Virus-like Particles Produced in the Baculovirus System Protect Hares from European Brown Hare Syndrome Virus (EBHSV) Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Cloning and Generation of Recombinant Baculovirus
2.2. Production and Purification of rEVP60-His6 Protein
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
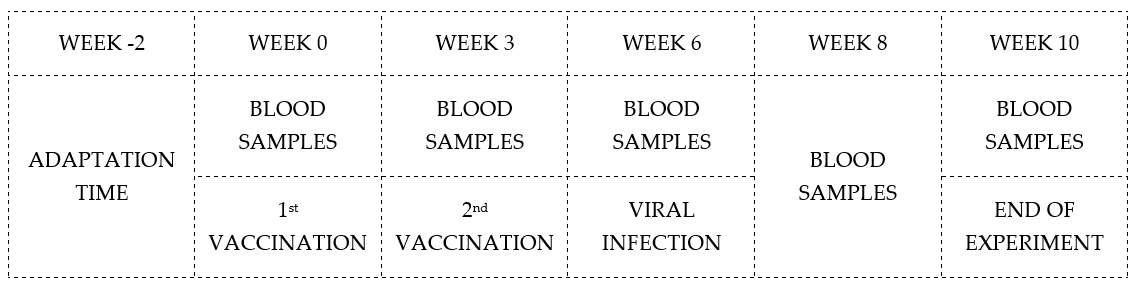
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.4.1. Virus Preparation
2.4.2. Immunisation Protocol and Challenge
2.5. Laboratory Analysis
2.5.1. Blood Sampling, Serological and Virological Assay
2.5.2. Histological Examination
2.5.3. Molecular Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Production of VLPs
3.2. Experimental Infection of Hares
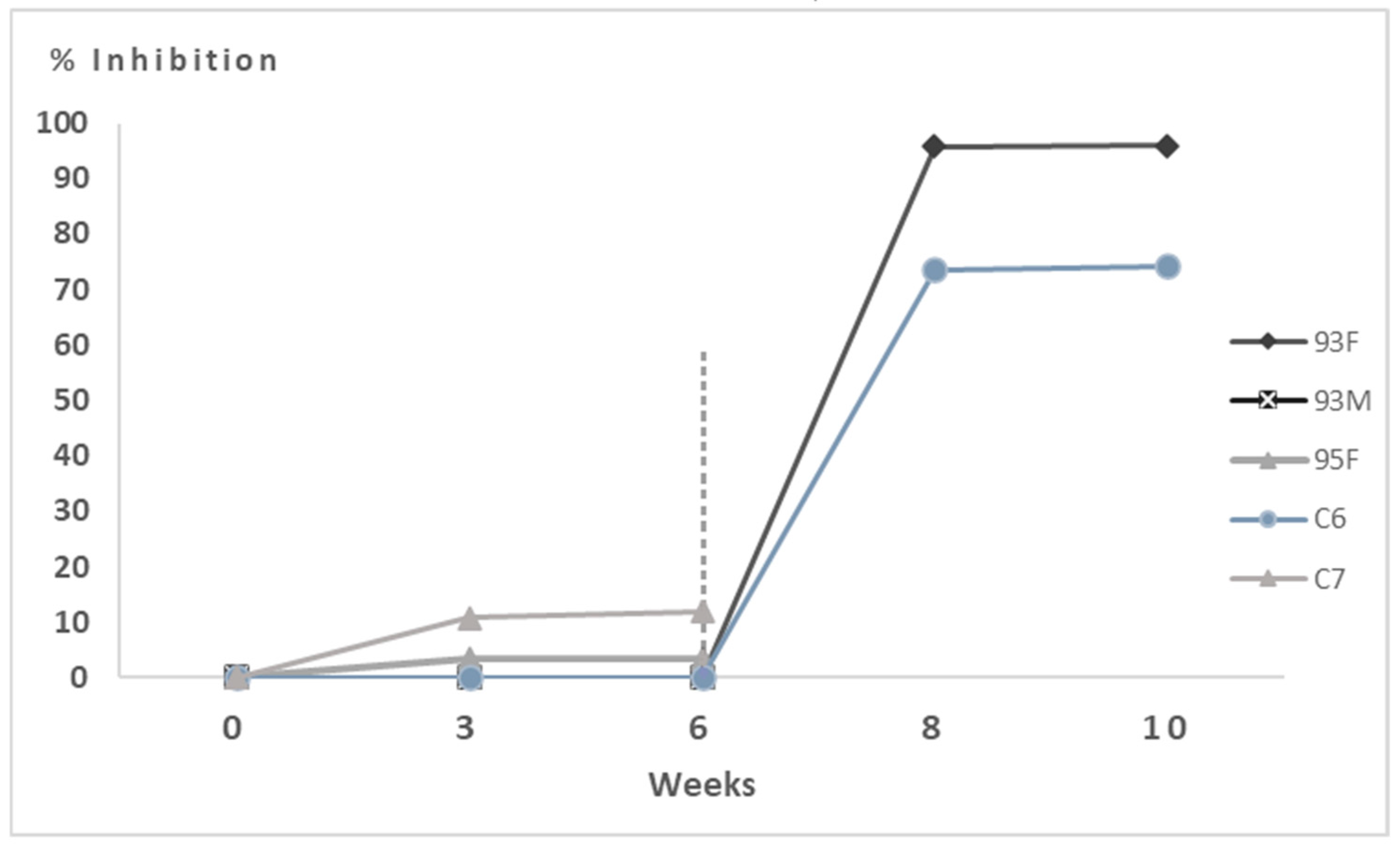
3.2.1. Control Group
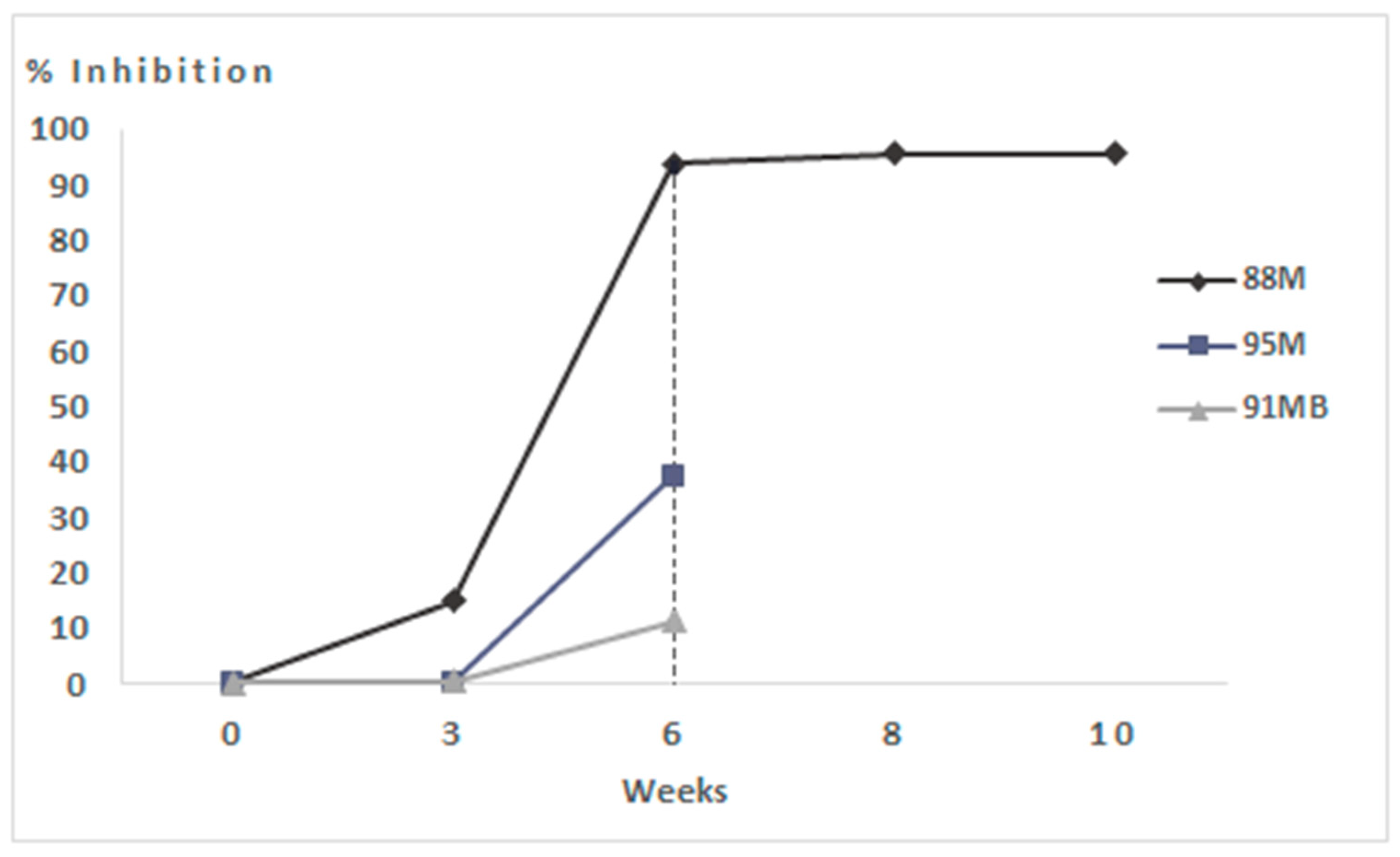
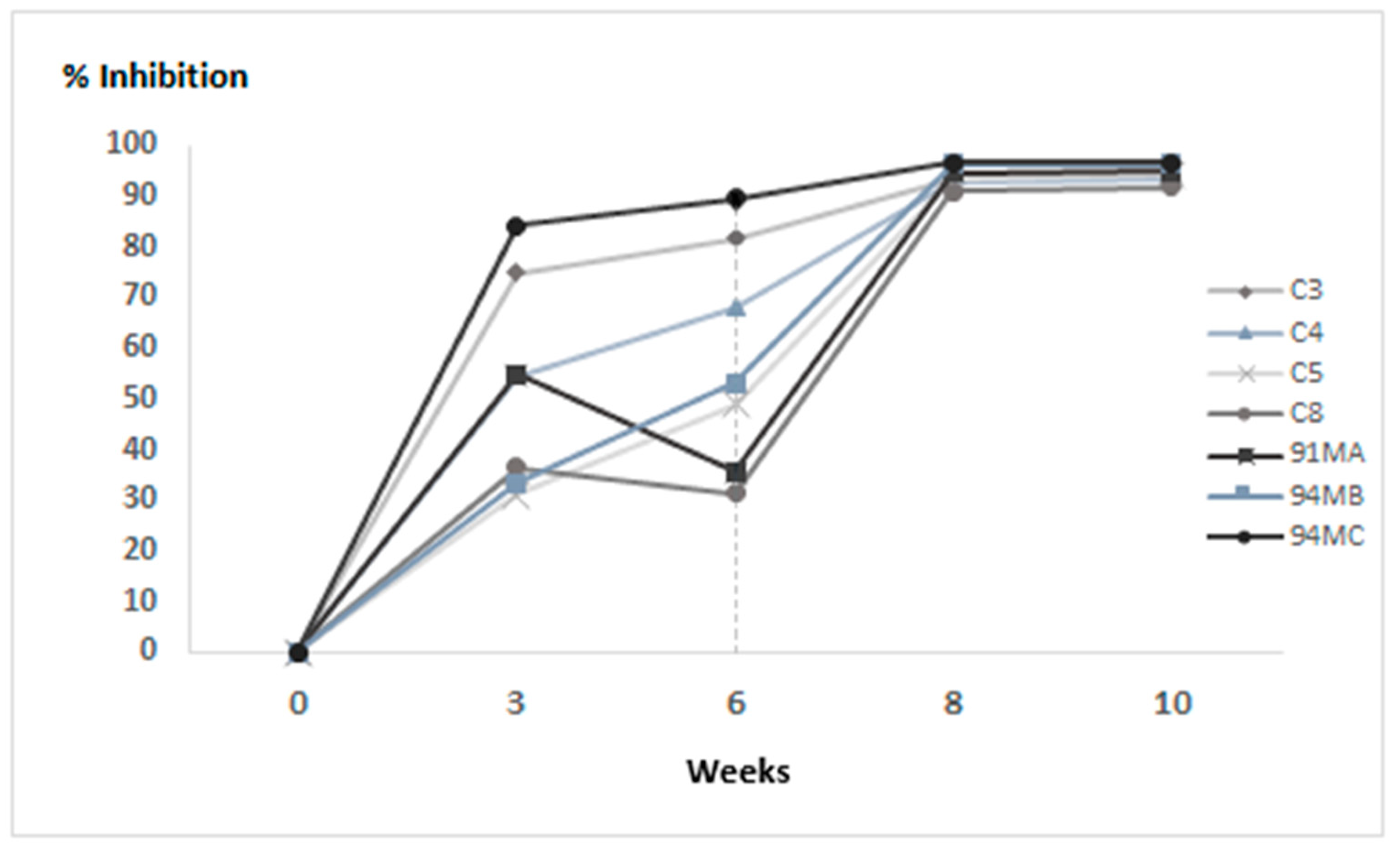
3.2.2. Hares Immunised with 50 μg of VLPs
3.2.3. Hares Immunised with 100 μg of VLPs
3.2.4. Histopathology
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frölich, K.; Lavazza, A. European Brown Hare Syndrome in Lagomorph Biology; Alves, P.C., Ferrand, N., Hacklaender, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzner, A.; Niedbalski, W.; Kęsy, A.; Rataj, B.; Flis, M. European brown hare syndrome in Poland: Current epidemiological situation. Viruses 2022, 14, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavier-Widén, D.; Mörner, T. Epidemiology and diagnosis of the European brown hare syndrome in Scandinavian countries: A review. Rev. Sci. Tech. Int. Off. Epizoot. 1991, 10, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, A.; Nigro, M.; Gallazzi, D.; Sironi, G.; Lavazza, A.; Gelmetti, D. Acute hepatosis in the European Brown Hare (Lepus europaeus) in Italy. J. Wild Dis. 1991, 27, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancellotti, F.M.; Renzi, M. Epidemiology and current situation of viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits and the European brown hare syndrome in Italy. Rev. Sci. Tech. Int. Off. Epizoot. 1991, 10, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frölich, K.; Meyer, H.H.; Pielowski, Z.; Ronsholt, L.; Seck-Lanzendorf, S.V.; Stolte, M. European brown hare syndrome in free-ranging hares in Poland. J. Wildl. Dis. 1996, 32, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, J.P.; Chasey, D.; Munro, R.; Wooldridge, M. European brown hare syndrome in England. Vet. Rec. 1994, 134, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frölich, K.; Haerer, G.; Bacciarini, L.; Janovsky, M.; Rudolph, M.; Giacometti, M. European brown hare syndrome in free-ranging European brown and mountain hares from Switzerland. J. Wildl. Dis. 2001, 37, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billinis, C.; Psychas, V.; Tontis, D.K.; Spyrou, V.; Birtsas, P.K.; Sofia, M.; Likotrafitis, F.; Maslarinou, O.M.; Kanteres, D. European brown hare syndrome in wild European brown hares from Greece. J. Wildl. Dis. 2005, 41, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frölich, K.; Fickel, J.; Ludwig, A.; Lieckfeldt, D.; Streich, W.J.; Jurčík, R.; Slamečka, J.; Wibbelt, G. New variants of European brown hare syndrome virus strains in free-ranging European brown hares (Lepus europaeus) from Slovakia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2007, 43, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savioli, M.; Pasquali, S.; Lavazza, A.; Zanoni, M.; Guberti, V.; Chiari, M.; Gilioli, G. EBHS in european brown hares (Lepus europaeus): Disease dynamics and control. Hystrix 2017, 28, 202–207. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Chiari, M.; Ferrari, N.; Giardiello, D.; Avisani, D.; Zanoni, M.; Alborali, G.L.; Lanfranchi, P.; Guberti, V.; Capucci, L.; Lavazza, A. Temporal dynamics of European brown hare syndrome infection in Northern Italian brown hares (Lepus europaeus). Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014, 60, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirblich, C.; Meyers, G.; Ohlinger, V.F.; Capucci, L.; Eskens, U.; Haas, B.; Thiel, H.J. European brown hare syndrome virus: Relationship to rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus and other caliciviruses. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5164–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanni, M.L.; Benassi, M.C.; Scicluna, M.T.; Lavazza, A.; Capucci, L. Clinical evolution and diagnosis of an outbreak of European brown hare syndrome in hares reared in captivity. Rev. Sci. Tech. Int. Off. Epizoot. 1993, 12, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, P.J.; Fletcher, M.R.; Berny, P. Review of the factors affecting the decline of the European brown hare, Lepus europaeus (Pallas, 1778) and the use of wildlife incident data to evaluate the significance of paraquat. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 79, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavazza, A.; Scicluna, M.T.; Corradini, L.; Poli, A.; Barigazzi, G.; Cammi, G.; Capucci, L. Diagnostic procedures for european brown hare syndrome; application in epidemiological surveys in two Italian regions. In Résumé de la 14° Conference de la Commisionrégionale de l’OIE Pour l’Europe; OIE: Paris, France, 1990; pp. 152–169. [Google Scholar]
- Chiari, M.; Molinari, S.; Cavadini, P.; Bertasi, B.; Zanoni, M.; Capucci, L.; Lavazza, A. Red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) feeding brown hares (Lepus europaeus) infected by European brown hare syndrome virus (EBHSv) might be involved in the spread of the virus. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2016, 62, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH). European-Brown-Hare-Syndrome-Virus; World Organisation Animal Health: Paris, France, 2021; Available online: https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2021/05/european-brown-hare-syndrome-virus-infection-with.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Desselberger, U. Caliciviridae other than noroviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, G.; Huguet, S.; Vende, P.; Vautherot, J.F.; Rasschaert, D. European brown hare syndrome virus: Molecular cloning and sequencing of the genome. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, G.; Wirblich, C.; Thiel, H.J. Genomic and subgenomic RNAs of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus are both protein-linked and packaged into particles. Virology 1991, 184, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, I.N.; Lambden, P.R. The molecular biology of caliciviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesha, H.S.; Wang, L.F.; Hyatt, A.D.; Morrissy, C.J.; Lenghaus, C.; Westbury, H.A. Self-assembly, antigenicity, and immunogenicity of the rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (Czechoslovakian strain V-351) capsid protein expressed in baculovirus. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, M.S.; Alonso, J.M.; Garcia, L.I.P.O.; Boga, J.A.; Argüello-Villares, J.; Casais, R.; Venugopal, K.; Jiang, W.; Gould, E.A.; Parra, F. Immunogenic properties of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus structural protein VP60 expressed by a recombinant baculovirus: An efficient vaccine. Virus Res. 1995, 39, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Vautherot, J.F.; Le Gall, G.; Madelaine, M.F.; Rasschaert, D. Structural, antigenic and immunogenic relationships between European brown hare syndrome virus and rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 2803–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z. Use of baculovirus expression system for generation of virus-like particles: Successes and challenges. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 90, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, K.P.; Podadera, A.; Alonso, J.M.M.; Sanz, I.C.; Rodríguez, Á.L.Á.; Casais, R.; Parra, F. Viral Disease in Lagomorphs: A Molecular Perspective. Lagomorpha Characteristics; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejmer-Rąbalska, M.; Peplińska, M.; Szewczyk, B.; Fitzner, A. Serological characterisation of Lagovirus virus-like particles originating from native and mutated VP60 of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus 2 and European brown hare syndrome virus. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 68, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Song, Y.; Fan, Z.; Jiang, P.; Hu, B.; Xue, J.; Wei, H.; Wang, F. Immunogenicity of different recombinant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus-like particles carrying CD8+ T cell epitope from chicken ovalbumin (OVA). Virus Res. 2014, 183, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Fernández, M.R.; Mourino, M.; Rivera, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Plana-Durán, J.; García, J.A. Protection of rabbits against rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus by immunization with the VP60 protein expressed in plants with a potyvirus-based vector. Virology 2001, 280, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vidal, J.; Gómez-Sebastián, S.; Bárcena, J.; Nuñez, M.D.C.; Martínez-Alonso, D.; Dudognon, B.; Guijarro, E.; Escribano, J.M. Improved production efficiency of virus-like particles by the baculovirus expression vector system. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnós, O.; Boué, O.; Parra, F.; Martín-Alonso, J.M.; Valdés, O.; Joglar, M.; Navea, L.; Naranjo, P.; Lleonart, R. High-level expression and immunogenic properties of the recombinant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus VP60 capsid protein obtained in Pichia pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 117, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boga, J.A.; Martín Alonso, J.M.; Casais, R.; Parra, F. A single dose immunization with rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus major capsid protein produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae induces protection. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 2315–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, J.; Tan, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Sun, S.; Liu, G. Self-assembly of virus-like particles of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus capsid protein expressed in Escherichia coli and their immunogenicity in rabbits. Antivir. Res. 2016, 131, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bárcena, J.L.; Guerra, B.; Angulo, I.; González, J.; Valcárcel, F.; Mata, C.P.; Caston, J.R.; Blanco, E.; Alejo, A. Comparative analysis of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) and new RHDV2 virus antigenicity, using specific virus-like particles. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Meng, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, G. Codon optimization of the rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) capsid gene leads to increased gene expression in Spodoptera frugiperda 9 (Sf9) cells. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 14, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plana-Duran, J.; Bastons, M.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Climent, I.; Cortés, E.; Vela, C.; Casal, I. Oral Immunization of Rabbits with VP60 Particles Confers Protection against Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldão, A.; Mellado, M.C.; Castilho, L.R.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Alves, P.M. Virus-like particles in vaccine development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 1149–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chackerian, B. Virus-like particles: Flexible platforms for vaccine development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2007, 6, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgacic, E.V.; Anderson, D.A. Virus-like particles: Passport to immune recognition. Methods 2006, 40, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, N.; Streatfield, S.J.; Yusibov, V. Virus-like particles as a highly efficient vaccine platform: Diversity of targets and production systems and advances in clinical development. Vaccine 2012, 31, 58–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooraei, S.; Bahrulolum, H.; Hoseini, Z.S.; Katalani, C.; Hajizade, A.; Easton, A.J.; Ahmadian, G. Virus-like particles: Preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH). Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. Section 3.7. Lagomorpha Chapter 3.7.2. Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Version adopted in May 2023. World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/fr/Health_standards/tahm/3.07.02_RHD.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Capucci, L.; Scicluna, M.T.; Lavazza, A. Diagnosis of viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits and the European brown hare syndrome. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 1991, 10, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sequence 5′-3′ | Primer |
|---|---|
| GATAGTCTCGAGGCCACCATGGAGGGTAAGCCTCGGGCTG | EBHS-VP60-F |
| GAGCCCGACAATTGGTGCACC | EBHS-VP60/ApaLI-R |
| CAGACAACAGGTGGGGTGCAC | EBHS-VP60/ApaLI-F |
| CCTAGGCCGGCGACATAGGAATATCCAGTGGT | EBHS-VP60/NgoMIV-R |
| Cellular Lysate | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dilution | Positive IgG | Negative IgG |
| 1:5 | 2.9 | 0.25 |
| 1:50 | 2.57 | 0.16 |
| 1:500 | 1.48 | 0.157 |
| 1:5000 | 0.361 | 0.182 |
| Group | Life Outcome | Animal | Virological Assay (L) | PCR | Real-Time PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Dead | 93M | (+) | (+) L, S, K, T | (+) L (Ct 20), S (Ct 15), K (Ct 23), T (Ct 22) |
| Dead | 95F | (+) | (+) L, S, Lu, K, T | (+) L (Ct 25), S (Ct 21), Lu (Ct 32), K (Ct 31), T (Ct 31) | |
| Dead | C7 | (+) | (+) L, S, Lu, K, T | (+) L (Ct 23), S (Ct 22), Lu (Ct 29), K (Ct 26), T (Ct 33) | |
| Survivor | 93F | (-) | (-) | (±) L (Ct 37) | |
| Survivor | C6 | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| Vaccinated (50 µg VLPs) | Dead | 95M | (-) | (+) S | (+) S (Ct 32); (±) K (Ct 38) |
| Dead | 91MB | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| Survivor | 88M | (-) | (-) | (±) L (Ct 39), T (Ct 38); | |
| Vaccinated (100 µg VLPs) | Survivor | 91MA | (-) | (-) | (-) |
| Survivor | 94MB | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| Survivor | 94MC | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| Survivor | C3 | (+) | (-) | (-) | |
| Survivor | C4 | (-) | (-) | (±) S (Ct 38) | |
| Survivor | C5 | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| Survivor | C8 | (-) | (-) | (-) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Severi, G.; Anzalone, L.; Madeo, L.; Serroni, A.; Colabella, C.; Di Paolo, A.; Mangili, P.M.; Manuali, E.; Felici, A.; Cagiola, M.; et al. Virus-like Particles Produced in the Baculovirus System Protect Hares from European Brown Hare Syndrome Virus (EBHSV) Infection. Vaccines 2025, 13, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13070731
Severi G, Anzalone L, Madeo L, Serroni A, Colabella C, Di Paolo A, Mangili PM, Manuali E, Felici A, Cagiola M, et al. Virus-like Particles Produced in the Baculovirus System Protect Hares from European Brown Hare Syndrome Virus (EBHSV) Infection. Vaccines. 2025; 13(7):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13070731
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeveri, Giulio, Lucia Anzalone, Laura Madeo, Anna Serroni, Claudia Colabella, Antonella Di Paolo, Pier Mario Mangili, Elisabetta Manuali, Andrea Felici, Monica Cagiola, and et al. 2025. "Virus-like Particles Produced in the Baculovirus System Protect Hares from European Brown Hare Syndrome Virus (EBHSV) Infection" Vaccines 13, no. 7: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13070731
APA StyleSeveri, G., Anzalone, L., Madeo, L., Serroni, A., Colabella, C., Di Paolo, A., Mangili, P. M., Manuali, E., Felici, A., Cagiola, M., Lavazza, A., Capucci, L., Pezzotti, G., & De Giuseppe, A. (2025). Virus-like Particles Produced in the Baculovirus System Protect Hares from European Brown Hare Syndrome Virus (EBHSV) Infection. Vaccines, 13(7), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13070731










