Mortality of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease following Introduction of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Greenland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Study Population, Definitions, and Data Sources
2.3. Statistical Methods and Measures of Mortality
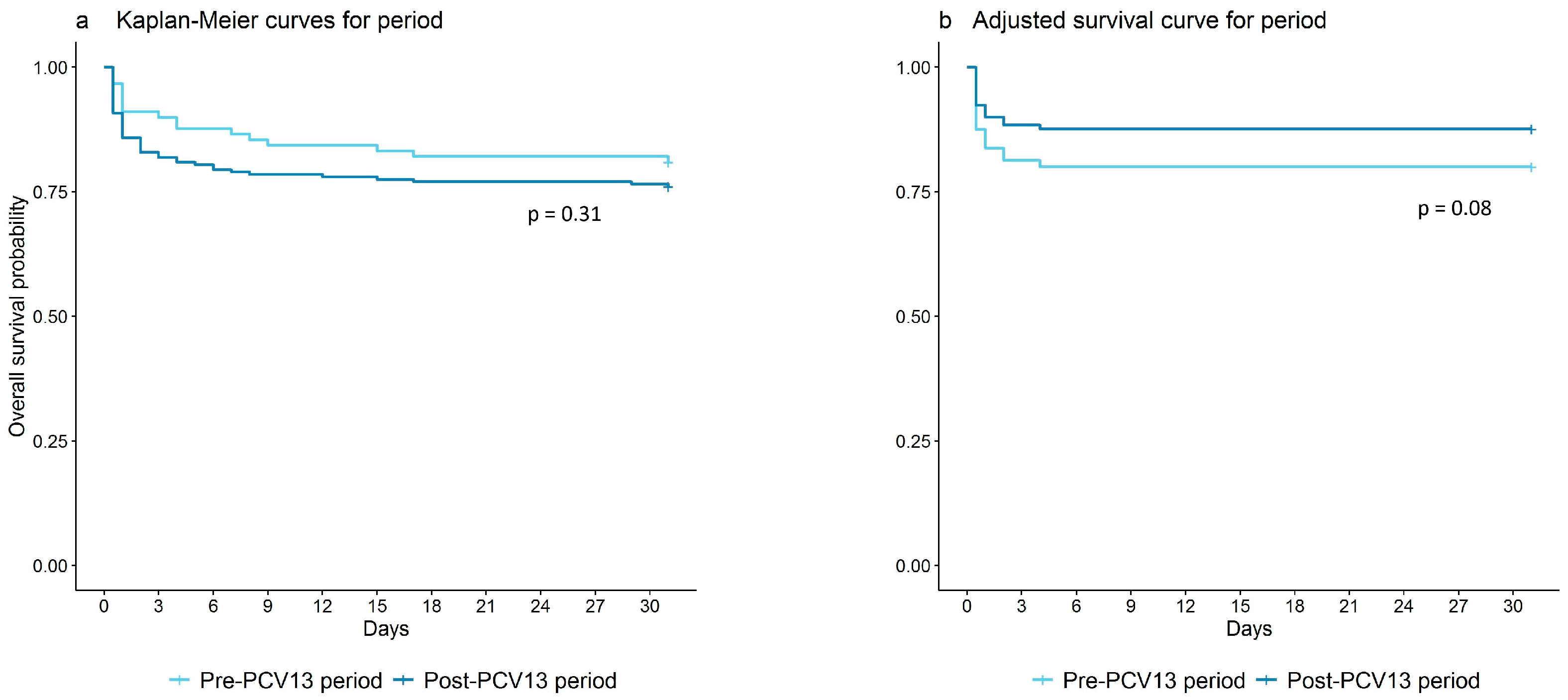
3. Results
3.1. Mortality Rates
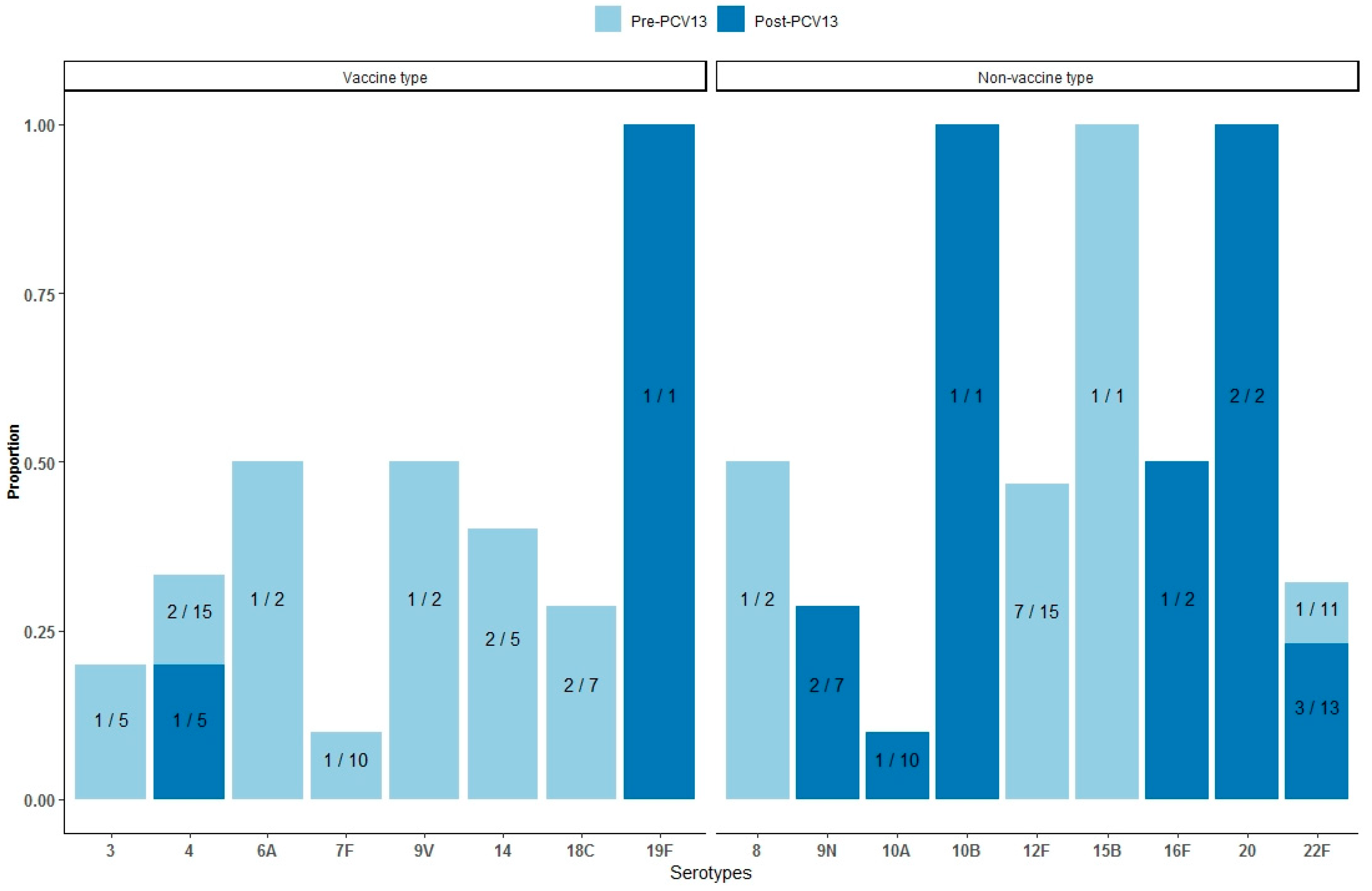
3.2. Mortality by Serotypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalcin, D.; Sieswerda, L.; Dubois, S.; Ulanova, M. Epidemiology of invasive pneumococcal disease in indigenous and non-indigenous adults in northwestern Ontario, Canada, 2006–2015. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navne, J.E.; Koch, A.; Slotved, H.C.; Andersson, M.; Melbye, M.; Ladefoged, K.; Borresen, M. Effect of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on nasopharyngeal carriage by respiratory pathogens among Greenlandic children. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2017, 76, 1309504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navne, J.E.; Borresen, M.L.; Slotved, H.C.; Hoffmann-Petersen, I.T.; Andersson, M.; Hoffmann, S.; Koch, A. Population-Based Study of Incidence, Risk Factors, and Mortality for Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Greenland; Statens Serum Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, M.; Parkinson, A.J.; Bulkow, L.R.; Fitzgerald, M.A.; Peters, H.V.; Parks, D.J. The epidemiology of invasive pneumococcal disease in Alaska, 1986-1990--ethnic differences and opportunities for prevention. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 170, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, A.J.; Bruce, M.G.; Zulz, T.; The International Circumpolar Surveillance Steering Committee. International Circumpolar Surveillance, An Arctic Network for the Surveillance of Infectious Diseases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, J.; Poulsen, P.; Ladefoged, K. Invasive pneumococcal disease in Greenland. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2004, 63, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Ladefoged, K.; Poulsen, P.; Koch, A. Population-based Survey of Invasive Bacterial Diseases, Greenland, 1995–2004. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, K.A.; Andersson, M.; Slotved, H.-C.; Koch, A. Effectiveness of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine on Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Greenland. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleist, F.S. Landslægeembedets Nyhedsbrev. 2010. Available online: https://nun.gl/-/media/landslaegeembedet/udgivelser/aarsrapport-2010/kap-5/aarsberetning-2010-dk-kapitel-5-boernevaccinationer.pdf?la=da&hash=D7CC918C695854294C4DF2E52AE3F602 (accessed on 16 October 2020).
- Albertsen, N.; Fencker, I.M.; Noasen, H.E.; Pedersen, M.L. Immunisation rates among children in Nuuk. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2018, 77, 1426948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for childhood immunization—WHO position paper. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2007, 82, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Alanee, S.R.; McGee, L.; Jackson, D.; Chiou, C.C.; Feldman, C.; Morris, A.J.; Ortqvist, A.; Rello, J.; Luna, C.M.; Baddour, L.M.; et al. Association of serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae with disease severity and outcome in adults: An international study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harboe, Z.B.; Thomsen, R.W.; Riis, A.; Valentiner-Branth, P.; Christensen, J.J.; Lambertsen, L.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Konradsen, H.B.; Benfield, T.L. Pneumococcal serotypes and mortality following invasive pneumococcal disease: A population-based cohort study. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, D.M.; Harboe, Z.B.; Sanders, E.A.; Ndiritu, M.; Klugman, K.P.; Ruckinger, S.; Dagan, R.; Adegbola, R.; Cutts, F.; Johnson, H.L.; et al. Association of serotype with risk of death due to pneumococcal pneumonia: A meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, B.; Kalin, M.; Örtqvist, Å.; Liljequist, B.O.; Almela, M.; Marrie, T.J.; Mufson, M.A.; Torres, A.; Woodhead, M.A.; Svenson, S.B.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae causing invasive disease in 5 countries. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Greenland. Greenland in Figures 2021. 18th Revised Edition Ed. 2021. Available online: https://stat.gl/publ/en/GF/2021/pdf/Greenland%20in%20Figures%202021.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Albertsen, N.; Lynge, A.R.; Skovgaard, N.; Olesen, J.S.; Pedersen, M.L. Coverage rates of the children vaccination programme in Greenland. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2020, 79, 1721983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, N.N. Easy way to learn standardization: Direct and indirect methods. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2000, 7, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division. The 2022 Revision of World Population Prospects. Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/ (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Kelsey, J.L.; Gold, E.B. Observational Epidemiology. In International Encyclopedia of Public Health, 2nd ed.; Quah, S.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 295–307. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics Greenland. StatBank Greenland. 1989. Available online: https://stat.gl/ (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2021: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Oligbu, G.; Collins, S.; Sheppard, C.L.; Fry, N.K.; Slack, M.; Borrow, R.; Ladhani, S.N. Childhood Deaths Attributable to Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in England and Wales, 2006–2014. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harboe, Z.B.; Dalby, T.; Weinberger, D.M.; Benfield, T.; Molbak, K.; Slotved, H.C.; Suppli, C.H.; Konradsen, H.B.; Valentiner-Branth, P. Impact of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccination in invasive pneumococcal disease incidence and mortality. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgalis, L.; Mozalevskis, A.; de Aragon, M.V.M.; Garrido-Estepa, M. Changes in the pneumococcal disease-related hospitalisations in Spain after the replacement of 7-valent by 13-valent conjugate vaccine. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-Dreps, S.; Blette, B.; Briceño, R.; Alemán, J.; Hudgens, M.G.; Moreno, G.; Ordoñez, A.; Rocha, J.; Weber, D.J.; Amaya, E. Changes in the incidence of pneumonia, bacterial meningitis, and infant mortality 5 years following introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in a “3+0” schedule. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, I.; Ardanuy, C.; Cubero, M.; Benitez, M.A.; Linares, J.; Pallares, R. Declining mortality from adult pneumococcal infections linked to children’s vaccination. J. Infect. 2016, 72, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.C.; Schuchat, A. Epidemiology of pneumococcal infections in the elderly. Drugs Aging 1999, 15 (Suppl. 1), 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helferty, M.; Rotondo, J.L.; Martin, I.; Desai, S. The epidemiology of invasive pneumococcal disease in the Canadian North from 1999 to 2010. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2013, 72, 21606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reslan, L.; Youssef, N.; Boutros, C.F.; Assaf-Casals, A.; Fayad, D.; Khafaja, S.; Akl, F.; Finianos, M.; Rizk, A.A.; Shaker, R.; et al. The impact of vaccination on the burden of invasive pneumococcal disease from a nationwide surveillance program in Lebanon: An unexpected increase in mortality driven by non-vaccine serotypes. Expert Rev. Vaccine 2022, 21, 1905–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, K.; Spindler, C.; Ortqvist, A.; Kalin, M.; Sandgren, A.; Kuhlmann-Berenzon, S.; Henriques-Normark, B. Clonal and capsular types decide whether pneumococci will act as a primary or opportunistic pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueggemann, A.B.; Peto, T.E.; Crook, D.W.; Butler, J.C.; Kristinsson, K.G.; Spratt, B.G. Temporal and geographic stability of the serogroup-specific invasive disease potential of Streptococcus pneumoniae in children. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoek, A.J.; Andrews, N.; Waight, P.A.; George, R.; Miller, E. Effect of serotype on focus and mortality of invasive pneumococcal disease: coverage of different vaccines and insight into non-vaccine serotypes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benadji, A.; Duval, X.; Danis, K.; Hoen, B.; Page, B.; Vernet-Garnier, V.; Strady, C.; Brieu, N.; Maulin, L.; Roy, C.; et al. Relationship between serotypes, disease characteristics and 30-day mortality in adults with invasive pneumococcal disease. Infection 2021, 50, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Period | Population | Observed Deaths | PYRS | World Weighted 1 Deaths | World Weighted 1 PYRS | MR (95% CI) | MR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed 2 | World Weighted 1,2 | ||||||
| Total Period (1995–2020) | Total, Greenland (1995–2020) | 12,189 | 1,309,007 | 19,058.1 | 1,309,007 | 9.3 (9.1–9.5) | 14.6 (14.4–14.8) |
| Pre-PCV13 Period (1995–2010) | Total, Greenland (1995–2020) | 7336 | 809,145 | 13,233.4 | 809,145 | 9.1 (8.9–9.3) | 16.4 (16.1–16.6) |
| Post-PCV13 Period (2010–2020) | Total, Greenland (1995–2020) | 5363 | 550,399 | 7062.6 | 550,399 | 9.7 (9.5–10.0) | 12.8 (12.5–13.1) |
| Total Period (1995–2020) | IPD patients, Greenland (1995–2020) | 66 | 20.1 | 61.5 | 20.1 | 3292 (2546–4188) | 3068 (2349–3936) |
| Pre-PCV13 Period (1995–2010) | IPD patients, Greenland (1995–2020) | 49 | 13.7 | 45.7 | 13.7 | 3589 (2655–4745) | 3347 (2448–4469) |
| Post-PCV13 Period (2010–2020) | IPD patients, Greenland (1995–2020) | 17 | 6.4 | 28.4 | 6.4 | 2658 (1548–4255) | 4441 (2961–6402) |
| Total Period (1995–2020) | Pre-PCV13 Period (1995–2010) | Post-PCV13 Period (2010–2020) | MRR (95% CI) 1 | p-Value 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | SMR (95% CI) | SMR (95% CI) | SMR (95% CI) | ||
| Total | 198.8 (156.2–253.1) | 267.6 (202.2–354.1) | 114.2 (71.0–183.7) | 0.43 (0.25–0.74) | 0.003 |
| Sex 3 | |||||
| Female | 191.7 (125.0–294.0) | 238.4 (150.2–378.4) | 88.1 (28.4–273.3) | 0.37 (0.11–1.26) | 0.111 |
| Male | 202.3 (151.1–271.0) | 288.1 (202.6–409.7) | 121.9 (72.2–205.9) | 0.42 (0.23–0.80) | 0.008 |
| Age group | |||||
| <5 | 443.8 (166.6–1182.5) | 502.4 (188.5–1338.6) | 0 | 0 | - |
| 5–39 | 435.5 (195.6–969.3) | 557.7 (250.5–1241.3) | 0 | 0 | - |
| 40–59 | 518.5 (372.2–722.1) | 563.3 (391.5–810.7) | 374.3 (168.2–833.2) | 0.66 (0.28–1.60) | 0.362 |
| ≥60 | 86.9 (56.7–133.3) | 88.6 (47.7–164.6) | 85.4 (47.3–154.3) | 0.96 (0.41–2.27) | 0.935 |
| Region 4,5 | |||||
| Nuuk | 194.4 (135.9–278.0) | 355.8 (240.4–526.6) | 59.5 (24.8–142.9) | 0.17 (0.06–0.44) | <0.001 |
| North | 539.9 (242.6–1201.9) | 761.1 (316.8–1828.6) | 220.1 (31.0–1562.8) | 0.29 (0.03–2.48) | 0.258 |
| South | 672.7 (372.6–1214.8) | 703.9 (352.0–1407.5) | 601.7 (194.1–1865.7) | 0.85 (0.23–3.22) | 0.817 |
| East | 145.4 (54.6–387.3) | 103.8 (26.0–415.2) | 242.3 (60.6–968.7) | 2.33 (0.33–16.56) | 0.397 |
| West | 204.6 (123.3–339.3) | 186.2 (96.9–357.8) | 240.2 (107.9–534.7) | 1.29 (0.46–3.63) | 0.629 |
| Ethnicity 6 | |||||
| Inuit | 200.9 (157.3–256.7) | 259.9 (195.3–345.9) | 123.5 (76.8–198.6) | 0.48 (0.27–0.83) | 0.009 |
| Non-Inuit | 113.6 (28.4–454.3) | 464.1 (116.1–1855.9) | 0 | 0 | - |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | |||||
| Low (0) | 285.0 (219.3–370.3) | 355.6 (262.8–481.2) | 178.5 (105.7–301.5) | 0.50 (0.27–0.92) | 0.026 |
| Moderate (1–2) | 44.7 (18.6–107.4) | 75.7 (28.4–201.6) | 17.0 (2.4–120.4) | 0.22 (0.03–2.01) | 0.181 |
| High (<3) | 211.5 (88.0–508.1) | 246.7 (79.6–764.8) | 174.2 (43.6–696.6) | 0.71 (0.12–4.23) | 0.703 |
| S. pneumoniae serotypes | |||||
| Vaccine type (VT) 7 | 110.6 (62.8–194.7) | 112.0 (60.2–208.1) | 104.2 (26.1–416.6) | 0.93 (0.20–4.25) | 0.926 |
| Non-vaccine type (NVT) | 135.0 (87.1–209.2) | 303.4 (163.3–563.9) | 86.8 (46.7–161.3) | 0.29 (0.12–0.69) | 0.005 |
| Not serotyped | 503.3 (349.8–724.3) | 531.5 (359.2–786.6) | 377.9 (141.8–1006.9) | 0.71 (0.25–2.04) | 0.527 |
| Not isolated | 283.2 (117.9–680.3) | 289.6 (108.7–771.7) | 259.9 (36.6–1845.4) | 0.90 (0.10–8.03) | 0.923 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alexandrova Nikolova, K.; Andersson, M.; Slotved, H.-C.; Koch, A. Mortality of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease following Introduction of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Greenland. Vaccines 2024, 12, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12020179
Alexandrova Nikolova K, Andersson M, Slotved H-C, Koch A. Mortality of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease following Introduction of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Greenland. Vaccines. 2024; 12(2):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12020179
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlexandrova Nikolova, Kristiana, Mikael Andersson, Hans-Christian Slotved, and Anders Koch. 2024. "Mortality of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease following Introduction of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Greenland" Vaccines 12, no. 2: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12020179
APA StyleAlexandrova Nikolova, K., Andersson, M., Slotved, H.-C., & Koch, A. (2024). Mortality of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease following Introduction of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Greenland. Vaccines, 12(2), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12020179






