SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Asymptomatic in Nearly Half of Adults with Robust Anti-Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody Response
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Collection and Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Testing
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
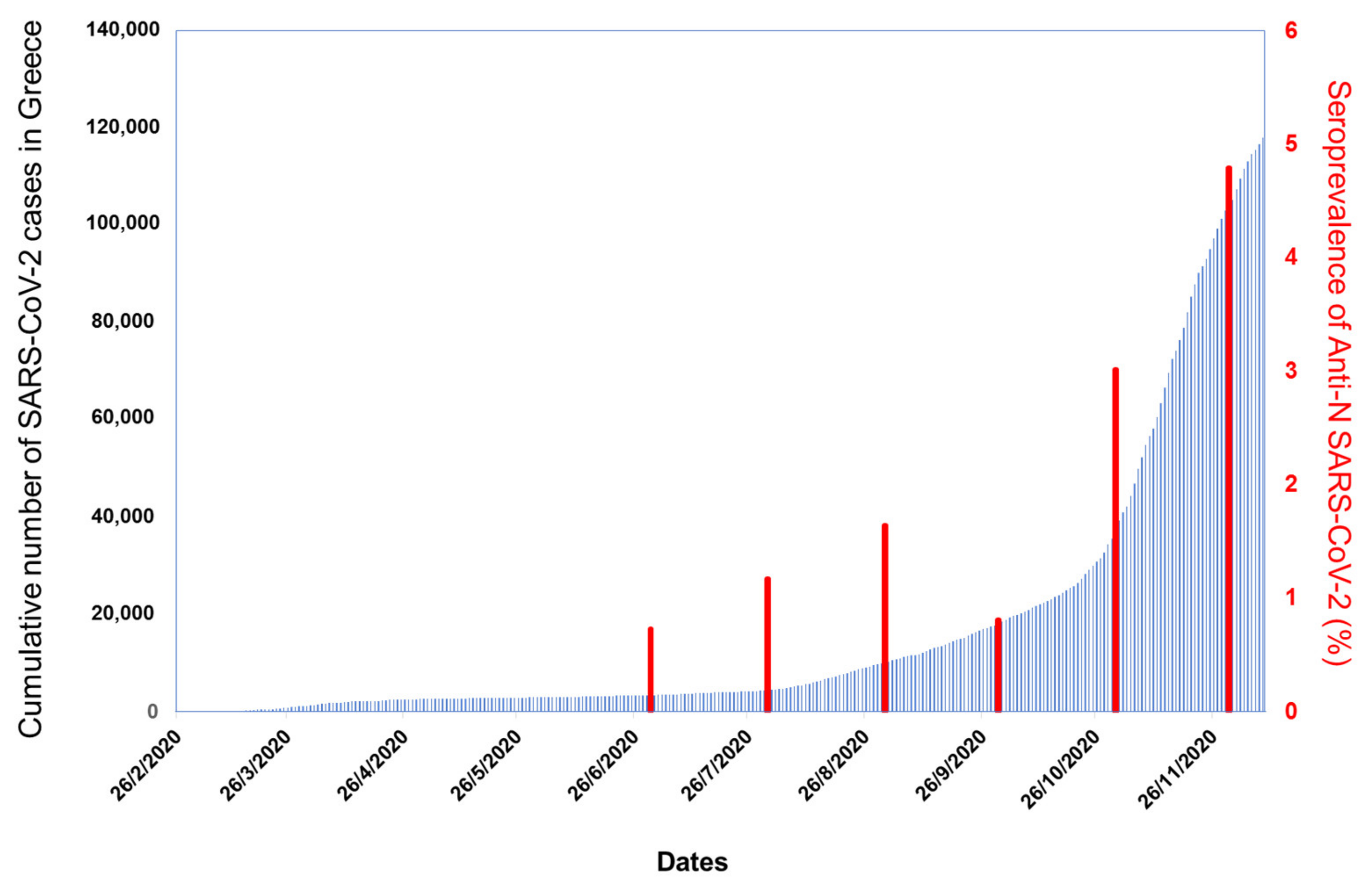
3.1. Seroepidemiology
3.1.1. Study Population
3.1.2. Seroprevalence Study
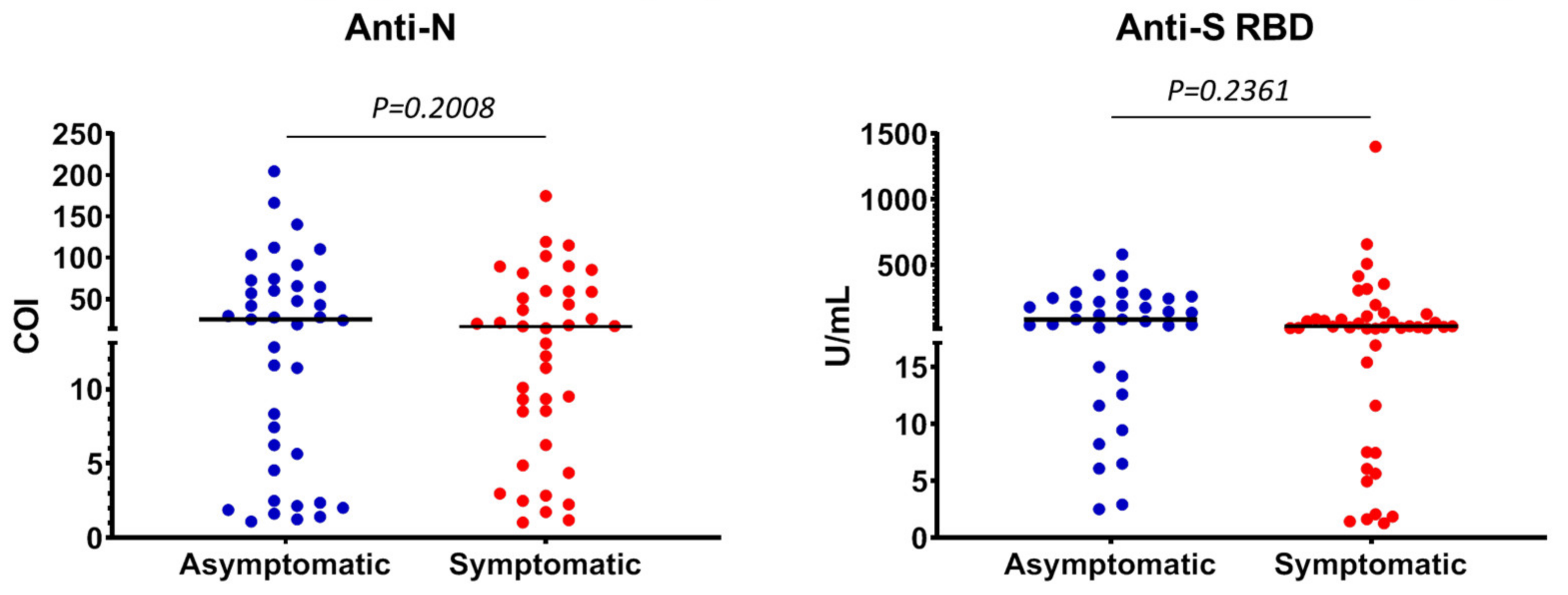
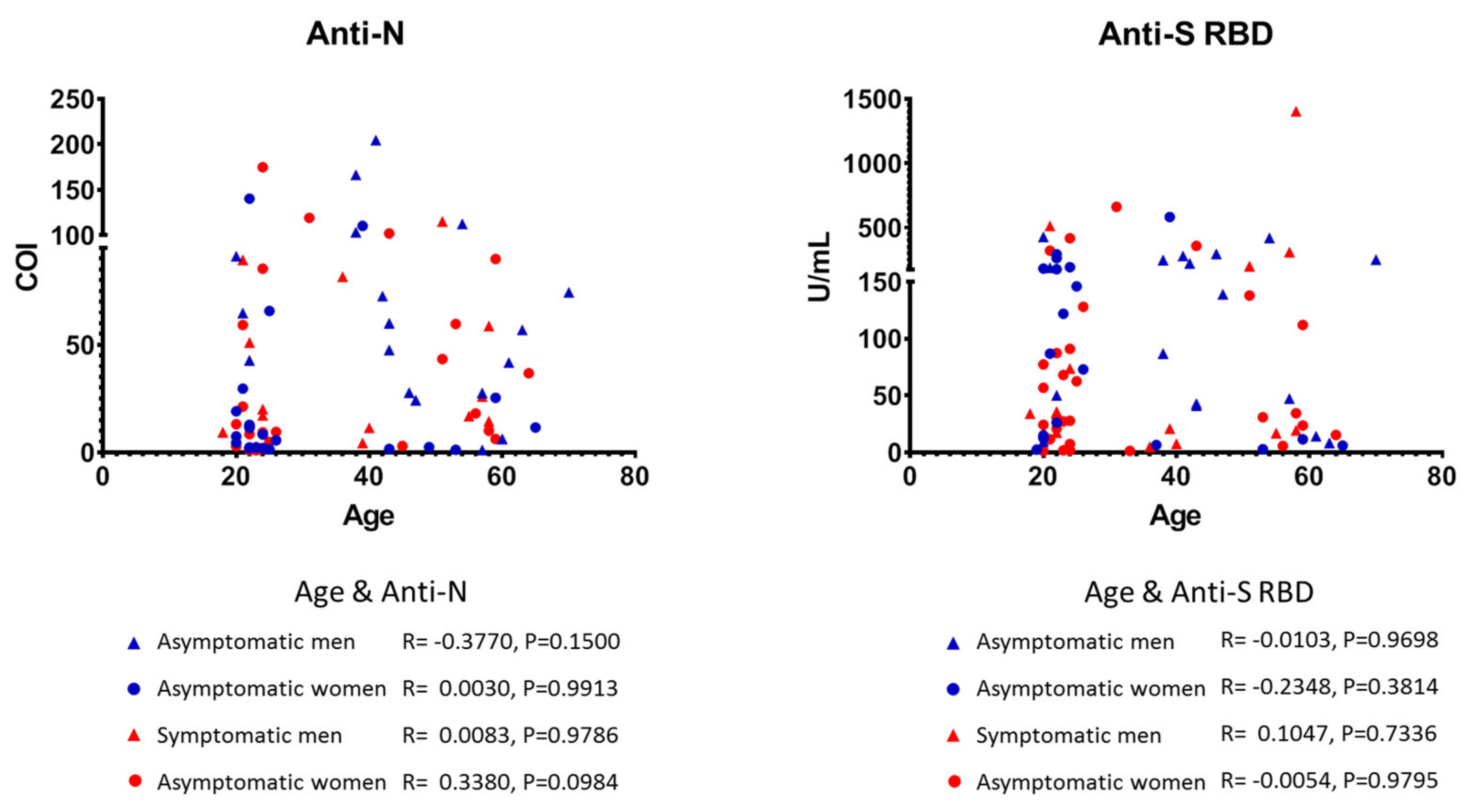
3.2. Characteristics of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Positive Individuals
3.3. Quantitative Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Weekly Epidemiological Update—15 December 2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Q.; Lessler, J.; Eckerle, I.; Lauer, S.A.; Kaiser, L.; Vuilleumier, N.; Cummings, D.A.T.; Flahault, A.; Petrovic, D.; Guessous, I.; et al. Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Insights from a population-based serological survey. MedRxiv Preprint 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitrago-Garcia, D.; Egli-Gany, D.; Counotte, M.J.; Hossmann, S.; Imeri, H.; Ipekci, A.M.; Salanti, G.; Low, N. Occurrence and transmission potential of asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections: A living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byambasuren, O.; Cardona, M.; Bell, K.; Clark, J.; McLaws, M.-L.; Glasziou, P. Estimating the extent of asymptomatic COVID-19 and its potential for community transmission: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMMI 2020, 5, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, C.; Bachmann, M.; Wei, S.; Gong, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Lu, K.; et al. Post-lockdown SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid screening in nearly ten million residents of Wuhan, China. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, M.R.; Geibe, J.R.; Sears, C.L.; Riegodedios, A.J.; Luse, T.; Von Thun, A.M.; McGinnis, M.B.; Olson, N.; Houskamp, D.; Fenequito, R.; et al. An outbreak of Covid-19 on an aircraft carrier. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, F.; Goyard, S.; Lalanne, A.I.; Nevo, F.; Gransagne, M.; Souque, P.; Louis, D.; Gillon, V.; Turbiez, I.; Bidard, F.-C.; et al. High seroprevalence but short-lived immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection in Paris. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, N.R.; Whitaker, A.N.; Strother, C.A.; Miles, A.K.; Grier, D.; McElvany, B.D.; Bruce, E.A.; Poynter, M.E.; Pierce, K.K.; Kirkpatrick, B.D.; et al. Kinetics and isotype assessment of antibodies targeting the spike protein receptor-binding domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 in COVID-19 patients as a function of age, biological sex and disease severity. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, e1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripperger, T.J.; Uhrlaub, J.L.; Watanabe, M.; Wong, R.; Castaneda, Y.; Pizzato, H.A.; Thompson, M.R.; Bradshaw, C.; Weinkauf, C.C.; Bime, C.; et al. Orthogonal SARS-CoV-2 serological assays enable surveillance of low-prevalence communities and reveal durable humoral immunity. Immunity 2020, 53, 925–933.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zuiani, A.; Fischinger, S.; Mullur, J.; Atyeo, C.; Travers, M.; Lelis, F.J.N.; Pullen, K.M.; Martin, H.; Tong, P.; et al. Quick COVID-19 healers sustain anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody production. Cell 2020, 183, 1496–1507.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Mentis, A.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Loss of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in mild Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitsilonis, O.E.; Paraskevis, D.; Lianidou, E.; Pierros, V.; Akalestos, A.; Kastritis, E.; Moutsatsou, P.; Scorilas, A.; Sphicopoulos, T.; Terpos, E.; et al. Seroprevalence of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 among the personnel and students of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece: A preliminary report. Life 2020, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Insert, Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Sandhofer Strasse 116, D-68305 Mannheim. Available online: www.roche.com (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S Insert, Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Sandhofer Strasse 116, D-68305 Mannheim. Available online: www.roche.com (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Slot, E.; Hogema, B.M.; Reusken, C.B.E.M.; Reimerink, J.; Molier, M.; Karregat, J.H.M.; IJlst, J.; Novotny, V.M.J.; VanLier, R.A.W.; Zaaijer, H.L. Low SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in blood donors in the early COVID-19 epidemic in the Netherlands. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Basteiro, A.L.; Moncunill, G.; Tortajada, M.; Vidal, M.; Guinovart, C.; Jiménez, A.; Santano, R.; Sanz, S.; Méndez, S.; Llupià, A.; et al. Seroprevalence of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 among health care workers in a large Spanish reference hospital. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, O.T.; Marimuthu, K.; Koh, V.; Pang, J.; Linn, K.Z.; Sun, J.; De Wang, L.; Chia, W.N.; Tiu, C.; Chan, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence and transmission risk factors among high-risk close contacts: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollán, M.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Oteo, J.; Hernán, M.A.; Pérez-Olmeda, M.; Sanmartín, J.L.; Fernández-García, A.; Cruz, I.; Fernández de Larrea, N.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Spain (ENE-COVID): A nationwide, population-based seroepidemiological study. Lancet 2020, 396, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavezzo, E.; Franchin, E.; Ciavarella, C.; Cuomo-Dannenburg, G.; Barzon, L.; Del Vecchio, C.; Rossi, L.; Manganelli, R.; Loregian, A.; Navarin, N.; et al. Suppression of a SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in the Italian municipality of Vo’. Nature 2020, 584, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, J.C.; Russell, T.W.; Liu, Y.; Hellewell, J.; Pearson, C.A.; Knight, G.M.; Eggo, R.M.; Kucharski, A.J.; Funk, S.; et al.; CMMID COVID-19 Working Group The contribution of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections to transmission on the Diamond Princess cruise ship. Elife 2020, 9, e58699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, A.; Fisher, K.A.; Silver, R.; Koh, M.; Arons, M.M.; Miller, D.A.; McIntyre, A.F.; Vuong, J.T.; Kim, K.; Takamiya, M.; et al. Identification of presymptomatic and asymptomatic cases using cohort-based testing approaches at a large correctional facility—Chicago, Illinois, USA, May 2020. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, e128–e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.M.; Algaissi, A.; Almahboub, S.A.; Alfaleh, M.A.; Abujamel, T.S.; Alamri, S.S.; Alluhaybi, K.A.; Hobani, H.I.; AlHarbi, R.H.; Alsulaiman, R.M.; et al. Early humoral response correlates with disease severity and outcomes in COVID-19 patients. Viruses 2020, 12, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Huang, B.; Wu, M.; Zhong, A.; Li, L.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; et al. Dynamic changes in anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery from COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Politou, M.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Mentis, A.; Rosati, M.; Stellas, D.; Bear, J.; Hu, X.; Felber, B.K.; Pappa, V.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses in convalescent plasma donors are increased in hospitalized patients; subanalyses of a phase 2 clinical study. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasisekharan, V.; Pentakota, N.; Jayaraman, A.; Tharakaraman, K.; Wogan, G.N.; Narayanasami, U. Orthogonal immunoassays for IgG antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 antigens reveal that immune response lasts beyond 4 mo post illness onset. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021615118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossberg, A.N.; Koza, L.A.; Ledreux, A.; Prusmack, C.; Krishnamurthy, H.K.; Jayaraman, V.; Granholm, A.C.; Linseman, D.A. A multiplex chemiluminescent immunoassay for serological profiling of COVID-19-positive symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shioda, K.; Lau, M.S.; Kraay, A.N.; Nelson, K.N.; Siegler, A.J.; Sullivan, P.S.; Collins, M.H.; Weitz, J.S.; Lopman, B.A. Estimating the cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the infection fatality ratio in light of waning antibodies. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerowitz, E.A.; Richterman, A.; Bogoch, I.I.; Low, N.; Cevik, M. Towards an accurate and systematic characterisationofpersistently asymptomatic infection with SARS-CoV-2. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 14, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Number of Participants | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | 4996 | 100.0 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 1726 | 34.5 |
| Female | 3270 | 65.4 |
| Age group (in years) | ||
| (18–34) | 2659 | 53.2 |
| (35–54) | 1688 | 33.8 |
| (55–82) | 602 | 12.1 |
| Not reported | 47 | 0.9 |
| Status at the NKUA | ||
| Undergraduate/postgraduate students | 2722 | 54.5 |
| Scientific affiliates | 751 | 15.0 |
| Faculty members/laboratory assistants | 536 | 10.7 |
| Administrative officers | 874 | 17.5 |
| Not reported | 113 | 2.3 |
| Characteristic | Number of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Positive Cases | Unweighted Prevalence (%) | Weighted Prevalence (%) (95% Confidence Interval) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 79 | 1.58 | 1.60 (0.92, 2.54) * |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 31 | 1.80 | 2.00 (0.87, 3.79) |
| Female | 48 | 1.48 | 1.31 (0.57, 2.51) |
| Unknown | 0 | - | - |
| Age group (in years) | |||
| (18–34) | 41 | 1.54 | 1.34 (0.91, 1.89) |
| (35–54) | 21 | 1.24 | 1.05 (0.57, 1.70) |
| (55–82) | 16 | 2.66 | 2.46 (1.33, 4.09) |
| Unknown | 1 | - | - |
| School of NKUA | |||
| Health Sciences | 26 | 1.57 | 1.87 (0.66, 3.99) |
| Non-health sciences | 40 | 1.72 | 1.46 (0.56, 3.03) |
| Other facility | 7 | 2.43 | 1.51 (0.31, 11.27) |
| Unknown | 6 | - | - |
| Status at the NKUA | |||
| Undergraduate/postgraduate Students | 44 | 1.62 | 0.77 (0.34, 5.44) |
| Scientific affiliates | 11 | 1.50 | 2.48 (0.71, 6.20) |
| Faculty members/ laboratory assistants | 11 | 2.05 | 1.15 (0.29, 23.50) |
| Administrative officers | 13 | 1.52 | 1.13 (0.31, 4.40) |
| Unknown | 0 | - | - |
| SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies | Asymptomatic | Symptomatic | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total n | n (%) | Median Age in Years (Range) | Male, n (%) | n (%) | Median Age in Years (Range) | Male n (%) | |
| Anti-N positive | 79 | 39 (49.4) | 38 (20–70) | 18 (46.2) | 40 (50.6) | 24.5 (18–64) | 13 (32.5) |
| Anti-S RBD positive | 79 | 35 (44.3) | 37 (19–70) | 17 (48.6) | 44 (55.7) | 24 (18–64) | 14 (31.8) |
| Anti-N & anti-S RBD positive | 70 | 32 (45.7) | 38 (20–70) | 16 (50.0) | 38 (54.3) | 24.5 (18–64) | 13 (34.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsitsilonis, O.E.; Paraskevis, D.; Lianidou, E.; Terpos, E.; Akalestos, A.; Pierros, V.; Kostaki, E.G.; Kastritis, E.; Moutsatsou, P.; Politou, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Asymptomatic in Nearly Half of Adults with Robust Anti-Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody Response. Vaccines 2021, 9, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030207
Tsitsilonis OE, Paraskevis D, Lianidou E, Terpos E, Akalestos A, Pierros V, Kostaki EG, Kastritis E, Moutsatsou P, Politou M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Asymptomatic in Nearly Half of Adults with Robust Anti-Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody Response. Vaccines. 2021; 9(3):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030207
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsitsilonis, Ourania E., Dimitrios Paraskevis, Evi Lianidou, Evangelos Terpos, Athanasios Akalestos, Vassilios Pierros, Evangelia Georgia Kostaki, Efstathios Kastritis, Paraskevi Moutsatsou, Marianna Politou, and et al. 2021. "SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Asymptomatic in Nearly Half of Adults with Robust Anti-Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody Response" Vaccines 9, no. 3: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030207
APA StyleTsitsilonis, O. E., Paraskevis, D., Lianidou, E., Terpos, E., Akalestos, A., Pierros, V., Kostaki, E. G., Kastritis, E., Moutsatsou, P., Politou, M., Scorilas, A., Sphicopoulos, T., Thomaidis, N., Trougakos, I. P., Tsakris, A., Voulgaris, N., Daskalaki, C. C., Evangelakou, Z., Fouki, C., ... Sfikakis, P. P. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Asymptomatic in Nearly Half of Adults with Robust Anti-Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody Response. Vaccines, 9(3), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030207

















