Plasma Membrane Lipids: An Important Binding Site for All Lipoprotein Classes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
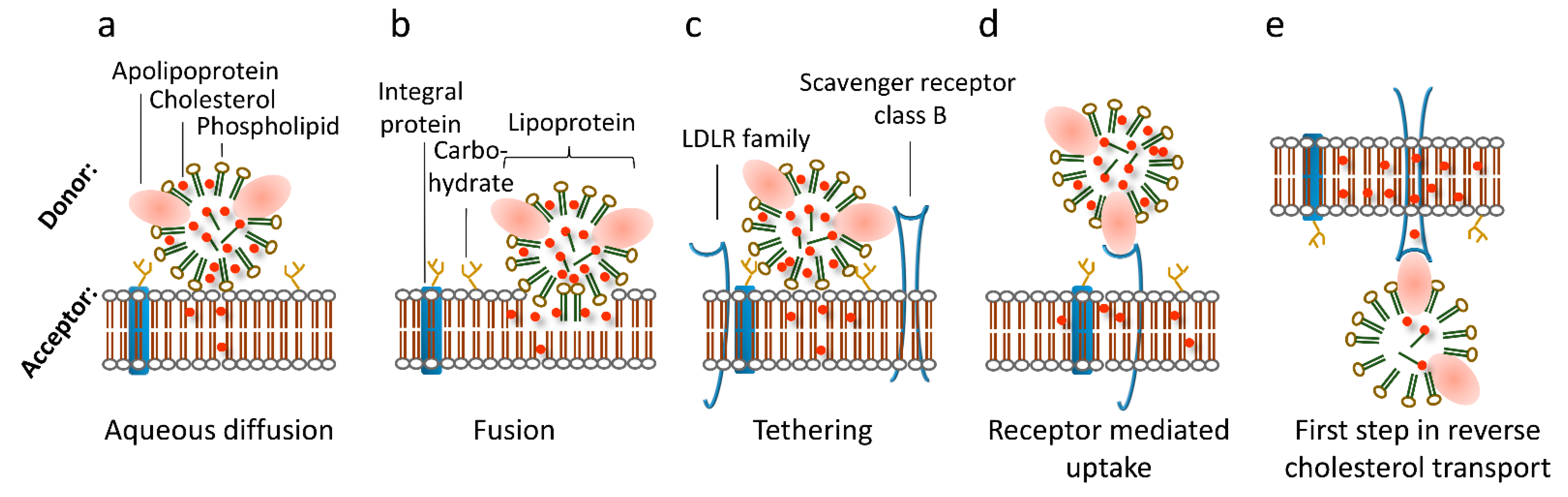
2. Intracellular Transfer Pathways
3. Receptor-Mediated Cholesterol Uptake, Efflux, and Transcytosis Pathways
4. Redundancy of Cholesterol Transfer Pathways
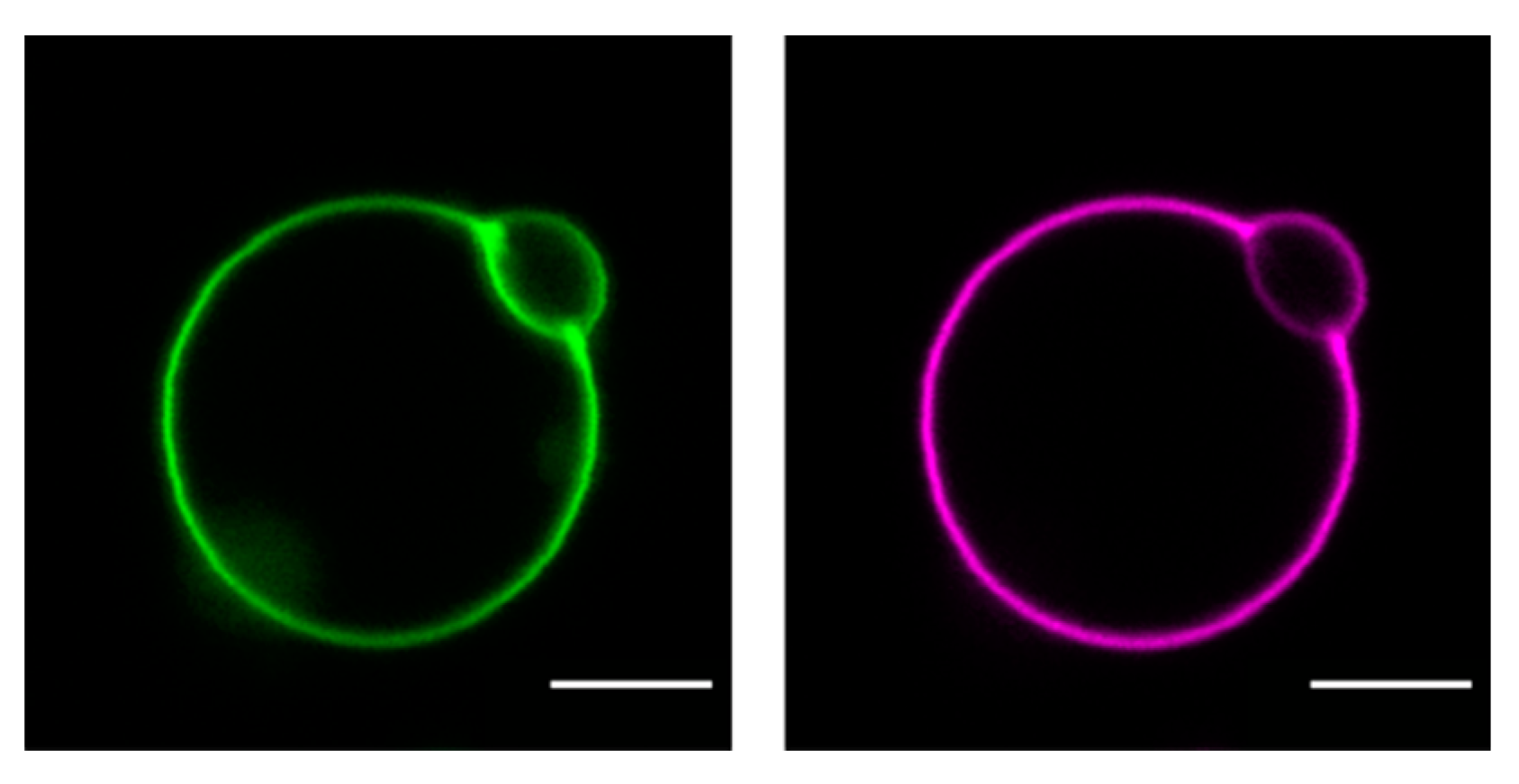
5. The Role of the Plasma Membrane Lipids for Cholesterol Uptake
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maxfield, F.R.; van Meer, G. Cholesterol, the central lipid of mammalian cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Meer, G. Lipid Traffic in Animal Cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1989, 5, 247–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkwart, K.; Schneider, F.; Lukoseviciute, M.; Sauka-Spengler, T.; Lyman, E.; Eggeling, C.; Sezgin, E. Nanoscale dynamics of cholesterol in the cell membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 12599–12609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikonen, E.; Zhou, X. Cholesterol transport between cellular membranes: A balancing act between interconnected lipid fluxes. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Brown, M.S.; Anderson, D.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Radhakrishnan, A. Three pools of plasma membrane cholesterol and their relation to cholesterol homeostasis. eLife 2014, 3, e02882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, R.E.; Radhakrishnan, A. Continuous transport of a small fraction of plasma membrane cholesterol to endoplasmic reticulum regulates total cellular cholesterol. eLife 2017, 6, e25466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.A.; Radhakrishnan, A. Accessibility of cholesterol at cell surfaces. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Yang, H.; Song, B.-L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Siperstein, M.D. Regulation of cholesterol synthesis in normal and malignant tissue. Fed. Proc. 1973, 32, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem, I.; Meaney, S. Brain Cholesterol: Long Secret Life Behind a Barrier. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwynne, J.T.; Strauss, J.F., 3rd. The Role of Lipoproteins in Steroidogenesis and Cholesterol Metabolism in Steroidogenic Glands. Endocr. Rev. 1982, 3, 299–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehuang, L.-H.; Eelvington, A.; Randolph, G.J. The role of the lymphatic system in cholesterol transport. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Axmann, M.; Strobl, W.M.; Plochberger, B.; Stangl, H. Cholesterol transfer at the plasma membrane. Atherosclerosis 2019, 290, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonen, E. Cellular cholesterol trafficking and compartmentalization. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonen, E.; Kanerva, K. Shuttling HDL Cholesterol to the Membrane via Metastable Receptor Multimers. Dev. Cell 2019, 50, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, W.A.; Toulmay, A.; Balla, T. The functional universe of membrane contact sites. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, J.; Li, S.; Fairall, L.; Pfisterer, S.G.; Gurnett, J.E.; Xiao, X.; Weston, T.A.; Vashi, D.; Ferrari, A.; Orozco, J.L.; et al. Aster Proteins Facilitate Nonvesicular Plasma Membrane to ER Cholesterol Transport in Mammalian Cells. Cell 2018, 175, 514–529.E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, A.; He, C.; Kennelly, J.P.; Sandhu, J.; Xiao, X.; Chi, X.; Jiang, H.; Young, S.G.; Tontonoz, P. Aster Proteins Regulate the Accessible Cholesterol Pool in the Plasma Membrane. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00255-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, A.; Goldstein, J.L.; McDonald, J.G.; Brown, M.S. Switch-like Control of SREBP-2 Transport Triggered by Small Changes in ER Cholesterol: A Delicate Balance. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesmin, B.; Bigay, J.; Polidori, J.; Jamecna, D.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Antonny, B. Sterol transfer, PI 4P consumption, and control of membrane lipid order by endogenous OSBP. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 3156–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, T.; Saheki, Y. GRAMD1-mediated accessible cholesterol sensing and transport. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 1986, 232, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S.; Anderson, R.G.W.; Russell, D.; Schneider, W.J. Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis: Concepts Emerging from the LDL Receptor System. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1985, 1, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. The LDL Receptor. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahley, R.W.; Ji, Z.S. Remnant lipoprotein metabolism: Key pathways involving cell-surface heparan sulfate proteo-glycans and apolipoprotein E. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Brecht, W.; Miranda, R.; Hussain, M.; Innerarity, T.; Mahley, R. Role of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the binding and uptake of apolipoprotein E-enriched remnant lipoproteins by cultured cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 10160–10167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Fazio, S.; Lee, Y.; Mahley, R. Secretion-capture role for apolipoprotein E in remnant lipoprotein metabolism involving cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 2764–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Fazio, S.; Mahley, R. Variable heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding of apolipoprotein E variants may modulate the expression of type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 13421–13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; van der Hoogt, C.C.; Espirito Santo, S.M.; Out, R.; Kypreos, K.; van Vlijmen, B.J.M.; Van Berkel, T.J.C.; Romijn, J.A.; Havekes, L.M.; van Dijk, K.W.; et al. The hepatic uptake of VLDL in lrpldlrvldlr mice is regulated by LPL activity and involves proteoglycans and SR-BI. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feingold, K.R. Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- von Eckardstein, A. Tachometer for Reverse Cholesterol Transport? J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2012, 1, e003723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.-J.; Azhar, S.; Kraemer, F. SR-B1: A Unique Multifunctional Receptor for Cholesterol Influx and Efflux. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018, 80, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acton, S.; Rigotti, A.; Landschulz, K.T.; Xu, S.; Hobbs, H.H.; Krieger, M. Identification of Scavenger Receptor SR-BI as a High Density Lipoprotein Receptor. Science 1996, 271, 518–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangl, H.; Strobl, W. Role of SR-BI in HDL Metabolism. In The HDL Handbook, 3rd ed.; Komoda, T., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz, K.T.; Pathak, R.K.; Rigotti, A.; Krieger, M.; Hobbs, H.H. Regulation of scavenger receptor, class B, type I, a high density lipoprotein receptor, in liver and steroidogenic tissues of the rat. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Trigatti, B.L.; Xu, S.; Acton, S.; Babitt, J.; Krieger, M. The Efficient Cellular Uptake of High Density Lipoprotein Lipids via Scavenger Receptor Class B Type I Requires Not Only Receptor-mediated Surface Binding but Also Receptor-specific Lipid Transfer Mediated by Its Extracellular Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26338–26348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothblat, G.; Mahlberg, F.; Johnson, W.; Phillips, M. Apolipoproteins, membrane cholesterol domains, and the regulation of cholesterol efflux. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.C.; Johnson, W.J.; Rothblat, G.H. Mechanisms and consequences of cellular cholesterol exchange and transfer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 906, 223–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scobey, M.W.; Johnson, F.L.; Rudel, L.L. Delivery of high-density lipoprotein free and esterified cholesterol to bile by the perfused monkey liver. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1989, 257, G644–G652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.C. Is ABCA1 a lipid transfer protein? J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, D.L.; de la Llera-Moya, M.; Thuahnai, S.T.; Lund-Katz, S.; Connelly, M.A.; Azhar, S.; Anantharamaiah, G.; Phillips, M.C. Binding and Cross-linking Studies Show That Scavenger Receptor BI Interacts with Multiple Sites in Apolipoprotein A-I and Identify the Class A Amphipathic α-Helix as a Recognition Motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18897–18904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Lawrence, R.; Krieger, M. Dissociation of the high density lipoprotein and low density lipoprotein binding activities of murine scavenger receptor class B type I (mSR-BI) using retrovirus library-based activity dissection. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9120–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigueza, W.V.; Thuahnai, S.T.; Temel, R.E.; Lund-Katz, S.; Phillips, M.C.; Williams, D.L. Mechanism of scavenger receptor class B type I-mediated selective uptake of cholesteryl esters from high density lipoprotein to adrenal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20344–20350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silver, D.L.; Wang, N.; Xiao, X.; Tall, A.R. High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Particle Uptake Mediated by Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1 Results in Selective Sorting of HDL Cholesterol from Protein and Polarized Cholesterol Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25287–25293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagler, T.A.; Rhode, S.; Neuhofer, A.; Laggner, H.; Strobl, W.; Hinterndorfer, C.; Volf, I.; Pavelka, M.; Eckhardt, E.R.; van der Westhuyzen, D.R.; et al. SR-BI-mediated High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Endocytosis Leads to HDL Resecretion Facilitating Cholesterol Efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11193–11204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Röhrl, C.; Meisslitzer-Ruppitsch, C.; Bittman, R.; Li, Z.; Pabst, G.; Prassl, R.; Strobl, W.; Neumüller, J.; Ellinger, A.; Pavelka, M.; et al. Combined light and electron microscopy using diaminobenzidine photooxidation to monitor trafficking of lipids derived from lipoprotein particles. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Röhrl, C.; Pagler, T.A.; Strobl, W.; Ellinger, A.; Neumüller, J.; Pavelka, M.; Stangl, H.; Meisslitzer-Ruppitsch, C. Characterization of endocytic compartments after holo-high density lipoprotein particle uptake in HepG2 cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 133, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Akmentin, W.; Connelly, M.A.; Lund-Katz, S.; Phillips, M.C.; Williams, D.L. Scavenger Receptor BI (SR-BI) Clustered on Microvillar Extensions Suggests that This Plasma Membrane Domain Is a Way Station for Cholesterol Trafficking between Cells and High-Density Lipoprotein. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Béaslas, O.; Cueille, C.; Delers, F.; Chateau, D.; Chambaz, J.; Rousset, M.; Carrière, V. Sensing of Dietary Lipids by Enterocytes: A New Role for SR-BI/CLA-1. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saddar, S.; Carrière, V.; Lee, W.-R.; Tanigaki, K.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Parathath, S.; Morel, E.; Warrier, M.; Sawyer, J.K.; Gerard, R.D.; et al. Scavenger Receptor Class B Type I Is a Plasma Membrane Cholesterol Sensor. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhainds, D.; Bourgeois, P.; Bourret, G.; Huard, K.; Falstrault, L.; Brissette, L. Localization and regulation of SR-BI in membrane rafts of HepG2 cells. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3095–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhainds, D.; Brissette, L. The role of scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) in lipid trafficking: Defining the rules for lipid traders. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 39–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, H.; Cao, G.; Wyne, K.L.; Hobbs, H.H. Scavenger Receptor, Class B, Type I-dependent Stimulation of Cholesterol Esterification by High Density Lipoproteins, Low Density Lipoproteins, and Nonlipoprotein Cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31002–31008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stangl, H.; Hyatt, M.; Hobbs, H.H. Transport of Lipids from High and Low Density Lipoproteins via Scavenger Receptor-BI. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32692–32698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Röhrl, C.; Fruhwürth, S.; Schreier, S.M.; Lohninger, A.; Dolischka, A.; Hüttinger, M.; Zemann, N.; Hermann, M.; Strobl, W.; Stangl, H. Scavenger receptor, Class B, Type I provides an alternative means for β-VLDL uptake independent of the LDL receptor in tissue culture. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romero-Garcia, S.; Lopez-Gonzalez, J.S.; Báez-Viveros, J.L.; Aguilar-Cazares, D.; Prado-Garcia, H. Tumor cell metabolism: An integral view. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goossens, P.; Rodriguez-Vita, J.; Etzerodt, A.; Masse, M.; Rastoin, O.; Gouirand, V.; Ulas, T.; Papantonopoulou, O.; Van Eck, M.; Auphan-Anezin, N.; et al. Membrane Cholesterol Efflux Drives Tumor-Associated Macrophage Reprogramming and Tumor Progression. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1376–1389 e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, E.; Robert, J.; Rohrer, L.; von Eckardstein, A.; Lee, W.L. Transendothelial transport of lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis 2020, 315, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, L.; Ohnsorg, P.M.; Lehner, M.; Landolt, F.; Rinninger, F.; von Eckardstein, A. High-Density Lipoprotein Transport Through Aortic Endothelial Cells Involves Scavenger Receptor BI and ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter G1. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soutar, A.K.; Naoumova, R.P. Mechanisms of Disease: Genetic causes of familial hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 4, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.K.; Wilund, K.; Arca, M.; Zuliani, G.; Fellin, R.; Maioli, M.; Calandra, S.; Bertolini, S.; Cossu, F.; Grishin, N.; et al. Autosomal Recessive Hypercholesterolemia Caused by Mutations in a Putative LDL Receptor Adaptor Protein. Science 2001, 292, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergeer, M.; Korporaal, S.J.; Franssen, R.; Meurs, I.; Out, R.; Hovingh, G.K.; Hoekstra, M.; Sierts, J.A.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Motazacker, M.M.; et al. Genetic Variant of the Scavenger Receptor BI in Humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzioch, M.; Orsó, E.; Klucken, J.; Langmann, T.; Böttcher, A.; Diederich, W.; Drobnik, W.; Barlage, S.; Büchler, C.; Porsch-Özcürümez, M.; et al. The gene encoding ATP-binding cassette transporter 1 is mutated in Tangier disease. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, K.E.; Tian, H.; Graf, G.A.; Yu, L.; Grishin, N.V.; Schultz, J.; Kwiterovich, P.; Shan, B.; Barnes, R.; Hobbs, H.H. Accumulation of Dietary Cholesterol in Sitosterolemia Caused by Mutations in Adjacent ABC Transporters. Science 2000, 290, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartuzi, P.; Billadeau, D.D.; Favier, R.; Rong, S.; Dekker, D.; Fedoseienko, A.; Fieten, H.; Wijers, M.; Levels, J.H.; Huijkman, N.; et al. CCC- and WASH-mediated endosomal sorting of LDLR is required for normal clearance of circulating LDL. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, R.J.; Yamada, N.; Shames, D.M. Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Animal model for familial hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosis 1989, 9, I33–I38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hofker, M.H.; van Vlijmen, B.J.; Havekes, L.M. Transgenic mouse models to study the role of APOE in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 1998, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Diet and Murine Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trommsdorff, M.; Gotthardt, M.; Hiesberger, T.; Shelton, J.; Stockinger, W.; Nimpf, J.; E Hammer, R.; A Richardson, J.; Herz, J. Reeler/Disabled-like Disruption of Neuronal Migration in Knockout Mice Lacking the VLDL Receptor and ApoE Receptor 2. Cell 1999, 97, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santo, S.M.S.E.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Goudriaan, J.R.; Bensadoun, A.; Bovenschen, N.; Voshol, P.J.; Havekes, L.M.; van Vlijmen, B.J.M. Triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism in unique VLDL receptor, LDL receptor, and LRP triple-deficient mice. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plump, A.S.; Erickson, S.K.; Weng, W.; Partin, J.S.; Breslow, J.L.; Williams, D.L. Apolipoprotein A-I is required for cholesteryl ester accumulation in steroidogenic cells and for normal adrenal steroid production. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2660–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigotti, A.; Trigatti, B.L.; Penman, M.; Rayburn, H.; Herz, J.; Krieger, M. A targeted mutation in the murine gene encoding the high density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor scavenger receptor class B type I reveals its key role in HDL metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12610–12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orsó, E.; Broccardo, C.; Kaminski, W.E.; Böttcher, A.; Liebisch, G.; Drobnik, W.; Götz, A.; Chambenoit, O.; Diederich, W.; Langmann, T.; et al. Transport of lipids from Golgi to plasma membrane is defective in Tangier disease patients and Abc1-deficient mice. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.A.; Barrera, G.C.; Nakamura, K.; Baldán, Á.; Tarr, P.; Fishbein, M.C.; Frank, J.; Francone, O.L.; Edwards, P.A. ABCG1 has a critical role in mediating cholesterol efflux to HDL and preventing cellular lipid accumulation. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Hammer, R.E.; Li-Hawkins, J.; von Bergmann, K.; Lutjohann, D.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Disruption of Abcg5 and Abcg8 in mice reveals their crucial role in biliary cholesterol secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16237–16242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braun, A.; Trigatti, B.L.; Post, M.J.; Sato, K.; Simons, M.; Edelberg, J.M.; Rosenberg, R.D.; Schrenzel, M.; Krieger, M. Loss of SR-BI Expression Leads to the Early Onset of Occlusive Atherosclerotic Coronary Artery Disease, Spontaneous Myocardial Infarctions, Severe Cardiac Dysfunction, and Premature Death in Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mice. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingwood, D.; Simons, K. Lipid Rafts As a Membrane-Organizing Principle. Science 2010, 327, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chernomordik, L.; Chanturiya, A.; Green, J.; Zimmerberg, J. The hemifusion intermediate and its conversion to complete fusion: Regulation by membrane composition. Biophys. J. 1995, 69, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawle, R.J.; van Lengerich, B.; Chung, M.; Bendix, P.M.; Boxer, S.G. Vesicle Fusion Observed by Content Transfer across a Tethered Lipid Bilayer. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, L37–L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akimov, S.A.; Molotkovsky, R.J.; Kuzmin, P.I.; Galimzyanov, T.R.; Batishchev, O.V. Continuum Models of Membrane Fusion: Evolution of the Theory. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Maxfield, F.R. Role of Membrane Organization and Membrane Domains in Endocytic Lipid Trafficking. Traffic 2000, 1, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, D.M. Membranes are more mosaic than fluid. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 438, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, N.; Rand, R. The Influence of Lysolipids on the Spontaneous Curvature and Bending Elasticity of Phospholipid Membranes. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plochberger, B.; Sych, T.; Weber, F.; Novacek, J.; Axmann, M.; Stangl, H.; Sezgin, E. Lipoprotein Particles Interact with Membranes and Transfer Their Cargo without Receptors. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 4421–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axmann, M.; Sezgin, E.; Karner, A.; Novacek, J.; Brodesser, M.D.; Röhrl, C.; Preiner, J.; Stangl, H.; Plochberger, B. Receptor-Independent Transfer of Low Density Lipoprotein Cargo to Biomembranes. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plochberger, B.; Röhrl, C.; Preiner, J.; Rankl, C.; Brameshuber, M.; Madl, J.; Bittman, R.; Ros, R.; Sezgin, E.; Eggeling, C.; et al. HDL particles incorporate into lipid bilayers—A combined AFM and single molecule fluorescence microscopy study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldie, S.; Sebastiani, F.; Browning, K.; Maric, S.; Lind, T.K.; Yepuri, N.; Darwish, T.A.; Moulin, M.; Strohmeier, G.; Pichler, H.; et al. Lipoprotein ability to exchange and remove lipids from model membranes as a function of fatty acid saturation and presence of cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maric, S.; Lind, T.K.; Raida, M.R.; Bengtsson, E.; Fredrikson, G.N.; Rogers, S.; Moulin, M.; Haertlein, M.; Forsyth, V.T.; Wenk, M.R.; et al. Time-resolved small-angle neutron scattering as a probe for the dynamics of lipid exchange between human lipoproteins and naturally derived membranes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, M.J.; Koeppe, E.K., III; Andersen, O.S. Docosahexaenoic acid alters bilayer elastic properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9638–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahn, E.; Baarine, M.; Dauphin, A.; Ragot, K.; Tissot, N.; Seguin, A.; Ménétrier, F.; Kattan, Z.; Bachelet, C.-M.; Frouin, F.; et al. Impact of 7-ketocholesterol and very long chain fatty acids on oligodendrocyte lipid membrane organization: Evaluation via LAURDAN and FAMIS spectral image analysis. Cytom. Part A 2011, 79, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, S.J.; Fasulo, J.M. Delineation of a novel hepatic route for the selective transfer of unesterified sterols from high-density lipoproteins to bile: Studies using the perfused rat liver. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüstner, D. Mathematical Analysis of Hepatic High Density Lipoprotein Transport Based on Quantitative Imaging Data. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 6766–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wüstner, D.; Mondal, M.; Huang, A.; Maxfield, F. Different transport routes for high density lipoprotein and its associated free sterol in polarized hepatic cells. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robins, S.J.; Fasulo, J.M.; Leduc, R.; Patton, G.M. The transport of lipoprotein cholesterol into bile: A reassessment of kinetic studies in the experimental animal. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 1004, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, E.; Botham, K.; Mindham, M.A.; Mayes, P.A.; Marinelli, T.; Cantafora, A. Evaluation in vivo of the differential uptake and processing of high-density lipoprotein unesterified cholesterol and cholesteryl ester in the rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1215, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Axmann, M.; Plochberger, B.; Mikula, M.; Weber, F.; Strobl, W.M.; Stangl, H. Plasma Membrane Lipids: An Important Binding Site for All Lipoprotein Classes. Membranes 2021, 11, 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110882
Axmann M, Plochberger B, Mikula M, Weber F, Strobl WM, Stangl H. Plasma Membrane Lipids: An Important Binding Site for All Lipoprotein Classes. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110882
Chicago/Turabian StyleAxmann, Markus, Birgit Plochberger, Mario Mikula, Florian Weber, Witta Monika Strobl, and Herbert Stangl. 2021. "Plasma Membrane Lipids: An Important Binding Site for All Lipoprotein Classes" Membranes 11, no. 11: 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110882
APA StyleAxmann, M., Plochberger, B., Mikula, M., Weber, F., Strobl, W. M., & Stangl, H. (2021). Plasma Membrane Lipids: An Important Binding Site for All Lipoprotein Classes. Membranes, 11(11), 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110882





