Antigen Presentation of mRNA-Based and Virus-Vectored SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Presentation
2.1. Presentation of SARS-CoV-2 Antigens during COVID-19
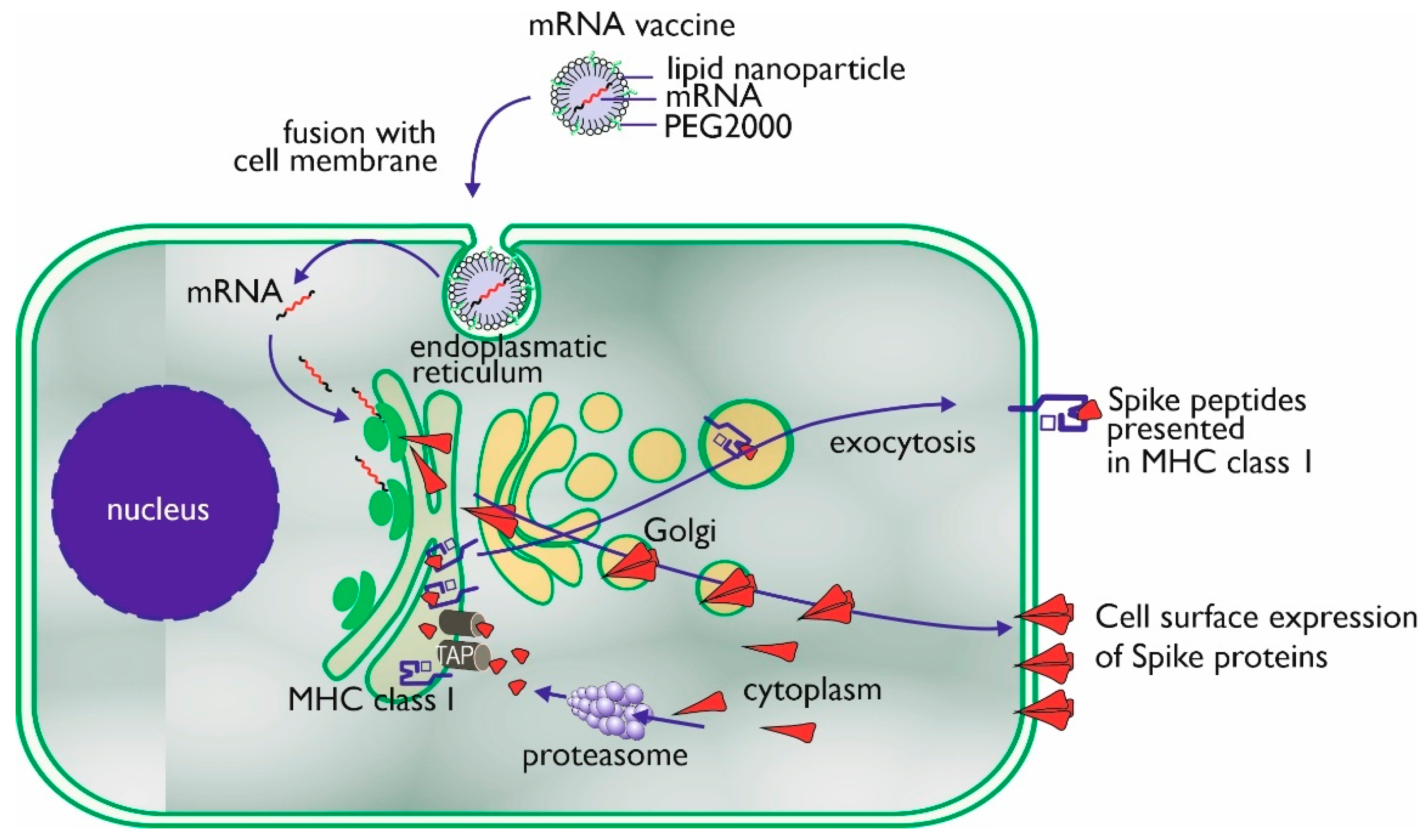
2.2. mRNA Vaccines
2.2.1. mRNA
2.2.2. Protein Sequence
2.2.3. Lipid Nano Particle (LNP)
2.2.4. Immune Response
2.3. Adenoviral Vector Vaccines
3. Antigen Presentation of Corona Vaccine Additives
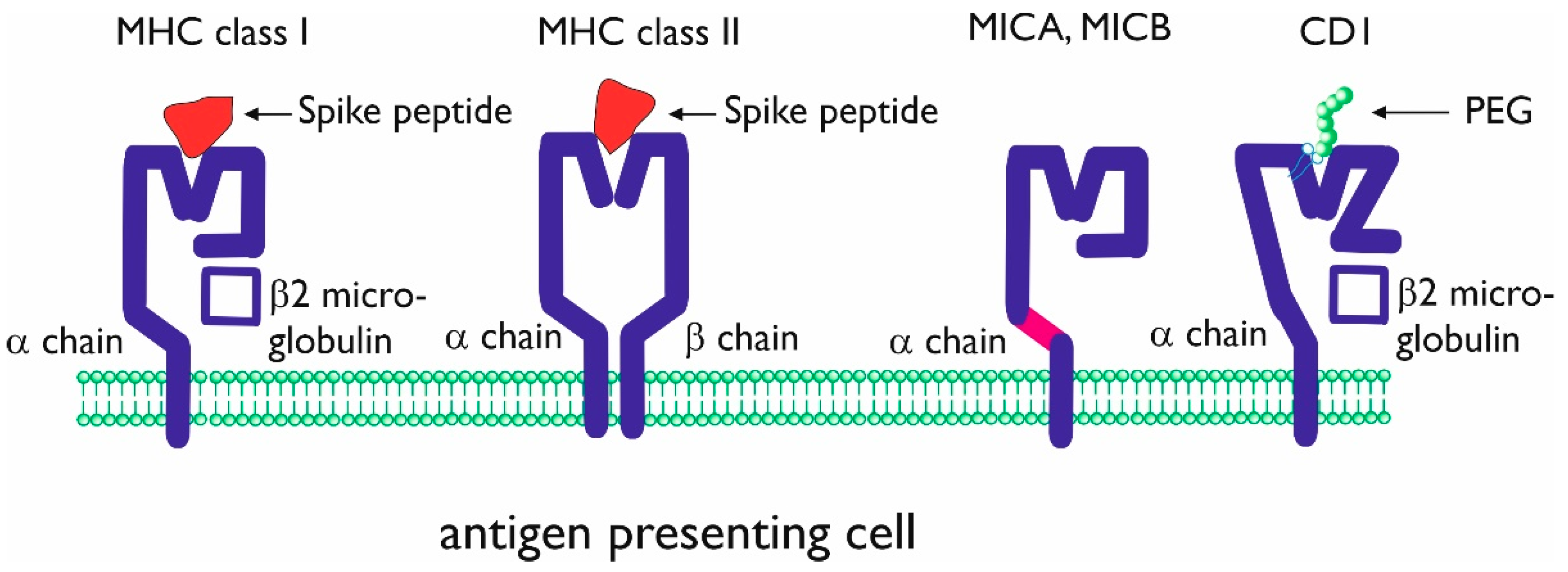
3.1. Unconventional Antigen Presentation Molecules
3.2. Hypersensitivity and PEG Antigen Presentation
3.3. Antigen Presentation of PEG
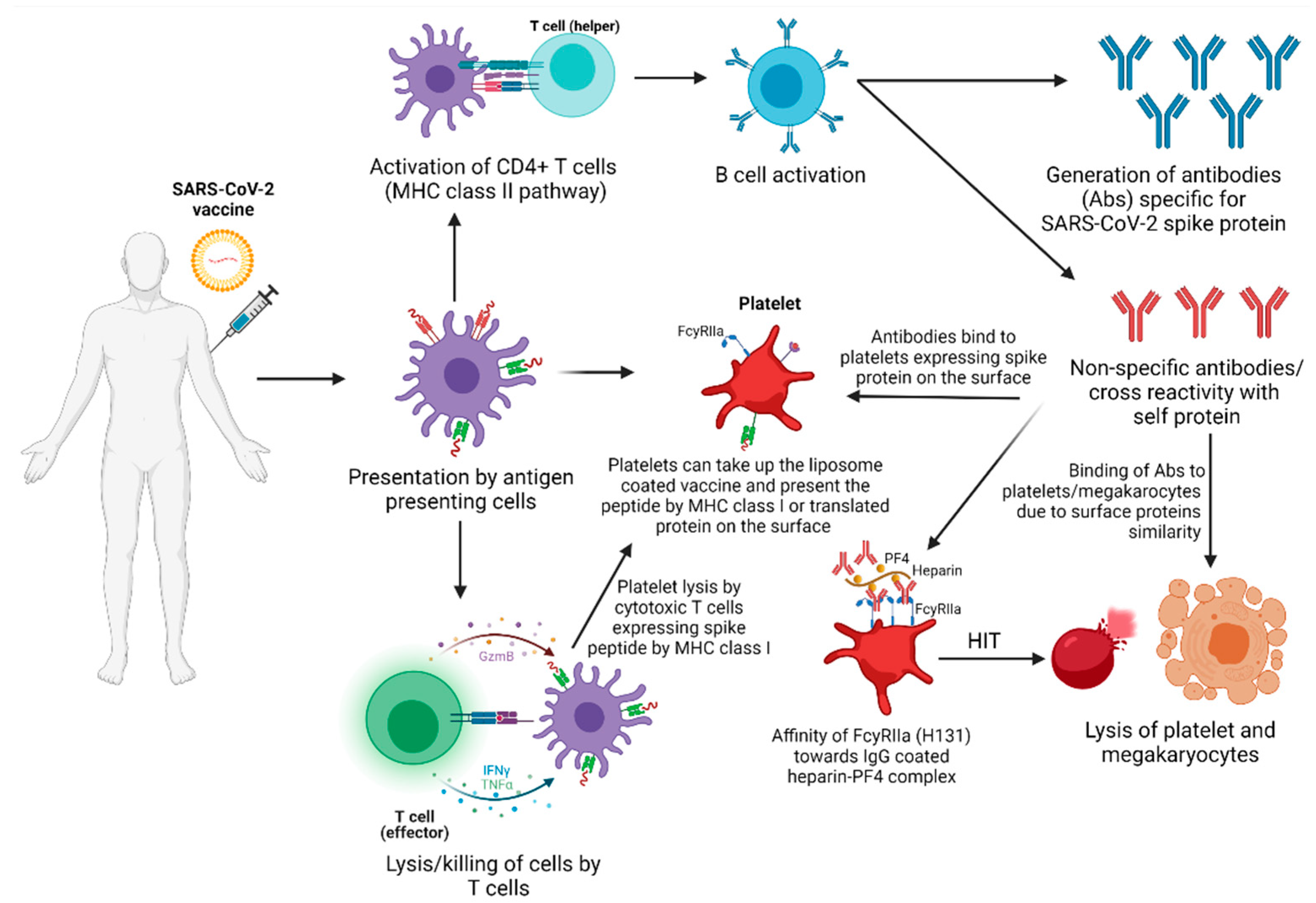
3.4. Thrombosis and Vaccine-Induced Thrombocytopenia (VITP)
3.4.1. Possible Mechanisms or Etiology of Vaccine-Induced ITP
Molecular Mimicry
Molecular Mimicry between SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Angiotensin-I
Translation and Antigen Presentation by MHC Class I by Platelets
PF4 Complex
FcγRIIa Polymorphism
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA)
Human Proteins or Peptides Present in Vaccines
Autoimmune Disorders
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cines, D.B.; Bussel, J.B. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2254–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Singh, D.; Lown, R.; Poles, A.; Solomon, T.; Levi, M.; Goldblatt, D.; Kotoucek, P.; Thomas, W.; Lester, W. Pathologic Antibodies to Platelet Factor 4 after Chadox1 Ncov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (Covid-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Prüβ, B.M. Current State of the First Covid-19 Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogliani, P.; Chetta, A.; Cazzola, M.; Calzetta, L. Sars-Cov-2 Neutralizing Antibodies: A Network Meta-Analysis across Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatatos, L.; Czartoski, J.; Wan, Y.H.; Homad, L.J.; Rubin, V.; Glantz, H.; Neradilek, M.; Seydoux, E.; Jennewein, M.F.; MacCamy, A.J.; et al. Mrna Vaccination Boosts Cross-Variant Neutralizing Antibodies Elicited by Sars-Cov-2 Infection. Science 2021, 372, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisgin, A.; Sanlioglu, A.D.; Eksi, Y.E.; Griffith, T.S.; Sanlioglu, S. Current Update on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Vaccine Development with a Special Emphasis on Gene Therapy Viral Vector Design and Construction for Vaccination. Hum. Gene. Ther. 2021, 32, 541–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.E.; Luz, B.; Niehaus, L.; Bhogal, P.; Bäzner, H.; Henkes, H. Thrombocytopenia and Intracranial Venous Sinus Thrombosis after ‘Covid-19 Vaccine Astrazeneca’ Exposure. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, J.M. Anaphylactic Reactions to Novel Mrna Sars-Cov-2/Covid-19 Vaccines. Vaccine 2021, 39, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, K.; Fujiogi, M.; Koutsogiannaki, S. Covid-19 Pathophysiology: A Review. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell Entry Mechanisms of Sars-Cov-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11727–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V’Kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus Biology and Replication: Implications for Sars-Cov-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.K.; Firmal, P.; Alam, A.; Ganguly, D.; Chattopadhyay, S. Overview of Immune Response During Sars-Cov-2 Infection: Lessons from the Past. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azkur, K.A.; Akdis, M.; Azkur, D.; Sokolowska, M.; van de Veen, W.; Brüggen, M.C.; O’Mahony, L.; Gao, Y.; Nadeau, K.; Akdis, C.A. Immune Response to Sars-Cov-2 and Mechanisms of Immunopathological Changes in Covid-19. Allergy 2020, 75, 1564–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, J.B.; Geall, A.J. Recent Innovations in Mrna Vaccines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 41, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavarone, C.; O’Hagan, T.D.; Yu, D.; Delahaye, N.F.; Ulmer, J.B. Mechanism of Action of Mrna-Based Vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, A.; Aljabbari, A.; Lokras, A.; Foged, C.; Thakur, A. Opportunities and Challenges in the Delivery of Mrna-Based Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, A.L.; Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Coler, R.N.; McCullough, M.P.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, J.L.; et al. An Mrna Vaccine against Sars-Cov-2—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1920–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two Rna-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, P.F.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the Bnt162b2 Mrna Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, M.J.; Lyke, K.E.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Raabe, V.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A.; et al. Phase i/Ii Study of Covid-19 Rna Vaccine Bnt162b1 in Adults. Nature 2020, 586, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schäfer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. Sars-Cov-2 Mrna Vaccine Design Enabled by Prototype Pathogen Preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.B.; Kanevsky, I.; Che, Y.; Swanson, K.A.; Muik, A.; Vormehr, M.; Kranz, L.M.; Walzer, K.C.; Hein, S.; Güler, A.; et al. Bnt162b Vaccines Protect Rhesus Macaques from Sars-Cov-2. Nature 2021, 592, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Vogler, I.; Derhovanessian, E.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Quandt, J.; Bidmon, N.; Ulges, A.; Baum, A.; et al. Bnt162b2 Vaccine Induces Neutralizing Antibodies and Poly-Specific T Cells in Humans. Nature 2021, 595, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.; Sorensen, E.W.; Mintri, S.; Rabideau, A.E.; Zheng, W.; Besin, G.; Khatwani, N.; Su, S.V.; Miracco, E.J.; Issa, W.J.; et al. Impact of Mrna Chemistry and Manufacturing Process on Innate Immune Activation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, P.J.; Wang, B.; Reid, D.W.; Presnyak, V.; McFadyen, I.J.; Morris, D.R.; Seelig, G. Human 5′ Utr Design and Variant Effect Prediction from a Massively Parallel Translation Assay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlandini von Niessen, A.G.; Poleganov, M.A.; Rechner, C.; Plaschke, A.; Kranz, L.M.; Fesser, S.; Diken, M.; Löwer, M.; Vallazza, B.; Beissert, T.; et al. Improving Mrna-Based Therapeutic Gene Delivery by Expression-Augmenting 3’ Utrs Identified by Cellular Library Screening. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holtkamp, S.; Kreiter, S.; Selmi, A.; Simon, P.; Koslowski, M.; Huber, C.; Türeci, O.; Sahin, U. Modification of Antigen-Encoding Rna Increases Stability, Translational Efficacy, and T-Cell Stimulatory Capacity of Dendritic Cells. Blood 2006, 108, 4009–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karikó, K.; Buckstein, M.; Ni, H.; Weissman, D. Suppression of Rna Recognition by Toll-Like Receptors: The Impact of Nucleoside Modification and the Evolutionary Origin of RNA. Immunity 2005, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karikó, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Welsh, F.A.; Ludwig, J.; Kato, H.; Akira, S.; Weissman, D. Incorporation of Pseudouridine into Mrna Yields Superior Nonimmunogenic Vector with Increased Translational Capacity and Biological Stability. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Ludwig, J.; Weissman, D. Generating the Optimal Mrna for Therapy: Hplc Purification Eliminates Immune Activation and Improves Translation of Nucleoside-Modified, Protein-Encoding Mrna. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andries, O.; Cafferty, S.M.; de Smedt, S.C.; Weiss, R.; Sanders, N.N.; Kitada, T. N(1)-Methylpseudouridine-Incorporated Mrna Outperforms Pseudouridine-Incorporated Mrna by Providing Enhanced Protein Expression and Reduced Immunogenicity in Mammalian Cell Lines and Mice. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, K.J.; Mir, F.F.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Kaczmarek, J.C.; Hurtado, J.E.; Yang, J.H.; Webber, M.J.; Kowalski, P.S.; Heartlein, M.W.; DeRosa, F.; et al. Efficacy and Immunogenicity of Unmodified and Pseudouridine-Modified Mrna Delivered Systemically with Lipid Nanoparticles In vivo. Biomaterials 2016, 109, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauger, D.M.; Cabral, B.J.; Presnyak, V.; Su, S.V.; Reid, D.W.; Goodman, B.; Link, K.; Khatwani, N.; Reynders, J.; Moore, M.J.; et al. Mrna Structure Regulates Protein Expression through Changes in Functional Half-Life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24075–24083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Svitkin, Y.V.; Cheng, Y.M.; Chakraborty, T.; Presnyak, V.; John, M.; Sonenberg, N. N1-Methyl-Pseudouridine in Mrna Enhances Translation through Eif2α-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms by Increasing Ribosome Density. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 6023–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramps, T.; Probst, J. Messenger Rna-Based Vaccines: Progress, Challenges, Applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2013, 4, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. Mrna Vaccines—A New Era in Vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thess, A.; Grund, S.; Mui, B.L.; Hope, M.J.; Baumhof, P.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Schlake, T. Sequence-engineered mRNA Without Chemical Nucleoside Modifications Enables an Effective Protein Therapy in Large Animals. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Derhovanessian, E.; Vogler, I.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K.; Quandt, J.; Maurus, D.; et al. Covid-19 Vaccine Bnt162b1 Elicits Human Antibody and T(H)1 T Cell Responses. Nature 2020, 586, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutard, B.; Valle, C.; de Lamballerie, X.; Canard, B.; Seidah, N.G.; Decroly, E. The Spike Glycoprotein of the New Coronavirus 2019-Ncov Contains a Furin-Like Cleavage Site Absent in Cov of the Same Clade. Antiviral. Res. 2020, 176, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallesen, J.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Wrapp, D.; Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Turner, H.L.; Cottrell, C.A.; Becker, M.M.; Wang, L.; Shi, W.; et al. Immunogenicity and Structures of a Rationally Designed Prefusion Mers-Cov Spike Antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7348–E7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Yan, J. Covid-19 Mrna Vaccines. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Fernández, S.; Lacroix, C.; Exposito, J.Y.; Verrier, B. Tailoring Mrna Vaccine to Balance Innate/Adaptive Immune Response. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, M.; Ansell, S.M.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Butler, D.; Eltepu, L.; Matsuda, S.; Narayanannair, J.K.; et al. Maximizing the Potency of Sirna Lipid Nanoparticles for Hepatic Gene Silencing in Vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 8529–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, K.J.; Benenato, K.E.; Jacquinet, E.; Lee, A.; Woods, A.; Yuzhakov, O.; Himansu, S.; Deterling, J.; Geilich, B.M.; Ketova, T.; et al. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Intramuscular Administration of Mrna Vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.; Ashwanikumar, N.; Robinson, E.; DuRoss, A.; Sun, C.; Murphy-Benenato, K.E.; Mihai, C.; Almarsson, Ö.; Sahay, G. Boosting Intracellular Delivery of Lipid Nanoparticle-Encapsulated MRNA. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5711–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.A.; Jayaraman, M.; Matsuda, S.; Liu, J.; Barros, S.; Querbes, W.; Tam, Y.K.; Ansell, S.M.; Kumar, V.; Qin, J.; et al. Biodegradable Lipids Enabling Rapidly Eliminated Lipid Nanoparticles for Systemic Delivery of RNAI Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brito, L.A.; Chan, M.; Shaw, C.A.; Hekele, A.; Carsillo, T.; Schaefer, M.; Archer, J.; Seubert, A.; Otten, G.R.; Beard, C.W.; et al. A cationic nanoemulsion for the delivery of next-generation RNA vaccines. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, F.; Lindgren, G.; Lin, A.; Thompson, E.A.; Ols, S.; Röhss, J.; John, S.; Hassett, K.; Yuzhakov, O.; Bahl, K.; et al. Efficient Targeting and Activation of Antigen-Presenting Cells In vivo after Modified Mrna Vaccine Administration in Rhesus Macaques. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2635–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eifer, M.; Tau, N.; Alhoubani, Y.; Kanana, N.; Domachevsky, L.; Shams, J.; Keret, N.; Gorfine, M.; Eshet, Y. Covid-19 mRNA Vaccination: Age and Immune Status and its Association with Axillary Lymph Node PET/CT Uptake. J. Nucl. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, G.; Ols, S.; Liang, F.; Thompson, E.A.; Lin, A.; Hellgren, F.; Bahl, K.; John, S.; Yuzhakov, O.; Hassett, K.J.; et al. Induction of Robust B Cell Responses after Influenza Mrna Vaccination Is Accompanied by Circulating Hemagglutinin-Specific Icos+ Pd-1+ Cxcr3+ T Follicular Helper Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Widge, A.T.; Jackson, L.A.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Sars-Cov-2 Mrna-1273 Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2427–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, K.S.; Flynn, B.; Foulds, K.E.; Francica, J.R.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Werner, A.P.; Flach, B.; O’Connell, S.; Bock, K.W.; Minai, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Mrna-1273 Vaccine against Sars-Cov-2 in Nonhuman Primates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, O.P.; Segura, E.; Savina, A.; Amigorena, S. Cross-Presentation by Dendritic Cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, P.A. Potential Cross-Reactive Immunity to Sars-Cov-2 from Common Human Pathogens and Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 586984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alameh, M.G.; Weissman, D.; Pardi, N. Messenger Rna-Based Vaccines against Infectious Diseases. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ewer, K.J.; Lambe, T.; Rollier, C.S.; Spencer, A.J.; Hill, A.V.; Dorrell, L. Viral Vectors as Vaccine Platforms: From Immunogenicity to Impact. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 41, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, W.S.; Toth, K. Adenovirus Vectors for Gene Therapy, Vaccination and Cancer Gene Therapy. Curr. Gene. Ther. 2013, 13, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Bishop, E.S.; Zhang, R.; Yu, X.; Farina, E.M.; Yan, S.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, Z.; Shu, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Adenovirus-Mediated Gene Delivery: Potential Applications for Gene and Cell-Based Therapies in the New Era of Personalized Medicine. Genes Dis. 2017, 4, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystal, R.G. Adenovirus: The First Effective in Vivo Gene Delivery Vector. Hum. Gene Ther. 2014, 25, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Mese, K.; Bunz, O.; Ehrhardt, A. State-of-the-Art Human Adenovirus Vectorology for Therapeutic Approaches. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 3609–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tatsis, N.; Ertl, H.C. Adenoviruses as Vaccine Vectors. Mol. Ther. 2004, 10, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, A.; Hage, E.; Ganzenmueller, T.; Böttcher, S.; Hofmann, J.; Hamprecht, K.; Obermeier, P.; Rath, B.; Hausmann, F.; Dobner, T.; et al. Molecular Evolution of Human Adenovirus (Hadv) Species, C. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiver, J.W.; Fu, T.M.; Chen, L.; Casimiro, D.R.; Davies, M.E.; Evans, R.K.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Simon, A.J.; Trigona, W.L.; Dubey, S.A.; et al. Replication-Incompetent Adenoviral Vaccine Vector Elicits Effective Anti-Immunodeficiency-Virus Immunity. Nature 2002, 415, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shott, J.P.; McGrath, S.M.; Pau, M.G.; Custers, J.H.; Ophorst, O.; Demoitié, M.A.; Dubois, M.C.; Komisar, J.; Cobb, M.; Kester, K.E.; et al. Adenovirus 5 and 35 Vectors Expressing Plasmodium Falciparum Circumsporozoite Surface Protein Elicit Potent Antigen-Specific Cellular Ifn-Gamma and Antibody Responses in Mice. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, K.; Tatsis, N.; Korioth-Schmitz, B.; Lasaro, M.O.; Hensley, S.E.; Lin, S.W.; Li, Y.; Giles-Davis, W.; Cun, A.; Zhou, D.; et al. Effect of Preexisting Immunity to Adenovirus Human Serotype 5 Antigens on the Immune Responses of Nonhuman Primates to Vaccine Regimens Based on Human- or Chimpanzee-Derived Adenovirus Vectors. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6594–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Z.; Gao, G.; Reyes-Sandoval, A.; Cohen, C.J.; Li, Y.; Bergelson, J.M.; Wilson, J.M.; Ertl, H.C. Novel, Chimpanzee Serotype 68-Based Adenoviral Vaccine Carrier for Induction of Antibodies to a Transgene Product. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Cun, A.; Yang, W.; Ellenberg, S.; Switzer, W.M.; Kalish, M.L.; Ertl, H.C. Chimpanzee Adenovirus Antibodies in Humans, Sub-Saharan Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seregin, S.S.; Amalfitano, A. Overcoming Pre-Existing Adenovirus Immunity by Genetic Engineering of Adenovirus-Based Vectors. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Bailey, M.; Hensley, L.; Asiedu, C.; Geisbert, J.; Stanley, D.; Honko, A.; Johnson, J.; Mulangu, S.; Pau, M.G.; et al. Recombinant Adenovirus Serotype 26 (Ad26) and Ad35 Vaccine Vectors Bypass Immunity to Ad5 and Protect Nonhuman Primates against Ebolavirus Challenge. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4222–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanley, D.A.; Honko, A.N.; Asiedu, C.; Trefry, J.C.; Lau-Kilby, A.W.; Johnson, J.C.; Hensley, L.; Ammendola, V.; Abbate, A.; Grazioli, F.; et al. Chimpanzee Adenovirus Vaccine Generates Acute and Durable Protective Immunity against Ebolavirus Challenge. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1126–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffon, K.J.D.A. The Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor: Virological and Biological Beauty. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, F.L.; Smiley, J.; Russell, W.C.; Nairn, R. Characteristics of a Human Cell Line Transformed by DNA from Human Adenovirus Type 5. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 36, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemckert, A.A.C.; Grimbergen, J.; Smits, S.; Hartkoorn, E.; Holterman, L.; Berkhout, B.; Barouch, D.H.; Vogels, R.; Quax, P.; Goudsmit, J.; et al. Generation of a Novel Replication-Incompetent Adenoviral Vector Derived from Human Adenovirus Type 49: Manufacture on Per.C6 Cells, Tropism and Immunogenicity. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Mondal, M.; Zhou, D. Development of Novel Vaccine Vectors: Chimpanzee Adenoviral Vectors. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bezbaruah, R.; Borah, P.; Kakoti, B.B.; Al-Shar, I.N.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Jaradat, D.M.M.; Al-Zeer, M.A.; Abu-Romman, S. Developmental Landscape of Potential Vaccine Candidates Based on Viral Vector for Prophylaxis of Covid-19. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 635337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, K.E.; le Gars, M.; Sadoff, J.; de Groot, A.M.; Heerwegh, D.; Truyers, C.; Atyeo, C.; Loos, C.; Chandrashekar, A.; McMahan, K.; et al. Immunogenicity of the Ad26.Cov2.S Vaccine for Covid-19. JAMA 2021, 325, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoff, J.; le Gars, M.; Shukarev, G.; Heerwegh, D.; Truyers, C.; de Groot, A.M.; Stoop, J.; Tete, S.; van Damme, W.; Leroux-Roel, I.s.; et al. Interim Results of a Phase 1-2a Trial of Ad26.Cov2.S Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, M.D.; Spencer, A.J.; Edwards, N.J.; Wadell, G.; Bojang, K.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hill, A.V.; Cottingham, M.G. A Novel Chimpanzee Adenovirus Vector with Low Human Seroprevalence: Improved Systems for Vector Derivation and Comparative Immunogenicity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Logunov, D.Y.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Shcheblyakov, D.V.; Tukhvatulin, A.I.; Zubkova, O.V.; Dzharullaeva, A.S.; Kovyrshina, A.V.; Lubenets, N.L.; Grousova, D.M.; Erokhova, A.S.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of an Rad26 and Rad5 Vector-Based Heterologous Prime-Boost Covid-19 Vaccine: An Interim Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Phase 3 Trial in Russia. Lancet 2021, 397, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.C.; Guan, X.H.; Li, Y.H.; Huang, J.Y.; Jiang, T.; Hou, L.H.; Li, J.X.; Yang, B.F.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.J.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of a Recombinant Adenovirus Type-5-Vectored Covid-19 Vaccine in Healthy Adults Aged 18 Years or Older: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.; Kumari, P.; Saha, L. Covid-19 Vaccine: A Recent Update in Pipeline Vaccines, Their Design and Development Strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 892, 173751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Craft, J. T Follicular Helper Cell Heterogeneity: Time, Space, and Function. Immunol Rev. 2019, 288, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro, T.; Nair, N. Allergic Reactions Including Anaphylaxis after Receipt of the First Dose of Pfizer-Biontech Covid-19 Vaccine. JAMA 2021, 325, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. Covid-19: Latest Updates. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/public-health-threats/coronavirus-disease-covid-19/covid-19-latest-updates (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Stone, C.A.; Liu, Y., Jr.; Relling, M.V.; Krantz, M.S.; Pratt, A.L.; Abreo, A.; Hemler, J.A.; Phillips, E.J. Immediate Hypersensitivity to Polyethylene Glycols and Polysorbates: More Common Than We Have Recognized. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1533–1540.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogiuri, G.; Foti, C.; Nettis, E.; di Leo, E.; Macchia, L.; Vacca, A. Polyethylene Glycols and Polysorbates: Two Still Neglected Ingredients Causing True Ige-Mediated Reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2509–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaturay, P.; Nasser, S.; Ewan, P. Polyethylene Glycol-Induced Systemic Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Choi, J.; Lee, K.C.; Na, D.H. Emerging Pegylated Non-Biologic Drugs. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2019, 24, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenande, E.; Garvey, L.H. Immediate-Type Hypersensitivity to Polyethylene Glycols: A Review. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, E.C.; de Castro, M.V.; Naslavsky, M.S.; Scliar, M.O.; Silva, N.S.B.; Andrade, H.S.; Souza, A.S.; Pereira, R.N.; Castro, C.F.B.; Mendes-Junior, C.T.; et al. Immunogenetics of Resistance to Sars-Cov-2 Infection in Discordant Couples. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salabei, J.K.; Fishman, T.J.; Asnake, Z.T.; Ali, A.; Iyer, U.G. Covid-19 Coagulopathy: Current Knowledge and Guidelines on Anticoagulation. Heart Lung 2021, 50, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Banerjee, M. Immune Thrombocytopenia Secondary to Covid-19: A Systematic Review. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VAERS. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, USA. Available online: https://vaers.hhs.gov/data.html (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Perricone, C.; Ceccarelli, F.; Nesher, G.; Borella, E.; Odeh, Q.; Conti, F.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Valesini, G. Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) Associated with Vaccinations: A Review of Reported Cases. Immunol. Res. 2014, 60, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, J. Covid-19: European Countries Suspend Use of Oxford-Astrazeneca Vaccine after Reports of Blood Clots. BMJ 2021, 372, n699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanduc, D.; Shoenfeld, Y. On the Molecular Determinants of the Sars-Cov-2 Attack. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanduc, D. Peptide Cross-Reactivity: The Original Sin of Vaccines. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2012, 4, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oldstone, M.B. Molecular Mimicry: Its Evolution from Concept to Mechanism as a Cause of Autoimmune Diseases. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2014, 33, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanduc, D.; Shoenfeld, Y. Molecular Mimicry between Sars-Cov-2 Spike Glycoprotein and Mammalian Proteomes: Implications for the Vaccine. Immunol. Res. 2020, 68, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyrich, A.S.; Schwertz, H.; Kraiss, L.W.; Zimmerman, G.A. Protein Synthesis by Platelets: Historical and New Perspectives. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after Chadox1 Ncov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, M.; Berger, J.S. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (Hit): Review of Incidence, Diagnosis, and Management. Vasc. Med. 2020, 25, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Al-Tamimi, M.; Baker, R.I.; Andrews, R.K.; Gardiner, E.E. The Platelet Fc Receptor, Fcγriia. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 268, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavkovic, M.; Petlichkovski, A.; Karanfilski, O.; Cevreska, L.; Stojanovic, A. Fc Gamma Receptor Polymorphisms in Patients with Immune Thrombocytopenia. Hematology 2018, 23, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clancy, R.; el Bannoudi, H.; Rasmussen, S.E.; Bornkamp, N.; Allen, N.; Dann, R.; Reynolds, H.; Buyon, J.P.; Berger, J.S. Human Low-Affinity Igg Receptor Fcγriia Polymorphism H131r Associates with Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Increased Platelet Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arepally, G.; McKenzie, S.E.; Jiang, X.M.; Poncz, M.; Cines, D.B. Fc Gamma Riia H/R 131 Polymorphism, Subclass-Specific Igg Anti-Heparin/Platelet Factor 4 Antibodies and Clinical Course in Patients with Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia and Thrombosis. Blood 1997, 89, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Mendonça, L.; Allen, E.R.; Howe, A.; Lee, M.; Allen, J.D.; Chawla, H.; Pulido, D.; Donnellan, F.; Davies, H.; et al. Native-Like Sars-Cov-2 Spike Glycoprotein Expressed by Chadox1 Ncov-19/Azd1222 Vaccine. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahévas, M.; Moulis, G.; Andres, E.; Riviere, E.; Garzaro, M.; Crickx, E.; Guillotin, V.; Malphettes, M.; Galicier, L.; Noel, N.; et al. Clinical Characteristics, Management and Outcome of Covid-19-Associated Immune Thrombocytopenia: A French Multicentre Series. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, e224–e229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althaus, K.; Marini, I.; Zlamal, J.; Pelzl, L.; Singh, A.; Häberle, H.; Mehrländer, M.; Hammer, S.; Schulze, H.; Bitzer, M.; et al. Antibody-Induced Procoagulant Platelets in Severe Covid-19 Infection. Blood 2021, 137, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J. What Are Autoimmune Disorders? WebMD LLC. Available online: https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/autoimmune-diseases (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Velikova, T.; Georgiev, T. Sars-Cov-2 Vaccines and Autoimmune Diseases Amidst the Covid-19 Crisis. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Cines, D.B.; Gernsheimer, T.; Kessler, C.; Michel, M.; Tarantino, M.D.; Semple, J.W.; Arnold, D.M.; Godeau, B.; Lambert, M.P.; et al. Thrombocytopenia Following Pfizer and Moderna Sars-Cov-2 Vaccination. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, H.A. Covid Vaccines and Thrombotic Events: Ema Issued Warning to Patients and Healthcare Professionals. J. Pharm. Policy Pract. 2021, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rijkers, G.T.; Weterings, N.; Obregon-Henao, A.; Lepolder, M.; Dutt, T.S.; van Overveld, F.J.; Henao-Tamayo, M. Antigen Presentation of mRNA-Based and Virus-Vectored SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080848
Rijkers GT, Weterings N, Obregon-Henao A, Lepolder M, Dutt TS, van Overveld FJ, Henao-Tamayo M. Antigen Presentation of mRNA-Based and Virus-Vectored SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. Vaccines. 2021; 9(8):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080848
Chicago/Turabian StyleRijkers, Ger T., Nynke Weterings, Andres Obregon-Henao, Michaëla Lepolder, Taru S. Dutt, Frans J. van Overveld, and Marcela Henao-Tamayo. 2021. "Antigen Presentation of mRNA-Based and Virus-Vectored SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines" Vaccines 9, no. 8: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080848
APA StyleRijkers, G. T., Weterings, N., Obregon-Henao, A., Lepolder, M., Dutt, T. S., van Overveld, F. J., & Henao-Tamayo, M. (2021). Antigen Presentation of mRNA-Based and Virus-Vectored SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. Vaccines, 9(8), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080848






