Vaccine Composition Formulated with a Novel Lactobacillus-Derived Exopolysaccharides Adjuvant Provided High Protection against Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Ethics Statement
2.2. Bacterial Strains
2.3. Extraction and Purification of EPS30
2.4. Expression Analysis of Recombinant MntC
2.5. Vaccination
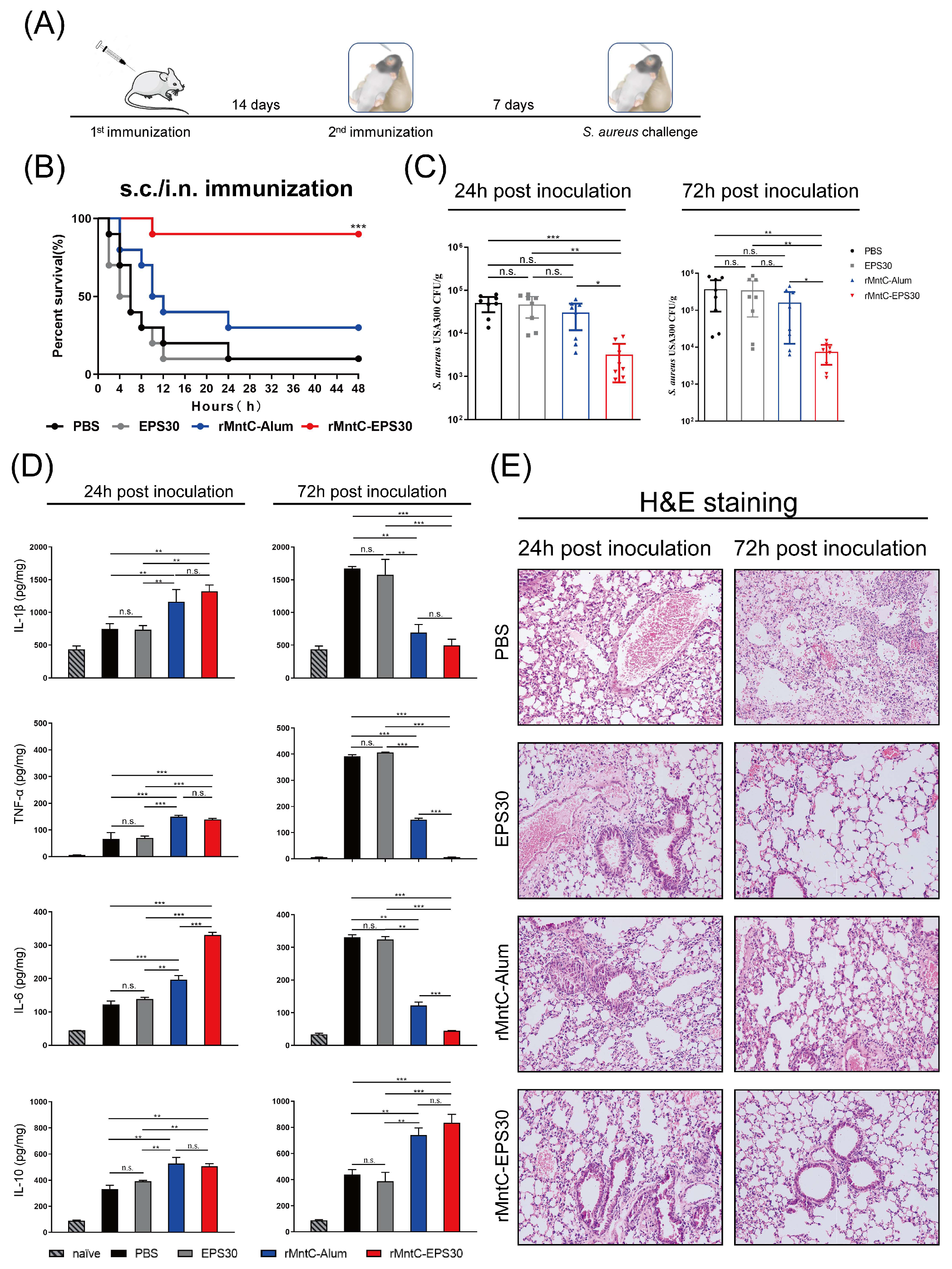
2.6. Murine Pneumonia Model
2.7. Murine Skin Infection Model
2.8. ELISA for Specific Antibodies
2.9. Cytokine Determination
2.10. Intracellular Cytokine Staining
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. rMntC-EPS30 Vaccination Provided High Protection against S. aureus-Induced Pneumonia
3.2. rMntC-EPS30 Vaccination Induced Superior Humoral Immune Response
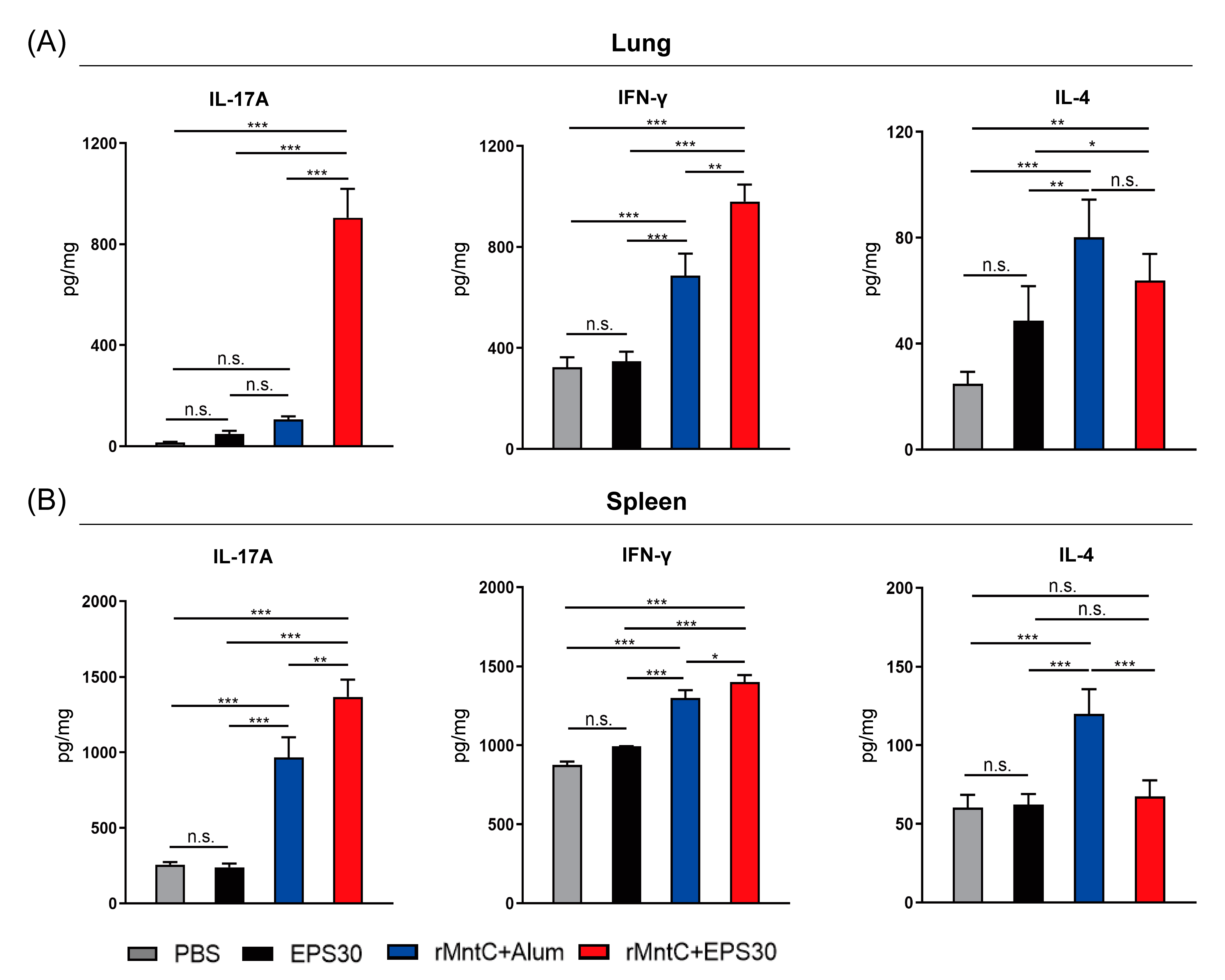
3.3. rMntC-EPS30 Vaccination Induced High Levels of IL-17A and IFN-γ Both in Lung and Spleen
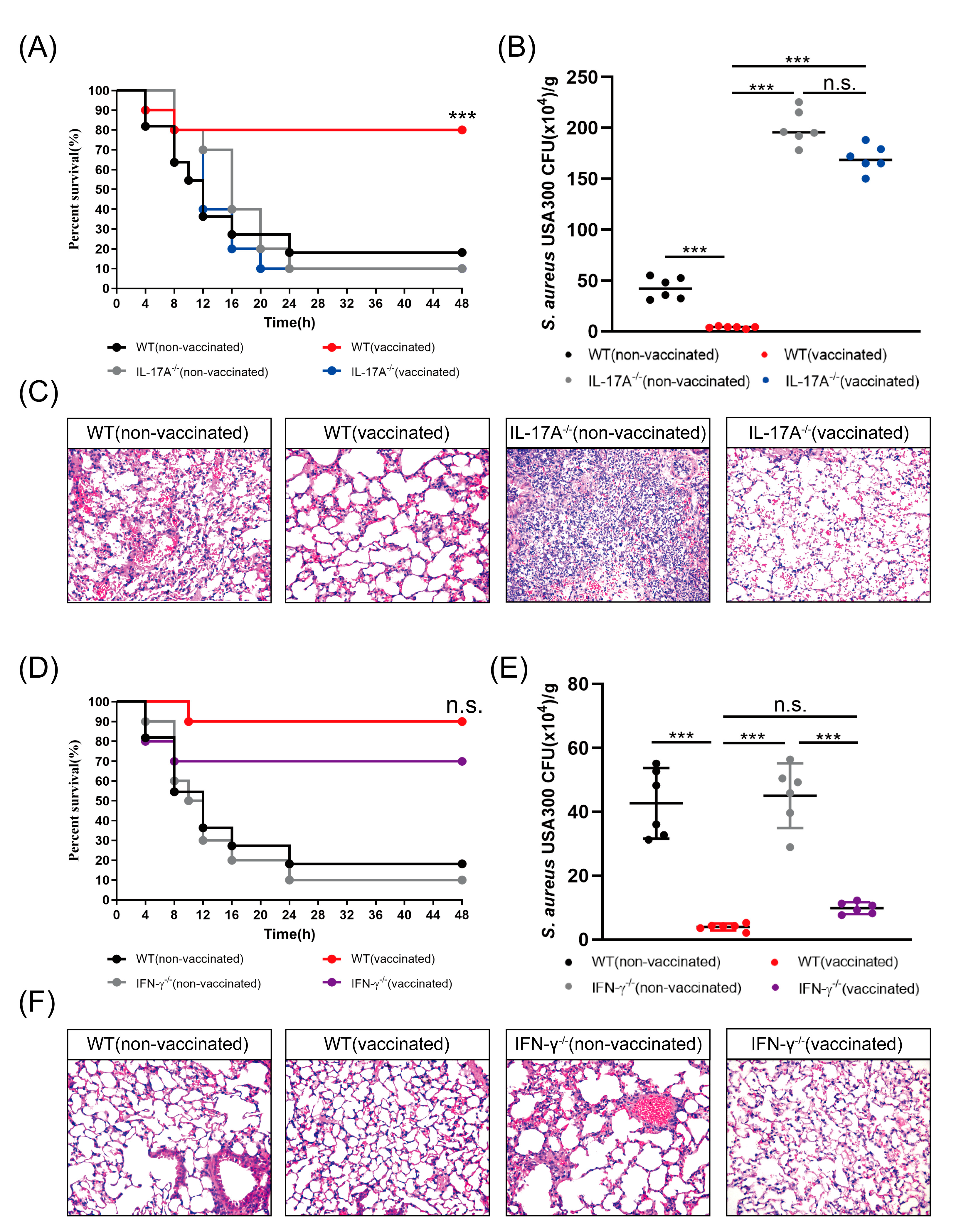
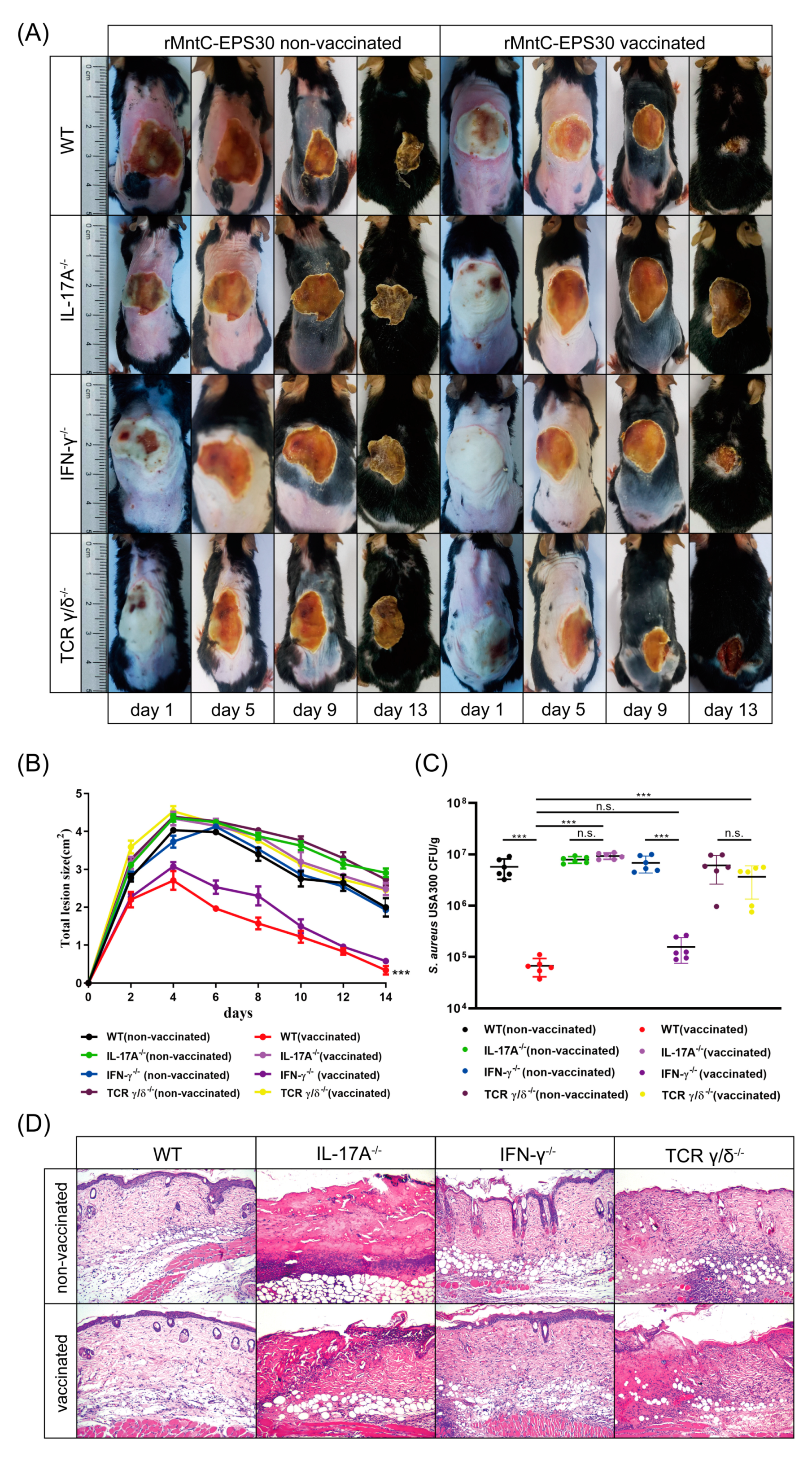
3.4. rMntC-EPS Vaccination Provided Protective Effect Was Significantly Reduced in the IL-17A-Deficient Mice But Not in IFN-γ-Deficient Mice
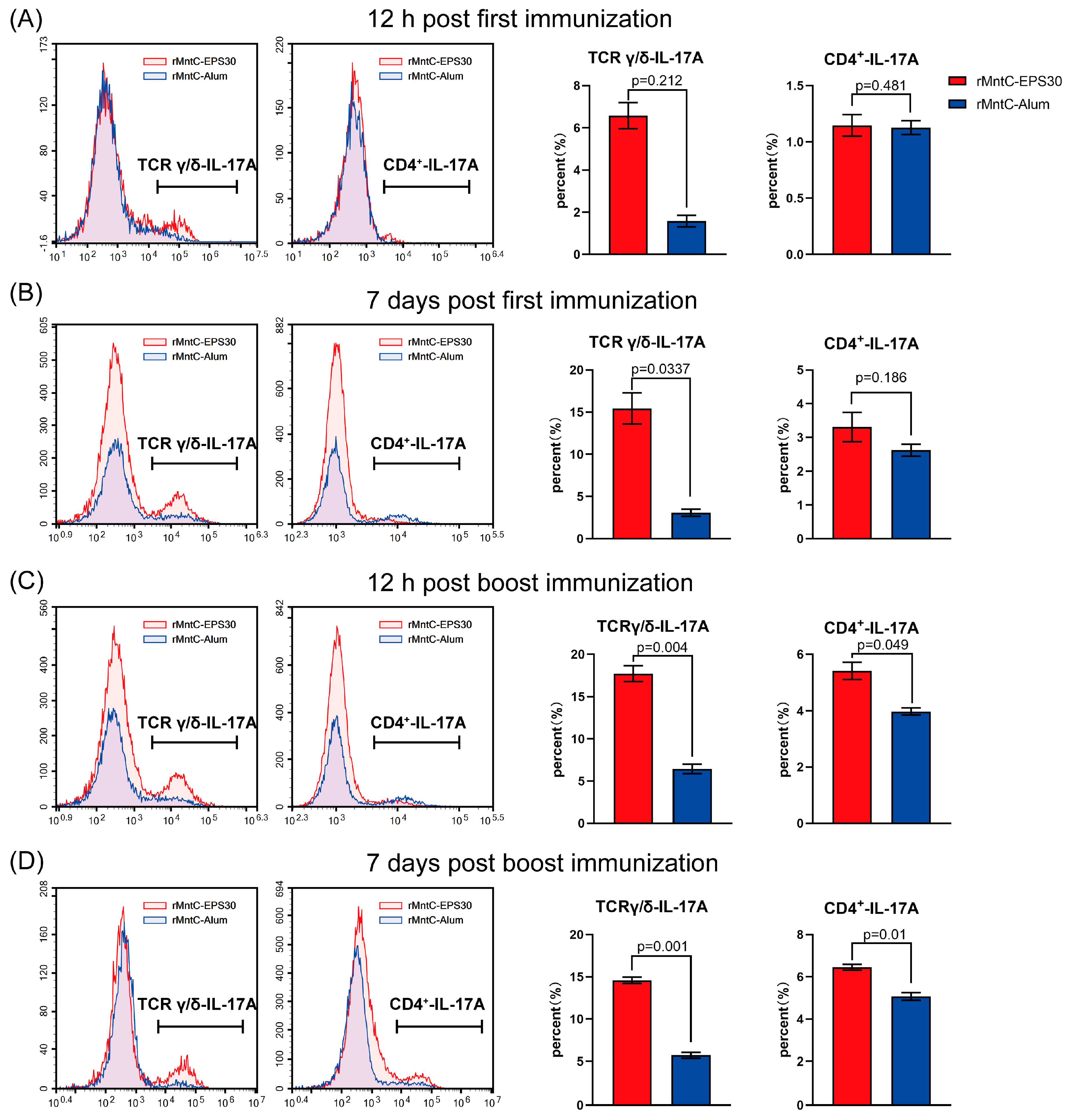
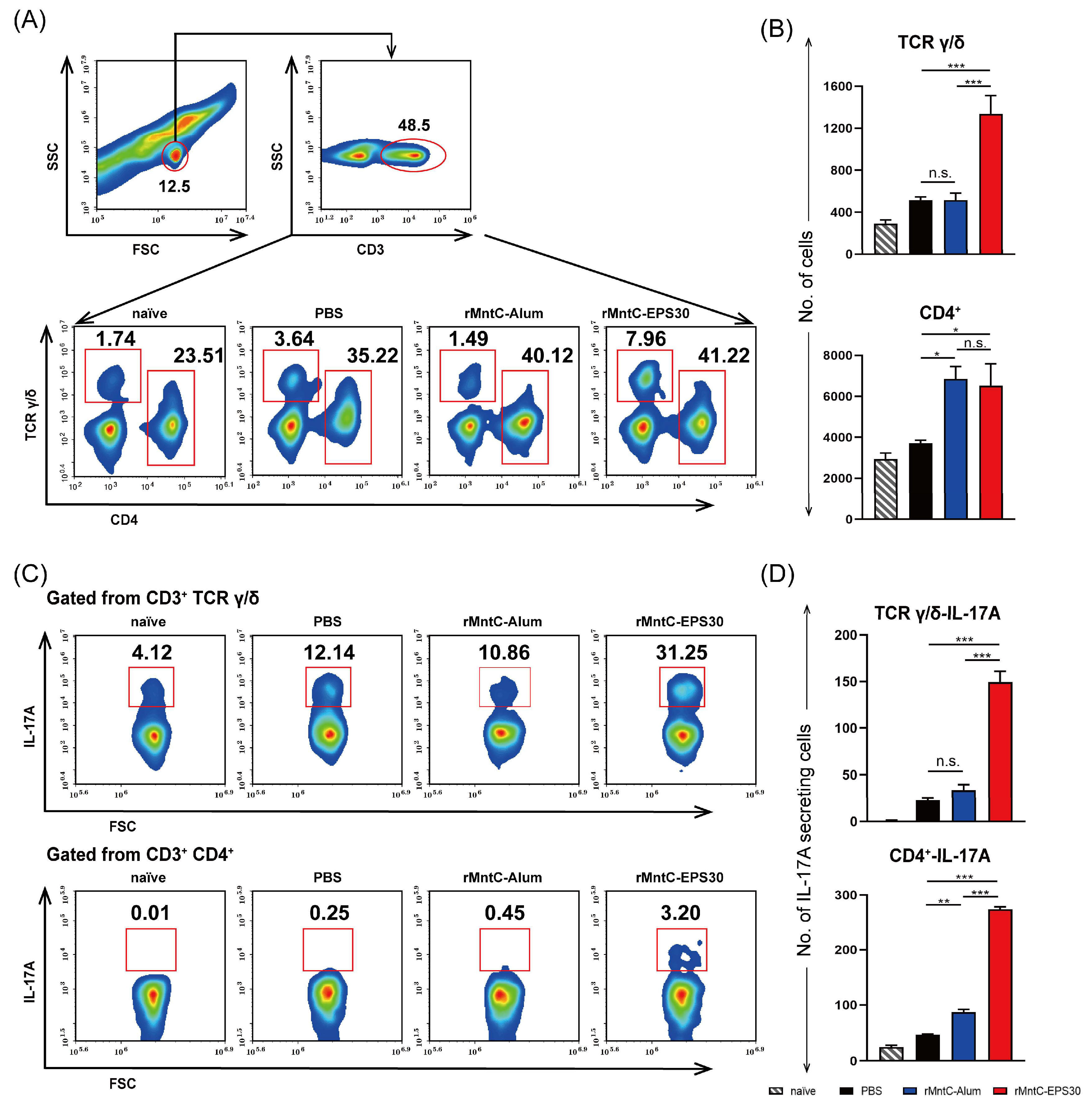
3.5. rMntC-EPS30 Vaccination Induced Robust Th17/γδ T 17 Primary and Recall Responses
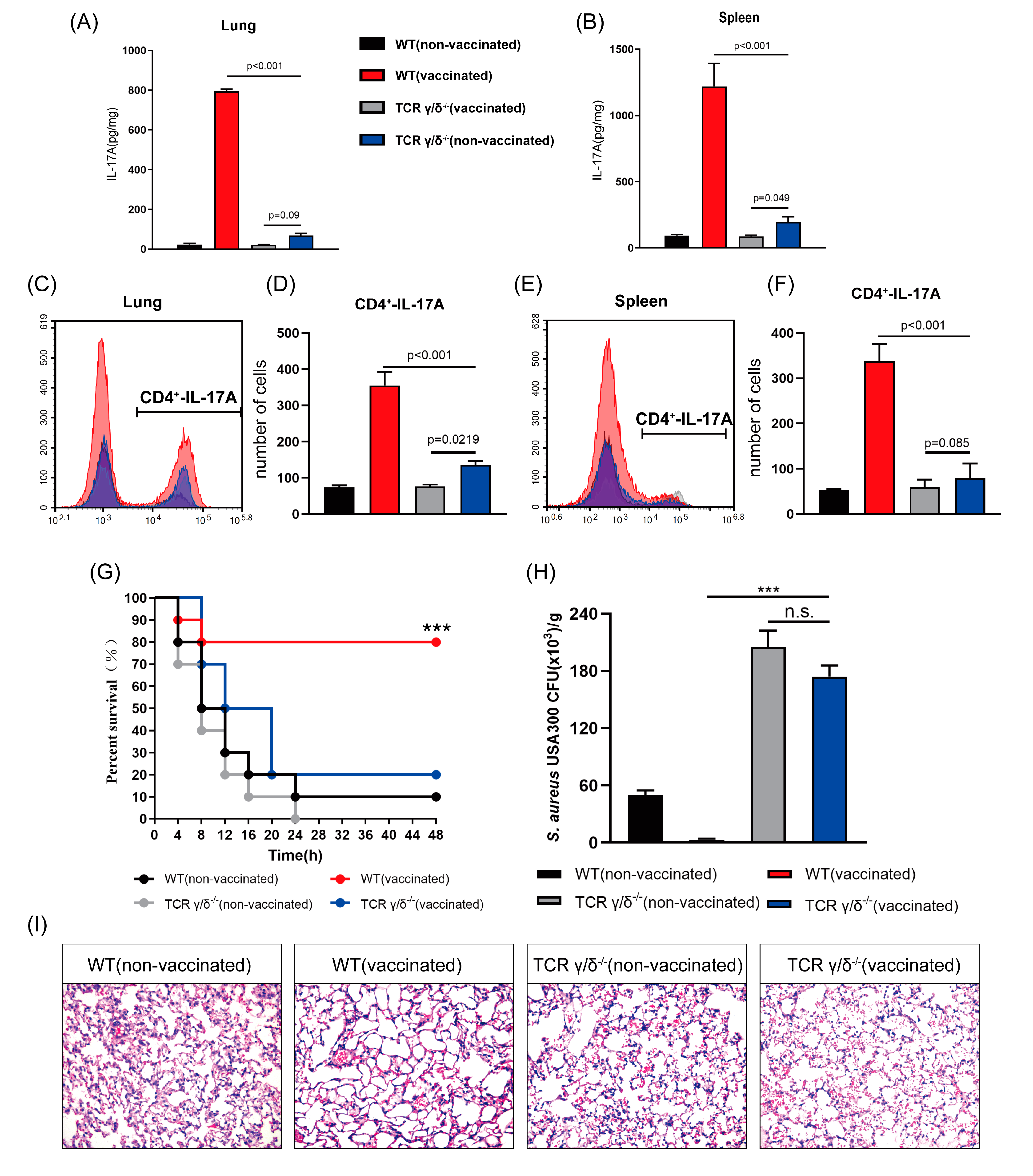
3.6. rMntC-EPS30 Lost Both Its Increased IL-17A Secreting and Superior Protection Post-Vaccination in TCRγ/δ Knockout Mice
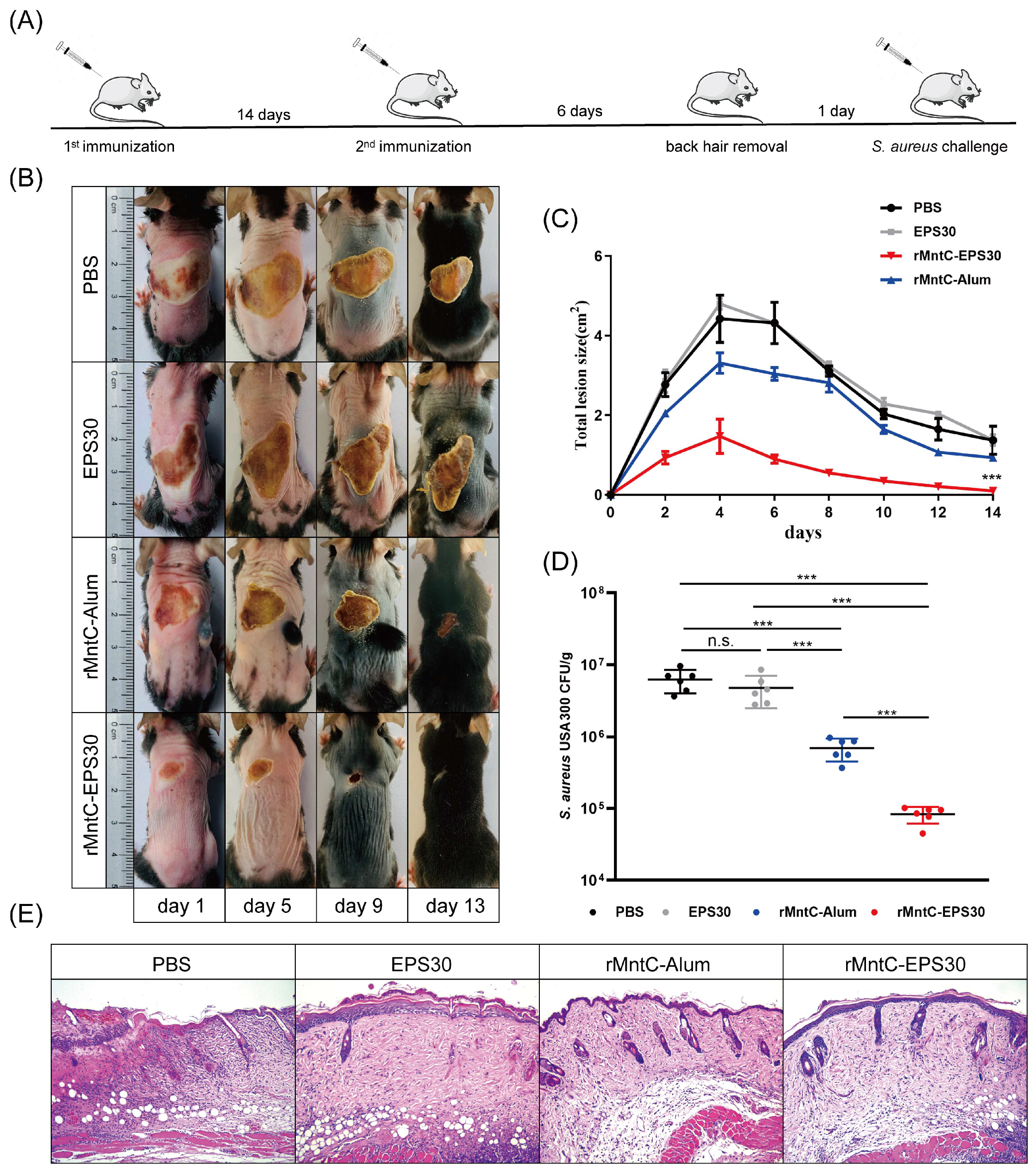
3.7. rMntC-EPS30 Vaccination Promoted Resistance to S. aureus Skin Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klevens, R.M.; Morrison, M.A.; Nadle, J.; Petit, S.; Gershman, K.; Ray, S.; Harrison, L.H.; Lynfield, R.; Dumyati, G.; Townes, J.M.; et al. Invasive Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA 2007, 298, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howard, L.S.G.E.; Sillis, M.; Pasteur, M.C.; Kamath, A.V.; Harrison, B.D.W. Microbiological profile of community-acquired pneumonia in adults over the last 20 years. J. Infect. 2005, 50, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Pang, R.; Zeng, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Prevalence and characterization of food-related Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreassen, A.E.S.; Jacobsen, C.M.; de Blasio, B.; White, R.; Kristiansen, I.S.; Elstrøm, P. The impact of Methicillin-resistant S. aureus on length of stay, readmissions and costs: A register based case-control study of patients hospitalized in Norway. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giersing, B.K.; Dastgheyb, S.S.; Modjarrad, K.; Moorthy, V. Status of vaccine research and development of vaccines for Staphylococcus aureus. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2962–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabio, B.; Sylvie, B.; Guido, G. Inferring reasons for the failure of Staphylococcus aureus vaccines in clinical trials. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Xu, X.; Farber, J.M.; Avanesian, V.; Baquir, B.; Fu, Y.; French, S.W.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Spellberg, B. Th1-Th17 cells mediate protective adaptive immunity against Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans infection in mice. PLOS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, A.; Buonocore, S.M.; Auquier, P.; Nicolas, I.; Wallemacq, H.; Boutriau, D.; van der Most, R.G. Role and plasticity of Th1 and Th17 responses in immunity to Staphylococcus aureus. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 2980–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, S.; Quadery, A.F. Staphylococcus aureus lipoprotein induces skin inflammation, accompanied with IFN-γ-producing T cell accumulation through dermal dendritic cells. Pathogens 2018, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.R.; Hong, S.W.; Choi, E.B.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, Y.K. Staphylococcus aureus-derived extracellular vesicles induce neutrophilic pulmonary inflammation via both Th1 and Th17 cell responses. Allergy 2012, 67, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigame, H.; Kakuta, S.; Nagai, T.; Kadoki, M.; Nambu, A.; Komiyama, Y.; Fujikado, N.; Tanahashi, Y.; Akitsu, A.; Kotaki, H.; et al. Differential roles of interleukin-17A and -17F in host defense against mucoepithelial bacterial infection and allergic responses. Immunity 2009, 30, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holley, M.M.; Kielian, T. Th1 and Th17 cells regulate innate immune responses and bacterial clearance during central nervous system infection. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.F.; Murphy, A.G.; Lalor, S.J.; Leech, J.M.; O’Keeffe, K.M.; Mac Aogáin, M.; O’Halloran, D.P.; Lacey, K.A.; Tavakol, M.; Hearnden, C.H.; et al. Memory Th1 cells are protective in invasive Staphylococcus aureus infection. PLOS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.A.; Sophia, B.R.; Manuel, M.F.; Rahman, Q.K.; Maria, S.C.; Julia, B.; Matthias, E.; Eva, S. Probiotic lactobacilli modulate Staphylococcus aureus-Induced activation of conventional and unconventional T cells and NK cells. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, P.; Liu, T.; Zhou, W.Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Peng, L.S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yin, Z.N.; Mao, X.H.; Guo, G.; Shi, Y. Role of gamma-delta T cells in host response against Staphylococcus aureus-induced pneumonia. BMC Immunol. 2012, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dillen, C.A.; Pinsker, B.L.; Marusina, A.I.; Merleev, A.A.; Farber, O.N.; Liu, H.; Archer, N.K.; Lee, D.B.; Wang, Y.; Ortines, R.V.; et al. Clonally expanded γδ T cells protect against Staphylococcus aureus skin reinfection. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1026–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Cao, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, D. Pivotal role of IL-17-producing γδ T cells in mouse chronic mastitis experimentally induced with Staphylococcus aureus. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 7, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, B.M.; Mulcahy, M.E.; Murphy, A.G.; Wilk, M.; O’Keeffe, K.M.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Lavelle, E.C.; Mcloughlin, R.M.; Morrison, R.P. Nlrp-3-driven interleukin 17 production by γδT cells controls infection outcomes during surgical site infection. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 4478–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, A.G.; O’Keeffe, K.M.; Lalor, S.J.; Maher, B.M.; Mcloughlin, R.M. Staphylococcus aureus infection of mice expands a population of memory γδ T cells that are protective against subsequent infection. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.S.; Pietras, E.M.; Garcia, N.C.; Ramos, R.I.; Farzam, D.M.; Monroe, H.R.; Magorien, J.E.; Blauvelt, A.; Kolls, J.K.; Cheung, A.L.; et al. IL-17 is essential for host defense against cutaneous Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coffman, R.L.; Sher, A.; Seder, R.A. Vaccine adjuvants: Putting innate immunity to work. Immunity 2010, 33, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrovsky, N.; Aguilar, J.C. Vaccine adjuvants: Current state and future trends. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbarth, S.C.; Colegio, O.R.; O’Connor, W.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Flavell, R.A. Crucial role for the Nalp3 inflammasome in the immunostimulatory properties of aluminium adjuvants. Nature 2008, 453, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bhatt, P.C.; Sharma, K.; Rahman, M.; Patel, D.K.; Sethi, N.; Kumar, A.; Sachan, N.K.; Kaithwas, G.; Al-Abbasi, F.A. Melastoma malabathricum Linn attenuates complete freund’s adjuvant-induced chronic inflammation in wistar rats via inflammation response. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiu, L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Guo, S.; Yang, M.; Du, R.; Wang, X. Immunostimulatory activity of exopolysaccharides from probiotic Lactobacillus casei WXD030 strain as a novel adjuvant in vitro and in vivo. Food Agric. Immunol. 2018, 29, 1086–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, S.-S.; Liu, C.-F.; Tseng, K.-C.; Mau, J.-L.; Pan, T.-M. Immunomodulatory effects of dead Lactobacillus on murine splenocytes and macrophages. Food Agric. Immunol. 2012, 23, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, C.; Hayakawa, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Katoh, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Hisa, K. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides Strain NTM048 as an Immunostimulant To Enhance the Mucosal Barrier and Influence the Systemic Immune Response. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7009–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkubo, Y.; Takashima, I.; Hashimoto, N.; Fujita, I. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for detection of IgM and IgG antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus in sera from experimentally infected swine. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 1984, 30, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wardenburg, J.B.; Patel, R.J.; Schneewind, O. Surface proteins and exotoxins are required for the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagnoli, F.; Fontana, M.; Soldaini, E.; Mishra, R.; Fiaschi, L.; Cartocci, E.; Nardi-Dei, V.; Ruggiero, P.; Nosari, S.; Falco, M.; et al. Vaccine composition formulated with a novel TLR7-dependent adjuvant induces high and broad protection against Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3680–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, E.C.; Mcloughlin, R.M. Considering the ‘alternatives’ for next-generation anti-Staphylococcus aureus vaccine development. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melandri, D.; Zlatareva, I.; Chaleil, R.A.G.; Dart, R.J.; Hayday, A.C. The γδTCR combines innate immunity with adaptive immunity by utilizing spatially distinct regions for agonist selection and antigen responsiveness. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1352–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Maupome, M.; Slate, J.R.; McGill, J.L. Gamma delta T cell function in ruminants. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2019, 35, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.E.; Bosch, M.E.; Yamada, K.J.; Aldrich, A.L.; Chaudhari, S.S.; Klinkebiel, D.; Gries, C.M.; Alqarzaee, A.A.; Li, Y.; Thomas, V.C.; et al. Lactate production by Staphylococcus aureus biofilm inhibits HDAC11 to reprogramme the host immune response during persistent infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, A. Staphylococcus aureus metabolites promote IL-10. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1183–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibulski, S.P.; Rivera-Patron, M.; Mourglia-Ettlin, G.; Casaravilla, C.; Yendo, A.C.A.; Fett-Neto, A.G.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Moreno, M.; Roehe, P.M.; Silveira, F. Quillaja brasiliensis saponin-based nanoparticulate adjuvants are capable of triggering early immune responses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13582–13596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.J.; Kato, Y.; Abraham, W.; Chang, J.Y.H.; Kulp, D.W.; Watson, N.; Turner, H.L.; Menis, S.; Abbott, R.K.; Bhiman, J.N.; et al. Engineered immunogen binding to alum adjuvant enhances humoral immunity. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.; Thomsen, I. Epidemiological and clinical evidence for the role of toxins in S. aureus human disease. Toxins 2020, 12, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, M.; Marshall, H.; Richmond, P.; Shakib, S.; Jiang, Q.; Cooper, D.; Rill, D.; Baber, J.; Eiden, J.; Gruber, W.; et al. A randomized phase I study of the safety and immunogenicity of three ascending dose levels of a 3-antigen Staphylococcus aureus vaccine (SA3Ag) in healthy adults. Vaccine 2015, 33, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begier, E.; Seiden, D.J.; Patton, M.; Zito, E.; Severs, J.; Cooper, D.; Eiden, J.; Gruber, W.C.; Jansen, K.U.; Anderson, A.S. SA4Ag, a 4-antigen Staphylococcus aureus vaccine, rapidly induces high levels of bacteria-killing antibodies. Vaccine 2017, 35, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennehy, P.H.; Goveia, M.G.; Dallas, M.J.; Heaton, P.M. The integrated Phase III safety profile of the pentavalent human-bovine (WC3) reassortant rotavirus vaccine. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Pan, N.; Ma, C.; Liu, B.; Xiu, L.; Tong, H.; Sheng, S.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, F.; et al. Vaccine Composition Formulated with a Novel Lactobacillus-Derived Exopolysaccharides Adjuvant Provided High Protection against Staphylococcus aureus. Vaccines 2021, 9, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070775
Zhang H, Pan N, Ma C, Liu B, Xiu L, Tong H, Sheng S, Liang Y, Li H, Ma F, et al. Vaccine Composition Formulated with a Novel Lactobacillus-Derived Exopolysaccharides Adjuvant Provided High Protection against Staphylococcus aureus. Vaccines. 2021; 9(7):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070775
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haochi, Na Pan, Cheng Ma, Bohui Liu, Lei Xiu, He Tong, Shouxin Sheng, Yanchen Liang, Haotian Li, Fangfei Ma, and et al. 2021. "Vaccine Composition Formulated with a Novel Lactobacillus-Derived Exopolysaccharides Adjuvant Provided High Protection against Staphylococcus aureus" Vaccines 9, no. 7: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070775
APA StyleZhang, H., Pan, N., Ma, C., Liu, B., Xiu, L., Tong, H., Sheng, S., Liang, Y., Li, H., Ma, F., Bao, X., Hu, W., & Wang, X. (2021). Vaccine Composition Formulated with a Novel Lactobacillus-Derived Exopolysaccharides Adjuvant Provided High Protection against Staphylococcus aureus. Vaccines, 9(7), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070775





