Analysis of Acute Phase Response Using Acute Phase Proteins Following Simultaneous Vaccination of Lumpy Skin Disease and Foot-and-Mouth Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.; Ha, J.; Moon, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, W.; Lee, C.; Kim, D.; Yi, J. Increased ruminoreticular temperature and body activity after Foot-and-Mouth vaccination in pregnant Hanwoo (Bos Taurus coreanae) cows. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenfeldt, C.; Heegaard, P.M.H.; Stockmarr, A.; Tjørnehøj, K.; Belsham, G.J. Analysis of the acute phase responses of Serum Amyloid A, Haptoglobin and Type 1 Interferon in cattle experimentally infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, A.A.; Patel, M.; Somagond, A.; Jeyakumar, S.; Selvan, R.P.T.; Gowane, G.R.; Krishnaswamy, N.; Joyappa, D.H.; Ramesha, K.; Vijayapillai, U.; et al. Effect of foot-and-mouth disease vaccination on acute phase response and milk production in the Holstein-Friesian crossbred cow. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2023, 51, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Kim, B.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.M.; Shin, S.H.; Hwan, S.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, B.; Park, J.H.; Lee, M.J. The HSP70-fused foot-and-mouth disease epitope elicits cellular and humoral immunity and drives broad-spectrum protective efficacy. npj Vaccines 2021, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Moon, J.; Ha, J.; Kim, D.; Yi, J. Effect of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccination on Acute Phase Immune Response and Anovulation in Hanwoo (Bos taurus coreanae). Vaccines 2021, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H. Requirements for improved vaccines against foot-and-mouth disease epidemics. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2013, 2, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ko, E.Y.; Jung, S.; Jeong, H.K.; Han, J.H.; Son, J.H. Effects of Foot-and-mouth disease vaccination location and injection device on the incidence of site lesions in pork. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sareyyüpoğlu, B.; Uzar, S.; Saraç, F.; Enül, H.; Adıay, C.; Çokçalışkan, C.; Arslan, A.; Öztap, G.; Gülyaz, V. Immune response against lumpy skin disease after simultaneous vaccination of cattle with sheep pox and goat pox and foot and mouth disease vaccines. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 281, 109726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, L.; Ward, M.P. The spread of lumpy skin disease virus across Southeast Asia: Insights from surveillance. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2023, 2023, 3972359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.J.; Lee, E.S.; Yoo, H.S. Lumpy skin disease as an emerging infectious disease. J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 24, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porco, A.; Chea, S.; Sours, S.; Nou, V.; Groenenberg, M.; Agger, C.; Tum, S.; Chhuon, V.; Sorn, S.; Hong, C.; et al. Case report: Lumpy skin disease in an endangered wild banteng (Bos javanicus) and initiation of a vaccination campaign in domestic livestock in Cambodia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1228505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulatu, E.; Feyisa, A. Review: Lumpy Skin Disease. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, J.; Boumart, Z.; Daouam, S.; Arkam, A.E.; Bamouh, Z.; Jazouli, M.; Tadlaoui, K.O.; Fihri, O.F.; Gavrilov, B.; Harrak, M.E. Development and evaluation of an inactivated lumpy skin disease vaccine for cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 245, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, J.; Bellaiche, M.; Gross, E.; Elad, D.; Oved, Z.; Haimovitz, M.; Wasserman, A.; Friedgut, O.; Stram, Y.; Bumbarov, V.; et al. Appearance of Skin Lesions in Cattle Populations Vaccinated against Lumpy Skin Disease: Statutory Challenge. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1500–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abutarbush, S.M.; Hananeh, W.M.; Ramadan, W.; Sheyab, O.M.A.; Alnajjar, A.R.; Zoubi, I.G.A.; Knowles, N.J.; Bachanek-Bankowska, K.; Tuppurainen, E.S.M. Adverse reactions to field vaccination against lumpy skin disease in Jordan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, e213–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoulos, P.D.; Chaintoutis, S.C.; Dovas, C.I.; Polizopoulou, Z.S.; Brellou, G.D.; Agianniotaki, E.I.; Tasioudi, K.E.; Chondrokouki, E.; Papadopoulos, O.; Karatzias, H.; et al. Investigation on the incidence of adverse reactions, viraemia and haematological changes following field immunization of cattle using a live attenuated vaccine against lumpy skin disease. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Yao, K.; Wang, S.; Yin, J.; Ma, Z.; Yin, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Understanding the research advances on lumpy skin disease: A comprehensive literature review of experimental evidence. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1065894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanović, M.; Dietze, L.; Milićević, V.; Radojičić, S.; Valčić, M.; Moritz, T.; Hoffmann, B. Humoral immune response to repeated lumpy skin disease virus vaccination and performance of serological tests. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshovi, H.R.; Norian, R.; Azadmehr, A.; Ahangarn, N.A. Immune response characteristics of Capri pox virus vaccines following emergency vaccination of cattle against lumpy skin disease virus. Iran. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 9, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Alsemgeest, S.P.; Kalsbeek, H.C.; Wensing, T.; Koeman, J.P.; van Ederen, A.M.; Gruys, E. Concentrations of serum amyloid-A (SAA) and haptoglobin (HP) as parameters of inflammatory diseases in cattle. Vet. Q. 1994, 16, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trela, M.; Domańska, D.; Witkowska-Piłaszewicz, O. Diagnostic Use of Serum Amyloid A in Dairy Cattle. Agriculture 2022, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, G.H., Jr. Serum amyloid A—A review. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Lu, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, H.; Liu, X. Adverse effects of inactivated foot-and-mouth disease vaccine—Possible causes analysis and countermeasures. World J. Vaccines 2018, 8, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gari, G.; Abie, G.; Gizaw, D.; Wubete, A.; Kidane, M.; Asgedom, H.; Bayissa, B.; Ayelet, G.; Oura, C.; Roger, F.; et al. Evaluation of the safety, immunogenicity and efficacy of three capripoxvirus vaccine strains against lumpy skin disease virus. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3256–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awate, S.; Babiuk, L.A.; Mutwiri, G. Mechanisms of action of adjuvants. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikcael, C.A.; Nakhla, O.E.; Mohamed, N.A. Study on the capability of a dual capripox vaccine in protection of cattle against LSD infection. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2017, 24, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrotek, S.; LeGrand, E.K.; Dzialuk, A.; Alcock, J. Let fever do its job: The meaning of fever in the pandemic era. Evol. Med. Public Health 2020, 9, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
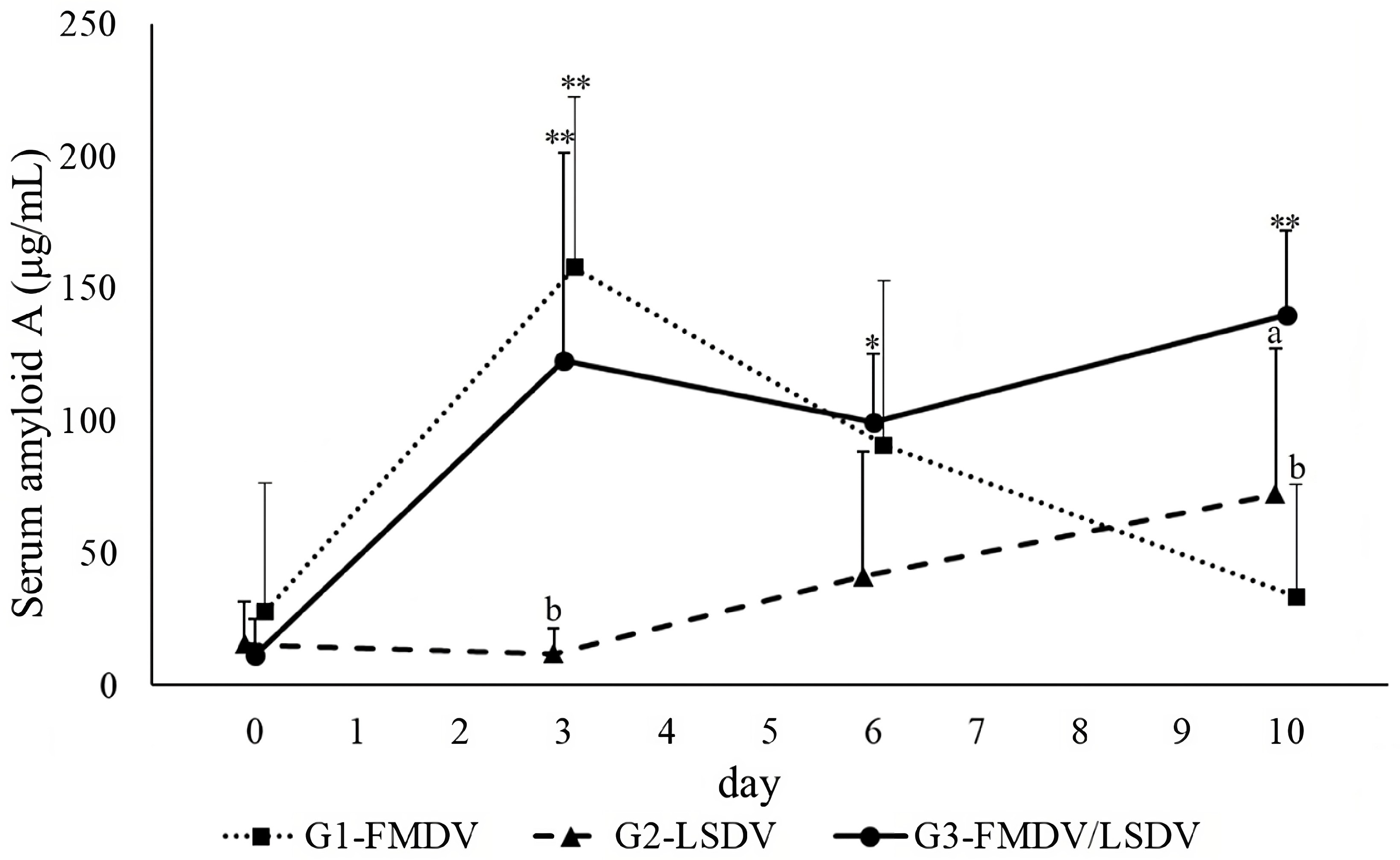
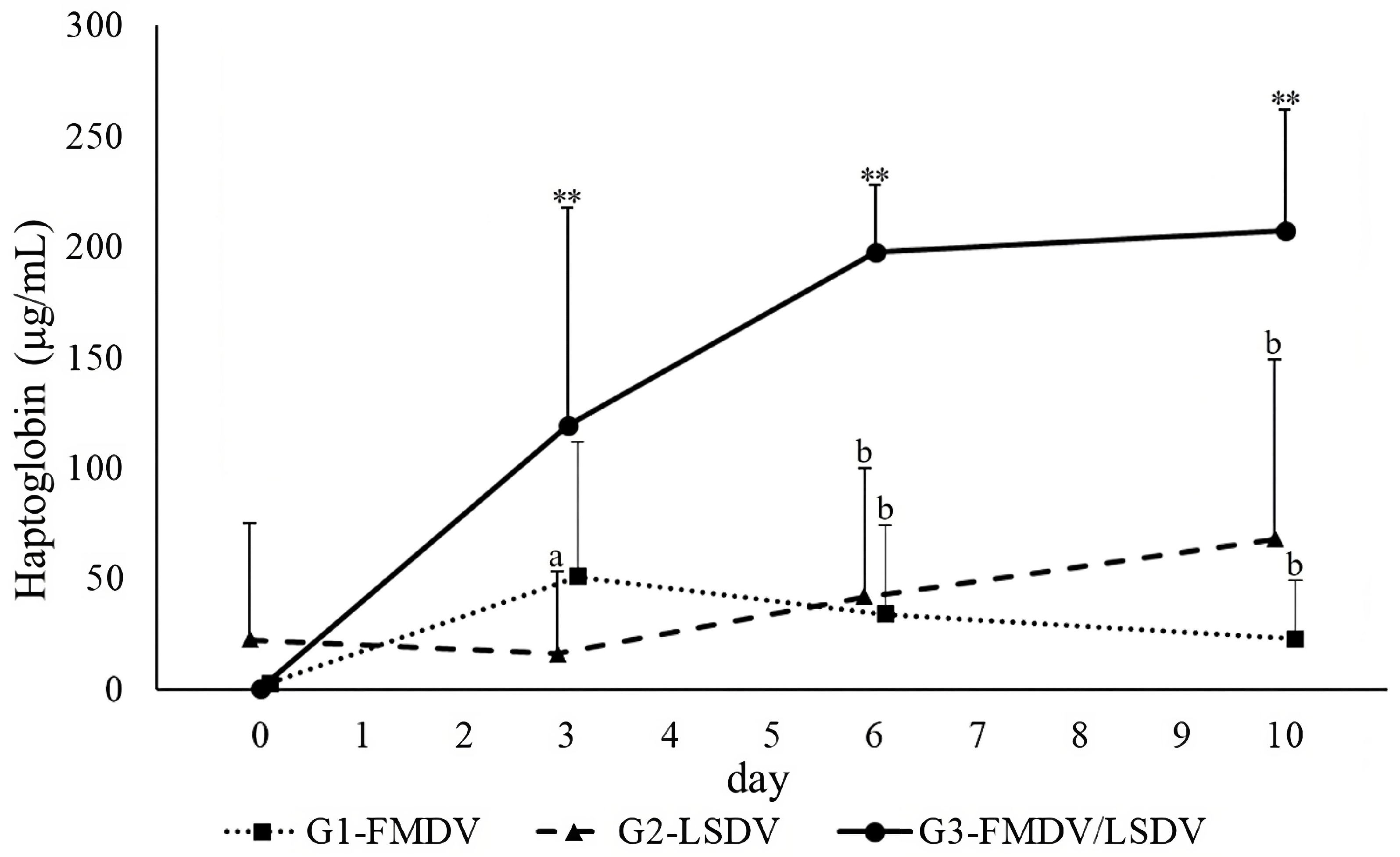
| Serum Amyloid A | |||||
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F-Ratio | p-Value |
| GROUP | 2 | 43,101.063 | 21,550.531 | 6.576 | 0.010 |
| TIME | 3 | 61,193.208 | 20,397.736 | 12.107 | <0.001 |
| GROUP × TIME | 6 | 67,421.821 | 11,236.970 | 6.670 | <0.001 |
| Haptoglobin | |||||
| Source | DF 1 | SS 2 | MS 3 | F-ratio | p-value |
| GROUP | 2 | 151,889.219 | 75,944.610 | 19.184 | <0.001 |
| TIME | 3 | 85,499.298 | 28,499.766 | 13.034 | <0.001 |
| GROUP × TIME | 6 | 86,930.508 | 1448.842 | 6.626 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Noh, H.; Hong, L.; Chun, E.; Kim, E.; Ro, Y.; Choi, W. Analysis of Acute Phase Response Using Acute Phase Proteins Following Simultaneous Vaccination of Lumpy Skin Disease and Foot-and-Mouth Disease. Vaccines 2024, 12, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12050556
Kim J, Kim D, Noh H, Hong L, Chun E, Kim E, Ro Y, Choi W. Analysis of Acute Phase Response Using Acute Phase Proteins Following Simultaneous Vaccination of Lumpy Skin Disease and Foot-and-Mouth Disease. Vaccines. 2024; 12(5):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12050556
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jiyeon, Danil Kim, Hyoeun Noh, Leegon Hong, Eunwoo Chun, Eunkyung Kim, Younghye Ro, and Woojae Choi. 2024. "Analysis of Acute Phase Response Using Acute Phase Proteins Following Simultaneous Vaccination of Lumpy Skin Disease and Foot-and-Mouth Disease" Vaccines 12, no. 5: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12050556
APA StyleKim, J., Kim, D., Noh, H., Hong, L., Chun, E., Kim, E., Ro, Y., & Choi, W. (2024). Analysis of Acute Phase Response Using Acute Phase Proteins Following Simultaneous Vaccination of Lumpy Skin Disease and Foot-and-Mouth Disease. Vaccines, 12(5), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12050556






