Humanized Major Histocompatibility Complex Transgenic Mouse Model Can Play a Potent Role in SARS-CoV-2 Human Leukocyte Antigen-Restricted T Cell Epitope Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Viruses and Animals
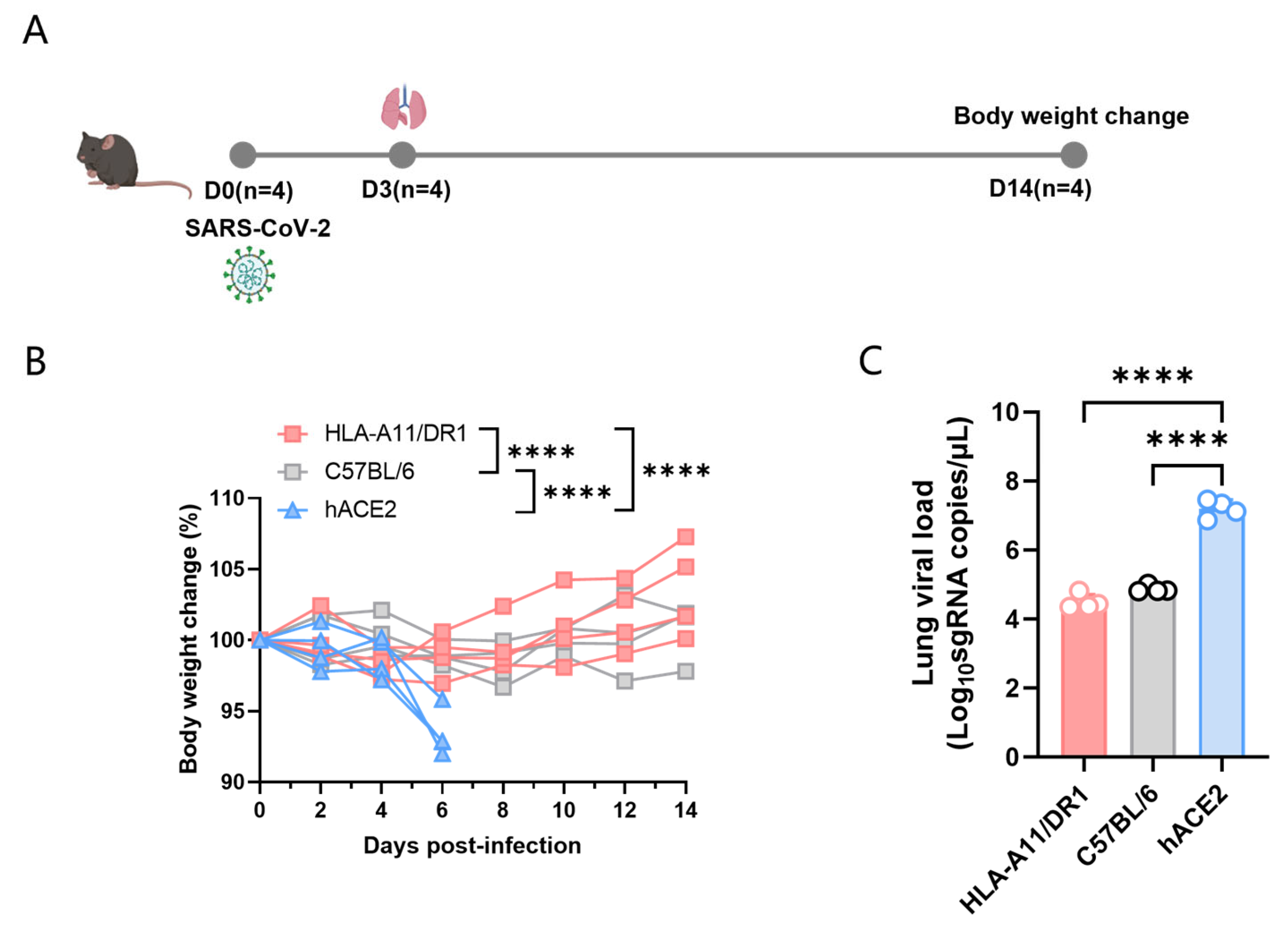
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Mice Experiment
2.4. Extraction of Viral RNA and qRT-PCR
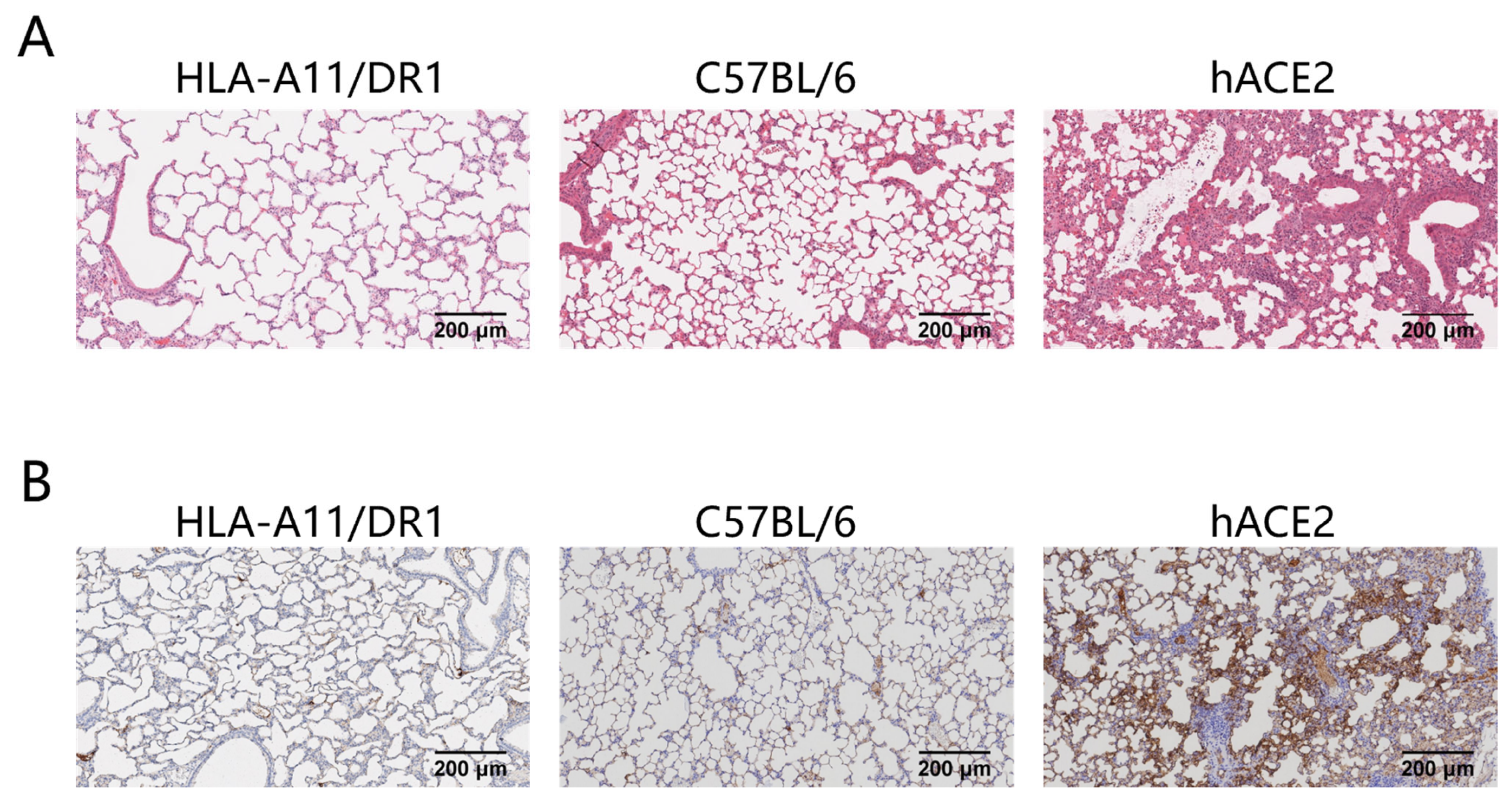
2.5. Histopathological Analysis
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
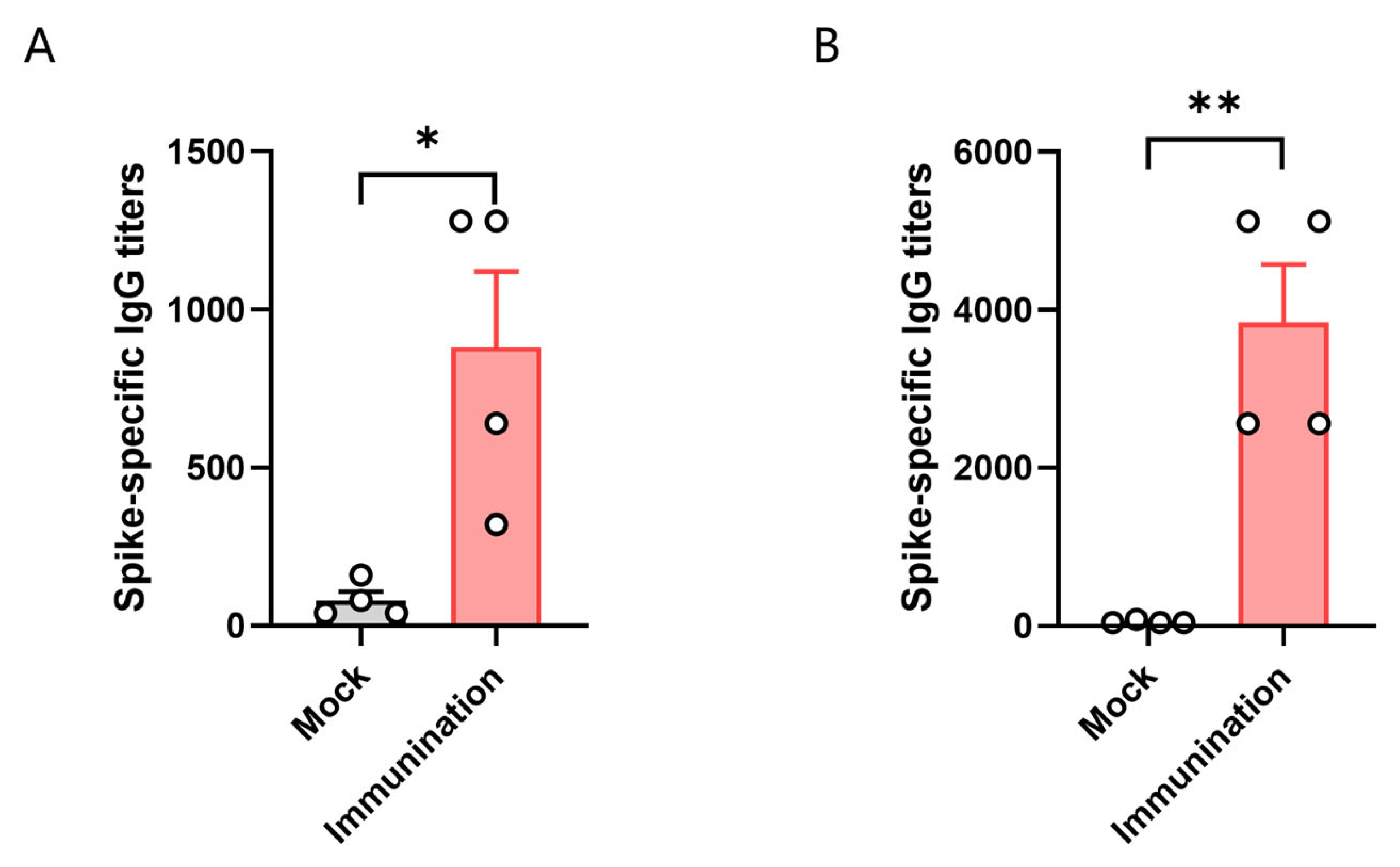
2.7. Immunization of Mice with SARS-CoV-2 Inactivated Virus
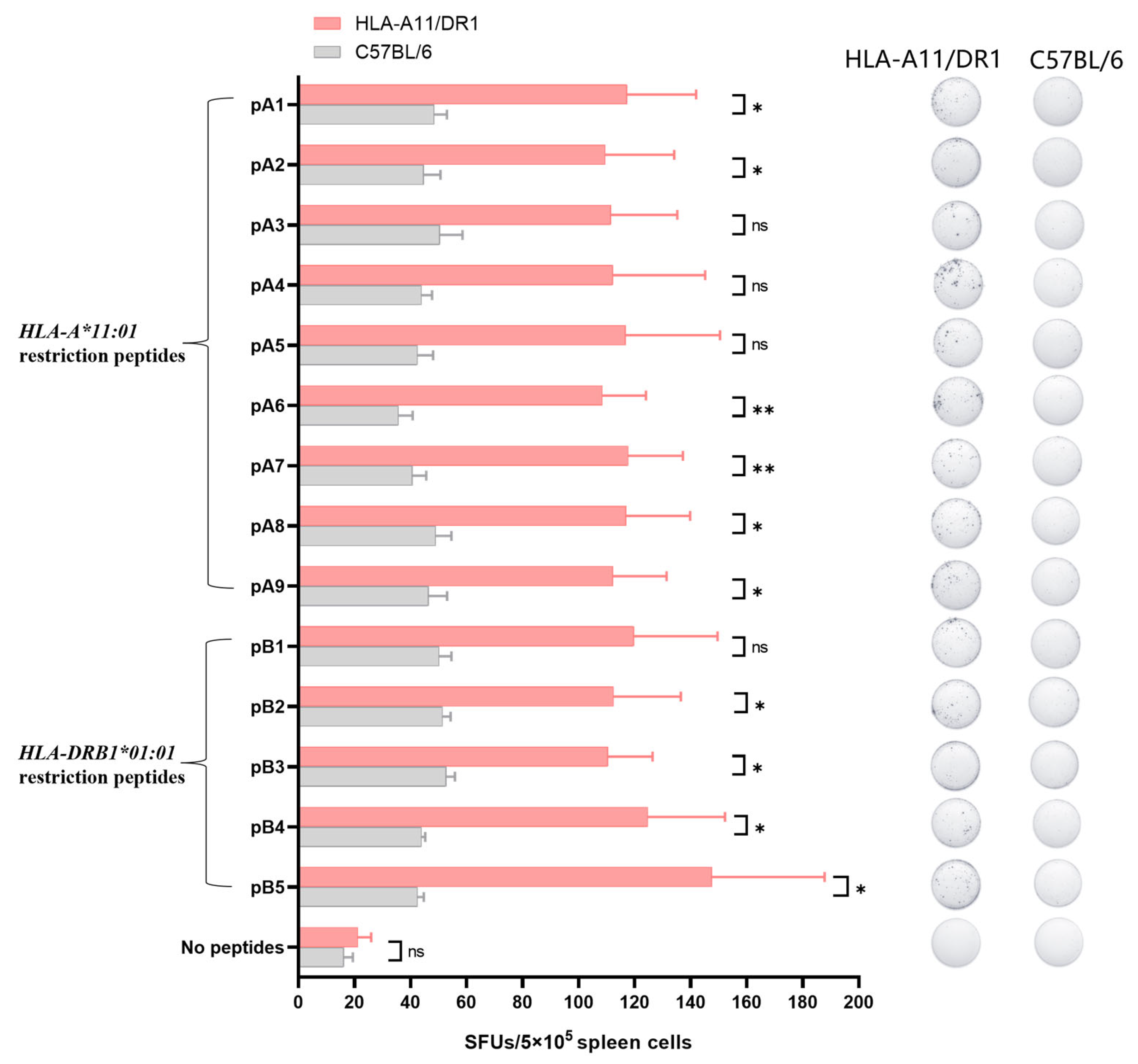
2.8. Screen HLA-Restricted Positive Epitope Peptides
2.9. ELISA
2.10. ELISpot
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Weight Changes and Viral Replication in HLA-A11/DR1 Mice After SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.2. Lung Tissue Pathological Changes and Nucleocapsid Protein Distribution in HLA-A11/DR1 Mice After SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.3. HLA-A11/DR1 Mice Can Generate Humoral Immune Responses
3.4. Screening for HLA-Restricted Positive Epitope Peptides
3.5. HLA-A11/DR1 Mice Are Capable of Producing a Normal Cellular Immune Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos-López, G.; Cortés-Hernández, P.; Vallejo-Ruiz, V.; Reyes-Leyva, J. SARS-CoV-2: Basic concepts, origin and treatment advances. Gac. Medica Mex. 2021, 157, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Rao, Z. Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidar, S.; Ambi, S.V.; Sekaran, S.; Krishnan, U.M. The emergence of COVID-19 as a global pandemic: Understanding the epidemiology, immune response and potential therapeutic targets of SARS-CoV-2. Biochimie 2020, 179, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Cossmann, A.; Richter, A.; Bdeir, N.; Graichen, L.; Moldenhauer, A.S.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Stankov, M.V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 enters lung cells and evades neutralizing antibodies with high efficiency. Cell 2024, 187, 596–608.E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, N.B.; Krieger, K.; Khan, F.M.; Huffman, W.; Chang, M.; Naik, A.; Yongle, R.; Hameed, I.; Krieger, K.; Girardi, L.N.; et al. The current state of animal models in research: A review. Int. J. Surg. 2019, 72, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, A.; Chen, F.; Li, S.; Guan, X.; Lv, C.; Tang, T.; He, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 immunity in animal models. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Chen, D.; Zhu, A.; Li, F.; Zhuang, Z.; Mok, C.K.P.; Dai, J.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.; et al. Mouse models susceptible to HCoV-229E and HCoV-NL63 and cross protection from challenge with SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2202820120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.H.; Chen, Q.; Gu, H.J.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.X.; Huang, X.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Zhang, N.N.; Li, X.F.; Xiong, R.; et al. A Mouse Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Pathogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 124–133.e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renn, M.; Bartok, E.; Zillinger, T.; Hartmann, G.; Behrendt, R. Animal models of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 for the development of prophylactic and therapeutic interventions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 228, 107931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Zhang, X.; Ansari, A.; Jadhav, P.; Tan, H.; Li, K.; Chopra, A.; Ford, A.; Chi, X.; Ruiz, F.X.; et al. Design of a SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease inhibitor with antiviral efficacy in a mouse model. Science 2024, 383, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawalagatti, V.; Kirthika, P.; Hewawaduge, C.; Park, J.Y.; Yang, M.S.; Oh, B.; So, M.Y.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.H. A Simplified SARS-CoV-2 Mouse Model Demonstrates Protection by an Oral Replicon-Based mRNA Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 811802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumeanu, T.D.; Vir, P.; Karim, A.F.; Kar, S.; Benetiene, D.; Lok, M.; Greenhouse, J.; Putmon-Taylor, T.; Kitajewski, C.; Chung, K.K.; et al. Human-Immune-System (HIS) humanized mouse model (DRAGA: HLA-A2.HLA-DR4.Rag1KO.IL-2RγcKO.NOD) for COVID-19. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2048622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, M.; Suzuki, T.; Pasquier, L.D. On the origins of the adaptive immune system: Novel insights from invertebrates and cold-blooded vertebrates. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijmans, C.M.C.; de Groot, N.G.; Bontrop, R.E. Comparative genetics of the major histocompatibility complex in humans and nonhuman primates. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2020, 47, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, R.J.; Martin, A.M.; Price, P. The mouse as a model for the effects of MHC genes on human disease. Immunol. Today 2000, 21, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressley, K.R.; Schwegman, L.; Montes De Oca Arena, M.; Chase Huizar, C.; Zamvil, S.S.; Forsthuber, T.G. HLA-transgenic mouse models to study autoimmune central nervous system diseases. Autoimmunity 2024, 57, 2387414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotturi, M.F.; Assarsson, E.; Peters, B.; Grey, H.; Oseroff, C.; Pasquetto, V.; Sette, A. Of mice and humans: How good are HLA transgenic mice as a model of human immune responses? Immunome Res. 2009, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, M.J.; Dhillon, P. Using the mouse to model human disease: Increasing validity and reproducibility. Dis. Models Mech. 2016, 9, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydyznski Moderbacher, C.; Ramirez, S.I.; Dan, J.M.; Grifoni, A.; Hastie, K.M.; Weiskopf, D.; Belanger, S.; Abbott, R.K.; Kim, C.; Choi, J.; et al. Antigen-Specific Adaptive Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Acute COVID-19 and Associations with Age and Disease Severity. Cell 2020, 183, 996–1012.E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, J.S.; Bilich, T.; Tandler, C.; Nelde, A.; Maringer, Y.; Marconato, M.; Reusch, J.; Jäger, S.; Denk, M.; Richter, M.; et al. A COVID-19 peptide vaccine for the induction of SARS-CoV-2 T cell immunity. Nature 2022, 601, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajot, A.; Michel, M.L.; Fazilleau, N.; Pancré, V.; Auriault, C.; Ojcius, D.M.; Lemonnier, F.A.; Lone, Y.C. A mouse model of human adaptive immune functions: HLA-A2.1-/HLA-DR1-transgenic H-2 class I-/class II-knockout mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 3060–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Kou, Z.; Lone, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhou, Y. Generation of human MHC (HLA-A11/DR1) transgenic mice for vaccine evaluation. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascolo, S.; Bervas, N.; Ure, J.M.; Smith, A.G.; Lemonnier, F.A.; Pérarnau, B. HLA-A2.1-restricted education and cytolytic activity of CD8(+) T lymphocytes from β2 microglobulin (β2m) HLA-A2.1 monochain transgenic H-2Db β2m double knockout mice. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Deng, W.; Huang, B.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Wei, Q.; Yu, P.; Xu, Y.; Qi, F.; et al. The pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 transgenic mice. Nature 2020, 583, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Mead, H.; Tian, L.; Park, J.G.; Garcia, J.I.; Jaramillo, S.; Barr, T.; Kollath, D.S.; Coyne, V.K.; Stone, N.E.; et al. The K18-Human ACE2 Transgenic Mouse Model Recapitulates Non-severe and Severe COVID-19 in Response to an Infectious Dose of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0096421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kared, H.; Redd, A.D.; Bloch, E.M.; Bonny, T.S.; Sumatoh, H.; Kairi, F.; Carbajo, D.; Abel, B.; Newell, E.W.; Bettinotti, M.P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T cell responses in convalescent COVID-19 individuals. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e145476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Ding, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Shen, A.; Wu, Y.; et al. Screening HLA-A-restricted T cell epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 and the induction of CD8(+) T cell responses in HLA-A transgenic mice. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2588–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redd, A.D.; Nardin, A.; Kared, H.; Bloch, E.M.; Pekosz, A.; Laeyendecker, O.; Abel, B.; Fehlings, M.; Quinn, T.C.; Tobian, A.A.R. CD8+ T-Cell Responses in COVID-19 Convalescent Individuals Target Conserved Epitopes From Multiple Prominent SARS-CoV-2 Circulating Variants. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, S.; Ren, L.; Zheng, P.; Hu, X.; Jin, T.; Tan, X. Profiling CD8(+) T cell epitopes of COVID-19 convalescents reveals reduced cellular immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 variants. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titov, A.; Shaykhutdinova, R.; Shcherbakova, O.V.; Serdyuk, Y.V.; Sheetikov, S.A.; Zornikova, K.V.; Maleeva, A.V.; Khmelevskaya, A.; Dianov, D.V.; Shakirova, N.T.; et al. Immunogenic epitope panel for accurate detection of non-cross-reactive T cell response to SARS-CoV-2. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e157699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Dijssel, J.; Hagen, R.R.; de Jongh, R.; Steenhuis, M.; Rispens, T.; Geerdes, D.M.; Mok, J.Y.; Kragten, A.H.; Duurland, M.C.; Verstegen, N.J.; et al. Parallel detection of SARS-CoV-2 epitopes reveals dynamic immunodominance profiles of CD8(+) T memory cells in convalescent COVID-19 donors. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2022, 11, e1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsten, H.; Cords, L.; Westphal, T.; Knapp, M.; Brehm, T.T.; Hermanussen, L.; Omansen, T.F.; Schmiedel, S.; Woost, R.; Ditt, V.; et al. High-resolution analysis of individual spike peptide-specific CD4(+) T-cell responses in vaccine recipients and COVID-19 patients. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2022, 11, e1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poluektov, Y.; George, M.; Daftarian, P.; Delcommenne, M.C. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell responses using MHC class I and II tetramers. Vaccine 2021, 39, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Srivastava, R.; Coulon, P.G.; Dhanushkodi, N.R.; Chentoufi, A.A.; Tifrea, D.F.; Edwards, R.A.; Figueroa, C.J.; Schubl, S.D.; Hsieh, L.; et al. Genome-Wide B Cell, CD4(+), and CD8(+) T Cell Epitopes That Are Highly Conserved between Human and Animal Coronaviruses, Identified from SARS-CoV-2 as Targets for Preemptive Pan-Coronavirus Vaccines. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 2566–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.M.; Malhotra, U.; Kim, Y.G.; Gomez, R.; Krist, M.P.; Wald, A.; Koelle, D.M.; Kwok, W.W. Cross-reactive and mono-reactive SARS-CoV-2 CD4+ T cells in prepandemic and COVID-19 convalescent individuals. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letko, M.; Marzi, A.; Munster, V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, M.; Wu, B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, R.; Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. A highly susceptible hACE2-transgenic mouse model for SARS-CoV-2 research. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1348405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tang, M.; Xu, W.; Meng, X.; Jin, H.; Han, M.; Pu, J.; Li, Y.; Jiao, F.; Sun, R.; et al. An inducible hACE2 transgenic mouse model recapitulates SARS-CoV-2 infection and pathogenesis in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2207210120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Chevalier, F.; Authié, P.; Chardenoux, S.; Bourgine, M.; Vesin, B.; Cussigh, D.; Sassier, Y.; Fert, I.; Noirat, A.; Nemirov, K.; et al. Mice humanized for MHC and hACE2 with high permissiveness to SARS-CoV-2 omicron replication. Microbes Infect. 2023, 25, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitag, T.L.; Fagerlund, R.; Karam, N.L.; Leppänen, V.M.; Ugurlu, H.; Kant, R.; Mäkinen, P.; Tawfek, A.; Jha, S.K.; Strandin, T.; et al. Intranasal administration of adenoviral vaccines expressing SARS-CoV-2 spike protein improves vaccine immunity in mouse models. Vaccine 2023, 41, 3233–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, E.J.; Wilsker, D.F.; Hayes, K.C.; Schoenfeld, D.; Simister, N.E. Increased clearance of IgG in mice that lack β2-microglobulin: Possible protective role of FcRn. Immunology 1996, 89, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, P. Broadly neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.O.; Jette, C.A.; Abernathy, M.E.; Dam, K.A.; Esswein, S.R.; Gristick, H.B.; Malyutin, A.G.; Sharaf, N.G.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Lee, Y.E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies. Nature 2020, 588, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Leng, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Li, C.; Ojcius, D.M.; Wang, P.; Jiang, S. Development of T cell antigen-based human coronavirus vaccines against nAb-escaping SARS-CoV-2 variants. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 2456–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Tang, L.L.; Yu, X.L.; Zhou, J.; Chang, Y.F.; Wu, X. Bioinformatics analysis of epitope-based vaccine design against the novel SARS-CoV-2. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Kang, N.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Zu, C.; Gao, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, N.; et al. Construction and efficacy testing of DNA vaccines containing HLA-A*02:01-restricted SARS-CoV-2 T-cell epitopes predicted by immunoinformatics. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2024, 56, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Rojas, L.J.; Ruíz-Manzano, R.A.; Velasco-Elizondo, M.A.; Carbajo-Mata, M.A.; Hernández-Silva, D.J.; Rocha-Solache, M.; Hernández, J.; Pérez-Serrano, R.M.; Zaldívar-Lelo de Larrea, G.; García-Gasca, T.; et al. An Evaluation of the Cellular and Humoral Response of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate Against COVID-19 with Different Alum Adjuvants. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Fang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Sun, K.; Zhou, H.; Qin, H.; Zhao, D.; et al. Humanized Major Histocompatibility Complex Transgenic Mouse Model Can Play a Potent Role in SARS-CoV-2 Human Leukocyte Antigen-Restricted T Cell Epitope Screening. Vaccines 2025, 13, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040416
Zhang J, Fang F, Zhang Y, Han X, Wang Y, Yin Q, Sun K, Zhou H, Qin H, Zhao D, et al. Humanized Major Histocompatibility Complex Transgenic Mouse Model Can Play a Potent Role in SARS-CoV-2 Human Leukocyte Antigen-Restricted T Cell Epitope Screening. Vaccines. 2025; 13(4):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040416
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiejie, Feimin Fang, Yue Zhang, Xuelian Han, Yuan Wang, Qi Yin, Keyu Sun, Haisheng Zhou, Hanxiong Qin, Dongmei Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Humanized Major Histocompatibility Complex Transgenic Mouse Model Can Play a Potent Role in SARS-CoV-2 Human Leukocyte Antigen-Restricted T Cell Epitope Screening" Vaccines 13, no. 4: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040416
APA StyleZhang, J., Fang, F., Zhang, Y., Han, X., Wang, Y., Yin, Q., Sun, K., Zhou, H., Qin, H., Zhao, D., Tai, W., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Yang, T., Wei, Y., Zhang, S., Li, S., Li, M., & Zhao, G. (2025). Humanized Major Histocompatibility Complex Transgenic Mouse Model Can Play a Potent Role in SARS-CoV-2 Human Leukocyte Antigen-Restricted T Cell Epitope Screening. Vaccines, 13(4), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040416





