The Best-Practice Organism for Single-Species Studies of Antimicrobial Efficacy against Biofilms Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
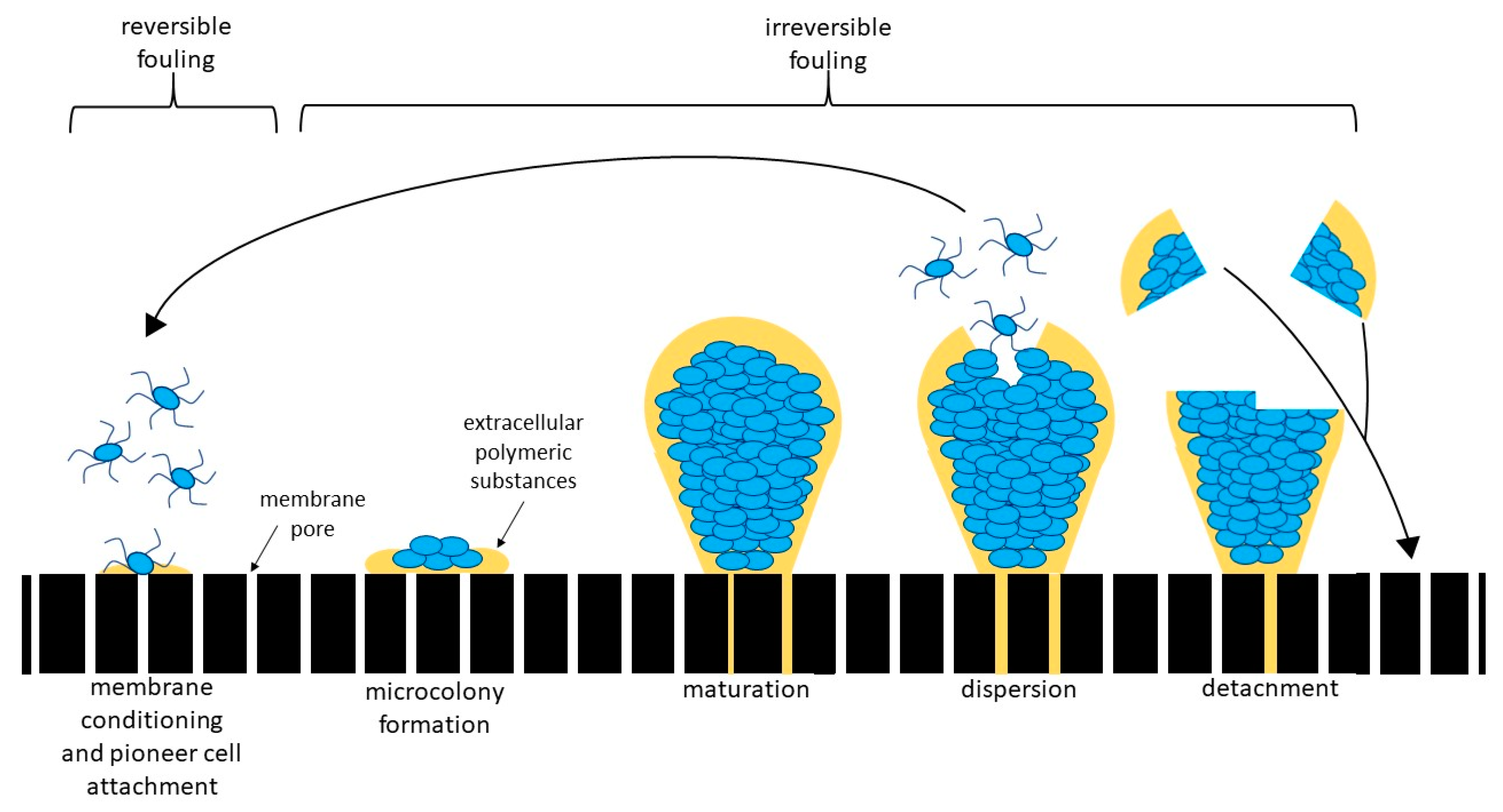
1. Introduction
- Which organisms are commonly used to test antimicrobial efficacy against biofilms on RO membranes?
- Which organisms are commonly identified via genetic analysis in biofilms on RO membranes?
- Based on the results of questions 1 and 2, we additionally answered the following question: Which of the identified organisms are pioneer organisms?
2. Semi-Systematic Review Methods
2.1. Semi-Systematic Review: Which Organisms Are Used for Anti-Biofouling Studies?
2.1.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.1.2. Search Strategy
2.1.3. Study Selection
2.1.4. Data Collection, Extraction, and Analysis
2.2. Semi-Systematic Review: Which Organisms Are Found in Biofilms on RO Membranes?
2.2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2.2. Search Strategy
2.2.3. Study Selection
2.2.4. Data Collection, Extraction, and Analysis
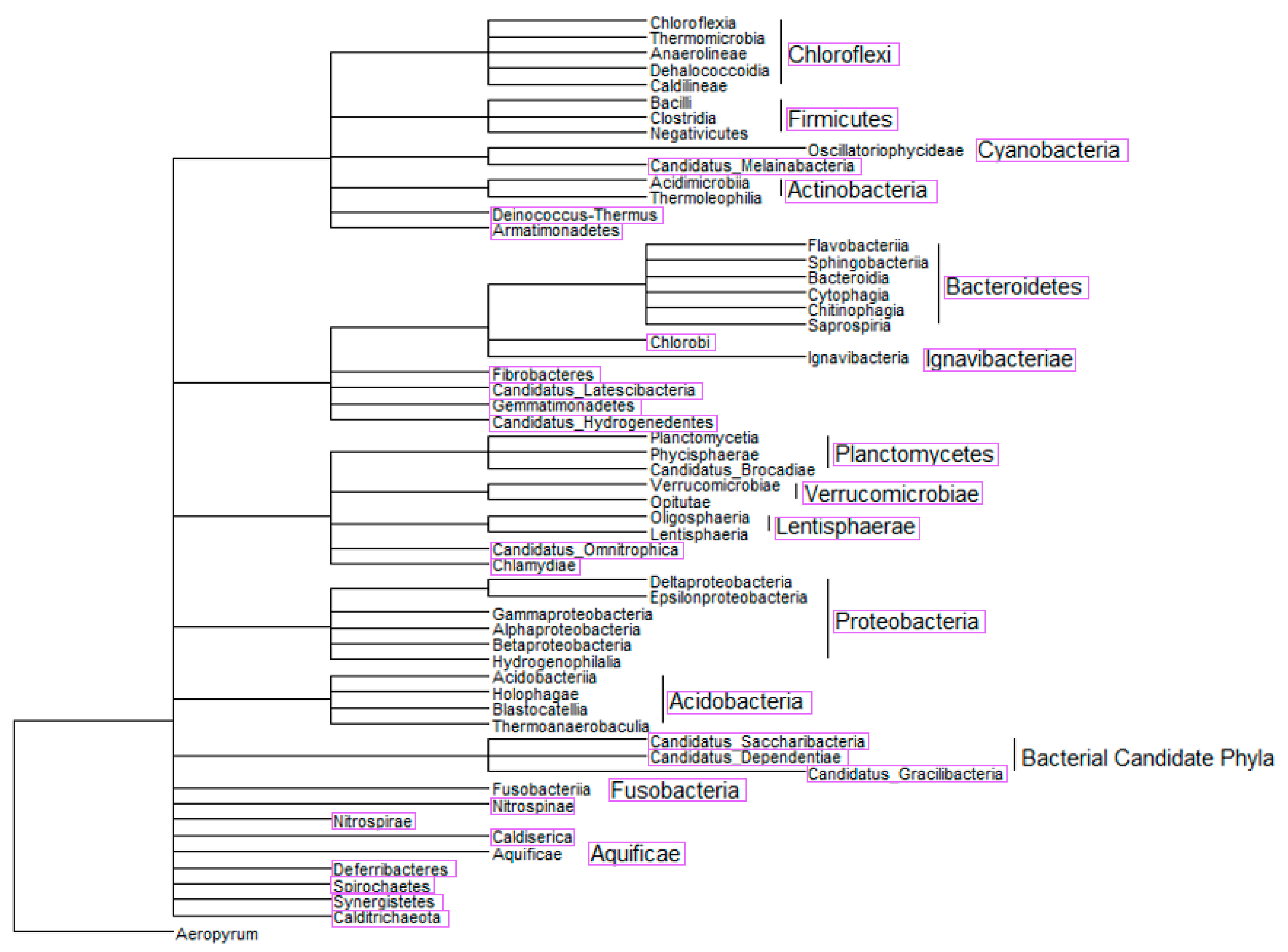
2.3. Phylogenetic Tree-Like Structure
3. Results
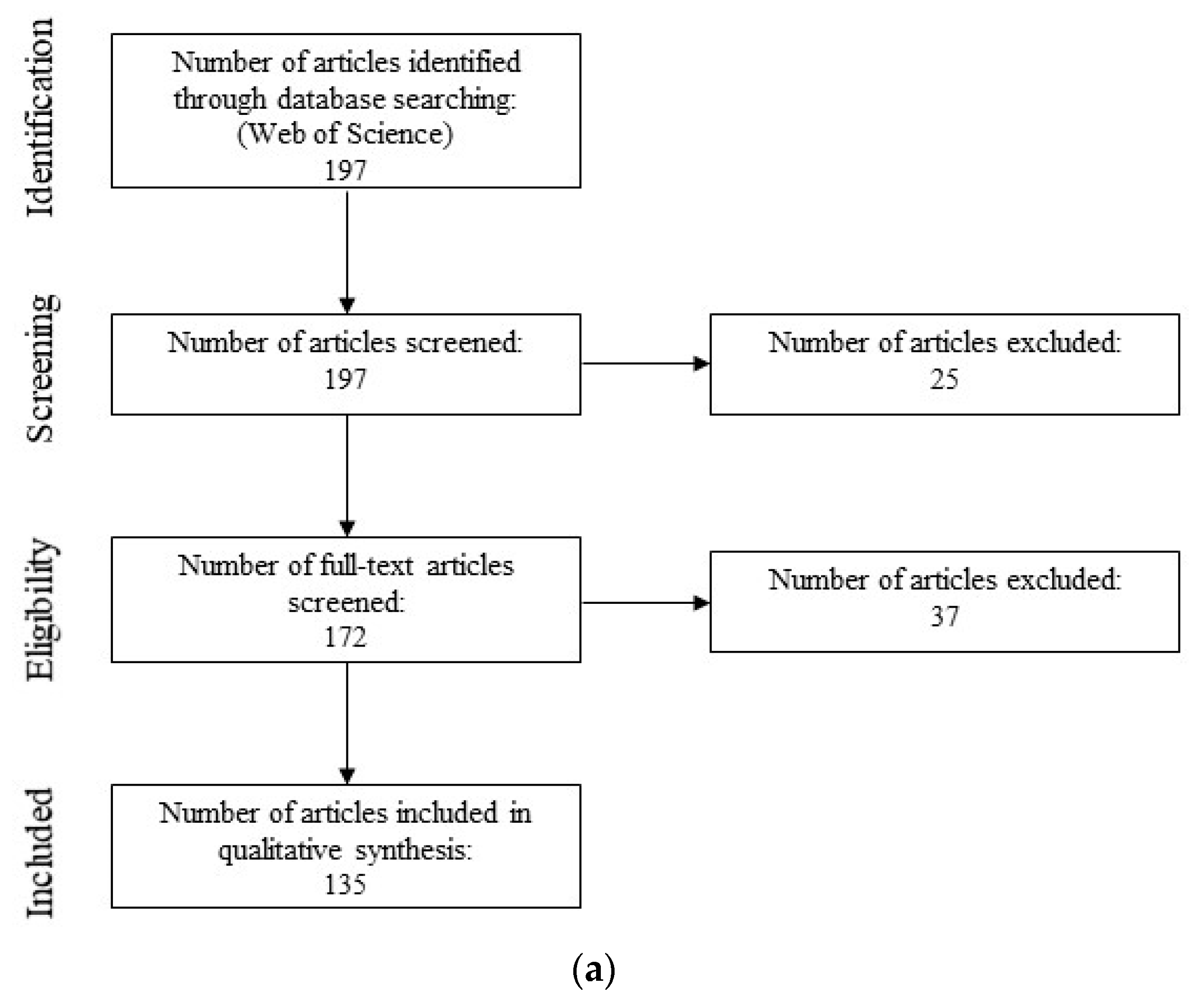
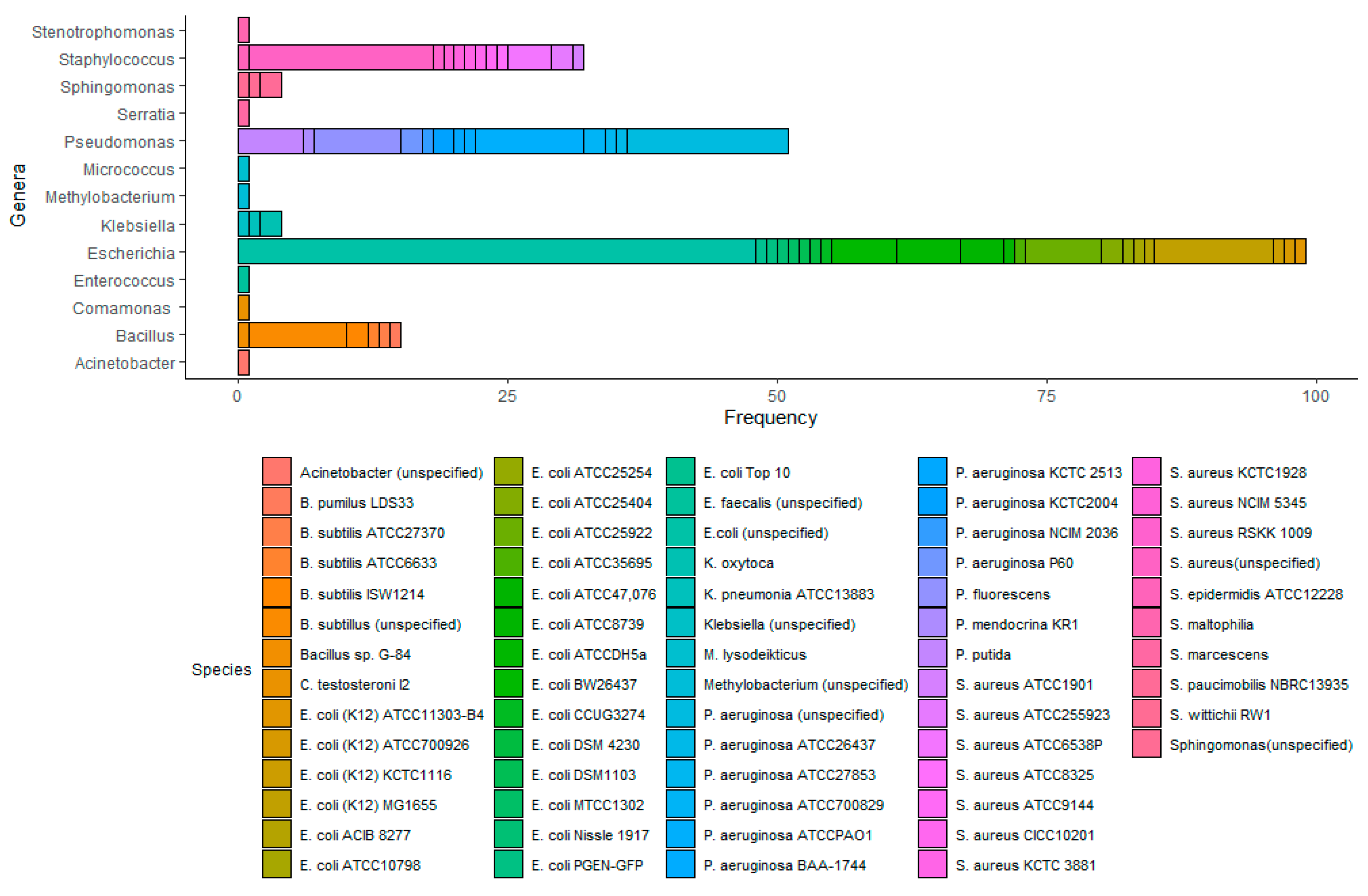
3.1. Semi-Systematic Review: Which Organisms Are Used for Anti-Biofouling Studies?
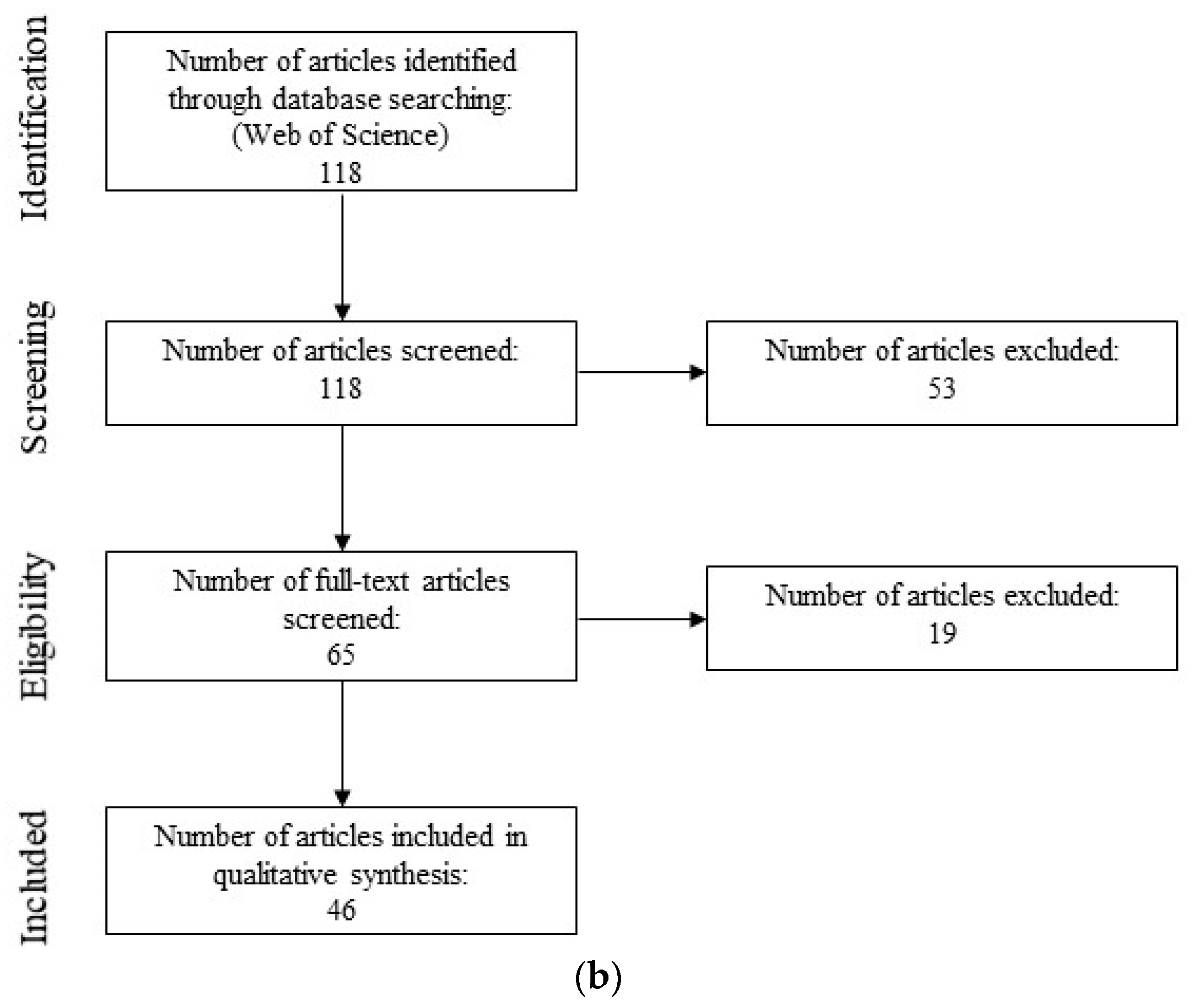
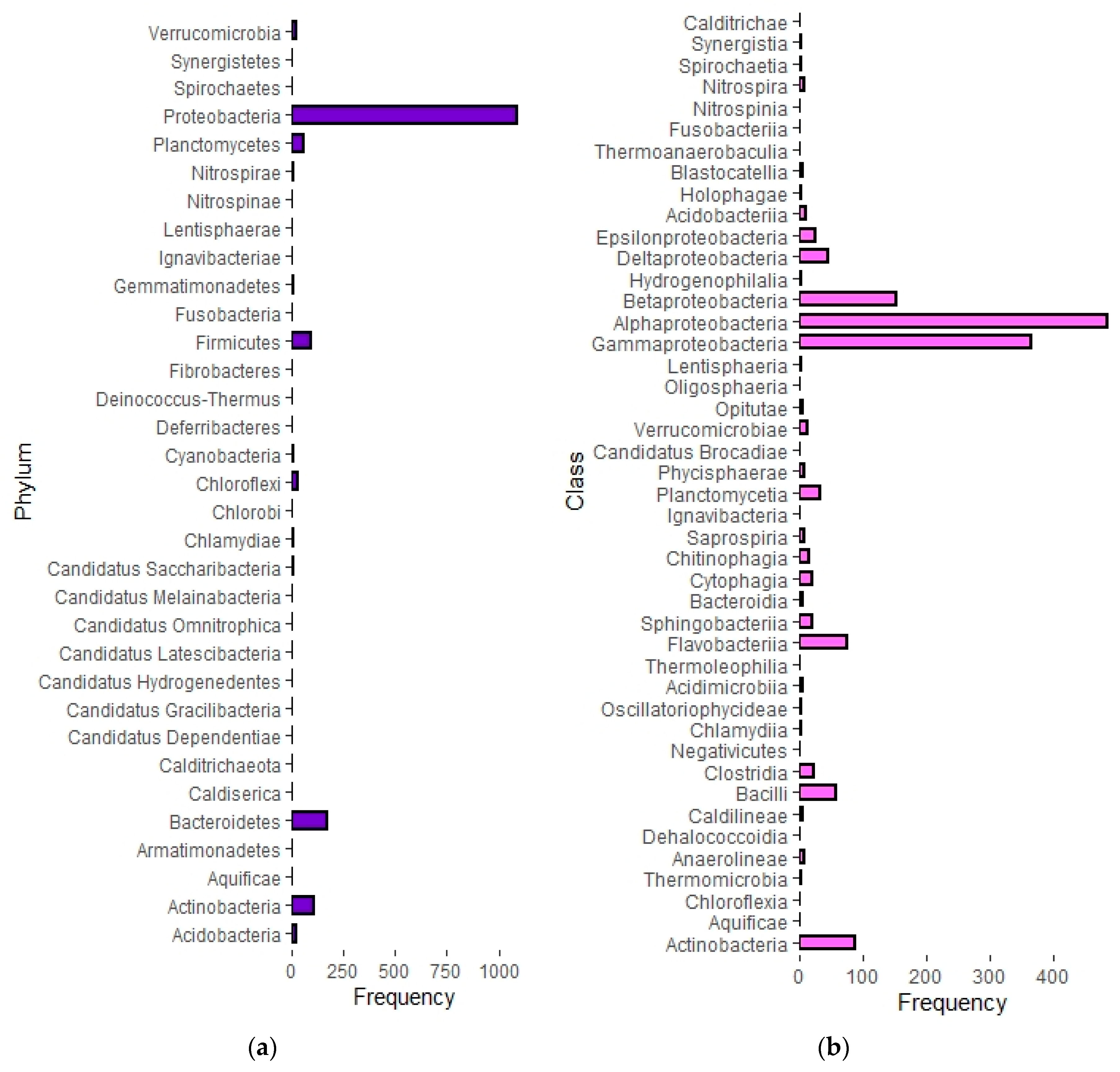
3.2. Semi-Systematic Review: Which Organisms Are Found in Biofilms on RO Membranes?
4. Discussion
4.1. Which Organisms Are Used for Anti-Biofouling Studies?
4.2. Which Organisms Are Found in Biofilms on RO Membranes?
4.3. Which of the Identified Organisms Are Pioneer Organisms?
4.4. Comparison
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maddah, H.; Chogle, A. Biofouling in reverse osmosis: Phenomena, monitoring, controlling and remediation. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Badrelzaman, M.; Darwish, N.N.; Darwish, N.A.; Hilal, N. Reverse osmosis desalination: A state-of-the-art review. Desalination 2019, 459, 59–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, H.A.; Baldwin, H.L. A Primer on Water Quality; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; pp. 1–27.
- Jakka Ravindran, S.; Kumar, R.; Srimany, A.; Philip, L.; Pradeep, T. Early detection of biofouling on water purification membranes by ambient ionization mass spectrometry imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Feo-García, J. Estimation of maximum water recovery in RO desalination for different feedwater inorganic compositions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 70, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabelas, A.J.; Mitrouli, S.T.; Kostoglou, M. Scaling in reverse osmosis desalination plants: A perspective focusing on development of comprehensive simulation tools. Desalination 2020, 474, 114193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melián-Martel, N.; Sadhwani Alonso, J.J.; Ruiz-García, A. Combined silica and sodium alginate fouling of spiral-wound reverse osmosis membranes for seawater desalination. Desalination 2018, 439, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuyfzand, P.J.; Osma, J. Clogging issues with aquifer storage and recovery of reclaimed water in the brackish werribee aquifer, Melbourne, Australia. Water 2019, 11, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L. Biofouling of water treatment membranes: A review of the underlying causes, monitoring techniques and control measures. Membranes 2012, 2, 804–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Zulhairun, A.K.; Ismail, A.F.; Hilal, N. Contemporary antibiofouling modifications of reverse osmosis desalination membrane: A review. Desalination 2019, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, J. Biofouling of polyamide membranes: Fouling mechanisms, current mitigation and cleaning strategies, and future prospects. Membranes 2019, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achinas, S.; Charalampogiannis, N.; Euverink, G.J.W. A brief recap of microbial adhesion and biofilms. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Choi, H.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Sorial, G.A.; Oerther, D.B. Identifying pioneer bacterial species responsible for biofouling membrane bioreactors. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatansever, C.; Turetgen, I. Investigating the effects of different physical and chemical stress factors on microbial biofilm. Water SA 2018, 44, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, T. Irreversible Fouling. In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Fudianto, R.; Cox, S.; Leslie, G. Assessing the oxidative degradation of polyamide reverse osmosis membrane-Accelerated ageing with hypochlorite exposure. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 347, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Nuez, I. Long-term performance decline in a brackish water reverse osmosis desalination plant. Predictive model for the water permeability coefficient. Desalination 2016, 397, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A. Evaluation of the first seven years operating data of a RO brackish water desalination plant in Las Palmas, Canary Islands, Spain. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 54, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Khan, Z.; Zaidi, S.M.J.; Boyce, M.C. Biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes for seawater desalination: Phenomena and prevention. Desalination 2011, 281, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Ha, P.T.; Powell, L.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Choi, D.; Lovitt, R.W.; Kim, I.S.; Mitra, S.S.; Chang, I.S. Exploring microbial communities and differences of cartridge filters (CFs) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes for seawater desalination processes. Desalination 2012, 298, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Ruiz-Saavedra, E. 80,000h operational experience and performance analysis of a brackish water reverse osmosis desalination plant. Assessment of membrane replacement cost. Desalination 2015, 375, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darton, T.; Annunziata, U.; del Vigo Pisano, F.; Gallego, S. Membrane autopsy helps to provide solutions to operational problems. Desalination 2004, 167, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, C.; Ridgway, H.; Olson, B.H. Evaluation of cleaning strategies for removal of biofilms from reverse-osmosis membranes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 48, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, A.S.; McIlroy, S.J.; Larsen, P.; Albertsen, M.; Hansen, A.A.; Heinen, N.; Nielsen, P.H. Dynamics of the fouling layer microbial community in a membrane bioreactor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watnick, P.; Kolter, R. Biofilm, city of Microbes. J. Bacteriol. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Ham, S.Y.; Jang, Y.; Sun, P.F.; Park, J.H.; Hoon Lee, J.; Park, H.D. Linoleic acid, a plant fatty acid, controls membrane biofouling via inhibition of biofilm formation. Fuel 2019, 253, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Barnes, R.J.; Tan, X.; Mcdougald, D.; Fane, A.G.; Zhuang, G.; Kjelleberg, S.; Cohen, Y.; Rice, S.A. The application of nitric oxide to control biofouling of membrane bioreactors. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanawar, H.; Bucs, S.; Pot, M.A.; Zlopasa, J.; Farhat, N.; Witkamp, G.J.; Kruithof, J.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Pilot-scale assessment of urea as a chemical cleaning agent for biofouling control in spiral-wound reverse osmosis membrane elements. Membranes 2019, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.F.; Ke, X.X.; Wang, T.Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, L.B.; Zheng, Y.M. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Embedded Electrospun PAN Nanofiber Thin-Film Composite Forward Osmosis Membrane to Enhance Performance and Antimicrobial Activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouamouha, M.; Gholikandi, G.B. Characterization and antibiofouling performance investigation of hydrophobic silver nanocomposite membranes: A comparative study. Membranes 2017, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Shannon, H.D.; Amirsoleimani, A.; Brion, G.M.; Escobar, I.C. Thiol-affinity immobilization of casein-coated silver nanoparticles on polymeric membranes for biofouling control. Polymers 2019, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhares, A.M.F.; Borges, C.P.; Fonseca, F.V. Investigation of biocidal effect of microfiltration membranes impregnated with silver nanoparticles by sputtering technique. Polymers 2020, 12, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Hwang, S.O.; Kim, T.S.; Cho, A.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, K.T.; Park, H.D.; Lee, J.H. Triclosan-immobilized polyamide thin film composite membranes with enhanced biofouling resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 443, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, A.; Sabri, S.; Al-Gaashani, R.; Atieh, M.A.; Kochkodan, V. Antibiofouling performance by polyethersulfone membranes cast with oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes and arabic gum. Membranes 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, S.; Najjar, A.; Manawi, Y.; Eltai, N.O.; Al-Thani, A.; Atieh, M.A.; Kochkodan, V. Antibacterial properties of polysulfone membranes blended with Arabic gum. Membranes 2019, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, A.; Sabri, S.; Al-Gaashani, R.; Kochkodan, V.; Atieh, M.A. Enhanced fouling resistance and antibacterial properties of novel graphene oxide-arabic gum polyethersulfone membranes. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, R.; Muppalla, H.; Veisi, Z.; Khan, W.S.; Asaduzzaman, A.; Nuraje, N. Study of hydrophilic electrospun nanofiber membranes for filtration of micro and nanosize suspended particles. Membranes 2013, 3, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Liu, P.; Xia, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, F. Anti-fouling and anti-bacterial modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane by blending with the capsaicin-based copolymer. Polymers 2019, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Panecka, M.; Tufenkji, N.; Rahaman, M.S. Bacteriophage-based strategies for biofouling control in ultrafiltration: In situ biofouling mitigation, biocidal additives and biofilm cleanser. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 523, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Oh, H.S.; Jo, S.J.; Yeon, K.M.; Lee, C.H.; Lim, D.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.K. Biofouling control with bead-entrapped quorum quenching bacteria in membrane bioreactors: Physical and biological effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouayed, N.; Dietrich, N.; Lafforgue, C.; Lee, C.H.; Guigui, C. Process-oriented review of bacterial quorum quenching for membrane biofouling mitigation in membrane bioreactors (MBRs). Membranes 2016, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, I.S. Microbial community in seawater reverse osmosis and rapid diagnosis of membrane biofouling. Desalination 2011, 273, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ashhab, A.; Sweity, A.; Bayramoglu, B.; Herzberg, M.; Gillor, O. Biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes: Effects of cleaning on biofilm microbial communities, membrane performance, and adherence of extracellular polymeric substances. Biofouling 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ashhab, A.; Gillor, O.; Herzberg, M. Biofouling of reverse-osmosis membranes under different shear rates during tertiary wastewater desalination: Microbial community composition. Water Res. 2014, 67, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiellini, C.; Iannelli, R.; Modeo, L.; Bianchi, V.; Petroni, G. Biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes used in river water purification for drinking purposes: Analysis of microbial populations. Biofouling 2012, 28, 969–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgini, D.R.B.; Dias, R.S.; Siqueira, V.M.; Valadares, L.A.B.; Albanese, J.M.; Souza, R.S.; Torres, A.P.R.; Sousa, M.P.; Silva, C.C.; De Paula, S.O.; et al. Culturable bacterial diversity from a feed water of a reverse osmosis system, evaluation of biofilm formation and biocontrol using phages. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2689–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, V.; Skillman, L.; Li, D.; Xie, Z.; Ho, G. Culturable bacteria from a full-scale desalination plant: Identification methods, bacterial diversity and selection of models based on membrane-biofilm community. Desalination 2019, 457, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberland, J.; Lessard, M.H.; Doyen, A.; Labrie, S.; Pouliot, Y. A sequencing approach targeting the 16S rRNA gene unravels the biofilm composition of spiral-wound membranes used in the dairy industry. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2017, 96, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayache, C.; Manes, C.; Pidou, M.; Croué, J.P.; Gernjak, W. Microbial community analysis of fouled reverse osmosis membranes used in water recycling. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3291–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, S.; Bae, H. Intermittent chlorination shifts the marine biofilm population on reverse osmosis membranes. Membr. Water Treat. 2019, 10, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belila, A.; El-Chakhtoura, J.; Otaibi, N.; Muyzer, G.; Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Saikaly, P.E.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Bacterial community structure and variation in a full-scale seawater desalination plant for drinking water production. Water Res. 2016, 94, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, A.; Bar-Zeev, E.; Elifantz, H.; Berman, T.; Berman-Frank, I. Characterization of microbial communities in water and biofilms along a large scale SWRO desalination facility: Site-specific prerequisite for biofouling treatments. Desalination 2016, 378, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jordan, I.K.; Mayer, W. Chapter 29: A Phylogenetic Perspective on Molecular Epidemiology. In Molecular Medical Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 517–536. [Google Scholar]
- Darienko, T.; Gustavs, L.; Eggert, A.; Wolf, W.; Pröschold, T. Evaluating the species boundaries of green microalgae (Coccomyxa, Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) using integrative taxonomy and DNA barcoding with further implications for the species identification in environmental samples. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, M.; Sutcliffe, I.; Chun, J. New Approaches to Prokaryotic Systematics, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification in the diagnostic laboratory: Pluses, perils, and pitfalls. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2761–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassivi, A.; Guilherme, S.; Bain, R.; Tilley, E.; Waygood, E.O.D.; Dorea, C. Drinking water accessibility and quantity in low and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.G. Combination of multiple databases is necessary for a valid systematic review. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Barrett, T.; Benson, D.A.; Bryant, S.H.; Canese, K.; Chetvernin, V.; Church, D.M.; Dicuccio, M.; Edgar, R.; Federhen, S.; et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federhen, S. The NCBI Taxonomy database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.Y. Ggtree: An R Package for Visualization and Annotation of Phylogenetic Trees with Their Covariates and Other Associated Data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Lam, T.T.Y.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y. Two methods for mapping and visualizing associated data on phylogeny using GGTree. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 3041–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Mayer, C.; Freger, V.; Ulbricht, M. Synthesis and characterization of poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate based hydrogel networks for anti-biofouling applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanouchi, S.; Nasuno, E.; Ohno, M.; Okano, C.; Iimura, K.; Okuda, T.; Nishijima, W.; Kato, N. Enhancement effects of cationic contaminants from bacteria on cake layer formation and biofouling on an RO membrane. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2017, 22, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, M.; He, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, V. Polymeric antimicrobial membranes enabled by nanomaterials for water treatment. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 550, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereschenko, L.A.; Stams, A.J.M.; Euverink, G.J.W.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Biofilm formation on reverse osmosis membranes is initiated and dominated by Sphingomonas spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narisawa, N.; Furukawa, S.; Ogihara, H.; Yamasaki, M. Estimation of the biofilm formation of Escherichia coli K-12 by the cell number. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoering, A.M.Y.L.; Lewis, K.I.M. Biofilms and Planktonic Cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Have Similar Resistance to Killing by Antimicrobials. Society 2001, 183, 6746–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiefel, P.; Rosenberg, U.; Schneider, J.; Mauerhofer, S.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. Is biofilm removal properly assessed? Comparison of different quantification methods in a 96-well plate system. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4135–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, V.E.; Iglewski, B.H.P. aeruginosa biofilms in CF infection. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2008, 35, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridier, A.; Dubois-Brissonnet, F.; Boubetra, A.; Thomas, V.; Briandet, R. The biofilm architecture of sixty opportunistic pathogens deciphered using a high throughput CLSM method. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 82, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feazel, L.M.; Baumgartner, L.K.; Peterson, K.L.; Frank, D.N.; Harris, J.K.; Pace, N.R. Opportunistic pathogens enriched in showerhead biofilms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16393–16398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, D.; Vlamakis, H.; Kolter, R. Biofilms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Sun, F.; Chen, L. Nanofiltration fouling propensity caused by wastewater effluent organic matters and surface-water dissolved organic matters. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivnitsky, H.; Katz, I.; Minz, D.; Volvovic, G.; Shimoni, E.; Kesselman, E.; Semiat, R.; Dosoretz, C.G. Bacterial community composition and structure of biofilms developing on nanofiltration membranes applied to wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3924–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörsch, P.; Gorenflo, A.; Fuder, C.; Deleage, A.; Frimmel, F.H. Biofouling of ultra- and nanofiltration membranes fordrinking water treatment characterized by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Desalination 2005, 172, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, I.; Mas, J.; Taberna, E.; Sanz, J.; Sánchez, O. Biological support media influence the bacterial biofouling community in reverse osmosis water reclamation demonstration plants. Biofouling 2015, 31, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.P. Bacterial diversity, community structure and function associated with biofilm development in a biological aerated filter in a recirculating marine aquaculture system. Mar. Biodivers. 2012, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.J.; Guo, X.S.; Ye, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.M. Bacterial Community Analysis of Different Sections of a Biofilter in a Full-Scale Marine Recirculating Aquaculture System. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2015, 77, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Estrada, Á.M.; Gollas-Galván, T.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Scheuren-Acevedo, S.M.; Emerenciano, M.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Diversity and bacterial succession of a phototrophic biofilm used as complementary food for shrimp raised in a super-intensive culture. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereschenko, L.A.; Heilig, G.H.J.; Nederlof, M.M.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Euverink, G.J.W. Molecular characterization of the bacterial communities in the different compartments of a full-scale reverse-osmosis water purification plant. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, R.J.; Low, J.H.; Bandi, R.R.; Tay, M.; Chua, F.; Aung, T.; Fane, A.G.; Kjelleberg, S.; Rice, S.A. Nitric oxide treatment for the control of reverse osmosis membrane biofouling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2515–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.T.; Manes, C.D.; Aubry, C.; Gutierrez, L.; Croue, J.P. Kinetic study of seawater reverse osmosis membrane fouling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10884–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Q.; Gu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal changes in bacterial community and microbial activity in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.; Nielsen, J.L.; Otzen, D.; Nielsen, P.H. Amyloid-like adhesins produced by floc-forming and filamentous bacteria in activated sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Bourven, I.; Guibaud, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Panico, A.; Pirozzi, F.; Esposito, G. Role of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production in bioaggregation: Application to wastewater treatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 9883–9905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsen, M.; Stensballe, A.; Nielsen, K.L.; Nielsen, P.H. Digging into the extracellular matrix of a complex microbial community using a combined metagenomic and metaproteomic approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Lv, P.; Zhang, J.; Fane, A.G.; McDougald, D.; Rice, S.A. Succession of biofilm communities responsible for biofouling of membrane bioreactors (MBRs). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Comorera, L.; Blanch, A.R.; Vilaró, C.; Galofré, B.; García-Aljaro, C. Pseudomonas-related populations associated with reverse osmosis in drinking water treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douterelo, I.; Sharpe, R.; Boxall, J. Bacterial community dynamics during the early stages of biofilm formation in a chlorinated experimental drinking water distribution system: Implications for drinking water discolouration. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanysacker, L.; Denis, C.; Declerck, P.; Piasecka, A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Microbial adhesion and biofilm formation on microfiltration membranes: A detailed characterization using model organisms with increasing complexity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, L.A.; Kolter, R. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli biofilm formation: Roles of flagella, motility, chemotaxis and type I pili. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhao, F.; Xia, Y.; Huang, X.; Waite, D.; Guan, J. Effect of temperature variation on membrane fouling and microbial community structure in membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol. 2013, 133, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Wang, X.; Wen, X.; Xia, Y. Microbial community structures in different wastewater treatment plants as revealed by 454-pyrosequencing analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2012, 117, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owoseni, M.; Olaniran, A.; Okoh, A. Chlorine tolerance and inactivation of Escherichia coli recovered from wastewater treatment plants in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, E.W.; Burke, J.; Spain, A. Fecal indicator bacteria are abundant in wet sand at freshwater beaches. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3978–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, A.; Gross, M.; Wylie, J.; Van Caeseele, P.; Plourde, P.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa necrotizing chondritis complicating high helical ear piercing case report: Clinical and public health perspectives. Can. J. Public Health 2007, 98, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.; Hawkins, C.H.; Änggård, E.E.; Harper, D.R. A controlled clinical trial of a therapeutic bacteriophage preparation in chronic otitis due to antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; A preliminary report of efficacy. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattemer, A.; Hauser, A.; Diaz, M.; Scheetz, M.; Shah, N.; Allen, J.P.; Porhomayon, J.; El-Solh, A.A. Bacterial and clinical characteristics of health care-and community-acquired bloodstream infections due to pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3969–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Curtin, A.M.; Thibodeau, M.C.; Buckley, H.L. The Best-Practice Organism for Single-Species Studies of Antimicrobial Efficacy against Biofilms Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Membranes 2020, 10, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090211
Curtin AM, Thibodeau MC, Buckley HL. The Best-Practice Organism for Single-Species Studies of Antimicrobial Efficacy against Biofilms Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090211
Chicago/Turabian StyleCurtin, Anna M., Matthew C. Thibodeau, and Heather L. Buckley. 2020. "The Best-Practice Organism for Single-Species Studies of Antimicrobial Efficacy against Biofilms Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Membranes 10, no. 9: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090211
APA StyleCurtin, A. M., Thibodeau, M. C., & Buckley, H. L. (2020). The Best-Practice Organism for Single-Species Studies of Antimicrobial Efficacy against Biofilms Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Membranes, 10(9), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090211




