Development of a Macrophage-Based ADCC Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Generation of Cell Lines
2.4. Macrophage Cell Culture
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. ADCC Assay
3. Results
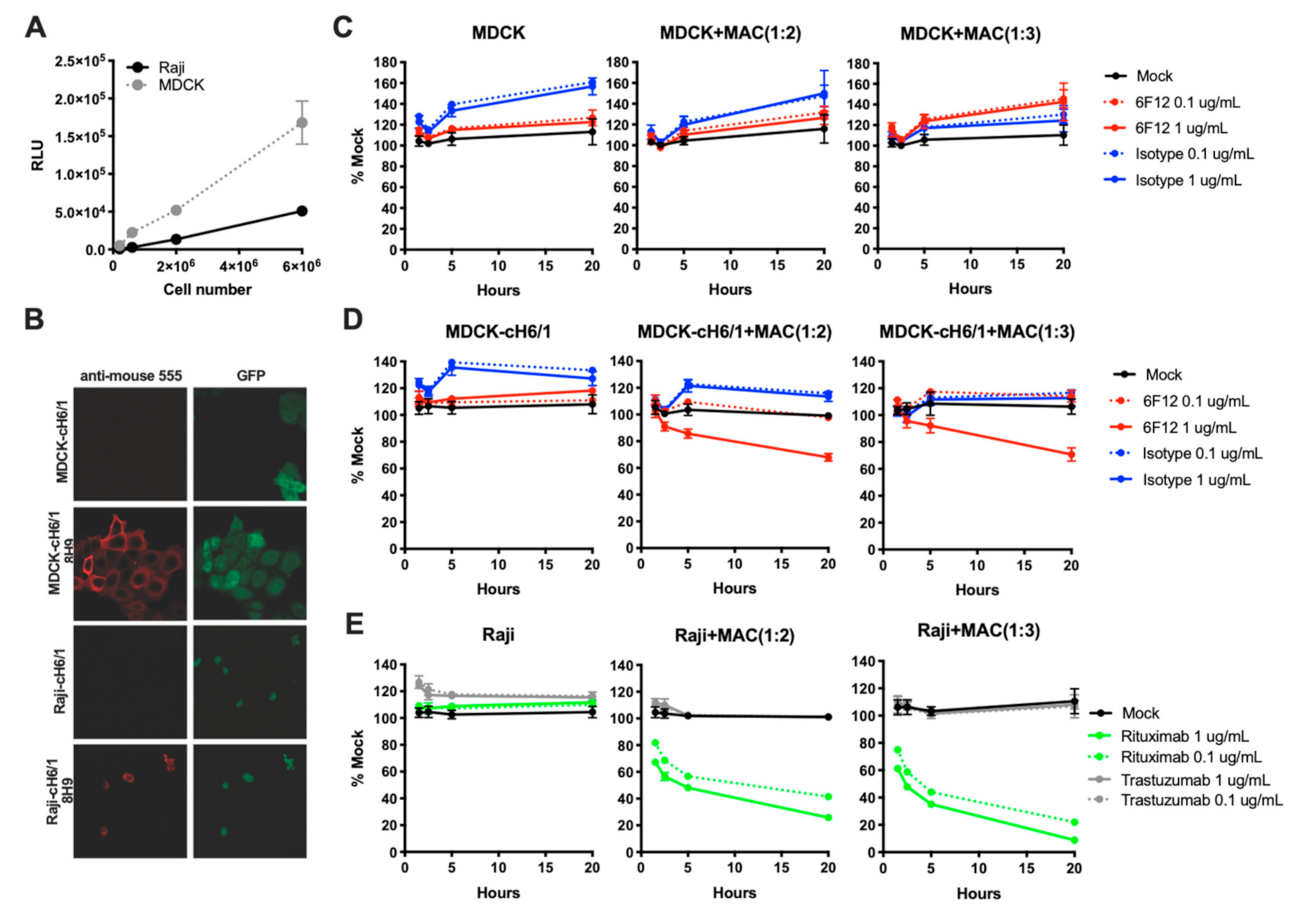
3.1. Development of a Macrophage-Based ADCC Assay
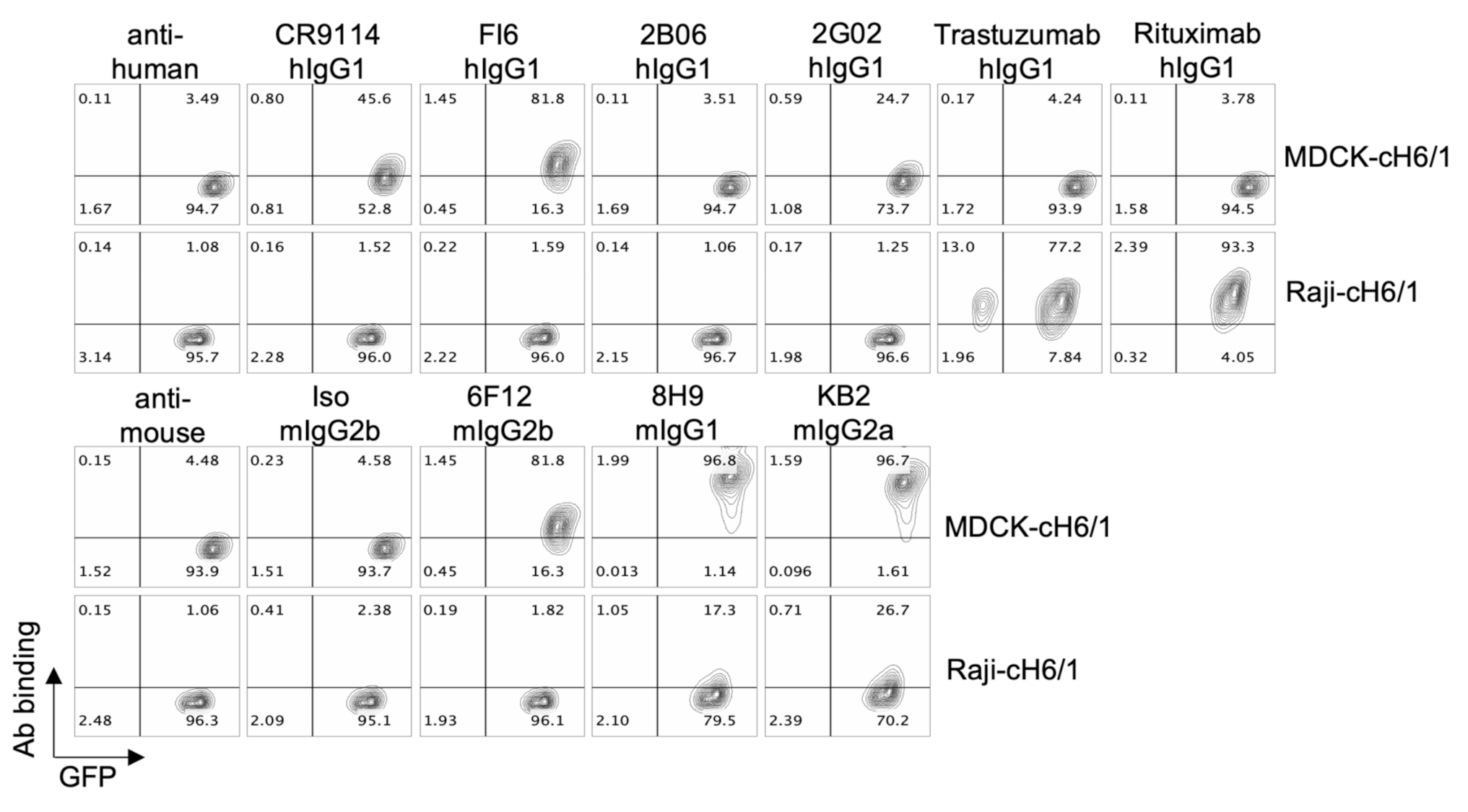
3.2. ADCC Activity of a Panel of HA-Specific Antibodies
3.3. Antibody Binding
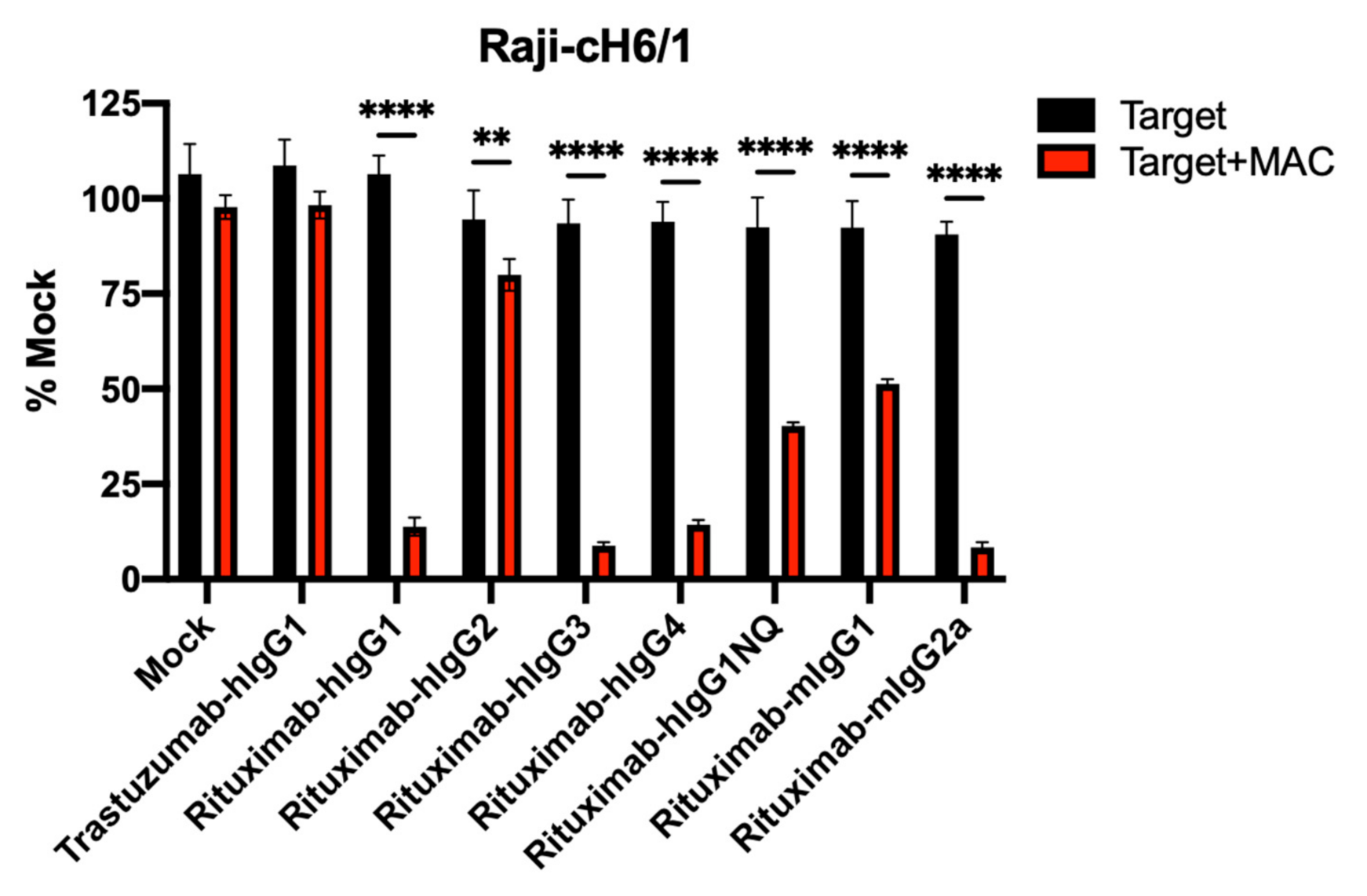
3.4. ADCC Activity of Human and Mouse Isotypes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, L.L.; Suscovich, T.J.; Fortune, S.M.; Alter, G. Beyond binding: Antibody effector functions in infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, N.; Van Egmond, M. Antibody-dependent phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages: A potent effector mechanism of monoclonal antibody therapy of cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5008–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, J.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Oliver, J.A.; Ravetch, J.V.; Poe, J.C.; Haas, K.M.; Tedder, T.F. The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through fc receptor–dependent mechanisms during Anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grugan, K.D.; McCabe, F.L.; Kinder, M.; Greenplate, A.; Harman, B.C.; Ekert, J.E.; Van Rooijen, N.; Anderson, G.M.; Nemeth, J.A.; Strohl, W.R.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promote Invasion while Retaining Fc-Dependent Anti-Tumor Function. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5457–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, G.L.; Chiorean, E.G.; Fishman, M.P.; Saboury, B.; Teitelbaum, U.R.; Sun, W.; Huhn, R.D.; Song, W.; Li, D.; Sharp, L.L.; et al. CD40 Agonists Alter Tumor Stroma and Show Efficacy against Pancreatic Carcinoma in Mice and Humans. Science 2011, 331, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Chen, C.-J.; Mullarkey, C.E.; Hamilton, J.R.; Wong, C.K.; Leon, P.E.; Uccellini, M.B.; Chromikova, V.; Henry, C.; Hoffman, K.W.; et al. Alveolar macrophages are critical for broadly-reactive antibody-mediated protection against influenza A virus in mice. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartron, G.; Zhao-Yang, L.; Baudard, M.; Kanouni, T.; Rouillé, V.; Quittet, P.; Klein, B.; Rossi, J.-F. Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Potentiates Rituximab in Patients With Relapsed Follicular Lymphoma: Results of a Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2725–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.P.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Tang, C.; Myklebust, J.H.; Varghese, B.; Gill, S.; Jan, M.; Cha, A.C.; Chan, C.K.; Tan, B.T.; et al. Anti-CD47 Antibody Synergizes with Rituximab to Promote Phagocytosis and Eradicate Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cell 2010, 142, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskopf, K.; Weissman, I.L. Macrophages are critical effectors of antibody therapies for cancer. mAbs 2015, 7, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, E.M.; Barouch, D.H.; Alter, G. Systems serology for evaluation of HIV vaccine trials. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantakamalakul, W.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; Jongrakthaitae, S.; Assawadarachai, V.; Ampol, S.; Sutthent, R. A novel EGFP-CEM-NKr flow cytometric method for measuring antibody dependent cell mediated-cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity in HIV-1 infected individuals. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 315, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, M.; Kitano, S.; Aikawa, H.; Kuchiba, A.; Hayashi, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Tamura, K.; Hamada, A. A novel method for evaluating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by flowcytometry using cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.L.; Kurman, C.C.; Serbousek, D.E. 51 Cr Release Assay of Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC). Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 1993, 8, 7.27.1–7.27.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Garvin, D.; Paguio, A.; Moravec, R.; Engel, L.; Fan, F.; Surowy, T. Development of a robust reporter-based ADCC assay with frozen, thaw-and-use cells to measure Fc effector function of therapeutic antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 414, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, B.S.; Berger, E.; Sibley, S.; Cahya, S.; Xiao, L.; LaCerte, M.A.; Vaillancourt, P.; Wooden, S.; Gately, D. Development and validation of an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity-reporter gene assay. mAbs 2012, 4, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.A.; Lee, E.; Bachmann, M.H.; Salicioni, A.M.; Behrens, E.M.; Kambayashi, T.; Baldwin, C.L. Measuring Cytotoxicity by Bioluminescence Imaging Outperforms the Standard Chromium-51 Release Assay. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oceguera-Yanez, F.; Kim, S.-I.; Matsumoto, T.; Tan, G.W.; Xiang, L.; Hatani, T.; Kondo, T.; Ikeya, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Inoue, H.; et al. Engineering the AAVS1 locus for consistent and scalable transgene expression in human iPSCs and their differentiated derivatives. Methods 2016, 101, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chromikova, V.; Tan, J.; Aslam, S.; Rajabhathor, A.; Bermudez-Gonzalez, M.; Ayllon, J.; Simon, V.; García-Sastre, A.; Salaun, B.; Nachbagauer, R.; et al. Activity of human serum antibodies in an influenza virus hemagglutinin stalk-based ADCC reporter assay correlates with activity in a CD107a degranulation assay. Vaccine 2020, 38, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiLillo, D.J.; Tan, G.S.; Palese, P.; Ravetch, J.V. Broadly neutralizing hemagglutinin stalk–specific antibodies require FcγR interactions for protection against influenza virus in vivo. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiLillo, D.J.; Palese, P.; Wilson, P.C.; Ravetch, J.V. Broadly neutralizing anti-influenza antibodies require Fc receptor engagement for in vivo protection. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velders, M.P.; Van Rhijn, C.M.; Oskam, E.; Fleuren, G.J.; Warnaar, S.O.; Litvinov, S.V. The impact of antigen density and antibody affinity on antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity: Relevance for immunotherapy of carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggemann, M.; Williams, G.T.; Bindon, C.I.; Clark, M.R.; Walker, M.R.; Jefferis, R.; Waldmann, H.; Neuberger, M.S. Comparison of the effector functions of human immunoglobulins using a matched set of chimeric antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 166, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, P.E.; He, W.; Mullarkey, C.E.; Bailey, M.; Miller, M.; Krammer, F.; Palese, P.; Tan, G.S. Optimal activation of Fc-mediated effector functions by influenza virus hemagglutinin antibodies requires two points of contact. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5944–E5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.G.; Calvo, K.; Pasillas, M.P.; Sykes, D.B.; Häcker, H.; Kamps, M.P. Quantitative production of macrophages or neutrophils ex vivo using conditional Hoxb8. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nardo, D.; Kalvakolanu, D.V.; Latz, E. Immortalization of Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1784, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antibody | Specificity | Isotype | Source/Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trastuzumab | HER2 | hIgG1 | Invivogen |
| Rituximab | CD20 | hIgG1 | Invivogen |
| Rituximab | CD20 | hIgG2 | Invivogen |
| Rituximab | CD20 | hIgG3 | Invivogen |
| Rituximab | CD20 | hIgG4 | Invivogen |
| Rituximab | CD20 | hIgG1NQ | Invivogen |
| Rituximab | CD20 | mIgG1 | Invivogen |
| Rituximab | CD20 | mIgG2a | Invivogen |
| CR9114 | Flu A and B stalk | hIgG1 | PMID 22878502 |
| FI6 | Flu A Group 1 and 2 HA stalk | hIgG1 | PMID 21798894 |
| 2B06 | Flu A Group 1 and 2 HA stalk | hIgG1 | PMID 25689254 |
| 2G02 | Flu A Group 1 and 2 HA stalk | hIgG1 | PMID 22615367 |
| Iso | unknown | mIgG2b | BD clone MPC-11 |
| 6F12 | Flu H1 stalk | mIgG2b | PMID 22491456 |
| 8H9 | Flu H6 head | mIgG1 | PMID 26512088 |
| KB2 | Flu H1 stalk | mIgG2a | PMID 22398287 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uccellini, M.B.; Aslam, S.; Liu, S.T.H.; Alam, F.; García-Sastre, A. Development of a Macrophage-Based ADCC Assay. Vaccines 2021, 9, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060660
Uccellini MB, Aslam S, Liu STH, Alam F, García-Sastre A. Development of a Macrophage-Based ADCC Assay. Vaccines. 2021; 9(6):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060660
Chicago/Turabian StyleUccellini, Melissa B., Sadaf Aslam, Sean T. H. Liu, Fahmida Alam, and Adolfo García-Sastre. 2021. "Development of a Macrophage-Based ADCC Assay" Vaccines 9, no. 6: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060660
APA StyleUccellini, M. B., Aslam, S., Liu, S. T. H., Alam, F., & García-Sastre, A. (2021). Development of a Macrophage-Based ADCC Assay. Vaccines, 9(6), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060660






