Immunomodulatory Strategies for Parapoxvirus: Current Status and Future Approaches for the Development of Vaccines against Orf Virus Infection
Abstract
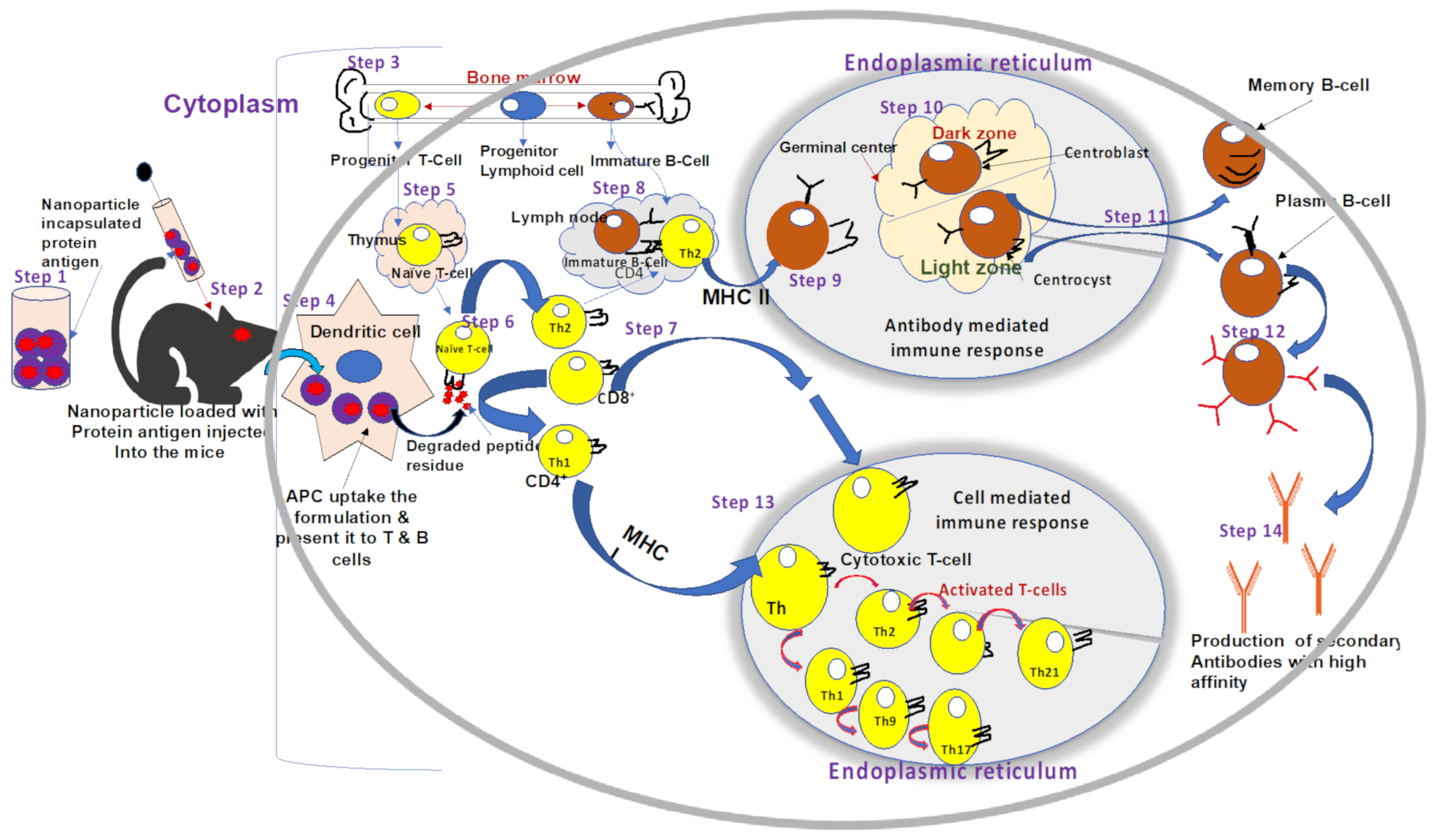
1. Introduction
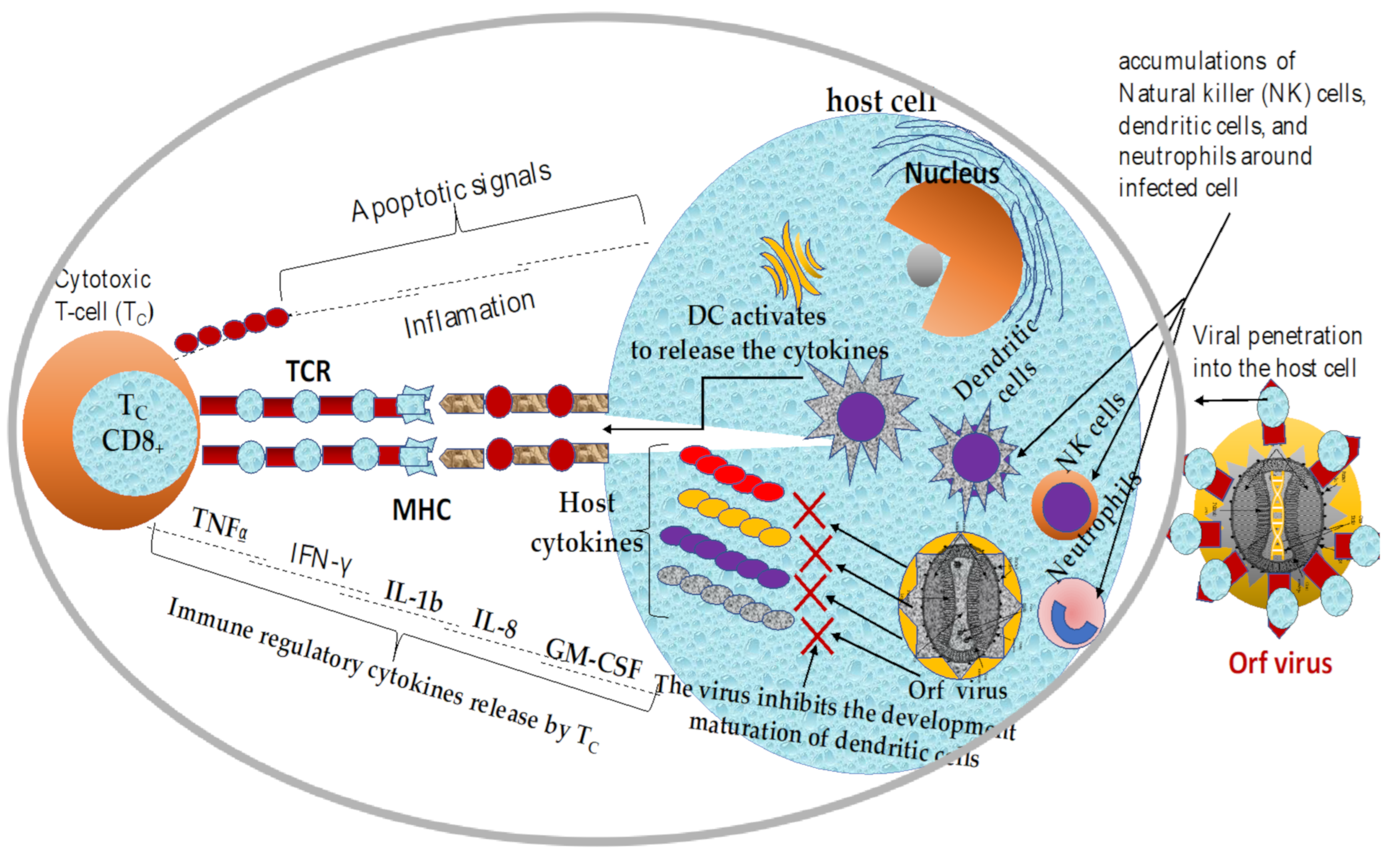
2. Mechanisms of Immune Response to ORFV Infection
2.1. Overview of Current Knowledge in Immune Responses Elicited by ORFV Infections
2.2. Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses against ORFV Infection
2.3. Immunomodulatory Properties of Orf Virus
3. Overview of Vaccines against Animal Viral Infections
3.1. Common Viral Vaccines of Veterinary Importance
3.2. Live Attenuated Vaccines
3.3. Inactivated (Killed) Vaccines
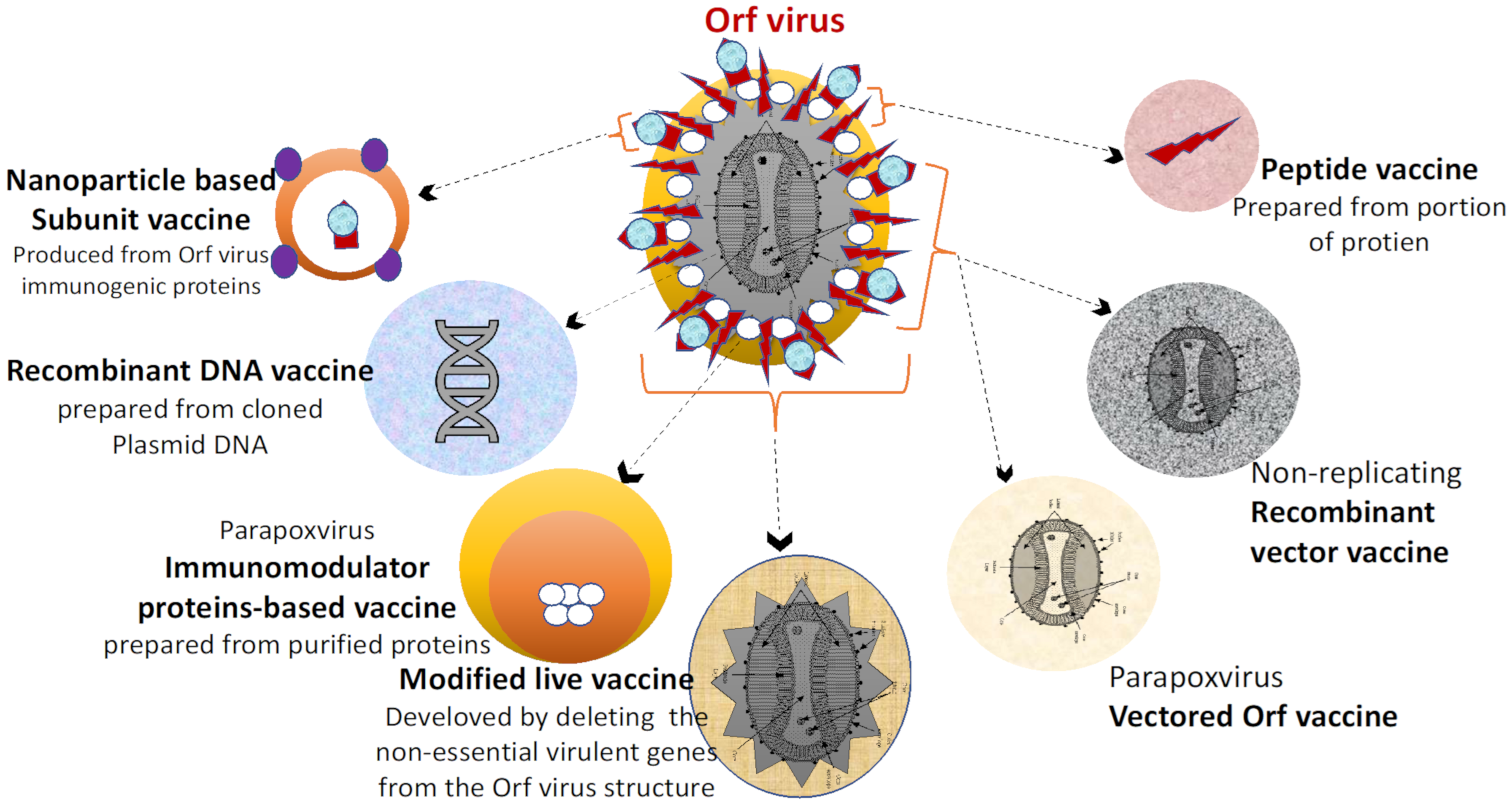
3.4. Subunit Vaccines
3.5. Recombinant Live Viral Vaccines
3.6. DNA Vaccines
| Vaccine Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Beample(s) | Immune Response | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live attenuated vaccines | They are highly immunogenic and are excellent for inducing sustained cell-mediated and humoral immunity with a single dose. | Risk of mutation and reversion to virulent strain in an immunised host. High cost of production and storage facilities. | Parvovirus, adenovirus-2 vaccines Rubella (MMR), Influenza, | Evoke vigorous T- and B-cell responses. | [134,157,169,170] |
| Inactivated vaccines | They are highly safe and are made from non-replicating whole-cell viruses that pose no risk of reversion to cause disease. | Poorly immunogenic and inefficient to stimulate prolonged duration of immunity, so vaccination of 2 to 4 weeks is needed | Rabies Vaccines Feline Leukemia vaccines, canine influenza vaccines | Immune response T helper 1-type cytokines | [151,168] |
| Subunit vaccines | Poorly immunogenic and inefficient to stimulate prolonged duration of immunity, so vaccination of 2 to 4 weeks is needed | Weaker immune response and it requires adjuvants | F1L recombinant protein was able to stimulate the production of antibody | ORFV-specific IgG, | [25,84,124,170] |
| DNA vaccines | induces both cellular and humoral immunity, ensuring a sustained immune response once the animal encounters the wild-type virus at a later time | Lower efficacy in large animals and serious safety issues due to activation of oncogenes and antibiotic resistance.Virus-specific IgG, T-cell immune responses. | Influenza and Herpes vaccines, parapoxvirus vaccines | Viral specific IgG, T-cell immune responses. | [8,134,150] |
| Peptide Vaccines | effective in preventing animal infections no possibility of return to pathogenic phenotype. | controlled antigen displays and relatively low immunogenicity. | Influenza vaccines | Evoke CD4+, CD8+, B-cells and IFN-γ | [165,166] |
| Recombinant Vaccines | Attenuated virus used to introduce microbial DNA into host cells. It induces a strong immune response. | Risk of mutation and reversion to a virulent strain in an immunized host. | ORFVD1701-V-RabG Recombinant vaccine | Elici tviral-specific IgG, and T-cell | [3,25,86,160,168] |
4. Current Status of Vaccines Development against ORFV Infections
4.1. The Current State of ORFV Vaccines
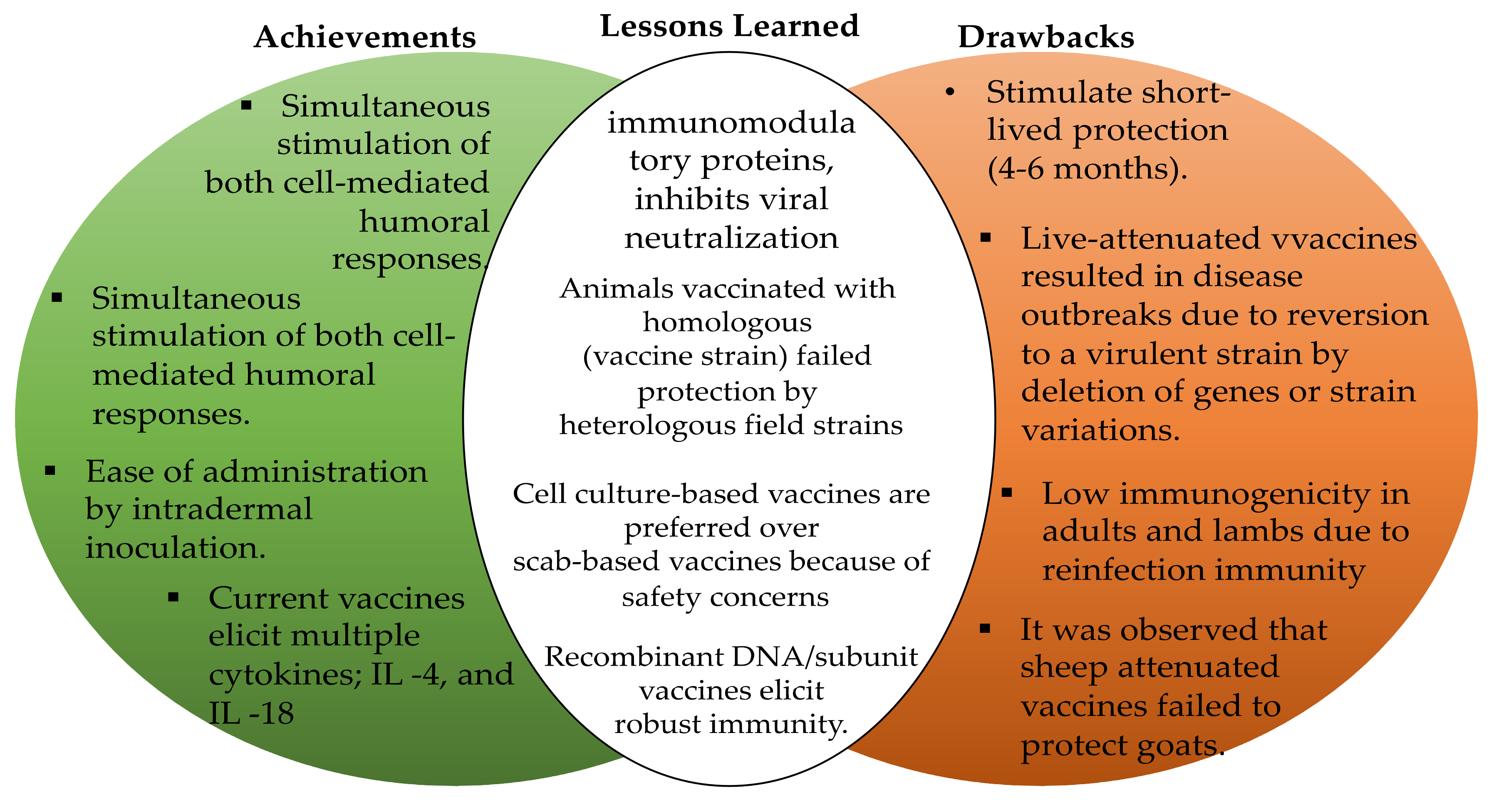
4.2. Safety and Efficiency Profile of Current Vaccines against ORFV Infections
4.3. Implications of Strain Genetic Variation for the Rational Design of ORFV Vaccines
4.4. Enhancement of the Current ORFV Vaccines
5. Future Strategies for the Development of Vaccines against ORFV Infection
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakraborty, S.; Kumar, A.; Tiwari, R.; Rahal, A.; Malik, Y.; Dhamma, K.; Prasad, M. Advances in diagnosis of respiratory diseases of small ruminants. Vet. Med. Int. 2014, 138, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babji, A.S.; Seri, S.C. The nutritional value of some processed meat products in Malaysia, Malays. J. Nutr. 1995, 1, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Minguijón, E.; Reina, R.; Pérez, M.; Polledo, L.; Villoria, M.; Ramírez, H. Juste, R.A. Small ruminant lentivirus infections and diseases. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, P.V.; Cox, S.J. The role of small ruminants in the epidemiology and transmission of foot-and-mouth disease. Vet. J. 1999, 158, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.K.; Yadav, N.; Khurana, S.M.P. Vaccines: Present Status and Applications. Vaccines 2014, 31, 491–508. [Google Scholar]
- Ouedraogo, A.; Luciani, L.; Zannou, O.; Biguezoton, A.; Pezzi, L.; Thirion, L.; Lempereur, L. Detection of two species of the genus parapoxvirus (Bovine papular stomatitis virus and pseudocowpox virus) in ticks infesting cattle in Burkina Faso. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, H. Recent developments in veterinary vaccinology. Vet. J. 2005, 170, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, R.; Allaudin, Z.N.; Lila, M.-A.M. Scaling-up recombinant plasmid DNA for clinical trial: Current concern, solution and status. Vaccine 2012, 30, 5914–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikøren, T.; Lillehaug, A.; Åkerstedt, J.; Bretten, T.; Haugum, M.; Tryland, M. A severe outbreak of contagious ecthyma (Orf) in a free-ranging musk ox (Ovibos moschatus) population in Norway. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 127, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, G.W. Oral vaccines for finfish: Academic theory or commercial reality? Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2004, 5, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, G.A.; Jacobson, R.M.; Poland, G.A.; Jacobson, R.M. Understanding those who do not understand: A brief review of the anti-vaccine movement. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2440–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, J.A.; Balakrishnan, K.N.; Abdullah, A.A.; Kimmy, T.; Abba, Y.; Bin Mohamed, R.; Jesse, F.F.A.; Haron, A.W.; Noordin, M.M.; Bitrus, A.A.; et al. Dermatopathology of Orf Virus (Malaysian Isolates) in Mice Experimentally Inoculated at Different Sites with and without Dexamethasone Administration. J. Pathog. 2018, 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafar, S.; Zro, K.; Ennaji, M.M. Capripoxvirus Diseases: Current Updates and Developed Strategies for Control. Emerg. Reemerging Viral Pathog. 2019, 8, 635–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-H.; Lee, J.-A.; Park, S.-Y.; Song, C.-S.; Choi, I.-S.; Lee, J.-B. A review of vaccine development and research for industry animals in Korea. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2012, 1, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Z.; Chiew, E.; Shamsudin, M. Government Incentives and Comparative Advantage of the Sheep Industry in Ma-laysia, Pertanika. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 1995, 3, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Reguzova, A.; Ghosh, M.; Müller, M.; Rziha, H.-J.; Amann, R. Orf Virus-Based Vaccine Vector D1701-V Induces Strong CD8+ T Cell Response against the Transgene but Not against ORFV-Derived Epitopes. Vaccines 2020, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, C.K.; Norlina, D.; Roshaslinda, D.; Zuraidah, O.; Zunaida, B.; Mohd, H.A.H.; Roslina, H. Case Report Molecular Diagnosis of Caprine ORF Virus (ORFV) from Penang, Malaysia. J. Malays. Vet. 2019, 10, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bergqvist, C.; Kurban, M.; Abbas, O. Orf virus infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 27, e1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesse, F.F.A.; Hambali, I.U.; Abba, Y.; Lin, C.C.; Chung, E.L.T.; Bitrus, A.A.; Abdullah, A.A.; Balakrishnan, K.N.; Bala, J.A.; Lila, M.A.M. Effect of dexamethasone administration on the pathogenicity and lesion severity in rats experimentally inoculated with Orf virus (Malaysian isolates). Comp. Haematol. Int. 2018, 27, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreesen, D.W. Animal Vaccines; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 517–530. [Google Scholar]
- Bahaman, A.R.; Joseph, P.G.; Siti-Khairani, B. A Review of the Epidemiology and Control of Brucellosis in Malaysia. J. Vet. Malays. 2007, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, L.; Zainalabidin, M. The economic impact attributable to bru-cellosis among goat farms in Peninsula Malaysia and cost benefit analysis. Res. Opin. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2015, 5, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zainalabidin, F.A.; Raimy, N.; Yaacob, M.H.; Musbah, A.; Bathmanaban, P.; Ismail, E.A.; Mamat, Z.C.; Zahari, Z.; Ismail, M.I.; Panchadcharam, C. The Prevalence of Parasitic Infestation of Small Ruminant Farms in Perak, Malaysia. Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2015, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.; Haut, L.; Reyes-Sandoval, A.; Pinto, A. Recombinant viruses as vaccines against viral diseases. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, S.; Dellagostin, O.A. The development of veterinary vaccines: A review of traditional methods and modern biotechnology approaches. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2017, 1, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.A.; Bin Ismail, M.F.; Balakrishnan, K.N.; Bala, J.A.; Hani, H.; Abba, Y.; Isa, M.K.A.; Abdullah, F.F.J.; Arshad, S.S.; Nazariah, Z.A.; et al. Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of caprine Orf virus in Malaysia. Virus Dis. 2015, 26, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeever, D.; Jenkinson, D.M.; Hutchison, G.; Reid, H. Studies of the pathogenesis of orf virus infection in sheep. J. Comp. Pathol. 1988, 99, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryland, M.; Beckmen, K.B.; Burek-Huntington, K.A.; Breines, E.M.; Klein, J. Orf virus infection in Alaskan mountain goats, Dall’s sheep, muskoxen, caribou and Sitka black-tailed deer. Acta Vet. Scand. 2018, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, J.; Fongue, J.; Khalil, J.Y.B.; David, L.; Mougari, S.; Le Bideau, M.; Abrahão, J.; Berbis, P.; La Scola, B. Human Infection with Orf Virus and Description of Its Whole Genome, France, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshale, A. Contagious Ecthyma and its Public Health Significance. J. Dairy Vet. Sci. 2018, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhshiteh, F.; Allaudin, Z.N.; Lila, M.A.B.M.; Hani, H. Size-related assessment on viability and insulin secretion of caprine islets in vitro. Xenotransplantation 2013, 20, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrou, V.; Valiakos, G. Orf virus infection in sheep or goats. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttner, M.; Rziha, H.-J. Parapoxviruses: From the Lesion to the Viral Genome. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2002, 49, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnke, R.L.; Dieterich, R.A.; Neiland, K.A.; Ranglack, G. Serologic and experimental investigations of contagious ecthyma in alaska. J. Wildl. Dis. 1983, 19, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasa, B.T.; Rathnamma, D.; Isloor, S.; Chandranaik, B.M.; Veeregowda, B.M.; Manjunath, R.G.B. Diagnosis of Orf virus infection in sheep and goats by virus isolation, polymerase chain reaction and sequencing. J. Exp. Biol. Agric. Sci. 2018, 6, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiba, G.A.; Thomas, D.R.; Morgan, K.L.; Bennett, M.; Salmon, R.L.; Chalmers, R.; Kench, S.M.; Coleman, T.J.; Meadows, D.; Morgan-Capner, P.; et al. Orf (contagious pustular dermatitis) in farmworkers: Prevalence and risk factors in three areas of England. Vet. Rec. 1999, 145, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saad, K.M.; Thweni, H.T.; Abdali, D.A.; Tarik, A.S. Clinical and Diagnostic Studies of Contagious Ecthyma (ORF) in Sheep. IOSR J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2017, 10, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosamani, M.; Scagliarini, A.; Bhanuprakash, V.; McInnes, C.J.; Singh, R.K. Orf: An update on current research and future perspectives. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2009, 7, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, A.; Adole, J.; Chima, N.; Maguda, A.; Dyek, D.; Jambol, A.; Anefu, E.; Shallmizhili, J.; Luka, P. Contagious ecthyma in three flocks of goats in Jos-south LGA, Plateau State, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Curran, P.; Cooke, R.; Ryan, C.A.; Connolly, K. Orf: Contagious pustular dermatitis. Ir. Med. J. 2010, 103, 971–972. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, A.J. Prevalence of contagious pustular dermatitis (orf) in six million lambs at slaughter: A three-year study. N. Zealand Vet. J. 1983, 31, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederman, E.R.; Green, G.M.; DeGroot, H.E.; Dahl, P.; Goldman, E.; Greer, P.W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Paddock, C.D.; Damon, I.K. Progressive Orf Virus Infection in a Patient with Lymphoma: Successful Treatment Using Imiquimod. Clin Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, e100–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.H.; Wang, L.L.; Hao, J.H.; Zhang, X.G.; Shen, C.C.; Zhang, D.J.; Zhang, K.S. Orf Virus VIR Antagonizes p53-Mediated Antiviral Effects to Facilitate Viral Replication. Viral Immunol. 2020, 33, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilardi, N.; Pappu, R.; Arron, J.R.; Chan, A.C. 30 Years of Biotherapeutics Development—What Have We Learned? Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 249–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; McFadden, G. Secreted Immunomodulatory Viral Proteins as Novel Biotherapeutics. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4765–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellucci, A.; Manolas, M.; Jin, S.; Dwyer, J.; Vick, G.; Wang, A.; Swiatlo, E.; Zheng, C. Orf virus infection after Eid al-Adha. IDCases 2020, 21, e00854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Concha-Bermejillo, A.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Waldron, D. Severe persistent orf in young goats. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2003, 15, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, J.A.; Balakrishnan, K.N.; Abdullah, A.; Mohamed, R.; Haron, A.W.; Jesse, F.F.A.; Noordin, M.M.; Mohd-Azmi, M.L. The re-emerging of orf virus infection: A call for surveillance, vaccination and effective control measures. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 120, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, S.K.; Chand, P.; Rajpurohit, B.S. A severe outbreak of contagious pustular dermatitis in a sheep flock. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 69, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yirrell, D.; Reid, H.; Norval, M.; Howie, S. Immune response of lambs to experimental infection with Orf virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1989, 22, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anziliero, D.; Weiblen, R.; Kreutz, L.C.; Spilki, F.; Flores, E. Inactivated Parapoxvirus ovis induces a transient increase in the expression of proinflammatory, Th1-related, and autoregulatory cytokines in mice. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Zhan, L.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, Z. Transcriptome analysis of sheep oral mucosa response to Orf virus infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.E.; Titball, R.; Williamson, D. Vaccine delivery using nanoparticles. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughton, I.; Hardy, W. Immunization of Sheep and Goats against Sore Mouth (Contagious Ecthyma). Tex. FARMER Collect. 1935, 504, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Haig, D.M.; McInnes, C. Immunity and counter-immunity during infection with the parapoxvirus orf virus. Virus Res. 2002, 88, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, D. Vaccination of sheep with cell culture grown orf virus. Aust. Vet. J. 1990, 67, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; De, U.K.; Chowdhury, S. Current status of contagious ecthyma or orf disease in goat and sheep—A global perspective. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 96, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, J.A.; Balakrishnan, K.N.; Abdullah, A.A.; Yi, L.C.; Bitrus, A.A.; Abba, Y.; Aliyu, I.A.; Peter, I.D.; Hambali, I.U.; Bin Mohamed, R.; et al. Sero-epidemiology of Contagious Ecthyma Based on Detection of IgG Antibody in Selected Sheep and Goats Farms in Malaysia. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2018, 6, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Luo, S. Orf virus: A promising new therapeutic agent. Rev. Med. Virol. 2019, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rziha, H.-J.; Büttner, M.; Müller, M.; Salomon, F.; Reguzova, A.; Laible, D.; Amann, R. Genomic Characterization of Orf Virus Strain D1701-V (Parapoxvirus) and Development of Novel Sites for Multiple Transgene Expression. Viruses 2019, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, A.; Friederichs, S.; Scholz, K.; Janssen, U.; Scholz, C.; Schlapp, T.; Mercer, A.; Siegling, A.; Volk, H.-D.; Weber, O. Characterization of immunostimulatory components of orf virus (parapoxvirus ovis). J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, R.A.; Cargnelutti, J.F.; Schild, C.O.; Flores, E.F.; Riet-Correa, F.; Giannitti, F. Outbreak of contagious ecthyma caused by Orf virus (Parapoxvirus ovis) in a vaccinated sheep flock in Uruguay. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2019, 50, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahaya, M.A.F.; Lila, M.A.M.; Ismail, S.; Zainol, M.; Afizan, N. Tumour-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) in Colon Cancer and How to Reeducate Them. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, S.B.; Wise, L.M.; Mercer, A.A. Molecular Genetic Analysis of Orf Virus: A Poxvirus That Has Adapted to Skin. Viruses 2015, 7, 1505–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLane, L.M.; Hakeem, M.A.; Wherry, E.J. CD8 T Cell Exhaustion during Chronic Viral Infection and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 457–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamri-Saad, M.; Effendy, A.; Israf, D.; Azmi, M.L.M. Cellular and humoral responses in the respiratory tract of goats following intranasal stimulation using formalin-killed Pasteurella haemolytica A2. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-M.; Shu, H.-B. Innate Immune Response to Cytoplasmic DNA: Mechanisms and Diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haig, D.M.; McInnes, C.J.; Hutchison, G.; Seow, H.-F.; Reid, H.W. Cyclosporin A abrogates the acquired immunity to cutaneous reinfection with the parapoxvirus orf virus. Immunology 1996, 89, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.B.; Mcfadden, G. Minireview Poxvirus Immunomodulatory Strategies: Current Perspectives. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6093–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, L.R.; Okda, F.A.; Singrey, A.; Maggioli, M.F.; Faccin, T.C.; Fernandes, M.H.V.; Diel, D.G. Passive immunity to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus following immunization of pregnant gilts with a recombinant orf virus vector expressing the spike protein. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2327–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeever, D.; Reid, H.; Inglis, N.; Herring, A. A qualitative and quantitative assessment of the humoral antibody response of the sheep to orf virus infection. Vet. Microbiol. 1987, 15, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.M.; McEwan, P.E.; Onwuka, S.K.; Moss, V.A.; Elder, H.Y.; Hutchison, G.; Reid, H.W. The Pathological Changes and Polymorphonuclear and Mast Cell Responses in the Skin of Specific Pathogen-free Lambs Following Primary and Secondary Challenge with Orf Virus. Vet. Dermatol. 1990, 1, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleton, P.F.; Brebner, J.; Pow, I.; Gilray, J.A.; Bell, G.D.; Reid, H.W. Tissue culture-propagated Orf virus vaccine protects lambs from orf virus challenge. Vet. Rec. 1996, 138, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bath, G.; Van Wyk, J.; Pettey, K. Control measures for some important and unusual goat diseases in southern Africa. Small Rumin. Res. 2005, 60, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeever, D.; Reid, H. The response of the supramammary lymph node of the sheep to secondary infection with orf virus. Vet. Microbiol. 1987, 14, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haig, D.M.; Deane, D.; Myatt, N.; Thomson, J.; Entrican, G.; Rothel, J.; Reid, H. The activation status of ovine CD45R+ and CD45R− efferent lymph T cells after orf virus reinfection. J. Comp. Pathol. 1996, 115, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassie, T.; Fanmei, Z.; Jiang, X.; Liu, G.; Girmay, S.; Min, Z.; Chenhui, L.; Bo, D.D.; Ahmed, S. Recombinant B2L and Kisspeptin-54 DNA Vaccine Induces Immunity against Orf Virus and Inhibits Spermatogenesis in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, R.; Wolf, G.; Mayr, A. Highly attenuated poxviruses induce functional priming of neutrophils in vitro. Arch. Virol. 1994, 136, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, M.J.; Johnston, S.A.; Sykes, K.F. Novel immune-modulator identified by a rapid, functional screen of the parapoxvirus ovis (Orf virus) genome. Proteome Sci. 2012, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.M.; Hutchison, G.; Onwuka, S.K.; Reid, H.W. Changes in the MHC Class II+ Dendritic Cell Population of Ovine Skin in Response to Orf Virus Infection. Vet. Dermatol. 1991, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.L.T.; Abdullah, F.F.J.; Ibrahim, H.H.; Marza, A.D.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Haron, A.W.; Lila, M.A.M.; Norsidin, M.J. Clinico-pathology, hematology and biochemistry responses in buffaloes towards Pasteurella multocida type B: 2 immunogen lypopolysaccharide via oral and intravenous routes of infection. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 91, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.L.; Symons, J.A.; Alcamı́, A. Poxviruses: Interfering with Interferon. Semin. Virol. 1998, 8, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, A.; Albina, E.; Barret, T.; Chapman, D.A.; Czub, M.; Dixon, L.K.; Keil, G.M.; Klonjkowski, B.; Le Potier, M.-F.; Libeau, G.; et al. Antigen delivery systems for veterinary vaccine development: Viral-vector based delivery systems. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6508–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcami, A.; Koszinowski, U.H. Viral mechanisms of immune evasion. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, O.; Siegling, A.; Friebe, A.; Limmer, A.; Schlapp, T.; Knolle, P.A.; Mercer, A.; Schaller, H.; Volk, H.-D. Inactivated parapoxvirus ovis (Orf virus) has antiviral activity against hepatitis B virus and herpes simplex virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Hardman, C.S.; Yadava, K.; Ogg, G. Innate Lymphocyte Mechanisms in Skin Diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 171–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.L.; Ueda, N.; Mercer, A.; Fleming, S.B. Investigation of Orf virus structure and morphogenesis using recombinants expressing FLAG-tagged envelope structural proteins: Evidence for wrapped virus particles and egress from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Vidal, S.M. Mechanisms of Natural Killer Cell Evasion through Viral Adaptation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 511–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, H.; Allaudin, Z.N.; Lila, M.A.M.; Ibrahim, T.A.T.; Othman, A.M. Caprine pancreatic islet xenotransplantation into diabetic immunosuppressed BALB /c mice. Xenotransplantation 2014, 21, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen Ni, L.; Allaudin, Z.N.; Mohd Lila, M.A.; Othman, A.M.; Othman, F. Selective apoptosis induction in MCF-7 cell line by truncated minimal functional region of Apoptin. BMC Cancer 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, A.A.; Wise, L.M.; Scagliarini, A.; McInnes, C.; Büttner, M.; Rziha, H.J.; McCaughan, C.A.; Fleming, S.B.; Ueda, N.; Nettleton, P.F. Vascular endothelial growth factors encoded by Orf virus show surprising sequence variation but have a conserved, functionally relevant structure. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, A.; Fraser, K.; Barns, G.; Robinson, A.J. The structure and cloning of orf virus DNA. Virology 1987, 157, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, L.M.; Veikkola, T.; Mercer, A.; Savory, L.J.; Fleming, S.B.; Caesar, C.; Vitali, A.; Makinen, T.; Alitalo, K.; Stacker, S.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-like protein from orf virus NZ2 binds to VEGFR2 and neuropilin-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3071–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slobedman, B.; Barry, P.A.; Spencer, J.V.; Avdic, S.; Abendroth, A. Virus-Encoded Homologs of Cellular Interleukin-10 and Their Control of Host Immune Function. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9618–9629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, S.B.; Anderson, I.E.; Thomson, J.; Deane, D.L.; McInnes, C.; McCaughan, C.A.; Mercer, A.; Haig, D.M. Infection with recombinant orf viruses demonstrates that the viral interleukin-10 is a virulence factor. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1922–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, Z.; Fleming, S.; Halliday, G.; Faulkner, L.; Mercer, A.; Baird, M.; Rziha, H.-J.; Bauer, B.; Adam, K.-H.; Röttgen, M.; et al. Orf virus-encoded interleukin-10 inhibits maturation, antigen presentation and migration of murine dendritic cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.; Rodrigues, F.S.; Joshi, L.R.; Jardim, J.C.; Flores, M.M.; Weiblen, R.; Diel, D.G. Orf virus ORFV112, ORFV117 and ORFV127 contribute to ORFV IA82 virulence in sheep. Vet. Microbiol 2021, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcamí, A.; Symons, J.A.; Collins, P.D.; Williams, T.J.; Smith, G.L. Blockade of chemokine activity by a soluble chemokine binding protein from vaccinia virus. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 624–633. [Google Scholar]
- Lacasta, D.; Reina, R.; Ruiz de Arcaute, M.; Ferrer, L.M.; Benito, A.A.; Tejedor, M.T.; Windsor, P.A. Effect of a Topical Formulation on Infective Viral Load in Lambs Naturally Infected with Orf Virus. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2021, 12, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, H.; Ibrahim, T.A.T.; Othman, A.M.; Lila, M.A.M.; Allaudin, Z.N.B. Isolation, density purification, and in vitro culture maintenance of functional caprine islets of Langerhans as an alternative islet source for diabetes study. Xenotransplantation 2010, 17, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic Neurochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012.
- González-Motos, V.; Kropp, K.A.; Viejo-Borbolla, A. Chemokine binding proteins: An immunomodulatory strategy going viral. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 30, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarieh, H.; Hernáez, B.; Alcamí, A. Immune modulation by virus-encoded secreted chemokine binding proteins. Virus Res. 2015, 209, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lateef, Z.; Baird, M.A.; Wise, L.M.; Young, S.; Mercer, A.; Fleming, S.B. The chemokine-binding protein encoded by the poxvirus orf virus inhibits recruitment of dendritic cells to sites of skin inflammation and migration to peripheral lymph nodes. Cell Microbiol. 2010, 12, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfadden, G.; Moyer, R. Parapoxvirus (Orf Virus) IL-10 Homolog; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.M.; Avia, M.; Martín, V.; Sevilla, N. IL-10: A Multifunctional Cytokine in Viral Infections. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.M. Delivery Systems for Immunomodulatory Proteins and Peptides. BioDrugs 1997, 7, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogisharadhya, R.; Kumar, A.; Bhanuprakash, V.; Shivachandra, S.B. Evaluation of a recombinant major envelope protein (F1L) based indirect—ELISA for sero-diagnosis of orf in sheep and goats. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 261, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallina, L.; Scagliarini, A.; Ciulli, S.; Prosperi, S. Cloning and Expression of the Orf Virus F1L Gene: Possible Use as a Subunit Vaccine. Vet. Res. Commun. 2004, 28, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; He, W.; Gao, W.; Lu, H.; Han, T.; Gaili, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, G.; Tiesuo, H.; et al. Orf virus DNA vaccines expressing ORFV 011 and ORFV 059 chimeric protein enhances immunogenicity. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, A.D.; Baca, M.; Wright, C.; Scotney, P.D. The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor-B (VEGF-B). Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 19, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achen, M.G.; Jeltsch, M.; Kukk, E.; Makinen, T.; Vitali, A.; Wilks, A.F.; Alitalo, K.; Stacker, S. Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) is a ligand for the tyrosine kinases VEGF receptor 2 (Flk1) and VEGF receptor 3 (Flt4). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.S.; Allaudin, Z.N.B.; Lila, M.A.B.M.; Othman, A.M.B.; Othman, F.B. Selective apoptosis induction in MCF-7 cell line by truncated minimal functional region of Apoptin. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, D.; McInnes, C.; Percival, A.; Wood, A.; Thomson, J.; Lear, A.; Gilray, J.; Fleming, S.; Mercer, A.; Haig, D. Orf Virus Encodes a Novel Secreted Protein Inhibitor of Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and Interleukin-2. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, V.; Kumar, R.M.; Suryanarayana, V.V.S. Past and present vaccine development strategies for the control of foot-and-mouth disease. Acta. Virol. 2004, 48, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zahoor, M.A.; Khurshid, M.; Qureshi, R.; Naz, A.; Shahid, M. Cell culture-based viral vaccines: Current status and future prospects. Futur. Virol. 2016, 11, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S. History of vaccination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12283–12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, O.; Mercer, A.; Friebe, A.; Knolle, P.A.; Volk, H.-D. Therapeutic immunomodulation using a virus—The potential of inactivated orf virus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 32, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dory, D.; Fischer, T.; Béven, V.; Cariolet, R.; Rziha, H.-J.; Jestin, A. Prime-boost immunization using DNA vaccine and recombinant Orf virus protects pigs against Pseudorabies virus (Herpes suid 1). Vaccine 2006, 24, 6256–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Miao, B.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Du, Q.; Huang, Y.; Tong, D. A novel porcine parvovirus DNA-launched infectious clone carrying stable double labels as an effective genetic platform. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Klinman, D.M.; Seder, R.A. DNA Vaccines: Immunology, Application, and Optimization. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 927–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delany, I.; Rappuoli, R.; De Gregorio, E. Vaccines for the 21st century. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddle, B.; Pulford, H. Effect of passively-acquired antibodies and vaccination on the immune response to contagious ecthyma virus. Vet. Microbiol. 1984, 9, 515–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, F. Adventures with poxviruses of vertebrates. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Joshi, L.; Rodrigues, F.D.S.; Anziliero, D.; Frandoloso, R.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L.; Weiblen, R.; Flores, E.F.; Diel, D.G. Immunogenicity of ORFV-based vectors expressing the rabies virus glycoprotein in livestock species. Virology 2017, 511, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, A.; Yirrell, D.L.; Reid, H.W.; Robinson, A.J. Lack of cross-protection between vaccinia virus and orf virus in hysterectomy-procured, barrier-maintained lambs. Vet. Microbiol. 1994, 41, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, A.; Siegling, A.; Friederichs, S.; Volk, H.-D.; Weber, O. Immunomodulatory Effects of Inactivated Parapoxvirus Ovis (Orf Virus) on Human Peripheral Immune Cells: Induction of Cytokine Secretion in Monocytes and Th1-Like Cells. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9400–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, P.A. Exploiting viral natural history for vaccine development. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, S.; Cresswell, L.; Lovatt, F.; Gummery, E.; Onyango, J.; McQuilkin, C.; Wapenaar, W. Do UK sheep farmers use orf vaccine correctly and could their vaccination strategy affect vaccine efficacy? Vet. Rec. 2019, 185, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hain, K.S.; Joshi, L.; Okda, F.; Nelson, J.; Singrey, A.; Lawson, S.; Martins, M.; Pillatzki, A.; Kutish, G.F.; Nelson, E.A.; et al. Immunogenicity of a recombinant parapoxvirus expressing the spike protein of Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2719–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.I.R.; Zachary, I. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family: Angiogenic factors in health and disease. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cottone, R.; Büttner, M.; Bauer, B.; Henkel, M.; Hettich, E.; Rziha, H.-J. Analysis of genomic rearrangement and subsequent gene deletion of the attenuated Orf virus strain D1701. Virus Res. 1998, 56, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.; Gill, H.; Haig, D.; Husband, A. In vivo T-cell subset depletion suggests that CD4+ T-cells and a humoral immune response are important for the elimination of orf virus from the skin of sheep. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2000, 74, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.; Jesse, F.F.A.; Saleh, W.M.M.; Chung, E.L.T.; Haron, A.W.; Saharee, A.A.; Lila, M.A.M.; Bin Ariff, A.; Mohammad, K.; Sharif, A. Histopathological changes of reproductive organs of goats immunized with Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis killed vaccine. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanuprakash, V.; Hosamani, M.; Venkatesan, G.; Balamurugan, V.; Yogisharadhya, R.; Singh, R.K. Animal poxvirus vaccines: A comprehensive review. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 1355–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercante, M.T.; Lelli, R.; Ronchi, G.F.; Pini, A. Production and efficacy of an attenuated live vaccine against contagious ovine ecthyma. Vet. Ital. 2010, 44, 537–547. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Edwards, J.; Ermel, R.; Taylor, C.; de la Concha-Bermejillo, A. Characterization of a North American orf virus isolated from a goat with persistent, proliferative dermatitis. Virus Res. 2003, 93, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, H.-S.; Mohd-Lila, M.-A.; Abdul-Rahman, S.-O.; Kiew, L.-J. Pathogenesis and vertical transmission of a transplacental rat cytomegalovirus. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housawi, F.M.; Abuelzein, E.M.; Gamee, A.A.; Alafaleq, A.I. Comparative study on three locally developed live orf virus vaccines for sheep in Saudi Arabia. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2012, 79, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, A.; Barcena, J.; Blanco, E.; Borrego, B.; Dory, D.; Escribano, J.M.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Ortego, J.; Dixon, L.K. Current strategies for subunit and genetic viral veterinary vaccine development. Virus Res. 2011, 157, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haig, D.M.; Hutchison, G.; Thomson, J.; Yirrell, D.; Reid, H.W. Cytolytic activity and associated serine protease expression by skin and afferent lymph CD8+ T cells during orf virus reinfection. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-Y.; Lin, F.-Y.; Cheng, S.-F.; Tscharke, D.; Chulakasian, S.; Chou, C.-C.; Hsu, W.-L. Functional Analysis of the Short Isoform of Orf Virus Protein OV20.0. J. Virolo. 2015, 89, 4966–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Onyango, J.; Mata, F.; McCormick, W.; Chapman, S. Prevalence, risk factors and vaccination efficacy of contagious ovine ecthyma (orf) in England. Vet. Rec. 2014, 175, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, J.A.; Balakrishnan, K.N.; Jesse, F.F.A.; Abdullah, A.A.; bin Noorzahari, M.S.; Ghazali, M.T.; Bin Mohamed, R.; Haron, A.W.; Noordin, M.M.; Mohd-Azmi, M.L. Identification of strain diversity and phylogenetic analysis based on two major essential proteins of Orf viruses isolated from several clinical cases reported in Malaysia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 77, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanberry, L.R.; Strugnell, R. Vaccines of the future. Perspect. Vaccinol. 2011, 1, 151–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, B. The contribution of vaccination to global health: Past, present and future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowersock, T.L.; Martin, S. Vaccine delivery to animals. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 38, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oirschot, J. Vaccinology: Present and future of veterinary viral vaccinology: A review. Vet. Q. 2001, 23, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, R.N.; Tik, W.B.; Memari, H.R.; Azaman, S.N.A.; Ling, T.C.; Tey, B.T.; Lila, M.A.M.; Abdullah, M.P.; Rahim, R.A.; Ariff, A.B. Effect of promoter strength and signal sequence on the periplasmic expression of human interferon-α2b in Escherichia coli. Afr. J. Biotechnology. 2010, 9, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Sarac, F.; Control, P.V.; Hasoksuz, M.; Uzar, S.; Control, P.V. The use of rabbits in studies of immunity and safety of Contagious Ecthyma (CE) vaccine The use of rabbits in studies of immunity and safety of Contagious Ecthyma (CE) vaccine. Front. Vet. sci. 2020, 31, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Cappellano, G.; Comi, C.; Chiocchetti, A.; Dianzani, U. Exploiting PLGA-Based Biocompatible Nanoparticles for Next-Generation Tolerogenic Vaccines against Autoimmune Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Scholzen, A.; Minigo, G.; David, C.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Mottram, P.L.; Plebanski, M. Pathogen recognition and development of particulate vaccines: Does size matter? Methods 2006, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharali, D.J.; Pradhan, V.; Elkin, G.; Qi, W.; Hutson, A.; Mousa, S.A.; Thanavala, Y. Novel nanoparticles for the delivery of recombinant hepatitis B vaccine. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2008, 4, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamo, T.; Poland, G.A. Nanovaccinology: The next generation of vaccines meets 21st century materials science and engineering. Vaccine 2012, 30, 6609–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S. Apoptosis and Clearance of Apoptotic Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laere, E.; Ling, A.P.K.; Wong, Y.P.; Koh, R.Y.; Lila, M.A.M.; Hussein, S. Plant-Based Vaccines: Production and Challenges. J. Bot. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, J.M.; Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, K.A.K.; Ghazali, M.M.; Jaafar, H.; Ideris, A.; Ali, A.M.; Omar, A.R.; Yusoff, K.; Lila, M.A.M.; et al. Molecular genetic analysis of BAX and cyclin D1 genes in patients with malignant glioma. Neurol. Res. 2007, 29, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, J.J.; Nuismer, S.L.; Antia, R. Recombinant vector vaccine evolution. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, D.R. ; Bioinformatics for Vaccinology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780470027110. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, J.J.; Smithson, M.W.; Nuismer, S.L. Transmissible Viral Vaccines. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, V.; Denizer, G.; Friedland, L.R.; Krishnan, J.; Shapiro, M. Understanding modern-day vaccines: What you need to know. Ann. Med. 2018, 50, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hall, T.; van der Burg, S.H. Mechanisms of Peptide Vaccination in Mouse Models. Adv. Immunol. 2012, 114, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malonis, R.J.; Lai, J.R.; Vergnolle, O. Peptide-Based Vaccines: Current Progress and Future Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3210–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, H.H.; Siegling, A.; Volk, H.D.; Friebe, A.; Knolle, P.; Limmer, A.; Weber, O. Inactivated orf virus (Parapoxvirus ovis) induces antitumoral activity in transplantable tumor models. Anticancer. Res. 2011, 31, 4185–4190. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.-Y.; Hussein, W.M.; Toth, I.; Skwarczynski, M. Advances in Peptide-based Human Papillomavirus Therapeutic Vaccines. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, S.; Heilman, C. Future Directions in Vaccines: The Payoffs of Basic Research. Health Aff. 2005, 24, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Singh, M.; O’Hagan, D.T. Recent advances in veterinary vaccine adjuvants. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgins, D.C.; Chattha, K.; Vlasova, A.; Parreño, V.; Corbeil, L.B.; Renukaradhya, G.J.; Saif, L.J. Mucosal Veterinary Vaccines. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 4, 1337–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, M.D.; Iqbal, M.; Nair, V. Recent advances in viral vectors in veterinary vaccinology. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeri, S.; Najafabadi, S.P.; Aali, E.; Karimpour, A.; Sarmadi, M.; Hasanvand, M.; Hasanvand, M.; Hoseini, L.; Zeinalipour, M.; Mahravani, H. A Comparative Study on Global Genetic Diversity and Population Genetic Analysis of Orf Virus Isolates from Outbreaks and it’s Implications for the Vaccine Development. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res. 2020, 8, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nino-Fong, R.; Johnston, J.B. Poxvirus-based vaccine platforms: Getting at those hard-to-reach places. Futur. Virol. 2008, 3, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giadinis, N.D.; Filliusis, G.; Lafi, S.Q.; Panousis, N.; Pourliotis, K.; Bojkovski, J.; Karatzias, H. Field evaluation of an Orf vaccine in sheep and goat flocks with high neonatal mortality. Vet. Glas. 2007, 61, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Takaiwa, A.; Takeshima, S.-N.; Okada, A.; Inoshima, Y. Genetic Variability of 3′-Proximal Region of Genomes of Orf Viruses Isolated From Sheep and Wild Japanese Serows (Capricornis crispus) in Japan. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Polymer-Based Nanomaterials and Applications for Vaccines and Drugs. Polym. 2018, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, G.J. Poxviral mimicry of complement and chemokine system components: what’s the end game? Immunol. Today 2000, 21, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, F.S.; El-Banna, H.A.; Elzorba, H.Y.; Galal, A.M. Application of some nanoparticles in the field of veterinary medicine. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2019, 7, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, J.M.B.; Waldron, D.F.; Taylor, C.A. Evaluation of homologous and heterologous protection induced by a virulent field strain of orf virus and an orf vaccine in goats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, J.M.B.; Taylor, C.A.; Guo, J.; Tizard, I.R.; Walker, J.W. Development of a contagious ecthyma vaccine for goats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagikgtok, J.; Horne, R.W. The Structure of Orf Virus. Virology 1964, 472, 461–472. [Google Scholar]
- Seet, B.T.; Johnston, J.B.; Brunetti, C.R.; Barrett, J.W.; Everett, H.; Cameron, C.; Sypula, J.; Nazarian, S.H.; Lucas, A.; McFadden, G.P. oxviruses and immune evasion. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 377–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheerin, D.; Openshaw, P.J.; Pollard, A.J. Issues in vaccinology: Present challenges and future directions. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrough, B.; Dowall, S.; Hewson, R. Emerging viruses and current strategies for vaccine intervention. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 196, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, A.; Kumar, V.; Chaudhary, D.; Bansal, N.; Kumar, A.; Kakker, N.; Maan, S. Past and Present Overview of “Orf. ” Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 2159–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razis, A.F.A.; Ismail, E.N.; Hambali, Z.; Abdullah, M.N.H.; Ali, A.M.; Lila, M.A.M. The periplasmic expression of recombi-nant human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) in Escherichia coli. Asia Pac. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 14, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Struzik, J.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L. NF-κB as an Important Factor in Optimizing Poxvirus-Based Vaccines against Viral Infections. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, S.S. Evolving views of viral evolution: Towards an evolutionary biology of viruses. Hist. Philos. Life Sci. 1992, 14, 1342725. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, S.T.G.; Nunn, F.; Nath, M.; Frew, D.; Wells, B.; Marr, E.J.; Huntley, J.F.; McNeilly, T.N.; Nisbet, A.J. A recombinant subunit vaccine for the control of ovine psoroptic mange (sheep scab). Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
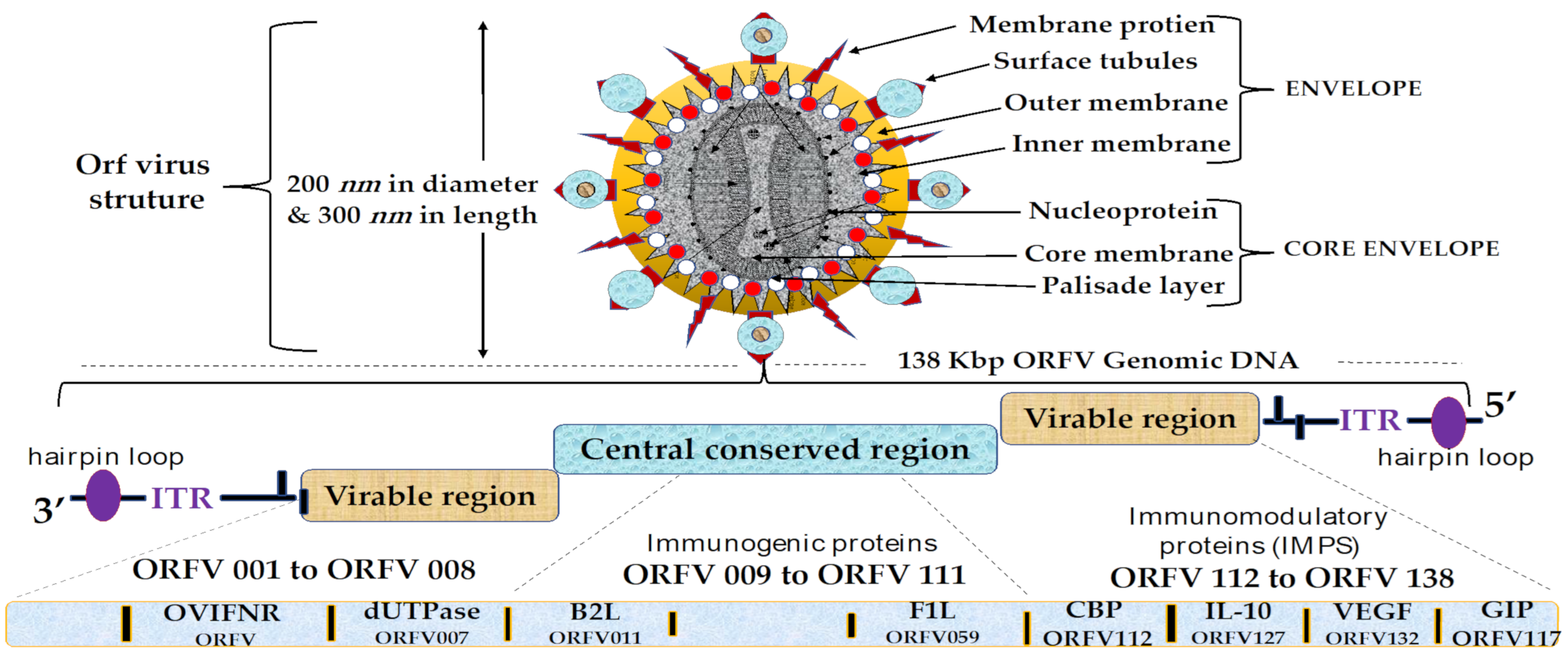
| Viral | Protein | Gene | Mechanism of Action | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| vVEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor | ORFV132 | inhibit the development and functional maturation of dendritic cells | [95,96,97] |
| vIL-10 | Viral Interleuken-10 | ORFV127 | inhibits the synthesis and trafficking of host’s cytokines | [98,99,100,106] |
| vCBP | Viral chemokine binding protein | ORFV112 | Stops the cruising and migration of dermal dendritic cells (DCs) to peripheral lymph nodes | [65,87,102,103,104] |
| GIP | GM-CSF/IL-2 inhibitory factor | ORFV117 | inhibits the biological activity of the cytokines GM-CSF and IL-2 (interleukin-2) | [98,101] |
| OVIFNR | Interferon resistant factor | ORFV020 | Inhibits the activities of the cellular IFN | [65,103] |
| Method of Preparation | Target Animal/Year Introduced) | Vaccine Characteristic(s) | Advantages | Disadvantages | Immune Response | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell culture-based vaccine | Sheep/goats (1999,1996,1998, 2008) | attenuated vaccines e.g., D1701 goat vaccine | Induce (4-8 months) humoral & cell-mediated immunity | short-lived immunity, possible reversion to virulence strain | Evokes broad immune responses; and CD4-T cells, CD8-T cells and the cytokine IFN-g (interferon-g) have been observed | [5,14,25,78,129,175] |
| Egg-based vaccine | Sheep (2008) | Ovine vaccine-egg-based vaccine | Induces antibody mediated immunity | short-lived immunity | ORFV-specific IgG, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-18. | [56,74,78,164] |
| Scab-based vaccine | sheep (1935, 1989, & 2012) | Homologous goats’ vaccine | 4–6-months cell mediated immunity in sheep | potential source of environmental contamination | Cellular immunity plays the main role, IL-4, and IL-18 and O RFV-specific IgG. | [56,120,125,178] |
| Inactivated Orf vaccine | Sheep/goats | D1701 ORFV | Cell-mediated and humoral immunity | short-lived immunity, | IFN-g & a type 1, IL-4 & IL-10 | [59,63,178,183] |
| Recombinant vaccine | Sheep/goats (2011, 2016, & 2019) | Chimeric DNA vaccine | Mimics adaptive immunity | required multiple boosters | IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-18 and ORFV-specific IgG. | [25,160,130,183] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bukar, A.M.; Jesse, F.F.A.; Abdullah, C.A.C.; Noordin, M.M.; Lawan, Z.; Mangga, H.K.; Balakrishnan, K.N.; Azmi, M.-L.M. Immunomodulatory Strategies for Parapoxvirus: Current Status and Future Approaches for the Development of Vaccines against Orf Virus Infection. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111341
Bukar AM, Jesse FFA, Abdullah CAC, Noordin MM, Lawan Z, Mangga HK, Balakrishnan KN, Azmi M-LM. Immunomodulatory Strategies for Parapoxvirus: Current Status and Future Approaches for the Development of Vaccines against Orf Virus Infection. Vaccines. 2021; 9(11):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111341
Chicago/Turabian StyleBukar, Alhaji Modu, Faez Firdaus Abdullah Jesse, Che Azurahanim Che Abdullah, Mustapha M. Noordin, Zaharaddeen Lawan, Hassana Kyari Mangga, Krishnan Nair Balakrishnan, and Mohd-Lila Mohd Azmi. 2021. "Immunomodulatory Strategies for Parapoxvirus: Current Status and Future Approaches for the Development of Vaccines against Orf Virus Infection" Vaccines 9, no. 11: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111341
APA StyleBukar, A. M., Jesse, F. F. A., Abdullah, C. A. C., Noordin, M. M., Lawan, Z., Mangga, H. K., Balakrishnan, K. N., & Azmi, M.-L. M. (2021). Immunomodulatory Strategies for Parapoxvirus: Current Status and Future Approaches for the Development of Vaccines against Orf Virus Infection. Vaccines, 9(11), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111341





