Naive and Memory B Cell BCR Repertoires in Individuals Immunized with an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cohort of Individuals
2.2. B Cell Expansion and Isolation Protocol
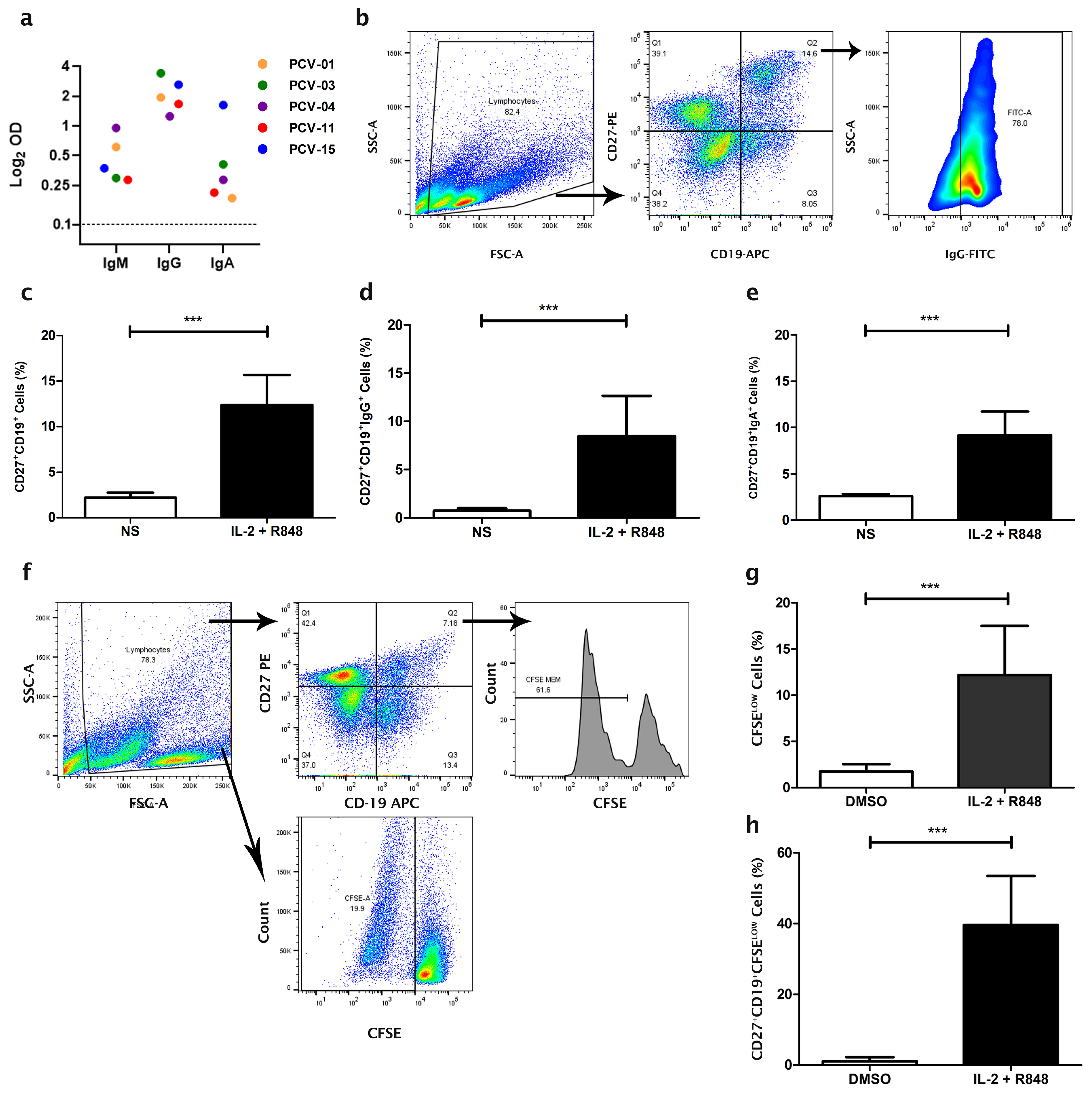
2.3. Analysis of Flow Cytometry
2.4. Cell Proliferation Analysis
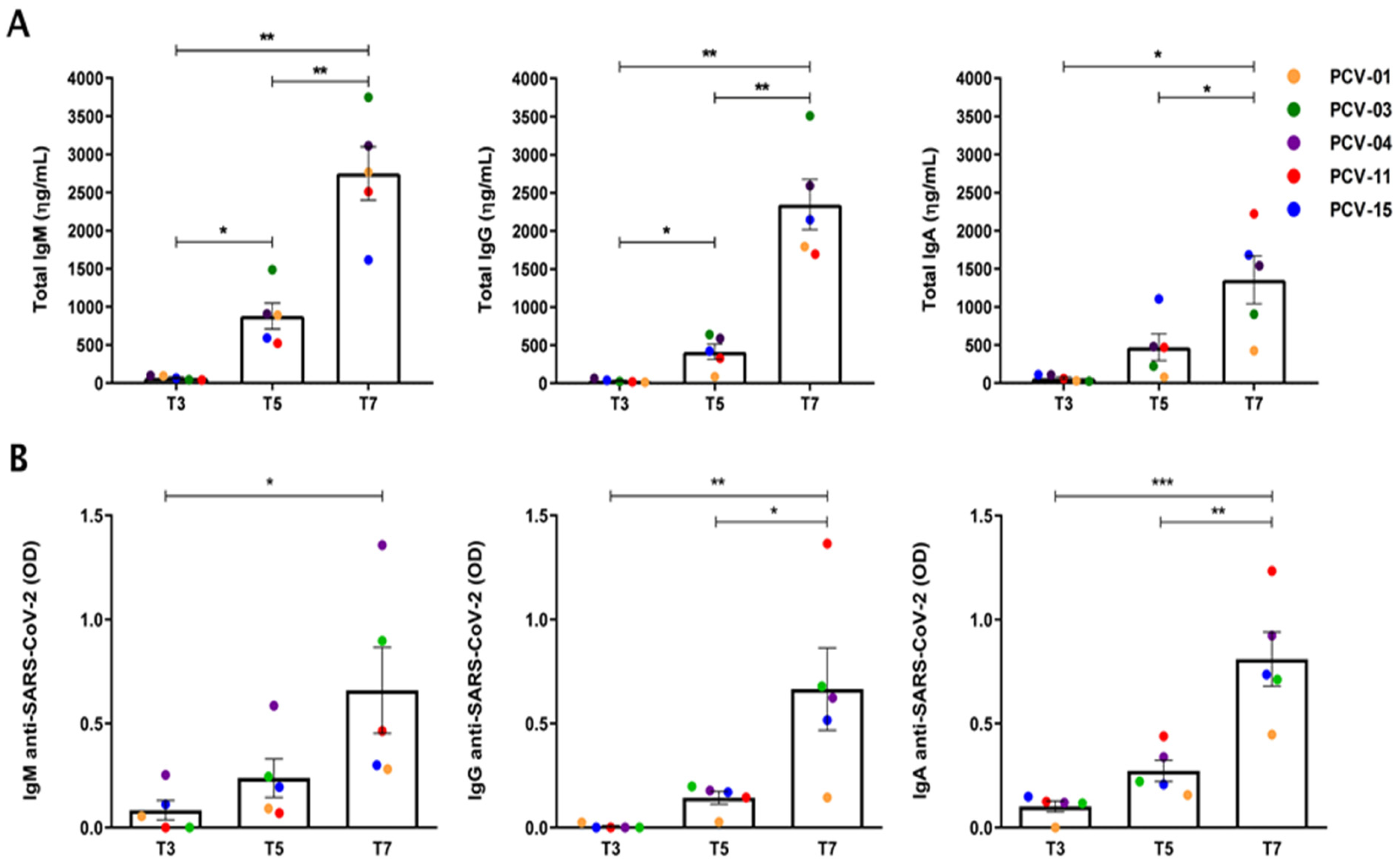
2.5. ELISA for Quantification of Total Immunoglobulins
2.6. Binding of Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2
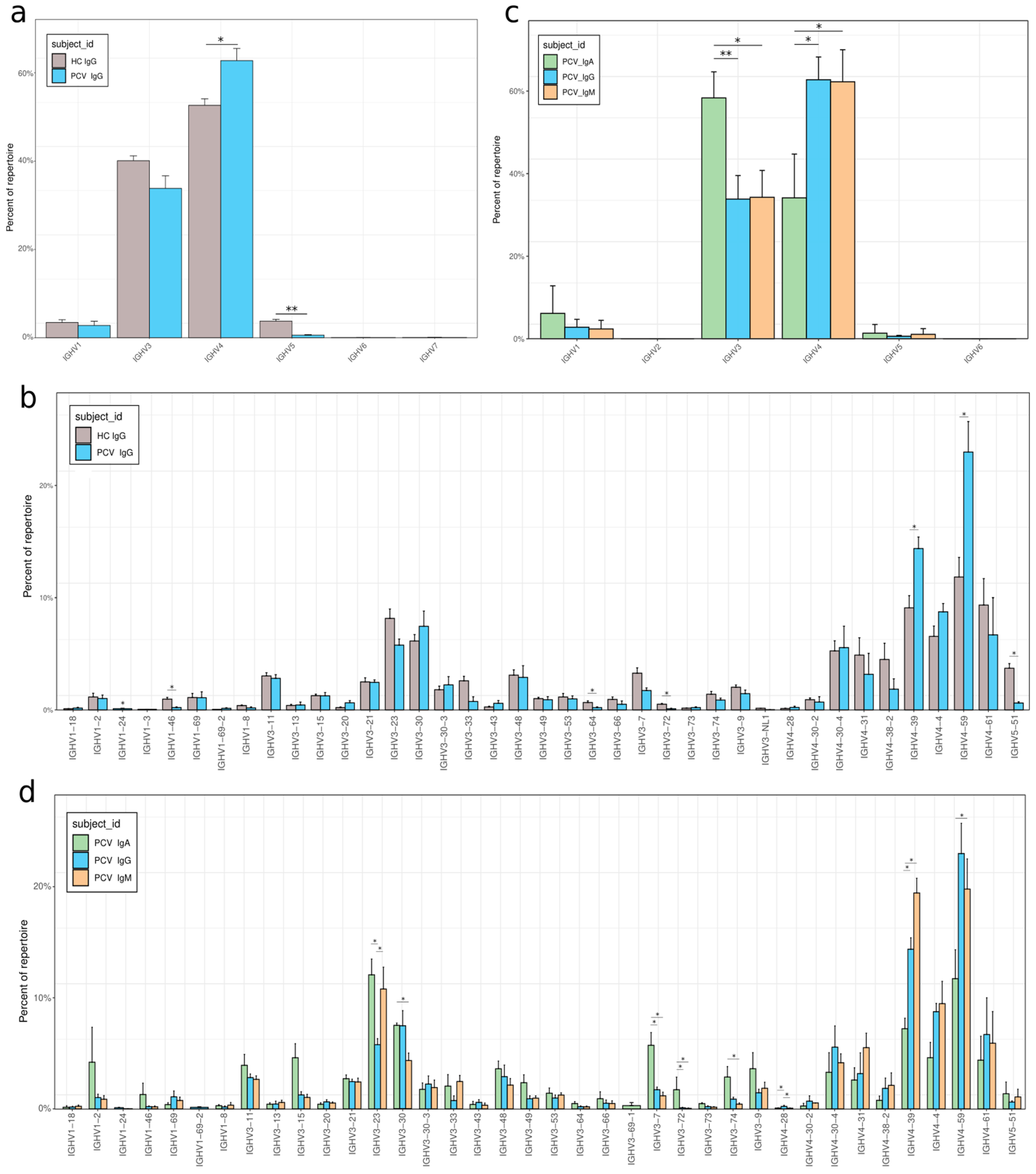
2.7. Amplification and Sequencing of Immunoglobulin Variable Domains
2.8. Sequence Processing
2.9. Visualization of Antibody Sample Relationships Using t-SNE
2.10. Principal Component Analysis
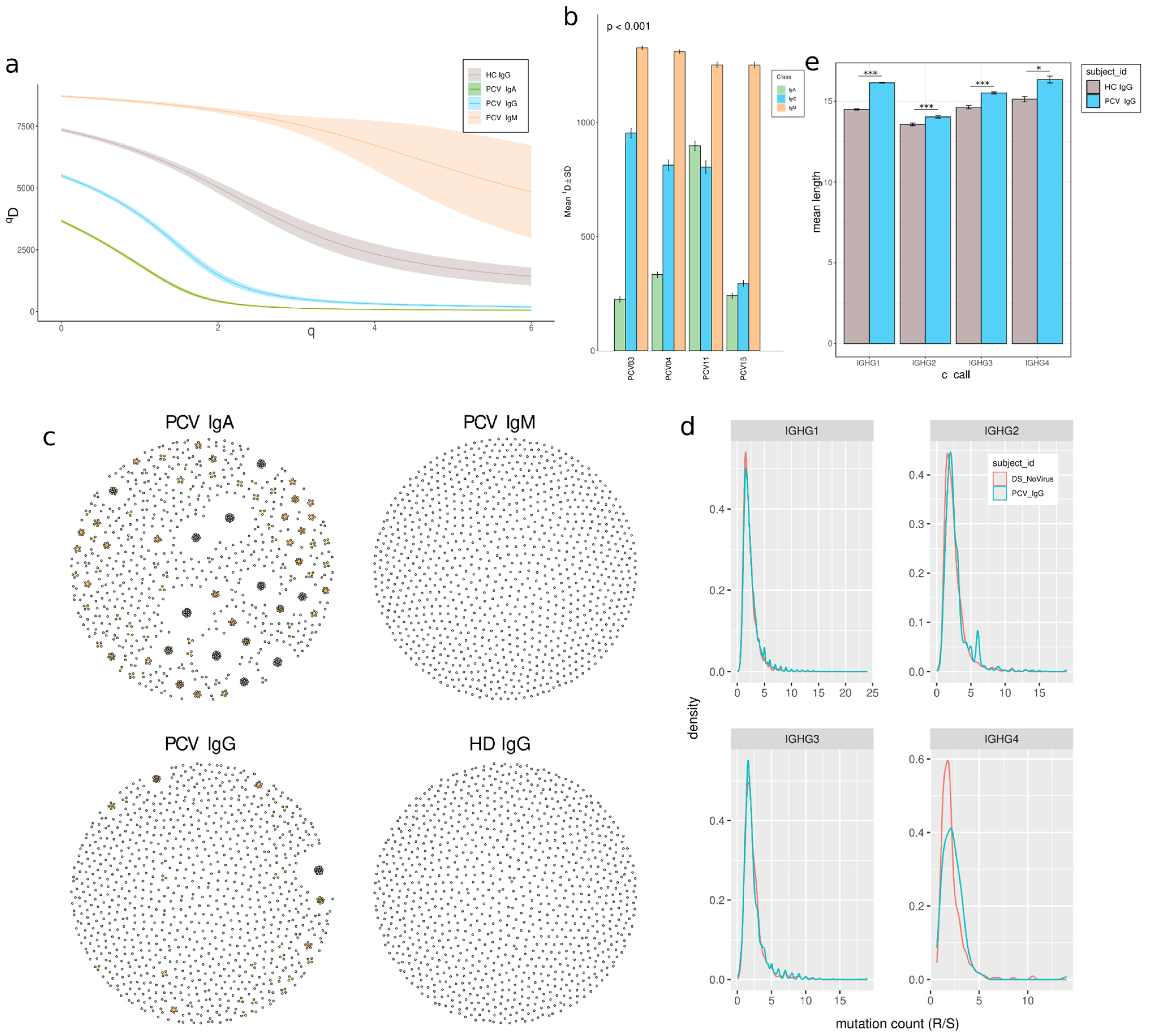
2.11. Network Analysis of CDRH3 Similarity
2.12. Somatic Hypermutation (SHM) Analysis
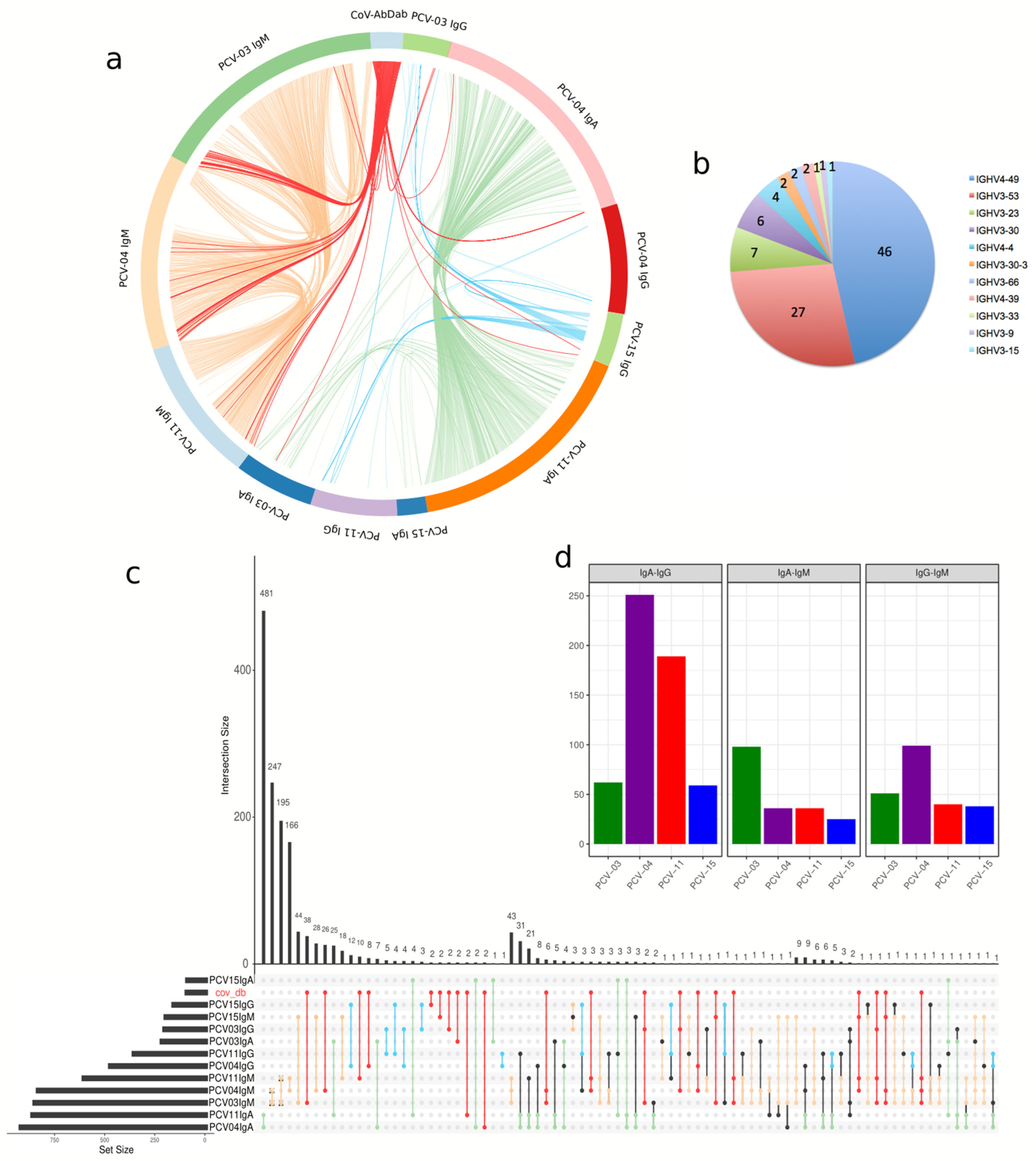
2.13. Analysis of Convergent Immune Responses
2.14. Statistical Analysis and Plotting
3. Results
3.1. Expansion of Memory B Cells from Individuals Vaccinated with CoronaVac
3.2. Expansion of the Number of Antibody-Secreting B Cells
3.3. Antibody Patterns Differentiate Vaccinated and Pre-Pandemic Individuals
3.4. VH Gene Usage Adaptations After Vaccination
3.5. Clonal Expansion and Reduced Diversity in Memory B Cells
3.6. Memory Repertoire Convergence After Vaccination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Focosi, D.; Franchini, M.; Maggi, F.; Shoham, S. COVID-19 therapeutics. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e0011923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, E.; Ananiev, J.; Yovchev, Y.; Arabadzhiev, G.; Abrashev, H.; Abrasheva, D.; Atanasov, V.; Kostandieva, R.; Mitev, M.; Petkova-Parlapanska, K.; et al. COVID-19 Complications: Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Mitochondrial and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira-Silva, T.; Katikireddi, S.V.; Oliveira, V.d.A.; Flores-Ortiz, R.; Júnior, J.B.; Paixão, E.S.; Robertson, C.; Penna, G.O.; Werneck, G.L.; Barreto, M.L.; et al. Vaccine effectiveness of heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 in Brazil. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, W.M.; Amorim, M.R.; Sesti-Costa, R.; Coimbra, L.D.; Brunetti, N.S.; A Toledo-Teixeira, D.; de Souza, G.F.; Muraro, S.P.; Parise, P.L.; Barbosa, P.P.; et al. Neutralisation of SARS-CoV-2 lineage P.1 by antibodies elicited through natural SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination with an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: An immunological study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e527–e535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.M.S.; Mok, C.K.P.; Leung, Y.W.Y.; Ng, S.S.; Chan, K.C.K.; Ko, F.W.; Chen, C.; Yiu, K.; Lam, B.H.S.; Lau, E.H.Y.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant BA.1 following homologous and heterologous CoronaVac or BNT162b2 vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harne, R.; Williams, B.; Abdelal, H.F.M.; Baldwin, S.L.; Coler, R.N. SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune responses. AIMS Microbiol. 2023, 9, 245–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galson, J.D.; Schaetzle, S.; Bashford-Rogers, R.J.M.; Raybould, M.I.J.; Kovaltsuk, A.; Kilpatrick, G.J.; Minter, R.; Finch, D.K.; Dias, J.; James, L.K.; et al. Deep Sequencing of B Cell Receptor Repertoires From COVID-19 Patients Reveals Strong Convergent Immune Signatures. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 605170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Luo, K.; He, P.; Hou, R.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Yi, H.; Liang, H.; Deng, Y.; et al. Analysis of B Cell Receptor Repertoires Reveals Key Signatures of the Systemic B Cell Response after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0160021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claër, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreer, C.; Zehner, M.; Weber, T.; Ercanoglu, M.S.; Gieselmann, L.; Rohde, C.; Halwe, S.; Korenkov, M.; Schommers, P.; Vanshylla, K.; et al. Longitudinal Isolation of Potent Near-Germline SARS-CoV-2-Neutralizing Antibodies from COVID-19 Patients. Cell 2020, 182, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; He, P.; Huang, X.; Luo, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, F.; Hou, R.; Fan, X.; et al. Germline IGHV3-53-encoded RBD-targeting neutralizing antibodies are commonly present in the antibody repertoires of COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.S.H.; Cheng, S.M.S.; Zhao, J.; Tsoi, A.Y.S.; Lau, K.K.M.; Chan, C.H.C.; Li, J.K.C.; Hui, D.S.C.; Peiris, M.; Yen, H. Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses to Coronaviruses Elicited by SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Vaccination. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2024, 18, e13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbach, H.; Eichhorn, E.M.; Liese, J.G.; Girschick, H.J. Reference values for B cell subpopulations from infancy to adulthood. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 162, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, D.; Corti, D.; Jarrossay, D.; Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A. Clonal dissection of the human memory B-cell repertoire following infection and vaccination. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltari, E.; McGeever, A.; Friedland, N.; Kim, P.S.; McCutcheon, K.M. Functional Enrichment and Analysis of Antigen-Specific Memory B Cell Antibody Repertoires in PBMCs. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.N.; Muir, L.; McKay, P.F.; Vassiliou, G.S.; Smith, K.G.C.; Lyons, P.A.; Russell, C.A.; Anderson, C.A.; Kellam, P.; Bashford-Rogers, R.J.M. Combined Influence of B-Cell Receptor Rearrangement and Somatic Hypermutation on B-Cell Class-Switch Fate in Health and in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnmatz, M.; Kesa, G.; Netterlid, E.; Buisman, A.M.; Thorstensson, R.; Ahlborg, N. Optimization of a human IgG B-cell ELISpot assay for the analysis of vaccine-induced B-cell responses. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 391, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; França, R.K.A.d.O.; Barros, P.H.; Fontinele, H.G.C.; Fonseca, S.G.; Brigido, M.M.; Maranhão, A.Q. Rescuing pathogen-specific memory B-cell from PBMC of prior Zika virus-infected individuals. Immunol. Lett. 2025, 271, 106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotagiri, P.; Mescia, F.; Rae, W.M.; Bergamaschi, L.; Tuong, Z.K.; Turner, L.; Hunter, K.; Gerber, P.P.; Hosmillo, M.; Hess, C.; et al. B cell receptor repertoire kinetics after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Assis, F.L.; Hoehn, K.B.; Zhang, X.; Kardava, L.; Smith, C.D.; El Merhebi, O.; Buckner, C.M.; Trihemasava, K.; Wang, W.; Seamon, C.A.; et al. Tracking B cell responses to the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vega, M.; Wan, H.; Reséndiz-Sandoval, M.; Hinojosa-Trujillo, D.; Valenzuela, O.; Mata-Haro, V.; Dehesa-Canseco, F.; Solís-Hernández, M.; Marcotte, H.; Pan-Hammarström, Q.; et al. Comparative single-cell transcriptomic profile of hybrid immunity induced by adenovirus vector-based COVID-19 vaccines. Genes Immun. 2024, 25, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, T.; Meffre, E.; Yurasov, S.; Tsuiji, M.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Wardemann, H. Efficient generation of monoclonal antibodies from single human B cells by single cell RT-PCR and expression vector cloning. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 334, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benckert, J.; Schmolka, N.; Kreschel, C.; Zoller, M.J.; Sturm, A.; Wiedenmann, B.; Wardemann, H. The majority of intestinal IgA+ and IgG+ plasmablasts in the human gut are antigen-specific. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsiero, E.; Bombardieri, M.; Carlotti, E.; Pratesi, F.; Robinson, W.; Migliorini, P.; Pitzalis, C. Single cell cloning and recombinant monoclonal antibodies generation from RA synovial B cells reveal frequent targeting of citrullinated histones of NETs. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Imkeller, K.; Busse, C.E.; Wardemann, H. Direct high-throughput amplification and sequencing of immunoglobulin genes from single human B cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2698–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.T.; Vander, J.A.; Uduman, M.; Gadala-Maria, D.; Yaari, G.; Kleinstein, S.H. Change-O: A toolkit for analyzing large-scale B cell immunoglobulin repertoire sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3356–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiden, J.A.V.; Yaari, G.; Uduman, M.; Stern, J.N.; O’connor, K.C.; Hafler, D.A.; Vigneault, F.; Kleinstein, S.H. pRESTO: A toolkit for processing high-throughput sequencing raw reads of lymphocyte receptor repertoires. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1930–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabernet, G.; Marquez, S.; Bjornson, R.; Peltzer, A.; Meng, H.; Aron, E.; Lee, N.Y.; Jensen, C.G.; Ladd, D.; Polster, M.; et al. nf-core/airrflow: An adaptive immune receptor repertoire analysis workflow employing the Immcantation framework. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1012265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ma, N.; Madden, T.L.; Ostell, J.M. IgBLAST: An immunoglobulin variable domain sequence analysis tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W34–W40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The Igraph Software Package for Complex Network Research, InterJournal, Complex Systems 1695. 2006. Available online: http://igraph.org (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Sofou, E.; Vlachonikola, E.; Zaragoza-Infante, L.; Brüggemann, M.; Darzentas, N.; Groenen, P.J.T.A.; Hummel, M.; Macintyre, E.A.; Psomopoulos, F.; Davi, F.; et al. Clonotype definitions for immunogenetic studies: Proposals from the EuroClonality NGS Working Group. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1750–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raybould, M.I.J.; Kovaltsuk, A.; Marks, C.; Deane, C.M. CoV-AbDab: The coronavirus antibody database. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 734–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yisimayi, A.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Xiao, T.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature 2022, 608, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Three epitope-distinct human antibodies from RenMab mice neutralize SARS-CoV-2 and cooperatively minimize the escape of mutants. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, C.; Li, T.; Gu, C.; Wang, K.; Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; et al. A Rapid and Efficient Screening System for Neutralizing Antibodies and Its Application for SARS-CoV-2. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 653189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Muecksch, F.; Muenn, F.; Cho, A.; Zong, S.; Raspe, R.; Ramos, V.; Johnson, B.; Ben Tanfous, T.; DaSilva, J.; et al. Humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 elicited by combination COVID-19 vaccination regimens. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20220826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, A.K.; Pymm, P.; Esterbauer, R.; Dietrich, M.H.; Lee, W.S.; Drew, D.; Kelly, H.G.; Chan, L.-J.; Mordant, F.L.; Black, K.A.; et al. Landscape of human antibody recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Viant, C.; Gaebler, C.; Cipolla, M.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Oren, D.A.; et al. Enhanced SARS-CoV-2 neutralization by dimeric IgA. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabf1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.; Muecksch, F.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Wang, Z.; Finkin, S.; Gaebler, C.; Ramos, V.; Cipolla, M.; Mendoza, P.; Agudelo, M.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain antibody evolution after mRNA vaccination. Nature 2021, 600, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zhao, J.; Sun, F.; Miao, M.; Sun, X.; He, J.; Li, Z. Comparison of the deep immune profiling of B cell subsets between healthy adults and Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winklmeier, S.; Eisenhut, K.; Taskin, D.; Rübsamen, H.; Gerhards, R.; Schneider, C.; Wratil, P.R.; Stern, M.; Eichhorn, P.; Keppler, O.T.; et al. Persistence of functional memory B cells recognizing SARS-CoV-2 variants despite loss of specific IgG. iScience 2022, 25, 103659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, L.; McKay, P.F.; Petrova, V.N.; Klymenko, O.V.; Kratochvil, S.; Pinder, C.L.; Kellam, P.; Shattock, R.J. Optimisation of ex vivo memory B cell expansion/differentiation for interrogation of rare peripheral memory B cell subset responses. Wellcome Open Res. 2017, 2, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, N.L.; Onai, N.; Lanzavecchia, A. A role for Toll-like receptors in acquired immunity: Up-regulation of TLR9 by BCR triggering in naive B cells and constitutive expression in memory B cells. Blood 2003, 101, 4500–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsman, C.; Verhoeven, D.; Koers, J.; Rispens, T.; Brinke, A.T.; van Ham, S.M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Optimized Protocols for In-Vitro T-Cell-Dependent and T-Cell-Independent Activation for B-Cell Differentiation Studies Using Limited Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 815449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Beukema, M.; De Vries-Idema, J.; Huckriede, A. Assessing human B cell responses to influenza virus vaccines and adjuvants in a PBMC-derived in vitro culture system. Vaccine 2025, 44, 126563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.-X.; Jia, Y.-J.; Wang, X.; Deng, H.-J.; Cao, X.-X.; Yuan, J.; Fang, L.; Cheng, X.-R.; Luo, C.; He, A.-R.; et al. Immune memory in convalescent patients with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kang, B.H.; Ishida, E.; Zhou, T.; Griesman, T.; Sheng, Z.; Wu, F.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Zhang, B.; McKee, K.; et al. Identification of a CD4-Binding-Site Antibody to HIV that Evolved Near-Pan Neutralization Breadth. Immunity 2016, 45, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auladell, M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Garcillán, B.; Mackay, F.; Kedzierska, K.; Fox, A. Distinguishing naive- from memory-derived human B cells during acute responses. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2019, 8, e01090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, Z.; Ruder, J.; Thomas, O.G.; Bronge, M.; Soto, L.D.L.P.; Grönlund, H.; Olsson, T.; Martin, R. Enhanced and cross-reactive in vitro memory B cell response against Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1334720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, Y.; Jirholt, P.; Ohlin, M. Length of the antibody heavy chain complementarity determining region 3 as a specificity-determining factor. J. Mol. Recognit. 2004, 17, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Jin, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, W.; Luo, M.; Luo, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, P.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Z.; et al. Global characterization of B cell receptor repertoire in COVID-19 patients by single-cell V(D)J sequencing. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kaku, C.I.; Song, G.; Yuan, M.; Andrabi, R.; Burton, D.R.; Walker, L.M.; Wilson, I.A. Human antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 with a recurring YYDRxG motif retain binding and neutralization to variants of concern including Omicron. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Supasa, P.; Liu, C.; Dijokaite-Guraliuc, A.; Duyvesteyn, H.M.E.; Selvaraj, M.; Mentzer, A.J.; Das, R.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Temperton, N.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody response to SD1 and its evasion by BA.2.86. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Lv, H.; Peng, J.; Wilson, I.A.; Wu, N.C. A large-scale systematic survey reveals recurring molecular features of public antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2. Immunity 2022, 55, 1105–1117.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshev, M.; Sakharkar, M.; Connor, R.I.; Dugan, H.L.; Sheward, D.J.; Rappazzo, C.G.; Stålmarck, A.; Forsell, M.N.E.; Wright, P.F.; Corcoran, M.; et al. Vaccination of SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals expands a broad range of clonally diverse affinity-matured B cell lineages. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, J.; Rogers, T.F.; Jaffe, D.B.; Adams, B.A.; Bangaru, S.; Garcia, E.; Capozzola, T.; Messmer, T.; Sharma, P.; Song, G.; et al. Deep repertoire mining uncovers ultra-broad coronavirus neutralizing antibodies targeting multiple spike epitopes. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadevara, N.; Shiakolas, A.R.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Binshtein, E.; Chen, R.E.; Case, J.B.; Kramer, K.J.; Armstrong, E.C.; Myers, L.; Trivette, A.; et al. An antibody targeting the N-terminal domain of SARS-CoV-2 disrupts the spike trimer. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e159062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinti, I.; Mortari, E.P.; Salinas, A.F.; Milito, C.; Carsetti, R. IgA Antibodies and IgA Deficiency in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 655896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchais, C.; Fernández, I.; Bruel, T.; de Melo, G.D.; Prot, M.; Beretta, M.; Guardado-Calvo, P.; Dufloo, J.; Molinos-Albert, L.M.; Backovic, M.; et al. Potent human broadly SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing IgA and IgG antibodies effective against Omicron BA.1 and BA.2. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20220638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.C.; Yang, F.; Jackson, K.J.; Hoh, R.A.; Röltgen, K.; Jean, G.H.; Stevens, B.A.; Lee, J.-Y.; Rustagi, A.; Rogers, A.J.; et al. Human B Cell Clonal Expansion and Convergent Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 516–525.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Wang, Z.; Cho, A.; Agudelo, M.; Barnes, C.O.; Gazumyan, A.; Finkin, S.; et al. Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Nature 2020, 584, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, F. CoronaVac: A review of efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2022, 18, 2096970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, C.; Peñaloza, H.F.; Schultz, B.M.; Piña-Iturbe, A.; Ríos, M.; Moreno-Tapia, D.; Pereira-Sánchez, P.; Leighton, D.; Orellana, C.; Covarrubias, C.; et al. Humoral and cellular response induced by a second booster of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in adults. EBioMedicine 2023, 91, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, S.; Teng, Z.; Tian, M.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Fan, X.; et al. Effectiveness of the booster dose of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine against Omicron BA.5 infection: A matched cohort study of adult close contacts. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jia, Z.; Bao, L.; Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Chi, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Memory B cell repertoire from triple vaccinees against diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nature 2022, 603, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Luo, M.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; Jin, X.; Xu, Z.; Juan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; et al. Single cell RNA and immune repertoire profiling of COVID-19 patients reveal novel neutralizing antibody. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Liu, S.; Xu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lv, K.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Yue, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Comparative global B cell receptor repertoire difference induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination via single-cell V(D)J sequencing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 2007–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, E.R.; Khanal, S.; Pierce, S.H.; LeMaster, C.A.; McLennan, R.; Pastinen, T.; Bradley, T. Effects of Prior Infection with SARS-CoV-2 on B Cell Receptor Repertoire Response during Vaccination. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Binds | Neutralize | Epitope | Subject ID | C Call | V Call | J Call | CDRH3 * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD55-1970 10D12 Ab_56D7 | CoV2 | yes | RBD | PCV-04 | IgA | IGHV3-66 | IGHJ6 | ARDLDYYGMDV (×3) ARRLDYYVMDV | [35,36,37] |
| AZ262 | CoV2 | yes | RBD | PCV-03 | IgA | IGHV4-39 | IGHJ6 | ARLTRGYSYGYSMDV ARDGRGYSYGYGMDV | [38] |
| WCSL-36 | CoV2 | yes | RBD | PCV-15 | IgG | IGHV3-23 | IGHJ5 | AKSRQLAFDP AKSRDLVFDP | [39] |
| Wang-C443 | CoV2 | yes | RBD | PCV-03 | IgG | IGHV3-33 | IGHJ4 | AREDYYDSSGSLDY ARENYYDSSGYLDY | [40] |
| C1414 | CoV2 | yes | RBD | PCV-04 PCV-03 | IgM IgG | IGHV4-59 | IGHJ5 | ARHYDSSGYTYNWFDP ARTYDSSGYYPNWFDP ARTYDTSGYYANWFDP ** | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
França, R.K.A.d.O.; Barros, P.H.A.; Silva, J.M.; Fontinele, H.G.C.; Maranhão, A.Q.; Brigido, M.d.M. Naive and Memory B Cell BCR Repertoires in Individuals Immunized with an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Vaccines 2025, 13, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040393
França RKAdO, Barros PHA, Silva JM, Fontinele HGC, Maranhão AQ, Brigido MdM. Naive and Memory B Cell BCR Repertoires in Individuals Immunized with an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Vaccines. 2025; 13(4):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040393
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrança, Renato Kaylan Alves de Oliveira, Pedro Henrique Aragão Barros, Jacyelle Medeiros Silva, Hitallo Guilherme Costa Fontinele, Andrea Queiroz Maranhão, and Marcelo de Macedo Brigido. 2025. "Naive and Memory B Cell BCR Repertoires in Individuals Immunized with an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine" Vaccines 13, no. 4: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040393
APA StyleFrança, R. K. A. d. O., Barros, P. H. A., Silva, J. M., Fontinele, H. G. C., Maranhão, A. Q., & Brigido, M. d. M. (2025). Naive and Memory B Cell BCR Repertoires in Individuals Immunized with an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Vaccines, 13(4), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040393







