Effect of Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Antibody on Middle Ear Mucosal Immune Response to Intranasal Administration of Haemophilus influenzae Outer Membrane Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Immunogen and Adjuvant
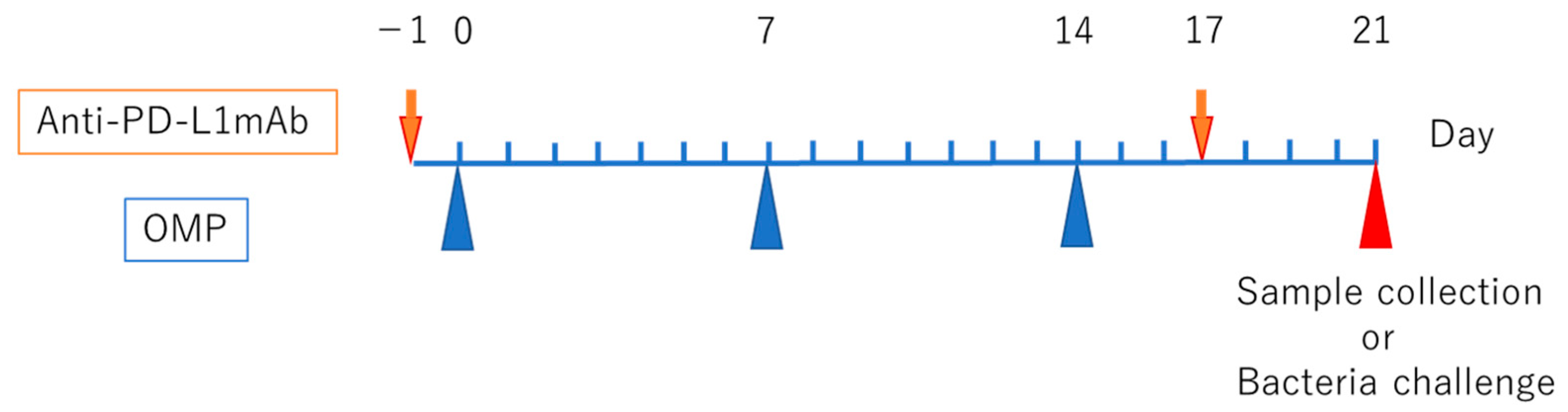
2.3. Intranasal Immunization Mouse Model
2.4. PD-L1 Antibody Delivery Model
2.5. Detection of OMP-Specific Antibodies by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.6. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay
2.8. Bacterial Challenge and Sampling
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in OMP-Specific Antibody Titers and Effects of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Administration
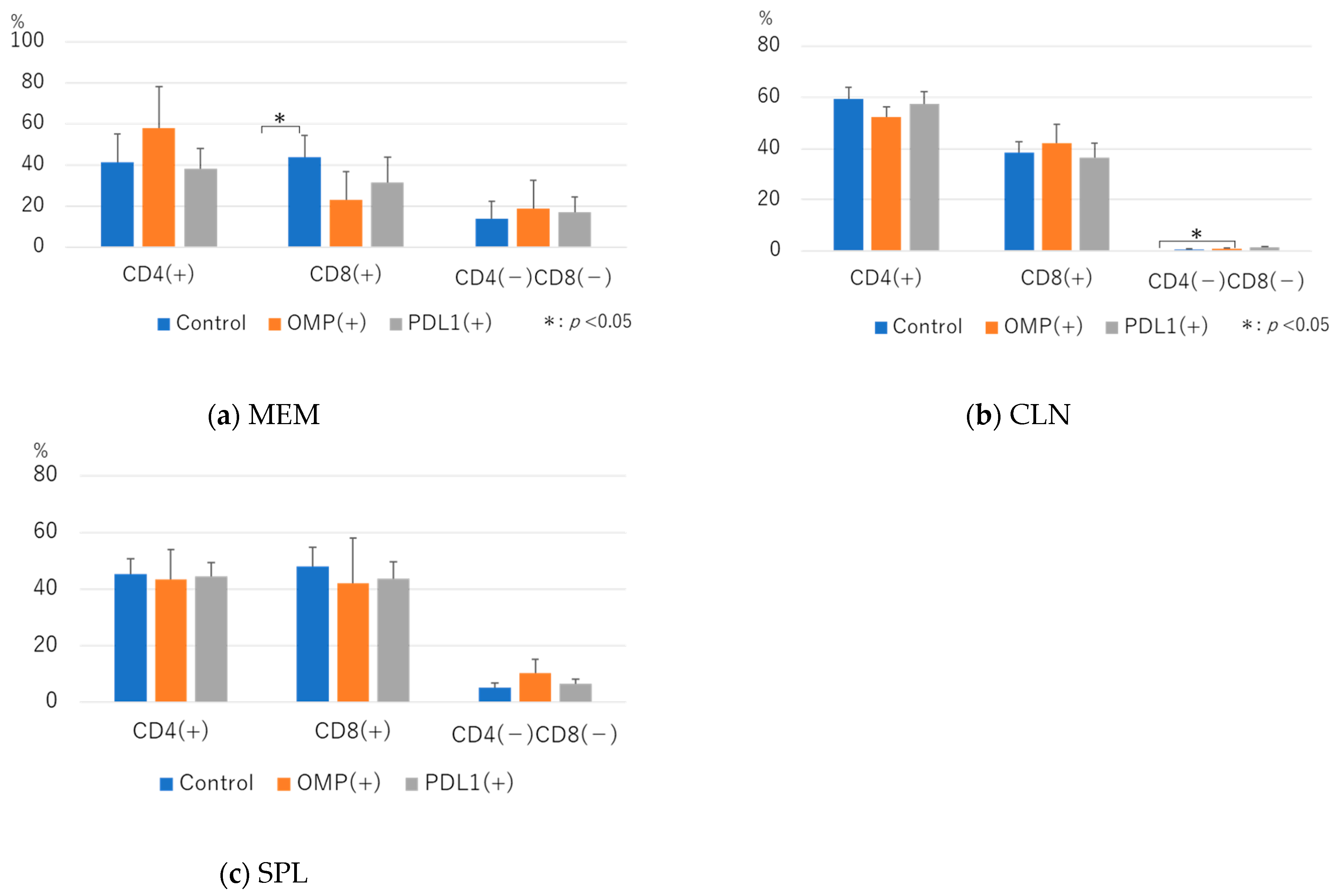
3.2. Flow Cytometry Analysis
3.2.1. Effect of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Administration on the CD3+ T-Cell Fraction
3.2.2. Analysis of CD4+ T-Cell Dynamics After Administration of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody
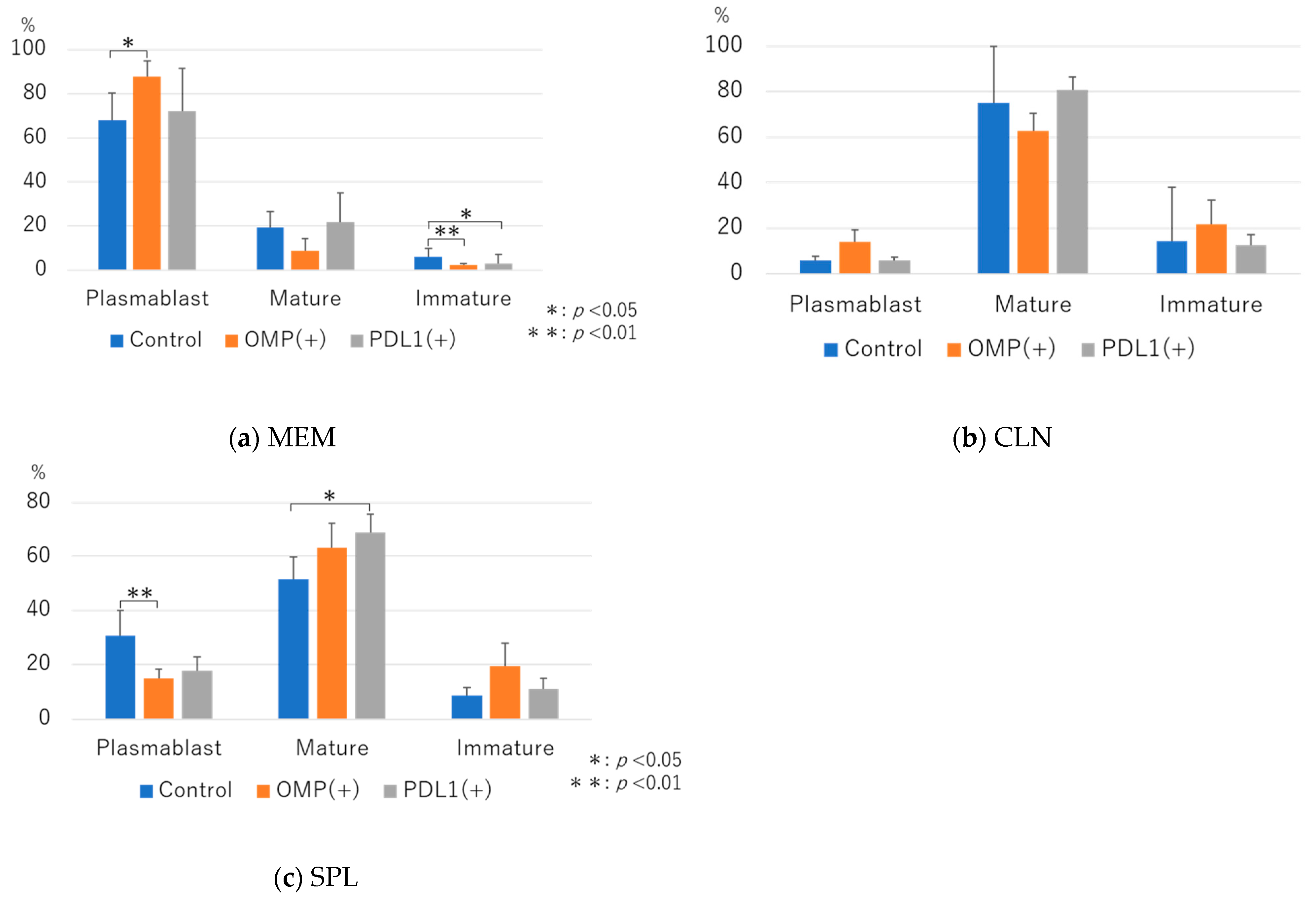
3.2.3. Analysis of B-Cell Dynamics Following Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Administration
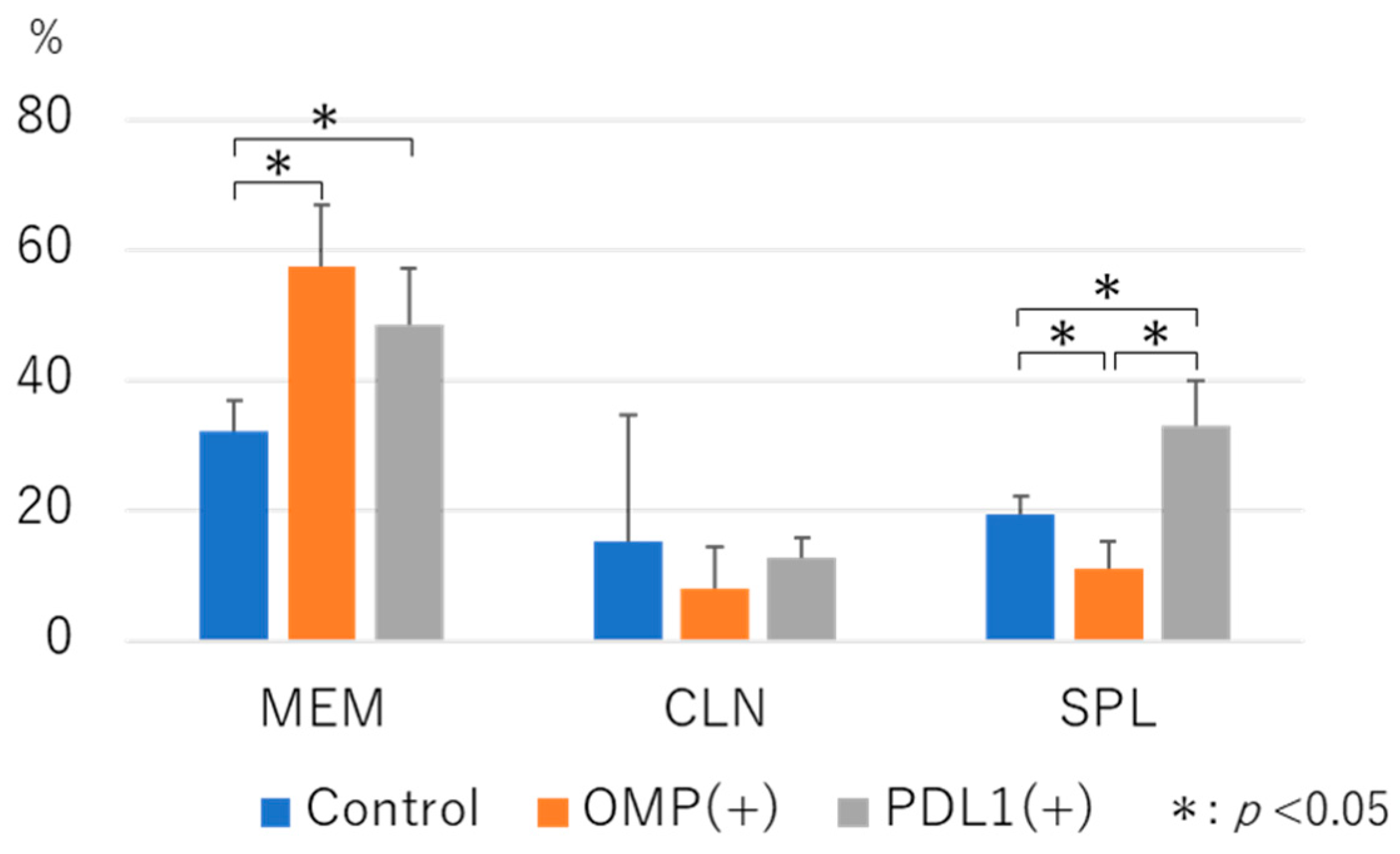
3.2.4. Analysis of the Dynamics of CD3+CD4+CD185+ T Cells After the Administration of the Anti-PD-L1 Antibody
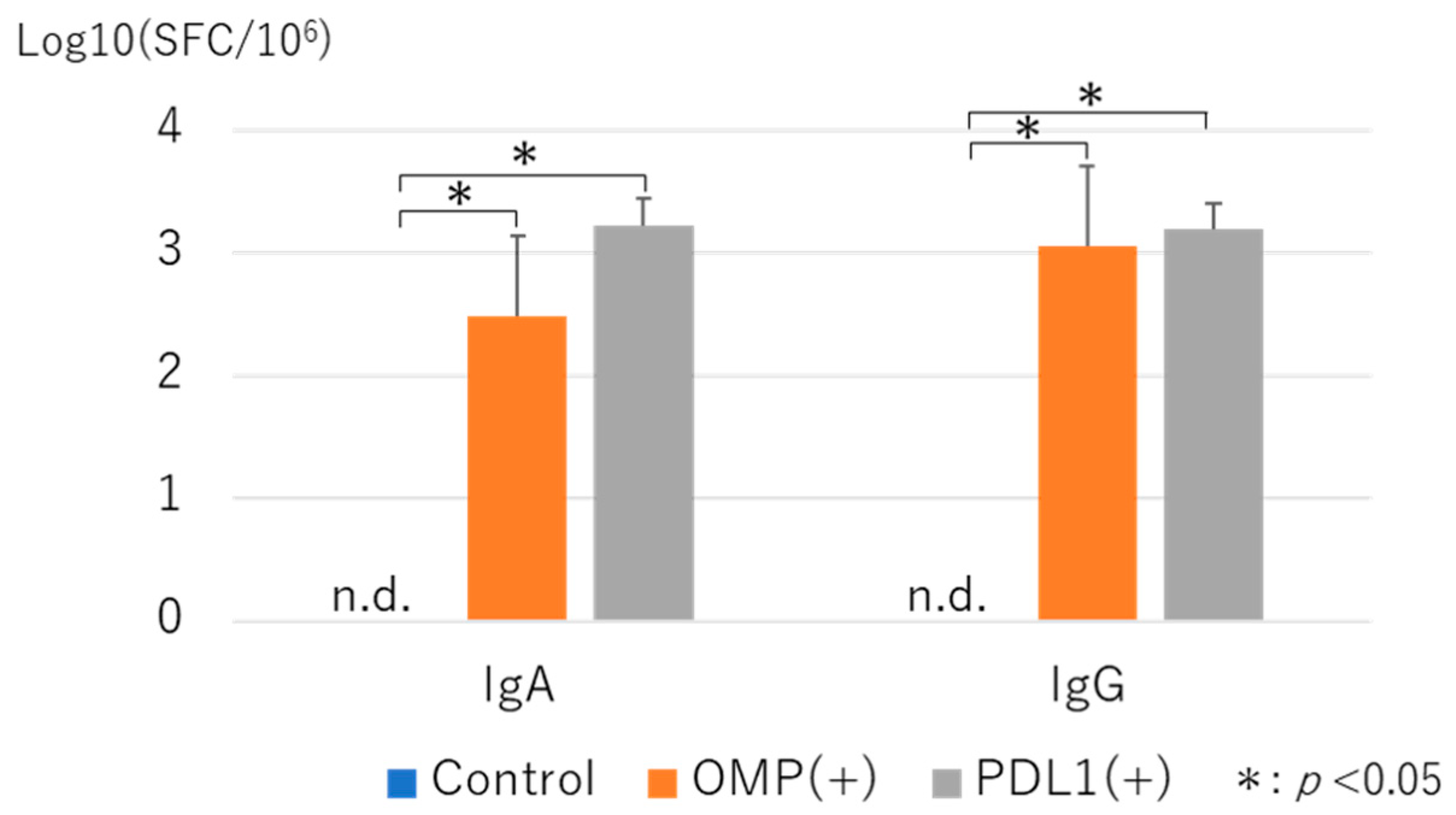
3.3. Measurement of Antibody-Producing Cells by ELISPOT Asssay with Administration of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody
3.4. Bacterial Clearance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Feghaly, R.E.; Nedved, A.; Katz, S.E.; Frost, H.M. New insights into the treatment of acute otitis media. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2023, 21, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Morris, M.; Pichichero, M.E. Epidemiology of acute otitis media in the postpneumococcal conjugate vaccine era. Pediatrics 2017, 140, 20170181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, S. Otitis Media in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, I.; Gober, A.E. Microbiologic characteristics of persistent otitis media. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1998, 124, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Commisso, R.; Romero-Orellano, F.; Montanaro, P.B.; Romero-Moroni, F.; Romero-Diaz, R. Acute otitis media: Bacteriology and bacterial resistance in 205 pediatric patients. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2000, 56, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo1, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, G.J.; Long, A.J.; Iwai, Y.; Bourque, K.; Chernova, T.; Nishimura, H.; Fitz, L.J.; Malenkovich, N.; Okazaki, T.; Byrne, M.C.; et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, Y.; Terawaki, S.; Ikegawa, M.; Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T. PD-1 inhibits antiviral immunity at the effector phase in the liver. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti–PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malas, S.; Harrasser, M.; Lacy, K.E.; Karagiannis, S.N. Antibody therapies for melanoma: New and emerging, opportunities to activate immunity (review). Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Läubli, H.; Balmelli, C.; Kaufmann, L.; Stanczak, M.; Syedbasha, M.; Vogt, D.; Hertig, A.; Müller, B.; Gautschi, O.; Stenner, F.; et al. Influenza vaccination of cancer patients during PD-1 blockade induces serological protection but may raise the risk for immune-related adverse events. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Kodama, S.; Moriyama, M.; Kawano, T.; Suzuki, M. The role of toll-like receptor 4 in eliciting acquired immune responses against nontypeable haemophilus influenzae following intranasal immunization with outer membrane protein. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 73, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.F.; Nelson, M.B.; Dudas, K.C.; Mylotte, J.M.; Apicella, M.A. Identification of a specific epitope of haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 152, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Hirano, T.; Kodama, S.; Kadowaki, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Kawano, T.; Suzuki, M. Monophosphoryl Lipid A enhances nontypeable haemophilus influenzae-specific mucosal and systemic immune responses by intranasal immunization. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 97, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurono, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Mogi, G.; Yamamoto, M.; Fujihashi, K.; McGhee, J.R.; Kiyono, H. Effects of intranasal immunization on protective immunity against otitis media. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1999, 49, S227–S229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channappanavar, R.; Twardy, B.S.; Suvas, S. Blocking of PDL-1 interaction enhances primary and secondary CD8 T cell response to herpes simplex virus-1 infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Hirano, T.; Hou, Y.; Gu, X.-X. Specific immune responses and enhancement of murine pulmonary clearance of Moraxella catarrhalis by Intranasal immunization with a detoxified lipooligosaccharide conjugate vaccine. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5982–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.L.; Wherry, E.J.; Masopust, D.; Zhu, B.; Allison, J.P.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Ahmed, R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 2006, 439, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphorst, A.O.; Ahmed, R. Manipulating the PD-1 pathway to improve immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, L. Immunological mechanisms behind anti--PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade: Intratumoral reinvigoration or systemic induction? Biomedicines 2024, 12, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velu, V.; Titanji, K.; Zhu, B.; Husain, S.; Pladevega, A.; Lai, L.; Vanderford, T.H.; Chennareddi, L.; Silvestri, G.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. Enhancing Siv-specific immunity in vivo by PD-1 blockade. Nature 2009, 458, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, H.; Minato, N.; Nakano, T.; Honjo, T. Immunological studies on PD-1 deficient mice: Implication of PD-1 as a negative regulator for B cell responses. Int. Immunol. 1998, 10, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Xie, S.; Gao, J.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, E.; Yang, X.; Jin, Z.; Long, H.; Zhang, A.; Yang, F.; et al. NK cell transfer overcomes resistance to PD-(L)1 therapy in aged mice. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, J.M.; Redhu, N.S.; Cheung, E.; Robertson, N.G.; Patik, I.; Sayed, S.E.; Thompson, C.M.; Herd, M.; Lucas, K.B.; Conaway, E.; et al. Generation of protective pneumococcal-specific nasal resident memory CD4+ T cells via parenteral immunization. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, G.; Romano, M.; Nova-Lamperti, E.; Sunderland, M.W.; Nerviani, A.; Scottà, C.; Bombardieri, M.; Quezada, S.A.; Sacks, S.H.; Noelle, R.J.; et al. PD-L1 signaling on human memory CD4+ T cells induces a regulatory phenotype. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, S. T follicular helper cell biology: A decade of discovery and diseases. Immunity 2019, 50, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Spoerl, S.; Xiao, Y.; Habenicht, K.M.; Haeusl, S.S.; Sandner, I.; Winkler, J.; Strieder, N.; Eder, R.; Stanewsky, H.; et al. Oligoclonal CD4+CXCR5+ T cells with a cytotoxic phenotype appear in tonsils and blood. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Hams, E.; Floudas, A.; Sparwasser, T.; Weaver, C.T.; Fallon, P.G. PD-L1hi B cells are critical regulators of humoral immunity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.E.; Song, E.; Moriyama, M.; Wong, P.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, R.; Strohmeier, S.; Kleinstein, S.H.; Krammer, F.; Iwasaki, A. Intranasal priming induces local lung-resident b cell populations that secrete protective mucosal antiviral IgA. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabj5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





|
Mean Total Number of MNCs (×106) | Control | OMP(+) | PD-L1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MEM | 0.36 ± 0.29 | 0.27 ± 0.10 | 0.41 ± 0.20 |
| CLN | 0.80 ± 0.42 | 1.24 ± 0.21 | 1.75 ± 0.73 |
| SPL | 1.52 ± 0.82 | 2.21 ± 1.22 | 1.11 ± 0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshinaga, K.; Hirano, T.; Umemoto, S.; Kadowaki, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Suzuki, M. Effect of Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Antibody on Middle Ear Mucosal Immune Response to Intranasal Administration of Haemophilus influenzae Outer Membrane Protein. Vaccines 2025, 13, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030313
Yoshinaga K, Hirano T, Umemoto S, Kadowaki Y, Matsunaga T, Suzuki M. Effect of Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Antibody on Middle Ear Mucosal Immune Response to Intranasal Administration of Haemophilus influenzae Outer Membrane Protein. Vaccines. 2025; 13(3):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030313
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshinaga, Kazuhiro, Takashi Hirano, Shingo Umemoto, Yoshinori Kadowaki, Takayuki Matsunaga, and Masashi Suzuki. 2025. "Effect of Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Antibody on Middle Ear Mucosal Immune Response to Intranasal Administration of Haemophilus influenzae Outer Membrane Protein" Vaccines 13, no. 3: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030313
APA StyleYoshinaga, K., Hirano, T., Umemoto, S., Kadowaki, Y., Matsunaga, T., & Suzuki, M. (2025). Effect of Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Antibody on Middle Ear Mucosal Immune Response to Intranasal Administration of Haemophilus influenzae Outer Membrane Protein. Vaccines, 13(3), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030313





