Dimensional Nanofillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Pervaporation Separations: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
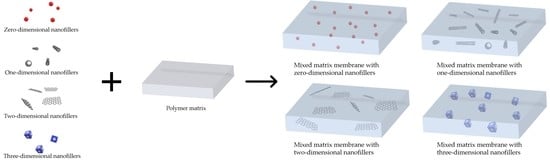
2. Nanofillers Used in MMMs
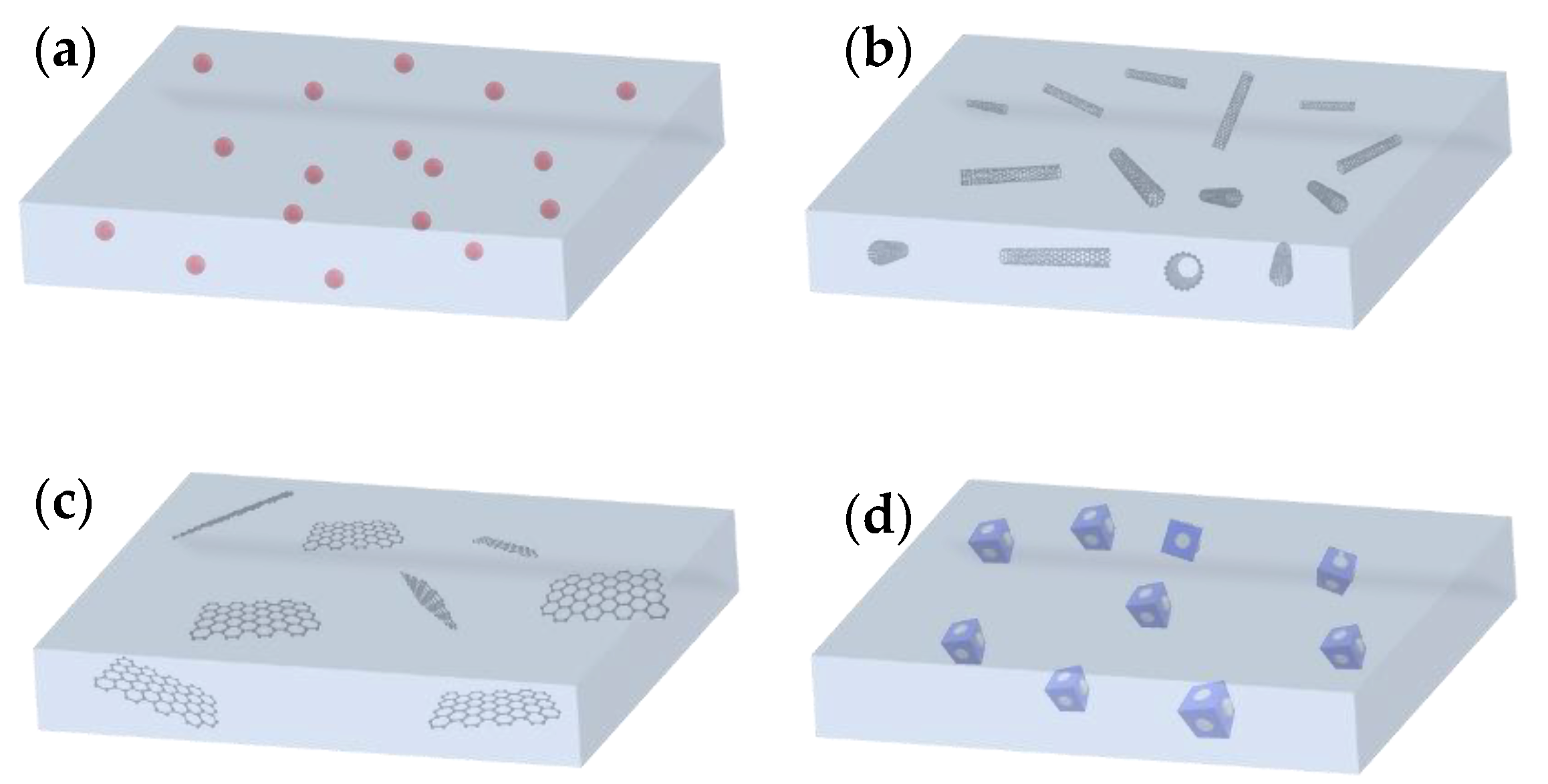
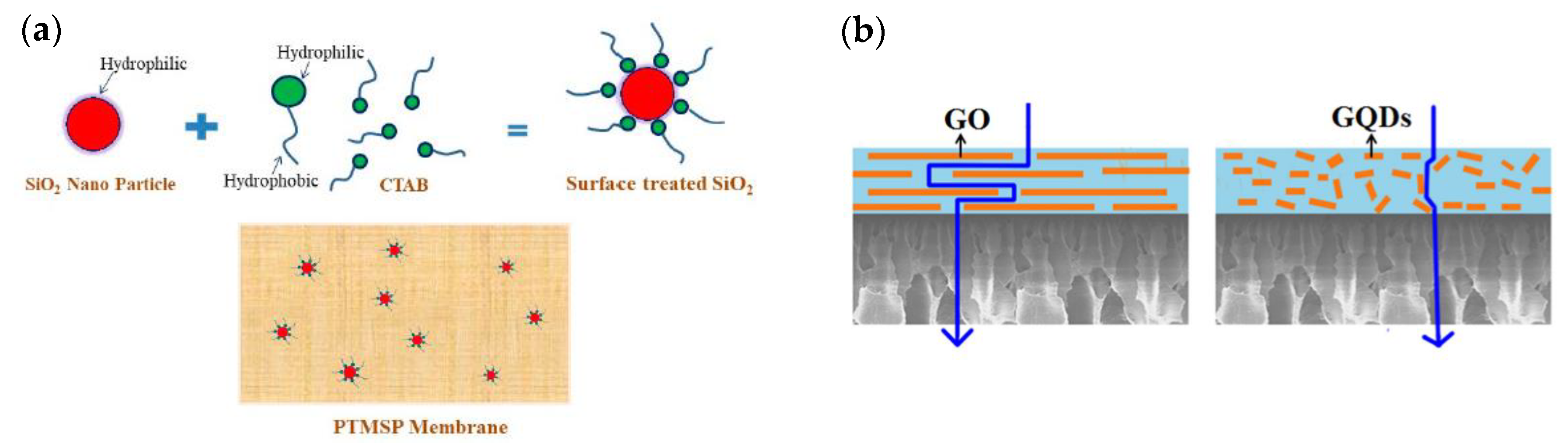
2.1. Zero-Dimensional Nanofillers
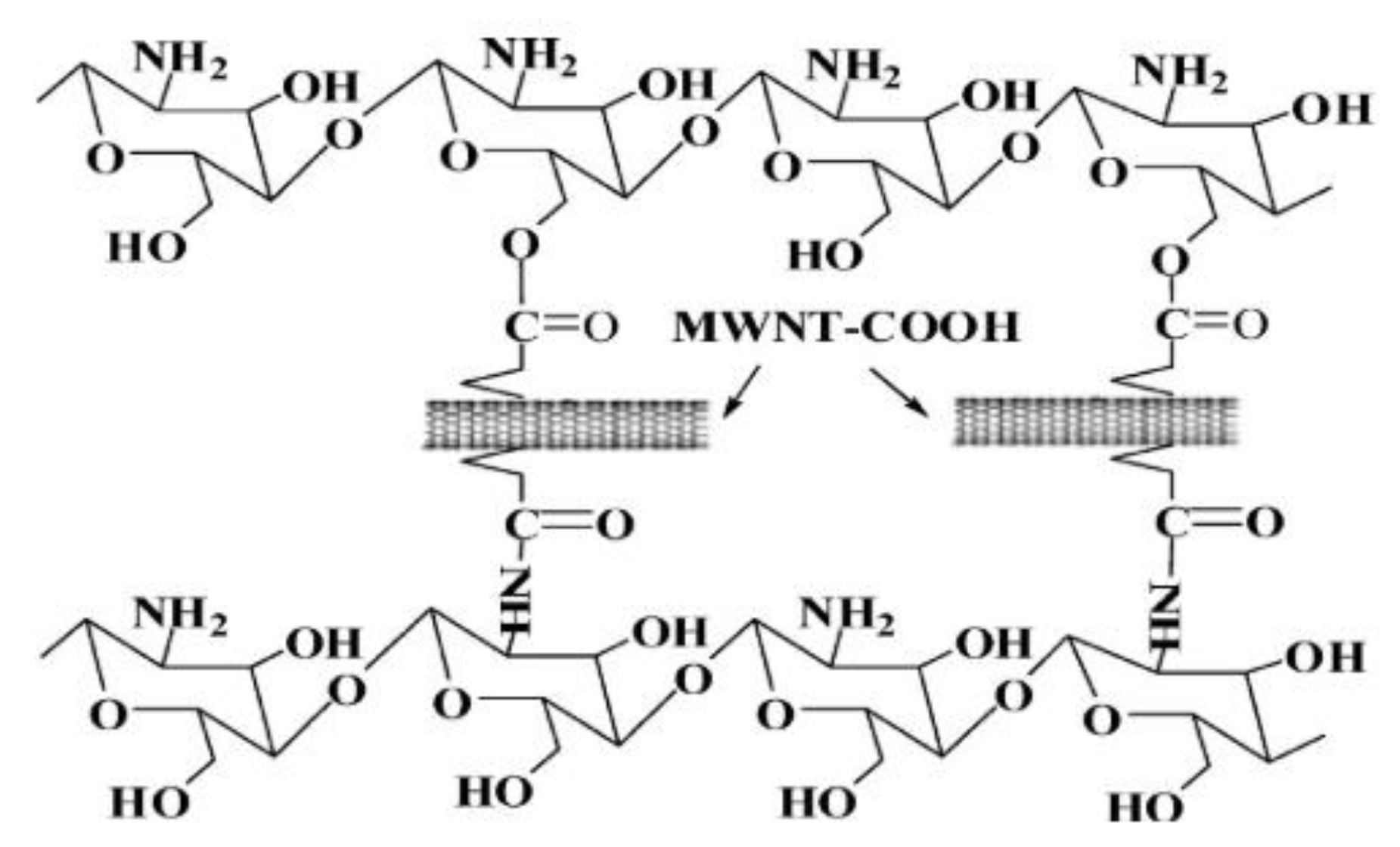
2.2. One-Dimensional Nanofillers
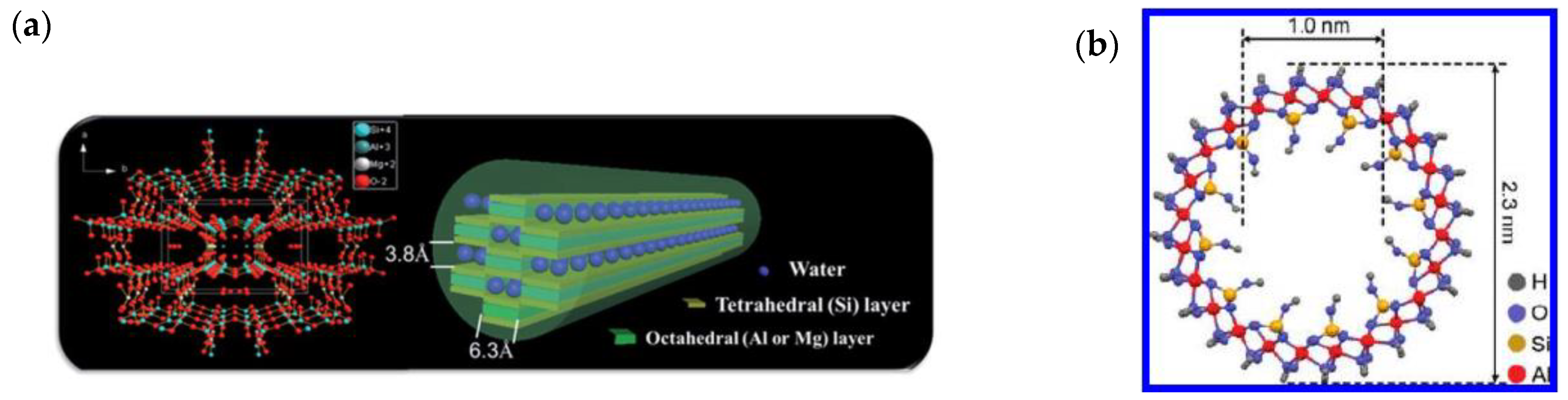
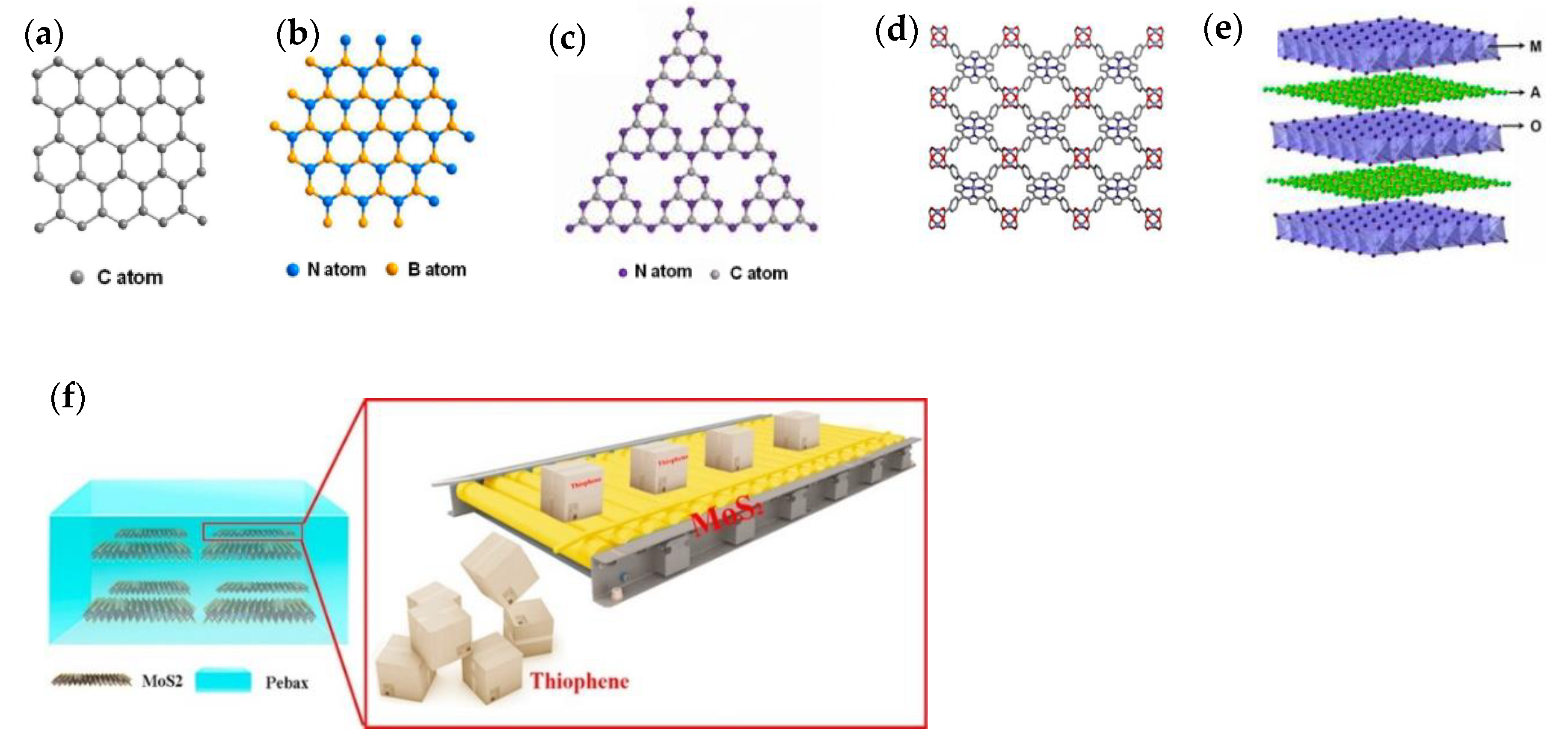
2.3. Two-Dimensional Nanofillers
2.4. Three-Dimensional Nanofillers
3. Effect of Nanofillers on Polymer Matrix
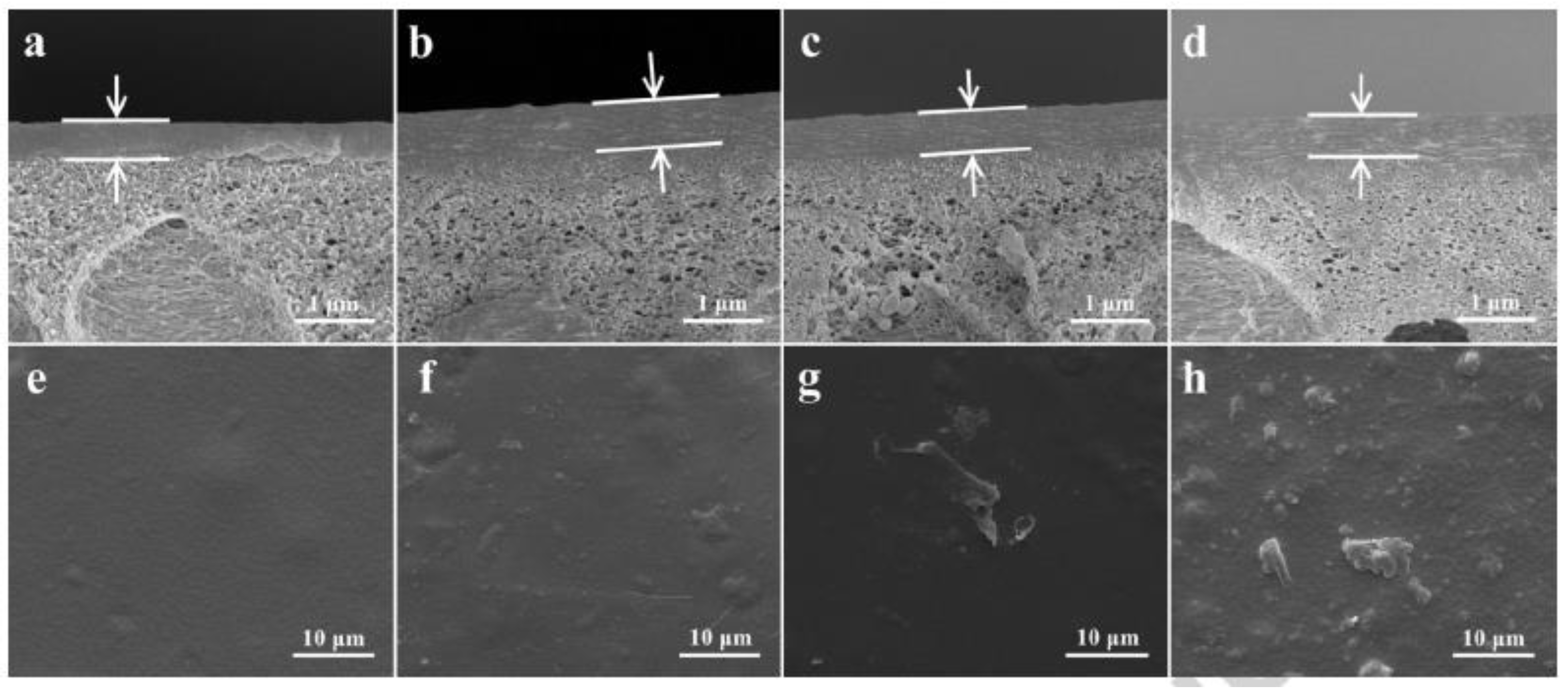
3.1. Effect of Nanofillers on Morphology of MMMS
3.2. Effect of Nanofillers on Free Volume Properties
3.3. Effect of Nanofillers on Swelling
3.4. Effect of Nanofillers on Surface Properties
3.5. Effect of Nanofillers on Thermal Properties
3.6. Effect of Nanofillers on Polymer Crystallinity
3.7. Effect of Nanofillers on Chemical Properties
4. Application of Nanofiller MMMs for PV Processes
4.1. Applications of Nanofillers in Hydrophilic PV
4.1.1. Dehydration of Organic Solvents
4.1.2. Desalination
4.2. Applications of Nanofillers in Organophilic PV
4.2.1. Removal of Organic Solvents from Water
4.2.2. Separation of Organics from Organic Mixtures
5. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fane, A.G.; Wang, R.; Hu, M.X. Synthetic membranes for water purification: Status and future. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 3368–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werber, J.R.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.K.; Shi, G.M.; Le, N.L.; Tang, Y.P.; Zuo, J.; Nunes, S.P.; Chung, T.-S. Recent membrane development for pervaporation processes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 57, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane Gas Separation: A Review/State of the Art. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wei, W.; Jin, W. Pervaporation Membranes for Biobutanol Production. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rayess, Y.; Albasi, C.; Bacchin, P.; Taillandier, P.; Raynal, J.; Mietton-Peuchot, M.; Devatine, A. Cross-flow microfiltration applied to oenology: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 382, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Feng, X. Polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration: Fundamentals, applications and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 586, 53–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Rui, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z. A Review on Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes for Water Purification. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Badrelzaman, M.; Darwish, N.N.; Darwish, N.A.; Hilal, N. Reverse osmosis desalination: A state-of-the-art review. Desalination 2019, 459, 59–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Huang, R.Y.M. Liquid Separation by Membrane Pervaporation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 1048–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, G.; Keshav, A.; Anandkumar, J. Review on Pervaporation: Theory, Membrane Performance, and Application to Intensification of Esterification Reaction. J. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.C.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Fundamentals and applications of pervaporation through zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.l.; Lau, C.H.; Cao, B.; Li, P. Elucidating the impact of polymer crosslinking and fixed carrier on enhanced water transport during desalination using pervaporation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 575, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Shen, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, G.; Xiong, J.; Yang, J.; Jin, W. Ultrathin two-dimensional MXene membrane for pervaporation desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, E.; Muthu, S.; Ruff, L.; Brant, J.A. Feasibility assessment of pervaporation for desalinating high-salinity brines. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2014, 4, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Huang, R.Y.M. Polymeric membrane pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doguparthy, S.P. Pervaporation of aqueous alcohol mixtures through a photopolymerised composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 185, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh-Thang, H.; Kaliaguine, S. Predictive models for mixed-matrix membrane performance: A review. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4980–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; König, A. Mixed-Matrix Membrane for Gas Separation: Polydimethylsiloxane Filled with Zeolite. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Sanip, S.M.; Ng, B.C.; Aziz, M. Recent advances of inorganic fillers in mixed matrix membrane for gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. A review on inorganic membranes for desalination and wastewater treatment. Desalination 2018, 434, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechnik, J.; Gascon, J.; Doonan, C.J.; Janiak, C.; Sumby, C.J. Mixed-Matrix Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9292–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Ji, S. Chitosan/graphene oxide mixed matrix membrane with enhanced water permeability for high-salinity water desalination by pervaporation. Desalination 2018, 438, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Hoang, M.; Duong, T.; Ng, D.; Dao, B.; Gray, S. Sol–gel derived poly(vinyl alcohol)/maleic acid/silica hybrid membrane for desalination by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Hu, C.; Pan, F.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. PVA–GPTMS/TEOS hybrid pervaporation membrane for dehydration of ethylene glycol aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, L.; Chen, X. Chitosan/TiO2 nanocomposite pervaporation membranes for ethanol dehydration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3130–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, F.; Pan, F.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; Wang, B. Enhanced pervaporation dehydration performance of ultrathin hybrid membrane by incorporating bioinspired multifunctional modifier and TiCl4 into chitosan. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Zhen, H.-G.; Ahmad, A.; Zhang, A.-S.; Zhao, Z.-P. In situ fabrication of MOF nanoparticles in PDMS membrane via interfacial synthesis for enhanced ethanol permselective pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-f.; Wu, G.-l.; Dong, L.-l.; Tang, J.; Bai, Y.-x.; Zhu, Y.-h.; Liu, Q.-s.; Sun, Y.-p.; Gu, J. Preparation of jujube-cake structure membranes through in situ polymerization of hyperbranched polysiloxane in ethylene-vinyl acetate matrix for separation of ethyl acetate from water. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 18308–18318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Villaluenga, J.P.G.; Valentin, J.L.; López-Manchado, M.A.; Mengual, J.I.; Seoane, B. Filled poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) dense membranes by silica and silane modified silica nanoparticles: Characterization and application in pervaporation. Polymer 2005, 46, 9881–9891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Vatanpour, V.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Zarrabi, H. Improvement in flux and antifouling properties of PVC ultrafiltration membranes by incorporation of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, C.; Jiao, K. Enhanced sensitivity for deoxyribonucleic acid electrochemical impedance sensor: Gold nanoparticle/polyaniline nanotube membranes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 616, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perezjuste, J.; Pastorizasantos, I.; Lizmarzan, L.; Mulvaney, P. Gold nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 1870–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cao, S.; Li, J.; Du, Z.; Cheng, F. Anti-fouling TiO2 nanowires membrane for oil/water separation: Synergetic effects of wettability and pore size. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. 2D Laminar Membranes for Selective Water and Ion Transport. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 1902014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Cheng, H.-M. The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 2012, 50, 3210–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhah, O.; Liu, J.; Fischer, R.A.; Woll, C. MOF thin films: Existing and future applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1081–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangnekar, N.; Mittal, N.; Elyassi, B.; Caro, J.; Tsapatsis, M. Zeolite membranes—A review and comparison with MOFs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7128–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.; Wijmans, J.G.; Huang, Y. Permeability, permeance and selectivity: A preferred way of reporting pervaporation performance data. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, V.P.; Tleuova, A.; Hosseini, S.; Vopicka, O. Selective Separation of 1-Butanol from Aqueous Solution through Pervaporation Using PTSMP-Silica Nano Hybrid Membrane. Membranes (Basel) 2020, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.T.; Wang, F.J.; Lue, S.J. Sorption, diffusion, and pervaporation of benzenekyclohexane mixtures on silver-Nafion membranes. Desalination 2002, 149, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecaros, R.L.G.; Bismonte, M.E.; Doma, B.T.; Hung, W.-S.; Hu, C.-C.; Tsai, H.-A.; Huang, S.-H.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Alcohol dehydration performance of pervaporation composite membranes with reduced graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots homostructured filler. Carbon 2020, 162, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pan, F.; Yang, L.; Song, Y.; Wu, H.; Cheng, X.; Liu, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Graphene oxide quantum dots incorporated nanocomposite membranes with high water flux for pervaporative dehydration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xie, Z.; Cran, M.; Ng, D.; Gray, S. Enhanced desalination performance of poly (vinyl alcohol)/carbon nanotube composite pervaporation membranes via interfacial engineering. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Gomaa, H.; Pan, F. Enhanced pervaporative performance of hybrid membranes containing Fe3O4@CNT nanofillers. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Pan, F.; Zhao, J.; Cao, K.; Gao, C.; Yang, S.; Liu, G.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Enhancing the permeation selectivity of sodium alginate membrane by incorporating attapulgite nanorods for ethanol dehydration. RSC Advances 2016, 6, 14381–14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, Z.; Moheb, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Alibouri, M. Titanate nanotubes–incorporated poly(vinyl alcohol) mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation separation of water-isopropanol mixtures. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 145, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.Y.; Tong, H.M.; Zang, J.; Choudhury, R.P.; Sholl, D.S.; Beckham, H.W.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Single-walled aluminosilicate nanotube/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehian, P.; Chung, T.-S. Thermally treated ammonia functionalized graphene oxide/polyimide membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; Ye, H.; Jin, W.; Cui, Z. Two-dimensional MXene incorporated chitosan mixed-matrix membranes for efficient solvent dehydration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xing, R.; Yang, S.; Gao, C.; Pan, F. Highly water-selective hybrid membrane by incorporating g-C3N4 nanosheets into polymer matrix. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Ding, H.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, B.; Cao, X. Constructing facilitated transport pathway in hybrid membranes by incorporating MoS2 nanosheets. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xiangli, F.; Wei, W.; Liu, S.; Jin, W. Improved performance of PDMS/ceramic composite pervaporation membranes by ZSM-5 homogeneously dispersed in PDMS via a surface graft/coating approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, S.; Khosravi, T.; Bakhtiari, O.; Mohammadi, T. Zeolite filled polyimide membranes for dehydration of isopropanol through pervaporation process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, G.; Zhao, X.; Jin, W. Hydrophobic-ZIF-71 filled PEBA mixed matrix membranes for recovery of biobutanol via pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adoor, S.G.; Sairam, M.; Manjeshwar, L.S.; Raju, K.V.S.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Sodium montmorillonite clay loaded novel mixed matrix membranes of poly(vinyl alcohol) for pervaporation dehydration of aqueous mixtures of isopropanol and 1,4-dioxane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 285, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, J. Removing benzene from aqueous solution using CMS-filled PDMS pervaporation membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 48, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shi, L.; Zeng, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y. Sharp molecular-sieving of alcohol-water mixtures over phenyldiboronic acid pillared graphene oxide framework (GOF) hybrid membrane. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2015, 51, 7345–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Gupta, U. A review on applications of nanoparticles for the preconcentration of environmental pollutants. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Gnus, M.; Turczyn, R.; Strzelewicz, A.; Krasowska, M. Pervaporation with chitosan membranes containing iron oxide nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.V.; Acquah, S.F.A.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Sokolova, M.P.; Mikhailova, M.E.; Polyakov, E.S.; Ermakov, S.S.; Markelov, D.A.; Roizard, D. Improvement of pervaporation PVA membranes by the controlled incorporation of fullerenol nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.B.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, H.G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, Z.P.; Mi, Y.J.; Yang, S.R. Preparation, mechanical and thermal properties of functionalized graphene/polyimide nanocomposites. Compos. Part A 2012, 43, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.; Jiang, Z.; Livingston, A.G. Sub–10 nm polyamide nanofilms with ultrafast solvent transport for molecular separation. Science 2015, 348, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Gao, S.; Ding, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, J.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Photothermal-Responsive SingleWalled Carbon Nanotube-Based Ultrathin Membranes for On/Off Switchable Separation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 5, 4835–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panahian, S.; Raisi, A.; Aroujalian, A. Multilayer mixed matrix membranes containing modified-MWCNTs for dehydration of alcohol by pervaporation process. Desalination 2015, 355, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jiang, Y.-y.; Shen, J.-n.; Wu, L.-g.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Dong, C.-y. Preparation of Ag Nanoparticles on MWCNT Surface via Adsorption Layer Reactor Synthesis and Its Enhancement on the Performance of Resultant Polyurethane Hybrid Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Pan, F.; Sun, H.; Lu, L.; Jiang, Z. Novel nanocomposite pervaporation membranes composed of poly(vinyl alcohol) and chitosan-wrapped carbon nanotube. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xie, Z.; Doherty, C.M.; Cran, M.; Ng, D.; Gray, S. Understanding the transport enhancement of poly (vinyl alcohol) based hybrid membranes with dispersed nanochannels for pervaporation application. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, K.; Baek, Y.; Kim, D.G.; Shim, J.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.C. High-performance reverse osmosis CNT/polyamide nanocomposite membrane by controlled interfacial interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2819–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Farha, O.K.; Roberts, J.; Scheidt, K.A.; Nguyen, S.T.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Cao, X.; Wu, X.J.; He, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Han, S.; Nam, G.H.; et al. Recent Advances in Ultrathin Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6225–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Cai, W.; Chen, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, J. Preparation of graphene oxide/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite membrane and pervaporation performance for ethanol dehydration. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15457–15465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhas, D.P.; Raghu, A.V.; Jeong, H.M.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Graphene-loaded sodium alginate nanocomposite membranes with enhanced isopropanol dehydration performance via a pervaporation technique. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17120–17130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Hsiao, B.S. Enhanced pervaporation performance of polyamide membrane with synergistic effect of porous nanofibrous support and trace graphene oxide lamellae. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 196, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manshad, S.; Sazegar, M.R.; Nawawi, M.G.M.; Hassan, H.b. Fabrication of nanohybrid polyetherimide/graphene oxide membranes: Biofuel dehydration by pervaporation process. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 103888–103894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hou, J.; Uliana, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, M.; Van der Bruggen, B. The rapid emergence of two-dimensional nanomaterials for high-performance separation membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3773–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gascon, J.; Li, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Metal-organic frameworks based membranes for liquid separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7124–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Chung, T.-S. High-performance UiO-66/polyimide mixed matrix membranes for ethanol, isopropanol and n-butanol dehydration via pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 531, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konietzny, R.; Koschine, T.; Rätzke, K.; Staudt, C. POSS-hybrid membranes for the removal of sulfur aromatics by pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 123, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising organic polymers with dispersed inorganic fillers for gas separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, F.; Georgopanos, P.; Shishatskiy, S.; Filiz, V.; Brinkmann, T.; Abetz, V. Development and Characterization of Defect-Free Matrimid((R)) Mixed-Matrix Membranes Containing Activated Carbon Particles for Gas Separation. Polymers (Basel) 2018, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Ng, D.; Shen, S.; Zhou, Z. Poly(ether sulfone) supported hybrid poly(vinyl alcohol)-maleic acid-silicone dioxide membranes for the pervaporation separation of ethanol-water mixtures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44839–44850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzetakis, N.; Doherty, C.M.; Thornton, A.W.; Chen, X.C.; Cotanda, P.; Hill, A.J.; Balsara, N.P. Membranes with artificial free-volume for biofuel production. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; He, G.; Xing, R.; Pan, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; Wang, B. Incorporating Zwitterionic Graphene Oxides into Sodium Alginate Membrane for Efficient Water/Alcohol Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Hoang, M.; Ng, D.; Doherty, C.; Hill, A.; Gray, S. Effect of heat treatment on pervaporation separation of aqueous salt solution using hybrid PVA/MA/TEOS membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 127, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.M.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F. Enhanced hydrophilicity and salt rejection study of graphene oxide-polysulfone mixed matrix membrane. Desalination 2013, 313, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ou, R.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Simon, G.P.; Wang, H. Non-swelling graphene oxide-polymer nanocomposite membrane for reverse osmosis desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 562, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Hua, Y.; Sun, J.; Duan, J.; Jin, W. High efficient water/ethanol separation by a mixed matrix membrane incorporating MOF filler with high water adsorption capacity. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecaros, R.L.G.; Deseo, K.M.; Hung, W.-S.; Tayo, L.L.; Hu, C.-C.; An, Q.-F.; Tsai, H.-A.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Influence of integrating graphene oxide quantum dots on the fine structure characterization and alcohol dehydration performance of pervaporation composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 576, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, L.; Shen, J.; Shi, J.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J.; Duan, J.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Improved ethanol recovery through mixed-matrix membrane with hydrophobic MAF-6 as filler. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 178, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, K.; Nair, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, J.; Gomaa, H.; Wu, H.; Pan, F. Pervaporation performance comparison of hybrid membranes filled with two-dimensional ZIF-L nanosheets and zero-dimensional ZIF-8 nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.; Uddin, A. Organic—Inorganic hybrid solar cells: A comparative review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 107, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šupová, M.; Martynková, G.S.; Barabaszová, K. Effect of Nanofillers Dispersion in Polymer Matrices: A Review. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2011, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, S.K.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Development of novel composite membranes using quaternized chitosan and Na+-MMT clay for the pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.V.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Savon, N.A.; Missyul, A.B.; Mazur, A.S.; Kuzminova, A.I.; Zolotarev, A.A.; Mikhailovskii, V.; Lahderanta, E.; Markelov, D.A.; et al. Novel mixed-matrix membranes based on polyvinyl alcohol modified by carboxyfullerene for pervaporation dehydration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, S.; Balzano, L.; Gioffredi, E.; Maffettone, P.L.; Grizzuti, N. Effects of the degree of undercooling on flow induced crystallization in polymer melts. Polymer 2004, 45, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Shen, B.; He, X.; Ghazi, Z.A.; Khan, N.A.; Sin, H.; Khattak, A.M.; Li, L.; et al. Microporous membranes comprising conjugated polymers with rigid backbones enable ultrafast organic-solvent nanofiltration. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.N.; Cadek, M.; Blake, R.; Nicolosi, V.; Ryan, K.P.; Belton, C.; Fonseca, A.; Nagy, J.B.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Blau, W.J. High Performance Nanotube-Reinforced Plastics: Understanding the Mechanism of Strength Increase. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, C.; Gao, C.; Pan, F.; Wang, B.; Cao, X.; Yang, J. Enhanced water permeation through sodium alginate membranes by incorporating graphene oxides. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirilargani, M.; Sadatnia, B. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8) mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.; Tran, T.; Hoang, M.; Xie, Z. Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.L.; Li, C.L.; Wang, Y. In-situ crosslinked PVA/organosilica hybrid membranes for pervaporation separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Q.L.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Chen, Y. Anti-trade-off in dehydration of ethanol by novel PVA/APTEOS hybrid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ng, D.; Hoang, M.; Duong, T.; Gray, S. Separation of aqueous salt solution by pervaporation through hybrid organic–inorganic membrane: Effect of operating conditions. Desalination 2011, 273, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wu, L.; Shi, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Preparation and Pervaporation Property of Chitosan Membrane with Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11667–11675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.M.; Pal, R.; Moon, G.Y. Characteristics of sodium alginate membranes for the pervaporation dehydration of ethanol±water and isopropanol±water mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 160, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adoor, S.G.; Manjeshwar, L.S.; Bhat, S.D.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Aluminum-rich zeolite beta incorporated sodium alginate mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration and esterification of ethanol and acetic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Wang, Z.-X.; Du, G.-Q.; Fan, L.-H.; Mu, Y.; Ren, J.-G.; Bai, F.-W. Integration of ethanol removal using carbon nanotube (CNT)-mixed membrane and ethanol fermentation by self-flocculating yeast for antifouling ethanol recovery. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, S.I.; Ohya, H.; Soontarapa, K. Hydrophilic membranes for pervaporation: An analytical review. Desalination 1997, 110, 251–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipnizki, F.; Field, R.W.; Ten, P.-K. Pervaporation-based hybrid process: A review of process design, applications and economics. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 153, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, M.S.; Reddy, K.R.; Soontarapa, K.; Naveen, S.; Raghu, A.V.; Kulkarni, R.V.; Suhas, D.P.; Shetti, N.P.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Membranes for dehydration of alcohols via pervaporation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, H.T.; Rode, S.; Roizard, D.; Mouzon-Pelletier, S.; Tretjak, S. Dehydration of reactive industrial mixtures by pervaporation: An innovative approach in acrylic esters processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 120, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-X.; Wang, N.; Zhao, C.; Ji, S.; Li, J.-R. Membrane materials in the pervaporation separation of aromatic/aliphatic hydrocarbon mixtures—A review. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wen, R.; Guo, Y.; Su, J.; Matsuura, T. Multilayer poly(vinyl alcohol)–zeolite 4A composite membranes for ethanol dehydration by means of pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lu, Y.; Yao, L.; Cui, P. A highly hydrophilic benzenesulfonic-grafted graphene oxide-based hybrid membrane for ethanol dehydration. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20358–20367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Chen, J.H.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y.; Dong, X. Amine-functionalized metal organic framework (NH2-MIL-125(Ti)) incorporated sodium alginate mixed matrix membranes for dehydration of acetic acid by pervaporation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 99008–99017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Qu, X.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Silane-modified NaA zeolite/PAAS hybrid pervaporation membranes for the dehydration of ethanol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 3390–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorribas, S.; Kudasheva, A.; Almendro, E.; Zornoza, B.; de la Iglesia, Ó.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Pervaporation and membrane reactor performance of polyimide based mixed matrix membranes containing MOF HKUST-1. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 124, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairam, M.; Naidu, B.V.K.; Nataraj, S.K.; Sreedhar, B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-iron oxide nanocomposite membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol, 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korin, E.; Ladizhensky, I.; Korngold, E. Hydrophilic hollow fiber membranes for water desalination by the pervaporation method. Chem. Eng. Process. 1996, 35, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.P.; Kruchinina, E.V.; Baklagina, Y.G.; Khripunov, A.K.; Tulupova, O.A. Deep desalination of water by evaporation through polymeric membranes. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2007, 80, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, M.; Jiang, J.; Templeton, M.; Huth, E.; Brant, J.; Bond, T. Salt rejection and water flux through a tubular pervaporative polymer membrane designed for irrigation applications. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwijnenberg, H.; Koops, G.; Wessling, M. Solar driven membrane pervaporation for desalination processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 250, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Oh, K.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Yeo, J.G.; Sharma, P. Pervaporative seawater desalination using NaA zeolite membrane: Mechanisms of high water flux and high salt rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, M.C.; Mee, S.; da Costa, J.C. Performance of porous inorganic membranes in non-osmotic desalination. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3998–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, S.; Jansen, J.C.; Kapteijn, F. Production of ultra pure water by desalination of seawater using a hydroxy sodalite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 356, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawski, W.; Krajewska, S.; Kujawski, M.; Gazagnes, L.; Larbot, A.; Persin, M. Pervaporation properties of fluoroalkylsilane (FAS) grafted ceramic membranes. Desalination 2007, 205, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhan, W.; Qi, G.; Lin, S.; Nan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cao, B.; Pan, K. High performance graphene oxide/polyacrylonitrile composite pervaporation membranes for desalination applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5140–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, A.; Toth, A.J.; Haaz, E.; Fozer, D.; Szanyi, A.; Hegyesi, N.; Mizsey, P. Preparation and characterization of PVA/GA/Laponite membranes to enhance pervaporation desalination performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Feng, B. Synthesis of novel graphene oxide-polyimide hollow fiber membranes for seawater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hou, J.; Ye, Y.; Mansouri, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, V. Suppressing Salt Transport through Composite Pervaporation Membranes for Brine Desalination. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitha, B.; Suhanya, D.; Sridhar, S.; Ramakrishna, M. Separation of organic–organic mixtures by pervaporation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 241, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-R.; Teng, M.-Y.; Hsub, T.-N.; Laib, J.-Y. A study on pervaporation of aqueous ethanol solution by modi®ed polyurethane membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 162, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampranpiboon, P.; Jiraratananon, R.; Uttapap, D.; Fenga, X.; Huang, R.Y.M. Pervaporation separation of ethyl butyrate and isopropanol with polyether block amide (PEBA) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, R.; Xiao, Z.; Shi, E.; Yang, J. Preparation and pervaporation performances of fumed-silica-filled polydimethylsiloxane–Polyamide (PA) composite membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 3132–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Wan, Y. Separation of acetone, butanol and ethanol (ABE) from dilute aqueous solutions by silicalite-1/PDMS hybrid pervaporation membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.V.; Kerkhofs, S.; Martens, J.A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. PDMS mixed matrix membranes containing hollow silicalite sphere for ethanol / water separation by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 502, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Fang, M.; Wang, T.; Yu, L.; Li, J. ZIF-7/PDMS mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation recovery of butanol from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 163, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, N.; Ji, S.; Yan, H.; Zhang, G. Nanodisperse ZIF-8/PDMS hybrid membranes for biobutanol permselective pervaporation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 20947–20957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ali, M.; Ilyas, A.; Naik, P.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Gilani, M.A.; Bilad, M.R.; Sajjad, Z.; Khan, A.L. ZIF-67 filled PDMS mixed matrix membranes for recovery of ethanol via pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wee, L.H.; Martens, J.A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. ZIF-71 as a potential filler to prepare pervaporation membranes for bio-alcohol recovery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10034–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Yu, F.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y. Enhanced ethanol recovery of PDMS mixed matrix membranes with hydrophobically modified ZIF-90. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, P.; Cai, D.; Shan, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Qin, P.; Tan, T. Boosting pervaporation performance by promoting organic permeability and simultaneously inhibiting water transport via blending PDMS with COF-300. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, M.; Luque-Alled, J.M.; Gao, L.; Iliut, M.; Prestat, E.; Newman, L.; Haigh, S.J.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Budd, P.M.; Gorgojo, P. Enhanced organophilic separations with mixed matrix membranes of polymers of intrinsic microporosity and graphene-like fillers. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.R.; Buonomenna, M.G.; Golemme, G.; Budd, P.M.; Galiano, F.; Figoli, A.; Friess, K.; Hynek, V. New organophilic mixed matrix membranes derived from a polymer of intrinsic microporosity and silicalite-1. Polymer 2013, 54, 2222–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Wang, N.; Fan, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Ji, S. Enhanced flux of polydimethylsiloxane membrane for ethanol permselective pervaporation via incorporation of MIL-53 particles. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.L.; Wang, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Pebax/POSS mixed matrix membranes for ethanol recovery from aqueous solutions via pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Liu, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Niu, Q. Gasoline desulfurization by a TiO2-filled ethyl cellulose pervaporation membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 43409–43518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Hu, C.; Jiang, Z. Novel ploy(vinyl alcohol)/carbon nanotube hybrid membranes for pervaporation separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 297, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, H.; Pan, F.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Cao, X. Elevated pervaporation performance of polysiloxane membrane using channels and active sites of metal organic framework CuBTC. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 481, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Pan, F.; Yang, S.; Ding, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Cao, X. Enhanced pervaporation performance of MIL-101 (Cr) filled polysiloxane hybrid membranes in desulfurization of model gasoline. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 135, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Fan, B.C.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhu, A.M.; Shi, F.F. A novel poly(dimethyl siloxane)/poly(oligosilsesquioxanes) composite membrane for pervaporation desulfurization. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeć, R.; Meller, M.; Kujawski, W.; Kujawa, J. Polyamide-6 based pervaporation membranes for organic–organic separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 110, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.Q.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, L.G.; Yu, X.Y.; Lin, J.Z.; Shi, S.X. Enhanced performance of polyimide hybrid membranes for benzene separation by incorporating three-dimensional silver-graphene oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 478, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Ji, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.-R. Metal–organic framework/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanohybrid membrane for the pervaporation of toluene/ n -heptane mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 489, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, S.B.; Calle, M.; Li, N. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-H-ZSM-5 zeolite mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation separation of methanol–benzene mixture. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation separation of toluene/alcohol mixtures using silicalite zeolite embedded chitosan mixed matrix membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ji, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, G. Poly(vinyl alcohol)–graphene oxide nanohybrid “pore-filling” membrane for pervaporation of toluene/n-heptane mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qian, L.; Wang, H.; Zhong, W.; Du, Q. Pervaporation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures through rhodium-loaded β-zeolite-filled polyvinyl chloride hybrid membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nanofiller | Polymer Matrix | Dimension | Size (nm) | Application (A/B Separation) | T (°C) | Flux (g m−2 h−1) | Separation Factor (A/B)/Salt Rejection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica | PVA | 0 | <10 | Desalination | 22 | 6930 | 99.5 (%) | [24] |
| CTAB-silica | PTMSP | 0 | - | Butanol/water | 63 | 1044 | 126 | [40] |
| TiO2 | CS | 0 | 100 | Water/ethanol | 80 | 340 | 196 | [26] |
| Ag | Nafion | 0 | - | Benzene/cyclohexane | 25 | 1.6 | 12.65 | [41] |
| GQDs | Alg | 0 | <20 | Water/methanol | 70 | 2323 | 29.5 | [42] |
| GOQDs | NaAlg | 0 | 3.9 | Water/ethanol | 76 | 2432 | 1152 | [43] |
| CNT | PVA | 1 | Length: 500–2000 Outer diameter: < 8 | Desalination | 55 | 11,860 | 99.9 (%) | [44] |
| Fe3O4/CNT | NaAlg | 1 | Fe3O4: 10 CNT diameter: 20–30 CNT length: - | Water/ethanol | 76 | 2211 | 1870 | [45] |
| Attapulgite nanorods | NaAlg | 1 | Length: 300–1000 Outer diameter: 20 | Water/ethanol | 76 | 1356 | 2030 | [46] |
| Titanate nanotubes | PVA | 1 | Length: 100–200 Outer diameter: 10-20 | Water/isopropanol | 50 | ~30 | 5520 | [47] |
| Aluminosilicate nanotubes | PVA | 1 | Length: ~500 Outer diameter: ~2.2 | Water/ethanol | 60 | 333 | - | [48] |
| GO | polyimide | 2 | Lateral size: <1000 Thickness: <2 | Water/isopropanol | 60 | 161.5 | >5000 | [49] |
| MXene | CS | 2 | Lateral size: 500–1000 Thickness: 1–2 | Water/ethanol | 50 | 1424 | 1421 | [50] |
| g-C3N4 | NaAlg | 2 | Lateral size: - Thickness: ~0.96 | Water/ethanol | 76 | 2469 | 1635 | [51] |
| MoS2 | Pebax | 2 | Lateral size: 1000–2000 Thickness: 6 | Thiophene/n-octane | 60 | 11,420 | - | [52] |
| ZSM-5 | PDMS | 3 | 4900 | Ethanol/water | 40 | 408 | 14 | [53] |
| zeolite 4A | polyimide | 3 | 300–400 | Water/isopropanol | 30 | 18 | 8991 | [54] |
| ZIF-71 | PEBA | 3 | 1000 | Butanol/acetone–ethanol–water | 37 | 96.8 | 18.8 | [55] |
| Na+-MMT | PVA | 3 | 800 | Water/isopropanol | 30 | 51 | 1116 | [56] |
| CMS | PDMS | 3 | <50,000 | Benzene/water | 40 | ~140 | 9000 | [57] |
| GOF | PVA | 3 | Lateral size: - Thickness: 6.5–9.1 | Water/ethanol | 70 | ~300 | 330 | [58] |
| Nanofiller | Polymer Matrix | Solvent | Water in Feed (wt%) | T (°C) | Flux (g m−2 h−1) | Separation Factor | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH2-MIL-125 | NaAlg | Acetic acid | 10 | 30 | 196.7 | 328.1 | [116] |
| rGO/GQD | Alg | Methanol | 30 | 70 | 2323 | 29.5 | [42] |
| zeolite 4A | PVA | Ethanol | 23.57 | 60 | 936 | 710 | [114] |
| Fe3O4/CNT | NaAlg | Ethanol | 10 | 76 | 2211 | 1870 | [45] |
| Attapulgite nanorods | NaAlg | Ethanol | 10 | 76 | 1356 | 2030 | [46] |
| GOQDs | NaAlg | Ethanol | 10 | 76 | 2432 | 1152 | [43] |
| NaA zeolite | Poly(acrylic acid) sodium | Ethanol | 10 | 30 | 533.2 | 435.7 | [117] |
| g-C3N4 | NaAlg | Ethanol | 10 | 76 | 2469 | 1653 | [51] |
| Cu3(BTC)2 | Polyimide | Ethanol | 10 | 42 | 430 | ~200 | [118] |
| MXene | CS | Ethyl acetate | 2 | 50 | 1471 | 4898 | [50] |
| UiO-66 | Polyimide | Isopropanol | 15 | 60 | 225.9 | 2209 | [78] |
| GO | Polyamide | Isopropanol | 10 | 70 | 6593 | 1491 | [74] |
| ZIF-8 | PVA | Isopropanol | 10 | 30 | 952 | 91 | [100] |
| GO | Polyetherimide | Butanol | 5 | 50 | 1100.26 | 89.39 | [75] |
| Fe3O4 | PVA | Tetrahydrofuran | 5 | 30 | 95 | 519 | [119] |
| Nanofiller | Polymer Matrix | NaCl in Feed (wt%) | T (°C) | Flux (g m−2 h−1) | Salt Rejection (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO | CS | 3.5 | 60 | 17,700 | 99.9 | [23] |
| GO | polyimide | 3.5 | 90 | 15,600 | 99.8 | [130] |
| GO | PVA | 10 | 65 | 28,000 | 99.9 | [131] |
| silica | PVA | 0.2 | 22 | 6930 | 99.5 | [24] |
| CNT | PVA | 3.5 | 55 | 11,860 | 99.9 | [44] |
| Laponite | PVA | 3 | 60 | 51,200 | 99.9 | [129] |
| Nanofiller | Polymer Matrix | Permeate | Water in Feed (wt%) | T (°C) | Flux (g m−2 h−1) | Separation Factor | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSM-5 | PDMS | Ethanol | 95 | 40 | 408 | 14 | [53] |
| CMS | PDMS | Benzene | 99.95 | 45 | 145 | 11,750 | [57] |
| MAF-6 | PDMS | Ethanol | 95 | 40 | 1200 | 14.9 | [90] |
| COF-300 | PDMS | Furfural | 95 | 80 | 2136 | 39.6 | [143] |
| ZIF-90 | PDMS | Ethanol | 95 | 60 | 99.5 | 15.1 | [142] |
| MIL-53 | PDMS | Ethanol | 95 | 70 | 5467 | 11.1 | [146] |
| Silica | PTMSP | Butanol | 98.5 | 63 | 165 | 126 | [40] |
| rGO | PIM-1 | Butanol | 95 | 65 | 649.7 | 27.1 | [144] |
| ZIF-71 | PEBA | Butanol | 98.8 | 37 | 96.8 | 18.8 | [55] |
| POSS | Pebax | Ethanol | 95 | 25 | 183.5 | 4.6 | [147] |
| Nanofiller | Polymer Matrix | Permeate | Feed | T (°C) | Flux (g m−2 h−1) | Separation Factor | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POSS | PDMS | Benzene | Benzene/n-heptane | 70 | ~82 | ~3.5 | [152] |
| POSS | PDMS | Thiophene | Thiophene /n-heptane | 70 | ~125 | ~4.2 | [152] |
| POSS | PDMS | Toluene | Toluene/n-heptane | 70 | ~70 | ~3.3 | [152] |
| Al2O3 | Polyamide | Methanol | Methanol/MTBE | 30 | 476 | 20 | [153] |
| Ag-GO | Polyimide | Benzene | Benzene/cyclohexane | 30 | 1560 | 35 | [154] |
| Cu3(BTC)2 | PVA | Toluene | Toluene/n-heptane | 40 | 133 | 17.9 | [155] |
| Zeolite | PVA | Methanol | Methanol/benzene | 30 | 71.03 | 47 | [156] |
| Silicalite | CS | Toluene | Toluene/methanol | 30 | 19 | 264 | [157] |
| GO | PVA | Toluene | Toluene/n-heptane | 40 | 27 | 12.9 | [158] |
| Zeolite | Polyvinyl chloride | Benzene | Benzene/cyclohexane | 80 | 329.7 | 8.04 | [159] |
| Ag/CNT | Polyurethane | Benzene | Benzene/cyclohexane | 30 | 2375 | 64.8 | [66] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, G.; Xie, Z.; Cran, M.; Wu, C.; Gray, S. Dimensional Nanofillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Pervaporation Separations: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090193
Yang G, Xie Z, Cran M, Wu C, Gray S. Dimensional Nanofillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Pervaporation Separations: A Review. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090193
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Guang, Zongli Xie, Marlene Cran, Chunrui Wu, and Stephen Gray. 2020. "Dimensional Nanofillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Pervaporation Separations: A Review" Membranes 10, no. 9: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090193
APA StyleYang, G., Xie, Z., Cran, M., Wu, C., & Gray, S. (2020). Dimensional Nanofillers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for Pervaporation Separations: A Review. Membranes, 10(9), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090193