Dissecting the NK Cell Population in Hematological Cancers Confirms the Presence of Tumor Cells and Their Impact on NK Population Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials, Subjects, and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. HL and AML Patients
2.3. Healthy Donor (HD)
2.4. Clinical Criteria for CMV-Seropositive Patients
2.5. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis and Antibodies
2.6. High Dimensional Reduction Analysis
2.7. Correlation Matrix Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
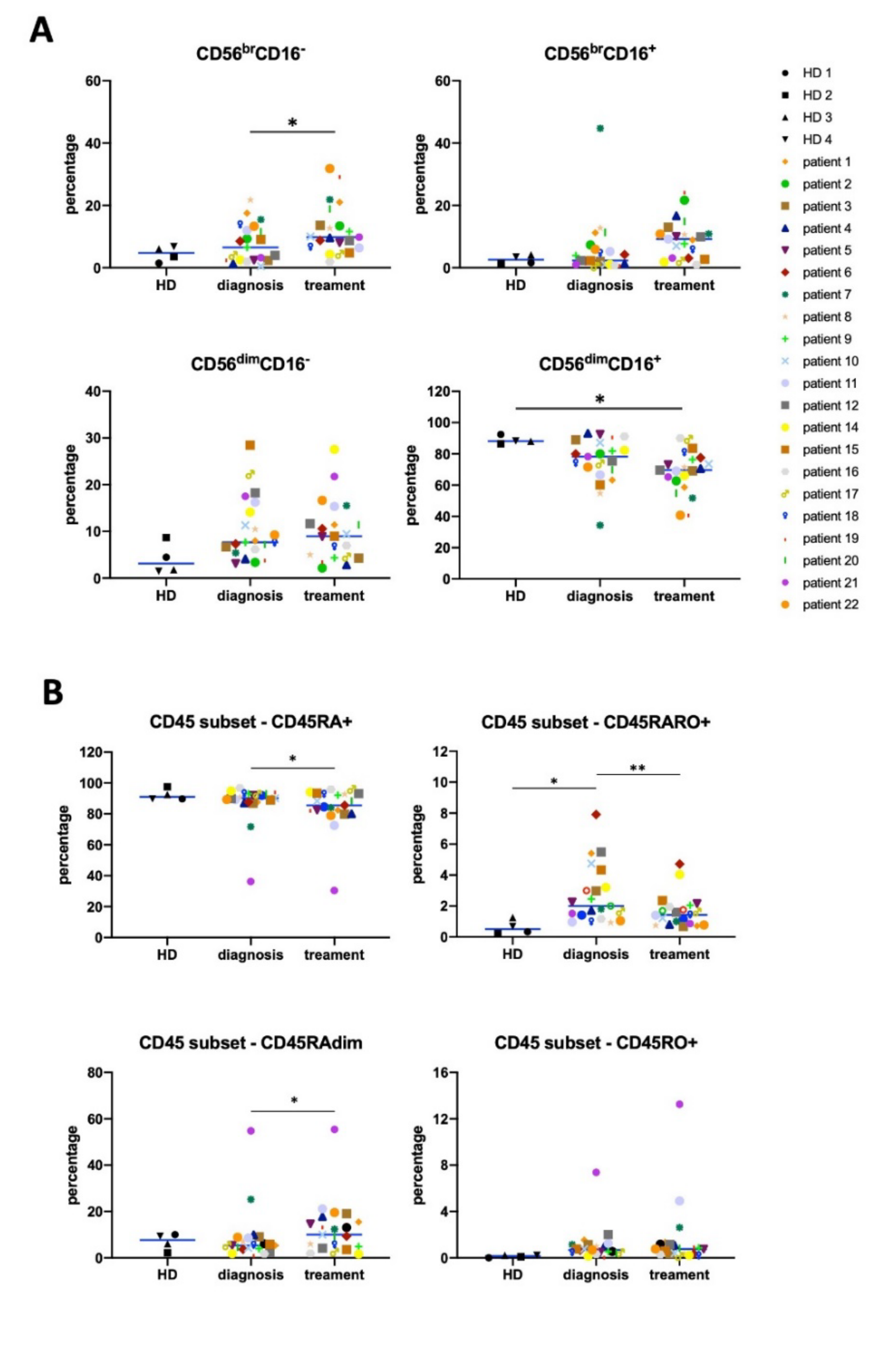
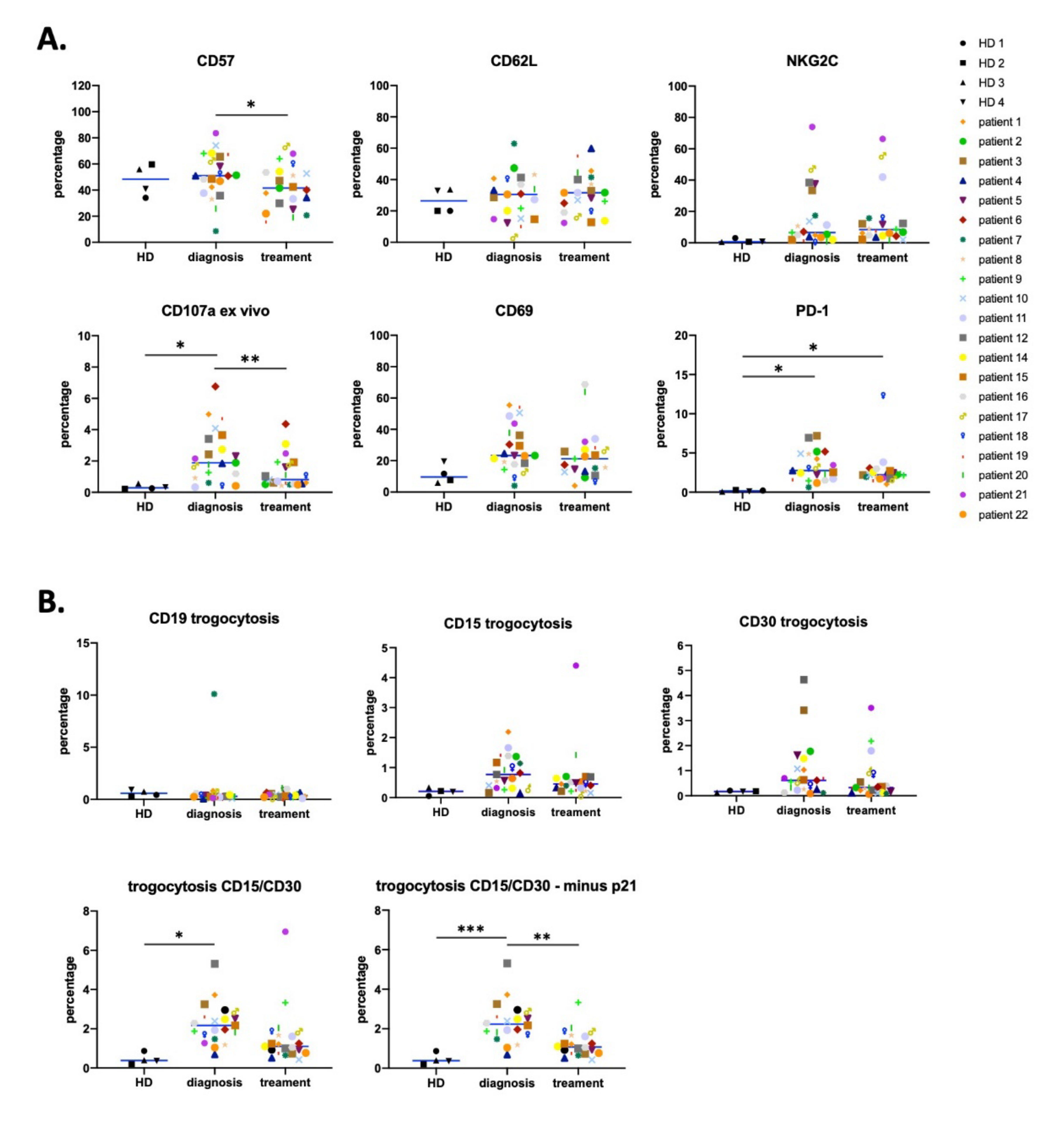
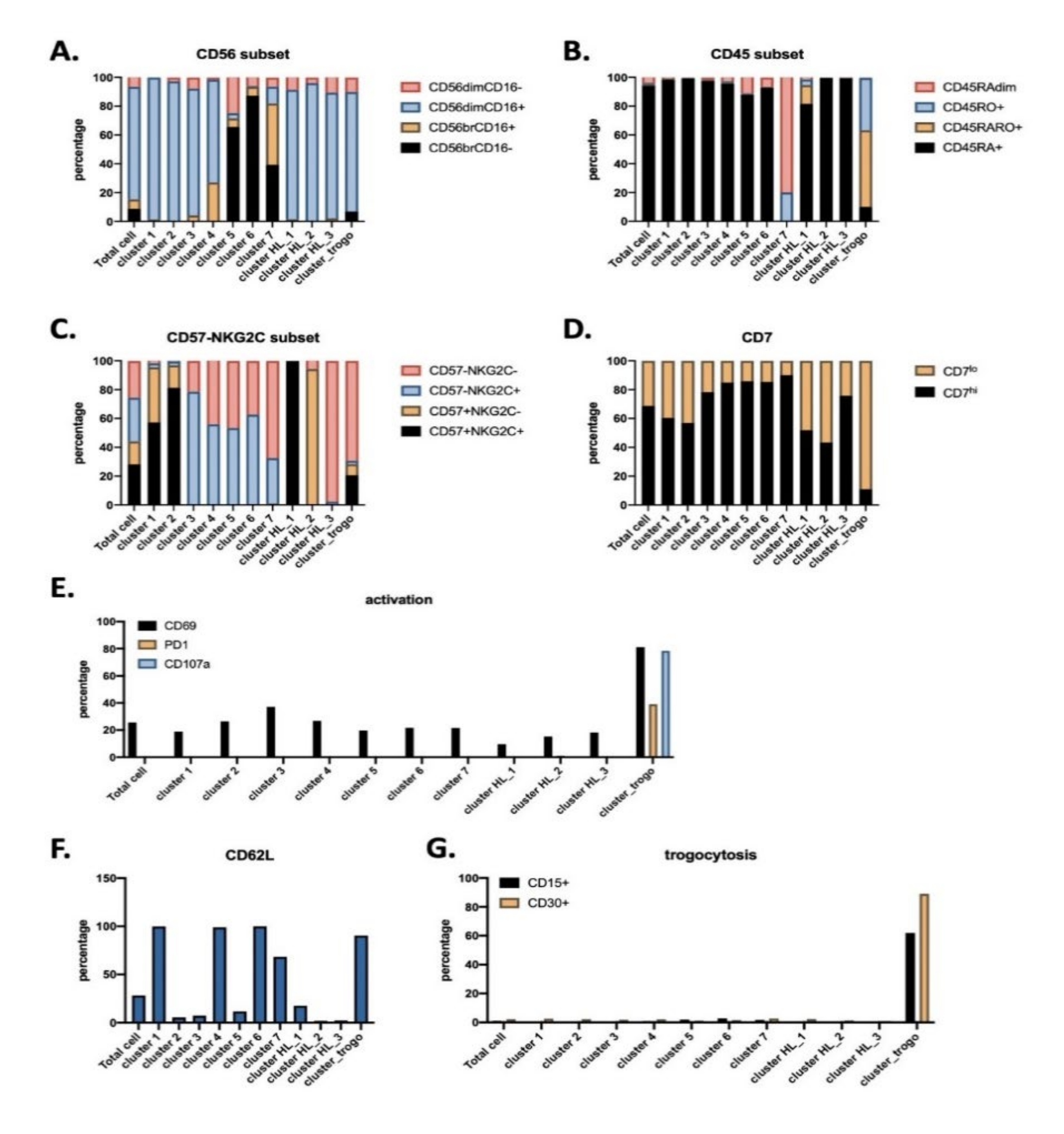
3.1. Antitumor NK Cells in HL Patients are Identified by CD45RARO and CD107 Expression
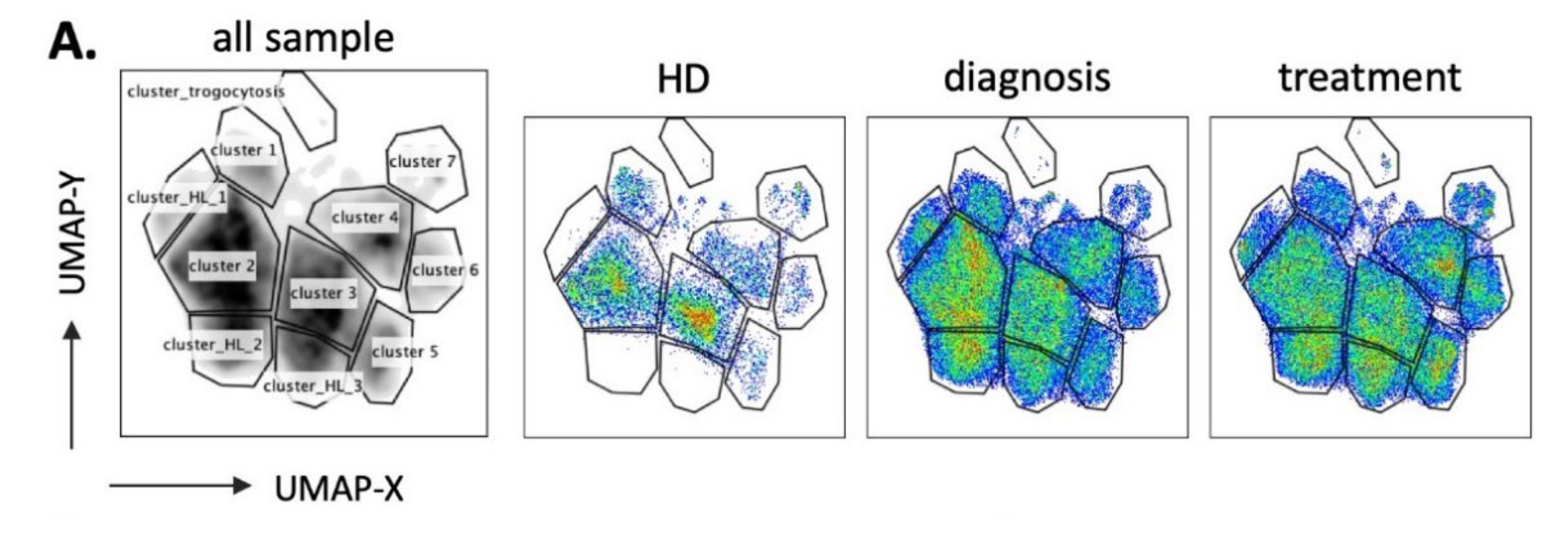
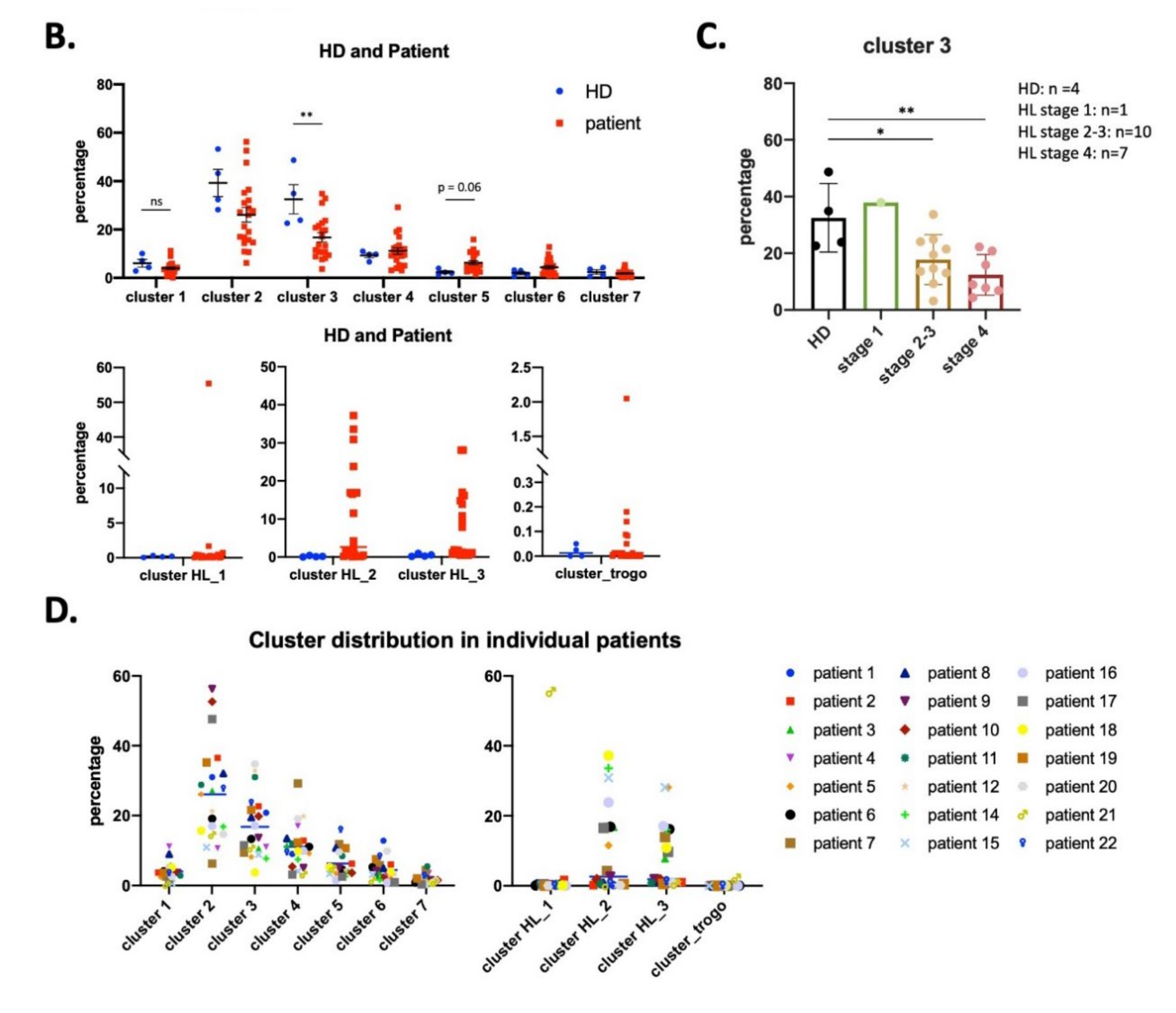
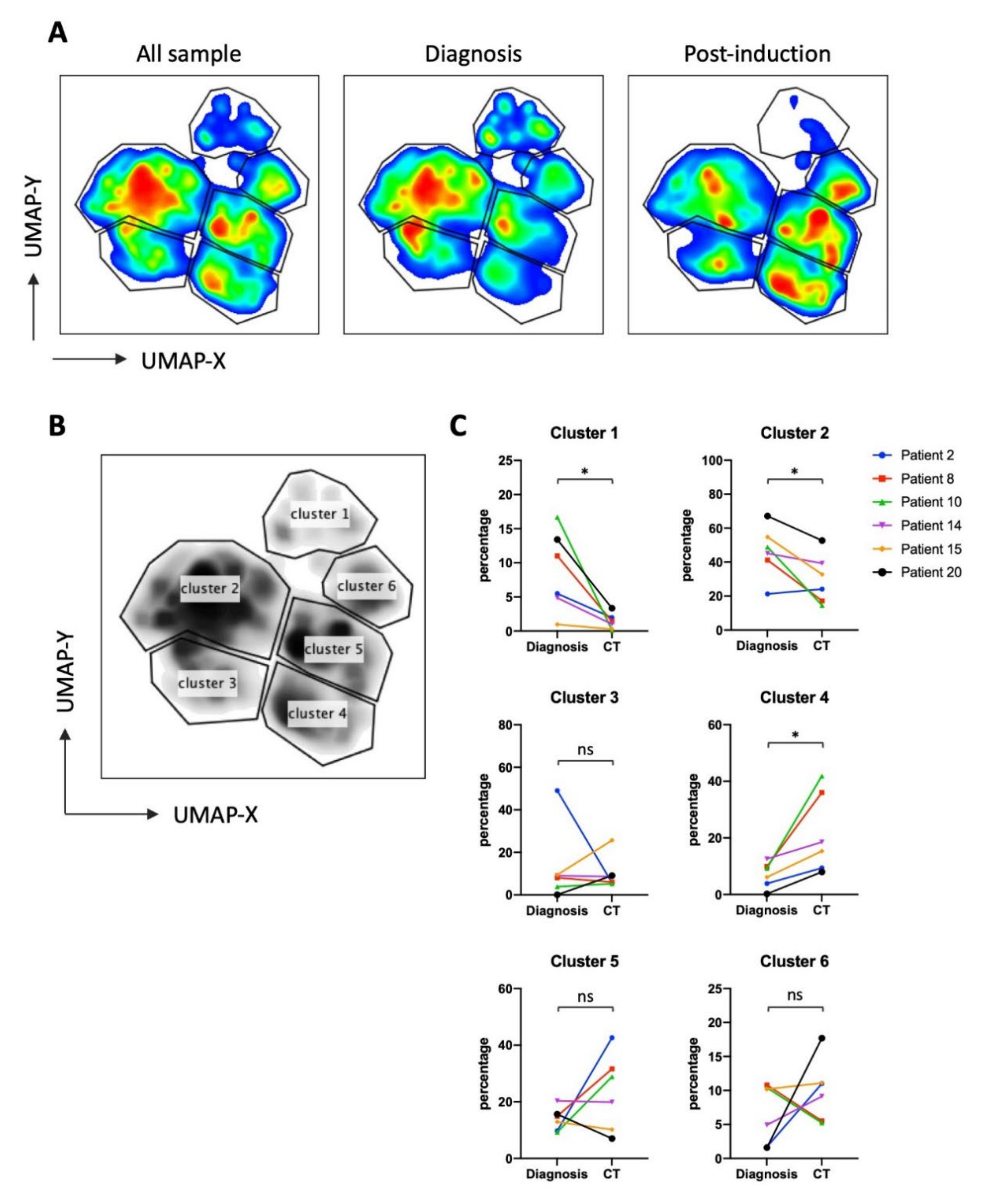
3.2. UMAP (Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection) Identifies New NK Cell Subsets
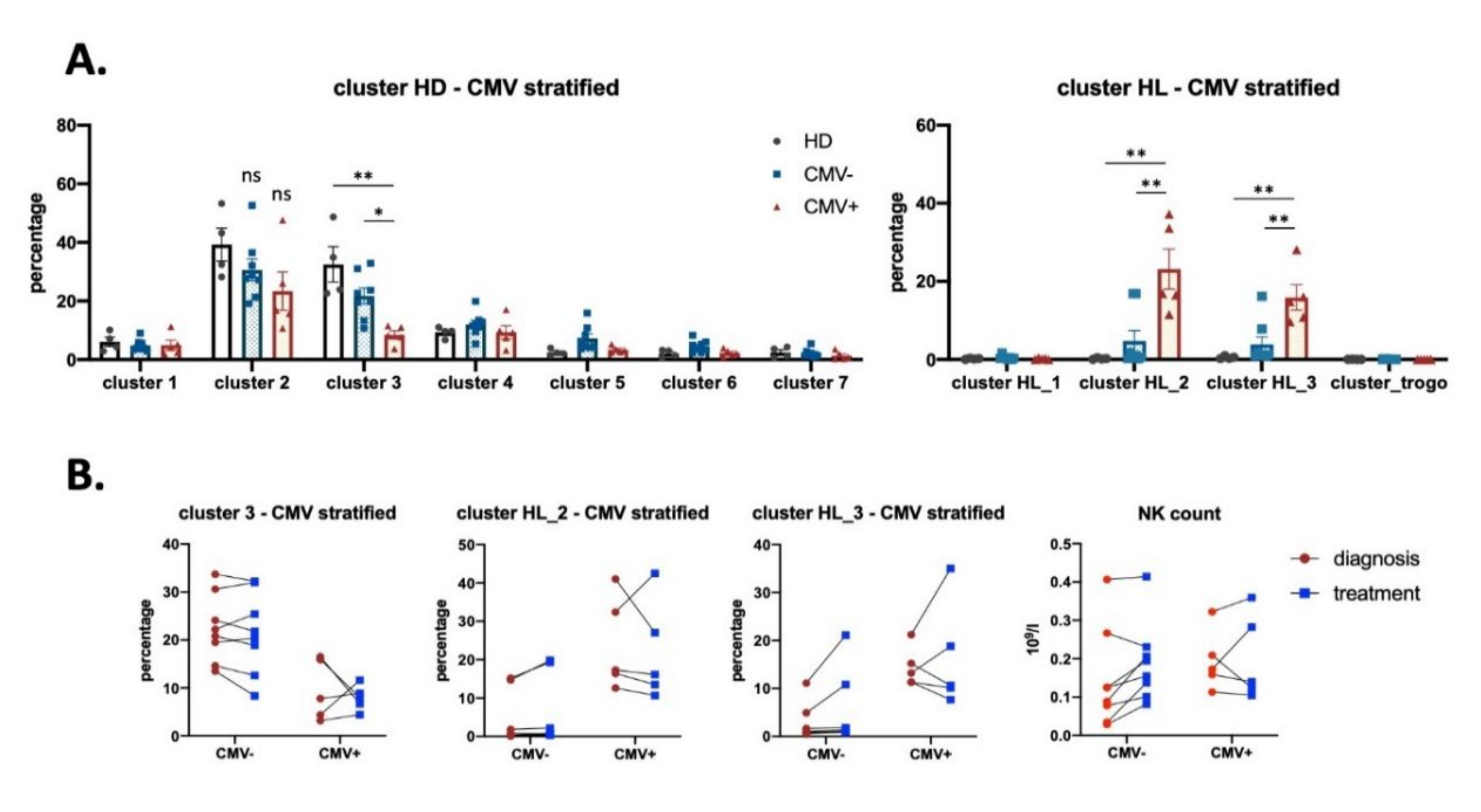
3.3. Effect of CMV Infection on NK Subsets in HL Patients
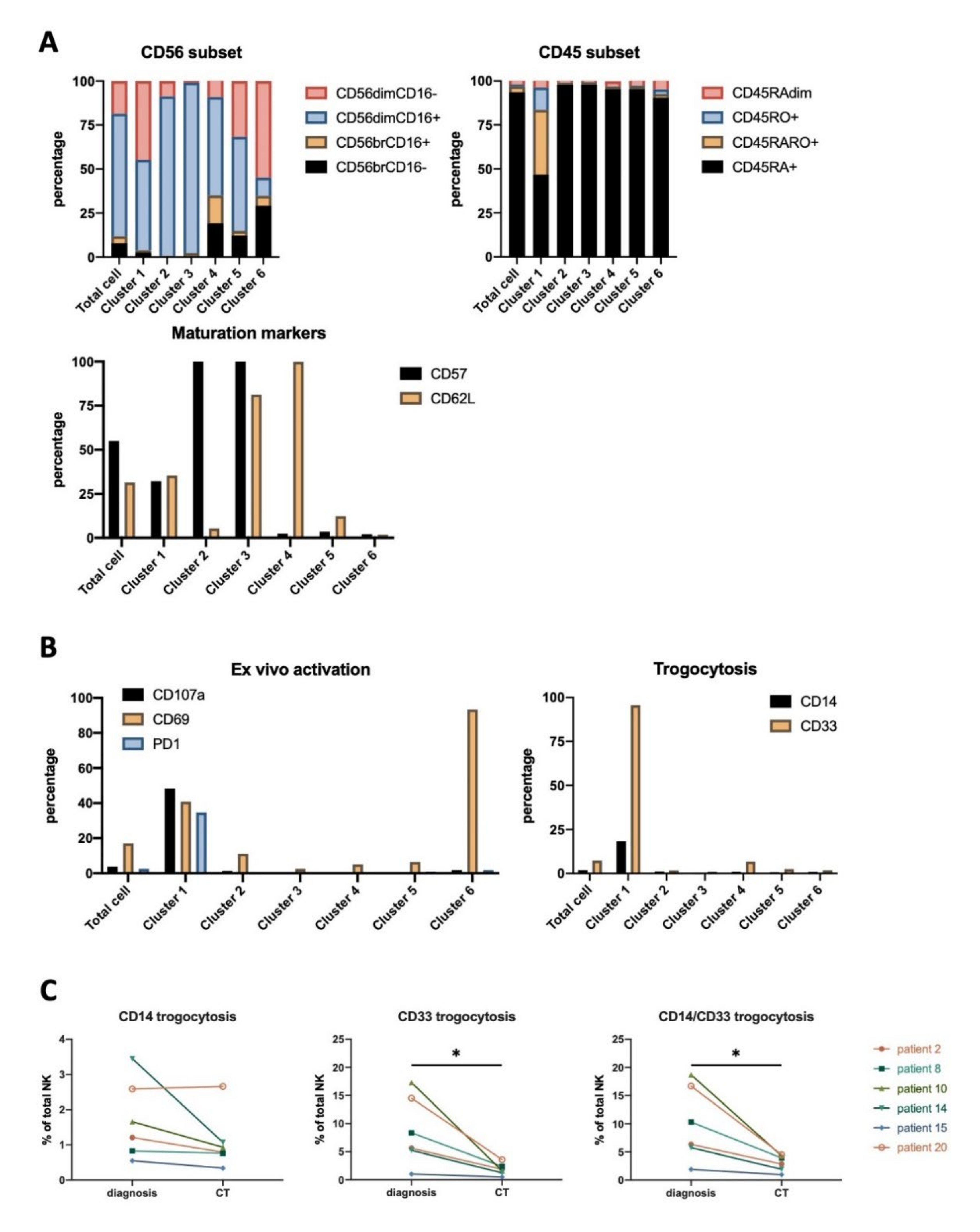
3.4. NK Cells Subsets in AML Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freud, A.G.; Mundy-Bosse, B.L.; Yu, J.; Caligiuri, M.A. The Broad Spectrum of Human Natural Killer Cell Diversity. Immunity 2017, 47, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, A.; Strauss-Albee, D.M.; Leipold, M.; Kubo, J.; Nemat-Gorgani, N.; Dogan, O.C.; Dekker, C.L.; Mackey, S.; Maecker, H.; Swan, G.E.; et al. Genetic and environmental determinants of human NK cell diversity revealed by mass cytometry. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 208ra145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Siebert, J.R.; Burns, R.; Gerbec, Z.J.; Bonacci, B.; Rymaszewski, A.; Rau, M.; Riese, M.J.; Rao, S.; Carlson, K.-S.; et al. Heterogeneity of human bone marrow and blood natural killer cells defined by single-cell transcriptome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassani, B.; Baci, D.; Gallazzi, M.; Poggi, A.; Bruno, A.; Mortara, L. Natural Killer Cells as Key Players of Tumor Progression and Angiogenesis: Old and Novel Tools to Divert Their Pro-Tumor Activities into Potent Anti-Tumor Effects. Cancers 2019, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinska, E.; Allende-Vega, N.; Cornillon, A.; Vo, D.N.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Panabieres, C.; Vilches, C.; Déchanet-Merville, J.; Hicheri, Y.; Rossi, J.-F.; et al. Identification of anti tumor cells carrying natural killer (NK) cell antigens in patients with hematological cancers. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinska, E.; Cornillon, A.; Allende-Vega, N.; Vo, D.N.; Rene, C.; Lu, Z.Y.; Pasero, C.; Olive, D.; Fegueux, N.; Ceballos, P.; et al. CD45 Isoform Profile Identifies Natural Killer (NK) Subsets with Differential Activity. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0150434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, D.N.; Alexia, C.; Allende-Vega, N.; Morschhauser, F.; Houot, R.; Menard, C.; Tarte, K.; Cartron, G.; Villalba, M. NK cell activation and recovery of NK cell subsets in lymphoma patients after obinutuzumab and lenalidomide treatment. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1409322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalba, M.; Alexia, C.; Bellin-Robert, A.; Fayd’herbe de Maudave, A.; Gitenay, D. Non-Genetically Improving the Natural Cytotoxicity of Natural Killer (NK) Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Botet, M.; Vilches, C.; Redondo-Pachon, D.; Muntasell, A.; Pupuleku, A.; Yelamos, J.; Pascual, J.; Crespo, M. Dual Role of Natural Killer Cells on Graft Rejection and Control of Cytomegalovirus Infection in Renal Transplantation. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumá, M.; Budt, M.; Sáez, A.; Brckalo, T.; Hengel, H.; Angulo, A.; López-Botet, M. Expansion of CD94/NKG2C+ NK cells in response to human cytomegalovirus-infected fibroblasts. Blood 2006, 107, 3624–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Tian, Z. Natural Killer Cell Memory: Progress and Implications. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Valentin, M.; Gras Navarro, A.; Rahman, A.M.; Kumar, S.; Retière, C.; Ulvestad, E.; Kristensen, V.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Lie, B.A.; Enger, P.Ø.; et al. Identification of a Natural Killer Cell Receptor Allele That Prolongs Survival of Cytomegalovirus-Positive Glioblastoma Patients. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5326–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gras Navarro, A.; Kmiecik, J.; Leiss, L.; Zelkowski, M.; Engelsen, A.; Bruserud, O.; Zimmer, J.; Enger, P.O.; Chekenya, M. NK cells with KIR2DS2 immunogenotype have a functional activation advantage to efficiently kill glioblastoma and prolong animal survival. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 6192–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chijioke, O.; Landtwing, V.; Münz, C. NK Cell Influence on the Outcome of Primary Epstein-Barr Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulak, J.; Oriolo, F.; Zaghi, E.; Di Vito, C.; Mavilio, D. Natural killer cells in HIV-1 infection and therapy. AIDS 2017, 31, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiani, C.M.; Palella, E.; Sottile, R.; Tallerico, R.; Garofalo, C.; Carbone, E. Human NK Cell Subsets in Pregnancy and Disease: Toward a New Biological Complexity. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrega, P.; Ferlazzo, G. Natural Killers Are Made Not Born: How to Exploit NK Cells in Lung Malignancies. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, M.; Janji, B.; Berchem, G. Activation of NK cells and disruption of PD-L1/PD-1 axis: Two different ways for lenalidomide to block myeloma progression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24031–24044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, C.; Fino, A.; Sanchez, C.; Farnault, L.; Rihet, P.; Kahn-Perles, B.; Costello, R.T. Natural Killer Cells Modulation in Hematological Malignancies. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z. Overcome the Impairment of NK Cells for Icon and Antibody Immunotherapy of Cancer. J. Immune Based Ther. Vaccines Antimicrob. 2013, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, M.; Lopez-Royuela, N.; Krzywinska, E.; Rathore, M.G.; Hipskind, R.A.; Haouas, H.; Allende-Vega, N. Chemical metabolic inhibitors for the treatment of blood-borne cancers. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalba, M.; Rathore, M.G.; Lopez-Royuela, N.; Krzywinska, E.; Garaude, J.; Allende-Vega, N. From tumor cell metabolism to tumor immune escape. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2013, 45, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikzad, R.; Angelo, L.S.; Aviles-Padilla, K.; Le, D.T.; Singh, V.K.; Bimler, L.; Vukmanovic-Stejic, M.; Vendrame, E.; Ranganath, T.; Simpson, L.; et al. Human natural killer cells mediate adaptive immunity to viral antigens. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becht, E.; McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Dutertre, C.-A.; Kwok, I.W.H.; Ng, L.G.; Ginhoux, F.; Newell, E.W. Dimensionality reduction for visualizing single-cell data using UMAP. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allende-Vega, N.; Krzywinska, E.; Orecchioni, S.; Lopez-Royuela, N.; Reggiani, F.; Talarico, G.; Rossi, J.F.; Rossignol, R.; Hicheri, Y.; Cartron, G.; et al. The presence of wild type p53 in hematological cancers improves the efficacy of combinational therapy targeting metabolism. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19228–19245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Martinez, D.; Allende-Vega, N.; Orecchioni, S.; Talarico, G.; Cornillon, A.; Vo, D.N.; Rene, C.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Krzywinska, E.; Anel, A.; et al. Expansion of Allogeneic NK Cells with Efficient Antibody-Dependent Cell Cytotoxicity against Multiple Tumor Cells. Theranostic 2018, 8, 3856–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. arXiv 2020, arXiv:180203426. [Google Scholar]
- Milush, J.M.; Long, B.R.; Snyder-Cappione, J.E.; Cappione, A.J.; York, V.A.; Ndhlovu, L.C.; Lanier, L.L.; Michaëlsson, J.; Nixon, D.F. Functionally distinct subsets of human NK cells and monocyte/DC-like cells identified by coexpression of CD56, CD7, and CD4. Blood 2009, 114, 4823–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowich, H.; Pricop, L.; Herberman, R.B.; Whiteside, T.L. Expression and function of CD7 molecule on human natural killer cells. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Foss, H.D.; Reusch, R.; Demel, G.; Lenz, G.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Hummel, M.; Stein, H. Frequent expression of the B-cell-specific activator protein in Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin’s disease provides further evidence for its B-cell origin. Blood 1999, 94, 3108–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryceson, Y.T.; Chiang, S.C.; Darmanin, S.; Fauriat, C.; Schlums, H.; Theorell, J.; Wood, S.M. Molecular mechanisms of natural killer cell activation. J. Innate Immun. 2011, 3, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juelke, K.; Killig, M.; Luetke-Eversloh, M.; Parente, E.; Gruen, J.; Morandi, B.; Ferlazzo, G.; Thiel, A.; Schmitt-Knosalla, I.; Romagnani, C. CD62L expression identifies a unique subset of polyfunctional CD56dim NK cells. Blood 2010, 116, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Verges, S.; Milush, J.M.; Pandey, S.; York, V.A.; Arakawa-Hoyt, J.; Pircher, H.; Norris, P.J.; Nixon, D.F.; Lanier, L.L. CD57 defines a functionally distinct population of mature NK cells in the human CD56dimCD16+ NK-cell subset. Blood 2010, 116, 3865–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, D.M.; Bakan, C.E.; Mishra, A.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Efebera, Y.; Becknell, B.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Smith, M.K.; et al. The PD-1/PD-L1 axis modulates the natural killer cell versus multiple myeloma effect: A therapeutic target for CT-011, a novel monoclonal anti-PD-1 antibody. Blood 2010, 116, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, S.; Ambinder, R.F. Hodgkin lymphoma: A review and update on recent progress. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, S.; Orsini, M.; Ceballos, P.; Fegueux, N.; Kanouni, T.; Caumes, B.; Klein, B.; Villalba, M.; Rossi, J.F. Controlled Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation After Allogeneic Tranplantation Is Associated With Improved Survival. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunz, B.; Hengst, J.; Deterding, K.; Manns, M.P.; Cornberg, M.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; Wedemeyer, H.; Björkström, N.K. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection irreversibly impacts human natural killer cell repertoire diversity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blish, C.A. Natural Killer Cell Diversity in Viral Infection: Why and How Much? Pathog. Immun. 2016, 1, 165–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntasell, A.; Pupuleku, A.; Cisneros, E.; Vera, A.; Moraru, M.; Vilches, C.; López-Botet, M. Relationship of NKG2C Copy Number with the Distribution of Distinct Cytomegalovirus-Induced Adaptive NK Cell Subsets. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2016, 196, 3818–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehravaran, H.; Makvandi, M.; Samarbaf Zade, A.; Neisi, N.; Kiani, H.; Radmehr, H.; Shahani, T.; Hoseini, S.Z.; Ranjbari, N.; Nahid Samiei, R. Association of Human Cytomegalovirus with Hodgkin’s Disease and Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2017, 18, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesa, A.; Ciuperca, G.; Louvet, V.; Pujo-Menjouet, L.; Génieys, S.; Dumontet, C.; Thomas, X.; Volpert, V. Diagnostics of the AML with immunophenotypical data. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 2006, 1, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Caselles, T.; Martínez-Esparza, M.; Pérez-Oliva, A.B.; Quintanilla-Cecconi, A.M.; García-Alonso, A.; Alvarez-López, D.M.R.; García-Peñarrubia, P. A study of CD33 (SIGLEC-3) antigen expression and function on activated human T and NK cells: Two isoforms of CD33 are generated by alternative splicing. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béziat, V.; Liu, L.L.; Malmberg, J.-A.; Ivarsson, M.A.; Sohlberg, E.; Björklund, A.T.; Retière, C.; Sverremark-Ekström, E.; Traherne, J.; Ljungman, P.; et al. NK cell responses to cytomegalovirus infection lead to stable imprints in the human KIR repertoire and involve activating KIRs. Blood 2013, 121, 2678–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss-Albee, D.M.; Blish, C.A. Human NK Cell Diversity in Viral Infection: Ramifications of Ramification. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, J.; Ernst, D.M.; Keating, A. Acquired Natural Killer Cell Dysfunction in the Tumor Microenvironment of Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsten, M.; Järås, M. Natural Killer Cells in Myeloid Malignancies: Immune Surveillance, NK Cell Dysfunction, and Pharmacological Opportunities to Bolster the Endogenous NK Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, S.P.; Cosma, G.; Foulds, G.A.; Johnson, C.; Reeder, S.; McArdle, S.E.; Khan, M.A.; Pockley, A.G. Identifying prostate cancer and its clinical risk in asymptomatic men using machine learning of high dimensional peripheral blood flow cytometric natural killer cell subset phenotyping data. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, P.; Loiacono, F.; Conte, R.; Moretta, L.; Vitale, C.; Mingari, M.C. IL-1beta inhibits ILC3 while favoring NK-cell maturation of umbilical cord blood CD34(+) precursors. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, L.; Pietra, G.; Vacca, P.; Pende, D.; Moretta, F.; Bertaina, A.; Mingari, M.C.; Locatelli, F.; Moretta, A. Human NK cells: From surface receptors to clinical applications. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 178, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Number | Stage at Diagnosis (Ann Arbor) | First Treatment | Response (Lugano) | Relapse | First Treatmenton Relapse | Response at the End of Treatment | Second Treatment on Relapse | Last Medical Status | CMV/HIV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | ABVD x3 + radiotherapy | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | na/− |
| 2 | 3 | BEACOPP x6 + AVD x2 | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | −/− |
| 3 | 1 | ABVD x2 + R-DHAC x4 + BEAM + autograft | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | −/− |
| 4 | 4 | PVABx6 | PR | Yes | DHAC x6 | Progression | Brentuximab + Bendamustine x6 | CR | +/− |
| 5 | 4 | BVAPx6 | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | +/− |
| 6 | 3 | BEACOPP x2 + ABVDx4 | PR | No | - | - | - | PR | −/− |
| 7 | 4 | EACOPP x6 | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | na/− |
| 8 | 4 | PVAB x4 | CR | Yes | R-DHAC x4 + autograft | Progression | R-CHOP x4 | CR | −/− |
| 9 | 2 | ABVD x3 + radiotherapy | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | na/− |
| 10 | 3 | BEACOPP x2 + ABVD-MP x4 | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | −/− |
| 11 | 1 | ABVD x8 | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | −/− |
| 12 | 2 | ABVD x4 + radiotherapy | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | −/− |
| 13 | 3 | ABVD-MP x6 | CR | Yes | DHACx4 | Progression | Brentuximab + bendamustine | CR | na/− |
| 14 | 4 | PVAB x6 | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | +/− |
| 15 | 2 | ABVD x4 + radiotherapy | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | na/− |
| 16 | 2 | ABVD x6 + radiotherapy | PR | No | - | - | - | PR | na/− |
| 17 | 2 | ABVD x3 + radiotherapy | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | +/− |
| 18 | 2 | ABVD x4 + radiotherapy | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | +/− |
| 19 | 3 | PVABx6 | CR | Yes | Nivolumab x13 | CR | - | CR | na/− |
| 20 | 1 | ABVD x3 + radiotherapy | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | na/− |
| 21 | 4 | BEACOPP x2 + ABVD x4 | CR | No | CR | na/+ | |||
| 22 | 4 | BEACOPP x2 + ABVD x4 | CR | No | - | - | - | CR | −/− |
| Patient Number | AML Subtype | Treatment Induction | Consolidation | Response | Allograft | Relapse | Treatment on Relapse | Last Medical Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | M4 | 1st induction: Idarubicine + cytarabine 2nd cytarabine-HD | cytarabine HD | RC | Yes | 6 months after graft | AMHAC + consolidation cytarabine-HD | deceased (myocard infarctus) |
| 8 | M2 | 1st induction: Idarubicine + cytarabine | cytarabine HD | RC | Yes | No | - | CR |
| 10 | M1 | 1st induction: daunorubicine + cytarabine | cytarabine HD | RC | Yes | 1 month after graft | - | Deceased (AML relapse + GvH D) |
| 14 | M4 | 1st induction: Idarubicine + cytarabine | cytarabine HD | RC | Yes | 2, 5 years after graft | gemtuzumab ozogamicin + mitoxantrone + allograft | CR |
| 15 | M0 | 1st induction: idarubicine + cytarabine. 2nd: cytarabine HD | cytarabine HD | RC | Yes | No | - | Deceased (GvH disease and infections) |
| 20 | M1 | 1st induction: cytarabine + idarubicine + azacitidine | - | RC | No | before graft | azaticidine + sorafenib | Deceased |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vo, D.-N.; Constantinides, M.; Allende-Vega, N.; Alexia, C.; Cartron, G.; Villalba, M. Dissecting the NK Cell Population in Hematological Cancers Confirms the Presence of Tumor Cells and Their Impact on NK Population Function. Vaccines 2020, 8, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040727
Vo D-N, Constantinides M, Allende-Vega N, Alexia C, Cartron G, Villalba M. Dissecting the NK Cell Population in Hematological Cancers Confirms the Presence of Tumor Cells and Their Impact on NK Population Function. Vaccines. 2020; 8(4):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040727
Chicago/Turabian StyleVo, Dang-Nghiem, Michael Constantinides, Nerea Allende-Vega, Catherine Alexia, Guillaume Cartron, and Martin Villalba. 2020. "Dissecting the NK Cell Population in Hematological Cancers Confirms the Presence of Tumor Cells and Their Impact on NK Population Function" Vaccines 8, no. 4: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040727
APA StyleVo, D.-N., Constantinides, M., Allende-Vega, N., Alexia, C., Cartron, G., & Villalba, M. (2020). Dissecting the NK Cell Population in Hematological Cancers Confirms the Presence of Tumor Cells and Their Impact on NK Population Function. Vaccines, 8(4), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040727






