Oral Vaccine Formulation for Immunocastration Using a Live-Attenuated Salmonella ΔSPI2 Strain as an Antigenic Vector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transformation of Attenuated S. Typhimurium with Plasmids Carrying the GnRXG/Q Gene
2.2. Intracellular Survival Assay of S. Typhimurium in Murine Macrophages RAW264.7
2.3. Antigen Expression and Detection via Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Preparation of Inoculum for Immunization
2.5. Mouse Immunization
2.6. Measurement of Antibody Levels Against GnRXG/Q
2.7. Measurement of Serum Testosterone Levels
2.8. Histological Evaluation of Testes
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
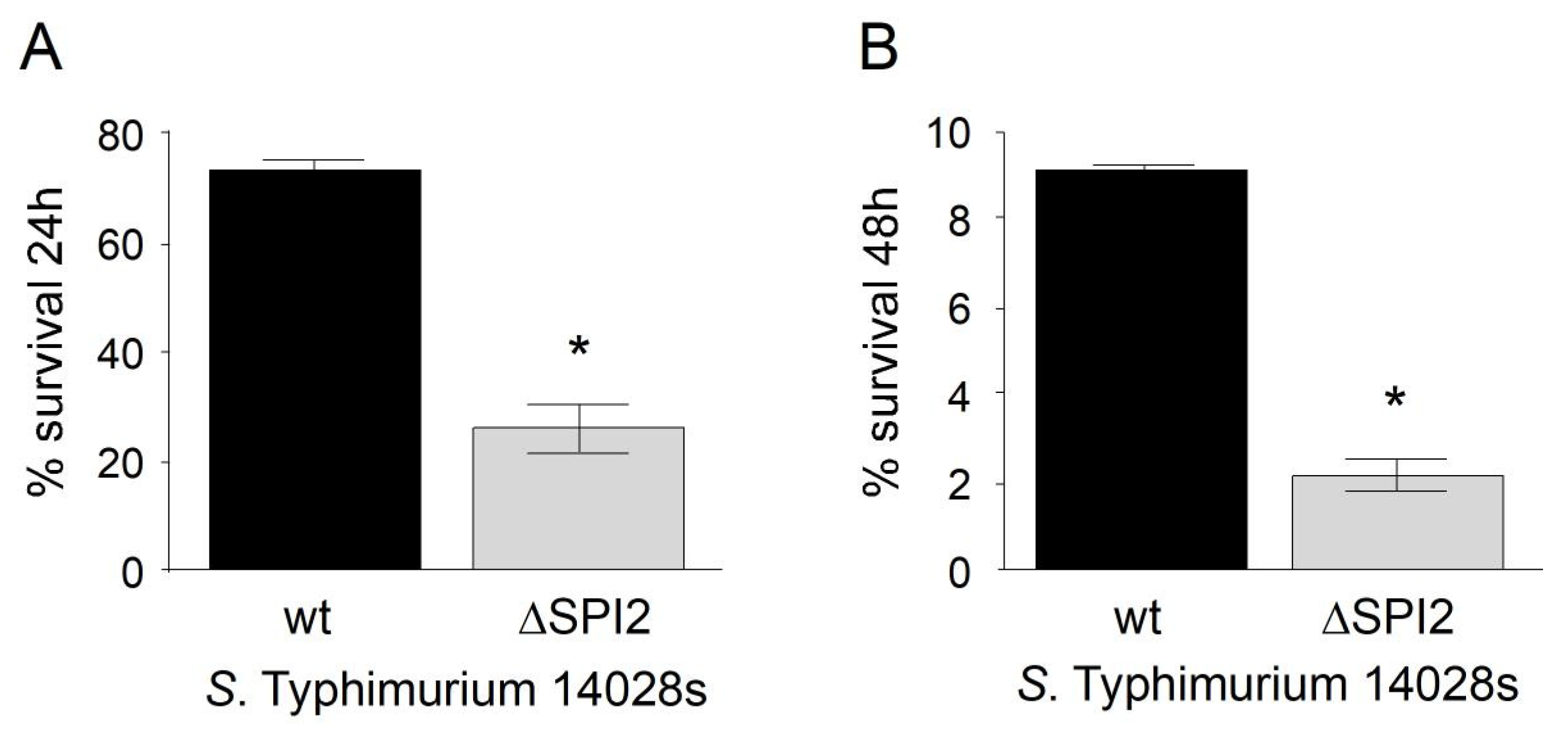
3.1. Intracellular Survival of S. Typhimurium in Murine Macrophages RAW264.7
3.2. Antigen Expression Detection via Western Blot Analysis
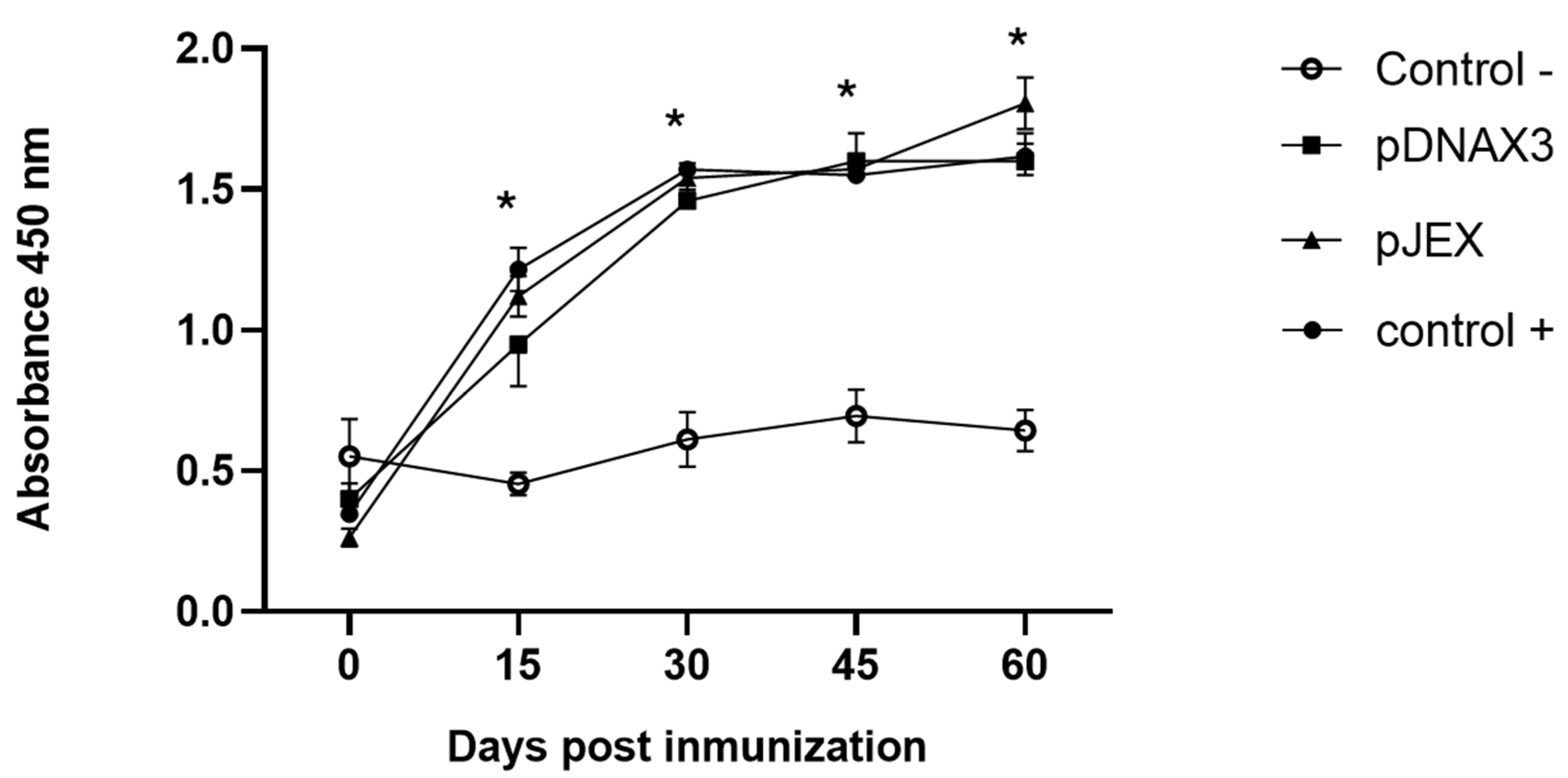
3.3. Antibody Levels Against GnRXG/Q
3.4. Measurement of Serum Testosterone Levels
3.5. Histological Testicular Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, Y.J.; Kim, D.G.; Nam, H.M.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Song, C.S.; Seo, K.H.; Kim, H.M.; Choi, I.S. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Immunocastration Vaccine Composed of Gonadotrophin-Releasing Hormone Conjugated with Salmonella Typhimurium Flagellin in Rats. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2012, 47, e47–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, A.; Yoshida, N.; Nakada, K.; Inohue, Y.; Hisaeda, K.; Inaba, T.; Domoto, N.; Ishiguro, Y.; Itoh, M.; Takahashi, E.; et al. Efficiency of Immunocastration with an Anti-Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Vaccine on Cryptorchid Bulls. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 85, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, C.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, M. GnRH-Immunocastration: An Alternative Method for Male Animal Surgical Castration. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1248879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D. Immunization against GnRH in Male Species (Comparative Aspects). Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2000, 60, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, L.; Neira-Carrillo, A.; Paredes, R.; Cortés, M.; Bucarey, S.; Arias, J.L. Chitosan Formulations Improve the Immunogenicity of a GnRH-I Peptide-Based Vaccine. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 369, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font i Furnols, M.; Garcia-Regueiro, J.A.; Diaz, I.; Bahí, M.; Velarde, A.; Oliver, M.; Martinell, M. Efecto de La Inmunocastración de Cerdos En Las Características de Calidad de Canal y Carne, Los Niveles de Androstenona y Escatol y La Composición En Ácidos Grasos. Eurocarne 2009, 181, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J.; Miller, L.; Crawford, P.; Ritchey, J.; Ross, M.; Fagerstone, K. GnRH Immunocontraception of Male Cats. Theriogenology 2004, 62, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, J.S.; Favre, R.N.; García, M.F.; Stornelli, M.C.; Sangache, W.C.; Rearte, R.; de la Sota, L.; Stornelli, M.A. Immunocontraception of Male Domestic Cats Using GnRH Vaccine Improvac. Theriogenology 2023, 198, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, C.H.; Phon, B.; Parhar, I. The Role of GnIH in Biological Rhythms and Social Behaviors. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 728862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.-J.; Moon, Y.-C.; Cho, I.-H.; Yeh, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-E.; Chang, W.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Song, C.-S.; Kim, H.-Y.; Park, K.-K.; et al. Induction of Castration by Immunization of Male Dogs with Recombinant Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)-Canine Distemper Virus (CDV) T Helper Cell Epitope P35. J. Vet. Sci. 2005, 6, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Jones, R.; Kraneburg, C.; Cochran, A.; Samoylov, A.; Wright, J.; Hutchinson, C.; Picut, C.; Cattley, R.; Martin, D.; et al. Phage Constructs Targeting Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone for Fertility Control: Evaluation in Cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020, 22, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, L.; Gong, T.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Co-Delivery of Antigen and Dual Adjuvants by Aluminum Hydroxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Immune Responses. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrlep, M.; Segula, B.; Zajec, M.; Kastelic, M.; Kosorok, S.; Fazarinc, G.; Candek-Potokar, M. Effect of Immunocastration (IMPROVAC®) in Fattening Pigs I: Growth Performance, Reproductive Organs and Malodorous Compounds. Slov. Vet. Res. 2010, 47, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Agudelo, J.; Estrada, J.; Guzman, P. Immunocastration: A Humane and Effective Alternative to Surgical Castration of Adult Boar. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Pecu. 2011, 24, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- R Huenchullan, P.; Vidal, S.; Larraín, R.; Saénz, L. Effectiveness of a New Recombinant antiGnRH Vaccine for Immunocastration in Bulls. Animals 2021, 11, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-i-Furnols, M.; Gispert, M.; Soler, J.; Diaz, M.; Garcia-Regueiro, J.A.; Diaz, I.; Pearce, M.C. Effect of Vaccination against Gonadotrophin-Releasing Factor on Growth Performance, Carcass, Meat and Fat Quality of Male Duroc Pigs for Dry-Cured Ham Production. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunius, C.; Zamaratskaia, G.; Andersson, K.; Chen, G.; Norrby, M.; Madej, A.; Lundström, K. Early Immunocastration of Male Pigs with Improvac®—Effect on Boar Taint, Hormones and Reproductive Organs. Vaccine 2011, 29, 9514–9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatayakul-Chantler, S.; Jackson, J.; Stegner, J.; King, V.; Rubio, L.; Howard, R.; Lopez, E.; Walker, J. Immunocastration of Bos Indicus x Brown Swiss Bulls in Feedlot with Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Vaccine Bopriva Provides Improved Performance and Meat Quality. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 3718–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Jiang, X.; Liu, G.; Sadiq, A.; Farooq, U.; Wassie, T.; Saleem, A.H.; Zubair, M. New Trends in Immunocastration and Its Potential to Improve Animal Welfare: A Mini Review. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siel, D.; Ubilla, M.J.; Vidal, S.; Loaiza, A.; Quiroga, J.; Cifuentes, F.; Hardman, T.; Lapierre, L.; Paredes, R.; Sáenz, L. Reproductive and Behavioral Evaluation of a New Immunocastration Dog Vaccine. Animals 2020, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolado-Sarabia, J.L.; Pérez-Linares, C.; Figueroa-Saavedra, F.; Tamayo-Sosa, A.R.; Barreras-Serrano, A.; Sánchez-López, E.; García-Reynoso, I.C.; Ríos-Rincón, F.G.; Rodríguez-Poché, M.Y.; García-Vega, L.A.; et al. Effect of Immunocastration on Behaviour and Blood Parameters (Cortisol and Testosterone) of Holstein Bulls. Austral J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 50, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydhmer, L.; Lundström, K.; Andersson, K. Immunocastration Reduces Aggressive and Sexual Behaviour in Male Pigs. Animal 2010, 4, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-G.; Zhao, H.-N.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, L.; Li, Z.-C.; Li, W.; Wu, H.-Y.; Chuang, K.-P.; Tong, D.-W.; Liu, H.-J. Oral Vaccination with Attenuated Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Expressing Cap Protein of PCV2 and Its Immunogenicity in Mouse and Swine Models. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Xie, Y.; Lin, X.; Xu, W. The Mucoadhesive Nanoparticle-Based Delivery System in the Development of Mucosal Vaccines. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 4579–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breau, C.; Cameron, D.; Desjardins, M.; Lee, B. Oral Immunization Using HgbA in a Recombinant Chancroid Vaccine Delivered by Attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium SL3261 in the Temperature-Dependent Rabbit Model. J. Immunol. Methods 2012, 375, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Rodríguez, M.; Yang, J.; Kader, R.; Alamuri, P.; Curtiss, R.; Clark-Curtiss, J. Live Attenuated Salmonella Vaccines Displaying Regulated Delayed Lysis and Delayed Antigen Synthesis to Confer Protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 815–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark-Curtiss, J.; Curtiss, R. Salmonella Vaccines: Conduits for Protective Antigens. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, J. Salmonella Interactions with Host Cells: Type III Secretion at Work. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 53–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, S.; Ideris, A.; Zakaria, Z.; Omar, A. Attenuated Salmonella typhimurium SV4089 as a Potential Carrier of Oral DNA Vaccine in Chickens. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 264986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, D.W.; Suo, Z.; Cao, L.; Avci, R.; Yang, X. Attenuating Gene Expression (AGE) for Vaccine Development. Virulence 2013, 4, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, C.; Chiara, D.; Agorio, C.; Baz, A.; Pasetti, M.; Schreiber, F.; Dematteis, S.; Martinez, M.; Sztein, M.; Chabalgoity, J. Towards New Immunotherapies: Targeting Recombinant Cytokines to the Immune System Using Live Attenuated Salmonella. Vaccine 2003, 21, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Briones, G.; Donis, R.; Galán, J. Optimization of the Delivery of Heterologous Proteins by the Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Type III Secretion System for Vaccine Development. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5826–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, W.; Hensel, M. Salmonella enterica as a Vaccine Carrier. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vola, M.; Mónaco, A.; Bascuas, T.; Rimsky, G.; Agorio, C.; Chabalgoity, J.; Moreno, M. TLR7 Agonist in Combination with Salmonella as an Effective Antimelanoma Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-Step Inactivation of Chromosomal Genes in Escherichia coli K-12 Using PCR Products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, W.; Huang, X.; Hu, L.; Kopecko, D. Differential Bacterial Survival, Replication, and Apoptosis-Inducing Ability of Salmonella Serovars within Human and Murine Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, A. Expresión de los Antígenos TBPB y PORA de Neisseria Meningitidis en la Cepa Vacuna Salmonella Entérica Serovar Typhimurium χ4550 y Evaluación de Respuesta Inmune en Ratones Vacunados Oralmente. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Austral de Chile, Valdivia, Chile, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Olfert, D.E. CCAC Guidelines on: Choosing an Appropriate Endpoint in Experiments Using Animals for Research, Teaching and Testing; Canadian Council on Animal Care: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, M.; Bi, S.; Ju, C.; Luo, Y. Recent Advances in Oral Vaccines for Animals. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Huang, L.; Jia, C.; Wang, B.; Ed-Dra, A.; Teng, L.; Li, Y.; Yue, M. The Evolution of Vaccines Development across Salmonella Serovars among Animal Hosts: A Systematic Review. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieye, Y.; Ameiss, K.; Mellata, M.; Curtiss, R. The Salmonella Pathogenicity Island (SPI) 1 Contributes More than SPI2 to the Colonization of the Chicken by Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Stratford, R.; Wu, T.; Mckelvie, N.; Bellaby, T.; Hindle, Z.; Sinha, K.A.; Eltze, S.; Mastroeni, P.; Pickard, D.; et al. Salmonella typhi and S. typhimurium Derivatives Harbouring Deletions in Aromatic Biosynthesis and Salmonella Pathogenicity Island-2 (SPI-2) Genes as Vaccines and Vectors. Vaccine 2003, 21, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasova, D.; Sebkova, A.; Havlickova, H.; Sisak, F.; Volf, J.; Faldyna, M.; Ondrackova, P.; Kummer, V.; Rychlik, I. Influence of 5 Major Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands on NK Cell Depletion in Mice Infected with Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyen, F.; Pasmans, F.; Van Immerseel, F.; Morgan, E.; Botteldoorn, N.; Heyndrickx, M.; Volf, J.; Favoreel, H.; Hernalsteens, J.-P.; Ducatelle, R.; et al. A Limited Role for SsrA/B in Persistent Salmonella Typhimurium Infections in Pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 128, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Lü, X.L.; Tian, Q.F.; Zhang, W.J.; Yi, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yu, S.Y. Deletion of Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands SPI-1, 2 and 3 Induces Substantial Morphological and Metabolic Alternation and Protective Immune Potential. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez, S.A.; Mora, A.Y.; Millanao, A.R.; Saavedra, C.P.; Bucarey, S.A.; Mora, G.C.; Villagra, N.A.; Hidalgo, A.A. Transcriptional Regulator MarT Negatively Regulates MarT-Regulated Motility Gene I, a New Gene Involved in Invasion and Virulence of Salmonella enterica. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1430982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.; Hall, J. Tratado de Fisiología Médica, 11th ed.; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, H.; Salazar, P.; Schmidt, N.; Torres, P.; Ossandon, E. Histologia testicular humana comparada, adulto joven y senil. Rev. Chil. Anat. 1999, 17, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.; Santana, A.; Souza, R.; Machado-Neves, M.; Oliveira, J.; dos Santos, E.; de Araujo, M.; da Cruz, T.; Barbosa, L. Testicular Morphometry as a Tool to Evaluate the Efficiency of Immunocastration in Lambs. Anim. Reprod. 2022, 19, e20210041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannesdóttir, S.; Han, X.; Lund, T.; Singh, M.; van der Zee, R.; Roitt, I.; Delves, P. Changes in the Reproductive System of Male Mice Immunized with a GnRH-Analogue Conjugated to Mycobacterial Hsp70. Reproduction 2004, 128, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ogita, K.; Ferro, V.; Kumasawa, K.; Tsutsui, T.; Kimura, T. Immunisation with a Plasmid DNA Vaccine Encoding Gonadotrophin Releasing Hormone (GnRH-1) and T-Helper Epitopes in Saline Suppresses Rodent Fertility. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Group | Transverse Tubulardiameter (µm) ± SEM | No. of Seminiferous Epithelial Cell Layers ± SEM |
|---|---|---|
| Control − | 206.485 ± 21.69 | 6.3 ± 0.57 |
| Control + | 142.908 ± 18.90 *** | 4.26 ± 0.63 *** |
| pDNAX3 | 128.625 ± 21.99 *** | 3.76 ± 0.56 *** |
| pJEX | 137.85 ± 13.27 *** | 4.7 ± 0.59 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bucarey, S.A.; Maldonado, L.D.; Duarte, F.; Hidalgo, A.A.; Sáenz, L. Oral Vaccine Formulation for Immunocastration Using a Live-Attenuated Salmonella ΔSPI2 Strain as an Antigenic Vector. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121400
Bucarey SA, Maldonado LD, Duarte F, Hidalgo AA, Sáenz L. Oral Vaccine Formulation for Immunocastration Using a Live-Attenuated Salmonella ΔSPI2 Strain as an Antigenic Vector. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121400
Chicago/Turabian StyleBucarey, Sergio A., Lucy D. Maldonado, Francisco Duarte, Alejandro A. Hidalgo, and Leonardo Sáenz. 2024. "Oral Vaccine Formulation for Immunocastration Using a Live-Attenuated Salmonella ΔSPI2 Strain as an Antigenic Vector" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121400
APA StyleBucarey, S. A., Maldonado, L. D., Duarte, F., Hidalgo, A. A., & Sáenz, L. (2024). Oral Vaccine Formulation for Immunocastration Using a Live-Attenuated Salmonella ΔSPI2 Strain as an Antigenic Vector. Vaccines, 12(12), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121400






