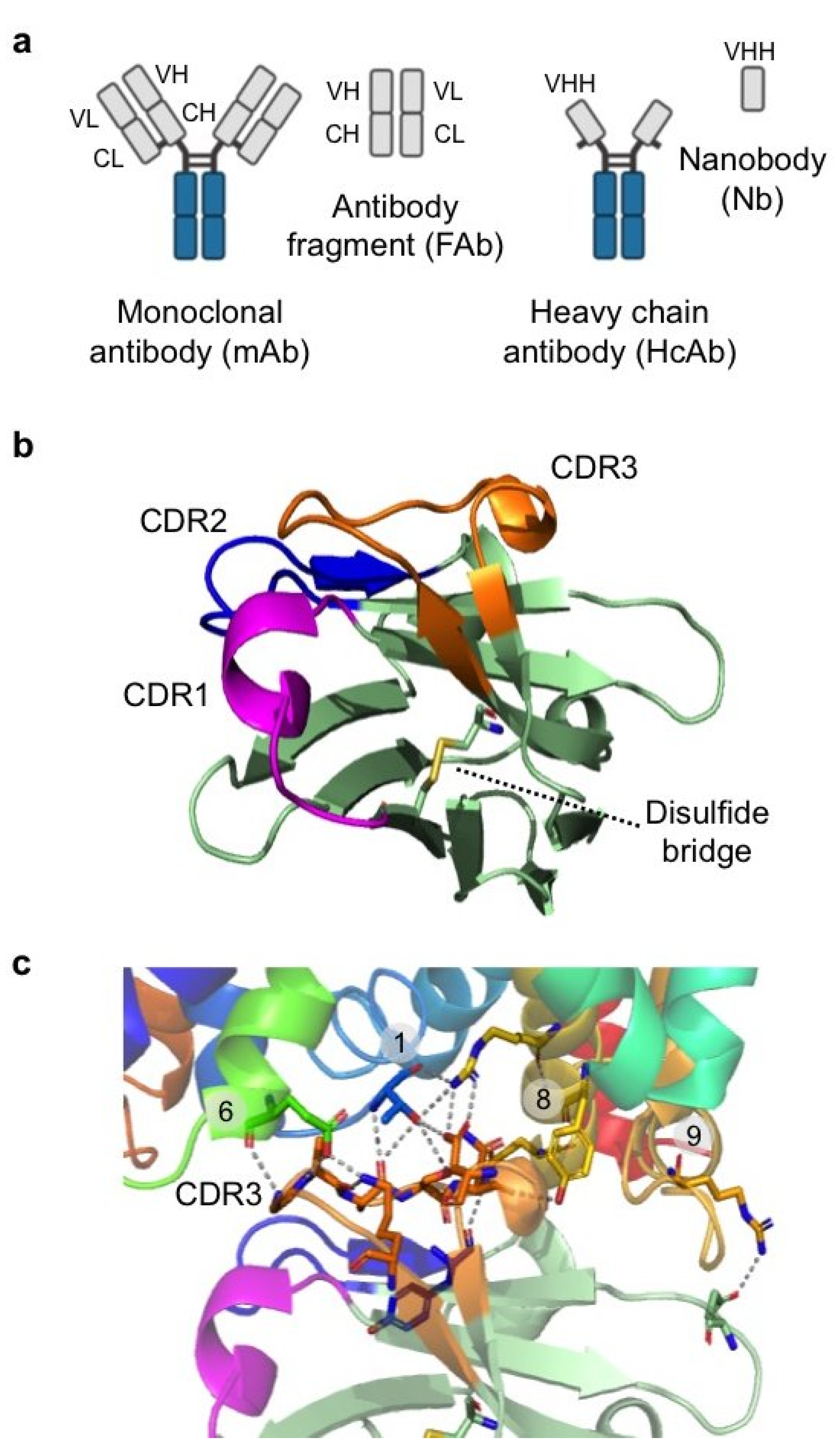
5.1. Nanobodies
5.2. Nanobody Applications in the Functional and Structural Biology of Membrane Proteins
6. Ligands
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overington, J.P.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Hopkins, A.L. How many drug targets are there? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggin, P.C.; Aldeghi, M.; Bodkin, M.J.; Heifetz, A. Beyond Membrane Protein Structure: Drug Discovery, Dynamics and Difficulties. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 922, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Flynn, A.D. Drugging Membrane Protein Interactions. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 18, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaudat, F.; Frelet-Barrand, A.; Pochon, N.; Dementin, S.; Hivin, P.; Boutigny, S.; Rioux, J.-B.; Salvi, D.; Seigneurin-Berny, D.; Richaud, P.; et al. Heterologous Expression of Membrane Proteins: Choosing the Appropriate Host. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Li, S.; Hall, J.; Mattern, M.R.; Tran, H.; Shoo, J.; Tan, R.; Weiss, S.R.; Butt, T.R. Enhanced Expression and Purification of Membrane Proteins by SUMO Fusion in Escherichia coli. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2005, 6, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubicek, J.; Block, H.; Maertens, B.; Spriestersbach, A.; Labahn, J. Expression and Purification of Membrane Proteins. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 541, pp. 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Shin, K.; Patterson, R.E.; Liu, X.-Q.; Rainey, J.K. Current strategies for protein production and purification enabling membrane protein structural biology. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 507–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laganowsky, A.; Reading, E.; Allison, T.M.; Ulmschneider, M.B.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Baldwin, A.J.; Robinson, C.V. Membrane proteins bind lipids selectively to modulate their structure and function. Nature 2014, 510, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, V.; Mendez-Villuendas, E.; Ingólfsson, H.I.; Gu, R.-X.; Siuda, I.; Melo, M.N.; Moussatova, A.; Degagné, L.J.; Sejdiu, B.I.; Singh, G.; et al. Lipid–Protein Interactions Are Unique Fingerprints for Membrane Proteins. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domene, C. Modulation of Membrane Proteins by Lipids. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 609a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickens, D.; Chiduza, G.N.; Wright, G.S.A.; Pirmohamed, M.; Antonyuk, S.V.; Hasnain, S.S. Modulation of LAT1 (SLC7A5) transporter activity and stability by membrane cholesterol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep43580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meury, M.; Costa, M.; Harder, D.; Stauffer, M.; Jeckelmann, J.-M.; Brühlmann, B.; Rosell, A.; Ilgü, H.; Kovar, K.; Palacín, M.; et al. Detergent-Induced Stabilization and Improved 3D Map of the Human Heteromeric Amino Acid Transporter 4F2hc-LAT2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosco, J.; Scalise, M.; Colas, C.; Galluccio, M.; Martini, R.; Rovella, F.; Mazza, T.; Ecker, G.F.; Indiveri, C. ATP modulates SLC7A5 (LAT1) synergistically with cholesterol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.J.Y.; Gabriel, F.; Tandale, A.; Nietlispach, D. Structure and Dynamics of GPCRs in Lipid Membranes: Physical Principles and Experimental Approaches. Molecules 2020, 25, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, A. GPCRs: Lipid-Dependent Membrane Receptors That Act as Drug Targets. Adv. Biol. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, I.; Garvey, M. Lipids in Amyloid-β Processing, Aggregation, and Toxicity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 855, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, J. Interactions between amyloid β peptide and lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, A.M.; Curnow, P.; Booth, P.J. Membrane proteins, lipids and detergents: Not just a soap opera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandan, A.; Vrielink, A. Detergents in Membrane Protein Purification and Crystallisation. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 922, pp. 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kotov, V.; Bartels, K.; Veith, K.; Josts, I.; Subhramanyam, U.K.T.; Günther, C.; Labahn, J.; Marlovits, T.C.; Moraes, I.; Tidow, H.; et al. High-throughput stability screening for detergent-solubilized membrane proteins. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, Y.; Newstead, S.; Hu, N.-J.; Alguel, Y.; Nji, E.; Beis, K.; Yashiro, S.; Lee, C.; Leung, J.; Cameron, A.D.; et al. Benchmarking Membrane Protein Detergent Stability for Improving Throughput of High-Resolution X-ray Structures. Structure 2011, 19, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawate, T.; Gouaux, E. Fluorescence-Detection Size-Exclusion Chromatography for Precrystallization Screening of Integral Membrane Proteins. Structure 2006, 14, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yao, H.; Li, T.; Hutter, C.A.J.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Seeger, M.A.; Li, D. An improved fluorescent tag and its nanobodies for membrane protein expression, stability assay, and purification. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deller, M.C.; Kong, L.; Rupp, B. Protein stability: A crystallographer’s perspective. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2016, 72, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, F.; Serrano-Vega, M.J.; Shibata, Y.; Abdul-Hussein, S.; Lebon, G.; Miller-Gallacher, J.; Singhal, A.; Strege, A.; Thomas, J.A.; Tate, C.G. A mutagenesis and screening strategy to generate optimally thermostabilized membrane proteins for structural studies. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1554–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojo, V.; Dessimoz, C.; Pomiankowski, A.; Lane, N. Membrane Proteins Are Dramatically Less Conserved than Water-Soluble Proteins across the Tree of Life. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2874–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, Y.; Nanekar, R.; Jaakola, V.-P. Defining thermostability of membrane proteins by western blotting. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2015, 28, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bill, R.M.; Henderson, P.J.F.; Iwata, S.; Kunji, E.R.S.; Michel, H.; Neutze, R.; Newstead, S.; Poolman, B.; Tate, C.G.; Vogel, H. Overcoming barriers to membrane protein structure determination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluis, M.W.; Godfroy, J.I.; Yin, H. Protein engineering methods applied to membrane protein targets. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2012, 26, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Bowie, J.U. Building a Thermostable Membrane Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 6975–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Banqueri, A.; Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Bartoccioni, P.; Kowalczyk, L.; Perálvarez-Marín, A.; Palacín, M.; Vázquez-Ibar, J.L. Stabilization of a prokaryotic LAT transporter by random mutagenesis. J. Gen. Physiol. 2016, 147, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydenreich, F.M.; Vuckovic, Z.; Matkovic, M.; Veprintsev, D.B. Stabilization of G protein-coupled receptors by point mutations. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Xu, C.; Sun, P.; Wu, J.; Yan, C.; Hu, M.; Yan, N. Crystal structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT1. Nature 2014, 510, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, L.; Ratera, M.; Paladino, A.; Bartoccioni, P.; Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Valencia, E.; Portella, G.; Bial, S.; Zorzano, A.; Fita, I.; et al. Molecular basis of substrate-induced permeation by an amino acid antiporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3935–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, R.F.S.; DeGrado, W.F. Helix-packing motifs in membrane proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13658–13663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenin, D.; Lazarova, T. Stable interactions between the transmembrane domains of the adenosine A2Areceptor. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbey, R.E.; Wang, P.; Kühn, A. Assembly of Bacterial Inner Membrane Proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidehi, N.; Grisshammer, R.; Tate, C.G. How Can Mutations Thermostabilize G-Protein-Coupled Receptors? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Vega, M.J.; Magnani, F.; Shibata, Y.; Tate, C.G. Conformational thermostabilization of the 1-adrenergic receptor in a detergent-resistant form. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penmatsa, A.; Wang, K.H.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structure of dopamine transporter elucidates antidepressant mechanism. Nature 2013, 503, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Lee, Y.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Takemoto, M.; Yamashita, K.; Nagamori, S.; Nishizawa, T.; Nureki, O. Consensus mutagenesis approach improves the thermal stability of system x c—Transporter, xCT, and enables cryo-EM analyses. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 2398–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlinkmann, K.M.; Plückthun, A. Directed Evolution of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors for High Functional Expression and Detergent Stability. Methods Enzymol. 2013, 520, 67–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenstein, K.; Kean, J.; Bortolato, A.; Cheng, R.K.Y.; Doré, A.S.; Jazayeri, A.; Cooke, R.M.; Weir, M.; Marshall, F.H. Structure of class B GPCR corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1. Nature 2013, 499, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doré, A.S.; Okrasa, K.; Patel, J.C.; Serranovega, M.J.; Bennett, K.; Cooke, R.M.; Errey, J.C.; Jazayeri, A.; Khan, S.; Tehan, B.; et al. Structure of class C GPCR metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain. Nature 2014, 511, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-H.; Weissman, J.S.; Kim, P.S. Contribution of individual side-chains to the stability of BPTI examined by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 249, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.D.; Shivaprasad, S.; Wetzel, R. Alanine Scanning Mutagenesis of Aβ(1-40) Amyloid Fibril Stability. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, V.; Dehez, F.; Chipot, C. AlaScan: A Graphical User Interface for Alanine Scanning Free-Energy Calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Damry, A.M.; Petrie, J.R.; Vanhercke, T.; Singh, S.P.; Jackson, C.J. Consensus Mutagenesis and Ancestral Reconstruction Provide Insight into the Substrate Specificity and Evolution of the Front-End Δ6-Desaturase Family. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternke, M.; Tripp, K.W.; Barrick, D. Consensus sequence design as a general strategy to create hyperstable, biologically active proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11275–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steipe, B. Evolutionary Approaches to Protein Engineering. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1999, 243, 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirri, E.; Brier, S.; Assal, R.; Canul-Tec, J.C.; Chamot-Rooke, J.; Reyes, N. Consensus designs and thermal stability determinants of a human glutamate transporter. eLife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.J.; Lim, H.Y.; Huang, J.; Kazlauskas, R.J. Comparison of Five Protein Engineering Strategies for Stabilizing an α/β-Hydrolase. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 6521–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullum, E.O.; Williams, B.A.R.; Zhang, J.; Chaput, J.C. Random Mutagenesis by Error-Prone PCR. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 634, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; De Vries, H.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Heitman, L.H. Scintillation proximity assay (SPA) as a new approach to determine a ligand’s kinetic profile. A case in point for the adenosine A1 receptor. Purinergic Signal. 2015, 12, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, U.; Krieger, G.; Avihou, Z.; Milo, R.; Schuldiner, M.; Davidi, D. Assessment of GFP Tag Position on Protein Localization and Growth Fitness in Yeast. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintaka, R.; Makanae, K.; Moriya, H. Cellular growth defects triggered by an overload of protein localization processes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.V.; Namba, K.; Minamino, T. GFP Fusion to the N-Terminus of MotB Affects the Proton Channel Activity of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor in Salmonella. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
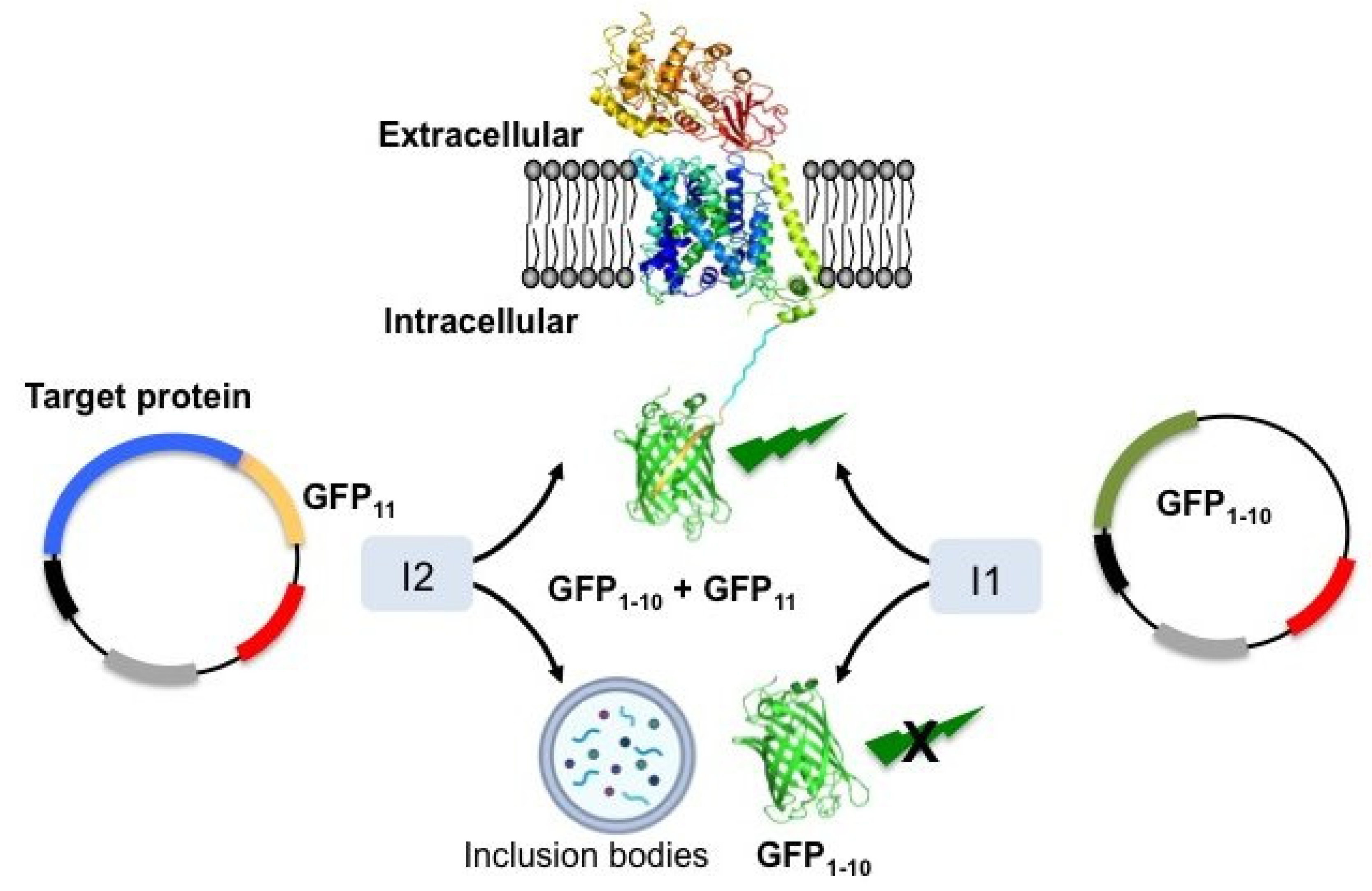
- Cabantous, S.; Waldo, G.S. In vivo and in vitro protein solubility assays using split GFP. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romei, M.G.; Boxer, S.G. Split Green Fluorescent Proteins: Scope, Limitations, and Outlook. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoyer, C.J.; Smith, S.E.; Gardner, J.M.; McCroskey, S.; Unruh, J.R.; Jaspersen, S.L. Distribution of Proteins at the Inner Nuclear Membrane Is Regulated by the Asi1 E3 Ligase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 2019, 211, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.B.; Garrison, J.C. Instability of the G-Protein β5Subunit in Detergent. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 268, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipot, C.; Dehez, F.; Schnell, J.R.; Zitzmann, N.; Pebay-Peyroula, E.; Catoire, L.J.; Miroux, B.; Kunji, E.R.S.; Veglia, G.; Cross, T.A.; et al. Perturbations of Native Membrane Protein Structure in Alkyl Phosphocholine Detergents: A Critical Assessment of NMR and Biophysical Studies. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 3559–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infed, N.; Hanekop, N.; Driessen, A.J.; Smits, S.H.; Schmitt, L. Influence of detergents on the activity of the ABC transporter LmrA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 2313–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancusso, R.; Karpowich, N.K.; Czyzewski, B.K.; Wang, D.-N. Simple screening method for improving membrane protein thermostability. Methods 2011, 55, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, T.O.C.; Reis, R.; Siligardi, G.; Hussain, R.; Cheruvara, H.; Moraes, I. Selection of Biophysical Methods for Characterisation of Membrane Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotboom, D.J.; Duurkens, R.H.; Olieman, K.; Erkens, G.B. Static light scattering to characterize membrane proteins in detergent solution. Methods 2008, 46, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergis, J.M.; Purdy, M.D.; Wiener, M.C. A high-throughput differential filtration assay to screen and select detergents for membrane proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 407, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alexandrov, A.I.; Mileni, M.; Chien, E.Y.; Hanson, M.A.; Stevens, R.C. Microscale Fluorescent Thermal Stability Assay for Membrane Proteins. Structure 2008, 16, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, D. Chapter 34 Detergents. Cellulases 2009, 463, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Mao, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Robertson, N.; Grisshammer, R.; Tate, C.G.; Vaidehi, N. How Do Short Chain Nonionic Detergents Destabilize G-Protein-Coupled Receptors? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15425–15433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Q.; An, J.; Hildebrandt, E.; Aleksandrov, L.A.; Kappes, J.C.; DeLucas, L.J.; Riordan, J.R.; Urbatsch, I.L.; et al. Membrane protein stability can be compromised by detergent interactions with the extramembranous soluble domains. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 769–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh-Hansen, U.; Le Maire, M.; Møller, J.V. The Mechanism of Detergent Solubilization of Liposomes and Protein-Containing Membranes. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 2932–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, S.; Møller, J.V. Biphasic kinetics of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase and the detergent-solubilized monomer. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 1654–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speers, A.E.; Wu, C.C. Proteomics of Integral Membrane ProteinsTheory and Application. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3687–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garidel, P.; Hildebrand, A.; Knauf, K.; Blume, A. Membranolytic Activity of Bile Salts: Influence of Biological Membrane Properties and Composition. Molecules 2007, 12, 2292–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newstead, S.; Hobbs, J.; Jordan, D.; Carpenter, E.P.; Iwata, S. Insights into outer membrane protein crystallization. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2008, 25, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulumello, D.V.; Deber, C.M. Efficiency of detergents at maintaining membrane protein structures in their biologically relevant forms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, J.D.; Sawicka, M.; Dutzler, R. Cryo-EM structures and functional characterization of murine Slc26a9 reveal mechanism of uncoupled chloride transport. eLife 2019, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhao, X.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Q. Structure of the human LAT1–4F2hc heteromeric amino acid transporter complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 568, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liao, L.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Chi, P.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Guo, L.; Sun, L.; Deng, D. Cryo-EM structure of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter CNT3. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkman, P.M.; Watts, A. Lipid modulation of early G protein-coupled receptor signalling events. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 2889–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitrac, H.; Mallampalli, V.K.P.S.; Bogdanov, M.; Dowhan, W. The lipid-dependent structure and function of LacY can be recapitulated and analyzed in phospholipid-containing detergent micelles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, H.E.; Booth, P.J. The folding, stability and function of lactose permease differ in their dependence on bilayer lipid composition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsdottir, H.; Hunte, C. Lipids in membrane protein structures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Jin, C.; Quan, L.; Ohgaki, R.; Okuda, S.; Kusakizako, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Oda, K.; Ishitani, R.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human L-type amino acid transporter 1 in complex with glycoprotein CD98hc. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laan, E.V.D.B.-V.D.; Killian, J.A.; De Kruijff, B. Nonbilayer lipids affect peripheral and integral membrane proteins via changes in the lateral pressure profile. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Ortiz, R.; Straub, J.E.; Dominguez, L. Influence of membrane lipid composition on the structure and activity of γ-secretase. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 27294–27304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, P.J.; Hwa, J.; Khorana, H.G. Structure and function in rhodopsin: Kinetic studies of retinal binding to purified opsin mutants in defined phospholipid–detergent mixtures serve as probes of the retinal binding pocket. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Caffrey, M. Structure and Functional Characterization of Membrane Integral Proteins in the Lipid Cubic Phase. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5104–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.R.; Grimme, S.; Bhattacharya, P.; Stowell, M.H.B.; Artinger, M.; Prabahakar, B.S.; Meriggioli, M.N. In vivo adsorption of autoantibodies in myasthenia gravis using Nanodisc-incorporated acetylcholine receptor. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 225, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, J.M.; Scheidelaar, S.; Koorengevel, M.C.; Dominguez, J.J.; Schäfer, M.; Van Walree, C.A.; Killian, J.A. The styrene–maleic acid copolymer: A versatile tool in membrane research. Eur. Biophys. J. 2016, 45, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayburt, T.H.; Sligar, S.G. Membrane protein assembly into Nanodiscs. FEBS Lett. 2009, 584, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denisov, I.G.; Sligar, S.G. Nanodiscs in Membrane Biochemistry and Biophysics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4669–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.M.P.; Shih, W.M.; Wagner, G.; Nasr, M.L. Large Nanodiscs: A Potential Game Changer in Structural Biology of Membrane Protein Complexes and Virus Entry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.J.; Atkins, W.M.; McClary, W.D. Preparation of Lipid Nanodiscs with Lipid Mixtures. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2019, 98, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, I.G.; McLean, M.A.; Shaw, A.W.; Grinkova, Y.V.; Sligar, S.G. Thermotropic Phase Transition in Soluble Nanoscale Lipid Bilayers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 15580–15588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinkova, Y.V.; Denisov, I.G.; Sligar, S.G. Functional reconstitution of monomeric CYP3A4 with multiple cytochrome P450 reductase molecules in Nanodiscs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschle, T.; Lin, C.; Jungmann, R.; Shih, W.M.; Wagner, G. Controlled Co-reconstitution of Multiple Membrane Proteins in Lipid Bilayer Nanodiscs Using DNA as a Scaffold. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 2448–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoccioni, P.; Fort, J.; Zorzano, A.; Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Palacín, M. Functional characterization of the alanine-serine-cysteine exchanger of Carnobacterium sp. AT7. J. Gen. Physiol. 2019, 151, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Fort, J.; Bartoccioni, P.; Díaz, L.; Pardon, E.; Carpena, X.; Espino-Guarch, M.; Zorzano, A.; Ziegler, C.; Steyaert, J.; et al. L amino acid transporter structure and molecular bases for the asymmetry of substrate interaction. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, E. Membrane Structure–Function Insights from Asymmetric Lipid Vesicles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, J.; Pondenis, H.; Fan, T.M.; Das, A. Direct Capture of Functional Proteins from Mammalian Plasma Membranes into Nanodiscs. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 6299–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominik, P.K.; Borowska, M.T.; Dalmas, O.; Kim, S.S.; Perozo, E.; Keenan, R.J.; Kossiakoff, A.A. Conformational Chaperones for Structural Studies of Membrane Proteins Using Antibody Phage Display with Nanodiscs. Structure 2016, 24, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardill, B.; Huang, J.; Tu, L.; Van Petegem, F.; Oxenoid, K.; Thomson, C.A. Nanodisc technology facilitates identification of monoclonal antibodies targeting multi-pass membrane proteins. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, H.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structures of LeuT in substrate-free outward-open and apo inward-open states. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 481, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.W.L.; McCoy, J.G.; Thompson, A.N.; Nichols, C.G.; Nimigean, C.M. Mechanism for selectivity-inactivation coupling in KcsA potassium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5272–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J.A.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Wen, P.-C.; Yoshioka, C.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Gouaux, E. Serotonin transporter–ibogaine complexes illuminate mechanisms of inhibition and transport. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 569, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishchenko, A.; Wacker, D.; Kapoor, M.; Zhang, A.; Han, G.W.; Basu, S.; Patel, N.; Messerschmidt, M.; Weierstall, U.; Liu, W.; et al. Structural insights into the extracellular recognition of the human serotonin 2B receptor by an antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8223–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hino, T.; Iwata, S.; Murata, T. Generation of functional antibodies for mammalian membrane protein crystallography. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardon, E.; Laeremans, T.; Triest, S.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Wohlkönig, A.; Ruf, A.; Muyldermans, S.; Hol, W.G.J.; Kobilka, B.K.; Steyaert, J. A general protocol for the generation of Nanobodies for structural biology. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 674–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flajnik, M.F.; Deschacht, N.; Muyldermans, S. A Case Of Convergence: Why Did a Simple Alternative to Canonical Antibodies Arise in Sharks and Camels? PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural Single-Domain Antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Genst, E.; Silence, K.; Decanniere, K.; Conrath, K.; Loris, R.; Kinne, J.; Muyldermans, S.; Wyns, L. Molecular basis for the preferential cleft recognition by dromedary heavy-chain antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Finer-Moore, J.S.; Jiang, X.; Smirnova, I.; Kasho, V.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Kaback, H.R.; Stroud, R.M. Crystal Structure of a ligand-bound LacY–Nanobody Complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8769–8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogenboom, H.R. Selecting and screening recombinant antibody libraries. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenken, L.; Hessing, J.; Hondel, C.V.D.; Verrips, C. Recent advances in the large-scale production of antibody fragments using lower eukaryotic microorganisms. Res. Immunol. 1998, 149, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, V.; Slivac, I.; Perret, S.; Bisson, L.; St-Laurent, G.; Murad, Y.; Zhang, J.; Durocher, Y. Stable Expression of Chimeric Heavy Chain Antibodies in CHO Cells. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2012, 911, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, D.; Vignard, J.; Fedor, Y.; Béry, N.; Olichon, A.; Crozatier, M.; Erard, M.; Cassard, H.; Ducommun, B.; Salles, B.; et al. Chromatibody, a novel non-invasive molecular tool to explore and manipulate chromatin in living cells. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 2673–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, B.-M.; Maier, J.; Secker, K.-A.; Egetemaier, S.-M.; Parfyonova, Y.; Rothbauer, U.; Traenkle, B. Chromobodies to Quantify Changes of Endogenous Protein Concentration in Living Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 2518–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchański, T.; Masiulis, S.; Fischer, B.; Kalichuk, V.; López-Sánchez, U.; Zarkadas, E.; Weckener, M.; Sente, A.; Ward, P.; Wohlkönig, A.; et al. Megabodies expand the nanobody toolkit for protein structure determination by single-particle cryo-EM. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manglik, A.; Kobilka, B.K.; Steyaert, J. Nanobodies to Study G Protein–Coupled Receptor Structure and Function. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2017, 57, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galazzo, L.; Meier, G.; Timachi, M.H.; Hutter, C.A.J.; Seeger, M.A.; Bordignon, E. Spin-labeled nanobodies as protein conformational reporters for electron paramagnetic resonance in cellular membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.G.F.; DeVree, B.T.; Zou, Y.; Kruse, A.C.; Chung, K.Y.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Chae, P.S.; Pardon, E.; Calinski, D.; et al. Crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor–Gs protein complex. Nature 2011, 477, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, M.; Hibbs, R.E.; Gouaux, E. A Fluorescence-Detection Size-Exclusion Chromatography-Based Thermostability Assay for Membrane Protein Precrystallization Screening. Structure 2012, 20, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celej, M.S.; Montich, G.G.; Fidelio, G.D. Protein stability induced by ligand binding correlates with changes in protein flexibility. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, D.; Fotiadis, D. Measuring substrate binding and affinity of purified membrane transport proteins using the scintillation proximity assay. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavrutskii, L.; Yeh, J.; Timofeeva, O.; Tarasov, S.G.; Pritt, S.; Stefanisko, K.; Tarasova, N. Protein Purification-free Method of Binding Affinity Determination by Microscale Thermophoresis. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 50541, e50541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.P.; Fleming, K.G. Using Tryptophan Fluorescence to Measure the Stability of Membrane Proteins Folded in Liposomes. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 492, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlstaedt, M.; Von Der Hocht, I.; Hilbers, F.; Thielmann, Y.; Michel, H. Development of a Thermofluor assay for stability determination of membrane proteins using the Na+/H+antiporter NhaA and cytochromecoxidase. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senisterra, G.A.; Ghanei, H.; Khutoreskaya, G.; Dobrovetsky, E.; Edwards, A.M.; Privé, G.G.; Vedadi, M. Assessing the Stability of Membrane Proteins to Detect Ligand Binding Using Differential Static Light Scattering. J. Biomol. Screen. 2010, 15, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Membrane Scaffold Protein (MSP) | Nanodisc Diameter (nm) | Features | Molecular Mass (Da) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSP1 | 9.7 | Original MSP1 (deletion 1–43 mutant of human Apo A-1) | 24,608 |
| MSP1TEV | 9.7 | MSP1 with removable 7-his tag | 26,930 |
| MSP1D1 | 9.7 | Deletion 1–11 mutant of MSP1TEV | 24,662 |
| MSP1D1 D73C | 9.6 | D73C MSP1D1 mutant in helix 2, Apo A-1 numbering | 24,650 |
| MSP1D1 (-) | 9.6 | MSP1D1 lacking 7-His tag | 22,044 |
| MSP1D2 | 9.6 | MSP1 variant lacking the first helix. | 24,608 |
| MSP1E1 | 10.4–10.6 | Extended MSP1, helix 4 repeated | 27,494 |
| MSP1E2 | 11.1–11.9 | Extended MSP1, helices 4 and 5 repeated | 30,049 |
| MSP1E3 | 12.1–12.9 | Extended MSP1, helices 4, 5, and 6 repeated | 32,546 |
| MSP1E1D1 | 10.5 | Extended MSP1D1, helix 4 repeated | 27,547 |
| MSP1E2D1 | 11.1 | Extended MSP1D1, helices 4 and 5 repeated | 30,103 |
| MSP1E3D1 | 12.1 | Extended MSP1D1, helices 4, 5, and 6 repeated | 32,600 |
| MSP2 | 9.5 | Fusion of two MSP1 with GT-linker | 48,020 |
| MSP2N2 | 15.0–16.5 | Fusion of MSP1D1 and MSP1D2 with GT linker | 45,541 |
| MSP2N3 | 15.2–17 | Fusion of MSP1D1 and MSP1D1-17 (deletion amino acids 1–17) with GT linker | 46,125 |
| MSP1FC | 9.7 | MSP1D1 with C-terminal FLAG-tag | 25,714 |
| MSP1FN | 9.6 | MSP1D1 with N-terminal FLAG-tag | 25,714 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Bartoccioni, P.; Palacín, M. Membrane Protein Stabilization Strategies for Structural and Functional Studies. Membranes 2021, 11, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11020155
Errasti-Murugarren E, Bartoccioni P, Palacín M. Membrane Protein Stabilization Strategies for Structural and Functional Studies. Membranes. 2021; 11(2):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11020155
Chicago/Turabian StyleErrasti-Murugarren, Ekaitz, Paola Bartoccioni, and Manuel Palacín. 2021. "Membrane Protein Stabilization Strategies for Structural and Functional Studies" Membranes 11, no. 2: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11020155
APA StyleErrasti-Murugarren, E., Bartoccioni, P., & Palacín, M. (2021). Membrane Protein Stabilization Strategies for Structural and Functional Studies. Membranes, 11(2), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11020155







