Design and Evaluation of a Broadly Multivalent Adhesins-Based Multi-Epitope Fusion Antigen Vaccine Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Plasmids
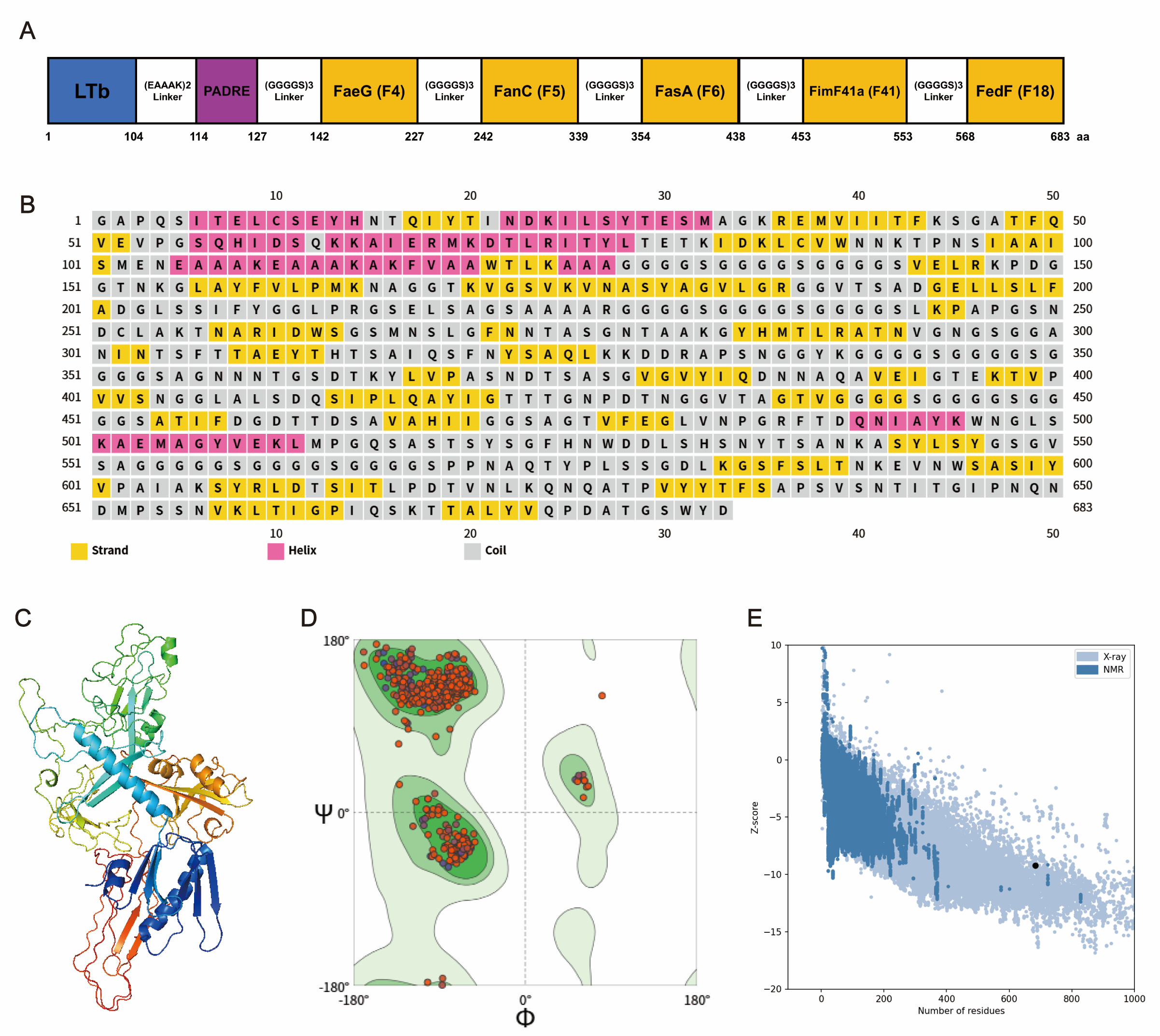
2.2. Construction and Computational Modeling of Fimbria MEFA Proteins
2.3. Prediction of Secondary Structure
2.4. Prediction, Refinement, and Quality Assessment of the 3D Structure of the MEFA Protein
2.5. Conformational Prediction of the B-Cell Epitope
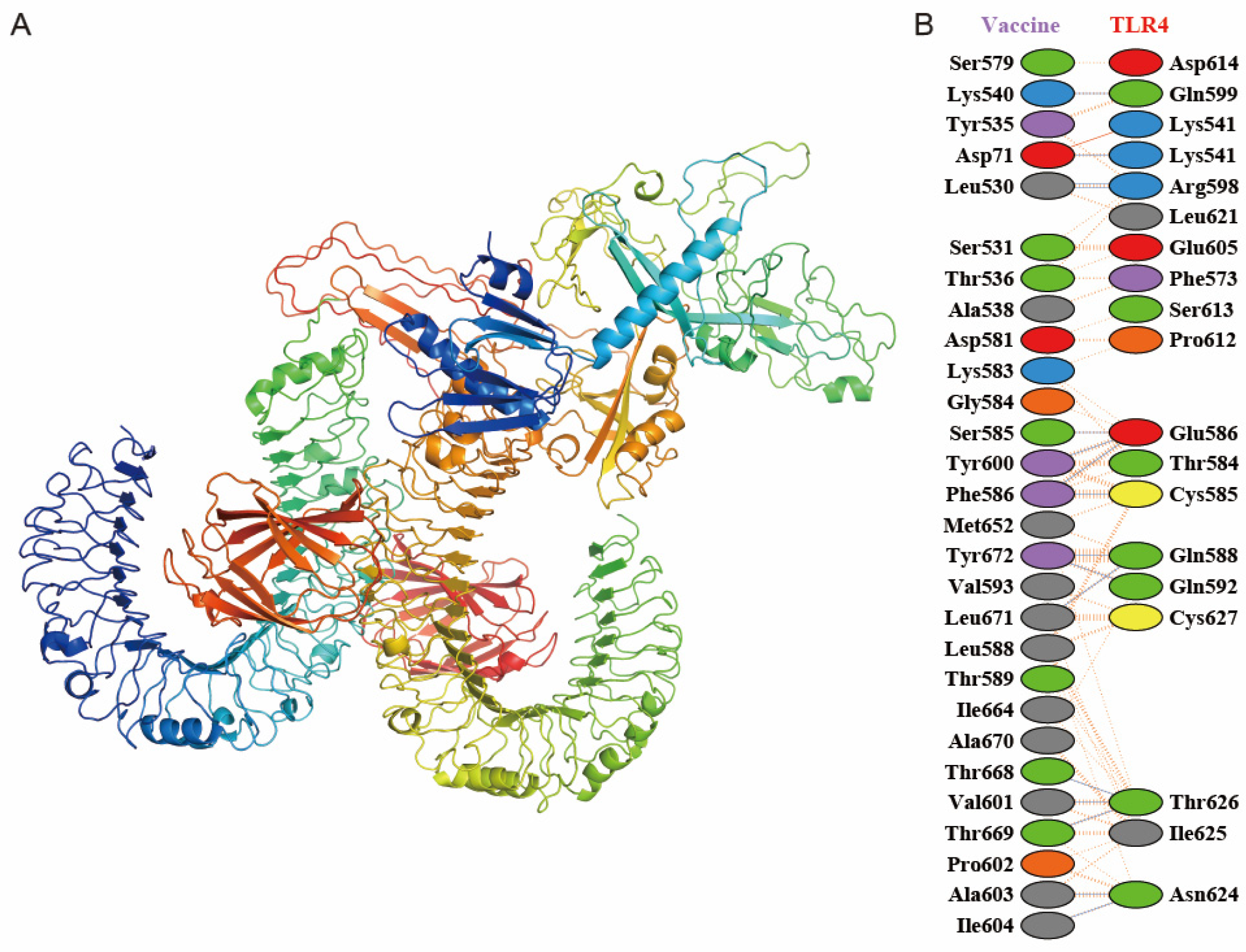
2.6. Molecular Docking of MEFA Protein with Toll-like Receptors
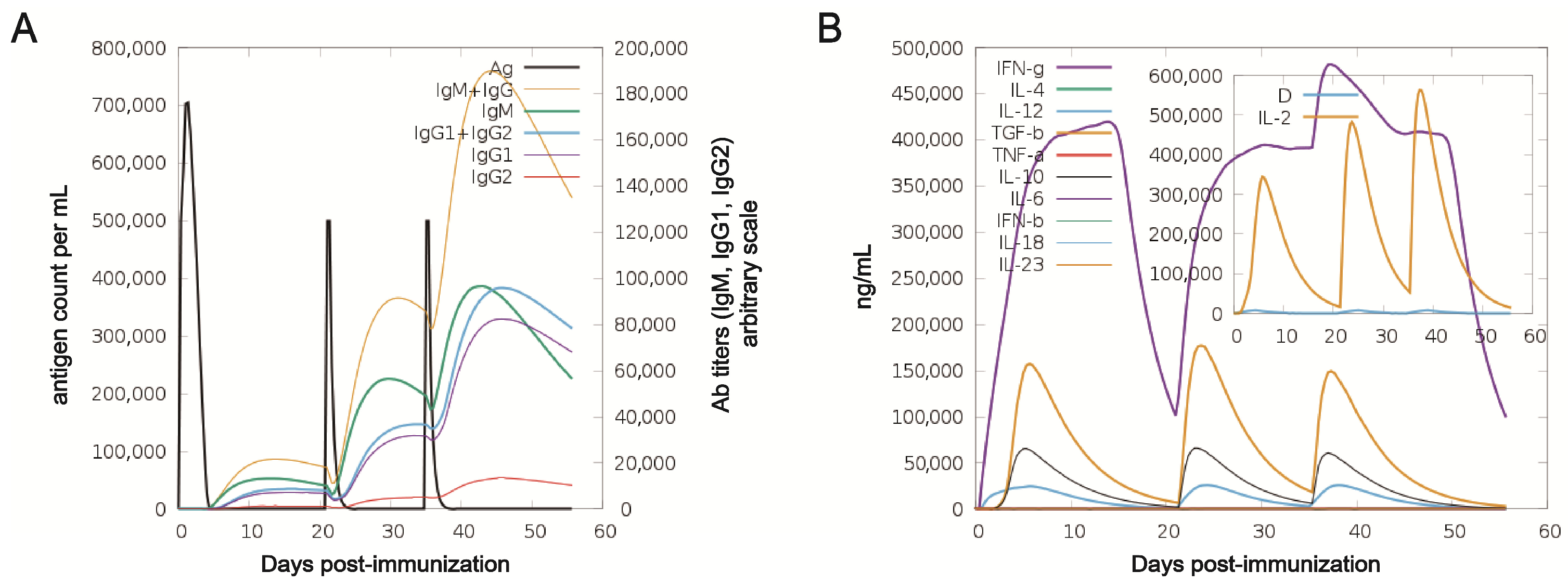
2.7. Immune Simulation Analysis
2.8. Expression Purification and Western Blot Identification of MEFA
2.9. Animal Assay
2.10. Determination of Serum Specific IgG Antibodies
2.11. Lymphocyte Proliferation Experiment
2.12. Determination of Specific IL-4 and IFN-γ Concentrations
2.13. Histopathological Study
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design and Computational Structure Analysis of MEFA
3.2. Prediction of B Cell Epitope Structure
3.3. Molecular Docking Exploration
3.4. Immune Response Simulation
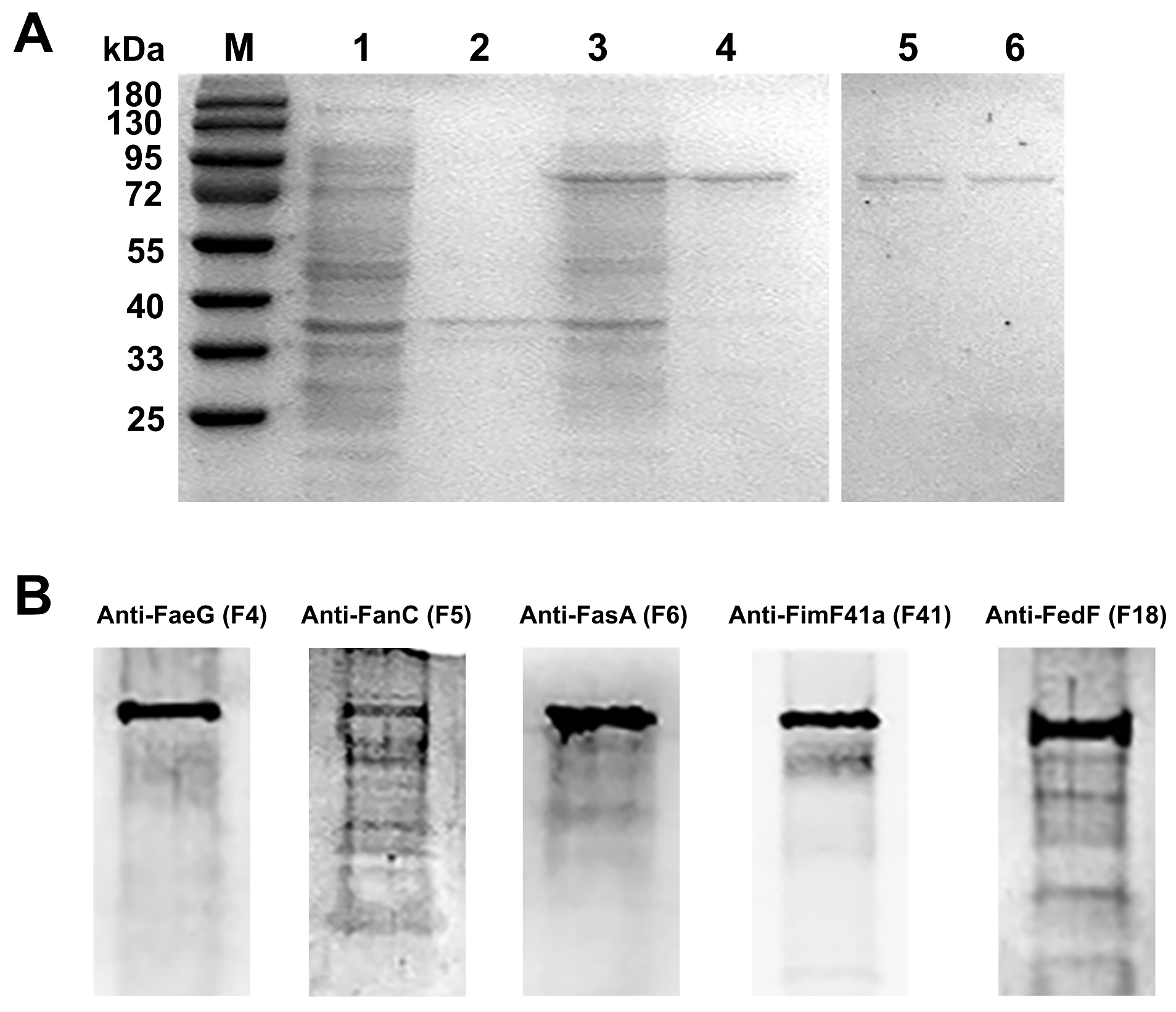
3.5. Expression, Purification and Western Blot Identification of MEFA
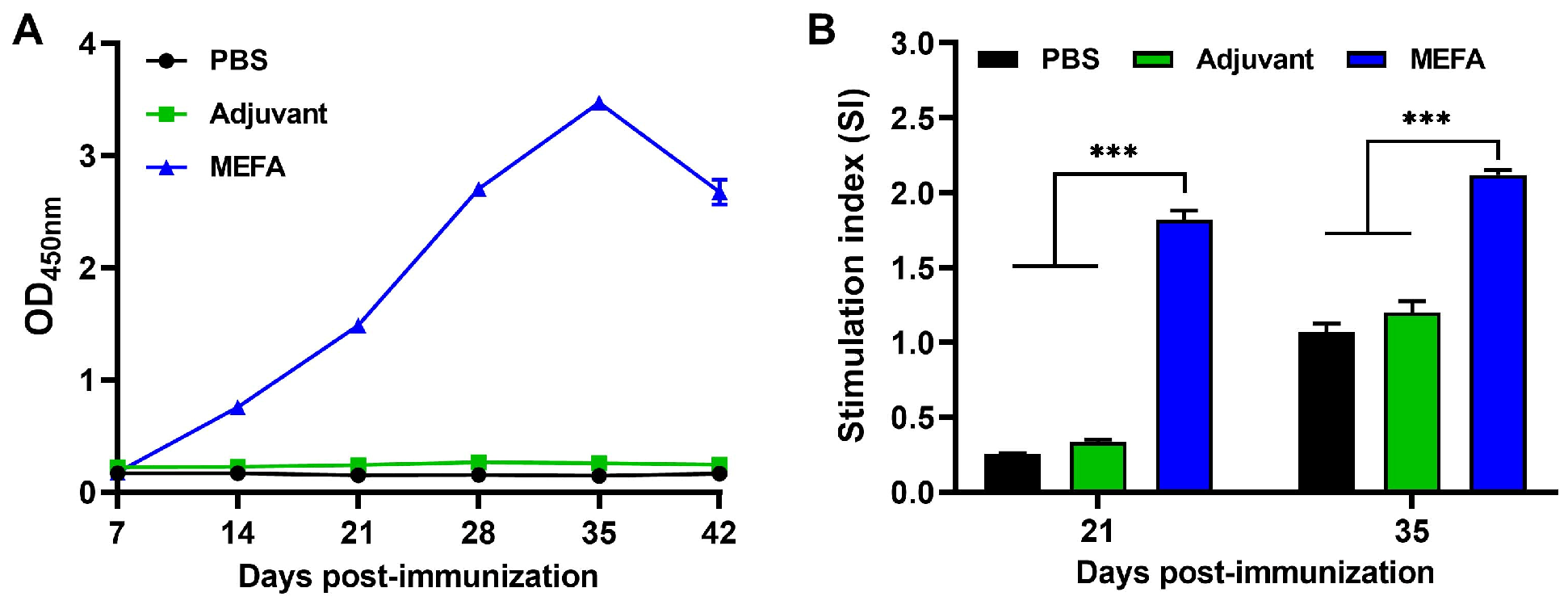
3.6. MEFA Protein Induced High Levels of Specific IgG Antibody in Mice
3.7. MEFA Effectively Stimulated Proliferation of Murine Splenic Lymphocytes
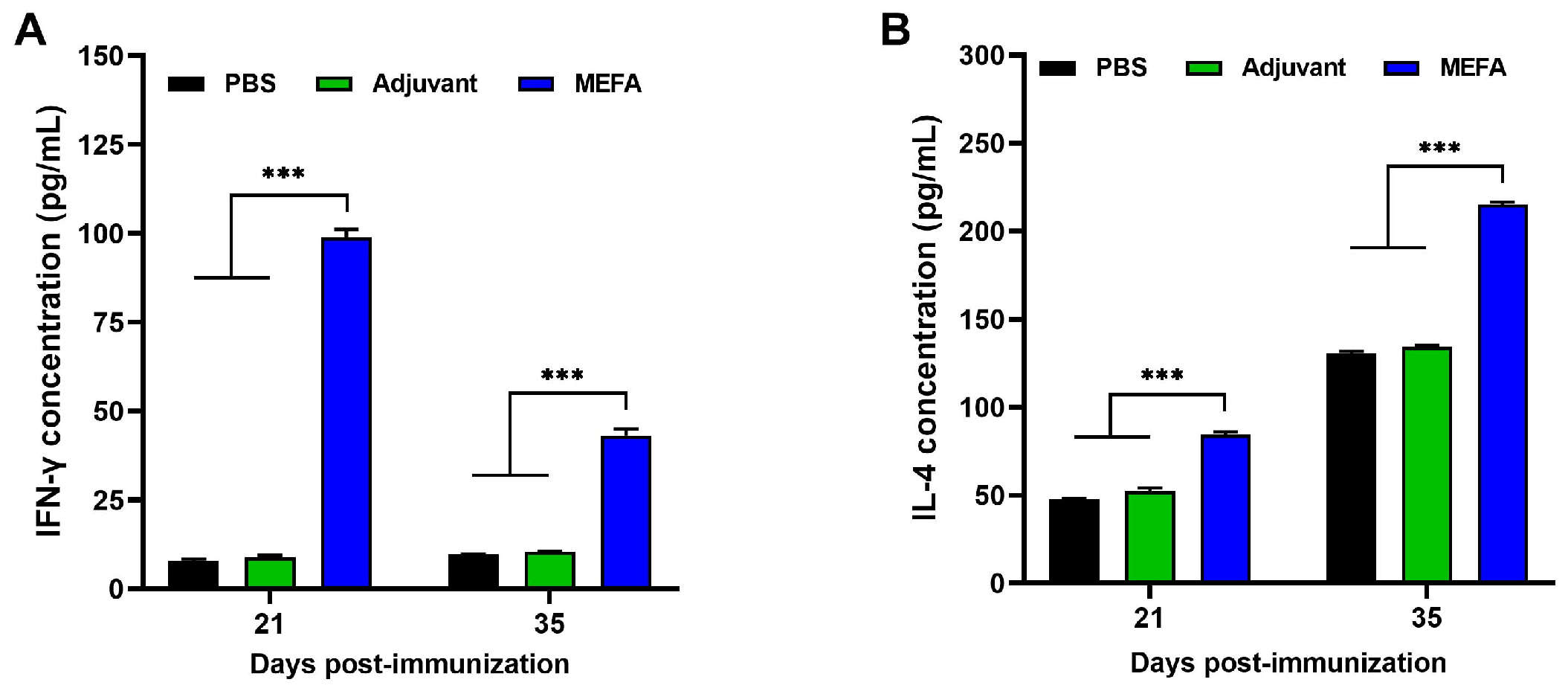
3.8. MEFA Stimulated the Production of Substantial Amounts of IFN-γ and IL-4 in Splenic Lymphocytes
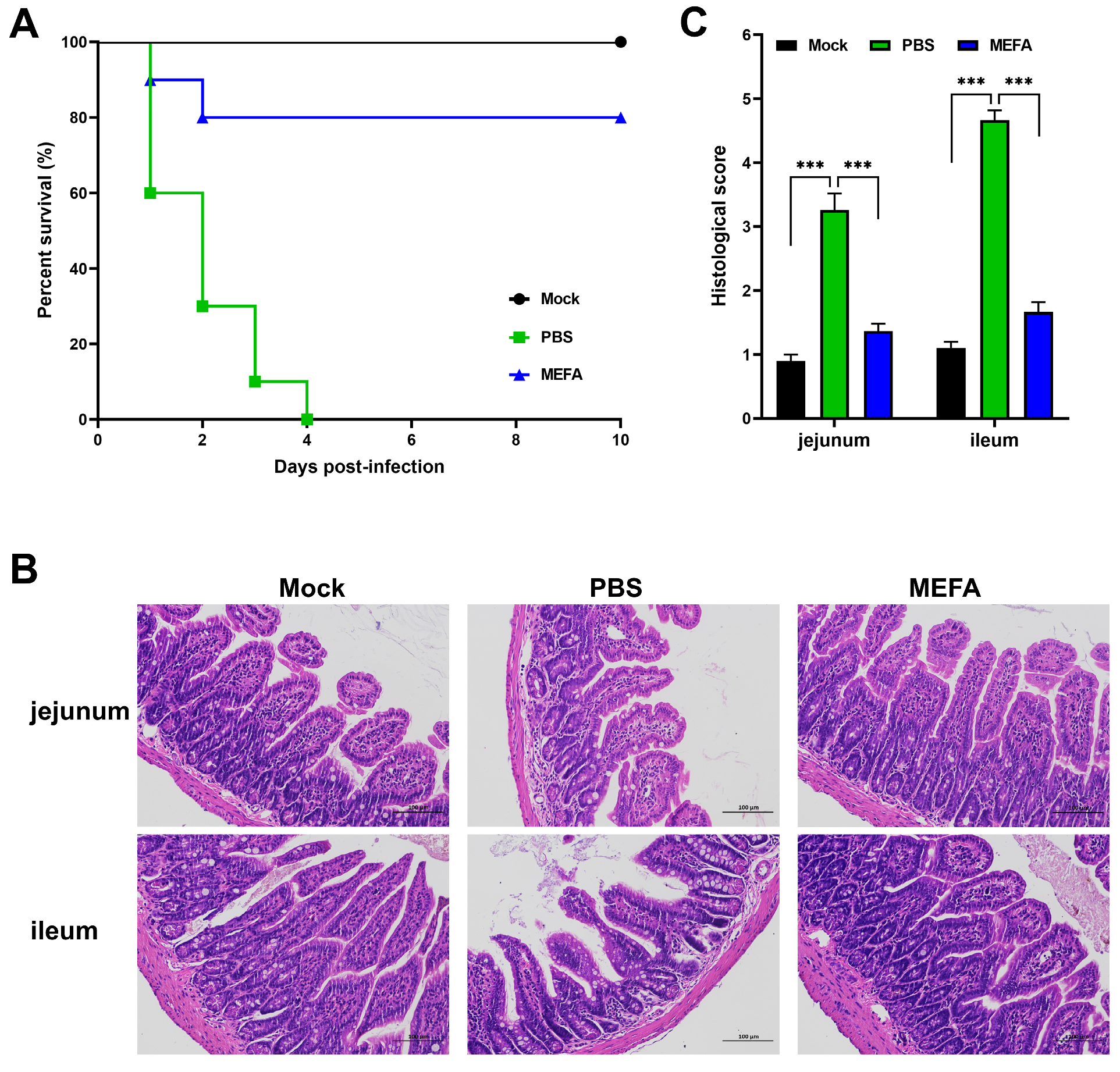
3.9. MEFA Protein Conferred Protection Against Lethal ETEC Challenge in Mice
3.10. MEFA Protein Prevented Intestinal Tissue Damage Induced by Lethal ETEC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Middelkoop, A.; Kettunen, H.; Guan, X.; Vuorenmaa, J.; Tichelaar, R.; Gambino, M.; Rydal, M.P.; Molist, F. Effect of dietary tall oil fatty acids and hydrolysed yeast in SNP2-positive and SNP2-negative piglets challenged with F4 enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, M.; Kushwaha, S.K.; Wu, Y.; van Haastrecht, P.; Klein-Sousa, V.; Lutz, V.T.; Bejaoui, S.; Jensen, C.M.C.; Bojer, M.S.; Song, W.; et al. Diversity and phage sensitivity to phages of porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0080724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Mentzer, A.; Svennerholm, A.M. Colonization factors of human and animal-specific enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-Erro, J.; Pastor, Y.; Gamazo, C. Targeting Enterotoxins: Advancing vaccine development for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli ETEC. Toxins 2025, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, I.; Parvej, S.M.D.; Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Lauder, K.L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Protein-based vaccine candidate MecVax broadly protects against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli intestinal colonization in a rabbit model. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e0027223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Xia, P.; Nandre, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G. Review of newly identified functions associated with the heat-labile toxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. Recent advances in nontoxic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin and its derivative adjuvants. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudner, B.C.; Giuliani, M.M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Rappuoli, R.; Junginger, H.E.; Giudice, G.D. The concomitant use of the LTK63 mucosal adjuvant and of chitosan-based delivery system enhances the immunogenicity and efficacy of intranasally administered vaccines. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3837–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.D.; Norton, E.B. The Mucosal Vaccine Adjuvant LT(R192G/L211A) or dmLT. mSphere 2018, 3, 00215-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.C.; Mathias-Santos, C.; Greene, C.J.; King-Lyons, N.D.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Hajishengallis, G.; Ferreira, L.C.; Connell, T.D. Intradermal administration of the Type II heat-labile enterotoxins LT-IIb and LT-IIc of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli enhances humoral and CD8+ T cell immunity to a co-administered antigen. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, C.J.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Medina-Armenteros, Y.; Farinha-Arcieri, L.E.; Ventura, A.M.; Boscardin, S.B.; Sbrogio-Almeida, M.E.; Ferreira, L.C. Parenteral adjuvant effects of an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli natural heat-labile toxin variant. Front. Immunol. 2014, 4, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Jia, H.; et al. Development of an oral gut-targeted rabies virus-like particles (RVLPs) vaccine with mucosal immune adjuvant LTB via delivering of localized-release microparticles. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2025, 14, 2515406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadri, F.; Svennerholm, A.M.; Faruque, A.S.; Sack, R.B. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in developing countries: Epidemiology, microbiology, clinical features, treatment, and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Nawrocki, E.M.; M’ikanatha, N.M.; Dudley, E.G. Host species shapes genotype, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence profiles of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) from livestock in the United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e00749-00724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Gao, T.; Liu, W.; Yang, K.; Yuan, F.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.; Guo, R.; et al. Prevalence, molecular characterization, and antimicrobial resistance profile of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates from pig farms in China. Foods 2025, 14, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Li, X.; Duan, X.; Yang, L.; Luo, B.; Wang, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, P. Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae EBY100/pYD1-FaeG: A candidate for an oral subunit vaccine against F4+ ETEC infection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e0181724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Qiu, T.; Ai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, D.; Luo, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Qiu, J. Advances of computational methods enhance the development of multi-epitope vaccines. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 26, bbaf055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Farhan, M.H.R.; Yang, X.H.; Guo, Y.; Sui, Y.X.; Chu, J.H.; Huang, L.; Cheng, G. A review on the development of bacterial multi-epitope recombinant protein vaccines via reverse vaccinology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282 Pt 5, 136827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xie, N.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, T.; Peng, J.; Li, R. Development of a novel multi-epitope vaccine against streptococcus anginosus infection via reverse vaccinology approach. Immunology 2025, 175, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, A.; Gibellini, M.; Gin, T.; Vangroenweghe, F.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Bauerfeind, R.; Bonilauri, P.; Labarque, G.; Hidalgo, A. Prevalence of virulence factors in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with post-weaning diarrhoea in Europe. Porc. Health Manag. 2016, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, N.; Gammeltoft, S.; Brunak, S. Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, D.W.A.; Jones, D.T. The PSIPRED protein analysis workbench: 20 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W402–W407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, R.; Mahajan, S.; Overton, J.A.; Dhanda, S.K.; Martini, S.; Cantrell, J.R.; Wheeler, D.K.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. The immune epitope database (IEDB): 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D339–D343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Park, H.; Heo, L.; Seok, C. GalaxyWEB server for protein structure prediction and refinement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W294–W297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Bui, H.H.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Bourne, P.E.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. ElliPro: A new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A. PDBsum: Summaries and analyses of PDB structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapin, N.; Lund, O.; Bernaschi, M.; Castiglione, F. Computational immunology meets bioinformatics: The use of prediction tools for molecular binding in the simulation of the immune system. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; She, Y.; Fu, F.; Xu, C. Production of a new tetravalent vaccine targeting fimbriae and enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 88, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Shen, S.; Dai, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, K. Methamphetamine induces intestinal inffammatory injury via Nod-Like receptor 3 protein (NLRP3) infammasome overexpression. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 8515–8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierick, M.; Van der Weken, H.; Rybarczyk, J.; Vanrompay, D.; Devriendt, B.; Cox, E. Porcine and bovine forms of lactoferrin inhibit growth of porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and degrade its virulence factors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00524-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tusiime, M.; Mwiine, F.N.; Afayoa, M.; Arojjo, S.; Erume, J. Molecular characterization of Escherichia coli virulence markers in neonatal and postweaning piglets from major pig-producing districts of Uganda. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Xia, J.; Cui, M.; Huang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, S.; et al. Genomic traits of multidrug resistant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates from diarrheic pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1244026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoling, A.; von Mentzer, A.; Svennerholm, A.M. Implications of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli genomics for vaccine development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lee, K.H.; Zhang, W. Multiepitope fusion antigen: MEFA, an epitope- and structure-based vaccinology platform for multivalent vaccine development. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2414, 151–169. [Google Scholar]
- Rendon-Marin, S.; Rincon-Tabares, D.S.; Tabares-Guevara, J.H.; Arbelaez, N.; Forero-Duarte, J.E.; Diaz, F.J.; Robledo, S.M.; Hernandez, J.C.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Evaluation of the safety and immunogenicity of a multiple epitope polypeptide from canine distemper virus (CDV) in mice. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Anvari, S.; Ptacek, G.; Upadhyay, I.; Kaminski, R.W.; Sack, D.A.; Zhang, W. A broadly immunogenic polyvalent Shigella multiepitope fusion antigen protein protects against Shigella sonnei and Shigella flexneri lethal pulmonary challenges in mice. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e0031623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhu, Y.; Aili, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ding, J. Bioinformatics analysis of HPV-68 E6 and E7 oncoproteins for designing a therapeutic epitope vaccine against HPV infection. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 81, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanshahi, Z.; Hashempour, A.; Ghasabi, F.; Moayedi, J.; Musavi, Z.; Dehghani, B.; Sharafi, H.; Joulaei, H. First report on molecular docking analysis and drug resistance substitutions to approved HCV NS5A and NS5B inhibitors amongst Iranian patients. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi Mamaghani, A.; Arab-Mazar, Z.; Heidarzadeh, S.; Ranjbar, M.M.; Molazadeh, S.; Rashidi, S.; Niazpour, F.; Naghi Vishteh, M.; Bashiri, H.; Bozorgomid, A.; et al. In-silico design of a multi-epitope for developing sero-diagnosis detection of SARS-CoV-2 using spike glycoprotein and nucleocapsid antigens. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2021, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, D.S.; Tzelepis, F.; Cunha, M.G.; Soares, I.S.; Rodrigues, M.M. The pan HLA DR-binding epitope improves adjuvant-assisted immunization with a recombinant protein containing a malaria vaccine candidate. Immunol. Lett. 2004, 92, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Sun, P.; Li, T.; Yan, X.; Ye, J.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H.; Pan, C. Production of promising heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) B subunit-based self-assembled bioconjugate nanovaccines against infectious diseases. Vaccines 2024, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Thornburg, T.; Holderness, K.; Suo, Z.; Cao, L.; Lim, T.; Avci, R.; Pascual, D.W. Serum Antibodies Protect against Intraperitoneal Challenge with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 632396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Sack, D.A.; Zhang, W. Genetic fusions of a CFA/I/II/IV MEFA (multiepitope fusion antigen) and a toxoid fusion of heat-stable toxin (STa) and heat-labile toxin (LT) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) retain broad anti-cfa and antitoxin antigenicity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.M., Jr.; Seo, H.; Zhang, W.; Sack, D.A. A multi-epitope fusion antigen candidate vaccine for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli is protective against strain B7A colonization in a rabbit model. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, N.; Pandey, R.K.; Prajapati, V.K. Exploring Leishmania secretory proteins to design B and T cell multi-epitope subunit vaccine using immunoinformatics approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlChalabi, R.; Al-Rahim, A.; Omer, D.; Suleiman, A.A. Immunoinformatics design of multi-epitope peptide-based vaccine against Haemophilus influenzae strain using cell division protein. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2023, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

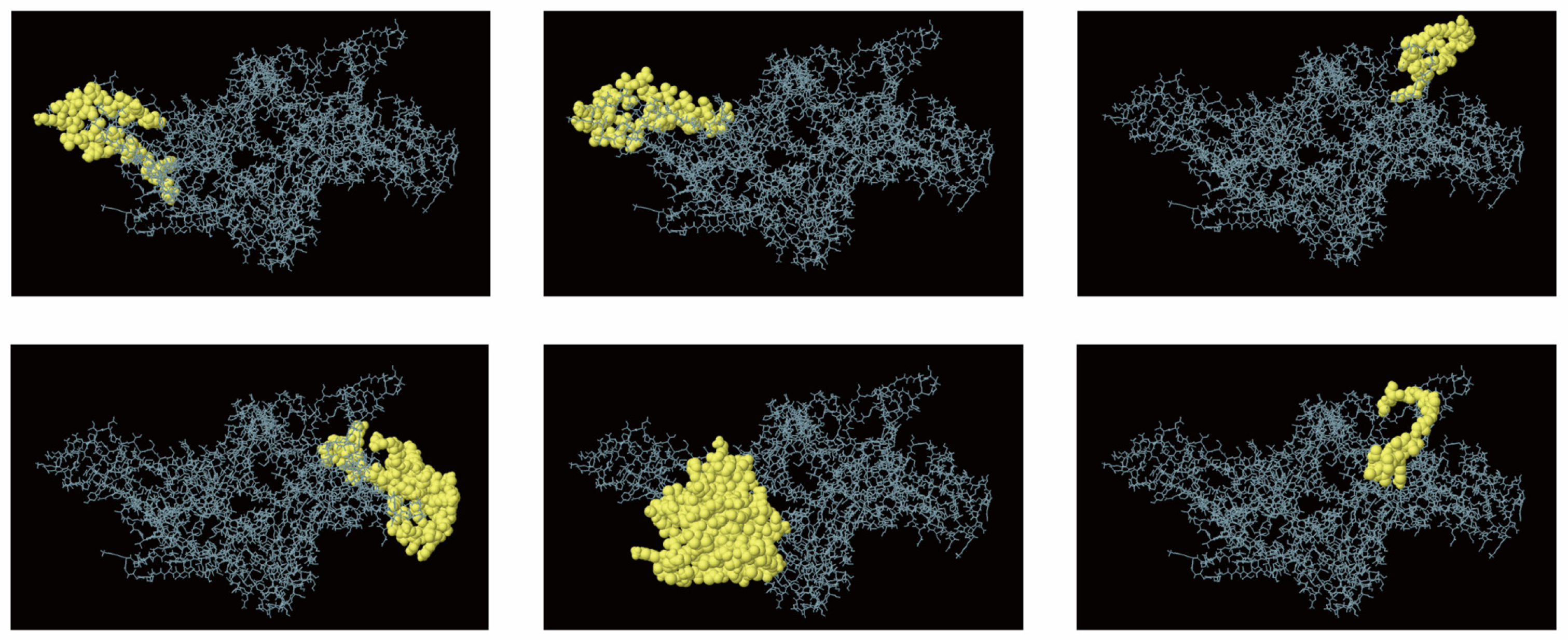
| Fimbrial Proteins | Dominant Epitopes | Selected Epitope Region |
|---|---|---|
| K88/FaeG | 23-MTGDFNGSVD-32 | 84–198 |
| 36-TITADDYRQK-45 | ||
| 61-LNDLTNGGTK-70 | ||
| 84-GRTKEAFATP-93 | ||
| 106-FTDYEGASVELRKPDGGTNK-125 | ||
| 134-PMKNAGGTKVGAVKVN-149 | ||
| 157-LGRGGVTSADGEL-168 | ||
| 184-LPRGSELSAGSAAAA-198 | ||
| K99/FanC | 40-IEPEVNGNRT-49 | 70–166 |
| 70-LKPAPGSNDC-79 | ||
| 103-SGNTAAKG-110 | ||
| 119-NVGNGSGGANIN-130 | ||
| 152-QLKKDDRAPSNGGYK-166 | ||
| 987P/FasA | 23-AAPAENNTSQA-33 | 97–180 |
| 67-LKATGKGPAK-76 | ||
| 97-AGNNNTGSDTKYLVPASNDTSASG-120 | ||
| 163-GTTTGNPDTNGGVTAGTV-180 | ||
| F41/Fim41a | 128-KNSGDNTEL-136 | 128–249 |
| 154-DGDTTDS-160 | ||
| 208-MPGQSASTSYS-218 | ||
| 233-WDDLSHPNYTSADKASYLSYGSGVSAG-249 | ||
| F18/FedF | 74 IPSSSGTLTCQAGT 87 | 74–262 |
| 115 NESQWGQQSQ 124 | ||
| 151 AQTYPLSSGD 160 | ||
| 148 PPNAQTYPLSSGDLK 162 | ||
| 226 PNQNDMPSSN 235 | ||
| 251 YVQPDATGSWYD 262 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Y.; Yang, K.; Sun, Q.; Guo, W.; Yang, Z.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Guo, R.; Ding, K.; Liao, C.; et al. Design and Evaluation of a Broadly Multivalent Adhesins-Based Multi-Epitope Fusion Antigen Vaccine Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection. Vaccines 2025, 13, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13101057
Jia Y, Yang K, Sun Q, Guo W, Yang Z, Duan Z, Zhang S, Guo R, Ding K, Liao C, et al. Design and Evaluation of a Broadly Multivalent Adhesins-Based Multi-Epitope Fusion Antigen Vaccine Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection. Vaccines. 2025; 13(10):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13101057
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Yanyan, Ke Yang, Qijuan Sun, Weiqi Guo, Zhihao Yang, Zihan Duan, Shiqu Zhang, Rongxian Guo, Ke Ding, Chengshui Liao, and et al. 2025. "Design and Evaluation of a Broadly Multivalent Adhesins-Based Multi-Epitope Fusion Antigen Vaccine Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection" Vaccines 13, no. 10: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13101057
APA StyleJia, Y., Yang, K., Sun, Q., Guo, W., Yang, Z., Duan, Z., Zhang, S., Guo, R., Ding, K., Liao, C., & Wang, S. (2025). Design and Evaluation of a Broadly Multivalent Adhesins-Based Multi-Epitope Fusion Antigen Vaccine Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection. Vaccines, 13(10), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13101057







