A Comparative Study on the Efficiency of Two Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP)-Derived Lipopeptides of L3P and L5P as Capture Antigens in an In-House Milk ELISA Test
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Selection of Milk Samples
2.3. In-House Milk ELISA (H-MELISA) on BTMs and Individual Milk Samples (MIF) Using L3P and L5P Lipopeptides
2.4. Milk Culture
2.5. Extraction of DNA from Milk Samples and Colonies
2.6. Restriction Enzyme (RE) Analysis on IS1311-Targeted PCR Products and Strain Typing (S- or C-Class)
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
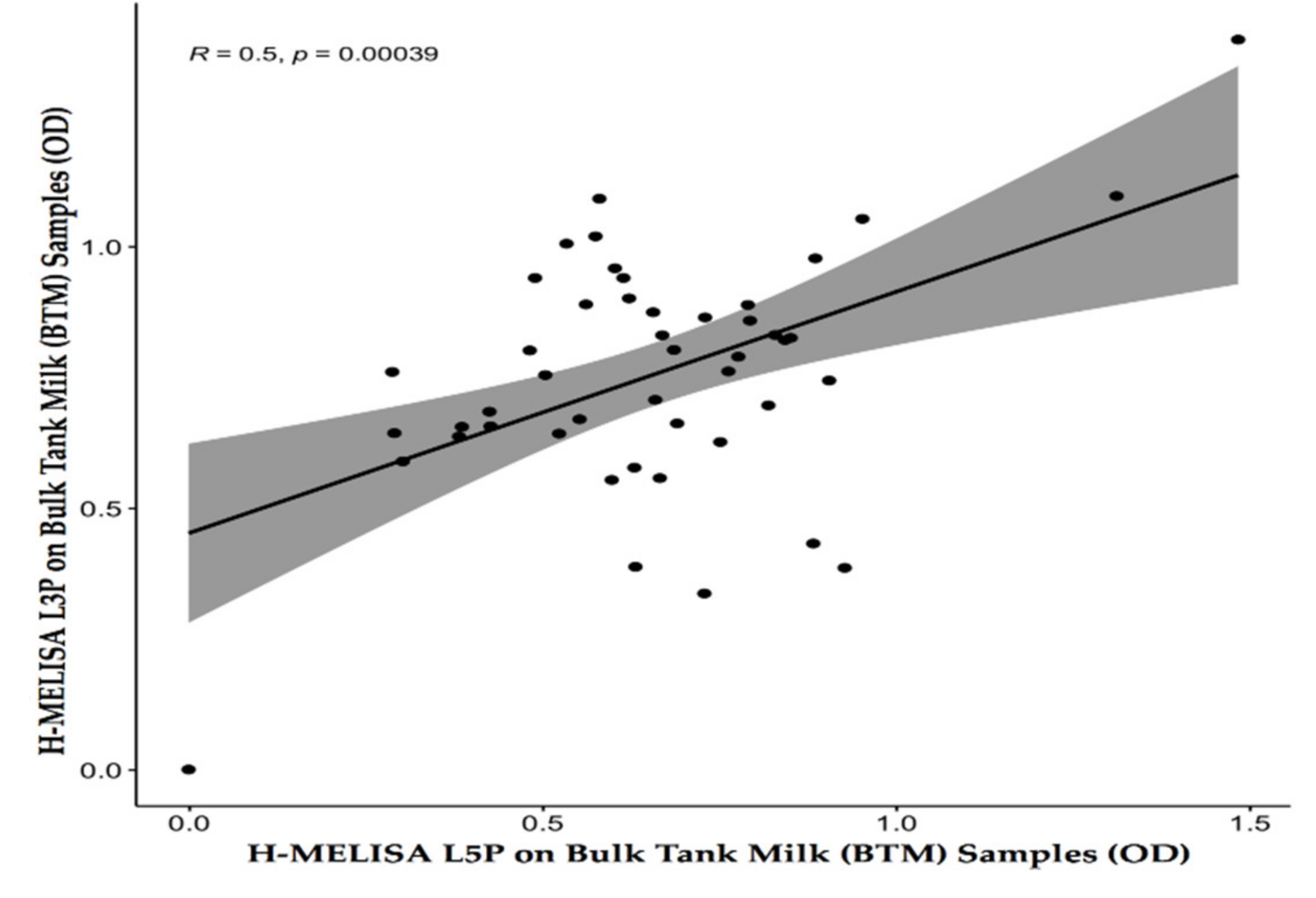
4.1. Homemade Milk ELISA with the L3P and L5P Epitopes on BTMs
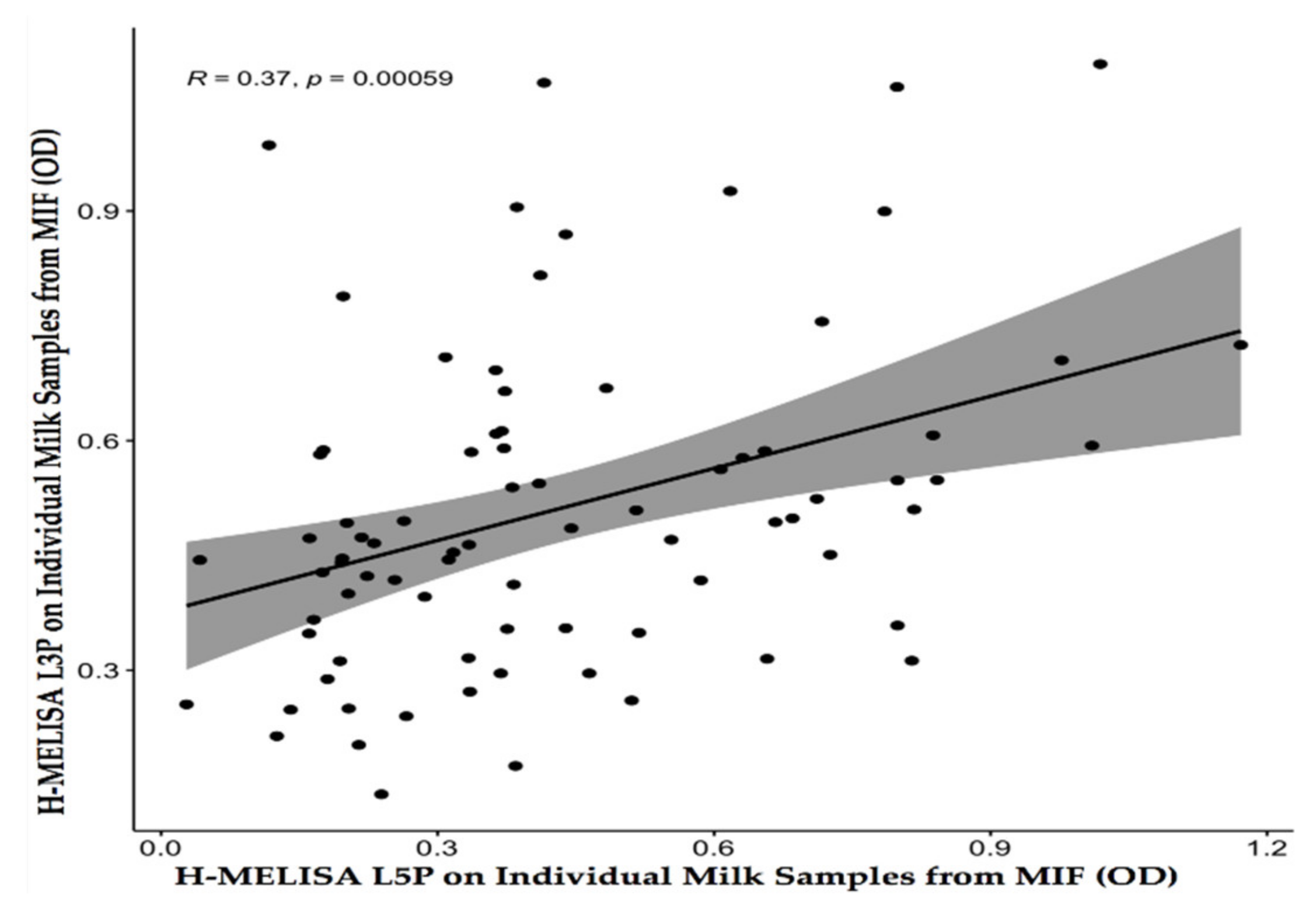
4.2. Homemade ELISA with L3P and L5P Epitopes on Individual Milk Samples from a MAP-Infected Flock (MIF)
4.3. Relationship between the Type of MAP Strain (S or C) and Reactivity against L3P/L5P in the In-House Milk ELISA (H-MELISA)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAP | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis |
| JD | Johne’s disease |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| S-type | Sheep type |
| C-type | Cow type |
| L3P | Lipotripeptide |
| L5P | Lipopentapeptide |
| BTM | Bulk Tank Milk |
| H-MELISA | Homemade Milk ELISA |
| MIF | MAP-infected Flock |
| RE | Restriction Enzyme |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| MqPCR | Milk qPCR |
| CMELISA | Commercial Milk ELISA |
| SELISA | Serum ELISA |
| FPCR | Fecal PCR |
| OD | Optical Density |
| SP | Specificity |
| SN | Sensitivity |
References
- Doré, E.; Paré, J.; Côté, G.; Buczinski, S.; Labrecque, O.; Roy, J.P.; Fecteau, G. Risk factors associated with transmission of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis to calves within dairy herd: A systematic review. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.T. Johne’s Disease (Paratuberculosis). In Food Animal Practice, 5th ed.; Anderson, D.E., Rings, D.M., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Saint Louis, MI, USA, 2009; pp. 65–69. ISBN 9781416035916. [Google Scholar]
- Mckenna, S.L.B.; Keefe, G.P.; Tiwari, A.; Vanleeuwen, J.; Barkema, H.W. Johne’s Disease in Canada Part II: Disease Impacts, Risk Factors, and Control Programs for Dairy Producers. Can. Vet. J. 2006, 47, 1089. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caldow, G.; Greig, A.; Gunn, G.J.; Humphry, R.; Low, C.J.; Ash-worth, S.W.; Jones, G.M.; Stott, A.W.; Cranwell, M.V.; Sharp, J.M.; et al. Assessment of Surveillance and Control of Johne’s Disease in Farm Animals in GB; Sruc Aberdeen Campus: Aberdeen, UK, 2002; pp. 1–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ayele, W.Y.; Svastova, P.; Roubal, P.; Bartos, M.; Pavlik, I. Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis Cultured from Locally and Commercially Pasteurized Cow’s Milk in the Czech Republic. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellingson, J.L.E.; Anderson, J.L.; Koziczkowski, J.J.; Radcliff, R.P.; Sloan, S.J.; Allen, S.E.; Sullivan, N.M. Detection of Viable Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in Retail Pasteurized Whole Milk by Two Culture Methods and PCR. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.B.; Shalloo, L. Invited review: The economic impact and control of paratuberculosis in cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 5019–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sechi, L.A.; Scanu, A.M.; Molicotti, P.; Cannas, S.; Mura, M.; Dettori, G.; Fadda, G.; Zanetti, S. Detection and isolation of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis from intestinal mucosal biopsies of patients with and without Crohn’s disease in Sardinia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mameli, G.; Cocco, E.; Frau, J.; Arru, G.; Caggiu, E.; Marrosu, M.G.; Sechi, L.A. Serum BAFF levels, Methypredsinolone therapy, Epstein-Barr Virus and Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection in Multiple Sclerosis patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masala, S.; Cossu, D.; Palermo, M.; Sechi, L.A. Recognition of Zinc Transporter 8 and MAP3865c Homologous Epitopes by Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Subjects from Sardinia: A Common Target with Type 1 Diabetes? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sechi, L.A.; Dow, C.T. Mycobacterium avium ss. paratuberculosis Zoonosis–The Hundred Year War–Beyond Crohn’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, D.M.; Gabric, D.M.; De Lisle, G.W. Identification of Two Groups of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis Strains by Restriction Endonuclease Analysis and DNA Hybridization. J. Clin. Microbial. 1990, 28, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Juan, L.; Mateos, A.; Domínguez, L.; Sharp, J.M.; Stevenson, K. Genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis isolates from goats detected by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 106, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, E.; Alvarez, J.; Aranaz, A.; Romero, B.; De Juan, L.; Bezos, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Stevenson, K.; Mateos, A.; Dominguez, L. Use of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in inh-A Gene to Characterize Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis into Types I, II and III. In Proceedings of the 9 International Colloquium on Paratuberculosis, Tsukuba, Japan, 28 October–2 November 2007; Nielsen, S.S., Ed.; International Association for Paratuberculosis, Inc., Publication Department: Bizkaia, Spain, 2007; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos, E.; Aranaz, A.; Romero, B.; de Juan, L.; Alvarez, J.; Bezos, J.; Rodríguez, S.; Stevenson, K.; Mateos, A.; Domínguez, L. Polymorphisms in gyrA and gyrB Genes among Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Type I, II, and III Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3439–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bryant, J.M.; Thibault, V.C.; Smith, D.G.E.; McLuckie, J.; Heron, I.; Sevilla, I.A.; Biet, F.; Harris, S.R.; Maskell, D.J.; Bentley, S.D.; et al. Phylogenomic exploration of the relationships between strains of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, K. Comparative differences between strains of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. In Paratuberculosis: Organism, Disease, Control; Behr, M.A., Collins, D.M., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2010; p. 126. ISBN 9781845936136. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, K. Genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis and the influence of strain type on infection and pathogenesis: A review Modeling Johne’s disease: From the inside out Dr Ad Koets and Prof Yrjo Grohn. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biet, F.; Sevilla, I.A.; Cochard, T.; Lefrançois, L.H.; Garrido, J.M.; Heron, I.; Juste, R.A.; McLuckie, J.; Thibault, V.C.; Supply, P.; et al. Inter- and Intra-subtype genotypic differences that differentiate Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosisstrains. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, D.C.; Turenne, C.Y.; Behr, M.A. Insertion and deletion events that define the pathogen Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conde, C.; Price-Carter, M.; Cochard, T.; Branger, M.; Stevenson, K.; Whittington, R.; Bannantine, J.P.; Biet, F. Whole-Genome Analysis of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis IS900Insertions Reveals Strain Type-Specific Modalities. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vansnick, E.; De Rijk, P.; Vercammen, F.; Geysen, D.; Rigouts, L.; Portaels, F. Newly developed primers for the detection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 100, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Albuquerque, P.P.F.; de Souza Santos, A.; de Souza Neto, O.L.; de C.P. Kim, P.; Cavalcanti, E.F.T.S.F.; de Oliveira, J.M.B.; Mota, R.A.; Júnior, J.W.P. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in bovine milk from the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whittington, R.; Marsh, I.; Choy, E.; Cousins, D. Polymorphisms in IS1311, an insertion sequence common to Mycobacterium avium and M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis, can be used to distinguish between and within these species. Mol. Cell. Probes 1998, 12, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.J.; Marsh, I.B.; Whitlock, R.H. Typing of IS1311 polymorphisms confirms that bison (Bison bison) with paratuberculosis in Montana are infected with a strain of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis distinct from that occurring in cattle and other domesticated livestock. Mol. Cell. Probes 2001, 15, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, I.; Singh, S.; Garrido, J.; Aduriz, G.; Rodríguez, S.; Geijo, M.; Whittington, R.; Saunders, V.; Whitlock, R.; Juste, R. Molecular typing of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis strains from different hosts and regions. Rev. Sci. Technol. 2006, 24, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, G.; Pinedo, F.A.; Mon, M.L.; Viale, M.; Gil, A.; Illia, M.C.; Gioffré, A.; Arese, A.; Travería, G.; Romano, M.I. Accuracy assessment and screening of a dairy herd with paratuberculosis by three different ELISAs. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.T.; Wells, S.J.; Petrini, K.R.; Collins, J.E.; Schultz, R.D.; Whitlock, R.H. Evaluation of Five Antibody Detection Tests for Diagnosis of Bovine Paratuberculosis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavers, C.J.; Barkema, H.W.; Dohoo, I.R.; McKenna, S.L.B.; Keefe, G.P. Evaluation of milk ELISA fordetection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis indairy herds and association with within-herd prevalence. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, M.P.; Kruze, J.; Collins, M.T. Evaluation of four commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the diagnosis of bovine paratuberculosis in Chilean dairy herds. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseiniporgham, S.; Cubeddu, T.; Rocca, S.; Sechi, L.A. Identification of mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis (map) in sheep milk, a zoonotic problem. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, J.E.; Byrem, T.M.; Wagner, B.A.; McCluskey, B.J. Comparison of milk and serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for diagnosis of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infection in dairy cattle. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2006, 18, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugden, E.A.; Stilwell, K.; Michaelides, A. A Comparison of Lipoarabinomannan with other Antigens used in Absorbed Enzyme Immunoassays for the Serological Detection of Cattle Infected with Mycobacterium Paratuberculosis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1997, 9, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bannantine, J.P.; Paustian, M.L.; Waters, W.R.; Stabel, J.R.; Palmer, M.V.; Li, L.; Kapur, V. Profiling Bovine Antibody Responses to Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Infection by Using Protein Arrays†. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bannantine, J.P.; Etienne, G.; Laval, F.; Stabel, J.R.; Lemassu, A.; Daffé, M.; Bayles, D.O.; Ganneau, C.; Bonhomme, F.; Branger, M.; et al. Cell wall peptidolipids of Mycobacterium avium: From genetic prediction to exact structure of a nonribosomal peptide. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 105, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biet, F.; Bay, S.; Thibault, V.C.; Euphrasie, D.; Grayon, M.; Ganneau, C.; Lanotte, P.; Daffé, M.; Gokhale, R.; Etienne, G.; et al. Lipopentapeptide induces a strong host humoral response and distinguishes Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis from M. avium subsp. avium. Vaccine 2008, 26, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, S.; Begg, D.; Ganneau, C.; Branger, M.; Cochard, T.; Bannantine, J.P.; Köhler, H.; Moyen, J.L.; Whittington, R.J.; Biet, F. Engineering Synthetic Lipopeptide Antigen for Specific Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Infection|Enhanced Reader. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 637841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Mutharia, L.; Raymond, M.; Odumeru, J. Improved template DNA preparation procedure for detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in milk by PCR. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 69, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradner, L.; Robbe-Austerman, S.; Beitz, D.C.; Stabel, J.R. Optimization of hexadecylpyridinium chloride decontamination for culture of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis from milk. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuni, J.B.; Dovas, C.I.; Loukopoulos, P.; Bouzalas, I.G.; Kateete, D.P.; Joloba, M.L.; Ojok, L. Isolation of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis from Ugandan cattle and strain differentiation using optimised DNA typing techniques. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaitanya, R.K.; Reddy, Y.K.M.; Thangavelu, A. Strain Typing of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis from Tamil Nadu, India based on Polymorphisms in MAP 1506 Locus and IS 1311 PCR-REA. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2015, 3, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelidou, E.; Kostoulas, P.; Leontides, L. Bayesian validation of a serum and milk ELISA for antibodies against Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis in Greek dairy goats across lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, K.L.; Devanarayan, V.; Kriauciunas, A.; Manetta, J.; Montrose, C.; Sittampalam, S. Immunoassay Methods. In Assay Guidance Manual [Internet]; Markossian, S., Sittampalam, G.S., Grossman, A., Brimacombe, K., Arkin, M., Auld, D., Austin, C.P., Baell, J., Chung, T.D.Y., Coussens, N.P., et al., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.S.; Toft, N. Ante mortem diagnosis of paratuberculosis: A review of accuracies of ELISA, interferon-γ assay and faecal culture techniques. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 129, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamberale, F.; Pietrella, G.; Sala, M.; Scaramella, P.; Puccica, S.; Antognetti, V.; Arrigoni, N.; Ricchi, M.; Cersini, A. Management of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in dairy farms: Selection and evaluation of different DNA extraction methods from bovine and buffaloes milk and colostrum for the establishment of a safe colostrum farm bank. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardner, I.A.; Nielsen, S.S.; Whittington, R.J.; Collins, M.T.; Bakker, D.; Harris, B.; Sreevatsan, S.; Lombard, J.E.; Sweeney, R.; Smith, D.R.; et al. Consensus-based reporting standards for diagnostic test accuracy studies for paratuberculosis in ruminants. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 101, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sohal, J.S.; Arsenault, J.; Leboeuf, A.; Hélie, P.; Buczinski, S.; Robinson, Y.; Labrecque, O.; Lachapelle, V.; Fecteau, G.; L’Homme, Y. Molecular characterization of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis C-type and S-type isolated from sheep and goats by using a combination of MIRU-VNTR loci. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 83, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Number/Type of Milk Sample | Number of Negative Control Samples | Number of MAP-Positive Control Samples |
|---|---|---|
| 47/BTM | 17 | 30 |
| 81/Individual (MIF) | 45 | 36 |
| Peptide | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Lipotripeptide (L3P) | CH3-(CH2)18-CONH-D-Phe-L-Nme-Val-L-Ala-OCH3 [36] |
| Lipopentapeptide (L5P) | CH3-(CH2)18-CONH-D-Phe-L-Nme-Val-L-Ile-L-Phe-L-Ala-OCH3 [36] |
| Primers | Sequences |
|---|---|
| IS1311-F (M56) | 5′-GCGTGAGGCTCTGTGGTGAA-3′ |
| IS1311-R (M119) | 5′-ATGACGACCGCTTGGGAGAC-3′ |
| IS900-F (AV1) | 5′-ATGTGGTTGCTGTGTTGGATGG-3′ |
| IS900-R (AV2) | 5′-CCGCCGCAATCAACTCCAG-3′ |
| Strain Type | Sample Type | RE 3 Fragments on Gel-Electrophoresis Based on Base Pair | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTM 1 % | MIF 2 % | 67-bp | 218-bp | 285-bp | 323-bp | |
| S | 26.67 | 75% | + | + | ||
| C | 46.67 | 12.5 | + | + | + | + |
| bison | 20 | 12.5 | + | + | + | |
| Sample Number | Strain Type | H-MELISA L3P (Cutoff = 0.8895) 1 (Cutoff = 0.406) 2 | H-MELISA L5P (Cutoff = 0.59925) 3 (Cutoff = 0.513) 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6B | C-type | 1.092 | 0.5795 |
| 10B | C-type | 0.5545 | 0.597 |
| 12B | Unknown | 0.627 | 0.7505 |
| 13B | S-type | 0.3865 | 0.9265 |
| 14B | C-type | 0.433 | 0.882 |
| 18B | bison | 0.7075 | 0.6585 |
| 19B | bison | 0.89 | 0.5605 |
| 20B | S-type | 0.822 | 0.842 |
| 23B | C-type | 0.978 | 0.885 |
| 28B | C-type | 0.978 | 1.311 |
| 29B | bison | 0.865 | 0.729 |
| 31B | S-type | 0.79 | 0.776 |
| 33B | S-type | 0.9015 | 0.6215 |
| 79B | C-type | 0.755 | 0.503 |
| 82B | C-type | 1.006 | 0.533 |
| 7V | S-type | 0.4725 | 0.161 |
| 62V | S-type | 0.509 | 0.5155 |
| 64V | bison | 0.4445 | 0.312 |
| 65V | C-type | 0.926 | 0.6175 |
| 72V | S-type | 0.418 | 0.2535 |
| 76 V | S-type | 0.175 | 0.3845 |
| 83V | S-type | 1.062 | 0.7985 |
| 93V | S-type | 0.2025 | 0.2145 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosseiniporgham, S.; Biet, F.; Ganneau, C.; Bannantine, J.P.; Bay, S.; Sechi, L.A. A Comparative Study on the Efficiency of Two Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP)-Derived Lipopeptides of L3P and L5P as Capture Antigens in an In-House Milk ELISA Test. Vaccines 2021, 9, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090997
Hosseiniporgham S, Biet F, Ganneau C, Bannantine JP, Bay S, Sechi LA. A Comparative Study on the Efficiency of Two Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP)-Derived Lipopeptides of L3P and L5P as Capture Antigens in an In-House Milk ELISA Test. Vaccines. 2021; 9(9):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090997
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosseiniporgham, Sepideh, Franck Biet, Christelle Ganneau, John P. Bannantine, Sylvie Bay, and Leonardo A. Sechi. 2021. "A Comparative Study on the Efficiency of Two Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP)-Derived Lipopeptides of L3P and L5P as Capture Antigens in an In-House Milk ELISA Test" Vaccines 9, no. 9: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090997
APA StyleHosseiniporgham, S., Biet, F., Ganneau, C., Bannantine, J. P., Bay, S., & Sechi, L. A. (2021). A Comparative Study on the Efficiency of Two Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP)-Derived Lipopeptides of L3P and L5P as Capture Antigens in an In-House Milk ELISA Test. Vaccines, 9(9), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090997








