Impacts of Flow Rate and Pulsed Electric Field Current Mode on Protein Fouling Formation during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidification of Skim Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
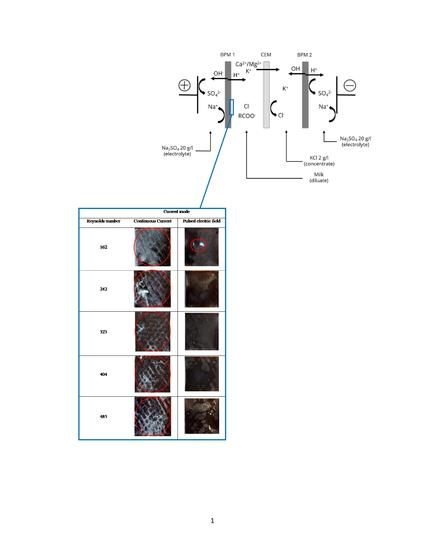
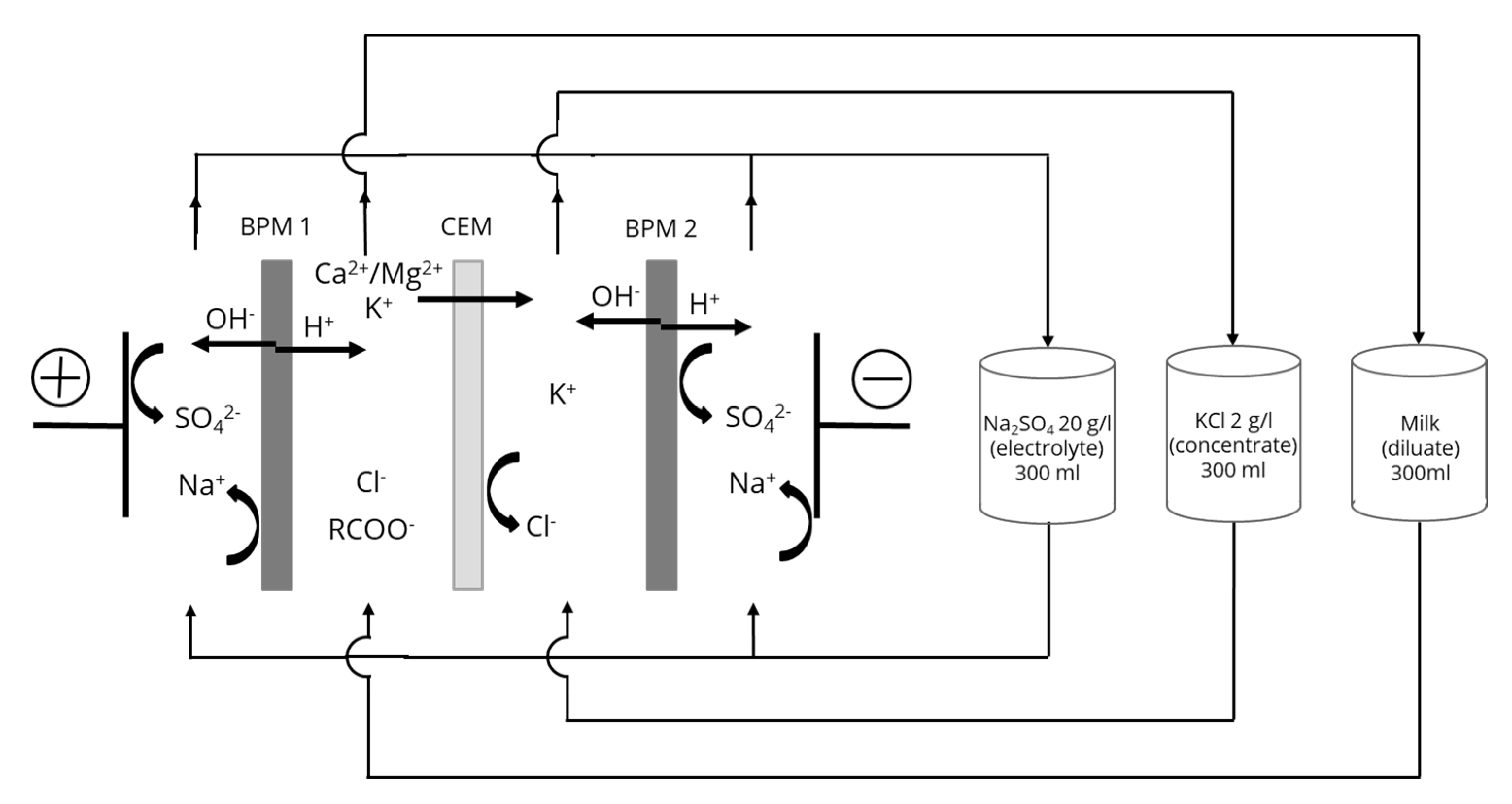
2.2.1. Electrodialysis Cell
2.2.2. Protocol
2.2.3. Solution Conductivity
2.2.4. Membrane Thickness and Electrical Conductivity
2.2.5. pH of the Diluate and Concentrate
2.2.6. Fouling Weight
2.2.7. Membrane Surface Photographs
2.2.8. Number of Charges Transported
2.2.9. Energy Consumptions
2.2.10. Reynolds Numbers
2.2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
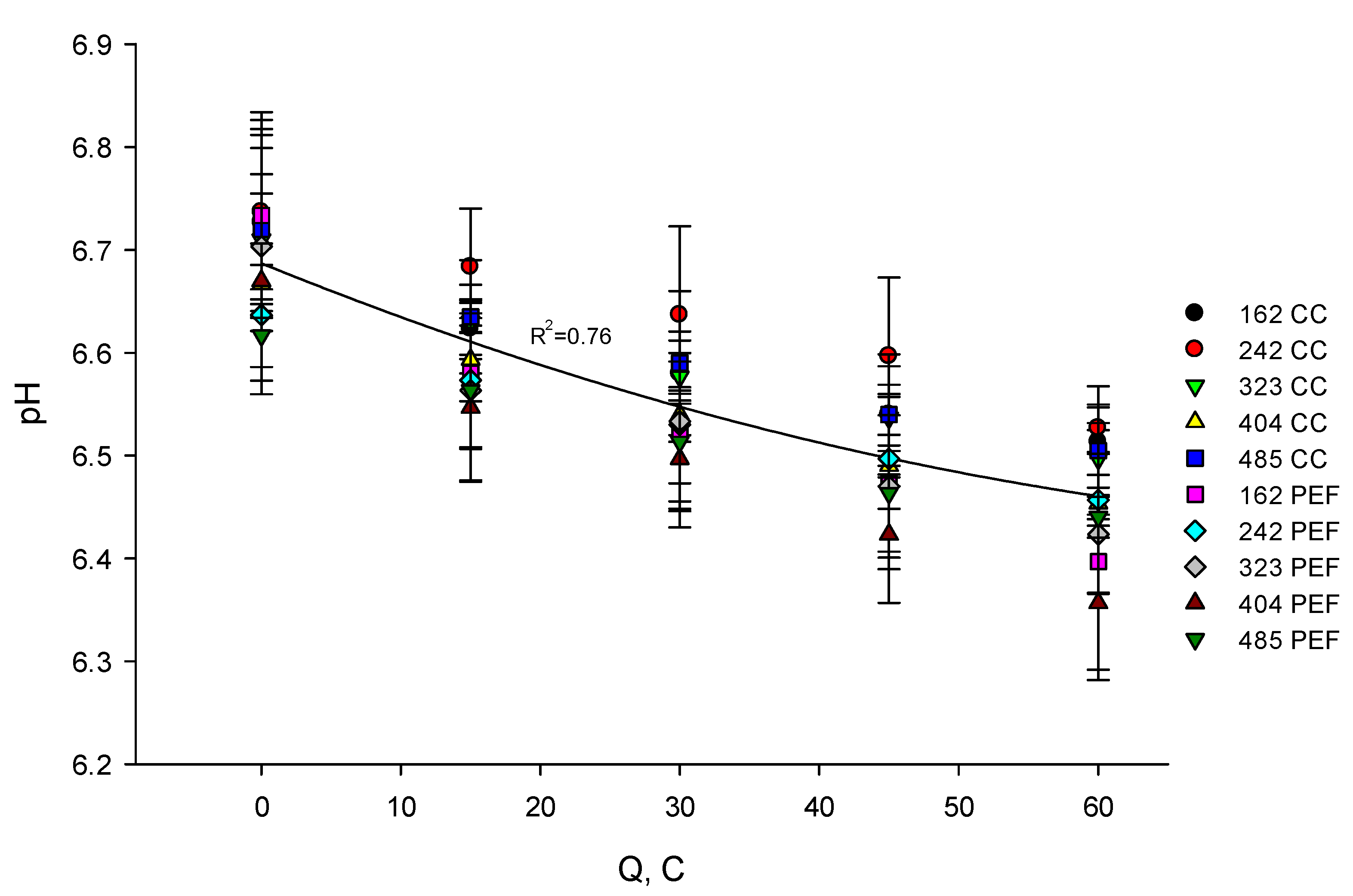
3.1. Evolution of PH
3.1.1. In Skim Milk
3.1.2. In KCl Solution
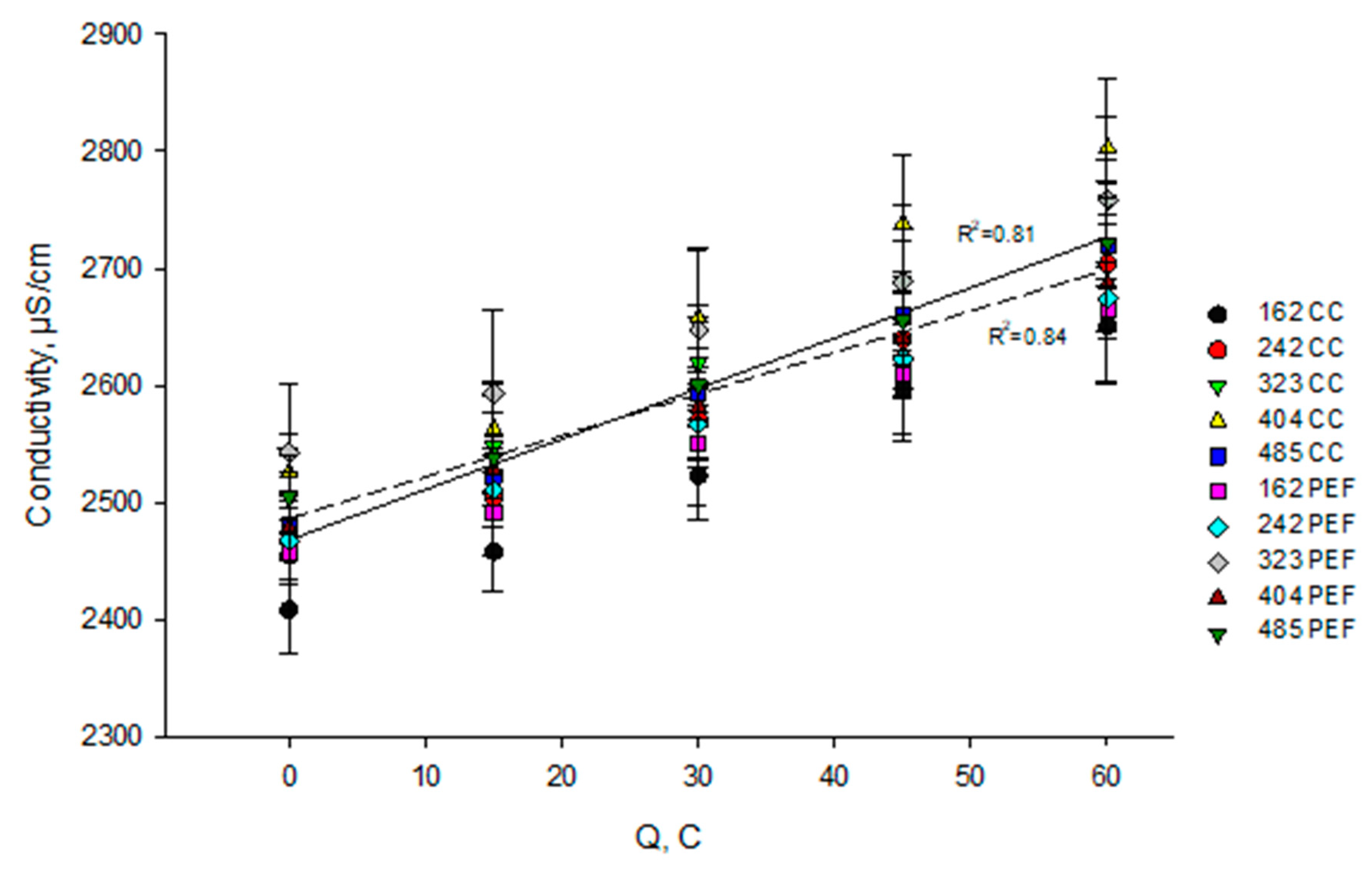
3.2. Evolution of Conductivity
3.2.1. In Skim Milk
3.2.2. In KCl Solution
3.3. Membrane Parameters
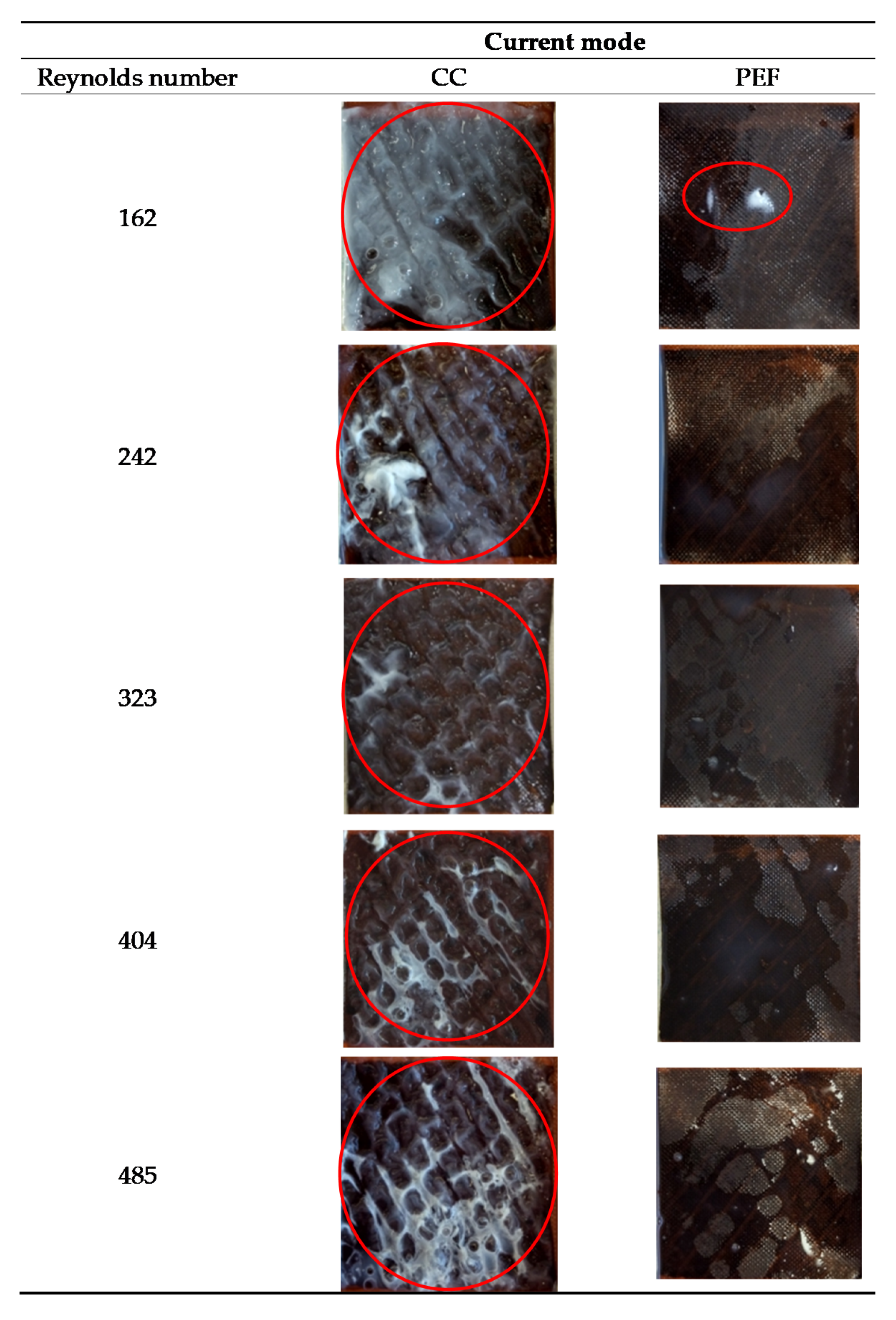
3.4. Membrane Surface Integrity and Quantification of Protein Fouling
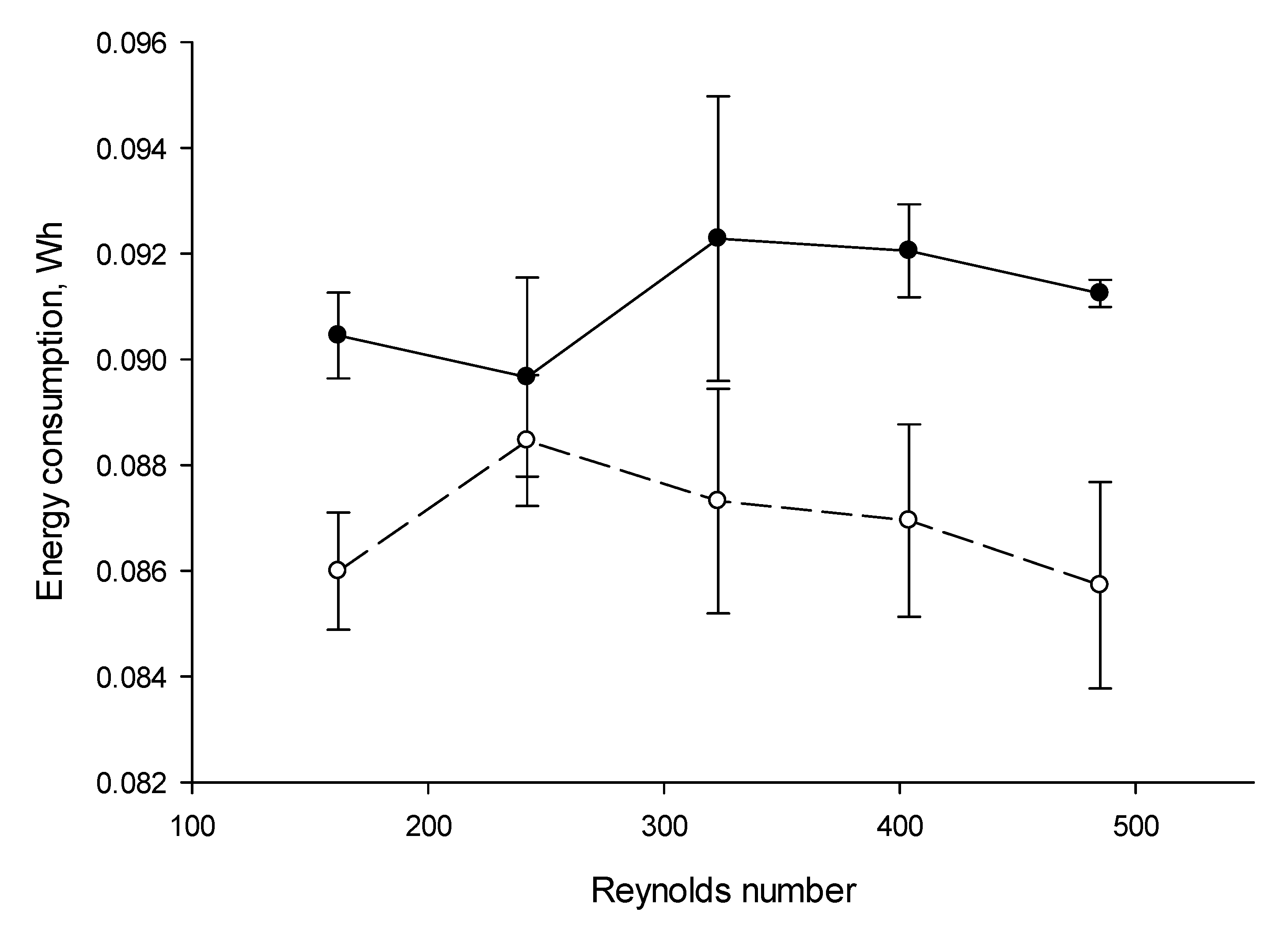
3.5. Energy Consumptions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dominguez-Salas, P.; Galie, A.; Omore, A.; Omosa, E.; Ouma, E. Contributions of Milk Production to Food and Nutrition Security. In Encyclopedia of Food Security and Sustainability; Ferranti, P., Berry, E.M., Anderson, J.R., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 278–291. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbatova, K.K.; Gunkova, P.I. Chemistry and Physics of Milk and Dairy Products; GIORDR: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2012; pp. 17–77. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mier, M.P.; Ibanez, R.; Ortiz, I. Influence of process variables on the production of bovine milk casein by electrodialysis with bipolar membranes. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 40, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audic, J.-L.; Chaufer, B.; Daufin, G. Non-food applications of milk components and dairy co-products: A review. Le Lait. 2003, 83, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Horst, H.C.; Timmer, J.M.K.; Robbertsen, T.; Leenders, J. Use of nanofiltration for concentration and demineralization in the dairy industry: Model for mass transport. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 104, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houldsworth, D.W. Demineralization of whey by means of ion-exchange and electrodialysis. J. Soc. Dairy Technol. 1980, 33, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Lamarche, F.; Ippersiel, D.; Amiot, J. Bipolar membrane electroacidification to produce bovine milk casein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 5291–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W.; Tremblay, A.Y. Fouling in steady and unsteady state electrodialysis. Desalination 1983, 47, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bleha, M.; Tishchenko, G.; Šumberová, V.; Kůdela, V. Characteristic of the critical state of membranes in ED-desalination of milk whey. Desalination 1992, 86, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Fouling on ion-exchange membranes: Classification, characterization and strategies of prevention and control. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, B.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Pourcelly, G.; Araya-Farias, M.; Bazinet, L. Application of relaxation periods during electrodialysis of a casein solution: Impact on anion-exchange membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufton, G.; Mikhaylin, S.; Gaaloul, S.; Bazinet, L. Positive Impact of Pulsed Electric Field on Lactic Acid Removal, Demineralization and Membrane Scaling during Acid Whey Electrodialysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N.; Pourcelly, G.; Choi, S.; Kwon, H.J.; Han, J.; Bazinet, L. How physico-chemical and surface properties of cation-exchange membrane affect membrane scaling and electroconvective vortices: Influence on performance of electrodialysis with pulsed electric field. Desalination 2016, 393, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Belova, E.I.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Pourcelly, G.; Larchet, C. Intensive current transfer in membrane systems: Modelling, mechanisms and application in electrodialysis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 160, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Ruiz, B.; Pourcelly, G.; Mareev, S.A.; Nikonenko, V.V. Effect of pulsed electric field on electrodialysis of a NaCl solution in sub-limiting current regime. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 164, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Sion, A.-V. Improvement of a sustainable hybrid technology for caseins isoelectric precipitation (electrodialysis with bipolar membrane/ultrafiltration) by mitigation of scaling on cation-exchange membrane. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Sarfert, F.; Strathmann, H.; Moon, S.-H. Designing of an electrodialysis desalination plant. Desalination 2002, 142, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlhoff, E.; Bennett, A.; McMahon, D. Milk and Dairy Products in Human Nutrition; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 41–90. [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes-Araya, N.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Impact of pulsed electric field on electrodialysis process performance and membrane fouling during consecutive demineralization of a model salt solution containing a high magnesium/calcium ratio. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, M.-E.; Bazinet, L. Ion-exchange membrane fouling by peptides: A phenomenon governed by electrostatic interactions. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Ion Exchange Membranes: Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 205–244. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, J.H.; Peterson, E.E. Buffers of milk and buffer value. J. Dairy Sci. 1927, 10, 224–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A.; Horne, D.S. Milk Salts: Technological Significance. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 351–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Graet, Y.; Brulé, G. Les équilibres minéraux du lait: Influence du pH et de la force ionique. Lait 1993, 73, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Law, A.J.R.; Leaver, J. Effects of acidification and storage of milk on dissociation of bovine casein micelles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 5008–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, H.; Kherouatou, N.; Ayadi, J. Acidification chimique directe du lait: Correlation entre la mobilité du matériel micellaire et les micro et macrostructures des laits acidifiés. Sci. Aliment. 2000, 20, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hooydonk, A.C.M.; Hagerdoorn, H.G.; Boerrigter, I.J. pH-induced physicochemical changes of casein micelles in milk and their effect on renneting. I. Effect of acidification on physichochemical properties. Neth. Milk Dairy J. 1986, 40, 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Bazinet, L.; Lamarche, F.; Ippersiel, D.; Gendron, C.; Mahdavi, B.; Amiot, J. Comparison of electrochemical and chemical acidification of skim milk. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, F.-A.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Production of calcium- and magnesium-enriched caseins and caseinates by an ecofriendly technology. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazinet, L.; Montpetit, D.; Ippersiel, D.; Amiot, J.; Lamarche, F. Identification of Skim Milk Electroacidification Fouling: A Microscopic Approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 237, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, N.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Voltage spike and electroconvective vortices generation during electrodialysis under pulsed electric field: Impact on demineralization process efficiency and energy consumption. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2019, 52, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaun, M.S.; Mietton, B.; Gaucheron, F. Buffering capacity of dairy products. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Pouliot, Y.; Castaigne, F. Relative contributions of charged species to conductivity changes in skim milk during electrochemical acidification. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 352, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Ippersiel, D.; Gendron, C.; Beaudry, J.; Mahdavi, B.; Amiot, J.; Lamarche, F. Cationic balance in skim milk during bipolar membrane electroacidification. J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 173, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin Teng Shee, F.; Arul, J.; Brunet, S.; Bazinet, L. Performing a three-step process for conversion of chitosan to its oligomers using a unique bipolar membrane electrodialysis system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10019–10026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravtsov, V.; Kulikova, I.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Alkalinization of acid whey by means of electrodialysis with bipolar membranes and analysis of induced membrane fouling. J. Food Eng. 2020, 277, 109891–109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Montpetit, D.; Ippersiel, D.; Mahdavi, B.; Amiot, J.; Lamarche, F. Neutralization of hydroxide generated during skim milk electroacidification and its effect on bipolar and cationic membrane integrity. J. Memb. Sci. 2003, 216, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campione, A.; Gurreri, L.; Ciofalo, M.; Micale, G.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A. Electrodialysis for water desalination: A critical assessment of recent developments on process fundamentals, models and applications. Desalination 2018, 434, 121–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Fat PLS 1, % w/w | Protein, % w/w | Lactose, % w/w | Solids, % w/w | SNF 2, % w/w | Casein, g/L | NPN/CU 3, mg/100g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.13 ± 0.01 | 3.37 ± 0.05 | 4.73 ± 0.05 | 9.14 ± 0.09 | 8.34 ± 0.09 | 27.07 ± 0.36 | 15.60 ± 1.72 |
| Current Mode | CC | PEF | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reynolds Number | 162 | 242 | 323 | 404 | 485 | 162 | 242 | 323 | 404 | 485 | ||
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | CEM | Before | 8.35 ± 0.20 a* | 8.68 ± 0.30 a | 8.49 ± 0.37 a | 8.33 ± 0.41 a | 8.53 ± 0.22 a | 8.33 ± 0.33 a | 8.35 ± 0.67 a | 8.34 ± 0.69 a | 8.02 ± 0.45 a | 8.54 ± 0.58 a |
| After | 7.01 ± 0.17 b | 7.41 ± 0.13 b | 7.14 ± 0.27 b | 7.16 ± 0.30 b | 7.30 ± 0.51 b | 7.25 ± 0.34 b | 6.99 ± 0.45 b | 7.04 ± 0.69 b | 7.33 ± 0.20 b | 7.30 ± 0.23 b | ||
| BPM1 | Before | 7.59 ± 0.36 a | 7.35 ± 0.40 a | 7.44 ± 0.46 a | 7.40 ± 0.18 a | 6.84 ± 1.09 a | 7.36 ± 0.21 a | 7.14 ± 0.38 a | 7.32 ± 0.14 a | 7.82 ± 0.15 a | 7.53 ± 0.17 a | |
| After | 6.67 ± 0.46 b | 6.55 ± 0.34 b | 6.74 ± 0.57 b | 6.70 ± 0.14 b | 6.53 ± 0.30 b | 6.58 ± 0.15 b | 6.05 ± 0.65 b | 6.35 ± 0.41 b | 6.75 ± 0.22 b | 6.87 ± 0.44 b | ||
| BPM2 | Before | 7.39 ± 0.31 a | 7.35 ± 0.23 a | 7.57 ± 0.64 a | 7.66 ± 0.46 a | 7.54 ± 0.34 a | 7.28 ± 0.18 a | 7.39 ± 0.33 a | 7.17 ± 0.08 a | 7.48 ± 0.32 a | 7.69 ± 0.07 a | |
| After | 7.11 ± 0.46 bA | 7.04 ± 0.39 bA | 7.65 ± 0.48 bA | 7.51 ± 0.46 bA | 7.18 ± 0.09 bA | 6.90 ± 0.06 bB | 6.79 ± 0.27 bB | 6.99 ± 0.34 bB | 7.29 ± 0.45 bB | 7.07 ± 0.47 bB | ||
| Thickness (mm) | CEM | Before | 0.151 ± 0.005 a | 0.149 ± 0.004 a | 0.151 ± 0.006 a | 0.144 ± 0.005 a | 0.153 ± 0.004 a | 0.151 ± 0.005 a | 0.151 ± 0.004 a | 0.148 ± 0.005 a | 0.152 ± 0.006 a | 0.143 ± 0.005 a |
| After | 0.150 ± 0.004 a | 0.150 ± 0.004 a | 0.148 ± 0.005 a | 0.146 ± 0.010 a | 0.149 ± 0.003 a | 0.149 ± 0.002 a | 0.148 ± 0.006 a | 0.144 ± 0.004 a | 0.155 ± 0.004 a | 0.145 ± 0.005 a | ||
| BPM1 | Before | 0.244 ± 0.004 a | 0.244 ± 0.011 a | 0.246 ± 0.002 a | 0.247 ± 0.003 a | 0.246 ± 0.003 a | 0.247 ± 0.002 a | 0.242 ± 0.006 a | 0.246 ± 0.005 a | 0.251 ± 0.001 a | 0.249 ± 0.005 a | |
| After | 0.240 ± 0.003 b | 0.243 ± 0.004 b | 0.244 ± 0.003 b | 0.238 ± 0.004 b | 0.240 ± 0.003 b | 0.242 ± 0.003 b | 0.243 ± 0.001 b | 0.242 ± 0.002 b | 0.246 ± 0.003 b | 0.245 ± 0.001 b | ||
| BPM2 | Before | 0.248 ± 0.004 a | 0.245 ± 0.005 a | 0.247 ± 0.007 a | 0.247 ± 0.007 a | 0.247 ± 0.005 a | 0.246 ± 0.002 a | 0.244 ± 0.004 a | 0.241 ± 0.002 a | 0.243 ± 0.004 a | 0.247 ± 0.004 a | |
| After | 0.241 ± 0.004 b | 0.241 ± 0.003 b | 0.245 ± 0.006 b | 0.238 ± 0.004 b | 0.245 ± 0.003 b | 0.241 ± 0.002 b | 0.238 ± 0.010 b | 0.241 ± 0.001 b | 0.243 ± 0.003 b | 0.242 ± 0.002 b | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nichka, V.S.; Geoffroy, T.R.; Nikonenko, V.; Bazinet, L. Impacts of Flow Rate and Pulsed Electric Field Current Mode on Protein Fouling Formation during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidification of Skim Milk. Membranes 2020, 10, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090200
Nichka VS, Geoffroy TR, Nikonenko V, Bazinet L. Impacts of Flow Rate and Pulsed Electric Field Current Mode on Protein Fouling Formation during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidification of Skim Milk. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090200
Chicago/Turabian StyleNichka, Vladlen S., Thibaud R. Geoffroy, Victor Nikonenko, and Laurent Bazinet. 2020. "Impacts of Flow Rate and Pulsed Electric Field Current Mode on Protein Fouling Formation during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidification of Skim Milk" Membranes 10, no. 9: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090200
APA StyleNichka, V. S., Geoffroy, T. R., Nikonenko, V., & Bazinet, L. (2020). Impacts of Flow Rate and Pulsed Electric Field Current Mode on Protein Fouling Formation during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidification of Skim Milk. Membranes, 10(9), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090200