Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common HCoVs in Hemodialysis Patients and Transplant Recipients: Data from the Dominican Republic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Subjects Ethics Statement
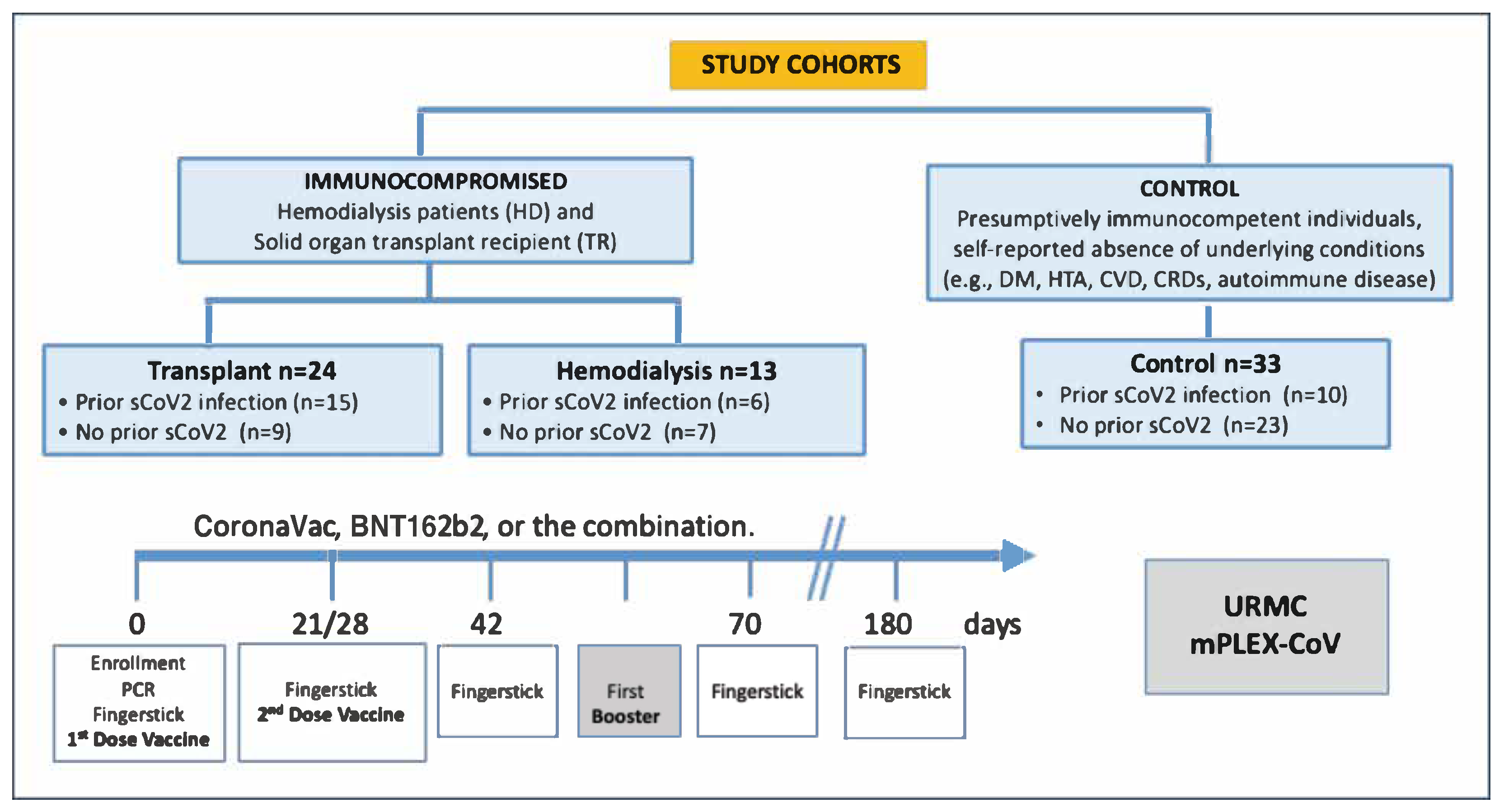
2.2. Study Design and Sample Collection
2.3. mPlex-CoV Assay
2.4. Measurement of Hemoglobin (Hgb) and Adjustment of Antibody Concentration
2.5. Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) and Multivariate Linear Mixed Model (MLMM) Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics, Vaccination Status, and COVID-19 History
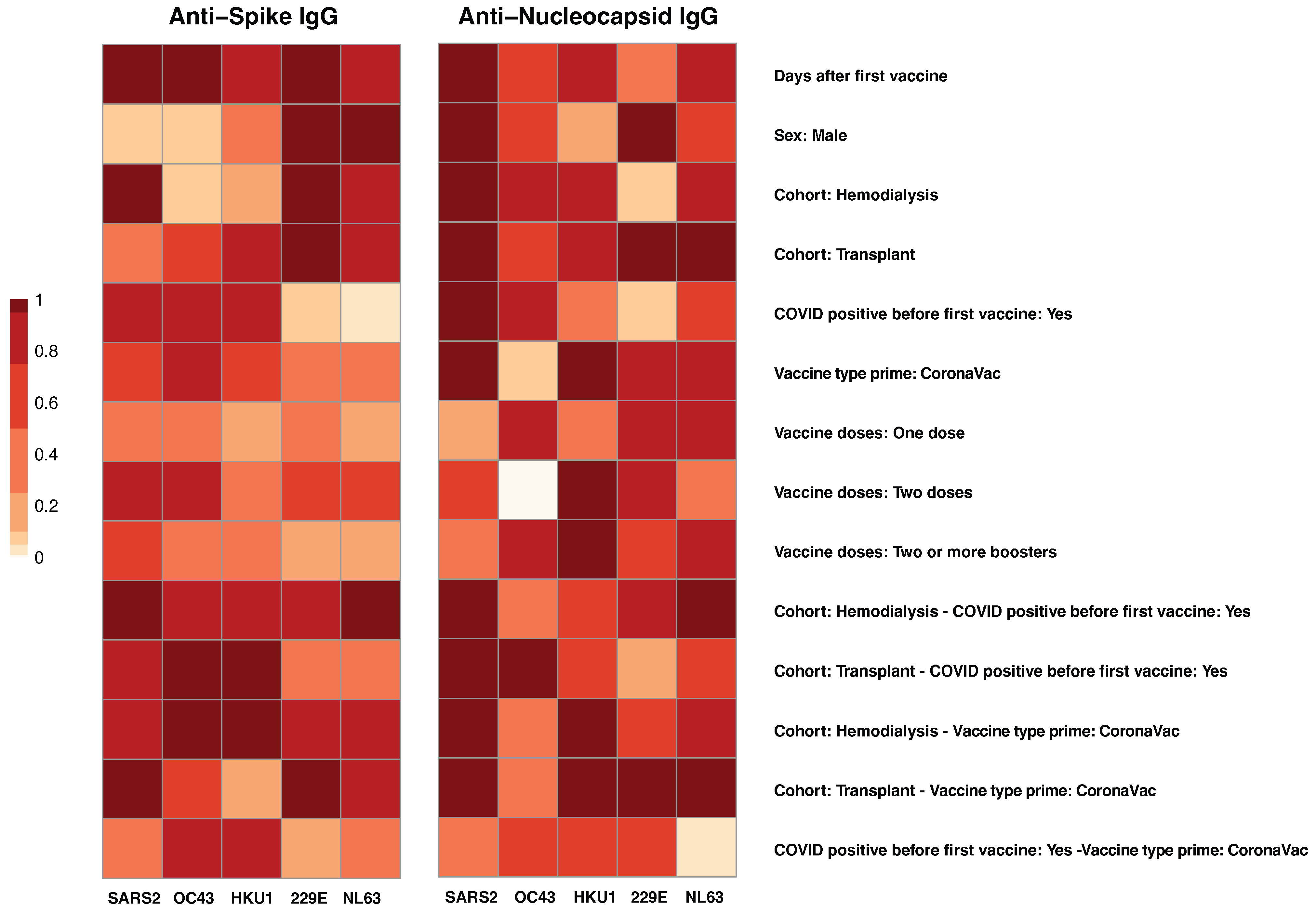
3.2. Co-Factor Analysis of Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs)
3.3. Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common Human Coronaviruses in Hemodialysis, Transplant, and Control Groups
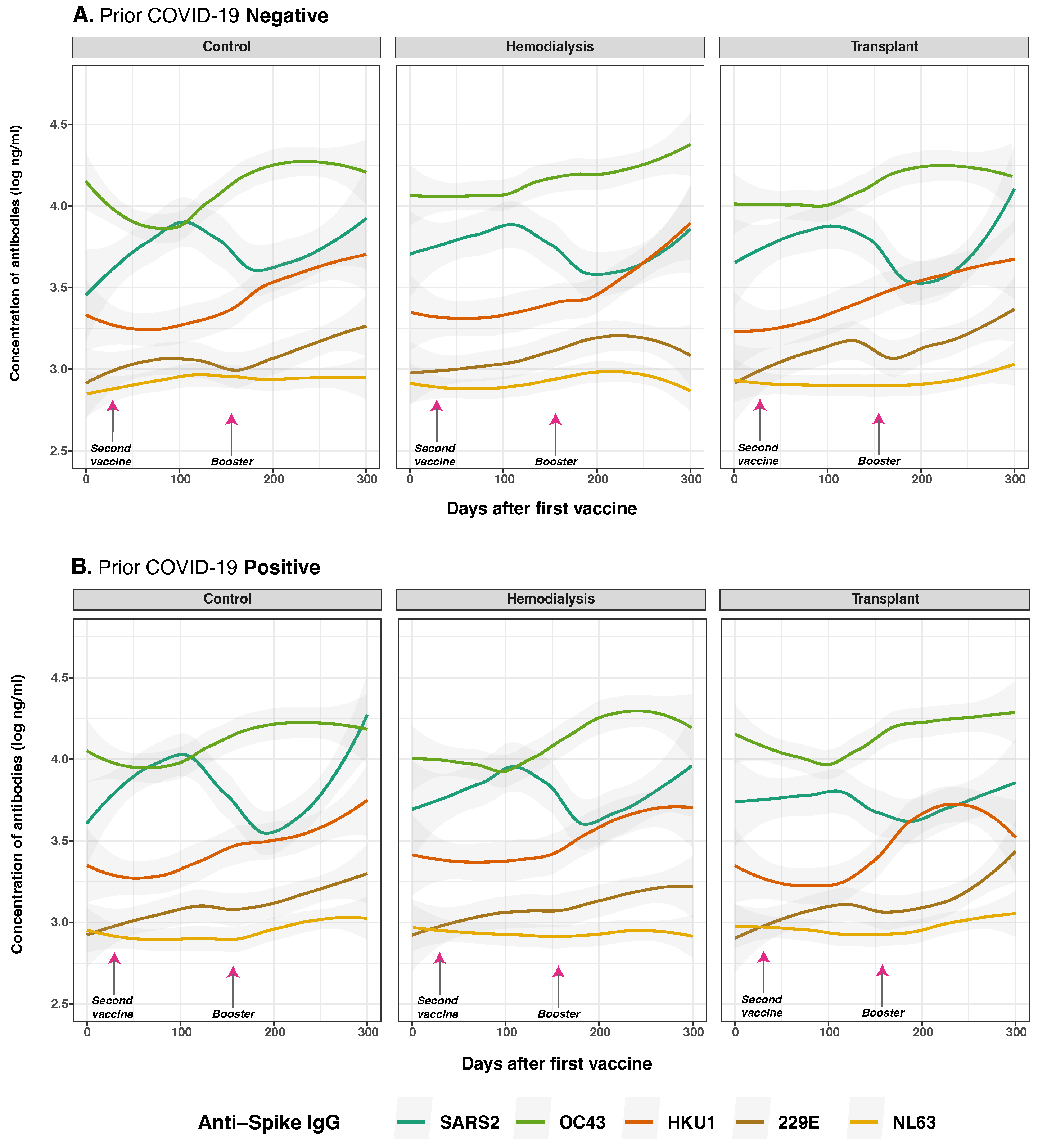
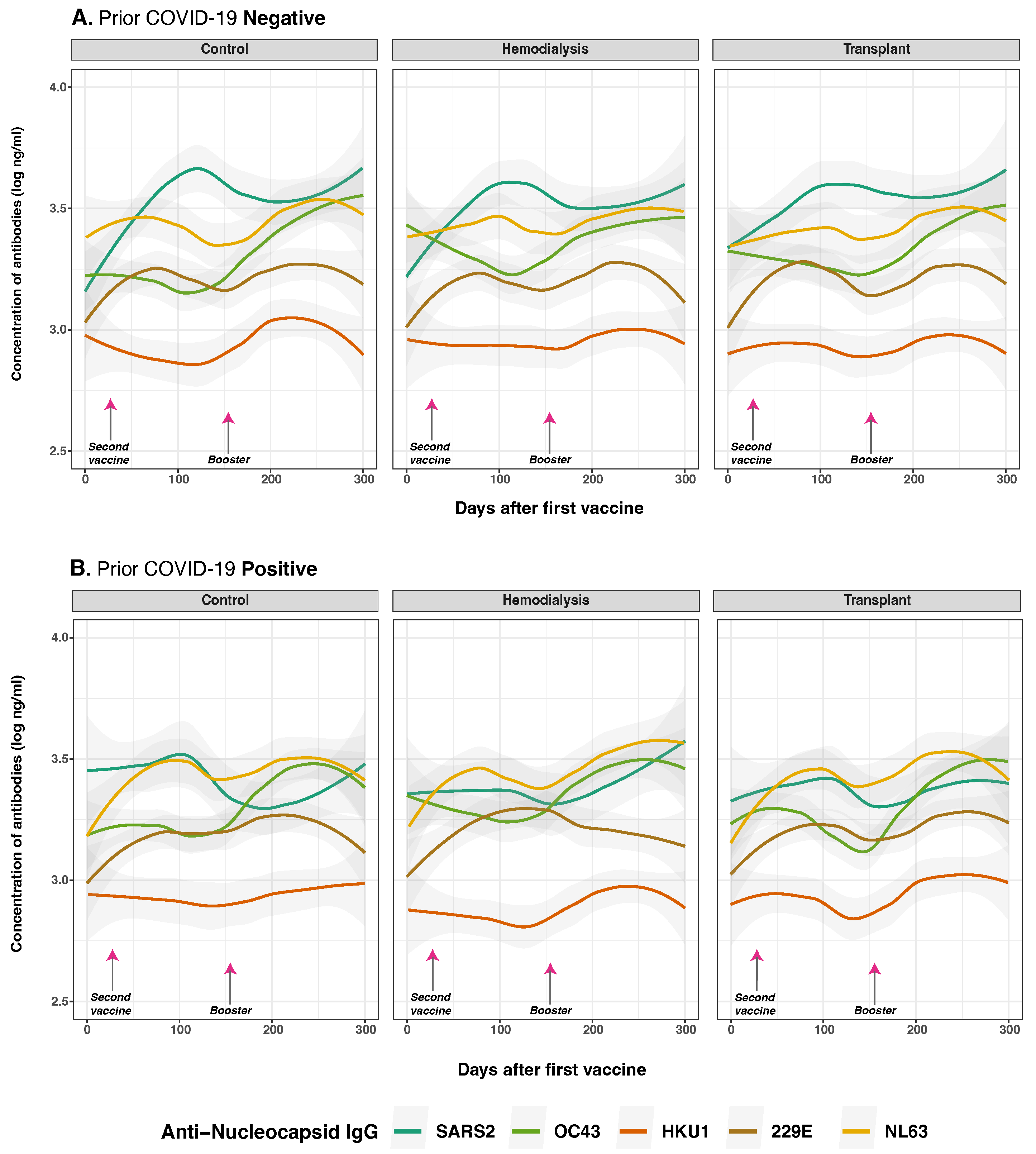
3.4. Anti-Spike and Anti-Nucleocapsid IgG Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common Human Coronaviruses in Previously Infected and Non-Infected Subjects
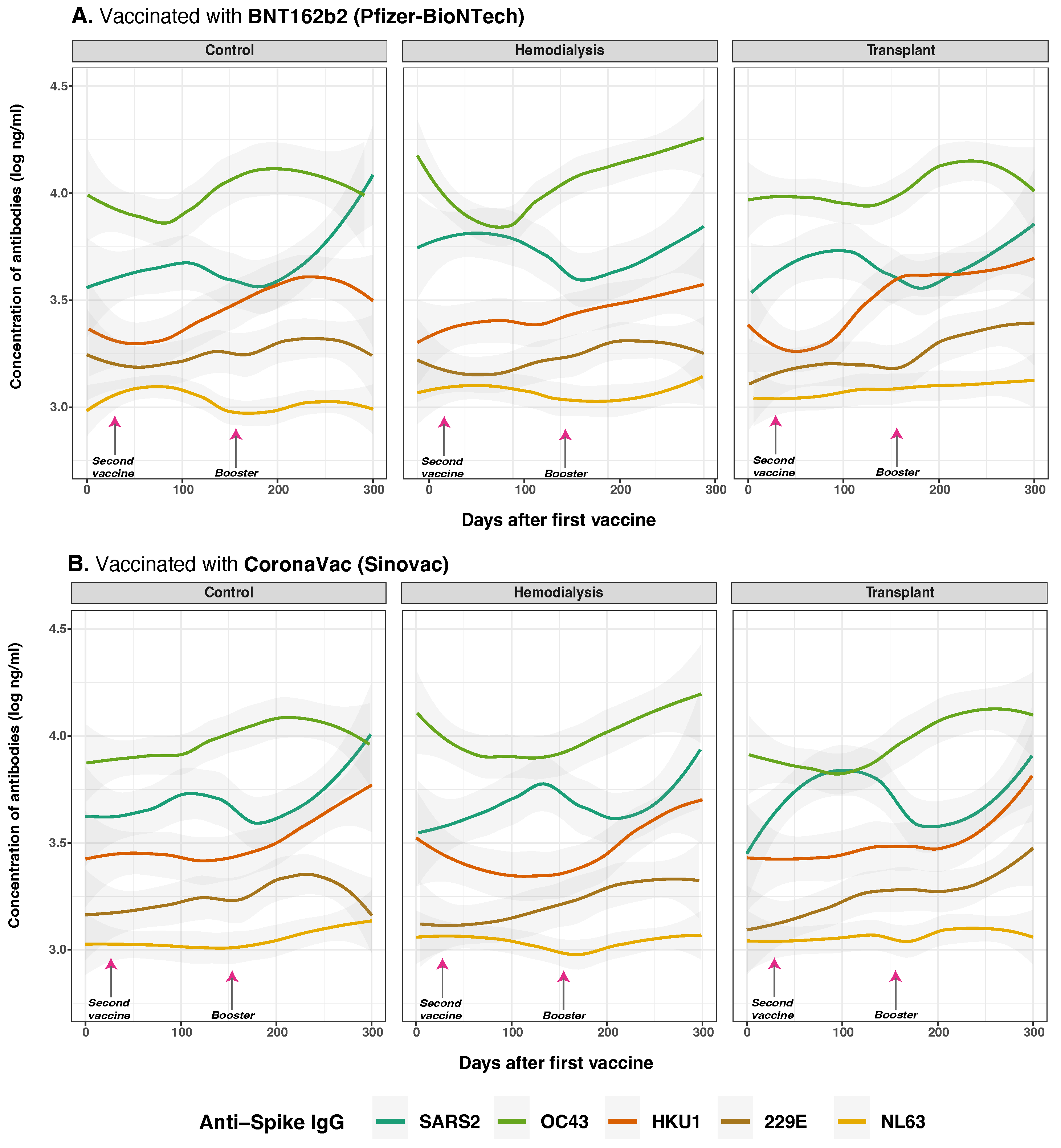
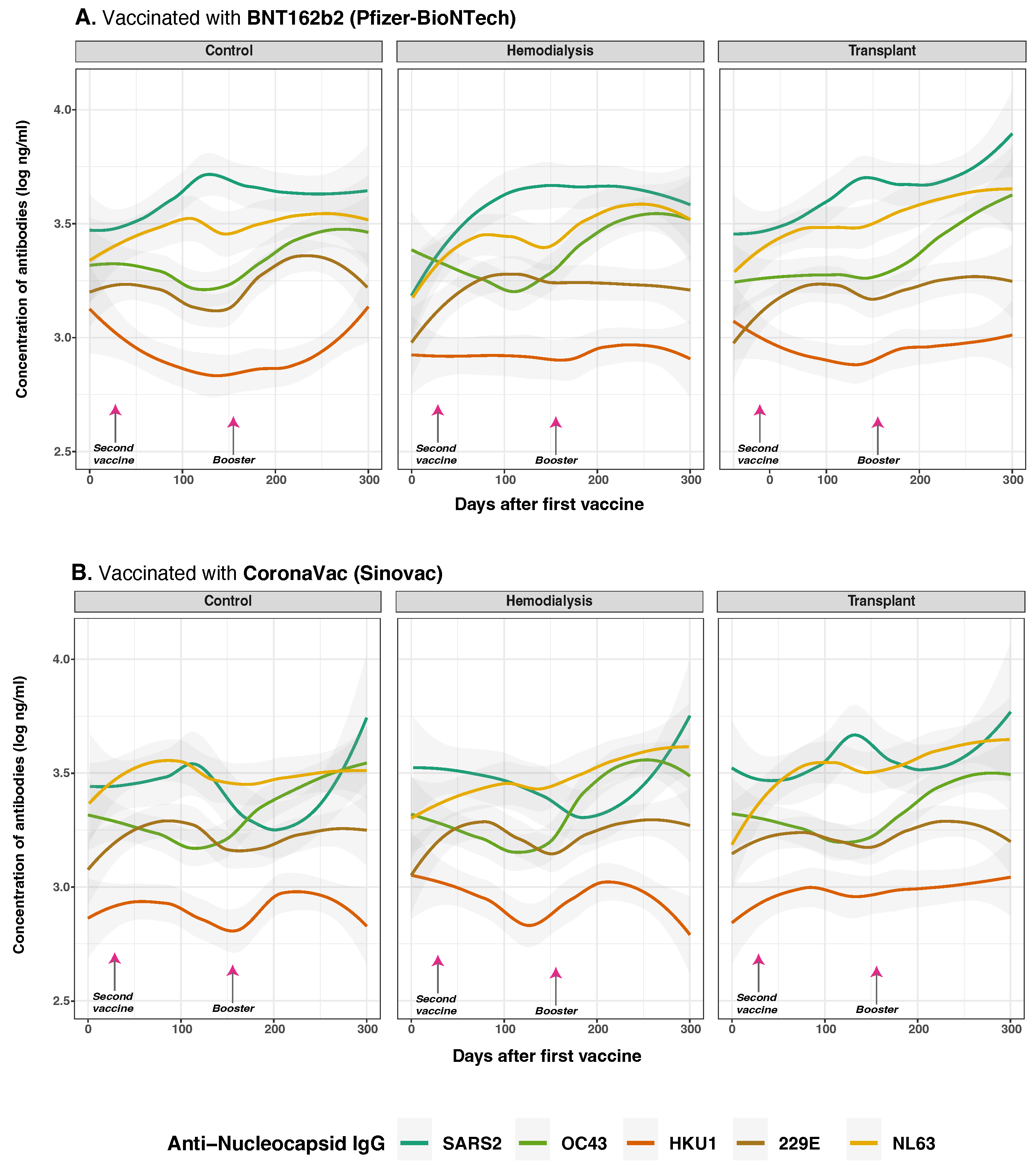
3.5. Anti-Spike and Anti-Nucleocapsid IgG Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common Human Coronaviruses and Vaccine Type
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 |
| ADE | Antibody-dependent enhancement |
| CO | Control group |
| CONABIOS | National Health Bioethics Committee of the Dominican Republic (the Spanish acronym) |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| DOAJ | Directory of Open Access Journals |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| HCoVs | Common Human Coronaviruses |
| HD | Hemodialysis Patients |
| Hgb | Hemoglobin |
| IgG | Immunoglobin G |
| INCORT | Instituto Nacional de Coordinación de Trasplante |
| IRB | Institutional Review Boards |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| MDS | Multidimensional Scaling |
| MLMM | Multivariate Linear Mixed Models |
| mPlex-CoV | Fluorescent Multiplex Assay |
| N | Nucleocapsid |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| S | Spike |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| TR | Transplant Recipients |
| VAMS | Volumetric Micro Sampling |
References
- Carr, E.J.; Kronbichler, A.; Graham-Brown, M.; Abra, G.; Argyropoulos, C.; Harper, L.; Lerma, E.V.; Suri, R.S.; Topf, J.; Willicombe, M.; et al. Systematic Review of Early Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2292–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobben, M.; van der Straten, K.; Brouwer, P.J.M.; Brinkkemper, M.; Maisonnasse, P.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; Appelman, B.; Lavell, A.H.A.; van Vught, L.A.; Burger, J.A.; et al. Cross-reactive antibodies after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. eLife 2021, 10, e70330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, A.Y.; Lee, P.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, D.J. Pre-existing Immunity to Endemic Human Coronaviruses Does Not Affect the Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Spike in a Murine Vaccination Model. Immune Netw. 2023, 23, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, T.D.; Moffitt, R.A.; Hajagos, J.G.; Amor, B.; Anand, A.; Bissell, M.M.; Bradwell, K.R.; Bremer, C.; Byrd, J.B.; Denham, A.; et al. Clinical Characterization and Prediction of Clinical Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among US Adults Using Data From the US National COVID Cohort Collaborative. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2116901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecora, N.D.; Zand, M.S. Measuring the Serologic Response to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2: Methods and Meaning. Clin. Lab. Med. 2020, 40, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Wiltse, A.; Emo, J.; Hilchey, S.P.; Zand, M.S. Application of volumetric absorptive microsampling (VAMS) to measure multidimensional anti-influenza IgG antibodies by the mPlex-Flu assay. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2019, 3, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, A.; Cranage, M.; Zipeto, D. Is Cross-Reactive Immunity Triggering COVID-19 Immunopathogenesis? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 567710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Zhou, Q.; Wiltse, A.; Zand, M.S. Antibody Mediated Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and Human Coronaviruses: Multiplex Beads Assay and Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling to Generate Immune Repertoire Cartography. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Dai, L.; Gao, G.F. Humoral and cellular immunity and the safety of COVID-19 vaccines: A summary of data published by 21 May 2021. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, T.A.; Weinstein, J.B.; Farley, S.; Leier, H.C.; Messer, W.B.; Tafesse, F.G. Cross-reactivity of SARS-CoV structural protein antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, J.; Svensson, M.K.; Albinsson, B.; Winqvist, O.; Pauksens, K. Humoral and cellular response to SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in hemodialysis patients. BMC Immunol. 2021, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asamoah-Boaheng, M.; Grunau, B.; Karim, M.E.; Jassem, A.N.; Bolster, J.; Marquez, A.C.; Scheuermeyer, F.X.; Goldfarb, D.M. Are higher antibody levels against seasonal human coronaviruses associated with a more robust humoral immune response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 954093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinotti, F.; Wikramaratna, P.S.; Obolski, U.; Paton, R.S.; Damineli, D.S.C.; Alcantara, L.C.J.; Giovanetti, M.; Gupta, S.; Lourenço, J. Potential impact of individual exposure histories to endemic human coronaviruses on age-dependent severity of COVID-19. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windpessl, M.; Bruchfeld, A.; Anders, H.J.; Kramer, H.; Waldman, M.; Renia, L.; Ng, L.F.P.; Xing, Z.; Kronbichler, A. COVID-19 vaccines and kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaan, E.; Elmaria, M.O.; Khedr, D.; Gaber, T.; Elsayed, A.G.; Shenouda, R.N.; Gamal, H.; Shahin, D.; Abousamra, N.K.; Shemies, R. Characterization of regulatory T cells in SARS-CoV-2 infected hemodialysis patients: Relation to clinical and radiological severity. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.W.; Faulkner, N.; Cornish, G.H.; Rosa, A.; Harvey, R.; Hussain, S.; Ulferts, R.; Earl, C.; Wrobel, A.G.; Benton, D.J.; et al. Preexisting and de novo humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in humans. Science 2020, 370, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, C. En República Dominicana, 5275 Pacientes Reciben Hemodiálisis y 500 Esperan un Riñón. Diario Libre, 10 March 2023. Available online: https://www.diariolibre.com/actualidad/salud/2023/03/10/en-rd-5275-reciben-hemodialisis-y-500-esperan-un-rinon/2250175 (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Instituto Nacional de Coordinación de Trasplante (INCORT). Trasplantes de Órganos y Tejidos de la República Dominicana 2008–2023 Report; INCORT: Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Salud Pública de La República Dominicana. Gobierno Presenta Plan Nacional de Vacunación Contra COVID-19; Ministerio de Salud Pública de La República Dominicana: Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dominican Today. Vaccines that the Dominican Republic Will Use Are Very Effective, 13 February 2021. Available online: https://dominicantoday.com/dr/health/2021/02/13/vaccines-that-the-country-will-use-are-very-effective/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- World Health Organization. WHO Caronavirus Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Cameron, A.; Porterfield, C.A.; Byron, L.; Wang, C.; Pearson, Z.; Bohrhunter, J.L.; Cardillo, A.B.; Ryan-Muntz, L.; Sorensen, R.A.; Caserta, M.; et al. A Multiplex Microsphere IgG Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Using ACE2-Mediated Inhibition as a Surrogate for Neutralization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara Sanchez, L.; Alvarez Guerra, E.; Li, D.; King, S.M.; Hilchey, S.P.; Zhou, Q.; Dewhurst, S.; Fiscella, K.; Zand, M.S. Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Transplant Recipients and Hemodialysis Patients: Data from the Dominican Republic. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompaniyets, L.; Pennington, A.F.; Goodman, A.B.; Rosenblum, H.G.; Belay, B.; Ko, J.Y.; Chevinsky, J.R.; Schieber, L.Z.; Summers, A.D.; Lavery, A.M.; et al. Underlying Medical Conditions and Severe Illness Among 540,667 Adults Hospitalized with COVID-19, March 2020–March 2021. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2021, 18, E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Analysis of classical multidimensional scaling: Clustering, dimension reduction, and visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2211300120. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA). Encuesta Nacional de Autopercepción Racial y Étnica en República Dominicana; UNFPA: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Montinaro, F.; Busby, G.B.; Pascali, V.L.; Myers, S.; Hellenthal, G.; Capelli, C. Unravelling the hidden ancestry of American admixed populations. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banham, G.D.; Godlee, A.; Faustini, S.E.; Cunningham, A.F.; Richter, A.; Harper, L.; on behalf of the COVID-HD Birmingham Study Group. Hemodialysis Patients Make Long-Lived Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 that May Be Associated with Reduced Reinfection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2140–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Gouma, S.; Hicks, P.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; et al. mRNA vaccines induce durable immune memory to SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern. Science 2021, 374, abm0829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.J.; Gibbons, J.M.; Pade, C.; Lin, K.M.; Sandoval, D.M.; Pieper, F.; Butler, D.K.; Liu, S.; Otter, A.D.; Boyton, R.J.; et al. Heterologous infection and vaccination shapes immunity against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science 2022, 375, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirthalingam, G.; Bernal, J.L.; Andrews, N.J.; Whitaker, H.; Gower, C.; Stowe, J.; Tessier, E.; Subbarao, S.; Ireland, G.; Ramsay, M.E.; et al. Serological responses and vaccine effectiveness for extended COVID-19 vaccine schedules in England. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemba, R.; Campbell, K.N.; Yang, T.H.; Schaeffer, S.E.; Mayo, K.M.; McGann, P.; Quinn, S.; Roach, J.; Huff, E.D. Excess Death Estimates in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease—United States, February–August 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benotmane, I.; Gautier, G.; Perrin, P.; Olagne, J.; Cognard, N.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Caillard, S. Antibody Response After a Third Dose of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Minimal Serologic Response to 2 Doses. JAMA 2021, 326, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Cell 2021, 184, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.M.; Goodwin, E.C.; Verma, A.; Arevalo, C.P.; Bolton, M.J.; Weirick, M.E.; Gouma, S.; McAllister, C.M.; Christensen, S.R.; Eller, M.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines induce broad antibody responses including cross-reactivity to seasonal coronaviruses. Cell 2021, 184, 1234–1242.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G. Immune Dysfunction in Uremia 2020. Toxins 2020, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydillo, T.; Rombauts, A.; Stadlbauer, D.; Aslam, S.; Abelenda-Alonso, G.; Escalera, A.; Amanat, F.; Jiang, K.; Krammer, F.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; et al. Immunological imprinting of the antibody response in COVID-19 patients. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garziano, M.; Cano Fiestas, M.; Vanetti, C.; Strizzi, S.; Murno, M.L.; Clerici, M.; Biasin, M. SARS-CoV-2 natural infection, but not vaccine-induced immunity, elicits cross-reactive immunity to OC43. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyarsky, B.J.; Werbel, W.A.; Avery, R.K.; Tobian, A.A.R.; Massie, A.B.; Segev, D.L.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M. Immunogenicity of a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA Vaccine in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. JAMA 2021, 325, 1784–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Marion, O.; Couat, C.; Izopet, J.; Del Bello, A. Three Doses of an mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrock, E.; Fujimura, E.; Kula, T.; Timms, R.T.; Lee, I.H.; Leng, Y.; Robinson, M.L.; Sie, B.M.; Li, M.Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity. Science 2020, 370, eabd4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarsky, B.J.; Werbel, W.A.; Avery, R.K.; Tobian, A.A.R.; Massie, A.B.; Segev, D.L.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M. Antibody Response to 2-Dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine Series in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. JAMA 2021, 325, 2204–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Borges, B.; Escobedo, M.; Egri, N.; Herrera, S.; Crespo, M.; Mirabet, S.; Arias-Cabrales, C.; Vilella, A.; Palou, E.; Mosquera, M.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Humoral and Cellular Immunity in a Cohort of Vaccinated Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekström, N.; Leino, T.; Juutinen, A.; Lehtonen, T.; Haveri, A.; Liedes, O.; Vara, S.; Salo, H.; Palmu, A.; Nohynek, H.; et al. Hybrid Immunity Improves the Immune Response after the Fourth COVID-19 Vaccine Dose in Individuals with Medical Conditions Predisposing to Severe COVID-19. Vaccines 2024, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, D.M.; Boyton, R.J. Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Science 2021, 371, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.A.; Clark, L.E.; Pan, J.; Coscia, A.; McKay, L.G.A.; Shankar, S.; Johnson, R.I.; Brusic, V.; Balazs, A.B.; Johnson, R.A. SARS-CoV-2 evolution in an immunocompromised host reveals shared neutralization escape mechanisms. Cell 2021, 184, 2605–2617.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Montez-Rath, M.E.; Han, J.; Garcia, P.; Cadden, L.; Hunsader, P.; Kerschmann, R.; Beyer, P.; Dittrich, M.; Block, G.A.; et al. Antibody Response to COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients Receiving Dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2435–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Muik, A.; Derhovanessian, E.; Vogler, I.; Kranz, L.M.; Vormehr, M.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K.; Quandt, J.; Maurus, D.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and TH1 T cell responses. Nature 2020, 586, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, V.J.; Foulkes, S.; Saei, A.; Andrews, N.; Oguti, B.; Charlett, A.; Wellington, E.; Stowe, J.; Gillson, N.; Atti, A.; et al. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against infection and COVID-19 vaccine coverage in healthcare workers in England: A test-negative case-control study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf, J.; Siepmann, T.; Lindner, T.; Karger, C.; Schwöbel, J.; Anders, L.; Faulhaber-Walter, R.; Schewe, J.; Martin, H.; Schirutschke, H.; et al. Humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in renal transplant versus dialysis patients: A prospective, multicenter observational study using mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Lancet Reg. Health—Europe 2021, 9, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narongkiatikhun, P.; Noppakun, K.; Chaiwarith, R.; Winichakoon, P.; Vongsanim, S.; Suteeka, Y.; Pongsuwan, K.; Kusirisin, P.; Wongsarikan, N.; Fanhchaksai, K.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Homologous and Heterologous Prime-Boost of CoronaVac(®) and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 among Hemodialysis Patients: An Observational Prospective Cohort Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, R.; McReynolds, C.; Yang, J.; Hammock, B.D.; Ikram, A.; Ali, A.; Bashir, A.; Zohra, T.; Chang, W.L.W.; Hartigan-O’Connor, D.J.; et al. Immune response dynamics in COVID-19 patients to SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, F. A correlate of protection for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines is urgently needed. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriover, M.D.; Doğanay, H.L.; Akova, M.; Güner, H.R.; Azap, A.; Akhan, S.; Köse, S.; Erdinç, F.S.; Akalın, E.H.; Aksu, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of an inactivated whole-virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac). Lancet 2021, 398, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, A.; Undurraga, E.A.; González, C.; Paredes, F.; Fontecilla, T.; Jara, G.; Pizarro, A.; Acevedo, J.; Leo, K.; Araos, R.; et al. Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Chile. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.Y.; Moreira, R.M.; Santos, C.F.D.; Strabelli, T.M.V.; Belizário, J.C.; Pinto, M.I.M.; Marinho, A.; Pereira, J.M.; Mello, L.S.; Ando, M.C.; et al. Immunogenicity of COVID-19 adsorbed inactivated vaccine (CoronaVac) and additional doses of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine in immunocompromised adults compared with immunocompetent persons. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2024, 66, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tu, P.; Beitsch, L.M. Confidence and Receptivity for COVID-19 Vaccines: A Rapid Systematic Review. Vaccines 2021, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.; Mount, P.F. COVID-19 beliefs and vaccination uptake in dialysis patients: Lessons from an anonymous patient survey. Intern. Med. J. 2022, 52, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.A.; Bloomstone, S.J.; Walder, J.; Crawford, S.; Fouayzi, H.; Mazor, K.M. Attitudes Toward a Potential SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine: A Survey of U.S. Adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Control, n = 33 1 | Hemodialysis, n = 13 1 | Transplant, n = 24 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.150 | |||
| 18–24 | 6 (18%) | 1 (7.7%) | 3 (13%) | |
| 25–44 | 21 (64%) | 5 (38%) | 11 (46%) | |
| 45–65 | 6 (18%) | 7 (54%) | 10 (42%) | |
| Sex | 0.200 | |||
| Female | 19 (58%) | 4 (31%) | 10 (42%) | |
| Male | 14 (42%) | 9 (69%) | 14 (58%) | |
| Race | <0.001 | |||
| Asian | 1 (3.0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Black | 15 (45%) | 10 (77%) | 24 (100%) | |
| White | 7 (21%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Not reported | 10 (30%) | 3 (23%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Ethnicity | 0.009 | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 19 (58%) | 10 (77%) | 19 (79%) | |
| Non-Hispanic or Non-Latino | 4 (12%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (21%) | |
| Not reported | 10 (30%) | 3 (23%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Education level | <0.001 | |||
| Less than high school | 1 (3.0%) | 5 (38%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| High school graduate | 4 (12%) | 3 (23%) | 7 (29%) | |
| Higher education | 9 (27%) | 0 (0%) | 15 (63%) | |
| Graduate education | 3 (9.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Not reported | 16 (48%) | 5 (38%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| Underlying conditions | <0.001 | |||
| None | 27 (82%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| At least one | 6 (18%) | 2 (15%) | 6 (25%) | |
| Two or more | 0 (0%) | 11 (85%) | 17 (71%) | |
| COVID-19 positive before first fingerstick | 0.053 | |||
| Yes | 10 (30%) | 6 (46%) | 15 (63%) | |
| No | 23 (70%) | 7 (54%) | 9 (38%) | |
| COVID-19 positive during the study | >0.900 | |||
| Yes | 8 (24%) | 2 (15%) | 5 (21%) | |
| Not reported | 25 (76%) | 11 (85%) | 19 (79%) | |
| Vaccine doses | <0.001 | |||
| One dose | 11 (33%) | 5 (38%) | 2 (8.3%) | |
| Two doses | 20 (61%) | 4 (31%) | 11 (46%) | |
| Fully vaccinated and one booster | 2 (6.1%) | 2 (15%) | 10 (42%) | |
| Two or more boosters | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.2%) | |
| Not reported | 0 (0%) | 2 (15%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Vaccine type (prime schedule) | 0.066 | |||
| BNT162b2 | 25 (76%) | 7 (64%) | 11 (46%) | |
| CoronaVac | 8 (24%) | 4 (36%) | 13 (54%) | |
| Booster schedule | 0.700 | |||
| Heterologous | 0 (0%) | 1 (50%) | 6 (55%) | |
| Homologous | 2 (100%) | 1 (50%) | 5 (45%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcantara Sanchez, L.; Alvarez Guerra, E.; Li, D.; King, S.M.; Hilchey, S.P.; Zhou, Q.; Dewhurst, S.; Fiscella, K.; Zand, M.S. Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common HCoVs in Hemodialysis Patients and Transplant Recipients: Data from the Dominican Republic. Vaccines 2025, 13, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090965
Alcantara Sanchez L, Alvarez Guerra E, Li D, King SM, Hilchey SP, Zhou Q, Dewhurst S, Fiscella K, Zand MS. Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common HCoVs in Hemodialysis Patients and Transplant Recipients: Data from the Dominican Republic. Vaccines. 2025; 13(9):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090965
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcantara Sanchez, Lisette, Eloy Alvarez Guerra, Dongmei Li, Samantha M. King, Shannon P. Hilchey, Qian Zhou, Stephen Dewhurst, Kevin Fiscella, and Martin S. Zand. 2025. "Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common HCoVs in Hemodialysis Patients and Transplant Recipients: Data from the Dominican Republic" Vaccines 13, no. 9: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090965
APA StyleAlcantara Sanchez, L., Alvarez Guerra, E., Li, D., King, S. M., Hilchey, S. P., Zhou, Q., Dewhurst, S., Fiscella, K., & Zand, M. S. (2025). Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Common HCoVs in Hemodialysis Patients and Transplant Recipients: Data from the Dominican Republic. Vaccines, 13(9), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090965







