Deep Mutational Scanning to Predict Escape from Bebtelovimab in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Protein Synthesis and Purification
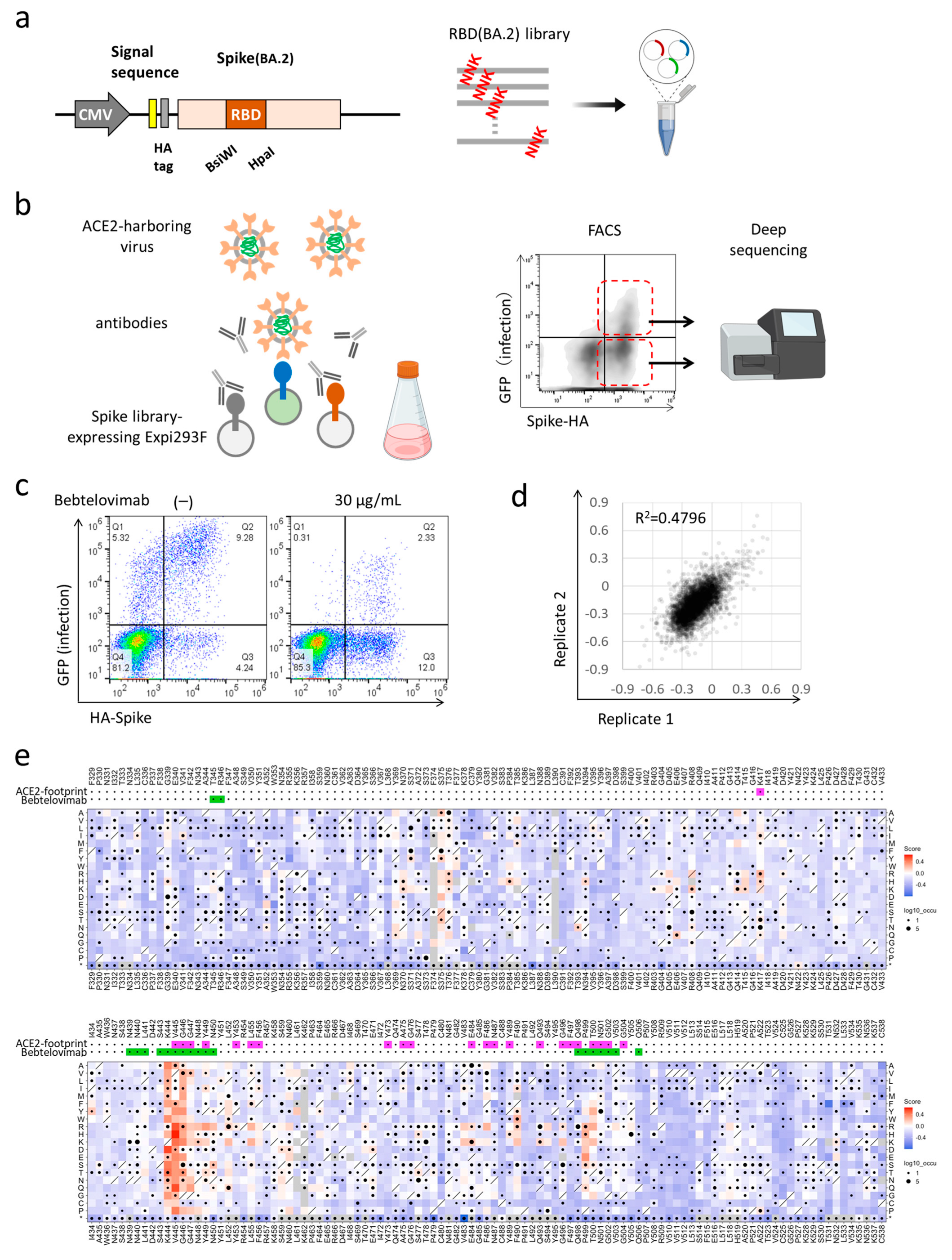
2.3. Deep Mutational Scanning for Escape from Monoclonal Antibodies
2.4. Pseudotyped Virus Neutralization Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Deep Mutational Scanning for Escape from Bebtelovimab in BA.2
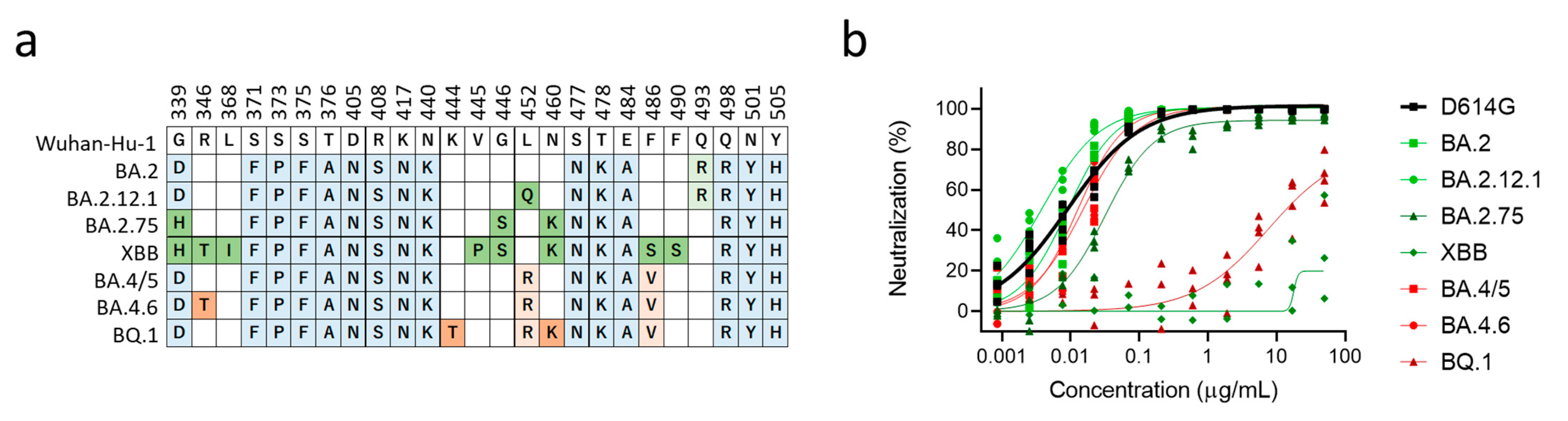
3.2. XBB and BQ.1 Evade Bebtelovimab Neutralization
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ikemura, N.; Taminishi, S.; Inaba, T.; Arimori, T.; Motooka, D.; Katoh, K.; Kirita, Y.; Higuchi, Y.; Li, S.; Suzuki, T.; et al. An engineered ACE2 decoy neutralizes the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and confers protection against infection in vivo. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabn7737. [Google Scholar]
- VanBlargan, L.A.; Errico, J.M.; Halfmann, P.J.; Zost, S.J.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Purcell, L.A.; Kawaoka, Y.; Corti, D.; Fremont, D.H.; Diamond, M.S. An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.H.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature 2021, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasoba, D.; Kosugi, Y.; Kimura, I.; Fujita, S.; Uriu, K.; Ito, J.; Sato, K.; Genotype to Phenotype Japan (G2P-Japan) Consortium. Neutralisation sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 942–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashita, E.; Kinoshita, N.; Yamayoshi, S.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Fujisaki, S.; Ito, M.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Halfmann, P.; Watanabe, S.; Maeda, K.; et al. Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariant BA.2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1475–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yisimayi, A.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Xiao, T.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature 2022, 608, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C. Subvariant ‘soup’ may drive wave. New Sci. 2022, 256, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.K.; Tan, T.J.C.; Narayanan, K.K.; Procko, E. An engineered decoy receptor for SARS-CoV-2 broadly binds protein S sequence variants. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Arimori, T.; Ikemura, N.; Mihara, E.; Kirita, Y.; Ohgitani, E.; Mazda, O.; Motooka, D.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Engineered ACE2 receptor therapy overcomes mutational escape of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giroglou, T.; Cinatl, J., Jr.; Rabenau, H.; Drosten, C.; Schwalbe, H.; Doerr, H.W.; von Laer, D. Retroviral vectors pseudotyped with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus S protein. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9007–9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Wang, W.J.; Wada, S.; McDermott-Roe, C.; Evans, C.S.; Gosis, B.; Morley, M.P.; Rathi, K.S.; Li, J.; Li, K.; et al. The ADP/ATP translocase drives mitophagy independent of nucleotide exchange. Nature 2019, 575, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddox, H.K.; Dingens, A.S.; Hilton, S.K.; Overbaugh, J.; Bloom, J.D. Mapping mutational effects along the evolutionary landscape of HIV envelope. Elife 2018, 7, e34420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Huddleston, J.; Doud, M.B.; Hooper, K.A.; Wu, N.C.; Bedford, T.; Bloom, J.D. Deep mutational scanning of hemagglutinin helps predict evolutionary fates of human H3N2 influenza variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8276–E8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westendorf, K.; Zentelis, S.; Wang, L.; Foster, D.; Vaillancourt, P.; Wiggin, M.; Lovett, E.; van der Lee, R.; Hendle, J.; Pustilnik, A.; et al. LY-CoV1404 (bebtelovimab) potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, T.N.; Greaney, A.J.; Stewart, C.M.; Walls, A.C.; Hannon, W.W.; Veesler, D.; Bloom, J.D. Deep mutational scans for ACE2 binding, RBD expression, and antibody escape in the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 receptor-binding domains. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, D.; Purcell, L.A.; Snell, G.; Veesler, D. Tackling COVID-19 with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Cell 2021, 184, 3086–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Tamura, T.; Zahradnik, J.; Deguchi, S.; Tabata, K.; Anraku, Y.; Kimura, I.; Ito, J.; Yamasoba, D.; Nasser, H.; et al. Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.75 variant. Cell Host Microb. 2022, 30, 1540–1555.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Nirula, A.; Heller, B.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Boscia, J.; Morris, J.; Huhn, G.; Cardona, J.; Mocherla, B.; Stosor, V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody LY-CoV555 in Outpatients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, A.; Ajithdoss, D.; Copin, R.; Zhou, A.; Lanza, K.; Negron, N.; Ni, M.; Wei, Y.; Mohammadi, K.; Musser, B.; et al. REGN-COV2 antibodies prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques and hamsters. Science 2020, 370, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gonzalez-Rojas, Y.; Juarez, E.; Crespo Casal, M.; Moya, J.; Falci, D.R.; Sarkis, E.; Solis, J.; Zheng, H.; Scott, N.; et al. Early Treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, T.N.; Greaney, A.J.; Addetia, A.; Hannon, W.W.; Choudhary, M.C.; Dingens, A.S.; Li, J.Z.; Bloom, J.D. Prospective mapping of viral mutations that escape antibodies used to treat COVID-19. Science 2021, 371, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, T.N.; Greaney, A.J.; Hilton, S.K.; Ellis, D.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.S.; Navarro, M.J.; Bowen, J.E.; Tortorici, M.A.; Walls, A.C.; et al. Deep Mutational Scanning of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Reveals Constraints on Folding and ACE2 Binding. Cell 2020, 182, 1295–1310.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcantara, M.C.; Higuchi, Y.; Kirita, Y.; Matoba, S.; Hoshino, A. Deep Mutational Scanning to Predict Escape from Bebtelovimab in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants. Vaccines 2023, 11, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030711
Alcantara MC, Higuchi Y, Kirita Y, Matoba S, Hoshino A. Deep Mutational Scanning to Predict Escape from Bebtelovimab in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030711
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcantara, Mellissa C., Yusuke Higuchi, Yuhei Kirita, Satoaki Matoba, and Atsushi Hoshino. 2023. "Deep Mutational Scanning to Predict Escape from Bebtelovimab in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030711
APA StyleAlcantara, M. C., Higuchi, Y., Kirita, Y., Matoba, S., & Hoshino, A. (2023). Deep Mutational Scanning to Predict Escape from Bebtelovimab in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants. Vaccines, 11(3), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030711





