An In Silico Deep Learning Approach to Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design: A Hepatitis E Virus Case Study
Abstract
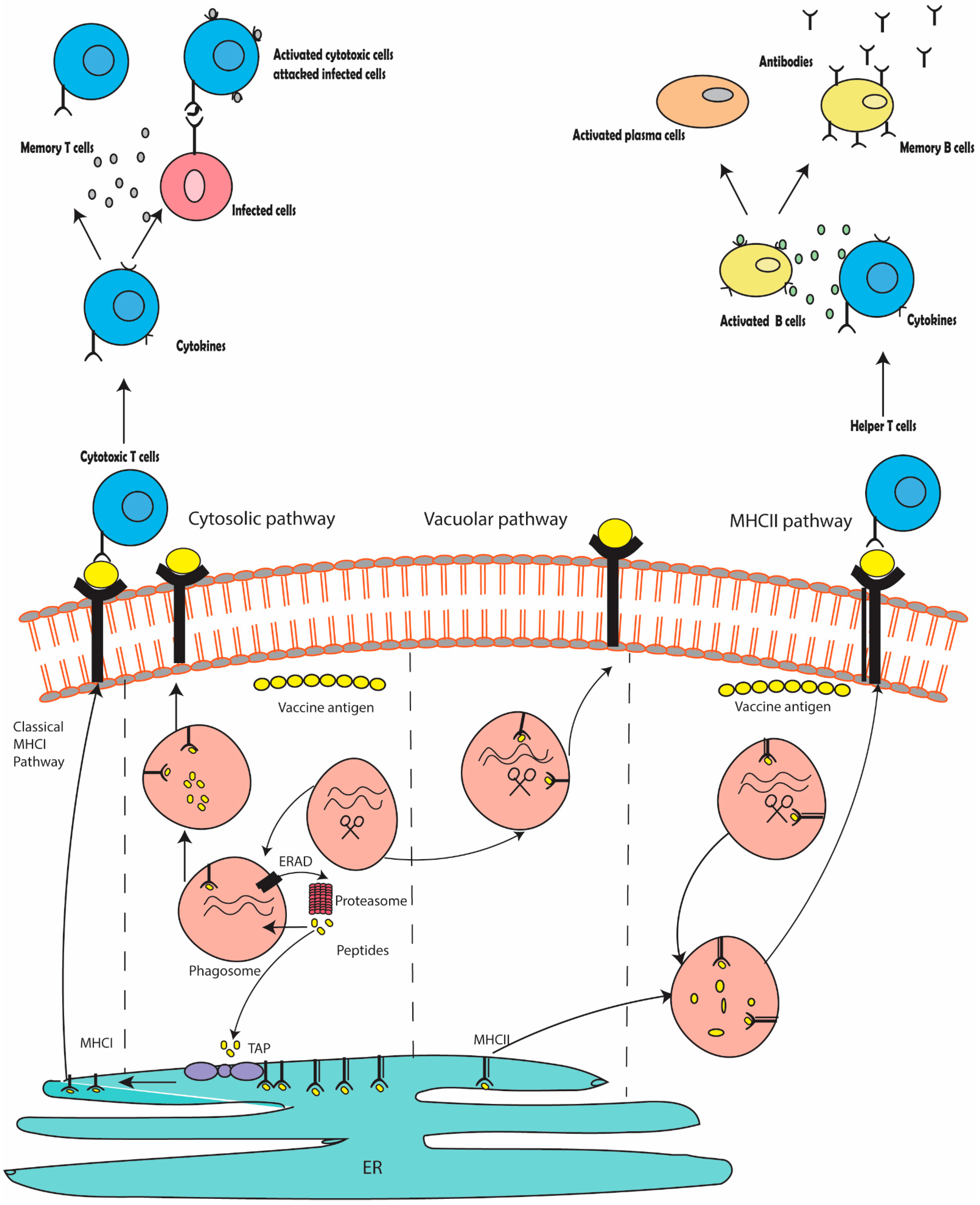
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Selection of conserved regions among the ORF2 region of the selected HEV genotypes (GT1, 3, and 4);
- Screening of experimentally-validated antigenic regions of conserved HEV ORF2 regions through data mining;
- Prediction of T cell, IFN-γ and B cell epitopes;
- Screening of overlapping T cell, IFN-γ and B cell, epitopes and experimentally-validated ORF2 antigenic regions;
- The fusion of immunogenic, antigenic epitopes with appropriate linkers and adjuvant;
- Validation of the proposed vaccine construct (Vu) structure and interactions.

2.1. Sequence Collection
2.2. Consensus Sequence
2.3. Retrieval of Antigenic Regions by Data Mining
2.4. Prediction of Epitopes
2.5. Selection of Epitopes
2.6. Comparative Analysis with Human Proteins
2.7. Construction of the Multi-Epitope Vaccine
2.8. Prediction of the 2D and 3D Structure
2.9. Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Molecular Docking
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Conserved Regions in HEV ORF2
3.2. Prediction of Antigenic Epitopes
3.3. Screening of Experimentally Validated Antigenic Regions through Data Mining
3.4. Designing of the Vaccine Construct (Vu)
3.5. Prediction and Validation of the Vaccine Structure
3.6. Molecular Simulations and Docking Analysis with TLR3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horvatits, T.; Schulze zur Wiesch, J.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Lohse, A.W.; Pischke, S. The clinical perspective on hepatitis E. Viruses 2019, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Casares, P.; Ramos-Romero, C.; Ramirez-Gonzalez, E.; Mas, A. Hepatitis E virus in industrialized countries: The silent threat. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9838041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Hepatitis E vaccine: WHO position paper, May 2015. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2015, 90, 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, M.P.; Scott, R.M.; Joshi, D.M.; Mammen, M.P., Jr.; Thapa, G.B.; Thapa, N.; Myint, K.S.A.; Fourneau, M.; Kuschner, R.A.; Shrestha, S.K. Safety and efficacy of a recombinant hepatitis E vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, A.; Chuah, C.; Majeed, A.B.A.; Leow, C.H.; Lim, B.H.; Leow, C.Y. Current progress of immunoinformatics approach harnessed for cellular-and antibody-dependent vaccine design. Pathog. Glob. Health 2018, 112, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanda, S.K.; Vir, P.; Raghava, G.P. Designing of interferon-gamma inducing MHC class-II binders. Biol. Direct 2013, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagioti, E.; Klenerman, P.; Lee, L.N.; Van Der Burg, S.H.; Arens, R. Features of effective T cell-inducing vaccines against chronic viral infections. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsmon, J.; Caraco, Y.; Ziv-Sefer, S.; Shaikevich, D.; Abramov, E.; Volokhov, I.; Bruzil, S.; Haima, K.Y.; Gottlieb, T.; Ben-Yedidia, T. Priming by a novel universal influenza vaccine (Multimeric-001)—A gateway for improving immune response in the elderly population. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5816–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.N.; Bunce, C.J.; Horlock, C.; Watson, J.M.; Warrington, S.J.; Georges, B.; Brown, C.B. A novel peptide-based pan-influenza A vaccine: A double blind, randomised clinical trial of immunogenicity and safety. Vaccine 2015, 33, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameel, S. Molecular biology and pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 1999, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Raghava, G. ProPred1: Prediction of promiscuous MHC Class-I binding sites. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shey, R.A.; Ghogomu, S.M.; Shintouo, C.M.; Nkemngo, F.N.; Nebangwa, D.N.; Esoh, K.; Yaah, N.E.; Manka’aFri, M.; Nguve, J.E.; Ngwese, R.A. Computational Design and Preliminary Serological Analysis of a Novel Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate Against Onchocerciasis and Related Filarial Diseases. Pathogens 2021, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carty, M.; Bowie, A.G. Recent insights into the role of Toll-like receptors in viral infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 161, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, M.; Ratho, R.; Chawla, Y.; Singh, M.P. Role of TLR gene expression and cytokine profiling in the immunopathogenesis of viral hepatitis E. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 73, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devhare, P.; Madiyal, M.; Mukhopadhyay, C.; Shetty, S.; Shastry, S. Interplay between Hepatitis E Virus and Host Cell Pattern Recognition Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, H.S.; Zhao, J.; Kazmierski, E.; Kinane, D.F.; Benakanakere, M.R. TLR3-Dependent activation of TLR2 endogenous ligands via the MyD88 signaling pathway augments the innate immune response. Cells 2020, 9, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qu, C.; Yu, P.; Ou, X.; Pan, Q.; Wang, W. The interplay between host innate immunity and hepatitis E virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matvienko, M. CLC bio Products and Supported Applications. Presented at the 8th Annual Sequencing, Finishing, Analysis in the Future Meeting (2013 SFAF Meeting), Santa Fe, NM, USA, 29–31 May 2013; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Joffre, O.P.; Segura, E.; Savina, A.; Amigorena, S. Cross-presentation by dendritic cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, X.-J.; Tang, Z.-M.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.-L.; Cai, W.; Zhang, K.; Xia, N.-S.; Zheng, Z.-Z. A comprehensive study of neutralizing antigenic sites on the hepatitis E virus (HEV) capsid by constructing, clustering, and characterizing a tool box. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 19910–19922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, M.; Pan, H.; Lin, Z.; Wang, K.; Weng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xin, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, S. Robust manufacturing and comprehensive characterization of recombinant hepatitis E virus-like particles in Hecolin®. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4039–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khudyakov, Y.E.; Lopareva, E.N.; Jue, D.L.; Crews, T.K.; Thyagarajan, S.; Fields, H.A. Antigenic domains of the open reading frame 2-encoded protein of hepatitis E virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2863–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell, M.A.; Li, F.; Anderson, D.A. Identification of immunodominant and conformational epitopes in the capsid protein of hepatitis E virus by using monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8011–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N.; Zhao, Q. Functional epitopes on hepatitis E virions and recombinant capsids are highly conformation-dependent. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, S.J.; Van Dijk, M.; Bonvin, A.M. The HADDOCK web server for data-driven biomolecular docking. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic 2021: Addressing New and Emerging Products; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, S.A.; Verma, N.; Koren, G. Hepatitis E infection during pregnancy. Can. Fam. Physician 2015, 61, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Huang, S.-J.; Zhu, F.-C.; Zhang, X.-F.; Ai, X.; Yan, Q.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Yang, C.-L.; Jiang, H.-M.; Liu, X.-H. Immunogenicity and safety of hepatitis E vaccine in healthy hepatitis B surface antigen positive adults. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 2474–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N.; Zhao, Q. Prophylactic Hepatitis E vaccines: Antigenic analysis and serological evaluation. Viruses 2020, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaka, A.O.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Martin, D.R.; Goboza, M.; Klein, A.; Madiehe, A.M.; Meyer, M. Immunoinformatics design of a novel epitope-based vaccine candidate against dengue virus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamili, S. Toward the development of a hepatitis E vaccine. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Thakur, M.; Sharma, L.K.; Chandra, K. Designing a multi-epitope peptide based vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, W.; Thompson, E.; Badger, C.; Mellquist, J.L.; Garrison, A.R.; Smith, J.M.; Paragas, J.; Hogan, R.J.; Schmaljohn, C. Influences of glycosylation on antigenicity, immunogenicity, and protective efficacy of ebola virus GP DNA vaccines. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1821–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| MHCI Epitopes | Name | References | MHCII | Name | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All genotypes (GT1, GT3, GT4) | |||||
| 23GQPSGRRRG31 | R1 | [24] | 8LLLLVLLPM16 | r1 | [24] |
| 134RQYNLSTSP142 | R2 | [24] | 11LVLLPMLP19 | r2 | [24] |
| 136NLSTSPLT144 | R3 | [24] | 132RRQYNLST140 | r3 | [24] |
| 162PLLPLQDGT170 | R4 | [24] | 187VVRATIRYR195 | r4 | [24] |
| 170NTHIMATEEASNY183 | R5 | [24] | 192IRYRPLVPN200 | r5 | [24] |
| 199PNAVGGYAISISFWPQTTTT218 | R6 | [24] | 202VGGYAISIS210 | r6 | [24] |
| 136YNLSTSPLT144 | R7 | [24] | 258WRSVETSGV266 | r7 | [24] |
| 162PLLPLQDGT170 | R8 | [24] | 275LVMLCIHGS283 | r8 | [24] |
| 170NTHIMATEEASNY183 | R9 | [24] | 308FRNLTPGNT316 | r9 | [24] |
| 199PNAVGGYAISISFWPQTTTT218 | R10 | [24] | 349FMKDLHFTG357 | r10 | [24] |
| 219PTSVDMNSITSTDV232 | R11 | [24] | 353LHFTGTNGV361 | r11 | [24] |
| 236VQPGIASEL244 | R12 | [24] | 373NLADTLLG381 | r12 | [23,24,26] |
| 251LHYRNQGWRSVET263 | R13 | [24] | 396FYSRPVVSA404 | r13 | [23,24,26] |
| 267AEEEATSGLV276 | R14 | [24] | 465LRANDVLWL473 | r14 | [23,24,26] |
| 303ALELEFRNLTPGNTNT218 | R15 | [24] | 500FVNVATGAQ509 | r15 | [23,24,26] |
| 339AELTTTAATR348 | R16 | [24] | 519VTLDGRPLT527 | r16 | [23,24,26] |
| 370LTLFNLADT378 | R17 | [23,24,26] | 536FFVLPLRGKLSFWE538 | r17 | [23,24,26] |
| 403SANGEPTVKLY413 | R18 | [23,24,26] | |||
| 413YTSVENAQQ421 | R19 | [23,24,26] | |||
| 440IQDYDNQHEQ449 | R20 | [23,24,26] | |||
| 465LRANDVLWL473 | R21 | [23,24,26] | |||
| 467NDVLWLSLTAAEYDQ482 | R22 | [23,24,26] | |||
| 544KLSFWEAGTTKAGYPYNYNTTA565 | R23 | [23,24,26] | |||
| 645AELQRLKMK653 | R24 | [23,24,26] | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikram, A.; Alzahrani, B.; Zaheer, T.; Sattar, S.; Rasheed, S.; Aurangzeb, M.; Ishaq, Y. An In Silico Deep Learning Approach to Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design: A Hepatitis E Virus Case Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030710
Ikram A, Alzahrani B, Zaheer T, Sattar S, Rasheed S, Aurangzeb M, Ishaq Y. An In Silico Deep Learning Approach to Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design: A Hepatitis E Virus Case Study. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030710
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkram, Aqsa, Badr Alzahrani, Tahreem Zaheer, Sobia Sattar, Sidra Rasheed, Muhammad Aurangzeb, and Yasmeen Ishaq. 2023. "An In Silico Deep Learning Approach to Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design: A Hepatitis E Virus Case Study" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030710
APA StyleIkram, A., Alzahrani, B., Zaheer, T., Sattar, S., Rasheed, S., Aurangzeb, M., & Ishaq, Y. (2023). An In Silico Deep Learning Approach to Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design: A Hepatitis E Virus Case Study. Vaccines, 11(3), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030710






