Vaccination against the Protozoan Parasite Histomonas meleagridis Primes the Activation of Toll-like Receptors in Turkeys and Chickens Determined by a Set of Newly Developed Multiplex RT-qPCRs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
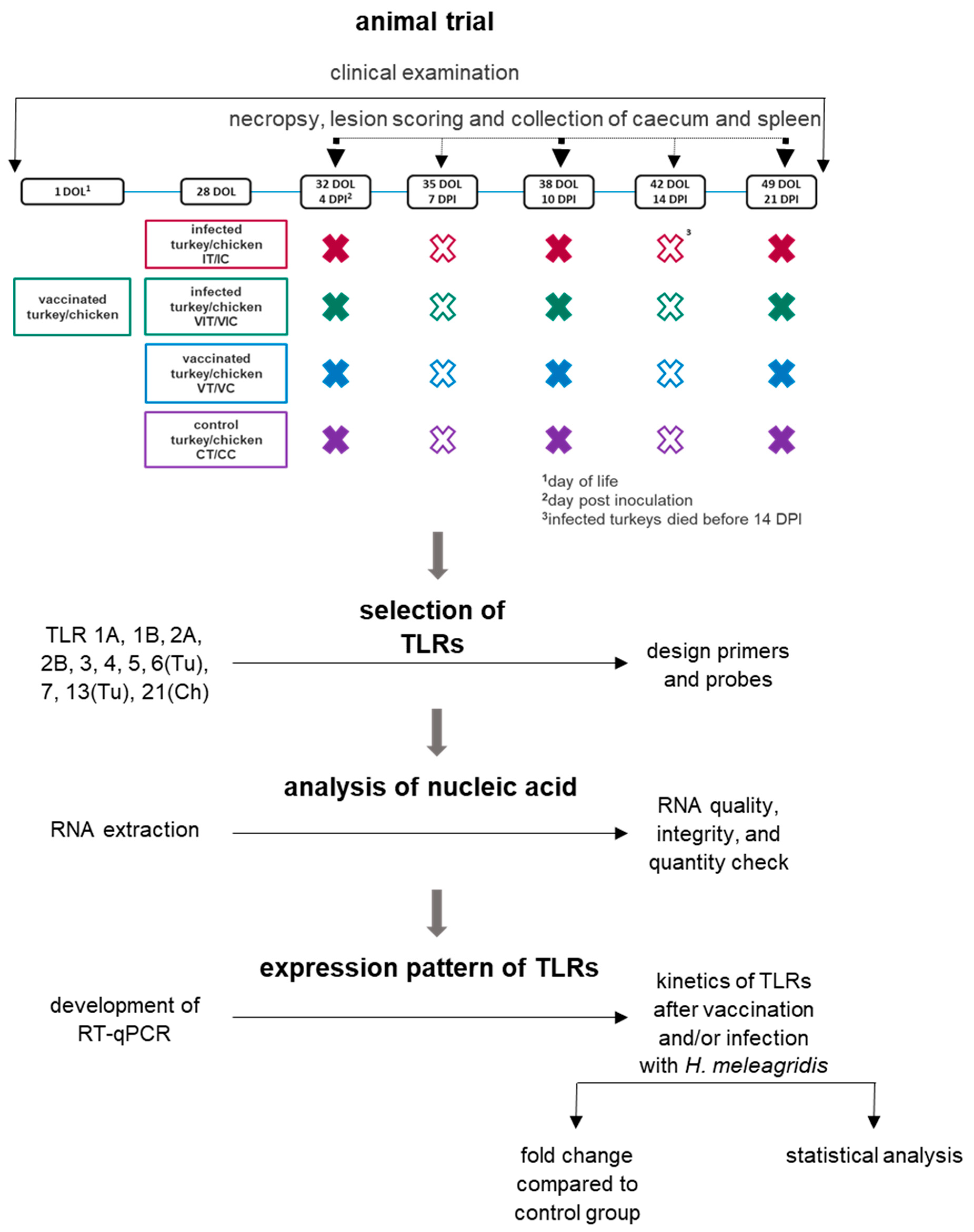
2.1. Animal Trial
2.2. Preparations of Parasites for Inoculation
2.3. Trial Setup
2.4. Gene Selection
2.5. Total RNA Extraction and Analysis for Purity and Integrity
2.6. RT-qPCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Establishment of RT-qPCR
3.2. Clinical Signs and Lesion Scores
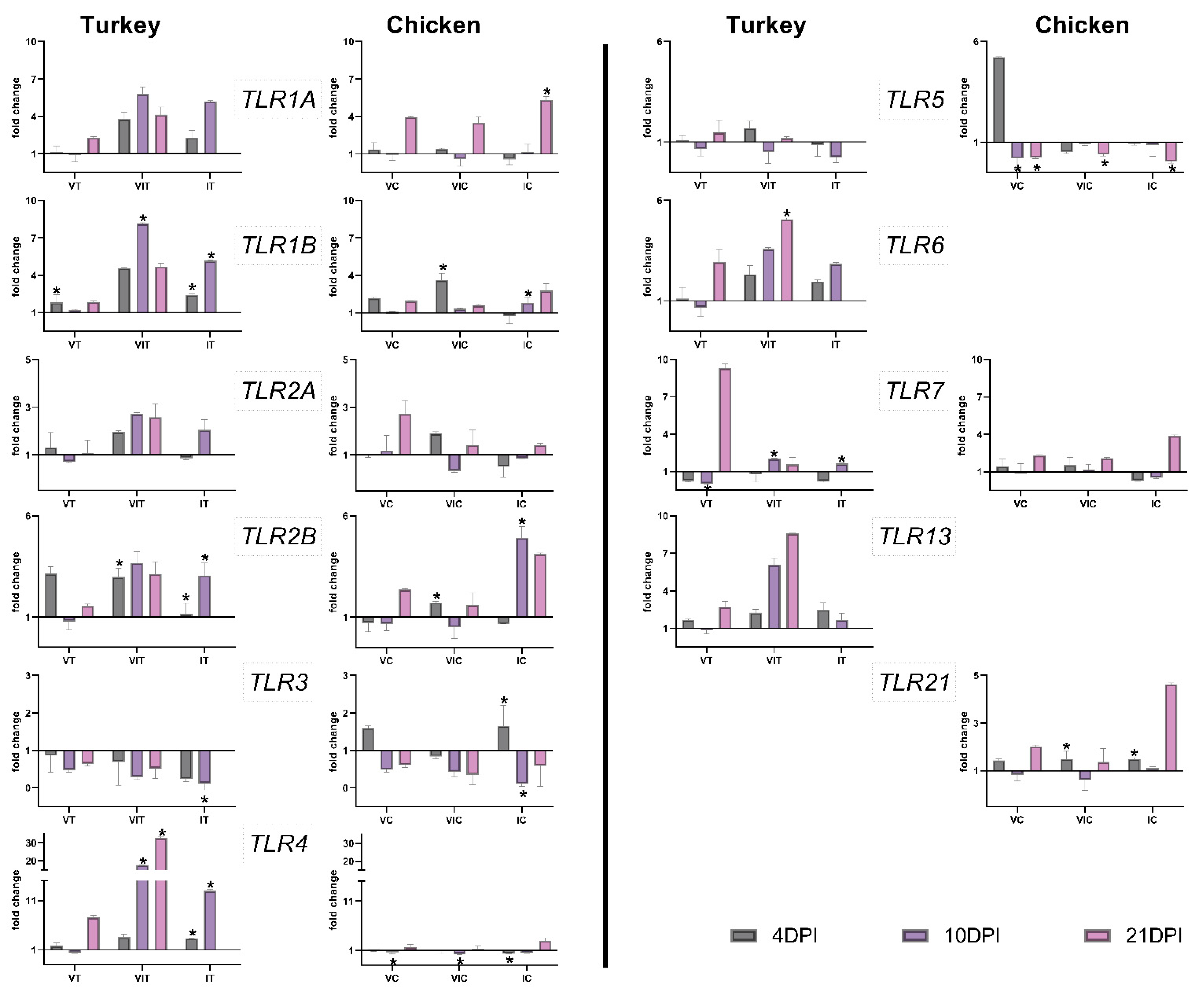
3.3. Gene Expression of TLRs
3.3.1. Local TLR Expression in the Caecum
3.3.2. Systemic TLR Expression in the Spleen
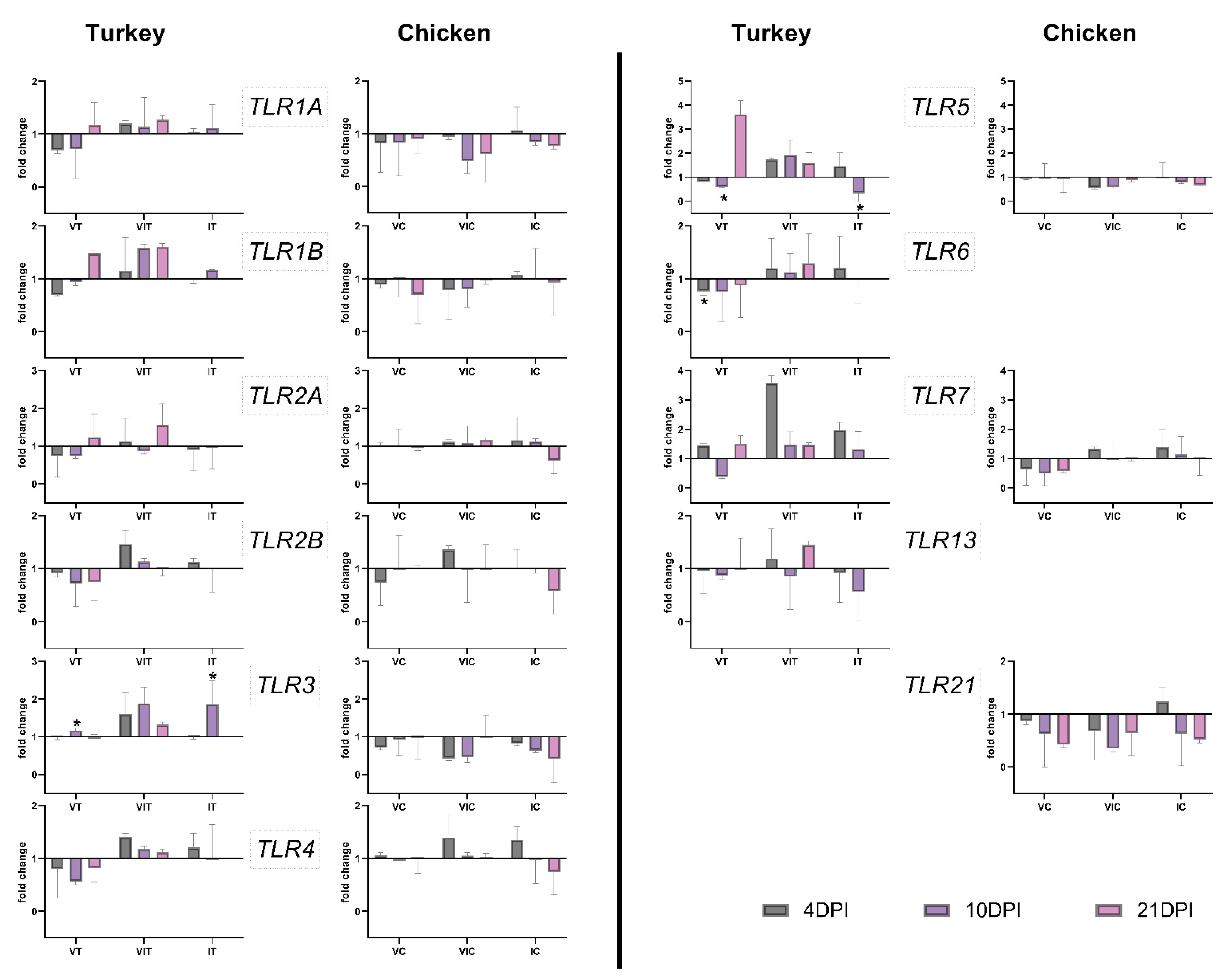
3.4. Gene Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
3.4.1. Caecum
3.4.2. Spleen
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, T. An infectious disease among turkeys caused by protozoa (infectious entero-hepatitis). USDA Bur. Anim. Ind. Bull. 1895, 8, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liebhart, D.; Hess, M. Spotlight on Histomonosis (blackhead disease): A re-emerging disease in turkeys and chickens. Avian Pathol. 2020, 49, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, M.; McDougald, L.R. Histomoniasis (Histomonosis, blackhead disease). In Disease of Poultry, 14th ed.; Swayne, D.E., Boulianne, M., Logue, C., McDougald, L.R., Nair, V., Suarez, D.L., Eds.; Wiley-Black: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1223–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, M.; Liebhart, D.; Bilic, I.; Ganas, P. Histomonas meleagridis—New insights into an old pathogen. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 208, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, T.; Kidane, F.A.; Hess, M.; Liebhart, D. Unravelling the immunity of poultry against the extracellular protozoan parasite Histomonas meleagridis is a cornerstone for vaccine development: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Paglino, J.; Eslami-Varzaneh, F.; Edberg, S.; Medzhitov, R. Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 2004, 118, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Temperley, N.D.; Berlin, S.; Paton, I.R.; Griffin, D.K.; Burt, W.D. Evolution of the chicken Toll-like receptor gene family: A story of gene gain and gene loss. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, A.; Shen, S.; Adelson, D.L.; Xavier, S.; Zhu, J.J. Identification and sequence analysis of chicken toll-like receptors. Immunogenetics 2005, 56, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, K.T.; Reddy, M.R.; Verma, P.C.; Murugesan, S. Expression analysis of turkey (Meleagris gallopavo) toll-like receptors and molecular characterization of avian specific TLR15. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 8539–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, L.H.; Miska, K.B.; Jenkins, M.C.; Fetterer, R.H.; Cox, C.M.; Kim, S.; Dalloul, R.A. Expression of Toll-like receptors and antimicrobial peptides during Eimeria praecox infection in chickens. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, B.; Cai, J.; Wang, M. Eimeria tenella: Expression profiling of toll-like receptors and associated cytokines in the cecum of infected day-old and three-week old SPF chickens. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 130, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cao, L.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, B.; Guo, Z.; Nie, K. Upregulation of chicken TLR4, TLR15 and MyD88 in heterophils and monocyte-derived macrophages stimulated with Eimeria tenella In Vitro. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 133, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Qin, B.; Nie, K. Expression of chicken Toll-like receptors and signal adaptors in spleen and cecum of young chickens infected with Eimeria tenella. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawab, A.; An, L.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, M. Chicken toll-like receptors and their significance in immune response and disease resistance. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 38, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, T.; Gerner, W.; Kidane, F.A.; Wernsdorf, P.; Hess, M.; Saalmüller, A.; Liebhart, D. Vaccination against histomonosis limits pronounced changes of B cells and T-cell subsets in turkeys and chickens. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4184–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Grabensteiner, E.; Liebhart, D. Rapid transmission of the protozoan parasite Histomonas meleagridis in turkeys and specific pathogen free chickens following cloacal infection with a mono-eukaryotic culture. Avian Pathol. 2006, 35, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, M.; Liebhart, D.; Grabensteiner, E.; Singh, A. Cloned Histomonas meleagridis passaged In Vitro resulted in reduced pathogenicity and is capable of protecting turkeys from histomonosis. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4187–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch, M.; Hess, M. Experimental infection of chickens with Histomonas meleagridis confirms the presence of antibodies in different parts of the intestine. Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, M.A.; Liebhart, D.; Hess, M. Progression of histomonosis in commercial chickens following experimental infection with an In Vitro propagated clonal culture of Histomonas meleagridis. Avian Dis. 2011, 55, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.S.; Brisbin, J.T.; Abdul-Careem, M.F.; Sharif, S. Immunostimulatory properties of toll-like receptor ligands in chickens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 152, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, F.L.; Rothwell, L.; Clarkson, M.J.; Kaiser, P. The turkey, compared to the chicken, fails to mount an effective early immune response to Histomonas meleagridis in the gut. Parasite Immunol. 2009, 31, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, T.; Bilic, I.; Hess, M.; Liebhart, D. The 60S ribosomal protein L13 is the most preferable reference gene to investigate gene expression in selected organs from turkeys and chickens, in context of different infection models. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, E.H.; Jacoby, D.B. Upping the antedrug: Is a novel anti-inflammatory toll-like receptor 7 agonist also a bronchodilator? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Kordahi, M.C.; Chac, D.; DePaolo, R.W. Toll-like receptor-6 signaling prevents inflammation and impacts composition of the microbiota during inflammation-induced colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2020, 13, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, I.; Salaiza, N.; Aguirre, M.; Delgado, J.; Carrillo-Carrasco, N.; Kobeh, L.G.; Ruiz, A.; Cervantes, R.; Torres, A.P.; Cabrera, N.; et al. Leishmania lipophosphoglycan (LPG) activates NK cells through toll-like receptor-2. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 130, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawn, T.R.; Ozinsky, A.; Underhill, D.M.; Buckner, F.S.; Akira, S.; Aderem, A. Leishmania major activates IL-1 alpha expression in macrophages through a MyD88-dependent pathway. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.H.; la Fata, G. Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the immune response in the human gut. Nutrients 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabral, E.S.; Gelderblom, H.; Hornung, R.L.; Munson, P.J.; Martin, R.; Marques, A.R. Borrelia burgdorferi lipoprotein-mediated TLR2 stimulation causes the down-regulation of TLR5 in human monocytes. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagler, J.; Schmidt, S.; Mitra, T.; Stadler, M.; Wernsdorf, P.; Grafl, B.; Hatfaludi, T.; Hess, M.; Gerner, W.; Liebhart, D. Comparative investigation of IFN-γ-producing T cells in chickens and turkeys following vaccination and infection with the extracellular parasite Histomonas meleagridis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 116, 103949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouzder, C.; Mukhuty, A.; Das, S.; Chattopadhyay, D. TLR Signaling on protozoan and helminthic parasite infection. In Toll-like Receptors; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira-Nascimento, L.; Massari, P.; Wetzler, L.M. The Role of TLR2 in infection and immunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, J.; Selvarajoo, K.; Tsuchiya, M.; Lee, G.; Choi, S. Toll-like receptor signal transduction. Exp. Mol. Med. 2007, 39, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Chakraborty, K.; Ray, P. Immunosuppressive MDSCs induced by TLR signaling during infection and role in resolution of inflammation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duthie, M.S.; Windish, H.P.; Fox, C.B.; Reed, S.G. Use of defined TLR ligands as adjuvants within human vaccines. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 239, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Species | NCBI Accession No | Primers and Probe Sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TLR1A | turkey | FJ477857.1 | F: TGTCACTACGAGCTGTACTTTG R: CTCGCAGGGATAACATATGGAG P: FAM-TAGTCCTGATCTTGCTGGAGCCGA-TAMRA |
| chicken | NM_001007488.4 | ||
| TLR1B | turkey | FJ477858.1 | F: CCATCACAAGTTGTTTAGC R: TCCAGGTAGGTTCTCTTG P: HEX-CCTGATCTTGCTGGAGCCGA-BHQ1 |
| chicken | DQ518918.1 | ||
| TLR2A | turkey | FJ477860.1 | F: CTGGCCCACAACAGGATAAA R: CCTCGTCTATGGAGCTGATTTG P: HEX-ACATGATCTGCAGCAGGCTGTGAA-BHQ1 |
| chicken | AB050005.2 | ||
| TLR2B | turkey | FJ477861.1 | F: GATCCCCAAGAGGTTCTG R: CTGCTGTTGCTCTTCATC P: FAM-CTGCGGAAGATAATGAACACCAAGAC-BHQ1 |
| chicken | AB046533.2 | ||
| TLR3 | turkey | XM_003205774.4 | F: GCATAAGAAGGAGCAGGAAGA R: GGAGTCTCGACTTTGCTCAATA P: ROX-TGGTGCAGGAGGTTTAAGGTGCAT-BHQ2 |
| chicken | EF137861.1 | ||
| TLR4 | turkey | XM_003211211.3 | F: CATACAAGCCACTCCAAGCC R: AGGATTTCCAGGGCTGAGTC P: CY5-CACAGCTCTGGATTTCAGCAACAACCA-BBQ |
| chicken | KF697090.1 | ||
| TLR5 | turkey | HQ436463.1 | F: AGCCTACTAGTGTGGCTAAATG R:ACACTGGTACACCTGCTAATG P: ROX-ACCAATGTAACCCTAGCTGGCTCA-BHQ2 |
| chicken | AJ626848.1 | ||
| TLR6 | turkey | XM_019615148.1 | F: CGAGCTGTACTTTGCCCATC R: GGTACCTCGCAGGGATAACA P: HEX-TGCTGGAGCCGATCCCTCCA-BHQ1 |
| chicken | NA # | ||
| TLR7 | turkey | XM_010726471.2 | F: CCAGATGCCTGCTATGATGC R: TCAGCTGAATGCTCTGGGAA P: FAM-TGGCTTCCAGGACAGCCAGTCT-BHQ1 |
| chicken | NM_001011688.2 | ||
| TLR13 | turkey | XP_019475306.1 | F-TGCTGGACCTGTCTCACAAT R: CAGGTTGCCCAAACTGTTGA P: ROX-CGGCTGACCACACTCGCCGA-BHQ2 |
| chicken | NA | ||
| TLR21 | turkey | NA | F: TCGCAACTGCATTGAGGATG R: ATGACAGATTGAGCGCGATG P: CY5-TTCCTGCAGTCGCCGGCCCT-BHQ2 |
| chicken | NM_001030558.1 |
| DPI | Vaccinated Turkeys (VT) | Vaccinated Chickens (VC) | Vaccinated and Infected Turkeys (VIT) | Vaccinated and Infected Chickens (VIC) | Infected Turkeys (IT) | Infected Chickens (IC) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caecum | Liver | Caecum | Liver | Caecum | liver | Caecum | Liver | Caecum | Liver | Caecum | Liver | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| 21 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | NA # | NA | 1 | 1 |
| Genes | Species | Vaccinated | Vaccinated and Infected | Infected | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caecum | Spleen | Caecum | Spleen | Caecum | Spleen | ||
| TLR1A | turkey | ||||||
| chicken | 21 | ||||||
| TLR1B | turkey | 4 | 10 | 4, 10 | |||
| chicken | 4 | 10 | |||||
| TLR2A | turkey | ||||||
| chicken | |||||||
| TLR2B | turkey | 4 | 4, 10 | ||||
| chicken | 4 | 10 | |||||
| TLR3 | turkey | 10 | 10 | 10 | |||
| chicken | 4, 10 | ||||||
| TLR4 | turkey | 10, 21 | 4, 10 | ||||
| chicken | 10 | 10 | 4 | ||||
| TLR5 | turkey | 10 | 10 | ||||
| chicken | 10, 21 | 21 | 21 | ||||
| TLR6 | turkey | 4 | 21 | ||||
| chicken | NA # | ||||||
| TLR7 | turkey | 10 | 10 | 10 | |||
| chicken | |||||||
| TLR13 | turkey | ||||||
| chicken | NA | ||||||
| TLR21 | turkey | NA | |||||
| chicken | 4 | 4 | |||||
| significant up-regulation at specific DPI p ≤ 0.05 | significant down-regulation at specific DPI p ≤ 0.05 | non-significant changes at all three DPI p ≥ 0.05 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitra, T.; Bramberger, B.; Bilic, I.; Hess, M.; Liebhart, D. Vaccination against the Protozoan Parasite Histomonas meleagridis Primes the Activation of Toll-like Receptors in Turkeys and Chickens Determined by a Set of Newly Developed Multiplex RT-qPCRs. Vaccines 2021, 9, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090960
Mitra T, Bramberger B, Bilic I, Hess M, Liebhart D. Vaccination against the Protozoan Parasite Histomonas meleagridis Primes the Activation of Toll-like Receptors in Turkeys and Chickens Determined by a Set of Newly Developed Multiplex RT-qPCRs. Vaccines. 2021; 9(9):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090960
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitra, Taniya, Beatrice Bramberger, Ivana Bilic, Michael Hess, and Dieter Liebhart. 2021. "Vaccination against the Protozoan Parasite Histomonas meleagridis Primes the Activation of Toll-like Receptors in Turkeys and Chickens Determined by a Set of Newly Developed Multiplex RT-qPCRs" Vaccines 9, no. 9: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090960
APA StyleMitra, T., Bramberger, B., Bilic, I., Hess, M., & Liebhart, D. (2021). Vaccination against the Protozoan Parasite Histomonas meleagridis Primes the Activation of Toll-like Receptors in Turkeys and Chickens Determined by a Set of Newly Developed Multiplex RT-qPCRs. Vaccines, 9(9), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090960








