Transport Properties and Mechanical Features of Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone/Organosilica Layered Materials Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sulfonation of Polyether Ether Ketone
2.3. Synthesis of Organsilica Layered Materials
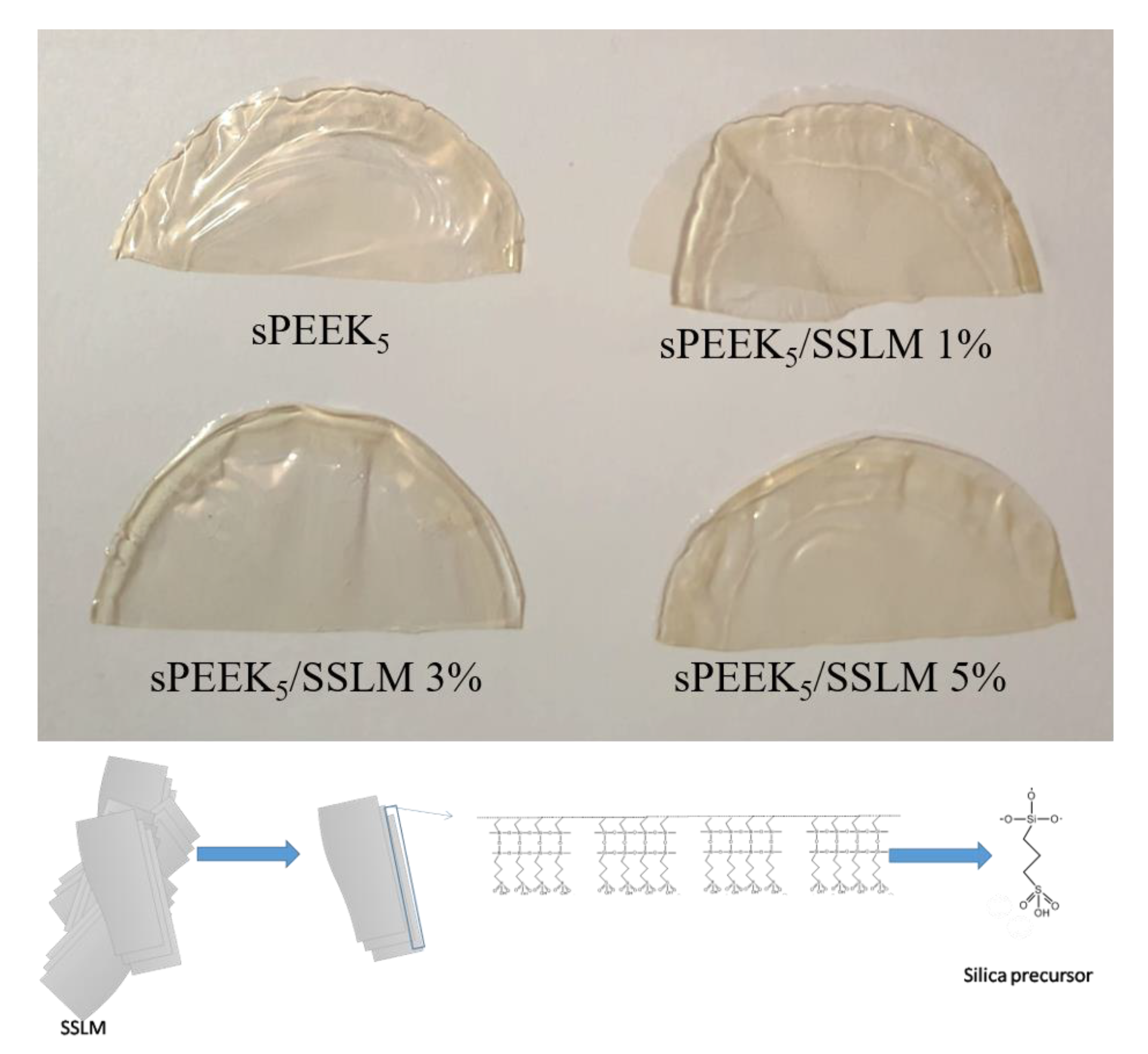
2.4. Membrane Preparation
2.5. Characterization
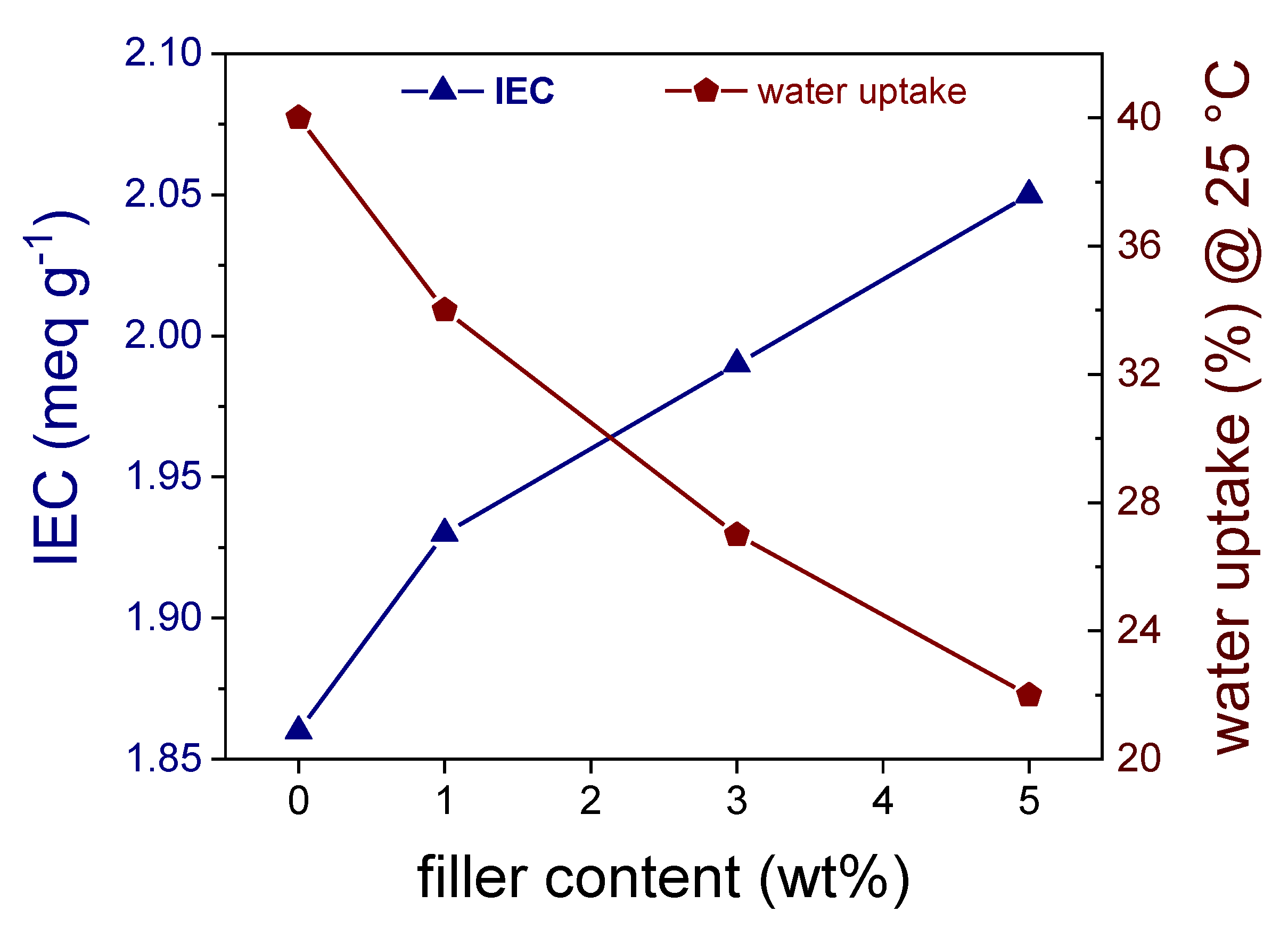
2.5.1. Ion Exchange Capacity, Sulfonation Degree and Water Uptake
2.5.2. NMR
2.5.3. Proton Conductivity
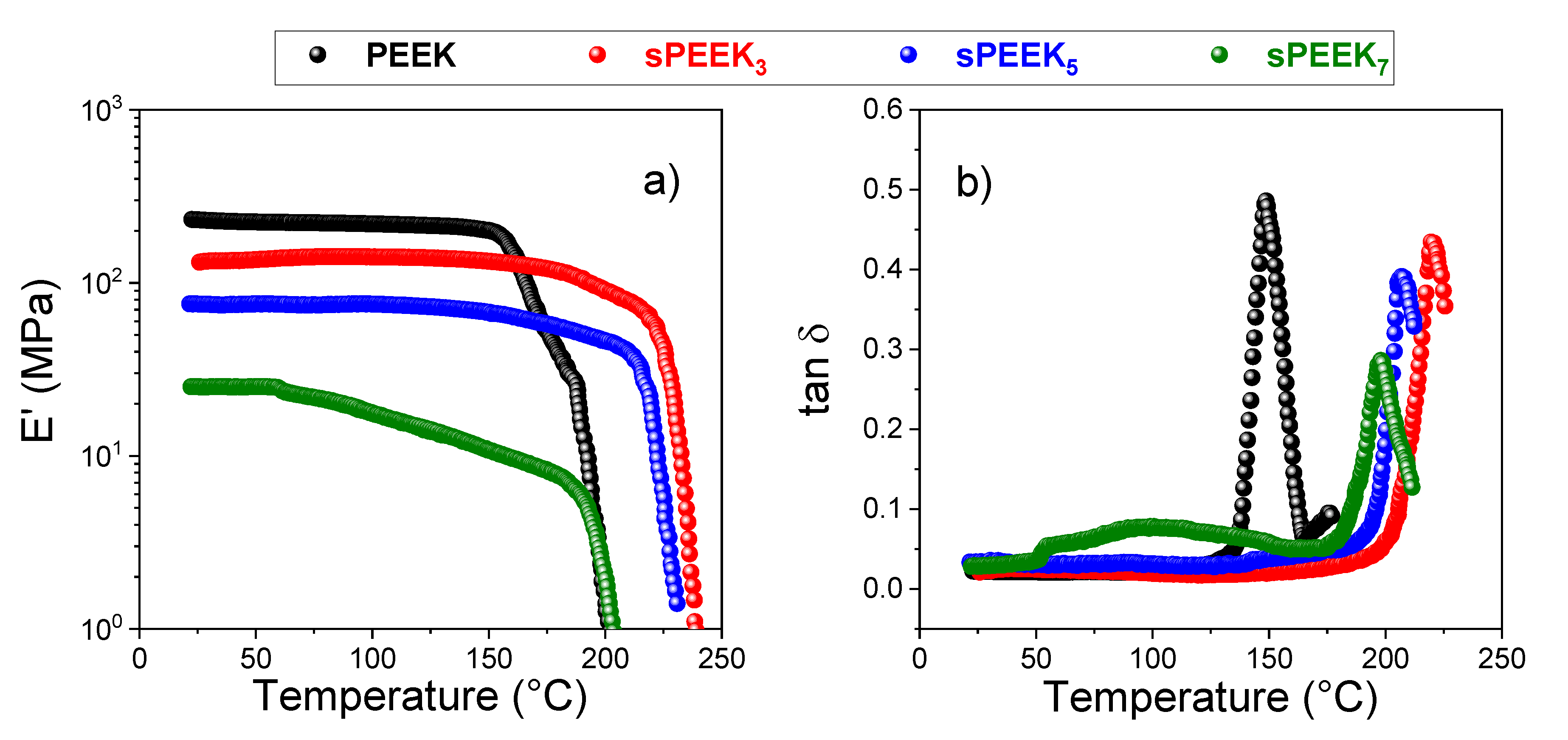
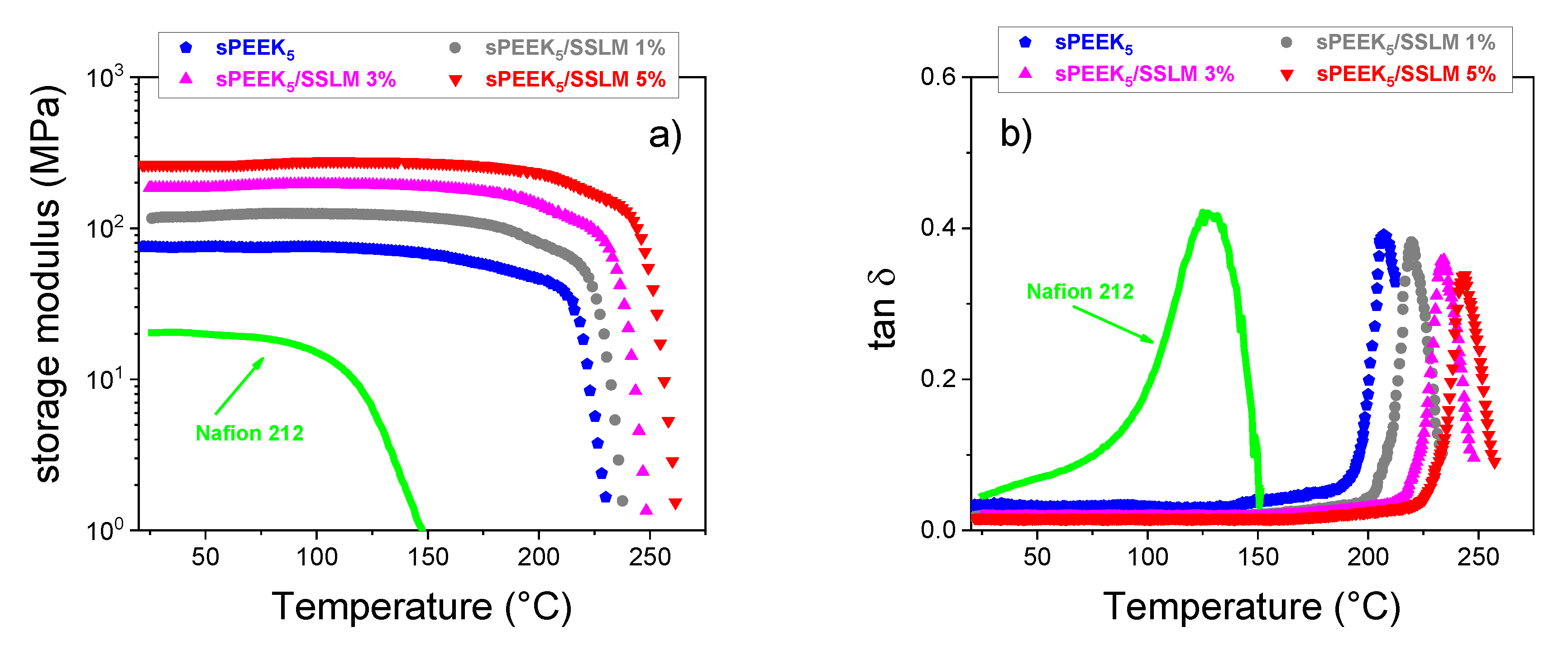
2.5.4. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
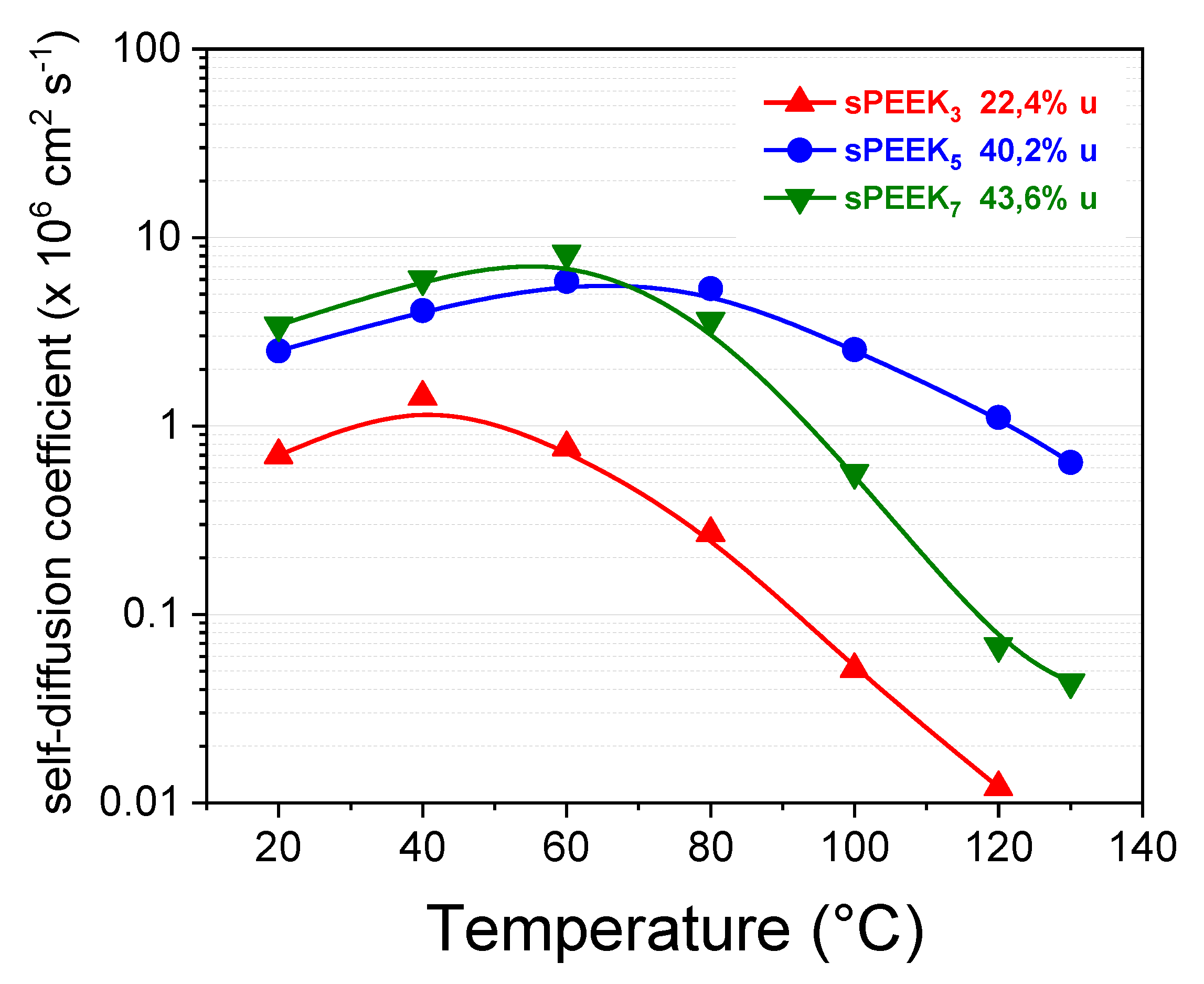
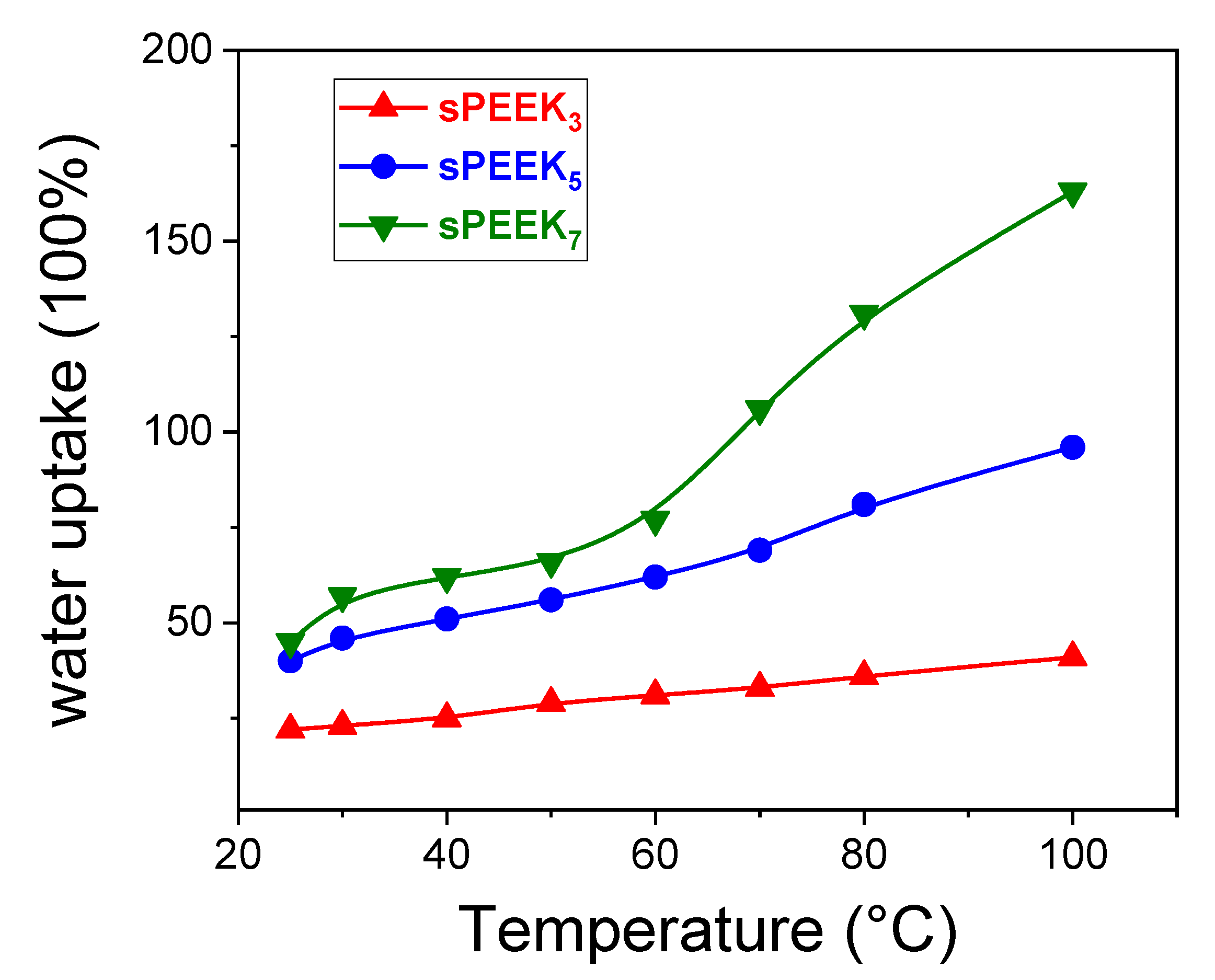
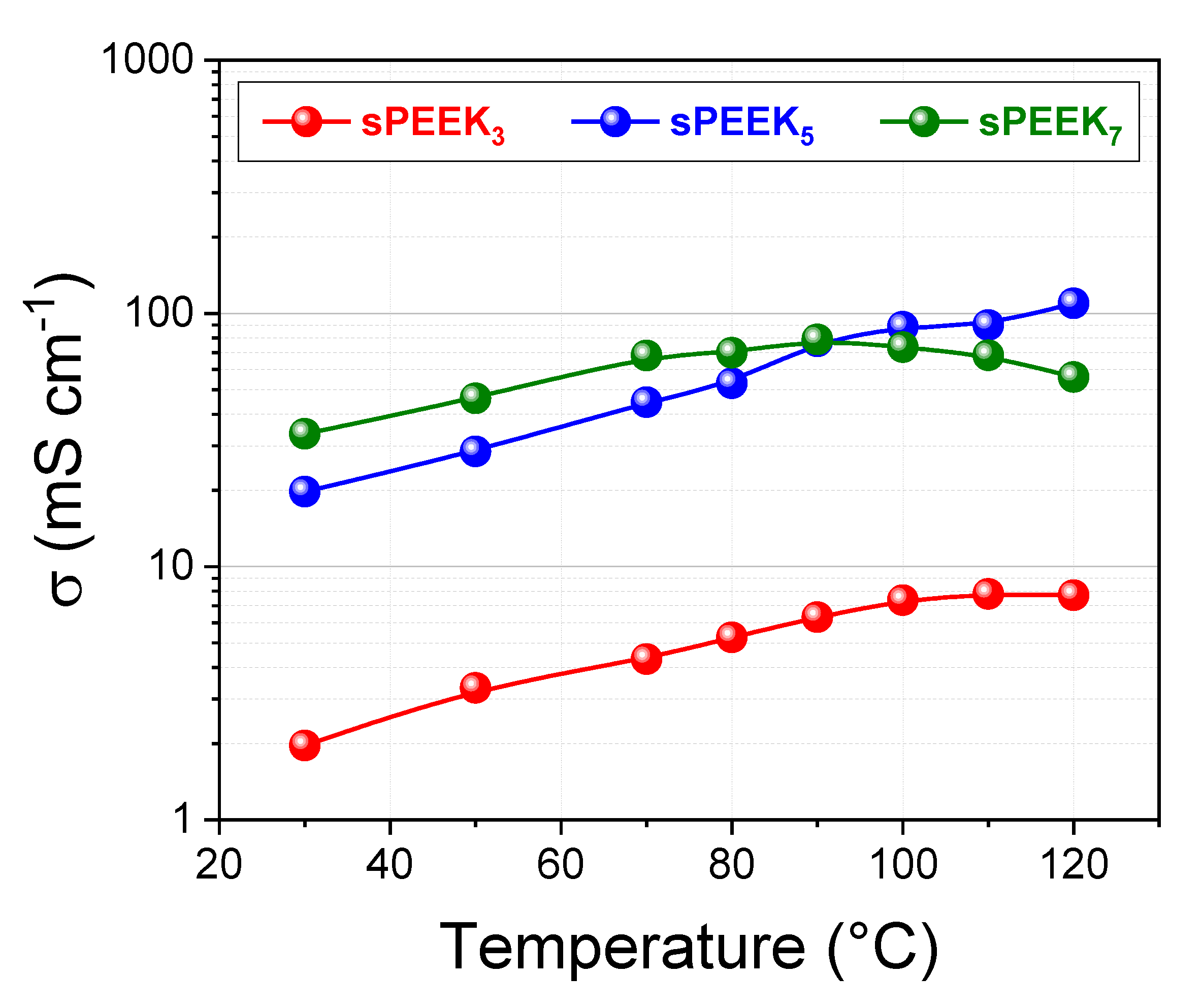
3.1. Effect of the Sulfonation Degree on sPEEK Membrane Properties
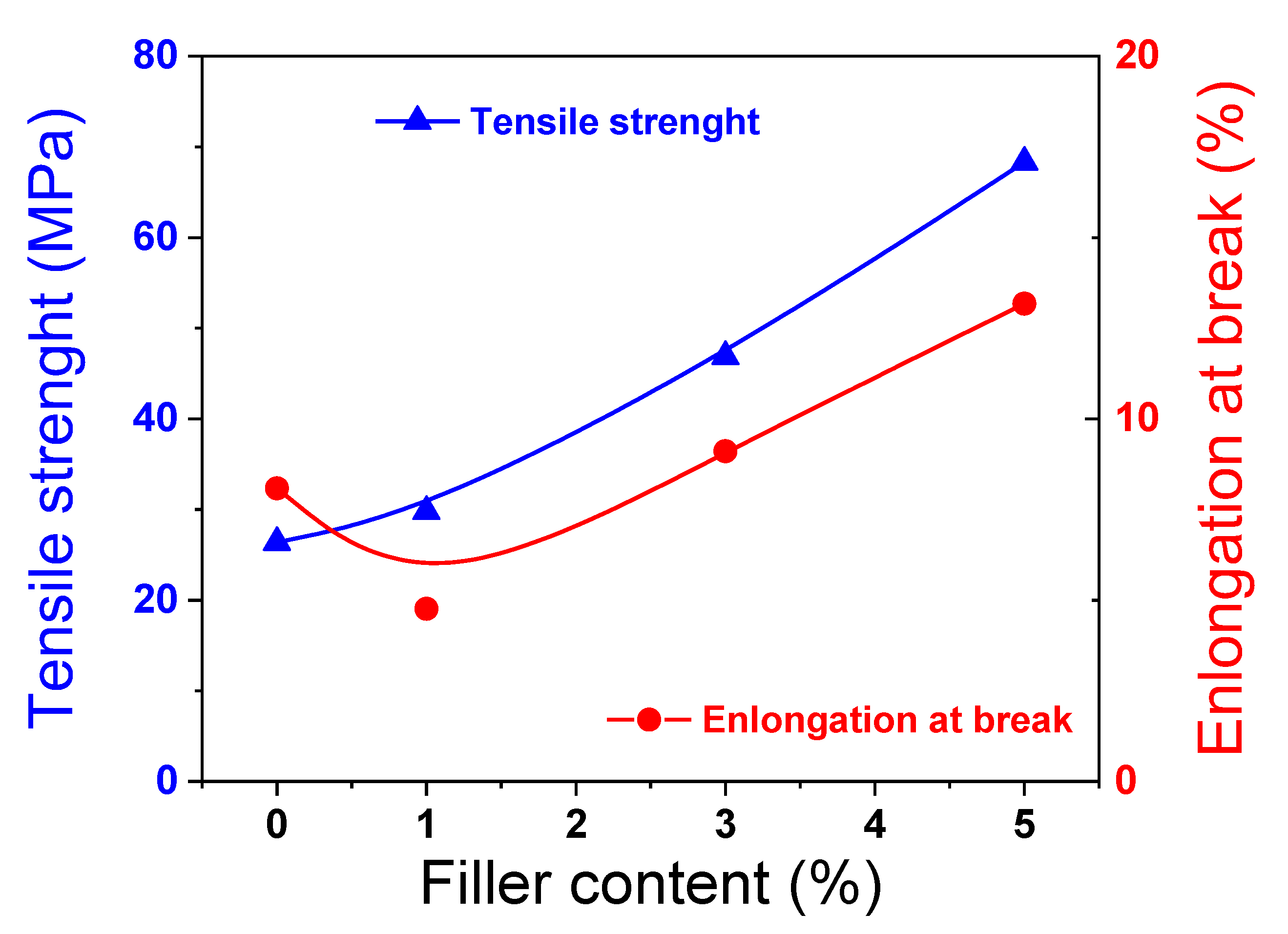
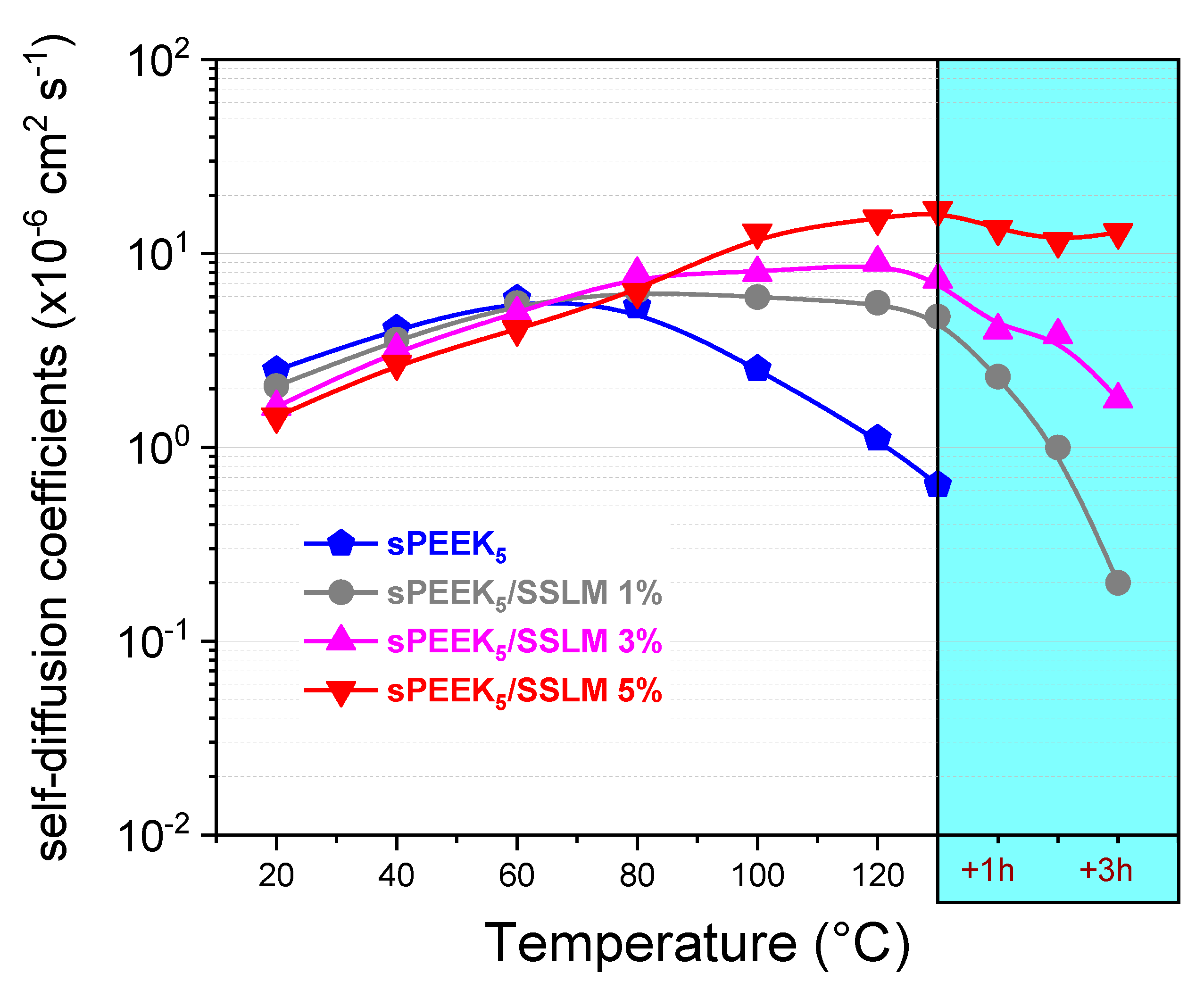
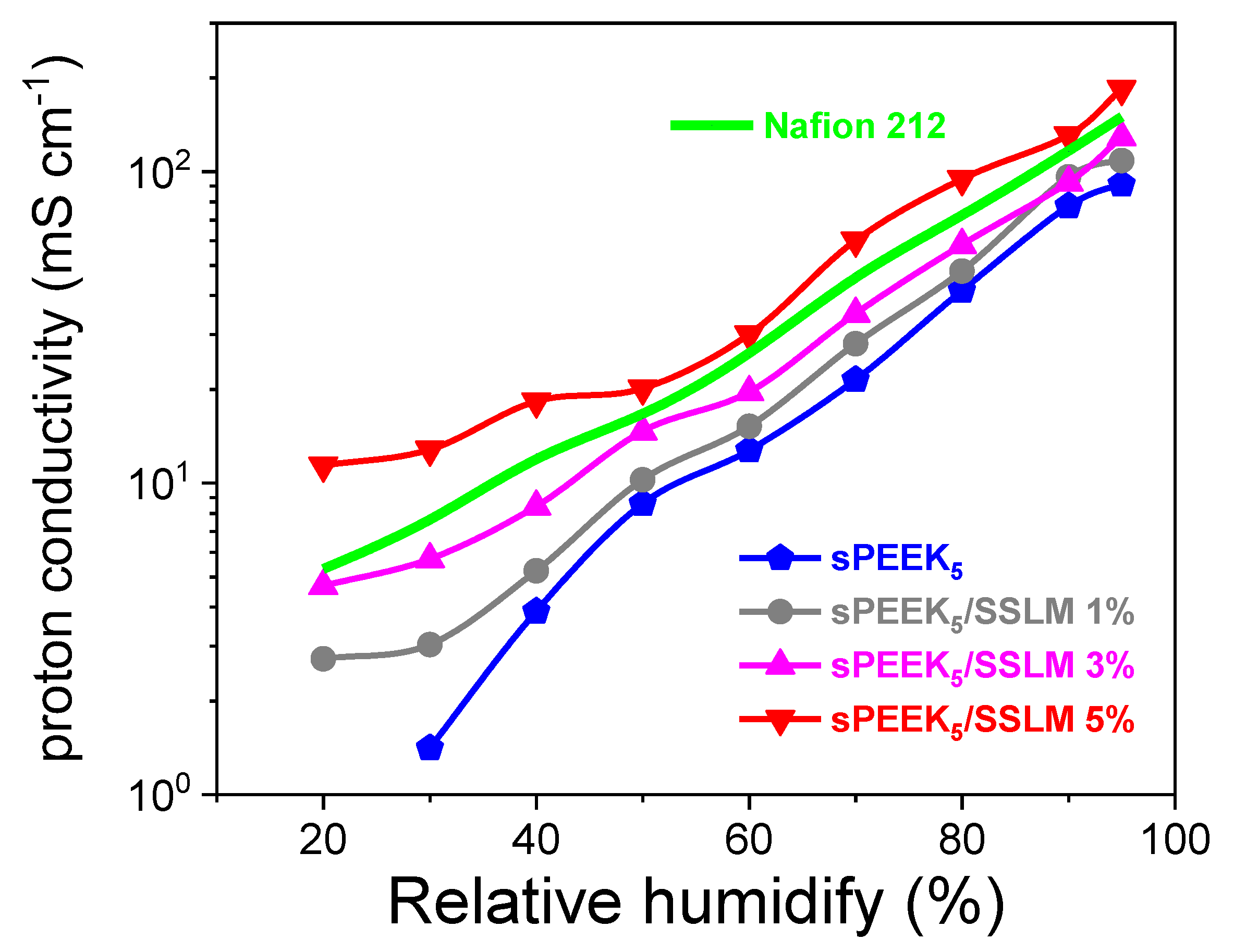
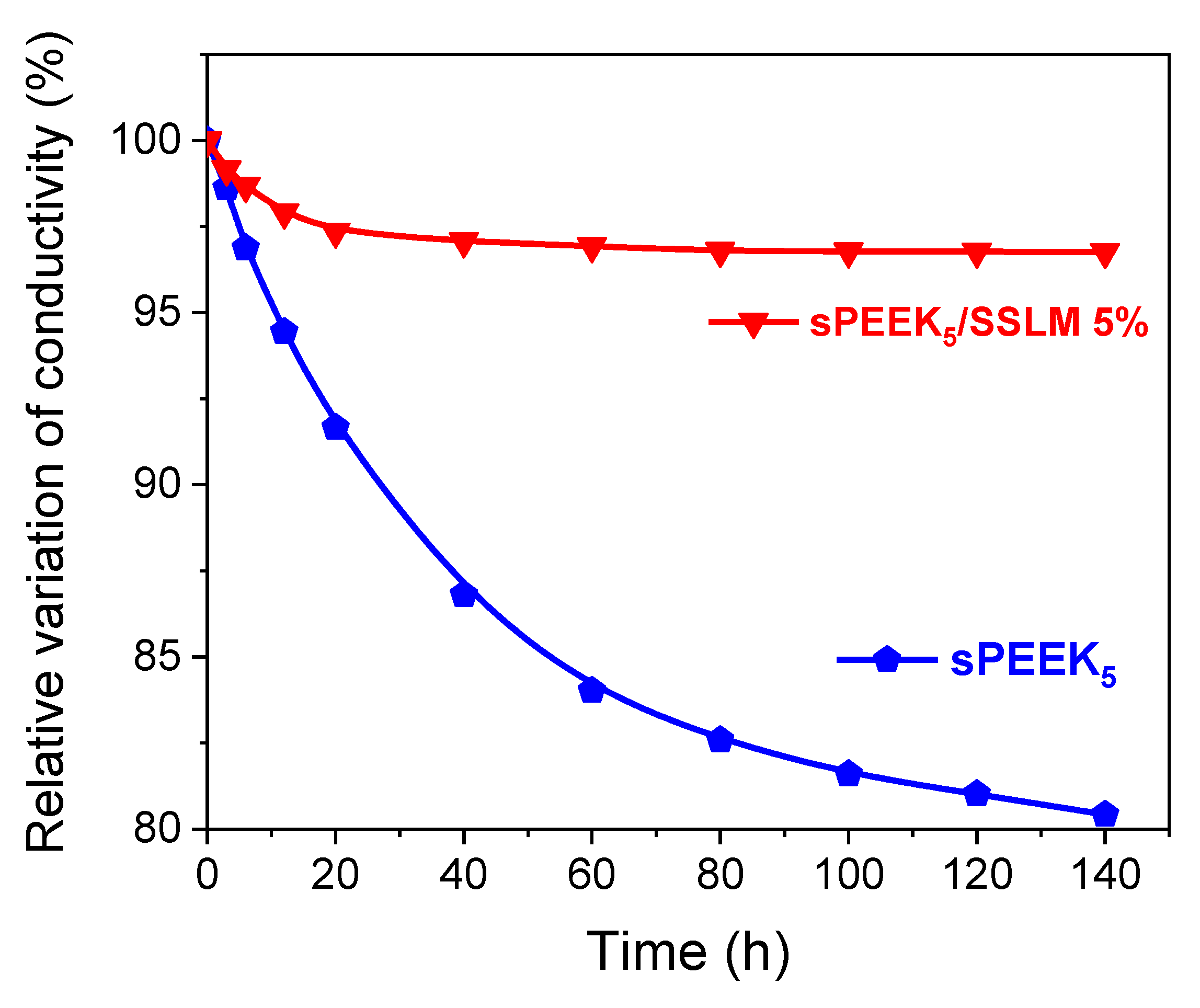
3.2. sPEEK-SSLM Nanocomposite Membrane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steele, B.C.H.; Heinzel, A. Materials for Fuel-Cell Technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, P.K. Recent development of polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2780–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of understanding of nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasile, N.S.; Monteverde Videla, A.H.A.; Simari, C.; Nicotera, I.; Specchia, S. Influence of membrane-type and flow field design on methanol crossover on a single-cell DMFC: An experimental and multi-physics modeling study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27995–28010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandrasits, M.; Lindell, M.; Schaberg, M.; Kurkowski, M. Increasing fuel cell efficiency by using ultra-low equivalent weight ionomers. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2017, 26, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossari, P.; Simari, C.; Cannavale, A.; Gigli, G.; Nicotera, I. Advanced processing and characterization of Nafion electrolyte films for solid-state electrochromic devices fabricated at room temperature on single substrate. Solid State Ionics 2018, 317, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, A.S.; Sebastian, D.; Schuster, M.; Bauer, B.; D’Urso, C.; Lufrano, F.; Baglio, V. Selectivity of direct methanol fuel cell membranes. Membranes 2015, 5, 793–809. [Google Scholar]
- Savadogo, O. Emerging membranes for electrochemical system. I. Solid polymer membranes for fuel cell systems. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2015, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Inzelt, G.; Pineri, M.; Schultze, J.W.; Vorotyntsev, M.A. Electron and proton conducting polymers: Recent developments and prospects. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2403–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houchins, C.; Kleen, G.J.; Spendelow, J.S.; Kopasz, J.; Peterson, D.; Garland, N.L.; Ho, D.L.; Marcinkoski, J.; Martin, K.E.; Tyler, R.; et al. U.S. doe progress towards developing low-cost, high performance, durable polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications. Membranes 2012, 2, 855–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Zhang, G.; Nam, C.; Chung, T.C.M. Characterization of polyethylene-Graft-sulfonated polyarylsulfone proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. Membranes 2015, 5, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savinell, R.F.; Litt, M.H. Proton Conducting Polymers Used as Membranes. US Patent 5525436, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kerres, J.; Ullrich, A.; Meier, F.; Haring, T. Synthesis and characterization of novel acid—Base polymer blends for application in membrane fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 1999, 125, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Kosma, V.; Simari, C.; Angioni, S.; Mustarelli, P.; Quartarone, E. Ion dynamics and mechanical properties of sulfonated polybenzimidazole membranes for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi Tashvigh, A.; Luo, L.; Chung, T.S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C. A novel ionically cross-linked sulfonated polyphenylsulfone (sPPSU) membrane for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Ghil, L.J. Annealing effect of highly sulfonated polyphenylsulfone polymer. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 11794–11800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Ohira, A.; Nakao, H. Chemically crosslinked sulfonated polyphenylsulfone (CSPPSU) membranes for PEM fuel cells. Membranes 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D. On the development of proton conducting polymer membranes for hydrogen and methanol fuel cells. J. Memb. Sci. 2001, 185, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Casciola, M.; Massinelli, L.; Bauer, B. Polymeric proton conducting membranes for medium temperature fuel cells (110–160 °C). J. Memb. Sci. 2001, 185, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bonis, C.; Simari, C.; Kosma, V.; Mecheri, B.; D’Epifanio, A.; Allodi, V.; Mariotto, G.; Brutti, S.; Suarez, S.; Pilar, K.; et al. Enhancement of proton mobility and mitigation of methanol crossover in sPEEK fuel cells by an organically modified titania nanofiller. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnadio, A.; Casciola, M.; Di Vona, M.L.; Tamilvanan, M. Conductivity and hydration of sulfonated polyethersulfone in the range 70–120 °C: Effect of temperature and relative humidity cycling. J. Power Sources 2012, 205, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Vecchio, C.L.; Enotiadis, A.; Davoli, M.; Baglio, V.; Nicotera, I. Toward optimization of a robust low-cost sulfonated-polyethersulfone containing layered double hydroxide for PEM fuel cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 47884, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Donnadio, A.; Jun, M.S.; Di Vona, M.L. Crosslinked SPES-SPPSU membranes for high temperature PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, F.; Gatto, I.; Staiti, P.; Antonucci, V.; Passalacqua, E. Sulfonated polysulfone ionomer membranes for fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 2001, 145, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.A. Development of ionomer membranes for fuel cells. J. Memb. Sci. 2001, 185, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, F.; Squadrito, G.; Patti, A.; Passalacqua, E. Sulfonated polysulfone as promising membranes for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 77, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Basile, A. Sulfonated PEEK-based polymers in PEMFC and DMFC applications: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 15241–15255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguti, C.A.; Dahmouche, K.; De Gomes, A.S. Nanostructure and properties of proton-conducting sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK) and zirconia-SPEEK hybrid membranes for direct alcohol fuel cells: Effect of the nature of swelling solvent and incorporation of heteropolyacid. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučera, F.; Jančář, J. Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Sulfonation of Polymers: A Review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.M.J.; Mikhailenko, S.D.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D.; Kaliaguine, S. Proton conducting composite membranes from polyether ether ketone and heteropolyacids for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 173, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, R.S.L.; Zhang, K.; Ladewig, B.P. The effects of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) ion exchange preparation conditions on membrane properties. Membranes 2013, 3, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Fu, R.; Wu, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Xu, T. Acid-base hybrid polymer electrolyte membranes based on SPEEK. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 350, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Kim, N.H.; Jung, D.; Lee, J.H. Enhanced mechanical properties and proton conductivity of Nafion-SPEEK-GO composite membranes for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 458, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, X.; Qian, H.; Xu, J.; Yue, Z.; Zou, Z.; Yang, H. Cross-linked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) electrolytes bearing pendent imidazole groups for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Polini, R.; Di Vona, M.L.; Liu, X.; Sgreccia, E.; Chailan, J.F.; Knauth, P. Thermal crosslinked and nanodiamond reinforced SPEEK composite membrane for PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 3346–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Silicate-based polymer-nanocomposite membranes for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 842–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, E.; Erdener, H.; Akay, R.G.; Yücel, H.; Baç, N.; Eroǧlu, I.I. Effects of sulfonated polyether-etherketone (SPEEK) and composite membranes on the proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Fu, T.; Shi, Y.; Na, H. Composite membranes based on highly sulfonated PEEK and PBI: Morphology characteristics and performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 308, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gogel, V.; Friedrich, K.A.; Kerres, J. Novel covalently cross-linked poly(etheretherketone) ionomer membranes. J. Power Sources 2006, 155, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, D.; Koshikawa, H.; Asano, M.; Maekawa, Y. Crosslinking and grafting of polyetheretherketone film by radiation techniques for application in fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Ma, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Han, M.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Na, H. Composite membranes based on a novel benzimidazole grafted PEEK and SPEEK for fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 11172–11179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J. Advances in the development of inorganic-organic membranes for fuel cell applications. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2008, 215, 219–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mecheri, B.; D’Epifanio, A.; Di Vona, M.L.; Traversa, E.; Licoccia, S.; Miyayama, M. Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone-Based Composite Membranes Doped with a Tungsten-Based Inorganic Proton Conductor for Fuel Cell Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Kuila, T.; Kim, N.H.; Ku, B.C.; Lee, J.H. Enhanced mechanical properties of silanized silica nanoparticle attached graphene oxide/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 79, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Sulfonated graphene oxide-silica for highly selective Nafion-based proton exchange membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16083–16092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Salarizadeh, P.; Sabooni Asre Hazer, M.; Hosseinabadi, P.; Kashefi, S.; Beydaghi, H. The effect of adding sulfonated SiO2 nanoparticles and polymer blending on properties and performance of sulfonated poly ether sulfone membrane: Fabrication and optimization. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 295, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha Rani, G.; Beera, M.K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Development of Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/ Zirconium Titanium Phosphate Composite Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, E45–E56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarizadeh, P.; Javanbakht, M.; Pourmahdian, S.; Bagheri, A.; Beydaghi, H.; Enhessari, M. Surface modification of Fe2TiO5 nanoparticles by silane coupling agent: Synthesis and application in proton exchange composite membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 472, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailenko, S.D.; Zaidi, S.M.J.; Kaliaguine, S. Sulfonated polyether ether ketone based composite polymer electrolyte membranes. Catal. Today 2001, 67, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecheri, B.; D’Epifanio, A.; Traversa, E.; Licoccia, S. Sulfonated polyether ether ketone and hydrated tin oxide proton conducting composites for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2008, 178, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarizadeh, P.; Bagheri, A.; Beydaghi, H.; Hooshyari, K. Enhanced properties of SPEEK with incorporating of PFSA and barium strontium titanate nanoparticles for application in DMFCs. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 4840–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarizadeh, P.; Javanbakht, M.; Pourmahdian, S.; Hazer, M.S.A.; Hooshyari, K.; Askari, M.B. Novel proton exchange membranes based on proton conductive sulfonated PAMPS/PSSA-TiO 2 hybrid nanoparticles and sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) for PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 3099–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Khalfan, A.; Goenaga, G.; Zhang, T.; Bocarsly, A.; Greenbaum, S. NMR investigation of water and methanol mobility in nanocomposite fuel cell membranes. Ionics 2008, 14, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. Sulfonated polyether ether ketone-sulfonated graphene oxide composite membranes for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Mishra, A.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, J.H. Synthesis of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/layered double hydroxide nanocomposite membranes for fuel cell applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 272, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Rodriguez, J.L.; Escorihuela, J.; García-Bernabé, A.; Giménez, E.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Compañ, V. Proton conducting electrospun sulfonated polyether ether ketone graphene oxide composite membranes. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 53481–53491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Kang, B.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Wang, W. Enhanced proton conductivity of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membranes at elevated temperature by incorporating (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane-grafted graphene oxide. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Nam, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.; Cho, S.M.; Jung, C.H.; Choi, H.G.; Chang, Y.; Kwon, Y.; Nam, J. Methanol and proton transport control by using layered double hydroxide nanoplatelets for direct methanol fuel cell. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Potsi, G.; Policicchio, A.; Perrotta, I.; Nicotera, I. Clay-Carbon Nanotubes Hybrid Materials for Nanocomposite Membranes: Advantages of Branched Structure for Proton Transport under Low Humidity Conditions in PEMFCs. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Nam, J. Optimum ionic conductivity and diffusion coefficient of ion-exchange membranes at high methanol feed concentrations in a direct methanol fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2006, 157, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Stallworth, P.; Peng, J.; Coppola, L.; Greenbaum, S.; Nicotera, I. Graphene oxide and sulfonated-derivative: Proton transport properties and electrochemical behavior of Nafion-based nanocomposites. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 297, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Simari, C.; Coppola, L.; Zygouri, P.; Gournis, D.; Brutti, S.; Minuto, F.D.; Aricò, A.S.; Sebastian, D.; Baglio, V. Sulfonated graphene oxide platelets in nafion nanocomposite membrane: Advantages for application in direct methanol fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.K.; Park, S.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, K.H.; Min, S.K.; Rhee, H.W. Characterization of polymer-layered silicate nanocomposite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, E.; Simari, C.; Lo Vecchio, C.; Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V.; Nicotera, I. Barrier properties of sulfonated polysulfone/layered double hydroxides nanocomposite membrane for direct methanol fuel cell operating at high methanol concentrations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Angjeli, K.; Coppola, L.; Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V. NMR and electrochemical investigation of the transport properties of methanol and water in Nafion and clay-nanocomposites membranes for DMFCs. Membranes 2012, 2, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enotiadis, A.; Boutsika, L.G.; Spyrou, K.; Simari, C.; Nicotera, I. A facile approach to fabricating organosilica layered material with sulfonic groups as an efficient filler for polymer electrolyte nanocomposites. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9489–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Simari, C.; Boutsika, L.G.; Coppola, L.; Spyrou, K.; Enotiadis, A. NMR investigation on nanocomposite membranes based on organosilica layered materials bearing different functional groups for PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27940–27949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Kar, K.K. Impact of degree of sulfonation on microstructure, thermal, thermomechanical and physicochemical properties of sulfonated poly ether ether ketone. Polymer 2017, 109, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Lufrano, E.; Coppola, L.; Nicotera, I. Composite gel polymer electrolytes based on organo-modified nanoclays: Investigation on lithium-ion transport and mechanical properties. Membranes 2018, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneduci, A.; Corrente, G.A.; Fabiano, E.; Maltese, V.; Cospito, S.; Ciccarella, G.; Chidichimo, G.; Gigli, G.; Capodilupo, A.L. Orthogonal electronic coupling in multicentre arylamine mixed-valence compounds based on a dibenzofulvene-thiophene conjugated bridge. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8960–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Baglio, V.; Lo Vecchio, C.; Aricò, A.S.; Agostino, R.G.; Coppola, L.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Nicotera, I. Reduced methanol crossover and enhanced proton transport in nanocomposite membranes based on clay−CNTs hybrid materials for direct methanol fuel cells. Ionics 2017, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.E. Use of the stimulated echo in NMR diffusion studies. J. Chem Phys. 1970, 52, 2523–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simari, C.; Enotiadis, A.; Lo Vecchio, C.; Baglio, V.; Coppola, L.; Nicotera, I. Advances in hybrid composite membranes engineering for high-performance direct methanol fuel cells by alignment of 2D nanostructures and a dual-layer approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Simari, C.; Agostini, M.; Enotiadis, A.; Brutti, S. A Novel Li + - Na fi on-Sulfonated Graphene Oxide Membrane as Single Lithium-Ion Conducting Polymer Electrolyte for Lithium Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 27406–27416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.T.; Karasz, F.E.; Russo, P.S.; Langley, K.H. Solubility and Properties of a Poly(aryl ether ketone) in Strong Acids. Macromolecules 1985, 18, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, L.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Proton exchange membranes from sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) reinforced with silica nanoparticles. High Perform. Polym. 2013, 25, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, J.; Weng, G.M.; Alhabeb, M.; Maleski, K.; Antonio, F.; Kong, J.; Gogotsi, Y.; Taylor, A.D. Mechanically strong and electrically conductive multilayer MXene nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 20295–20300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katti, K.S.; Katti, D.R. Why is nacre so tough and strong? Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B.; Cao, S.; Liu, J. Polydopamine-modified graphene oxide nanocomposite membrane for proton exchange membrane fuel cell under anhydrous conditions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9548–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, S.; Kulshrestha, V. Dramatic improvement in water retention and proton conductivity in electrically aligned functionalized CNT/SPEEK nanohybrid PEM. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, G.; Bhat, S.D. Carbon-Polymer Nanocomposite Membranes as Electrolytes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. In Membrane Technology; Sridhar, S., Ed.; Taylor and Francis(CrC press): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 299–316. ISBN 9781138095427. [Google Scholar]
- Rambabu, G.; Sasikala, S.; Bhat, S.D. Nanocomposite membranes of sulfonated poly(phthalalizinone ether ketone)-sulfonated graphite nanofibers as electrolytes for direct methanol fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 107507–107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrin, H.; Higgins, D.; Jun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fowler, M. Functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposite membrane for low humidity and high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 20774–20781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, S.; Sharma, P.P.; Kulshrestha, V.; Jha, P.K. SGO/SPES-based highly conducting polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5595–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.P.; Thakur, A.K.; Shahi, V.K. Sulfonated polyimide/acid-functionalized graphene oxide composite polymer electrolyte membranes with improved proton conductivity and water-retention properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16993–17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Cho, C.G. Preparation of poly(vinyl phosphate-b-styrene) copolymers and its blend with PPO as proton exchange membrane for DMFC applications. Solid State Ionics 2006, 177, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
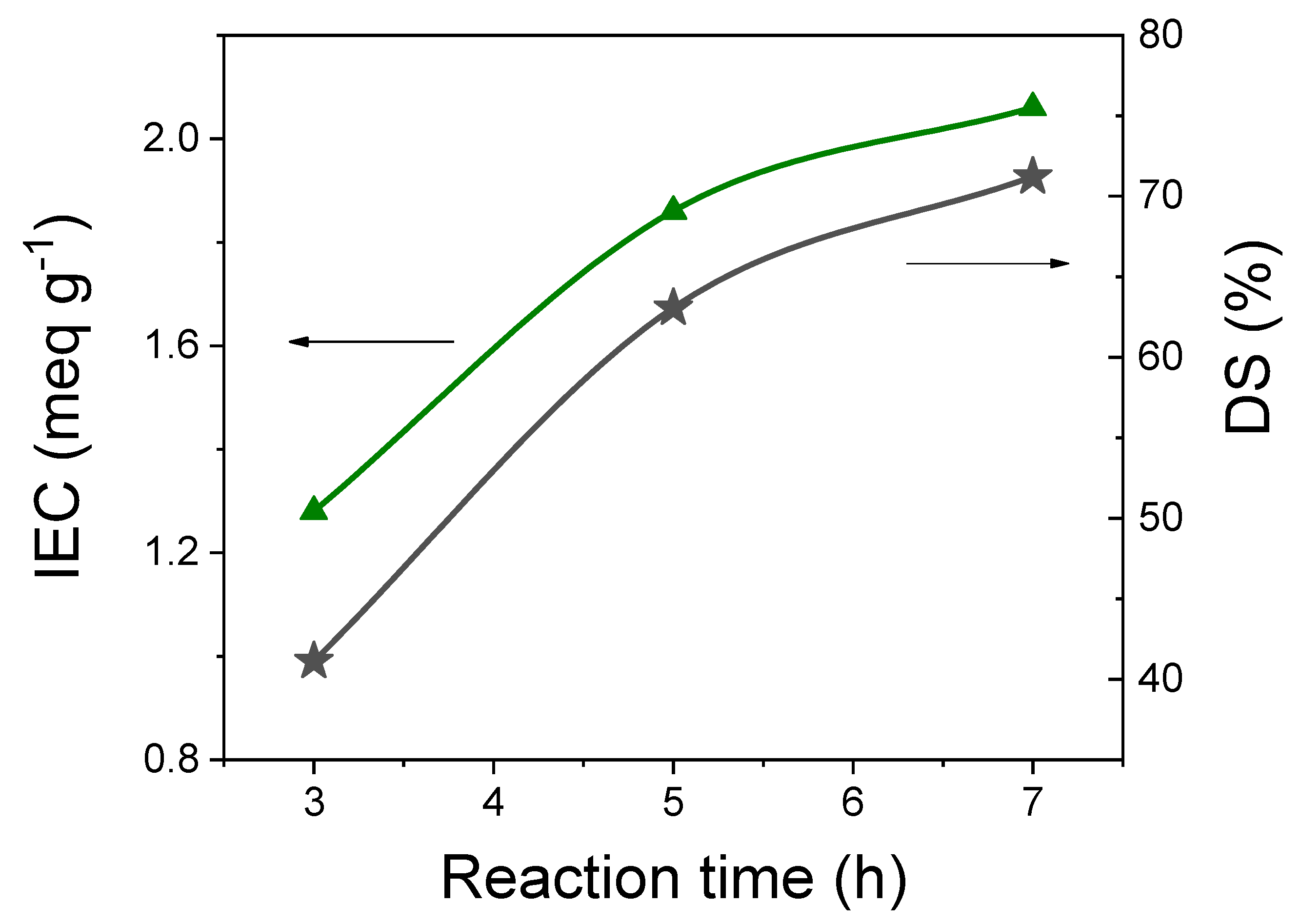
| Sample | Reaction Time [h] | IEC [meq g−1] | DS [%] | Water Uptake @ 25 °C [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEEK | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| sPEEK3 | 3 | 1.28 | 41 | 22 |
| sPEEK5 | 5 | 1.86 | 64 | 40 |
| sPEEK7 | 7 | 2.06 | 71 | 44 |
| Membrane | Temperature [°C] | Relative Humidity [%] | Proton Conductivity [mS cm−1] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sPEEK | 90 | 95 | 1.4 | This work |
| sPEEK/SSLM 5% | 90 | 95 | 184 | - |
| 90 | 30 | 13 | - | |
| sPEEK/2-AGO | 120 | 20 | 11 | [57] |
| sPEEK/DGO | 120 | 20 | 3 | [79] |
| sPEEK/TPA | 100 | 90 | 95 | [30] |
| sPEEK/WO3 | 100 | 100 | 19 | [43] |
| sPEEK/TPA | 100 | 100 | 95 | [49] |
| sPEEK/sCNT | 90 | 100 | 124 | [80] |
| sPEEK/PVA@GO-NF10 | 90 | 100 | 70 | [40] |
| sPEEK/PSSA-CNT | 80 | 95 | 87 | [81] |
| sPEEK/SGNF | 80 | 95 | 104 | [82] |
| sPEEK/MA3 | 80 | 100 | 214 | [55] |
| sPEEK/SGO | 80 | 30 | 55 | [54] |
| Other polymers | ||||
| Nafion/F-GO | 120 | 20 | 18 | [83] |
| sPES/sGO | 90 | 100 | 140 | [84] |
| SPI/SPSGO-8 | 90 | 100 | 72 | [85] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simari, C.; Enotiadis, A.; Nicotera, I. Transport Properties and Mechanical Features of Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone/Organosilica Layered Materials Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes 2020, 10, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050087
Simari C, Enotiadis A, Nicotera I. Transport Properties and Mechanical Features of Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone/Organosilica Layered Materials Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes. 2020; 10(5):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050087
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimari, Cataldo, Apostolos Enotiadis, and Isabella Nicotera. 2020. "Transport Properties and Mechanical Features of Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone/Organosilica Layered Materials Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications" Membranes 10, no. 5: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050087
APA StyleSimari, C., Enotiadis, A., & Nicotera, I. (2020). Transport Properties and Mechanical Features of Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone/Organosilica Layered Materials Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes, 10(5), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050087







