Light Scattering as an Easy Tool to Measure Vesicles Weight Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Liposomes Preparation
2.3. Stewart Assay
2.4. Light Scattering Assay to Evaluate Mass Concentration
2.5. Spectrofluorimetric Analysis to Evaluate Mass Concentration
2.6. Statistics and Errors Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Theory
3.1.1. LS-Based Method
- The weighted total mass of lipid components employed for the preparation of the starting film (M0);
- The recovered volume after the first extrusion cycle, V1;
- The recovered volume after the second extrusion cycle, V2;
- The total volume inserted into the extruder, VT, i.e., the sum of the starting volume injected and the volume of solvent which is added to perform the second extrusion and rinse the setup. The total volume VT does not correspond to V1 + V2, since some volume, the dead volume ΔV, remains trapped into the setup.
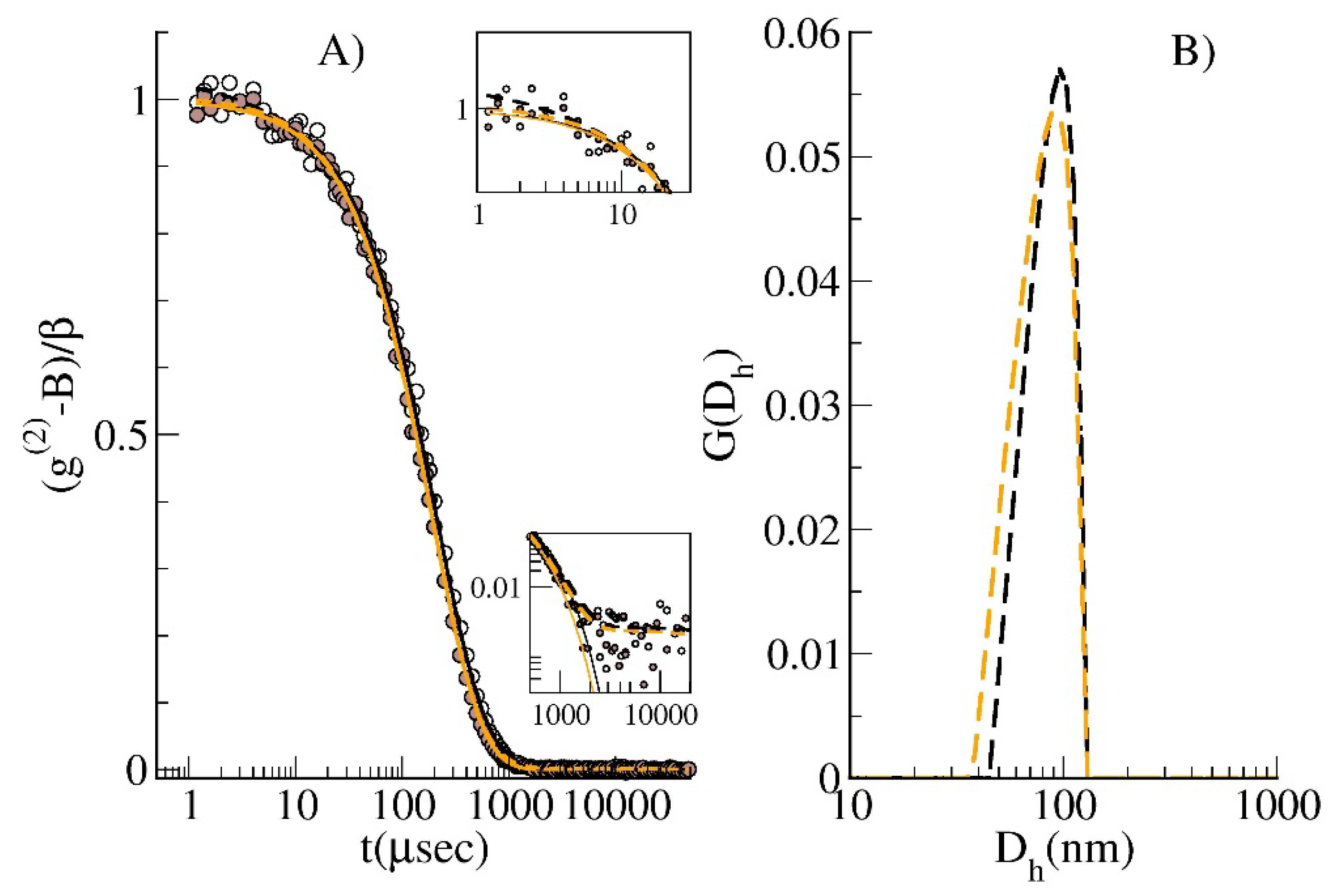
3.1.2. Samples Characterization by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
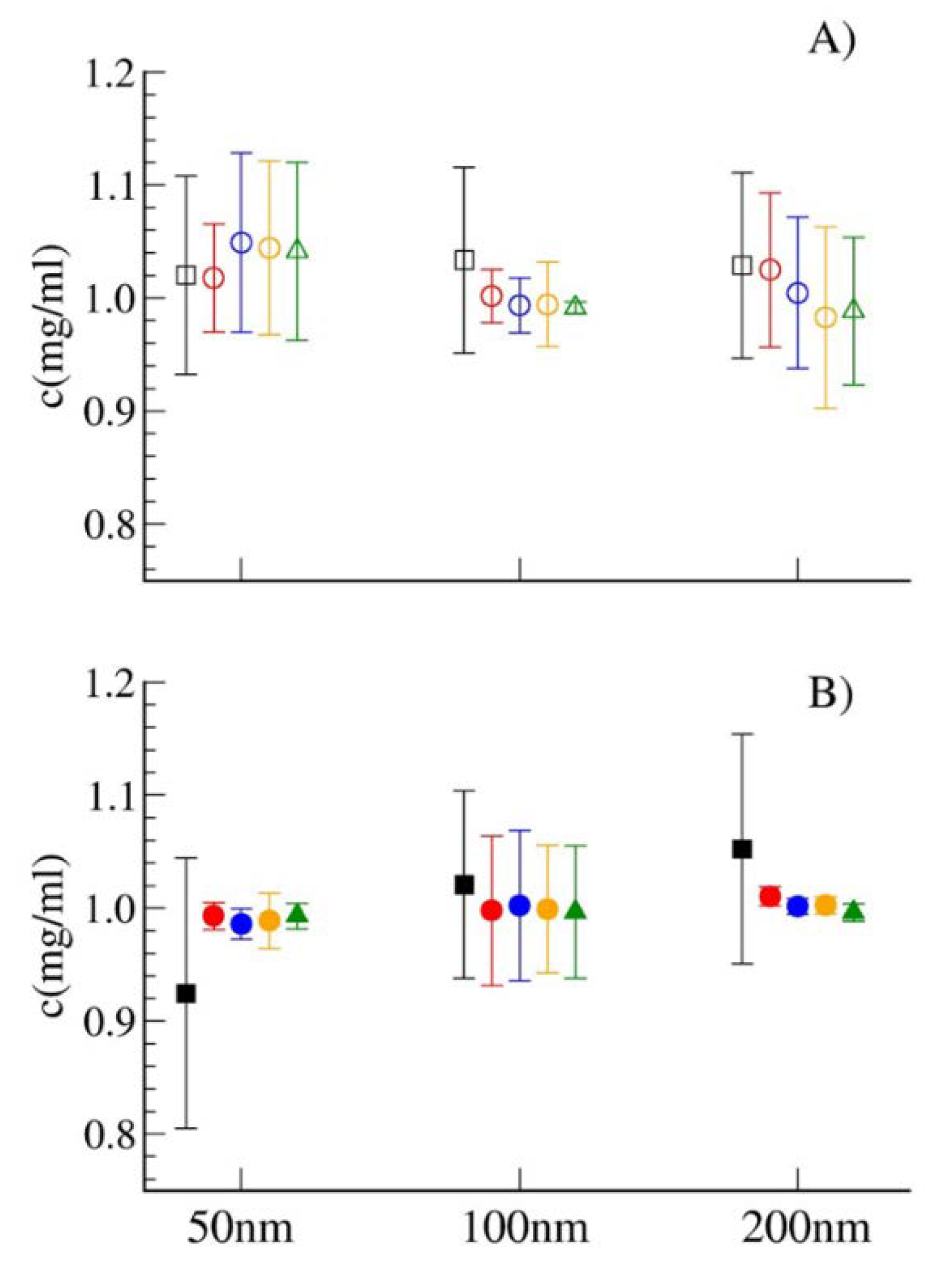
3.2. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu Lila, A.S.; Ishida, T. Liposomal Delivery Systems: Design Optimization and Current Applications. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, D.L.; Rems, L.; Boukany, P.E. Lipid vesicles in pulsed electric fields: Fundamental principles of the membrane response and its biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 248–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozafari, M.R. Nanoliposomes: Preparation and analysis. In Liposomes; Weissig, V., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 29–50. [Google Scholar]
- Walde, P.; Cosentino, K.; Engel, H.; Stano, P. Giant vesicles: Preparations and applications. Chembiochem 2010, 11, 848–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Swaay, D.; DeMello, A. Microfluidic methods for forming liposomes. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, R.; Dondapati, S.K.; Fenz, S.F.; Schmidt, T.; Kubick, S. Membrane protein synthesis in cell-free systems: From bio-mimetic systems to bio-membranes. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, H.; Fujii, S.; Yomo, T.; Kato, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Matsuura, T. In vitro membrane protein synthesis inside cell-sized vesicles reveals the dependence of membrane protein integration on vesicle volume. ACS Synth. Biol. 2014, 3, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Sood, A.K.; Hua, S. Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®--the first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszko, E.; Senge, M.O. Immunoliposomes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5239–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossann, M.; Kneidl, B.; Peller, M.; Lindner, L.; Winter, G. Thermosensitive liposomal drug delivery systems: State of the art review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ta, T.; Porter, T.M. Thermosensitive liposomes for localized delivery and triggered release of chemotherapy. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.H.; Catala, A.; Vignoni, M. Soybean phosphatidylcholine liposomes as model membranes to study lipid peroxidation photoinduced by pterin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, W.; Doherty, K.E. Model Phospholipid Liposomes to Study the β-Amyloid-Peptide-Induced Membrane Disruption. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1777, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, C.; Maccarini, M.; Falus, P.; Librizzi, F.; Mangione, M.R.; Moran, O.; Ortore, M.G.; Schweins, R.; Vilasi, S.; Carrotta, R. Amyloid β-Peptides Interaction with Membranes: Can Chaperones Change the Fate? J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 123, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastro, M.C.; Spigolon, D.; Librizzi, F.; Moran, O.; Ortore, M.G.; Bulone, D.; Biagio, P.L.S.; Carrotta, R. Amyloid β-peptide insertion in liposomes containing GM1-cholesterol domains. Biophys. Chem. 2016, 208, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozel, D.; Ursic, B.; Krek, J.L.; Stukelj, R.; Kralj-Iglic, V. Applicability of extracellular vesicles in clinical studies. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 47, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Brennan, M.; Lötvall, J.; Breakefield, X.O.; Andaloussi, S.E.L. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.C. Colorimetric determination of phospholipids with ammonium ferrothiocyanate. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 104, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidan, N.J.; De Vrueh, R.; Crommelin, D. Characterization of liposomes. In Liposomes; Torchilin, V.P., Weissing, V., Eds.; University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Barlett, G.R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 466–468. [Google Scholar]
- Takayama, M.; Itoh, S.; Nagasaki, T.; Tanimizu, I. A new enzymatic method for determination of serum choline-contining phospholipids. Clin. Chim. Acta 1977, 79, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hein, R.; Uzundal, C.B.; Hennig, A. Simple and rapid quantification of phospholipids for supramolecular membrane transport assays. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 2182–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.A.; Mangione, M.R.; Santonocito, R.; Passantino, R.; Giacomazza, D.; Librizzi, F.; Moran, O.; Carrotta, R. Biophysical characterization of asolectin-squalene liposomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahma, A.; De, D.; Bhattacharyya, D. Rayleigh Scattering Technique as a Method to Study Protein-Protein Interaction Using Spectrofluorimeters. Curr. Sci. 2009, 96, 940–946. [Google Scholar]
- Frisken, B.J. Revisiting the method of cumulants for the analysis of dynamic light-scattering data. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 4087–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szoka, F.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Comparative Properties and Methods of Preparation of Lipid Vesicles (Liposomes). Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 1980, 9, 467–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogendal, L. Light Scattering a Brief Introduction; University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W. Light Scattering: Principles and Development; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, A.; Faller, R. Examining the contributions of lipid shape and headgroup charge on bilayer behavior. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanek, P. Data analysis in dynamic light scattering. In Dynamic Light Scattering: The Method and Some Applications, 1st ed.; Brown, W., Ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; pp. 177–240. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, D. Advances in phospholipid quantification methods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 16, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, B.; Gupta, R.; Gulati, M.; Singh, S.K.; Khursheed, R.; Gupta, M. The Why, Where, Who, How, and What of the vesicular delivery systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 271, 101985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prima, G.D.; Librizzi, F.; Carrotta, R. Light Scattering as an Easy Tool to Measure Vesicles Weight Concentration. Membranes 2020, 10, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090222
Prima GD, Librizzi F, Carrotta R. Light Scattering as an Easy Tool to Measure Vesicles Weight Concentration. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090222
Chicago/Turabian StylePrima, Giulia Di, Fabio Librizzi, and Rita Carrotta. 2020. "Light Scattering as an Easy Tool to Measure Vesicles Weight Concentration" Membranes 10, no. 9: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090222
APA StylePrima, G. D., Librizzi, F., & Carrotta, R. (2020). Light Scattering as an Easy Tool to Measure Vesicles Weight Concentration. Membranes, 10(9), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090222






