Desalination Performance Assessment of Scalable, Multi-Stack Ready Shock Electrodialysis Unit Utilizing Anion-Exchange Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
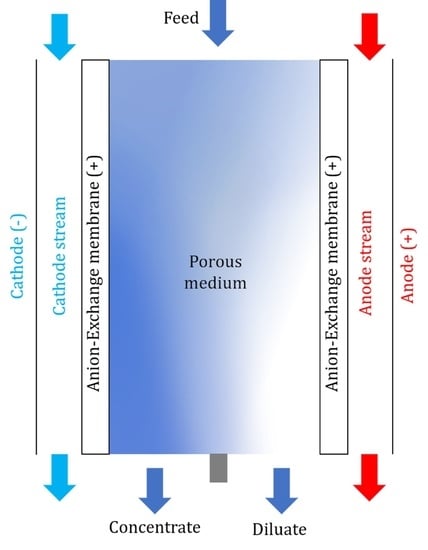
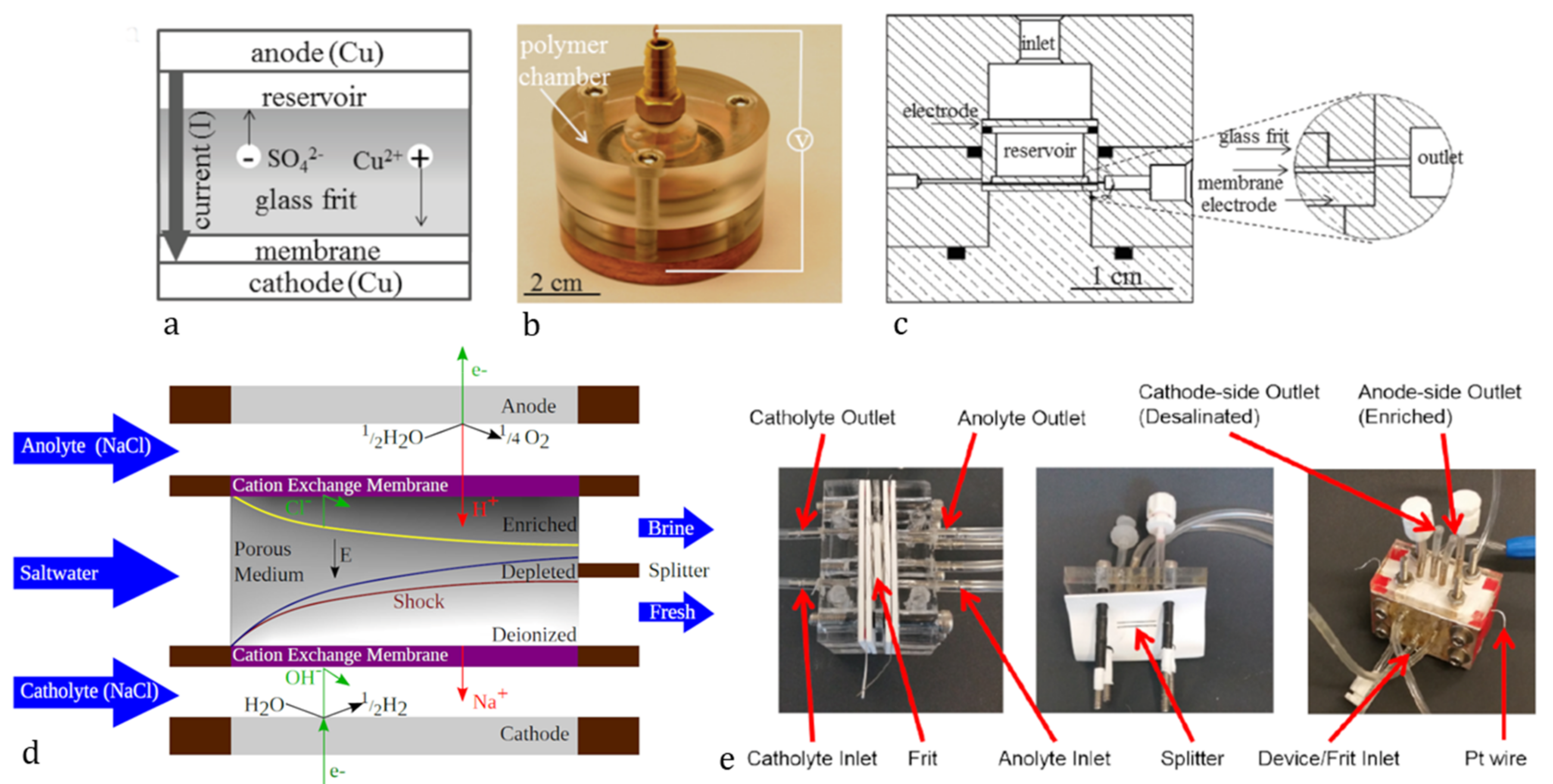
Development and Theory of Shock Electrodialysis
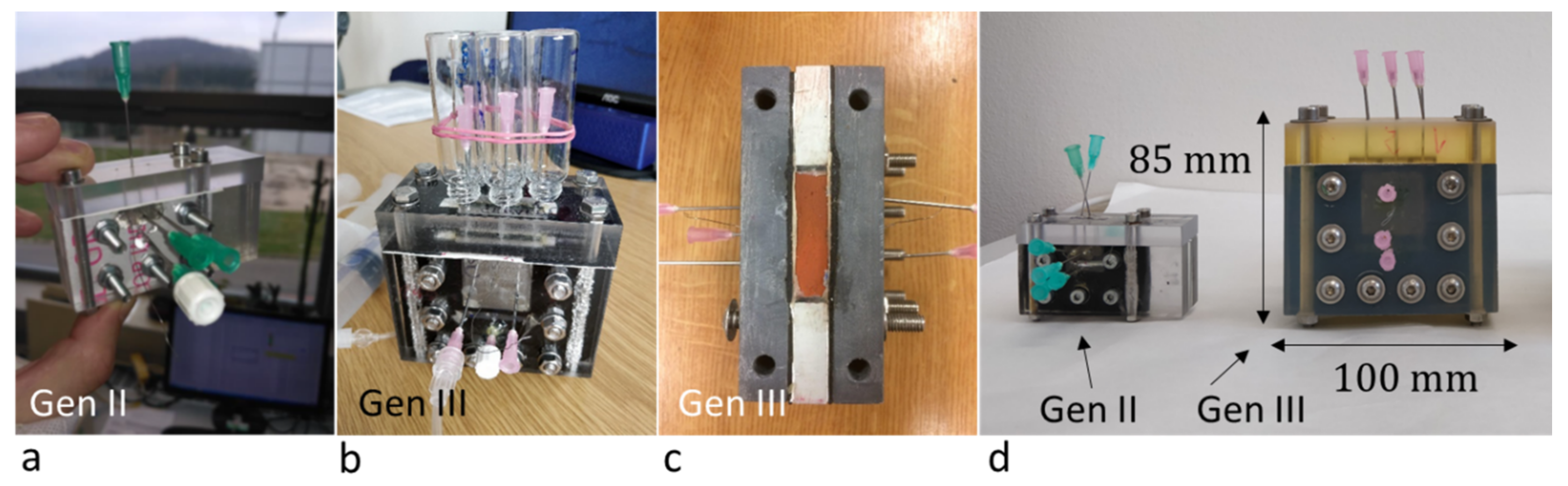
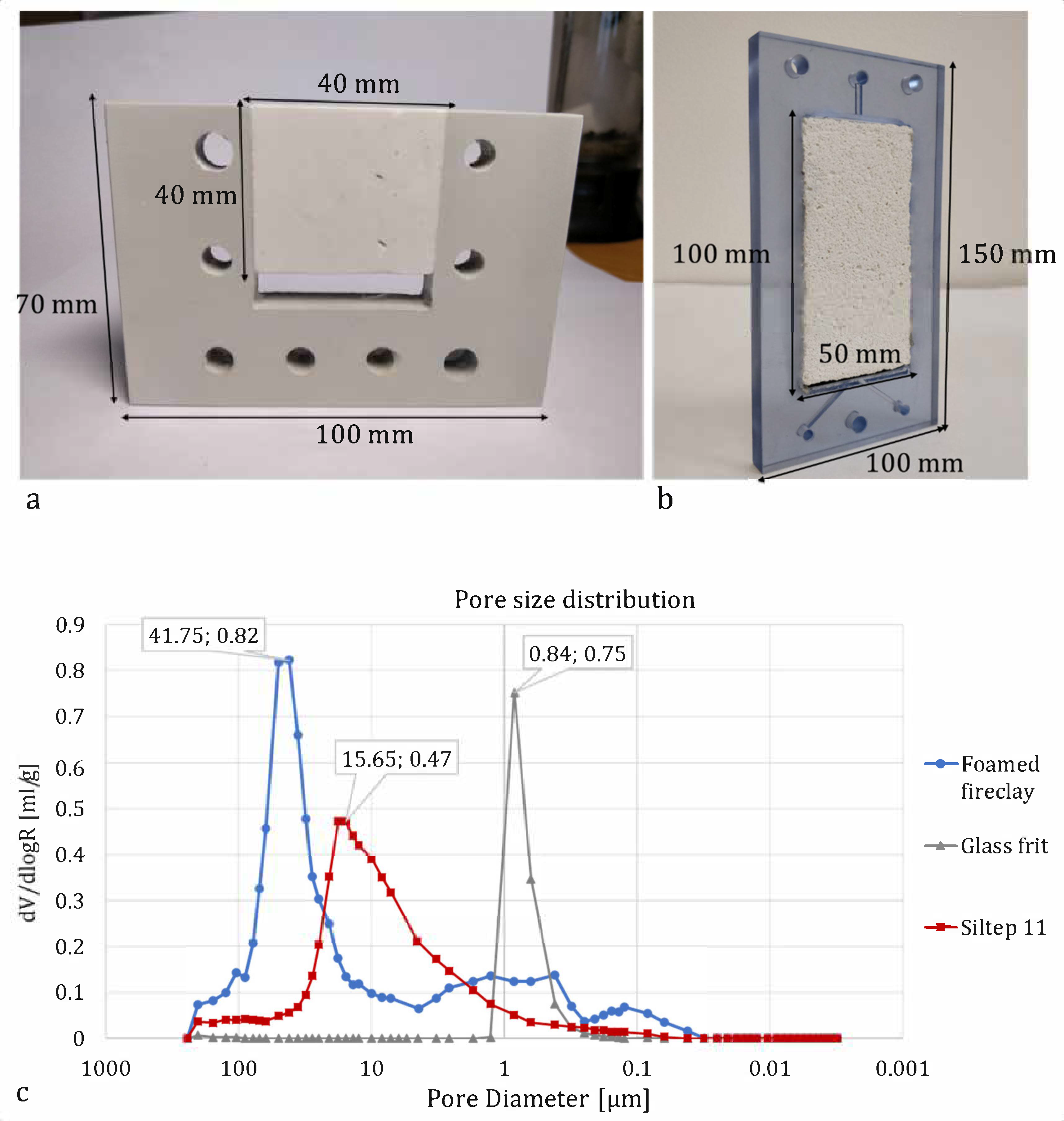
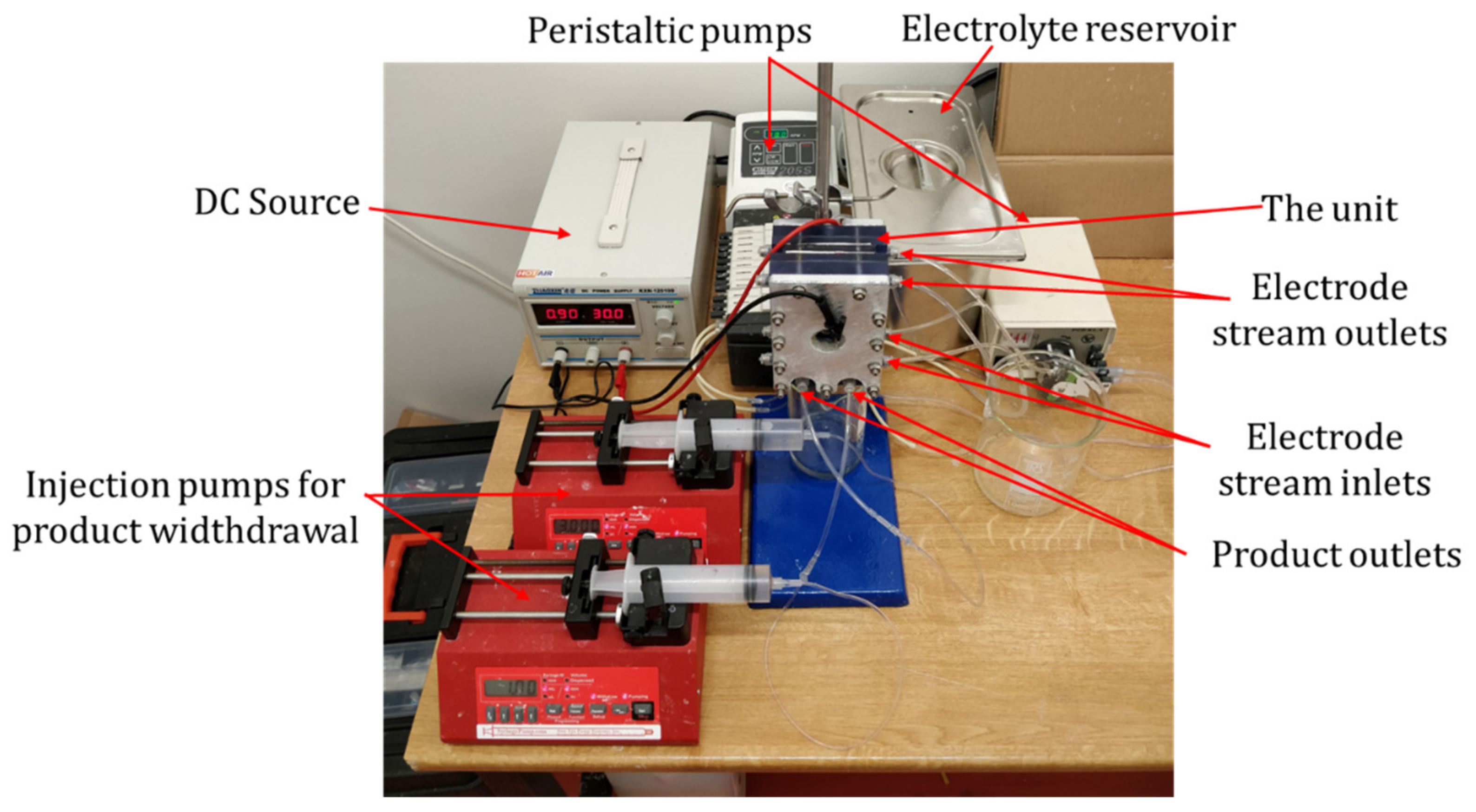
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
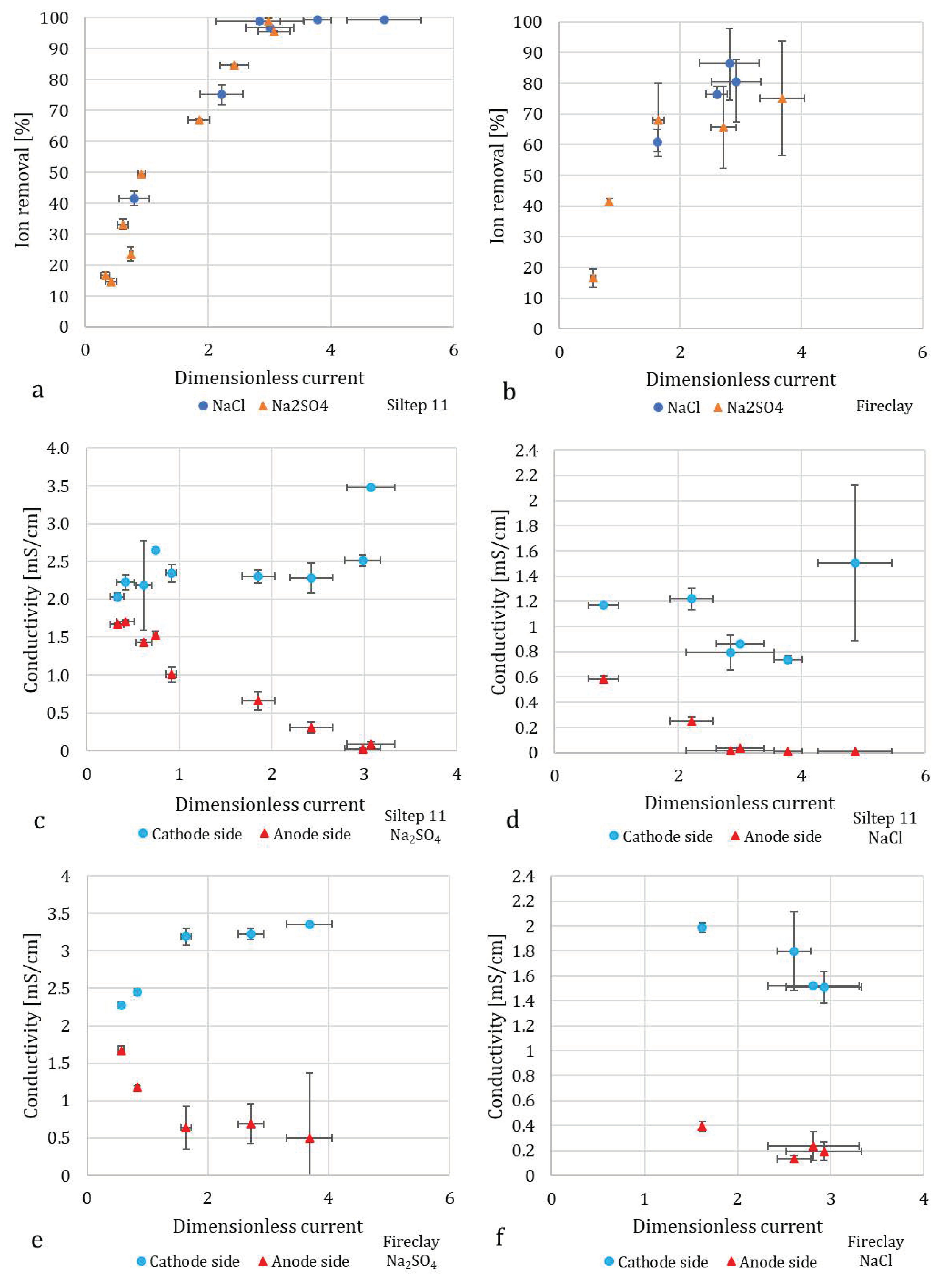
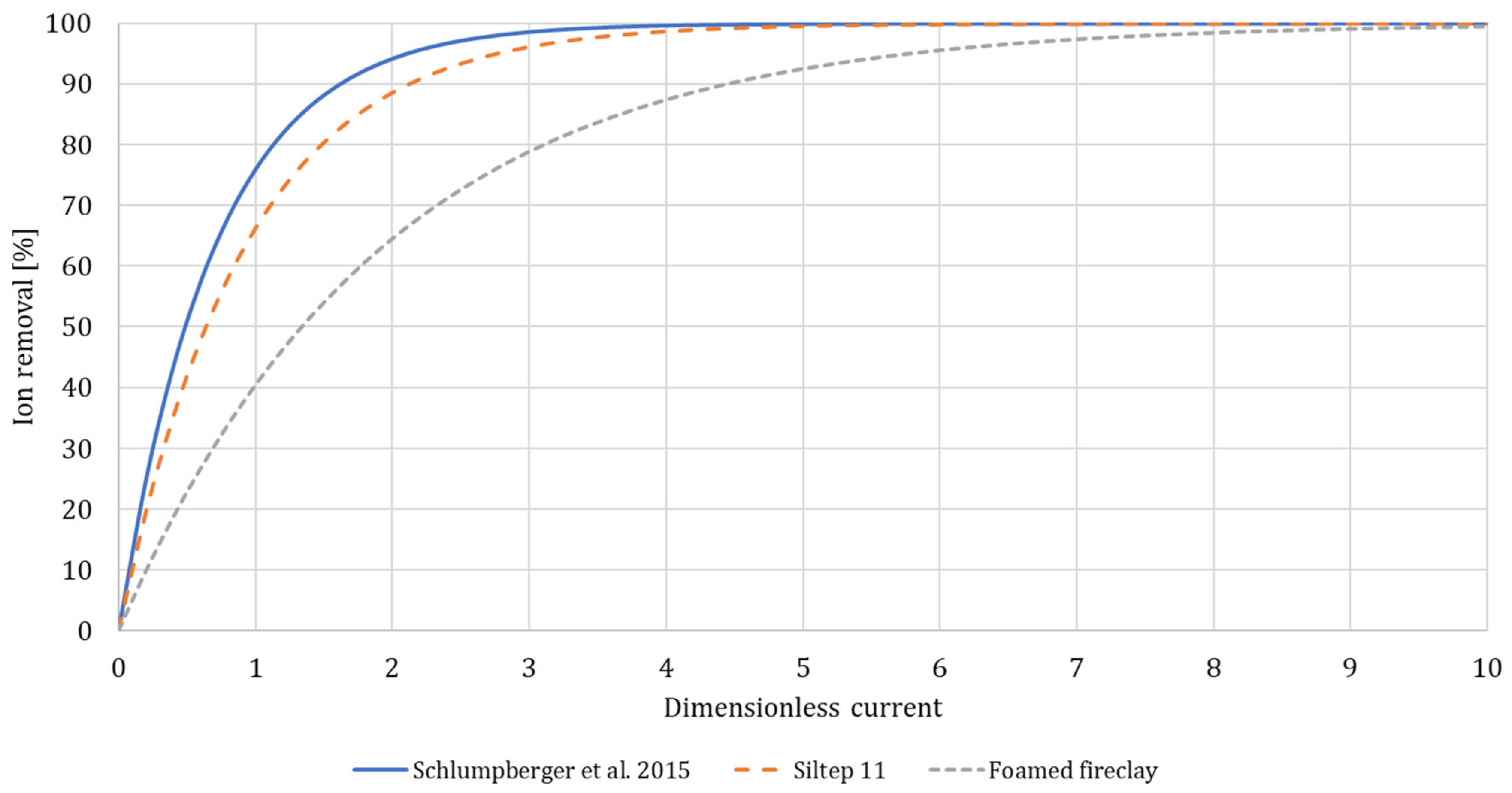
3.1. Desalination Performance
3.2. Flow Rates and Water Recovery
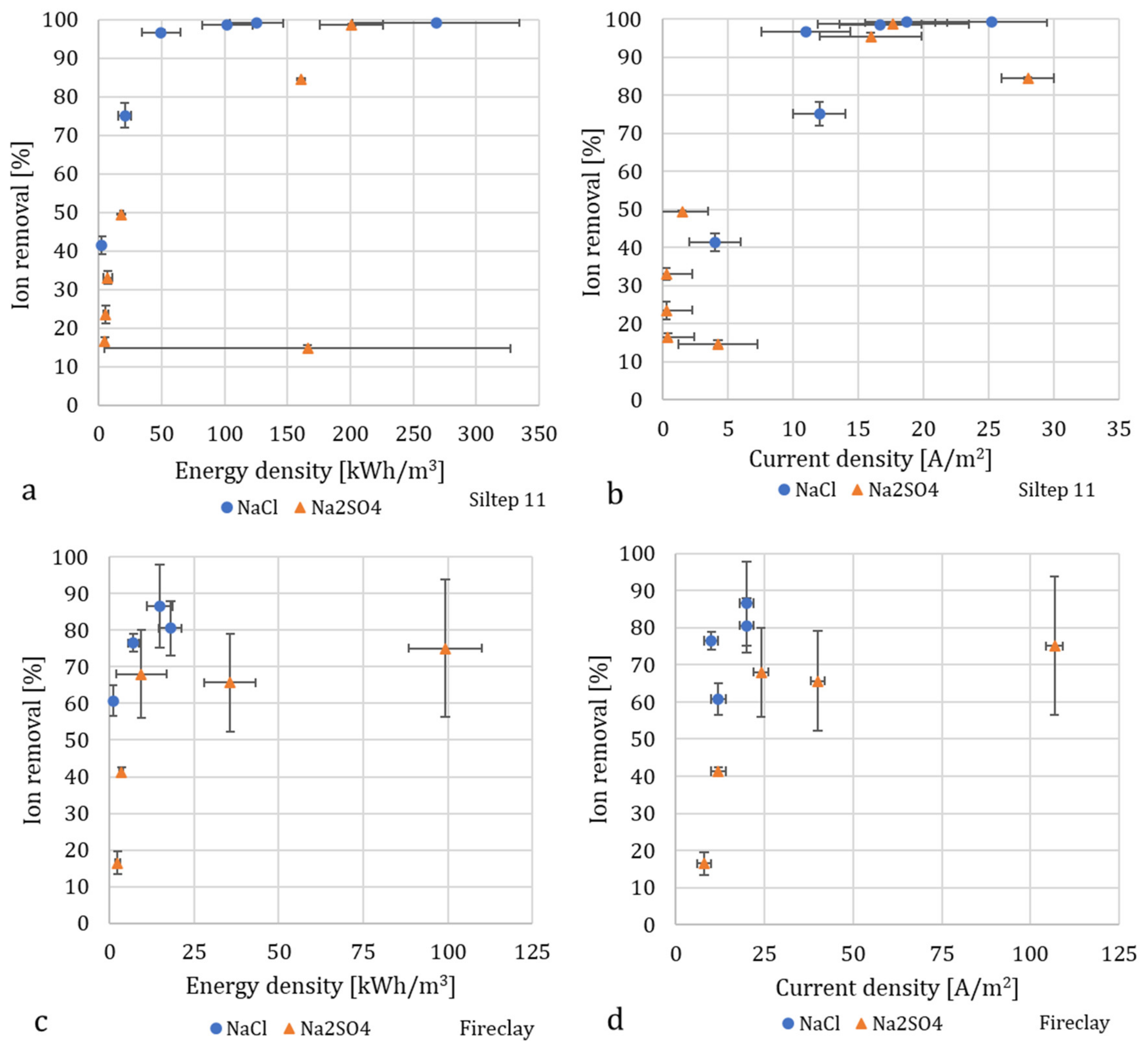
3.3. Energy Consumption
3.4. Porous Media Choice and Shape
3.5. The Practicality of Design and Scalability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, ‘Water Scarcity’. 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/land-water/water/water-scarcity/en/ (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Jones, E.; Qadir, M.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Smakhtin, V.; Kang, S. The state of desalination and brine production: A global outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; Chichester, West Sussex; John and Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhadra, M.A.; Conforti, K.M.; Gao, T.; Tian, H.; Bazant, M.Z. Continuous Separation of Radionuclides from Contaminated Water by Shock Electrodialysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Bruggen, B. Chapter 7—Ion-exchange membrane systems—Electrodialysis and other electromembrane processes. In Fundamental Modelling of Membrane Systems; Luis, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 251–300. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardes, A.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Ferreira, J.Z. (Eds.) Electrodialysis and Water Reuse: Novel Approaches; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R. Chapter 6—Desalination and On-site Energy for Groundwater Treatment in Developing Countries Using Fuel Cells. In Emerging Membrane Technology for Sustainable Water Treatment; Hankins, N.P., Singh, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 135–162. [Google Scholar]
- Mondor, M.; Ippersiel, D.; Lamarche, F. Electrodialysis in food processing. In Green Technologies in Food Production and Processing; Boye, J.I., Arcand, Y., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 295–326. [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, A.; Zangle, T.A.; Santiago, J.G. On the Propagation of Concentration Polarization from Microchannel−Nanochannel Interfaces Part I: Analytical Model and Characteristic Analysis. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3898–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangle, T.A.; Mani, A.; Santiago, J.G. On the Propagation of Concentration Polarization from Microchannel−Nanochannel Interfaces Part II: Numerical and Experimental Study. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, A.; Bazant, M.Z. Deionization shocks in microstructures. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 2011, 84, 061504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dydek, E.V.; Zaltzman, B.; Rubinstein, I.; Deng, D.S.; Mani, A.; Bazant, M.Z. Overlimiting Current in a Microchannel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 118301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Dydek, E.V.; Deng, D.; Mani, A. Desalination and Purification System. U.S. Patent 8999132B2, 7 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Dydek, E.V.; Deng, D.; Mani, A. Method and Apparatus for Desalination and Purification. U.S. Patent 8801910B2, 12 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D.; Aouad, W.; Braff, W.A.; Schlumpberger, S.; Suss, M.E.; Bazant, M.Z. Water purification by shock electrodialysis: Deionization, filtration, separation, and disinfection. Desalination 2015, 357, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Dydek, E.V.; Han, J.-H.; Schlumpberger, S.; Mani, A.; Zaltzman, B.; Bazant, M.Z. Overlimiting Current and Shock Electrodialysis in Porous Media. Langmuir 2013, 29, 16167–16177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhadra, M.A.; Gao, T.; Conforti, K.M.; Tian, H.; Bazant, M.Z. Small-scale desalination of seawater by shock electrodialysis. Desalination 2020, 476, 114219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, K.M.; Bazant, M.Z. Continuous ion-selective separations by shock electrodialysis. Aiche J. 2020, 66, e16751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumpberger, S.; Lu, N.B.; Suss, M.E.; Bazant, M.Z. Scalable and Continuous Water Deionization by Shock Electrodialysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, J.; Čížek, J.; Tvrzník, D. Optimizing porous material in shock electrodialysis unit. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 170, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizek, J. Optimization of Porous Material in Shock Electrodialysis Unit. Bachelor’s Thesis, Technical University of Liberec, Liberec, Czech Republic, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kosina, J. Separation of Diluate and Concentrate Stream in Shock Electrodialysis Unit. Bachelor’s Thesis, Technical University of Liberec, Liberec, Czech Republic, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marek, J.; Sláma, J.; Cizek, J.; Kosina, J. Ionexchange Membrane. Czech Patent 307917, 21 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Aho, A.; Vajglova, Z.; Gun’ko, V.; Heinmaa, I.; Kumar, N.; Eränen, K.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. Zeta Potential of Beta Zeolites: Influence of Structure, Acidity, pH, Temperature and Concentration. Molecules 2018, 23, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqion. Table of Diffusion Coefficients. 2015. Available online: https://www.aqion.de/site/194 (accessed on 29 April 2020).

| Desalination (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensionless Current (1.1.) | Gen. II Unit | Gen III Unit | Reference Unit |
| Ĩ ≈ 0.4 | 36 | - | ≈ 40 |
| Ĩ ≈ 0.6 | - | 40 | ≈ 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čížek, J.; Cvejn, P.; Marek, J.; Tvrzník, D. Desalination Performance Assessment of Scalable, Multi-Stack Ready Shock Electrodialysis Unit Utilizing Anion-Exchange Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110347
Čížek J, Cvejn P, Marek J, Tvrzník D. Desalination Performance Assessment of Scalable, Multi-Stack Ready Shock Electrodialysis Unit Utilizing Anion-Exchange Membranes. Membranes. 2020; 10(11):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110347
Chicago/Turabian StyleČížek, Jan, Petr Cvejn, Jaromír Marek, and David Tvrzník. 2020. "Desalination Performance Assessment of Scalable, Multi-Stack Ready Shock Electrodialysis Unit Utilizing Anion-Exchange Membranes" Membranes 10, no. 11: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110347
APA StyleČížek, J., Cvejn, P., Marek, J., & Tvrzník, D. (2020). Desalination Performance Assessment of Scalable, Multi-Stack Ready Shock Electrodialysis Unit Utilizing Anion-Exchange Membranes. Membranes, 10(11), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110347